Sterol Regulation of Development and 20-Hydroxyecdysone Biosynthetic and Signaling Genes in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Fly Stocks
2.4. D. melanogaster Diets
2.5. Developmental Timing Analysis
2.6. Total RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.7. Immunocytochemistry of Drosophila Tissues
2.8. Measurement of Free Cholesterol Level
2.9. Statistical Analysis of Data
3. Results
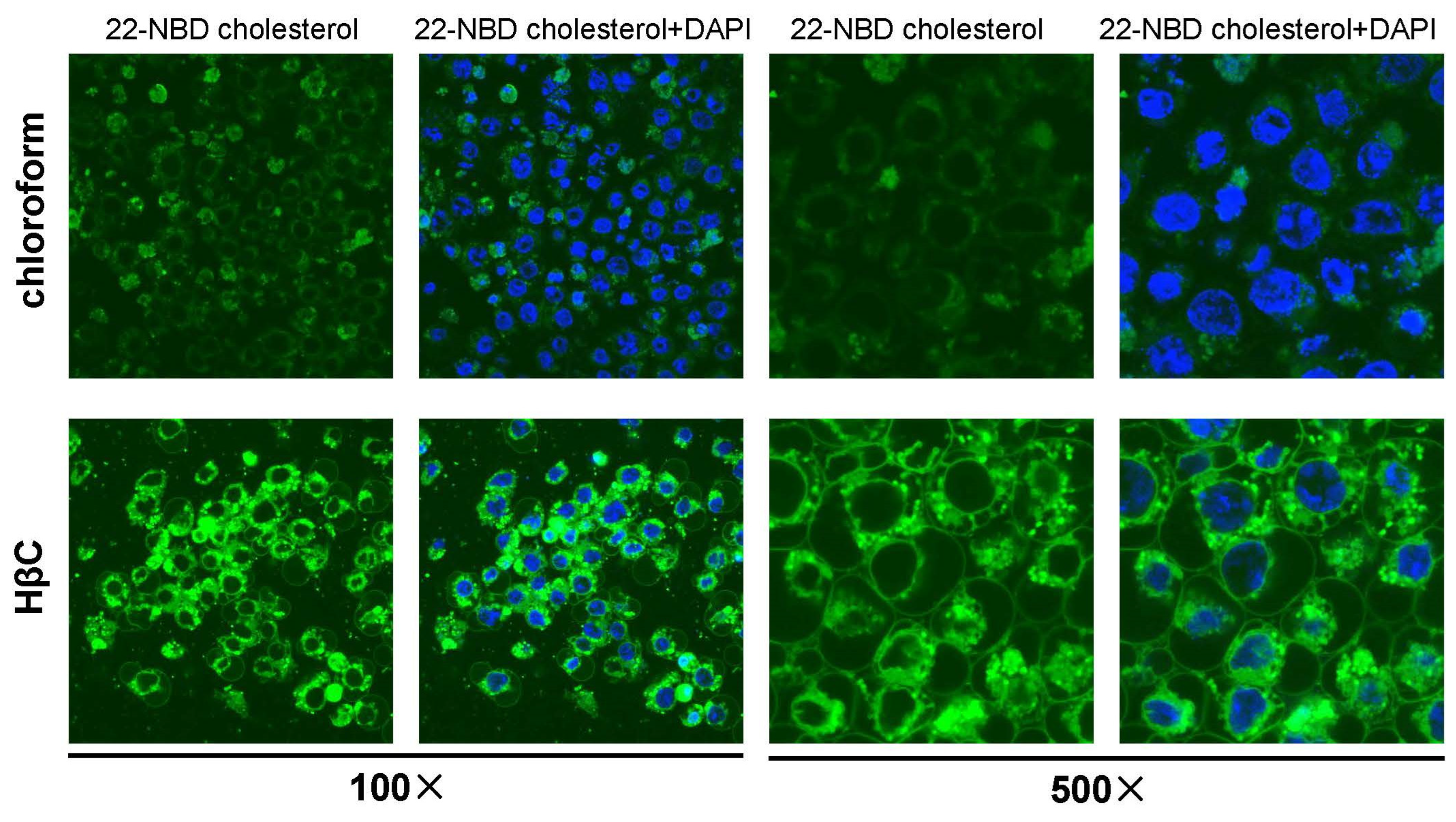
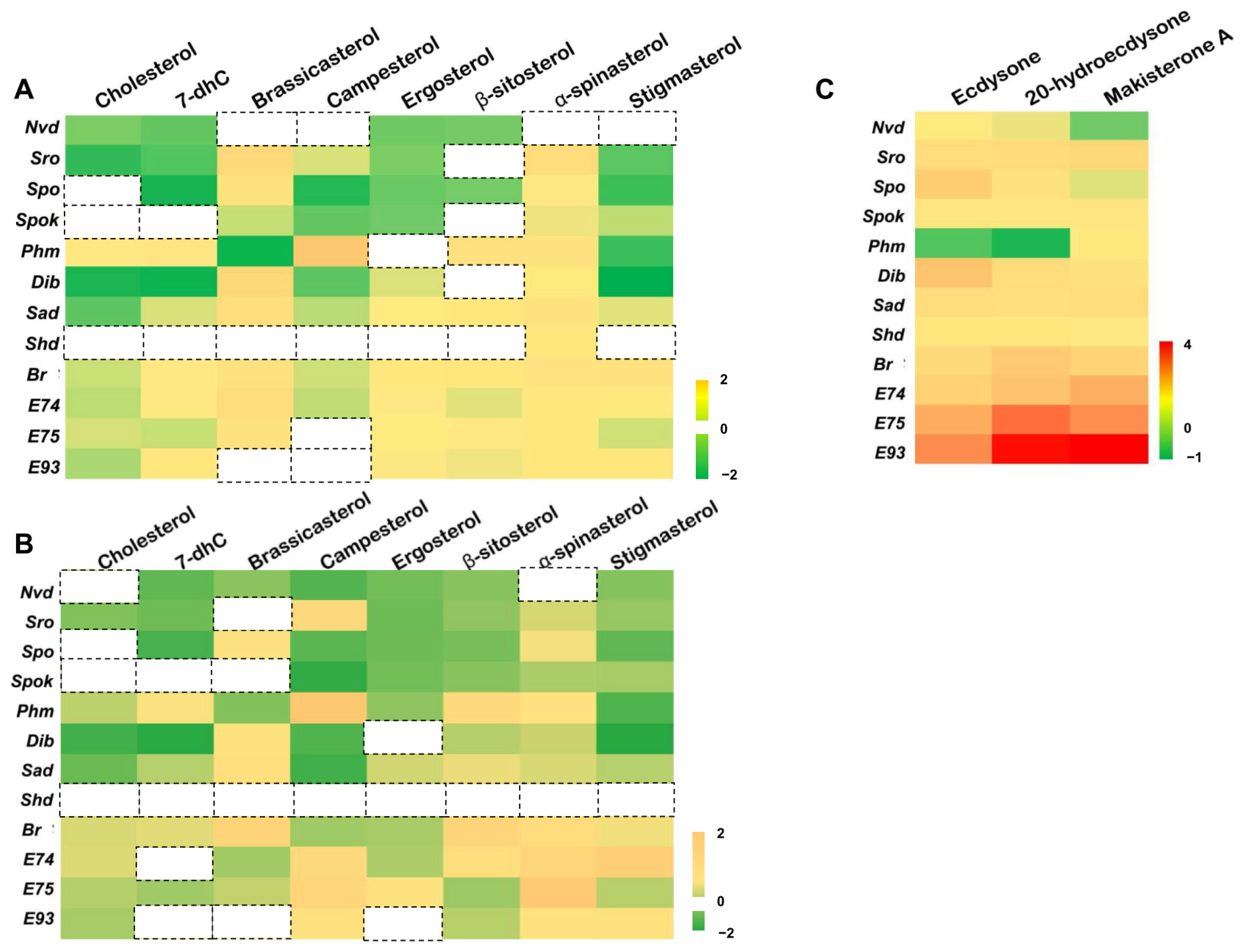
3.1. Dietary Sterols Inhibit the Most 20E Biosynthetic Genes but Activate the 20E Signaling Pathway in D. melanogaster Kc Cells
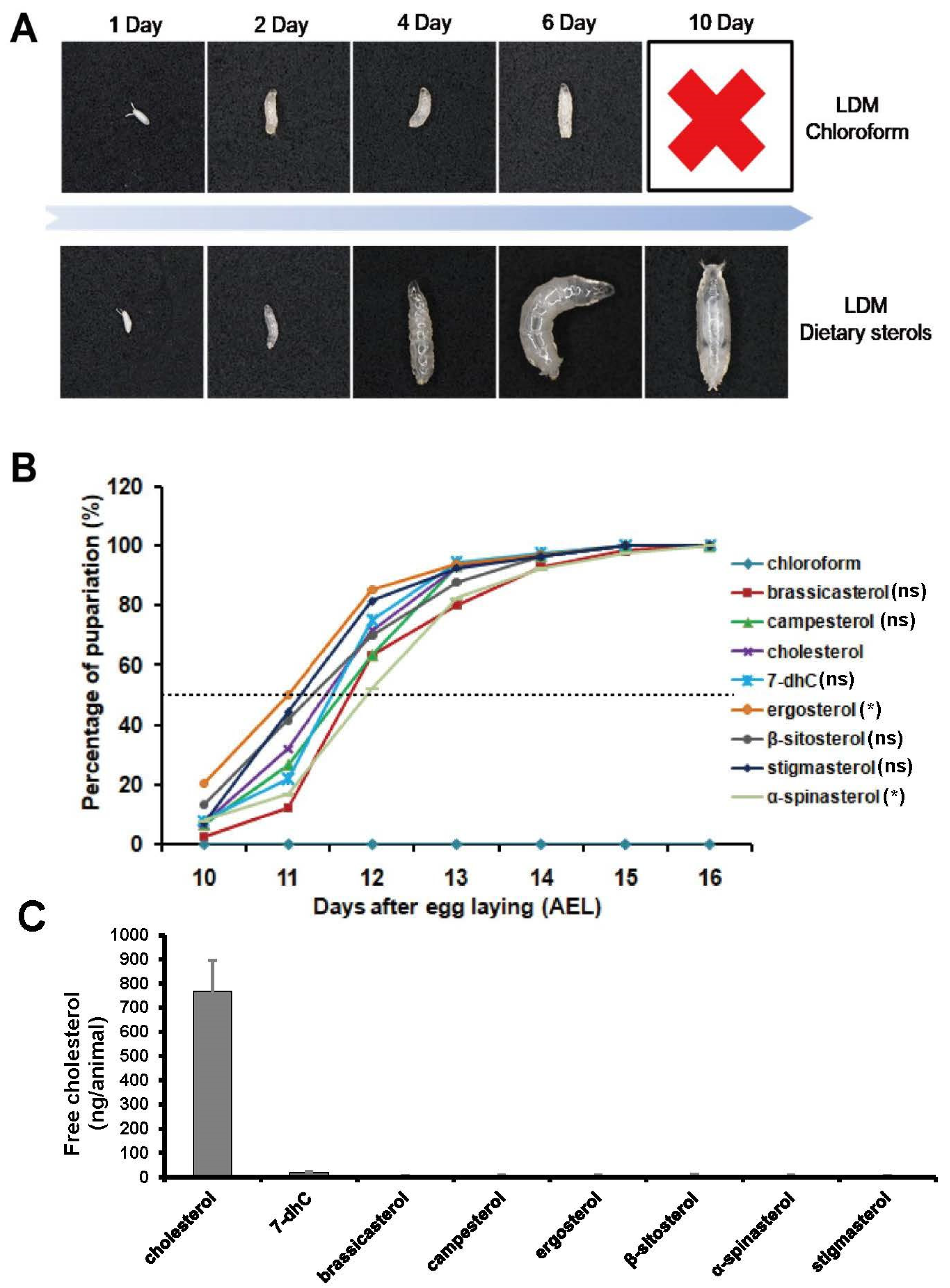
3.2. Single Dietary Sterol Is Enough to Support D. melanogaster Growth and Development
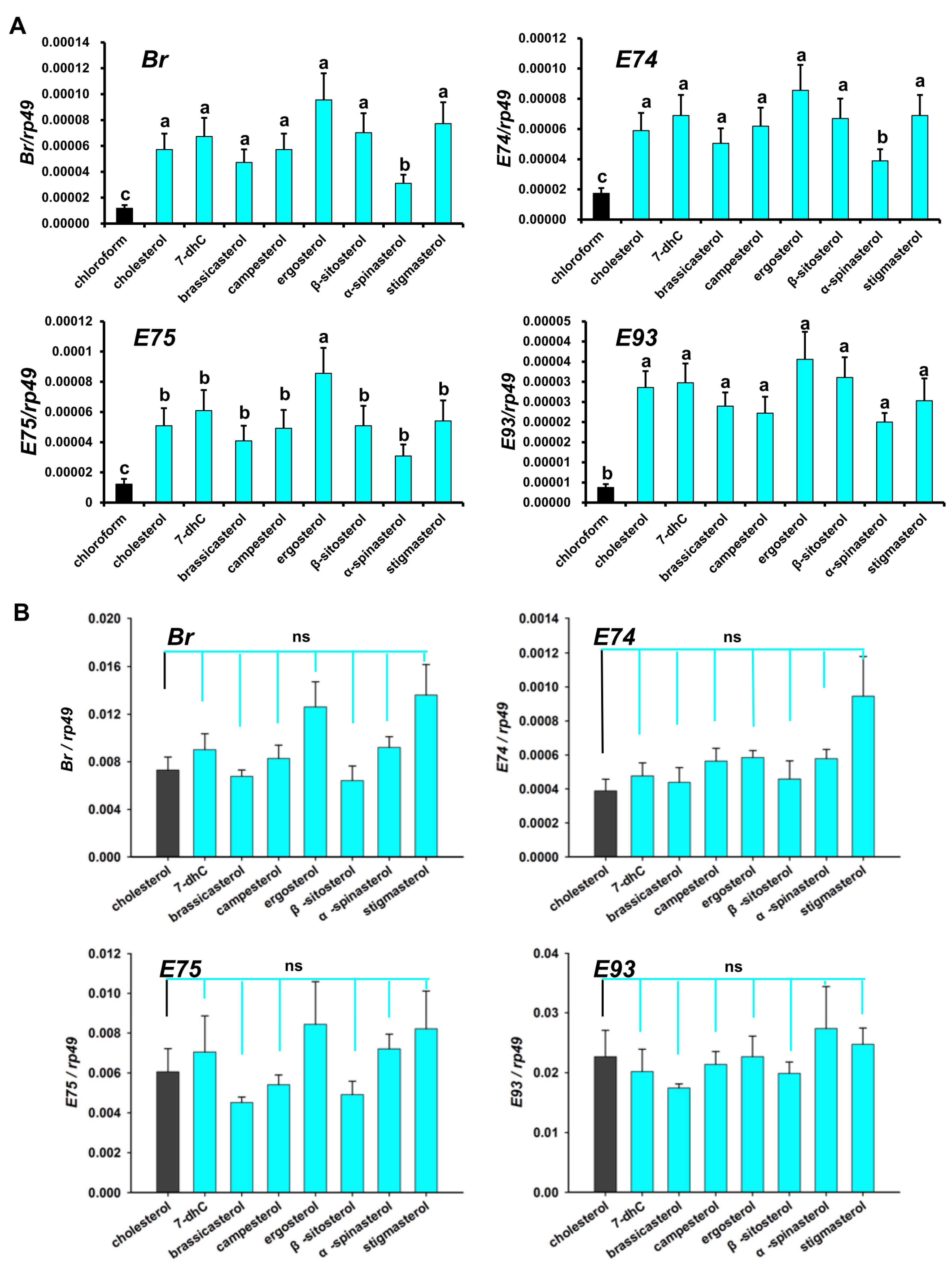
3.3. Effect of Dietary Sterols on 20E Biosynthetic Genes in D. melanogaster
3.4. Regulation of Dietary Sterols on 20E Signaling Pathway in D. melanogaster
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yamanaka, N.; Rewitz, K.F.; O’Connor, M.B. Ecdysone control of developmental transitions: Lessons from Drosophila research. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enya, S.; Ameku, T.; Igarashi, F.; Iga, M.; Kataoka, H.; Shinoda, T.; Niwa, R. A Halloween gene noppera-bo encodes a glutathione s-transferase essential for ecdysteroid biosynthesis via regulating the behaviour of cholesterol in Drosophila. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lavrynenko, O.; Rodenfels, J.; Carvalho, M.; Dye, N.A.; Lafont, R.; Eaton, S.; Shevchenko, A. The ecdysteroidome of Drosophila: Influence of diet and development. Development 2015, 142, 3758–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Igarashi, F.; Ogihara, M.H.; Iga, M.; Kataoka, H. Cholesterol internalization and metabolism in insect prothoracic gland, a steroidogenic organ, via lipoproteins. Steroids 2018, 134, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Creuzburg, D.; Oexle, S.; Wacker, A. Thresholds for sterol-limited growth of Daphnia magna: A comparative approach using 10 different sterols. J. Chem. Ecol. 2014, 40, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rewitz, K.F.; O’Connor, M.B.; Gilbert, L.I. Molecular evolution of the insect Halloween family of cytochrome P450s: Phylogeny, gene organization and functional conservation. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshiyama, T.; Namiki, T.; Mita, K.; Kataoka, H.; Niwa, R. Neverland is an evolutionally conserved rieske-domain protein that is essential for ecdysone synthesis and insect growth. Development 2006, 133, 2565–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saito, J.; Kimura, R.; Kaieda, Y.; Nishida, R.; Ono, H. Characterization of candidate intermediates in the Black Box of the ecdysone biosynthetic pathway in Drosophila melanogaster: Evaluation of molting activities on ecdysteroid-defective larvae. J. Insect Physiol. 2016, 93–94, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niwa, R.; Namiki, T.; Ito, K.; Shimadaniwa, Y.; Kiuchi, M.; Kawaoka, S.; Banno, Y.; Fujimoto, Y.; Shigenobu, S.; Kobayashi, S.; et al. Non-molting glossy/shroud encodes a short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase that functions in the ‘Black Box’ of the ecdysteroid biosynthesis pathway. Development 2010, 137, 1991–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ono, H.; Rewitz, K.F.; Shinoda, T.; Itoyama, K.; Petryk, A.; Rybczynski, R.; Jarcho, M.; Warren, J.T.; Marqués, G.; Shimell, M.J.; et al. Spook and spookier code for stage-specific components of the ecdysone biosynthetic pathway in Diptera. Dev. Biol. 2006, 298, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iga, M.; Kataoka, H. Recent studies on insect hormone metabolic pathways mediated by cytochrome P450 enzymes. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 35, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niwa, R.; Matsuda, T.; Yoshiyama, T.; Namiki, T.; Mita, K.; Fujimoto, Y.; Kataoka, H. CYP306A1, a cytochrome P450 enzyme, is essential for ecdysteroid biosynthesis in the prothoracic glands of Bombyx and Drosophila. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 35942–35949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warren, J.T.; Petryk, A.; Marques, G.; Jarcho, M.; Parvy, J.P.; Dauphin-Villemant, C.; O’Connor, M.B.; Gilbert, L. Molecular and biochemical characterization of two P450 enzymes in the ecdysteroidogenic pathway of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11043–11048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rewitz, K.F.; Rybczynski, R.; Warren, J.T.; Gilbert, L.I. The Halloween genes code for cytochrome P450 enzymes mediating synthesis of the insect moulting hormone. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2006, 34, 1256–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Park, Y.; Feyereisen, R.; Zhu, K.Y.; Ma, E.; Zhang, J.; et al. CYP303A1 has a conserved function in adult eclosion in Locusta migratoria and Drosophila melanogaster. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 113, 103210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petryk, A.; Warren, J.T.; Marqués, G.; Jarcho, M.P.; Gilbert, L.I.; Kahler, J.; Parvy, J.P.; Li, Y.; Dauphin-Villemant, C.; O’Connor, M.B. Shade is the Drosophila P450 enzyme that mediates the hydroxylation of ecdysone to the steroid insect molting hormone 20-hydroxyecdysone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13773–13778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cherbas, L.; Hu, X.; Zhimulev, I.; Belyaeva, E.; Cherbas, P. EcR isoforms in Drosophila: Testing tissue-specific requirements by targeted blockade and rescue. Development 2003, 130, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, Q.; Liu, S.; Wen, D.; Chen, Y.; Bendena, W.G.; Wang, J.; Li, S. Juvenile hormone and 20-hydroxyecdysone coordinately control the developmental timing of matrix metalloproteinase-induced fat body cell dissociation. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 21504–21516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Dai, F.; Guo, E.; Li, K.; Ma, L.; Tian, L.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Palli, S.R.; Li, S. 20-hydroxyecdysone (20E) primary response gene E93 modulates 20E signaling to promote Bombyx larval-pupal metamorphosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 27370–27383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, K.; Tian, L.; Guo, Z.; Guo, S.; Zhang, J.; Gu, S.-H.; Palli, S.R.; Cao, Y.; Li, S. 20-Hydroxyecdysone (20E) Primary Response Gene E75 Isoforms Mediate Steroidogenesis Autoregulation and Regulate Developmental Timing in Bombyx. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 18163–18175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, K.; Guo, E.; Hossain, M.S.; Li, Q.; Cao, Y.; Tian, L.; Deng, X.; Li, S. Bombyx E75 isoforms display stage- and tissue-specific responses to 20-hydroxyecdysone. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Jia, Q.; Tettamanti, G.; Li, S. Balancing crosstalk between 20-hydroxyecdysone-induced autophagy and caspase activity in the fat body during Drosophila larval-prepupal transition. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 43, 1068–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Li, S. E93 predominantly transduces 20-hydroxyecdysone signaling to induce autophagy and caspase activity in Drosophila fat body. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 45, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, S.; Drabløs, F. Gene regulation in the immediate-early response process. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2016, 62, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maurer, P.; Girault, J.P.; Larcheveque, M.; Lafont, R. 24-Epi-makisterone a (not makisterone A) is the major ecdysteroid in the leaf-cutting ant Acromyrmex octospinosus (reich) (hymenoptera, formicidae: Attini). Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 1993, 23, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, L.I. Halloween genes encode P450 enzymes that mediate steroid hormone biosynthesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2004, 215, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohidi-Esfahani, D.; Graham, L.D.; Hannan, G.N.; Simpson, A.M.; Hill, R.J. An ecdysone receptor from the pentatomomorphan, nezaraviridula, shows similar affinities for moulting hormones makisterone A and 20-hydroxyecdysone. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, K.; Gao, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, W.; Ge, W.; Feng, Q.; Palli, S.R.; Li, S. Antagonistic actions of juvenile hormone and 20-hydroxyecdysone within the ring gland determine developmental transitions in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, S. Mmp1 and mmp2 cooperatively induce Drosophila fat body cell dissociation with distinct roles. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carvalho, M.; Schwudke, D.; Sampaio, J.L.; Palm, W.; Riezman, I.; Dey, G.; Gupta, G.D.; Mayor, S.; Riezman, H.; Shevchenko, A.; et al. Survival strategies of a sterol auxotroph. Development 2010, 137, 3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Yang, L.; Huang, R.; Li, S.; Jia, Q. Matrix metalloproteinases are involved in eclosion and wing expansion in the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 131, 103551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarohia, G.S.; Garza, E.D.; Bhattacharya, S.K. Analyses of cholesterol metabolites of optic nerve using GC-MS methods. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1996, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Janson, E.M.; Grebenok, R.J.; Behmer, S.T.; Abbot, P. Same host-plant, different sterols: Variation in sterol metabolism in an insect herbivore community. J. Chem. Ecol. 2009, 35, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, J.; Sang, J.H. Utilization of sterols by larvae of Drosophila melanogaster. J. Insect Physiol. 1970, 16, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silberkang, M.; Havel, C.M.; Friend, D.S.; McCarthy, B.J.; Watson, J.A. Isoprene synthesis in isolated embryonic Drosophila cells. I. Sterol-deficient eukaryotic cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1983, 258, 8503–8511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blais, C.; Blasco, T.; Maria, A.; Dauphin-Villemant, C.; Lafont, R. Characterization of ecdysteroids in Drosophila melanogaster by enzyme immunoassay and nano-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2010, 878, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldlaufer, M.F.; Svoboda JAMakisterone, A. A 28-carbon insect ecdysteroid. Ecdysone 1986, 16, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Redfern, C.P. Evidence for the presence of makisterone A in Drosophila larvae and the secretion of 20-deoxymakisterone A by the ring gland. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 5643–5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, A.M. The Effects of Sterols on Drosophila melanogaster: Physiology and Biochemistry. Master’s Thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Piper, M.D.; Blanc, E.; Leitão-Gonçalves, R.; Yang, M.; He, X.; Linford, N.J.; Hoddinott, M.P.; Hopfen, C.; Soultoukis, G.A.; Niemeyer, C. A holidic medium for Drosophila melanogaster. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Gene Name | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Nvd | GGGGAGATTGACGATACATT | TTTGAGCCCAACTGCCATTA |
| Sro | CCACAACATCAAGTCGGAAGGAGC | ACCAGGCGAATGGAATCGGG |
| Spo | GCTGCGATATTCATCCTCCC | GCTTTGTTCCTTTGACGGTTC |
| Spok | ATCAACTATTGGACCAGCTTAC | TAATTGAACCGAACTGAACAC |
| Phm | GGATTTCTTTCGGCGCGATGTG | TGCCTCAGTATCGAAAAGCCGT |
| Dib | TGCCCTCAATCCCTATCTGGTC | ACAGGGTCTTCACACCCATCTC |
| Sad | CCGCATTCAGCAGTCAGTGG | ACCTGCCGTGTACAAGGAGAG |
| Shd | TACCCATTCCGACCTCCCACT | TGGTCCTTGCTCGTTCACAATT |
| BrC | CTCAACACGCACACCCAAT | GCTGAAGAGGGTCGAGGAG |
| E74 | GCCGGACATGAACTACGAGA | CTTGGGCACATCCACGAAC |
| E75 | CCTCAAGCAGCGCGAGTT | GCGATTTCCTTGTGGGTCT |
| E93 | GCTGAAGAATGTATGGGTCG | GGGATTGCTCTGGCTGAT |
| Rp49 | GACAGTATCTGATGCCCAACA | CTTCTTGGAGGAGACGCCGT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, D.; Chen, Z.; Wen, J.; Jia, Q. Sterol Regulation of Development and 20-Hydroxyecdysone Biosynthetic and Signaling Genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Cells 2023, 12, 1739. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12131739
Wen D, Chen Z, Wen J, Jia Q. Sterol Regulation of Development and 20-Hydroxyecdysone Biosynthetic and Signaling Genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Cells. 2023; 12(13):1739. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12131739
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Di, Zhi Chen, Jiamin Wen, and Qiangqiang Jia. 2023. "Sterol Regulation of Development and 20-Hydroxyecdysone Biosynthetic and Signaling Genes in Drosophila melanogaster" Cells 12, no. 13: 1739. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12131739
APA StyleWen, D., Chen, Z., Wen, J., & Jia, Q. (2023). Sterol Regulation of Development and 20-Hydroxyecdysone Biosynthetic and Signaling Genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Cells, 12(13), 1739. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12131739







