Role of Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns (DAMPs/Alarmins) in Severe Ocular Allergic Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
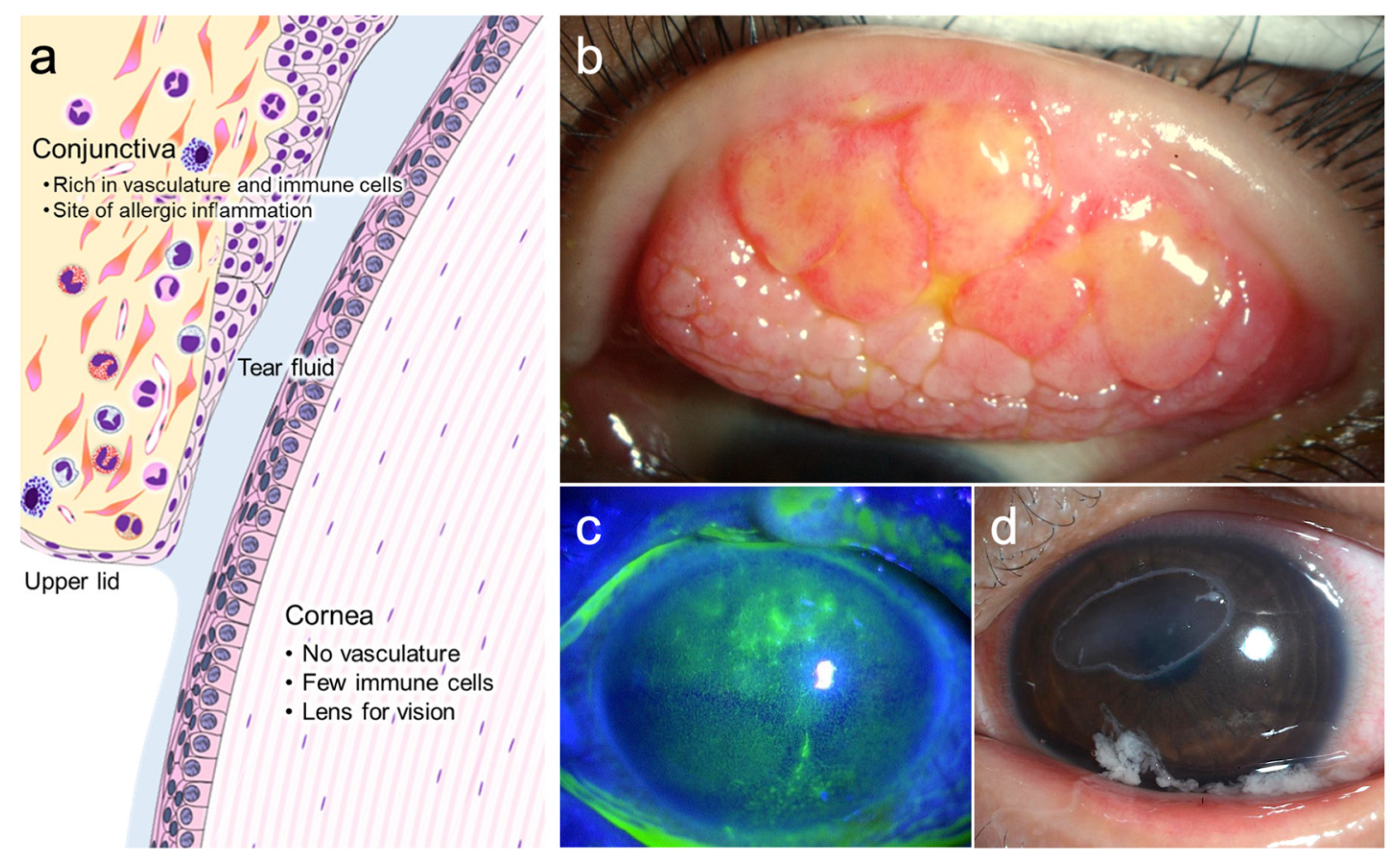
2. Corneal Involvements in Severe Ocular Allergic Diseases
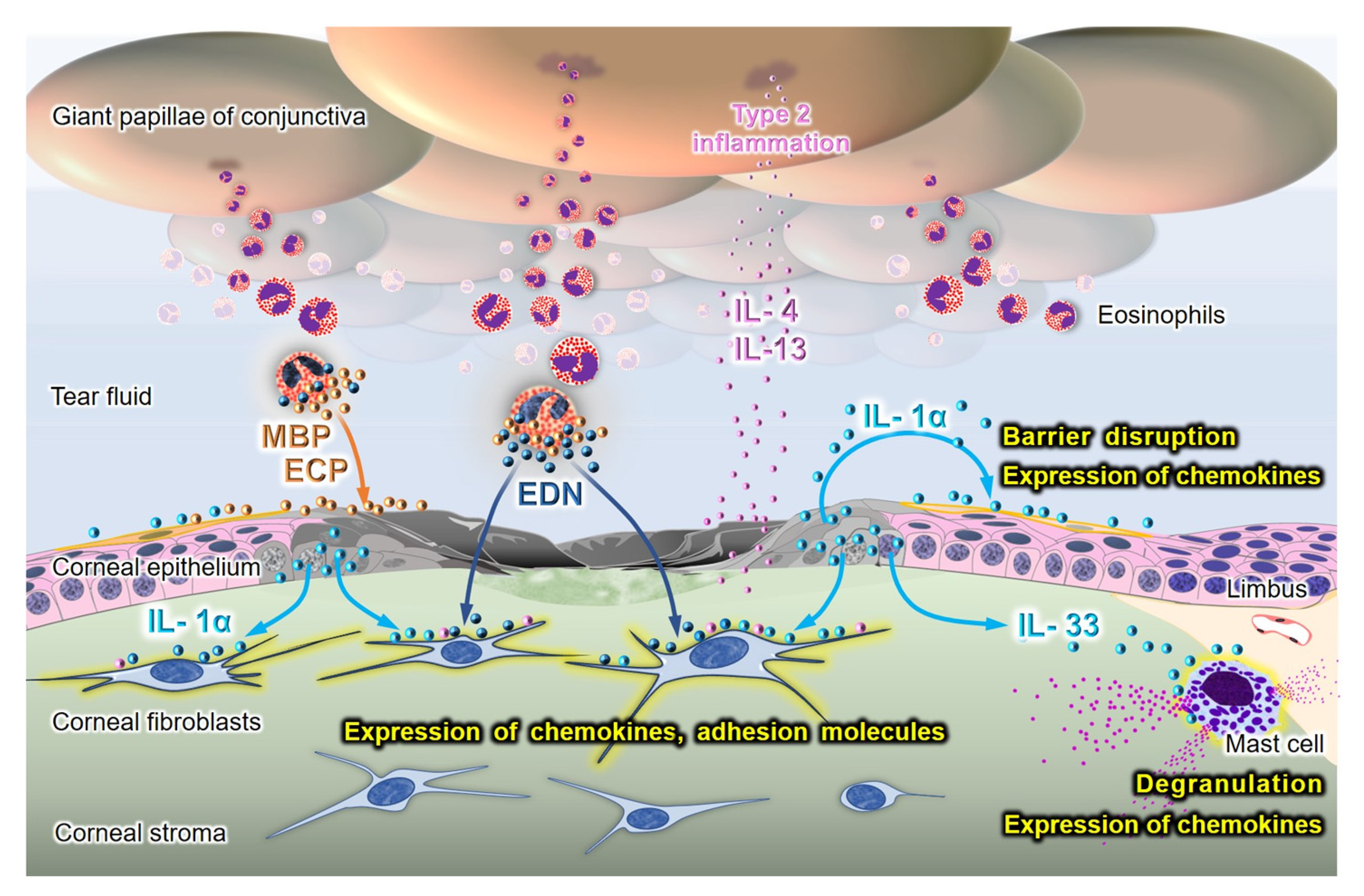
3. The Role of Alarmins/DAMPs in the Pathogenesis of Corneal Lesions in AKC/VKC
3.1. The Roles of Alarmins from Damaged Corneal Epithelial Cells
3.2. The Role of Alarmins in Eosinophils
3.3. The Role of Alarmins in Animal Models of Ocular Allergy
3.3.1. Corneal Epithelium Debridement Model
3.3.2. Mast Cells as Sensors of Alarmins
3.3.3. Role of IL-33 in Ocular Allergy Induced by Acquired and Innate Immune Systems
3.3.4. Role of TSLP and IL-25 in Ocular Allergy Induced by Acquired and Innate Immune Systems
3.3.5. Role of IL-1α in Mouse Mite-Induced AKC Model
3.4. The Expression of Alarmins in Patients with Ocular Allergy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Platts-Mills, T.A. The allergy epidemics: 1870–2010. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miyazaki, D.; Fukagawa, K.; Okamoto, S.; Fukushima, A.; Uchio, E.; Ebihara, N.; Shoji, J.; Namba, K.; Shimizu, Y. Epidemiological aspects of allergic conjunctivitis. Allergol. Int. 2020, 69, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, N.; Fukuda, K.; Fujitsu, Y.; Seki, K.; Nishida, T. Treatment of corneal lesions in individuals with vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Allergol. Int. 2005, 54, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyazaki, D.; Takamura, E.; Uchio, E.; Ebihara, N.; Ohno, S.; Ohashi, Y.; Okamoto, S.; Satake, Y.; Shoji, J.; Namba, K.; et al. Japanese guidelines for allergic conjunctival diseases 2020. Allergol. Int. 2020, 69, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, S.J. Vernal keratoconjunctivitis: Evidence for immunoglobulin E-dependent and immunoglobulin E-independent eosinophilia. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2003, 33, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Kumagai, N.; Fujitsu, Y.; Nishida, T. Fibroblasts as local immune modulators in ocular allergic disease. Allergol. Int. 2006, 55, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukuda, K. Corneal fibroblasts: Function and markers. Exp. Eye Res. 2020, 200, 108229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, N.; Fukuda, K.; Fujitsu, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Nishida, T. Role of structural cells of the cornea and conjunctiva in the pathogenesis of vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2006, 25, 165–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdis, C.A.; Arkwright, P.D.; Bruggen, M.C.; Busse, W.; Gadina, M.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Kabashima, K.; Mitamura, Y.; Vian, L.; Wu, J.; et al. Type 2 immunity in the skin and lungs. Allergy 2020, 75, 1582–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asada, Y. Roles of Type 2 Immune Response-Initiating Cytokines and Detection of Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Mouse Models of Allergic Conjunctivitis. Cornea 2020, 39 (Suppl. S1), S47–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asada, Y.; Nakae, S.; Ishida, W.; Hori, K.; Sugita, J.; Sudo, K.; Fukuda, K.; Fukushima, A.; Suto, H.; Murakami, A.; et al. Roles of Epithelial Cell-Derived Type 2-Initiating Cytokines in Experimental Allergic Conjunctivitis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 5194–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, A.; Okayama, Y.; Terai, N.; Yokoi, N.; Ebihara, N.; Tanioka, H.; Kawasaki, S.; Inatomi, T.; Katoh, N.; Ueda, E.; et al. The role of interleukin-33 in chronic allergic conjunctivitis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 4646–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoji, M.; Shoji, J.; Inada, N. Clinical Severity and Tear Biomarkers, Eosinophil Cationic Protein and CCL23, in Chronic Allergic Conjunctival Diseases. Semin. Ophthalmol. 2018, 33, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Secchi, A.; Leonardi, A.; Abelson, M. The role of eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) and histamine in vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 1995, 3, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucci, N.; Novembre, E.; Lombardi, E.; Cianferoni, A.; Bernardini, R.; Massai, C.; Caputo, R.; Campa, L.; Vierucci, A. Atopy and serum eosinophil cationic protein in 110 white children with vernal keratoconjunctivitis: Differences between tarsal and limbal forms. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2003, 33, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trocme, S.D.; Kephart, G.M.; Bourne, W.M.; Buckley, R.J.; Gleich, G.J. Eosinophil granule major basic protein deposition in corneal ulcers associated with vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1993, 115, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trocme, S.D.; Gleich, G.J.; Kephart, G.M.; Zieske, J.D. Eosinophil granule major basic protein inhibition of corneal epithelial wound healing. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1994, 35, 3051–3056. [Google Scholar]
- Fukagawa, K.; Nakajima, T.; Tsubota, K.; Shimmura, S.; Saito, H.; Hirai, K. Presence of eotaxin in tears of patients with atopic keratoconjunctivitis with severe corneal damage. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 103, 1220–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukagawa, K.; Nakajima, T.; Saito, H.; Tsubota, K.; Shimmura, S.; Natori, M.; Hirai, K. IL-4 induces eotaxin production in corneal keratocytes but not in epithelial cells. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2000, 121, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, N.; Fukuda, K.; Ishimura, Y.; Nishida, T. Synergistic induction of eotaxin expression in human keratocytes by TNF-α and IL-4 or IL-13. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 1448–1453. [Google Scholar]
- Adachi, T.; Fukuda, K.; Kondo, Y.; Nishida, T. Inhibition by tranilast of the cytokine-induced expression of chemokines and the adhesion molecule VCAM-1 in human corneal fibroblasts. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 3954–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumagai, N.; Fukuda, K.; Fujitsu, Y.; Nishida, T. Synergistic effect of TNF-α and either IL-4 or IL-13 on VCAM-1 expression by cultured human corneal fibroblasts. Cornea 2003, 22, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Fujitsu, Y.; Seki, K.; Kumagai, N.; Nishida, T. Differential expression of thymus- and activation-regulated chemokine (CCL17) and macrophage-derived chemokine (CCL22) by human fibroblasts from cornea, skin, and lung. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, N.; Fukuda, K.; Nishida, T. Synergistic effect of TNF-α and IL-4 on the expression of thymus- and activation-regulated chemokine in human corneal fibroblasts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 279, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppenheim, J.J.; Yang, D. Alarmins: Chemotactic activators of immune responses. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2005, 17, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, H.E.; Raucci, A. Alarmin(g) news about danger: Workshop on innate danger signals and HMGB1. EMBO Rep. 2006, 7, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cevikbas, F.; Steinhoff, M. IL-33: A novel danger signal system in atopic dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 1326–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holgate, S.T. Innate and adaptive immune responses in asthma. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnicozzi, M.; Sawyer, R.T.; Fenton, M.J. Innate immunity in allergic disease. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 242, 106–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebihara, N.; Matsuda, A.; Nakamura, S.; Matsuda, H.; Murakami, A. Role of the IL-6 classic- and trans-signaling pathways in corneal sterile inflammation and wound healing. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 8549–8557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Ishida, W.; Miura, Y.; Kishimoto, T.; Fukushima, A. Cytokine expression and barrier disruption in human corneal epithelial cells induced by alarmin released from necrotic cells. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 61, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, K.; Ishida, W.; Tanaka, H.; Harada, Y.; Matsuda, A.; Ebihara, N.; Fukushima, A. Alarmins from corneal epithelial cells upregulate CCL11 and VCAM-1 in corneal fibroblasts. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 5817–5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, A.; Borghesan, F.; Faggian, D.; Depaoli, M.; Secchi, A.G.; Plebani, M. Tear and serum soluble leukocyte activation markers in conjunctival allergic diseases. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2000, 129, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonini, S.; Magrini, L.; Rotiroti, G.; Lambiase, A.; Tomassini, M.; Rumi, C.; Bonini, S. The eosinophil and the eye. Allergy 1997, 52 (Suppl. S34), 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleich, G.J.; Frigas, E.; Loegering, D.A.; Wassom, D.L.; Steinmuller, D. Cytotoxic properties of the eosinophil major basic protein. J. Immunol. 1979, 123, 2925–2927. [Google Scholar]
- Motojima, S.; Frigas, E.; Loegering, D.A.; Gleich, G.J. Toxicity of eosinophil cationic proteins for guinea pig tracheal epithelium in vitro. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1989, 139, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trocme, S.D.; Hallberg, C.K.; Gill, K.S.; Gleich, G.J.; Tyring, S.K.; Brysk, M.M. Effects of eosinophil granule proteins on human corneal epithelial cell viability and morphology. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1997, 38, 593–599. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Chen, Q.; Su, S.B.; Zhang, P.; Kurosaka, K.; Caspi, R.R.; Michalek, S.M.; Rosenberg, H.F.; Zhang, N.; Oppenheim, J.J. Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin acts as an alarmin to activate the TLR2-MyD88 signal pathway in dendritic cells and enhances Th2 immune responses. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.C.; Heinzel, F.P.; Diaconu, E.; Sun, Y.; Hise, A.G.; Golenbock, D.; Lass, J.H.; Pearlman, E. Activation of toll-like receptor (TLR)2, TLR4, and TLR9 in the mammalian cornea induces MyD88-dependent corneal inflammation. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Martinez, S.; Cancino-Diaz, M.E.; Cancino-Diaz, J.C. Expression of CRAMP via PGN-TLR-2 and of alpha-defensin-3 via CpG-ODN-TLR-9 in corneal fibroblasts. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2006, 90, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Nishida, T.; Fukushima, A. Synergistic induction of eotaxin and VCAM-1 expression in human corneal fibroblasts by staphylococcal peptidoglycan and either IL-4 or IL-13. Allergol. Int. 2011, 60, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, S.W.; Chou, S.F.; Chuang, J.L. Mechanical corneal epithelium scraping and ethanol treatment up-regulate cytokine gene expression differently in rabbit cornea. J. Refract. Surg. 2008, 24, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stapleton, W.M.; Chaurasia, S.S.; Medeiros, F.W.; Mohan, R.R.; Sinha, S.; Wilson, S.E. Topical interleukin-1 receptor antagonist inhibits inflammatory cell infiltration into the cornea. Exp. Eye Res. 2008, 86, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukuda, K.; Nishida, T. Reciprocal interaction of the conjunctiva and cornea in ocular allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 493.e2–496.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, K.; Nishida, T. Ocular allergic inflammation: Interaction between the cornea and conjunctiva. Cornea 2010, 29 (Suppl. S1), S62–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enoksson, M.; Lyberg, K.; Moller-Westerberg, C.; Fallon, P.G.; Nilsson, G.; Lunderius-Andersson, C. Mast cells as sensors of cell injury through IL-33 recognition. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 2523–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elbasiony, E.; Mittal, S.K.; Foulsham, W.; Cho, W.; Chauhan, S.K. Epithelium-derived IL-33 activates mast cells to initiate neutrophil recruitment following corneal injury. Ocul. Surf. 2020, 18, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.K.; Mittal, S.K.; Foulsham, W.; Li, M.; Sangwan, V.S.; Chauhan, S.K. Mast Cells Initiate the Recruitment of Neutrophils Following Ocular Surface Injury. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 1732–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuba-Kitamura, S.; Yoshimoto, T.; Yasuda, K.; Futatsugi-Yumikura, S.; Taki, Y.; Muto, T.; Ikeda, T.; Mimura, O.; Nakanishi, K. Contribution of IL-33 to induction and augmentation of experimental allergic conjunctivitis. Int. Immunol. 2010, 22, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, K.; Fukuda, K.; Fukushima, A. Inhibition by tranilast of the synergistic induction of degranulation and IL-13 expression by IL-33 and FcεRI cross-linking in mast cells. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2017, 25, 841–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, J.; Asada, Y.; Ishida, W.; Iwamoto, S.; Sudo, K.; Suto, H.; Matsunaga, T.; Fukuda, K.; Fukushima, A.; Yokoi, N.; et al. Contributions of Interleukin-33 and TSLP in a papain-soaked contact lens-induced mouse conjunctival inflammation model. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2017, 5, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Chen, D.; Hua, X.; Bian, F.; Deng, R.; Lu, F.; Li, Z.; Pflugfelder, S.C.; et al. Pollen/TLR4 Innate Immunity Signaling Initiates IL-33/ST2/Th2 Pathways in Allergic Inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Imai, Y.; Hosotani, Y.; Ishikawa, H.; Yasuda, K.; Nagai, M.; Jitsukawa, O.; Gomi, F.; Nakanishi, K.; Yoshimoto, T.; Nakamura, T.; et al. Expression of IL-33 in ocular surface epithelium induces atopic keratoconjunctivitis with activation of group 2 innate lymphoid cells in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Ma, P.; de Paiva, C.S.; Cunningham, M.A.; Hwang, C.S.; Pflugfelder, S.C.; Li, D.Q. TSLP and downstream molecules in experimental mouse allergic conjunctivitis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 3076–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.Q.; Zhang, L.; Pflugfelder, S.C.; De Paiva, C.S.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, G.; Zheng, X.; Su, Z.; Qu, Y. Short ragweed pollen triggers allergic inflammation through Toll-like receptor 4-dependent thymic stromal lymphopoietin/OX40 ligand/OX40 signaling pathways. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 1318.e2–1325.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shiraki, Y.; Shoji, J.; Inada, N.; Tomioka, A.; Yamagami, S. IL-1α antibody inhibits dose-dependent exacerbation of eosinophilic inflammation by crude house-dust-mite antigen in the conjunctiva of an atopic keratoconjunctivitis mouse model. Curr. Eye Res. 2021, 46, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keane-Myers, A.M.; Miyazaki, D.; Liu, G.; Dekaris, I.; Ono, S.; Dana, M.R. Prevention of allergic eye disease by treatment with IL-1 receptor antagonist. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1999, 40, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar]
- Aso, H.; Shoji, J.; Shiraki, Y.; Inada, N.; Yamagami, S. Evaluation of Chemokine mRNA Expression to Assess Allergic Inflammation of the Ocular Surface in Chronic Allergic Conjunctival Diseases. Cornea 2019, 38, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, A.; Borghesan, F.; DePaoli, M.; Plebani, M.; Secchi, A.G. Procollagens and inflammatory cytokine concentrations in tarsal and limbal vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Exp. Eye Res. 1998, 67, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Xin, Y.; Qin, D.; Yan, A.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Z. Correlation of interleukin-33 with Th cytokines and clinical severity of dry eye disease. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 66, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, A.; Ebihara, N.; Yokoi, N.; Kawasaki, S.; Tanioka, H.; Inatomi, T.; de Waal Malefyt, R.; Hamuro, J.; Kinoshita, S.; Murakami, A. Functional role of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in chronic allergic keratoconjunctivitis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.D.; Deng, Y.X.; Ma, H.X.; Chen, X.G.; Chen, L.H.; Qu, J. Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin-Related Allergic Pathway in Patients with Vernal Keratoconjunctivitis. Cornea 2019, 38, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Yao, J.; Li, B. Expression of TSLP and Downstream Molecules IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 on the Eye Surface of Patients with Various Types of Allergic Conjunctivitis. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 2016, 5072781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caputo, R.; Pasti, M.; de Libero, C.; Mori, F.; Barni, S.; Danti, G.; Buonvicino, D.; Urru, M.; Chiarugi, A.; Pucci, N. Increased Lacrimal Fluid Level of HMGB1 in Vernal Keratoconjunctivitis. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2019, 27, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zicari, A.M.; Zicari, A.; Nebbioso, M.; Mari, E.; Celani, C.; Lollobrigida, V.; Cesoni Marcelli, A.; Occasi, F.; Duse, M. High-mobility group box-1 (HMGB-1) and serum soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products (sRAGE) in children affected by vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2014, 25, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratchataswan, T.; Banzon, T.M.; Thyssen, J.P.; Weidinger, S.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Phipatanakul, W. Biologics for Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis: Current Status and Future Prospect. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, L. Biologics and Allergy Immunotherapy in the Treatment of Allergic Diseases. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2020, 40, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Ebihara, N.; Kishimoto, T.; Fukushima, A. Amelioration of conjunctival giant papillae by dupilumab in patients with atopic keratoconjunctivitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 8, 1152–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roan, F.; Obata-Ninomiya, K.; Ziegler, S.F. Epithelial cell-derived cytokines: More than just signaling the alarm. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 1441–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porsbjerg, C.M.; Sverrild, A.; Lloyd, C.M.; Menzies-Gow, A.N.; Bel, E.H. Anti-alarmins in asthma: Targeting the airway epithelium with next-generation biologics. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2000260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fukuda, K.; Ishida, W.; Kishimoto, T.; Nakajima, I.; Miura, Y.; Sumi, T.; Yamashiro, K. Role of Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns (DAMPs/Alarmins) in Severe Ocular Allergic Diseases. Cells 2022, 11, 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11061051
Fukuda K, Ishida W, Kishimoto T, Nakajima I, Miura Y, Sumi T, Yamashiro K. Role of Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns (DAMPs/Alarmins) in Severe Ocular Allergic Diseases. Cells. 2022; 11(6):1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11061051
Chicago/Turabian StyleFukuda, Ken, Waka Ishida, Tatsuma Kishimoto, Isana Nakajima, Yusaku Miura, Tamaki Sumi, and Kenji Yamashiro. 2022. "Role of Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns (DAMPs/Alarmins) in Severe Ocular Allergic Diseases" Cells 11, no. 6: 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11061051
APA StyleFukuda, K., Ishida, W., Kishimoto, T., Nakajima, I., Miura, Y., Sumi, T., & Yamashiro, K. (2022). Role of Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns (DAMPs/Alarmins) in Severe Ocular Allergic Diseases. Cells, 11(6), 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11061051






