AV-101, a Pro-Drug Antagonist at the NMDA Receptor Glycine Site, Reduces L-Dopa Induced Dyskinesias in MPTP Monkeys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
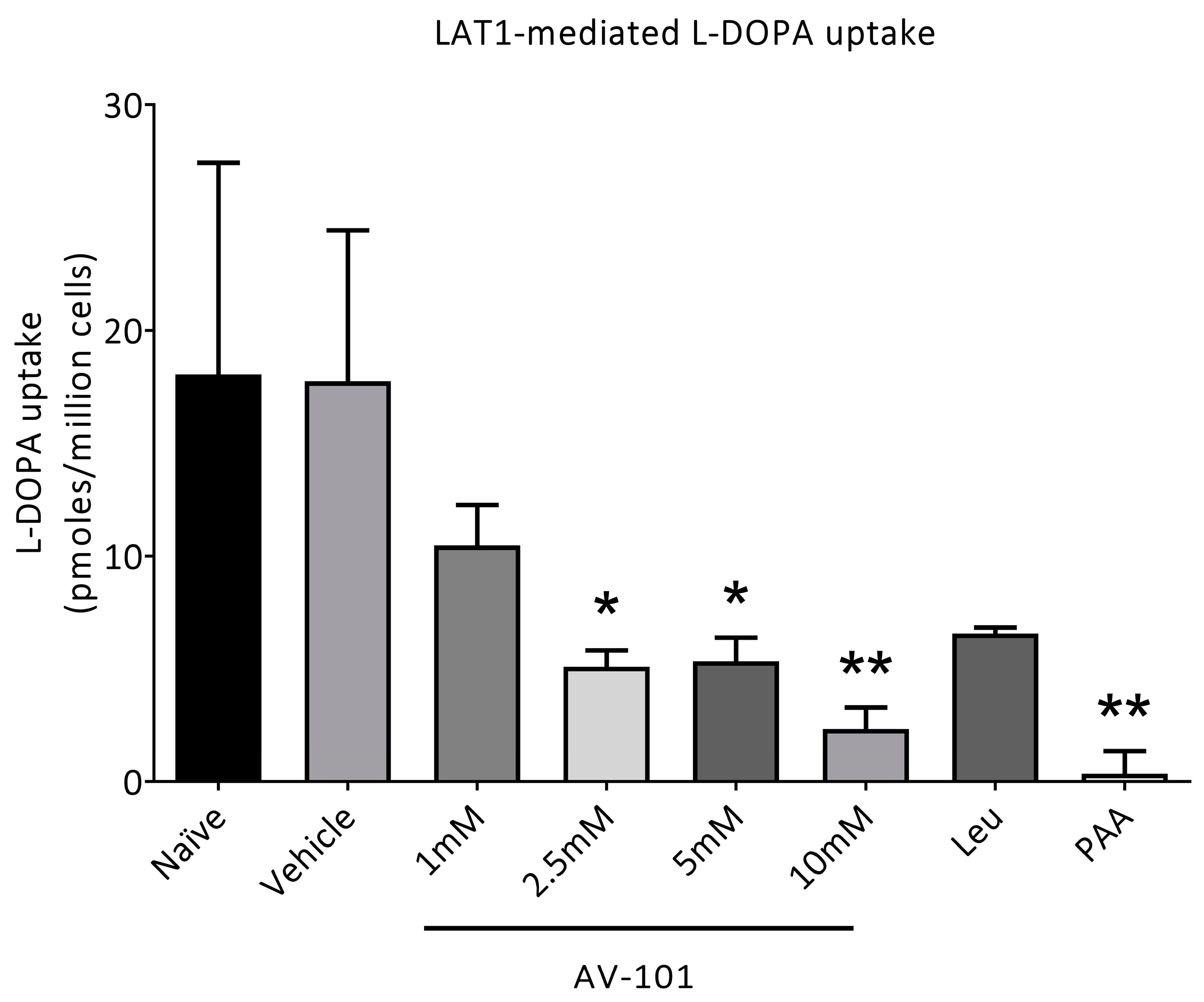
2.1. In Vitro Uptake of [3H]-L-Dopa
2.2. Animals
2.3. Drugs
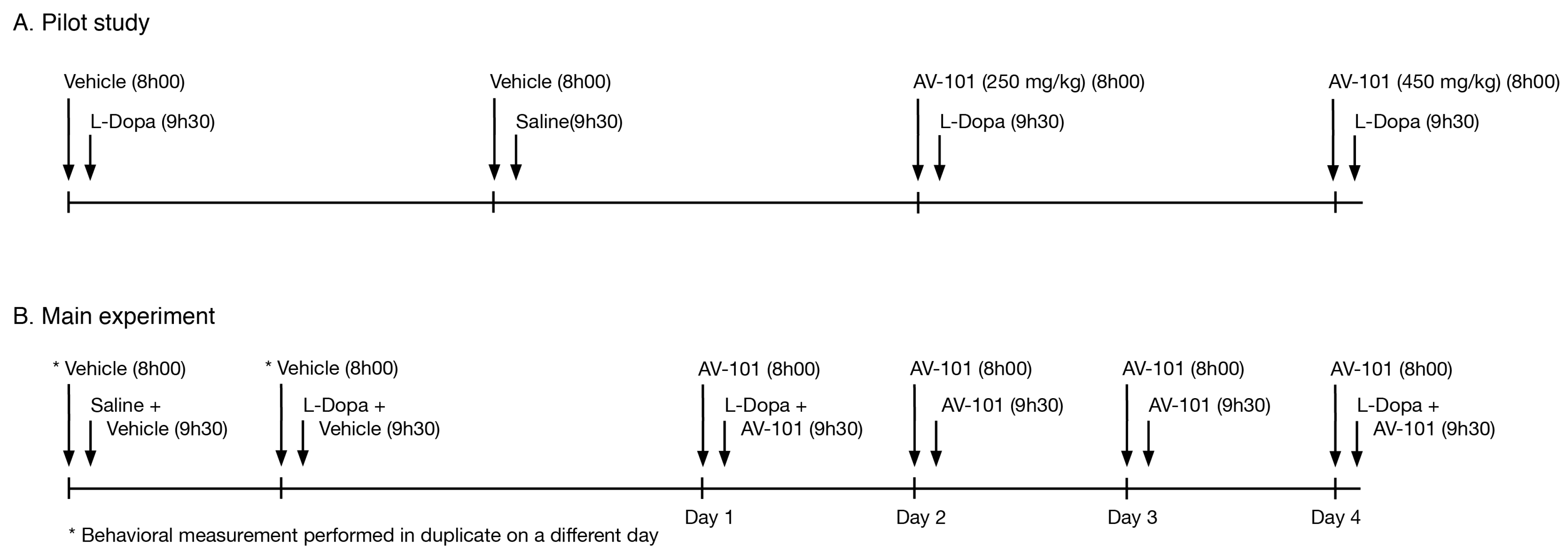
2.4. Pilot Study
2.5. Main Experiment
2.6. Behavioral Assessments
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. L-Dopa Transport via LAT1 Is Inhibited Only by High Concentrations of AV-101
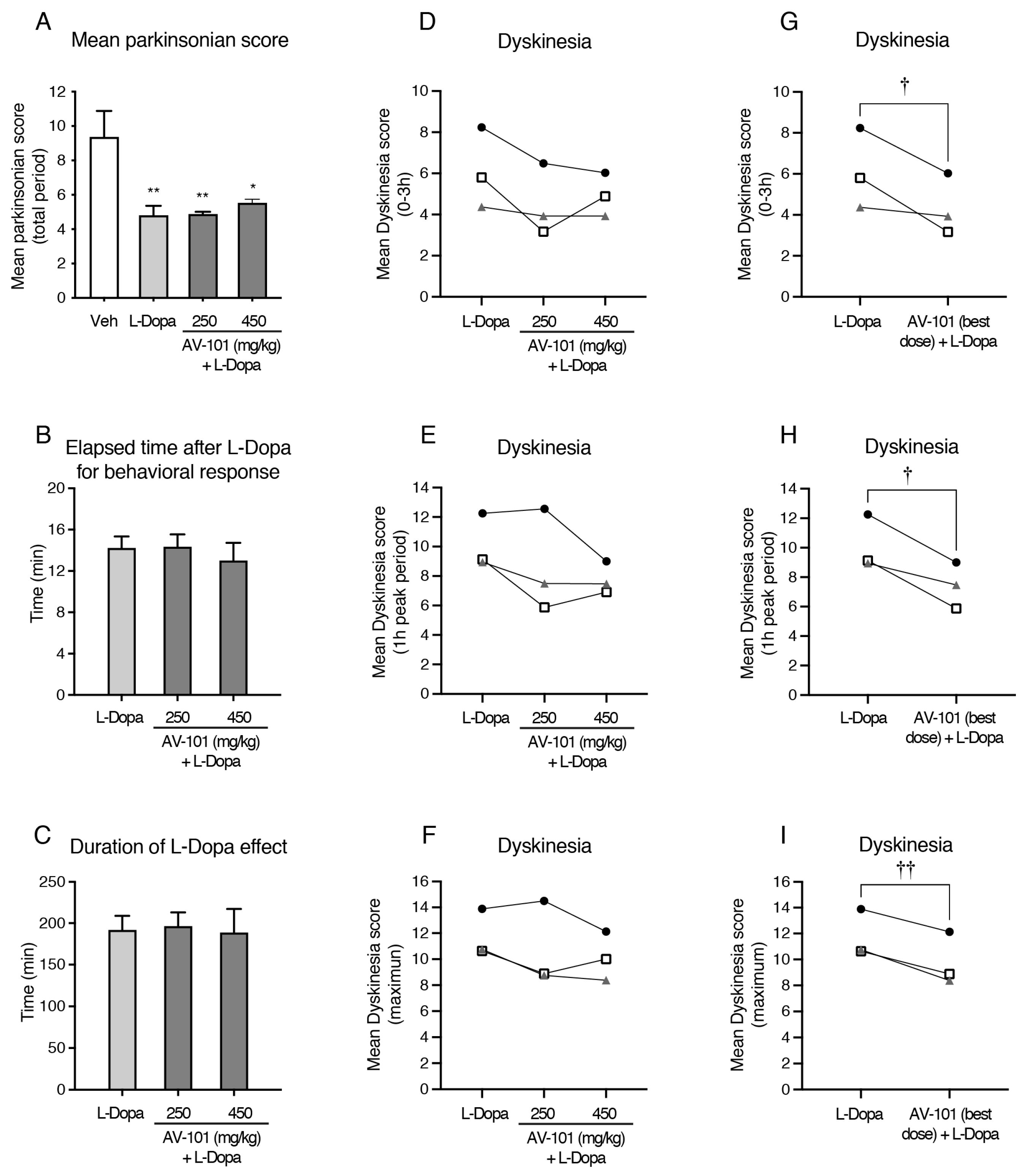
3.2. Acute Treatment with AV-101 and LID (Pilot Study)
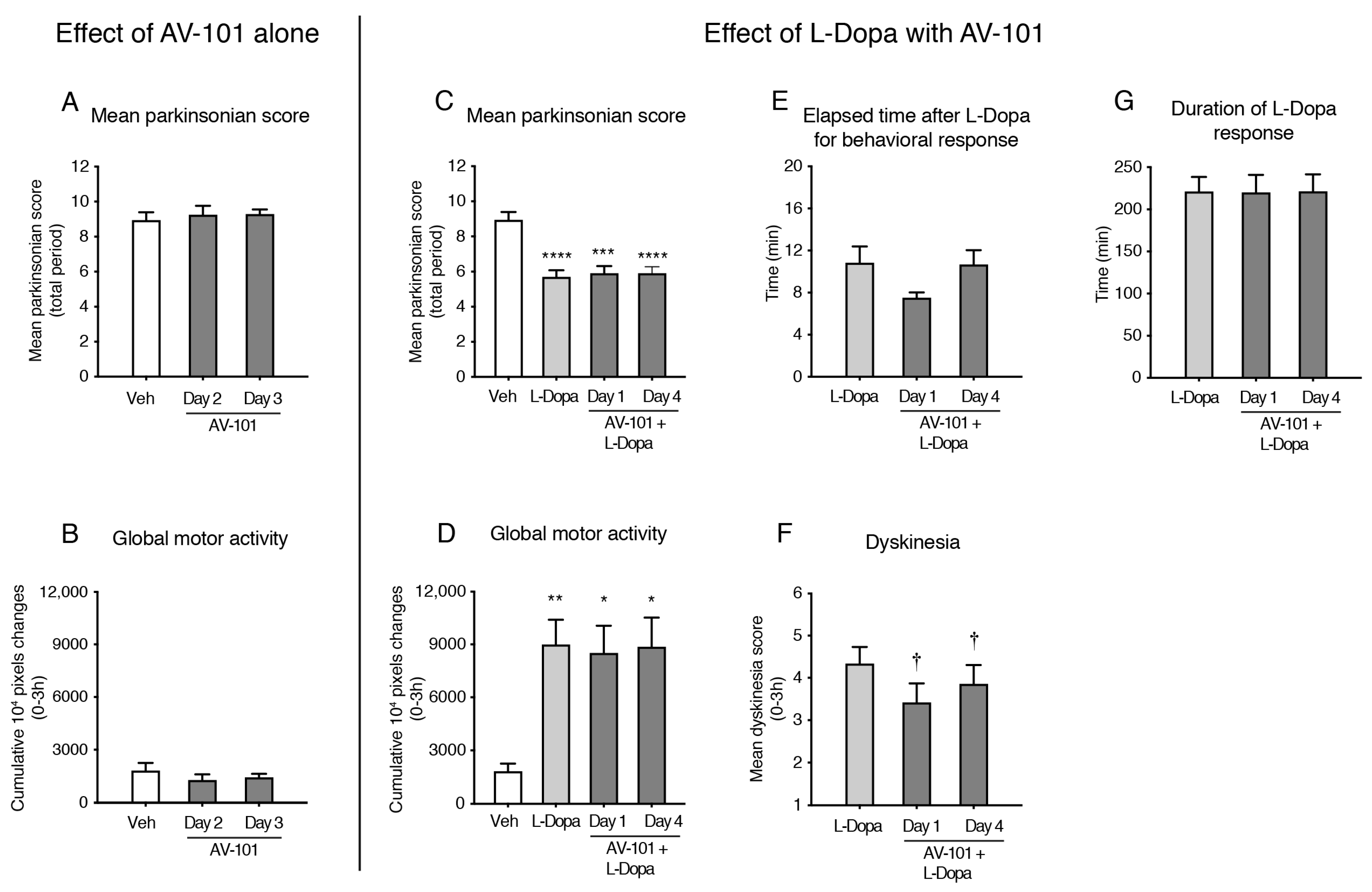
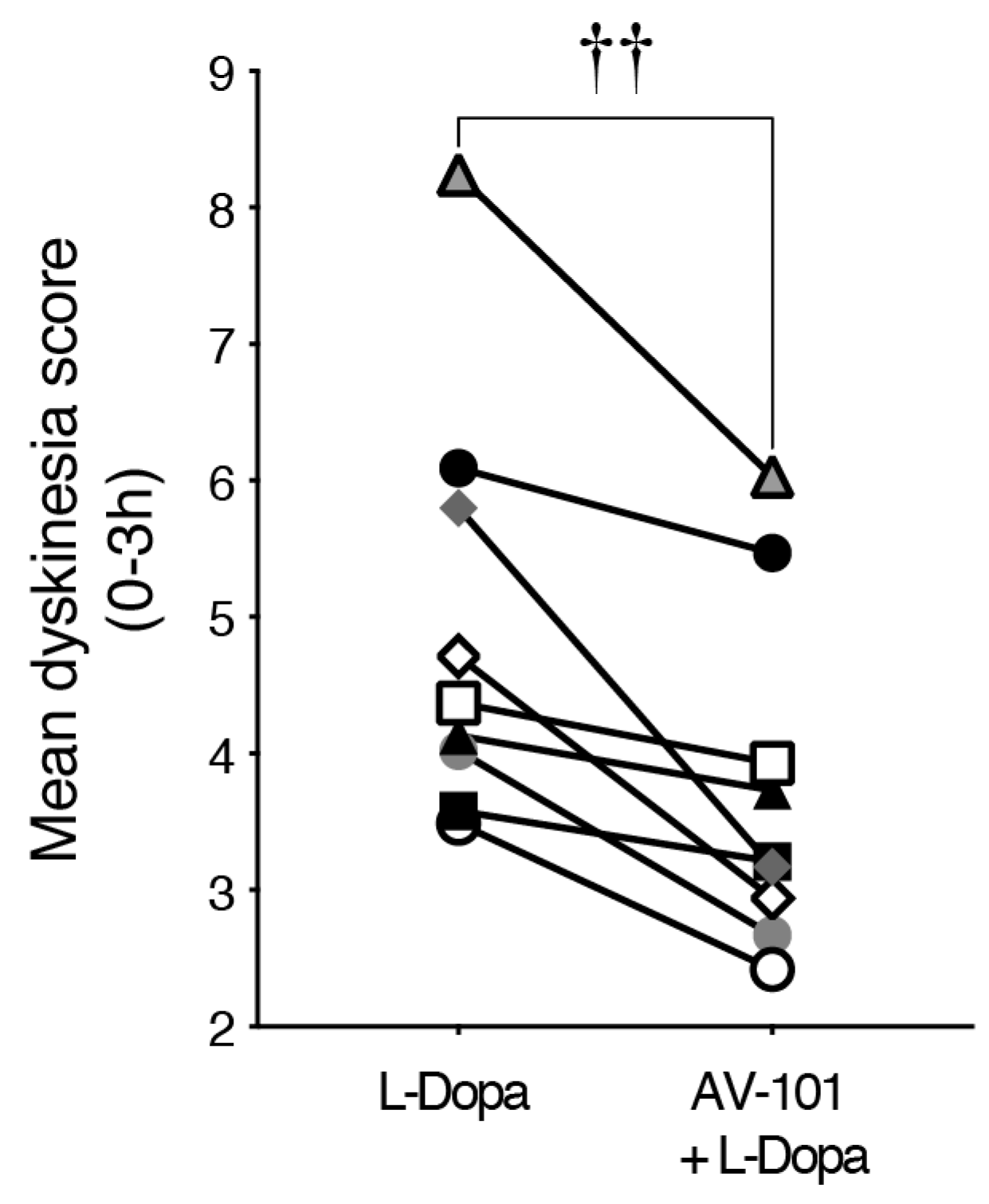
3.3. Repeated Treatment with AV-101 Decreases LID (Main Experiment)
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olanow, C.W.; Koller, W.C. An algorithm (decision tree) for the management of Parkinson’s disease: Treatment guidelines. American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 1998, 50, S1–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastide, M.F.; Meissner, W.G.; Picconi, B.; Fasano, S.; Fernagut, P.O.; Feyder, M.; Francardo, V.; Alcacer, C.; Ding, Y.; Brambilla, R.; et al. Pathophysiology of L-dopa-induced motor and non-motor complications in Parkinson’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2015, 132, 96–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, N.; Di Paolo, T. Pharmacological Treatments Inhibiting Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesias in MPTP-Lesioned Monkeys: Brain Glutamate Biochemical Correlates. Front. Neurol. 2014, 5, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajput, A.H.; Rajput, A.; Lang, A.E.; Kumar, R.; Uitti, R.J.; Galvez-Jimenez, N. New use for an old drug: Amantadine benefits levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Mov. Disord. 1998, 13, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhagen Metman, L.; Del Dotto, P.; Natte, R.; van den Munckhof, P.; Chase, T.N. Dextromethorphan improves levodopa-induced dyskinesias in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 1998, 51, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muir, K.W.; Lees, K.R. Clinical experience with excitatory amino acid antagonist drugs. Stroke 1995, 26, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, C.G.; Danysz, W.; Quack, G.; Hartmann, S.; Lorenz, B.; Wollenburg, C.; Baran, L.; Przegalinski, E.; Kostowski, W.; Krzascik, P.; et al. Novel systemically active antagonists of the glycine site of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor: Electrophysiological, biochemical and behavioral characterization. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 283, 1264–1275. [Google Scholar]
- Leeson, P.D.; Iversen, L.L. The glycine site on the NMDA receptor: Structure-activity relationships and therapeutic potential. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 4053–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundfeldt, C.; Wlaz, P.; Loscher, W. Anticonvulsant activity of antagonists and partial agonists for the NMDA receptor-associated glycine site in the kindling model of epilepsy. Brain Res. 1994, 653, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, S.M.; Auberson, Y.P.; Greenamyre, J.T. Prolongation of levodopa responses by glycineB antagonists in parkinsonian primates. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 56, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoire, L.; Rassoulpour, A.; Guidetti, P.; Samadi, P.; Bedard, P.J.; Izzo, E.; Schwarcz, R.; Di Paolo, T. Prolonged kynurenine 3-hydroxylase inhibition reduces development of levodopa-induced dyskinesias in parkinsonian monkeys. Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 186, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samadi, P.; Gregoire, L.; Rassoulpour, A.; Guidetti, P.; Izzo, E.; Schwarcz, R.; Bedard, P.J. Effect of kynurenine 3-hydroxylase inhibition on the dyskinetic and antiparkinsonian responses to levodopa in Parkinsonian monkeys. Mov. Disord. 2005, 20, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, J.A.; Foster, A.C.; Leeson, P.D.; Priestley, T.; Tridgett, R.; Iversen, L.L.; Woodruff, G.N. 7-Chlorokynurenic acid is a selective antagonist at the glycine modulatory site of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 6547–6550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salituro, F.G.; Tomlinson, R.C.; Baron, B.M.; Palfreyman, M.G.; McDonald, I.A. Enzyme-activated antagonists of the strychnine-insensitive glycine/NMDA receptor. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 334–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokari, M.; Wu, H.Q.; Schwarcz, R.; Smith, Q.R. Facilitated brain uptake of 4-chlorokynurenine and conversion to 7-chlorokynurenic acid. Neuroreport 1996, 8, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, L.T.; Kadriu, B.; Gould, T.D.; Zanos, P.; Greenstein, D.; Evans, J.W.; Yuan, P.; Farmer, C.A.; Oppenheimer, M.; George, J.M.; et al. A Randomized Trial of the N-Methyl-d-Aspartate Receptor Glycine Site Antagonist Prodrug 4-Chlorokynurenine in Treatment-Resistant Depression. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020, 23, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, M.; White, A.; Grako, K.A.; Lane, R.; Cato, A.J.; Snodgrass, H.R. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-escalation study: Investigation of the safety, pharmacokinetics, and antihyperalgesic activity of l-4-chlorokynurenine in healthy volunteers. Scand. J. Pain 2017, 17, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretschmer, B.D.; Bubser, M.; Schmidt, W.J. Behavioral and neurochemical actions of the strychnine-insensitive glycine receptor antagonist, 7-chlorokynurenate, in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 280, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Q.; Lee, S.C.; Scharfman, H.E.; Schwarcz, R. L-4-chlorokynurenine attenuates kainate-induced seizures and lesions in the rat. Exp. Neurol. 2002, 177, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidetti, P.; Wu, H.Q.; Schwarcz, R. In situ produced 7-chlorokynurenate provides protection against quinolinate- and malonate-induced neurotoxicity in the rat striatum. Exp. Neurol. 2000, 163, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Schwarcz, R. Excitotoxic injury stimulates pro-drug-induced 7-chlorokynurenate formation in the rat striatum in vivo. Neurosci. Lett. 2001, 304, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickens, D.; Chiduza, G.N.; Wright, G.S.; Pirmohamed, M.; Antonyuk, S.V.; Hasnain, S.S. Modulation of LAT1 (SLC7A5) transporter activity and stability by membrane cholesterol. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickens, D.; Webb, S.D.; Antonyuk, S.; Giannoudis, A.; Owen, A.; Radisch, S.; Hasnain, S.S.; Pirmohamed, M. Transport of gabapentin by LAT1 (SLC7A5). Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 1672–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, W.; Rimmer, L.; Smith, M.; Moss, L.; Smith, M.A.; Snodgrass, H.R.; Pirmohamed, M.; Alfirevic, A.; Dickens, D. Probenecid Increases the Concentration of 7-Chlorokynurenic Acid Derived from the Prodrug 4-Chlorokynurenine within the Prefrontal Cortex. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadj Tahar, A.; Grégoire, L.; Darre, A.; Bélanger, N.; Meltzer, L.; Bédard, P.J. Effect of a selective glutamate antagonist on L-dopa-induced dyskinesias in drug-naive parkinsonian monkeys. Neurobiol. Dis. 2004, 15, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, J.H.; Nutt, J.G.; Woodward, W.R.; Hatcher, L.F.; Trotman, T.L. Amount and distribution of dietary protein affects clinical response to levodopa in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 1989, 39, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutt, J.G.; Woodward, W.R.; Hammerstad, J.P.; Carter, J.H.; Anderson, J.L. The “on-off” phenomenon in Parkinson’s disease. Relation to levodopa absorption and transport. N. Engl. J. Med. 1984, 310, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Lloret, S.; Rascol, O. Efficacy and safety of amantadine for the treatment of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. J. Neural Transm. 2018, 125, 1237–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charvin, D.; Di Paolo, T.; Bezard, E.; Gregoire, L.; Takano, A.; Duvey, G.; Pioli, E.; Halldin, C.; Medori, R.; Conquet, F. An mGlu4-Positive Allosteric Modulator Alleviates Parkinsonism in Primates. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 1619–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoire, L.; Jourdain, V.A.; Townsend, M.; Roach, A.; Di Paolo, T. Safinamide reduces dyskinesias and prolongs L-DOPA antiparkinsonian effect in parkinsonian monkeys. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2013, 19, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, N.; Jourdain, V.A.; Di Paolo, T. Modeling dyskinesia in animal models of Parkinson disease. Exp. Neurol. 2014, 256, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morissette, M.; Di Paolo, T. Non-human primate models of PD to test novel therapies. J. Neural Transm. 2018, 125, 291–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamadjida, A.; Frouni, I.; Kwan, C.; Huot, P. Classic animal models of Parkinson’s disease: A historical perspective. Behav. Pharmacol. 2019, 30, 291–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.S.; Geng, W.S.; Jia, J.J. Neurotoxin-Induced Animal Models of Parkinson Disease: Pathogenic Mechanism and Assessment. ASN Neurol. 2018, 10, 1759091418777438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bourque, M.; Grégoire, L.; Patel, W.; Dickens, D.; Snodgrass, R.; Di Paolo, T. AV-101, a Pro-Drug Antagonist at the NMDA Receptor Glycine Site, Reduces L-Dopa Induced Dyskinesias in MPTP Monkeys. Cells 2022, 11, 3530. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11223530
Bourque M, Grégoire L, Patel W, Dickens D, Snodgrass R, Di Paolo T. AV-101, a Pro-Drug Antagonist at the NMDA Receptor Glycine Site, Reduces L-Dopa Induced Dyskinesias in MPTP Monkeys. Cells. 2022; 11(22):3530. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11223530
Chicago/Turabian StyleBourque, Mélanie, Laurent Grégoire, Waseema Patel, David Dickens, Ralph Snodgrass, and Thérèse Di Paolo. 2022. "AV-101, a Pro-Drug Antagonist at the NMDA Receptor Glycine Site, Reduces L-Dopa Induced Dyskinesias in MPTP Monkeys" Cells 11, no. 22: 3530. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11223530
APA StyleBourque, M., Grégoire, L., Patel, W., Dickens, D., Snodgrass, R., & Di Paolo, T. (2022). AV-101, a Pro-Drug Antagonist at the NMDA Receptor Glycine Site, Reduces L-Dopa Induced Dyskinesias in MPTP Monkeys. Cells, 11(22), 3530. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11223530






