Mast Cells and Acupuncture Analgesia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Characteristics of Mast Cells and Its Function
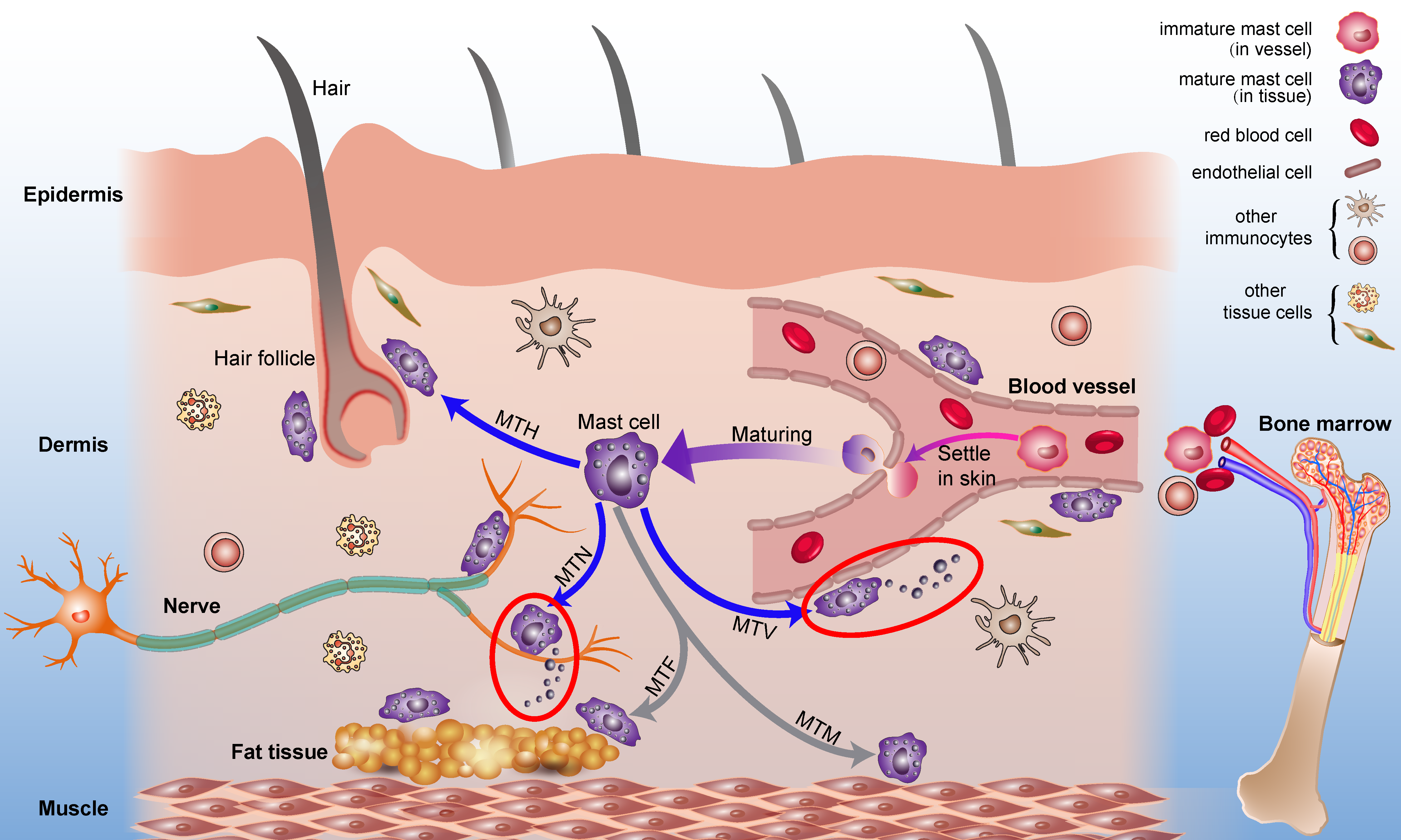
2.1. Origin and Distribution of Mast Cells
2.2. Mast Cell Degranulation and Its Function
2.3. Mast Cells and Acupoint Sensitization
3. Activation and Mechanical Sensitivity of Mast Cells
3.1. Degranulation of Mast Cells under Mechanical Stimulations
3.2. Mechanosensitive Channels of Mast Cells
4. Mast Cells and Acupuncture Analgesia
4.1. Mast Cells in Acupuncture Analgesia
4.2. Function of Mast Cells and Collagen at Acupoint
4.3. Mast Cell-Nerve Cell Interaction at Acupoint
5. Mathematical Model of Mast Cell Involvement in Acupuncture Analgesia
6. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heib, V.; Becker, M.; Taube, C.; Stassen, M. Advances in the understanding of mast cell function. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 142, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejler, G.; Ronnberg, E.; Waern, I.; Wernersson, S. Mast cell proteases: Multifaceted regulators of inflammatory disease. Blood 2010, 115, 4981–4990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Ding, G.H.; Shen, X.Y.; Yao, W.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Lin, J.; Gu, Q.B. Role of mast cells in acupuncture effect: A pilot study. Explore 2008, 4, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.F.; Dong, X.T.; Song, X.J.; Jiang, J.L.; Zhan, J.; Han, Y. Study on the dynamic compound structure composed of mast cells, blood vessels, and nerves in rat acupoint. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 160651. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.L.; Xu, D.S.; Bai, W.Z.; Cui, J.J.; Shu, H.M.; He, W.; Wang, X.Y.; Shi, H.; Su, Y.S.; Hu, L.; et al. Local cutaneous nerve terminal and mast cell responses to manual acupuncture in acupoint li4 area of the rats. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2015, 68, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, B. The sensitization phenomenon of acupoint and biological significances. Chin. Acupunct. Moxibustion 2019, 39, 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- He, T.F.; Chen, Y.F. Advances in studies on the correlation between acupuncture-moxibustion treatment and mast cells. Chin. Acupunct. Moxibustion 2010, 30, 84–87. [Google Scholar]
- Stokes, A.J.; Shimoda, L.M.N.; Koblan-Huberson, M.; Adra, C.N.; Turner, H. A trpv2–pka signaling module for transduction of physical stimuli in mast cells. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, H.; Del Carmen, K.A.; Stokes, A. Link between TRPV Channels and Mast Cell Function. In Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) Channels; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 457–471. [Google Scholar]
- Solís-López, A.; Kriebs, U.; Marx, A.; Mannebach, S.; Liedtke, W.B.; Caterina, M.J.; Freichel, M.; Tsvilovskyy, V.V. Analysis of trpv channel activation by stimulation of fcεri and mrgpr receptors in mouse peritoneal mast cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e171366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, M.; Xie, Y.Y.; Ding, G.H. Acupoint-injection of histamine induced analgesic effect in acute adjuvant-induced-arthritis rats. Acupunct. Res. 2010, 35, 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, N.; Jiang, J.; Qin, P.P.; Wang, Q.X.; Hu, J.T.; Li, Z.G. Mast cells are important regulator of acupoint sensitization via the secretion of tryptase, 5-hydroxytryptamine, and histamine. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e194022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Qi, Y.; Ming, C.; Li, Y.; Pan, S.; Liu, S.; Ma, T. Electroacupuncture improves cutaneous allergic reaction by inhibiting degranulation of intrape-ritoneal mast cells, mapk signaling and inflammatory factor levels in urticaria rats. Acupunct. Res. 2020, 45, 299–304. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, W.; Yang, H.W.; Li, Y.; Ding, G.H. Dynamics of calcium signal and leukotriene c-4 release in mast cells network induced by mechanical stimuli and modulated by interstitial fluid flow. Adv. Appl. Math. Mech. 2016, 8, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Yang, H.W.; Yin, N.; Ding, G.H. Mast cell-nerve cell interaction at acupoint: Modeling mechanotransduction pathway induced by acupuncture. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 10, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Huang, H.X.; Ding, G.H. A dynamic model of calcium signaling in mast cells and ltc_4 release induced by mechanical stimuli. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, U.; Falcone, F.H.; Nilsson, G. The history of mast cell and basophil research—Some lessons learnt from the last century. Allergy 2013, 68, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crivellato, E.; Beltrami, C.; Mallardi, F.; Ribatti, D. Paul Ehrlich’s doctoral thesis: A milestone in the study of mast cells. Br. J. Haematol. 2003, 123, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamur, M.C.; Oliver, C. Origin, maturation and recruitment of mast cell precursors. Front. Biosci. 2011, 3, 1390–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, M.; Lv, J.; Zhu, X. Advances in the research about recruitment of mast cell. Med. Recapitul. 2006, 588–590. [Google Scholar]
- Draber, P.; Sulimenko, V.; Draberova, E. Cytoskeleton in mast cell signaling. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Metcalfe, D.D.; Baram, D.; Mekori, Y.A. Mast cells. Physiol. Rev. 1997, 77, 1033–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metz, M.; Siebenhaar, F.; Maurer, M. Mast cell functions in the innate skin immune system. Immunobiology 2008, 213, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, S.C.; Kirsner, J.B. Mast cells and the gastrointestinal tract: A review. Gastroenterology 1960, 39, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franconi, G.M.; Rubinstein, I.; Levine, E.H.; Ikeda, S.; Nadel, J.A. Mechanical removal of airway epithelium disrupts mast-cells and releases granules. Am. J. Physiol. 1990, 259, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, L.C.J. The mast cell: Origin, morphology, distribution, and function. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 1997, 49, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, G.; Burnstock, G. A novel cell-to-cell interaction between mast cells and other cell types. Exp. Cell Res. 1983, 147, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.W.; Liu, X.Y.; Shen, Z.F.; Yao, W.; Gong, X.B.; Huang, H.X.; Ding, G.H. An investigation of the distribution and location of mast cells affected by the stiffness of substrates as a mechanical niche. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1142–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, K.; Tsai, M.; Saito, H.; Galli, S.J. Mast cells as sources of cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 282, 121–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulfone-Paus, S.; Nilsson, G.; Draber, P.; Blank, U.; Levi-Schaffer, F. Positive and negative signals in mast cell activation. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christy, A.L.; Brown, M.A. The multitasking mast cell: Positive and negative roles in the progression of autoimmunity. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 2673–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Espinosa, C.; Odom, S.; Olivera, A.; Hobson, J.P.; Martinez, M.E.C.; Oliveira-dos-Santos, A.; Barra, L.; Spiegel, S.; Penninger, J.M.; Rivera, J. Preferential signaling and induction of allergy-promoting lymphokines upon weak stimulation of the high affinity ige receptor on mast cells. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 1453–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, S.J.; Gaudenzio, N.; Tsai, M. Mast cells in inflammation and disease: Recent progress and ongoing concerns. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 38, 49–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tetè, G.; D’orto, B.; Ferrante, L.; Polizzi, E.; Cattoni, F. Role of mast cells in oral inflammation. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2021, 35, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Chen, N.; Tang, X.L.; Qian, X.H.; Cai, C.P. Immunomodulatory effects of IL-33 and IL-25 in an ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis mouse model. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2021, 35, 571–581. [Google Scholar]
- Theoharides, T.C.; Conti, P. Dexamethasone for COVID-19? Not so fast. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34, 1241–1243. [Google Scholar]
- Kempuraj, D.; Selvakumar, G.P.; Ahmed, M.E.; Raikwar, S.P.; Thangavel, R.; Khan, A.; Zaheer, S.A.; Iyer, S.S.; Burton, C.; James, D.; et al. COVID-19, mast cells, cytokine storm, psychological stress, and neuroinflammation. Neuroscientist 2020, 26, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reber, L.L.; Sibilano, R.; Starkl, P.; Roers, A.; Grimbaldeston, M.A.; Tsai, M.; Gaudenzio, N.; Galli, S.J. Imaging protective mast cells in living mice during severe contact hypersensitivity. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e92900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grimbaldeston, M.A.; Nakae, S.; Kalesnikoff, J.; Tsai, M.; Galli, S.J. Mast cell-derived interleukin 10 limits skin pathology in contact dermatitis and chronic irradiation with ultraviolet B. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; He, T.; Xu, Q.; Ling, L.T.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Shi, G.X.; Liu, C.Z. What is the acupoint? A preliminary review of acupoints. Pain Med. 2015, 16, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, L.; Yao, D.W.; Tang, L.; Huang, W.H.; Jiao, P.F.; Lu, Y.T.; Dai, Y.X.; Zhang, H.; He, Z.Q.; Zhong, S.Z. A study on morphological basis of chinese acupuncture and moxibustion from digital human body. Acta Anat. Sin. 2004, 35, 337–343. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, L.; Cheng, H.S.; Cai, D.H.; Yang, S.X.; Xu, J.R.; Chen, E.Y.; Dang, R.S.; Ding, G.H.; Shen, X.Y.; Tang, Y.; et al. Experimental exploration and research prospect of physical bases and functional characteristics of meridians. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1998, 43, 1233–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.J.; Ding, G.H.; Huang, H.; Lin, J.; Yao, W.; Zhan, R. Role of collagen fibers in acupuncture analgesia therapy on rats. Connect. Tissue Res. 2009, 50, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.M. Mast cells and meridian phenomena. Liaoning J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 1977, 4, 59–61. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.M. Preliminary observations on mast cells in acupuncture point tissue. Liaoning J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 1980, 3, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, J. Discovery of nerve-mast cell junctions in the meridian line in human skin II “Afferent” nerve-mast cell junctions and Xue Wang cells with efferent axons. J. Neuroanat. 1985, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, J. Discovery of nerve-mast cell junctions in the meridian line in human skin I. Efferent nerve-mast cell connections. J. Neuroanat. 1985, 1, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Wang, X.Y.; Shi, H.; Bai, W.Z.; Chen, B.; Su, Y.S.; Yu, X.C.; Jing, X.H.; Zhu, B. Cutaneous neurogenic inflammation in the sensitized acupoints induced by gastric mucosal injury in rats. BMC Complementary Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mou, Q.J.; JI, B.; Li, Y.J.; Zhao, G.Z.; Ren, J.Y.; Li, Z.G. Research on correlation between acupoint sensitization and mast cells. J. Clin. Acupunct. Moxibustion 2020, 36, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Cheng, B.; Li, J.H.; Chen, S.L.; Tan, Q.W.; Jin, Z.G.; Jing, X.H. Mast cell and substance p are involved in the process of acupoint sensitization induced by acute gastric mucosal injury. Acupunct. Res. 2010, 35, 323–329. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Wu, M.L.; Jing, X.H.; Bai, W.Z.; Zhu, B.; Yu, X.C. Entity of acupoint: Kinetic changes of acupoints in histocytochemistry. Chin. Acupunct. Moxibustion 2015, 35, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Z.; Huang, M.; Yang, H.W.; Zhang, D.; Yao, W.; Xia, Y.; Ding, G.H. Mast cell degranulation and adenosine release:acupoint specificity for effect of electroacupuncture on pituitrin-induced acute heart bradycardia in rabbits. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 1348914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimbori, C.; Upagupta, C.; Bellaye, P.S.; Ayaub, E.A.; Sato, S.; Yanagihara, T.; Zhou, Q.; Ognjanovic, A.; Ask, K.; Gauldie, J.; et al. Mechanical stress-induced mast cell degranulation activates tgf-beta 1 signalling pathway in pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax 2019, 74, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Spielmann, A.; Wang, L.; Ding, G.; Huang, F.; Gu, Q.; Schwarz, W. Mast-cell degranulation induced by physical stimuli involves the activation of transient-receptor-potential channel trpv2. Physiol. Res. 2012, 61, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.Z.; Chen, J.Y.; Zhou, L.W. Effects of shear stress on intracellular calcium change and histamine release in rat basophilic leukemia (rbl-2h3) cells. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2009, 28, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.N.; Ding, G.H.; Gu, Q.B.; Schwarz, W. Single-channel properties of a stretch-sensitive chloride channel in the human mast cell line hmc-1. Eur. Biophys. J. EBJ 2010, 39, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Li, L.; Chen, G. Progress in the study of mast cell function and mediator release mechanisms. Int. J. Lab. Med. 2010, 31, 834–836. [Google Scholar]
- Raboune, S.; Stuart, J.M.; Leishman, E.; Takacs, S.M.; Rhodes, B.; Basnet, A.; Jameyfield, E.; Mchugh, D.; Widlanski, T.; Bradshaw, H.B. Novel endogenous n-acyl amides activate trpv1-4 receptors, bv-2 microglia, and are regulated in brain in an acute model of inflammation. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fowlkes, V.; Wilson, C.G.; Carver, W.; Goldsmith, E.C. Mechanical loading promotes mast cell degranulation via rgd-integrin dependent pathways. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, X.; Liu, K.; Xu, D.; Zhang, Y.Y.; He, X.; Liu, H.; Gao, X.Y.; Zhu, B. Mast cell deficiency attenuates acupuncture analgesia for mechanical pain using c-kit gene mutant rats. J. Pain Res. 2018, 11, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, M.; Wang, X.Z.; Xing, B.B.; Yang, H.W.; Sa, Z.Y.; Zhang, D.; Yao, W.; Yin, N.; Xia, Y.; Ding, G.H. Critical roles of trpv2 channels, histamine h1 and adenosine a1 receptors in the initiation of acupoint signals for acupuncture analgesia. Sci. Rep.-UK 2018, 8, 6523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, M.; Zhang, D.; Sa, Z.Y.; Xie, Y.Y.; Gu, C.L.; Ding, G.H. In adjuvant-induced arthritic rats, acupuncture analgesic effects are histamine dependent: Potential reasons for acupoint preference in clinical practice. Evid.-Based Complementa. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 810512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, N.; Chen, M.; Fujita, T.; Xu, Q.; Peng, W.; Liu, W.; Jensen, T.K.; Pei, Y.; Wang, F.; Han, X.; et al. Adenosine a1 receptors mediate local anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheng, X.; Xing, J.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, X.; Zhang, X. Brief introduction of Zheng’s “golden hook fishing” technique in acupuncture. Chin. Acupunct. Moxibustion 2016, 36, 963–966. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.G. The Essence of Meridians Observed in A Special Case. Shanghai J. Acupunct. Moxibustion 1998, 17, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Langevin, H.M.; Churchill, D.L.; Cipolla, M.J. Mechanical signaling through connective tissue: A mechanism for the therapeutic effect of acupuncture. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 2275–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Villanueva, L.; Le Bars, D. Acupuncture analgesia and diffuse noxious inhibitory controls. Acta Acad. Med. Jiangxi 1991, 2, 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Sa, Z.Y.; Huang, M.; Zhang, D.; Ding, G.H. Correlation between local mast cell activity and peripheral nerve discharges at the “zushanli” point stimulated by manual acupuncture. Acupunct. Res. 2013, 38, 118–122. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.X.; Wang, J.; Che, Y.Q.; Deng, B.; Guo, Y.; Guo, Y.M.; Liu, Y.Y. Nonlinear characteristics extraction from electrical signals of dorsal spinal nerve root evoked by acupuncture at zusanli point. Acta Phys. Sin. 2010, 59, 5881–5888. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, N.; Yang, H.W.; Yao, W.; Ding, G.H. A mathematical model of histamine-mediated neural activation during acupuncture. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2017, 16, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blennerhassett, M.G.; Tomioka, M.; Bienenstock, J. Formation of contacts between mast-cells and sympathetic neurons invitro. Cell Tissue Res. 1991, 265, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, L.J.; Liu, Q.; Huang, F.; He, H.W.; Fan, W.G. Involvement of mast cells in the pathophysiology of pain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 665066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapaliya, M.; Ayudhya, C.C.N.; Amponnawarat, A.; Roy, S.; Ali, H. Mast cell-specific mrgprx2: A key modulator of neuro-immune interaction in allergic diseases. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2021, 21, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlin, J.S.; Maurer, M.; Metcalfe, D.D.; Pejler, G.; Sagi-Eisenberg, R.; Nilsson, G. The ingenious mast cell: Contemporary insights into mast cell behavior and function. Allergy 2021, 77, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frieling, T.; Cooke, H.J.; Wood, J.D. Neuroimmune communication in the submucous plexus of guinea-pig colon after sensitization to milk antigen. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 1994, 267, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banisacchi, T.; Barattini, M.; Bianchi, S.; Blandina, P.; Brunelleschi, S.; Fantozzi, R.; Mannaioni, P.F.; Masini, E. The release of histamine by parasympathetic stimulation in guinea-pig auricle and rat ileum. J. Physiol. 1986, 371, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kowalski, M.L.; Sliwinskakowalska, M.; Kaliner, M.A. Neurogenic inflammation, vascular permeability, and mast cells. J. Immunol. 1988, 140, 3905–3911. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deleuze, Y. A mathematical model of mast cell response to acupuncture needling. Comptes Rendus Math. 2013, 351, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, X.M.; Zheng, Y.F.; Liu, Z.R.; Yang, W.Z. A model of calcium signaling and degranulation dynamics induced by laser irradiation in mast cells. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 2315–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, M.F.; He, J.N.; Guo, Y.; Li, C.H.; Zhang, J.L. Study on different effects of electroacupuncture and moxibustion on degranulation of mast cells in “Dazhui” point area. Acupunct. Res. 2007, 32, 327–329. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.X.; Gao, S.; Ming, C.R. Study on the effect of mast cell degranulation on pituitary acth cells by electroacupuncture at the “Zushanli” point. Liaoning J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 1991, 10, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.J.; Zhan, R.; Huang, H.; Ding, G.H. Analysis on the difference of acupoint afferent mechanism of analgesic effect between hand acupuncture and electroacupuncture at “Zusanli” point. Acupunct. Res. 2008, 33, 310–315. [Google Scholar]



| Dist | Response Time of Em | [Ca2+]i Peak (µM) |
|---|---|---|
| 2 × 10−5 m | 22 s | 0.33 |
| 4 × 10−5 m | 24 s | 0.31 |
| 6 × 10−5 m | 27 s | 0.29 |
| 8 × 10−5 m | 33.1 s | 0.27 |
| 1 × 10−4 m | No | 0.24 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yao, W. Mast Cells and Acupuncture Analgesia. Cells 2022, 11, 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11050860
Li Y, Yu Y, Liu Y, Yao W. Mast Cells and Acupuncture Analgesia. Cells. 2022; 11(5):860. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11050860
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yingchen, Yi Yu, Yuhang Liu, and Wei Yao. 2022. "Mast Cells and Acupuncture Analgesia" Cells 11, no. 5: 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11050860
APA StyleLi, Y., Yu, Y., Liu, Y., & Yao, W. (2022). Mast Cells and Acupuncture Analgesia. Cells, 11(5), 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11050860







