Photobiomodulation Therapy on Brain: Pioneering an Innovative Approach to Revolutionize Cognitive Dynamics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying PBM Therapy
3.1. Mitochondrial Cytochrome C Oxidase
3.2. Light/Heat Sensitive Ion Channels
3.3. Retrograde Mitochondrial Signaling
4. Current Strategies for Delivering Light to Different Brain Regions
5. Depth of Light Penetration and Sources of Light
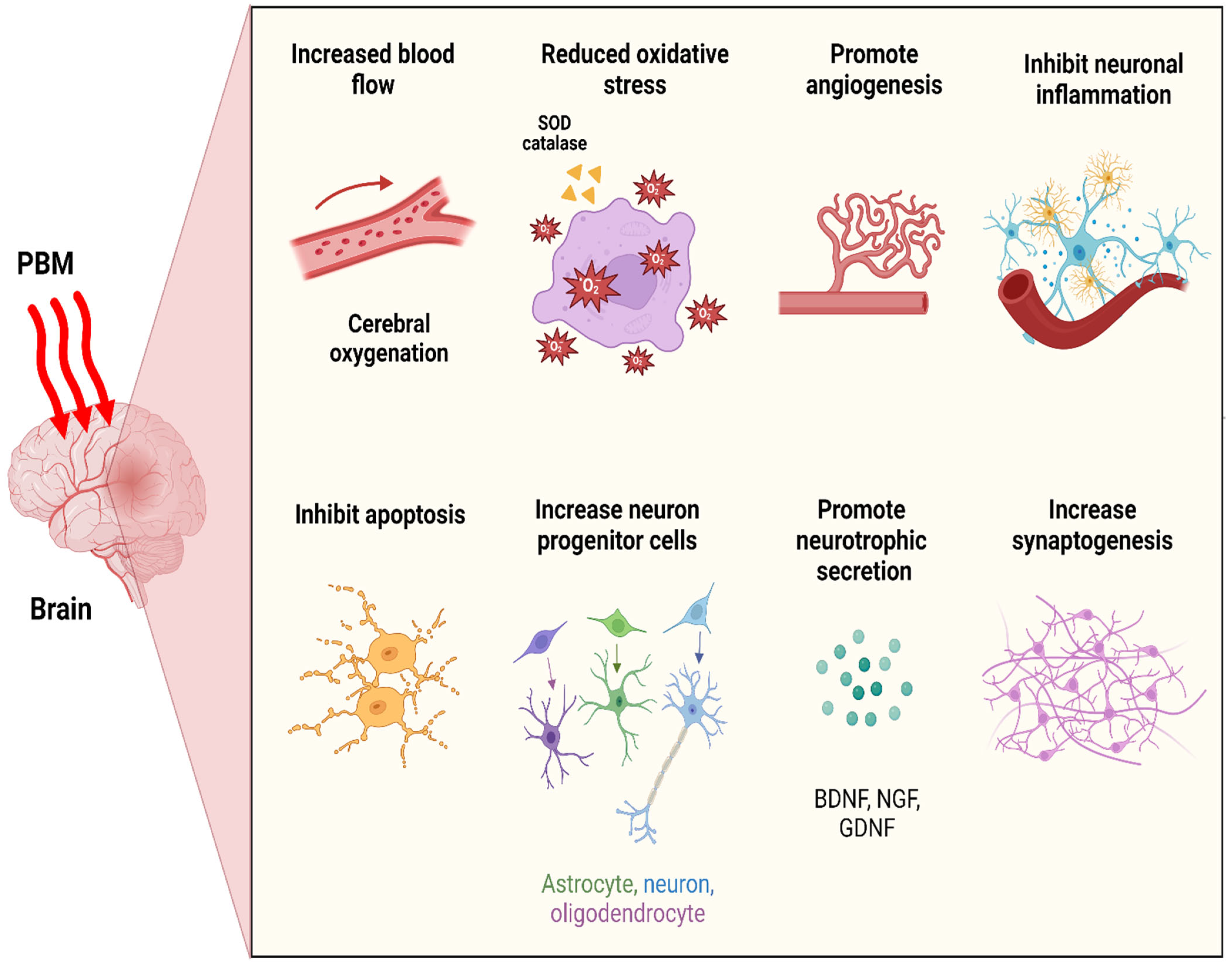
6. Neurobiological Consequences of Photobiomodulation Therapy
6.1. Neuronal Bioenergetics
6.2. Cerebral Blood Flow (CBF) and Angiogenesis
6.3. Oxidative Stress
6.4. Neuroinflammatory Suppression
6.5. Anti-Apoptosis and Neuroprotection
6.6. Neurogenesis and Synaptogenesis
6.7. Impacts on Intrinsic Brain Networks
7. Systemic Effects of PBM Therapy
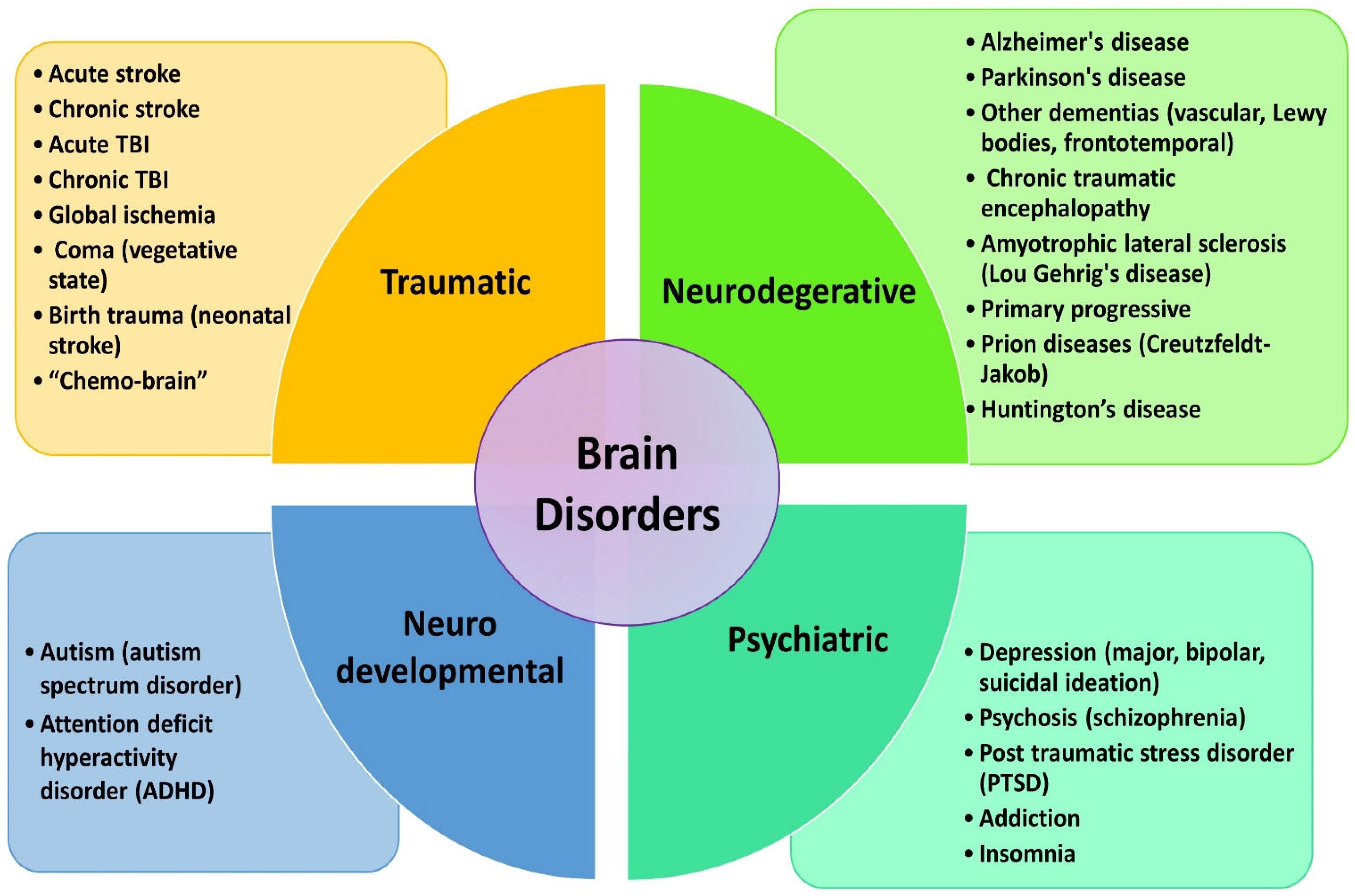
8. Clinical Applications of Brain PBM Therapy
8.1. Stroke
8.2. Acute and Chronic TBI
8.3. Alzheimer’s Disease
8.4. Parkinson’s Disease
8.5. Depression and Related Psychiatric Disorders
8.6. Cognitive Improvement among Healthy Subjects
9. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamblin, M.R. Shining light on the head: Photobiomodulation for brain disorders. BBA Clin. 2016, 6, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuff, P.E.; Deterling, R.A., Jr.; Gottlieb, L.S. Tumoricidal Effect of Laser Energy on Experimental and Human Malignant Tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 1965, 273, 490–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiman, T.H. Stimulated Optical Radiation in Ruby. Nature 1960, 187, 493–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mester, E.; Ludány, G.; Sellyei, M.; Szende, B.; Total, G.J. The Stimulating Effect of Low Power Laser Rays on Biological Systems. Laser Rev. 1968, 1, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Mester, E.; Szende, B.; Gartner, P. The Effect of Laser Beams on the Growth of Hair in Mice. Radiobiol. Radiother. 1968, 9, 621–626. [Google Scholar]
- Mester, E.; Mester, A.F.; Mester, A. The Biomedical Effects of Laser Application. Lasers Surg. Med. 1985, 5, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mester, E.; Nagylucskay, S.; Doklen, A.; Tisza, S. Laser Stimulation of Wound Healing. Acta Chir. Acad. Sci. Hung. 1976, 17, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hennessy, M.; Hamblin, M.R. Photobiomodulation and the Brain: A New Paradigm. J. Opt. 2016, 19, 013003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Freitas, L.F.; Hamblin, M.R. Proposed Mechanisms of Photobiomodulation or Low-Level Light Therapy. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2016, 22, 7000417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeser, M.A.; Hamblin, M.R. Potential for Transcranial Laser or LED Therapy to Treat Stroke, Traumatic Brain Injury, and Neurodegenerative Disease. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2011, 29, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Spielmann, A.; Wang, L.; Ding, G.; Huang, F.; Gu, Q.; Schwarz, W. Mast-cell Degranulation Induced by Physical Stimuli Involves the Activation of Transient-Receptor-Potential Channel TRPV2. Physiol. Res. 2012, 61, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q. Temperature Sensing by Thermal TRP Channels: Thermodynamic Basis and Molecular Insights. Curr. Top. Membr. 2014, 74, 19–50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.J.; Yoo, S.; Kim, K.Y.; Park, J.S.; Bang, S.; Lee, S.H.; Yang, T.J.; Cho, H.; Hwang, S.W. Laser Modulation of Heat and Capsaicin Receptor TRPV1 Leads to Thermal Antinociception. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, E.S.; Bec, J.M.; Desmadryl, G.; Chekroud, K.; Travo, C.; Gaboyard, S.; Bardin, F.; Marc, I.; Dumas, M.; Lenaers, G.; et al. TRPV4 Channels Mediate the Infrared Laser-Evoked Response in Sensory Neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2012, 107, 3227–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Q.; Wang, L.; Huang, F.; Schwarz, W. Stimulation of TRPV1 by Green Laser Light. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2012, 2012, 857123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karu, T.I. Mitochondrial Signaling in Mammalian Cells Activated by Red and Near-IR Radiation. Photochem. Photobiol. 2008, 84, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.C.; Arany, P.R.; Huang, Y.Y.; Tomkinson, E.M.; Sharma, S.K.; Kharkwal, G.B.; Saleem, T.; Mooney, D.; Yull, F.E.; Blackwell, T.S.; et al. Low-Level Laser Therapy Activates NF-kB via Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species in Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22453. [Google Scholar]
- Magrini, T.D. Low-level laser therapy on MCF-7 cells: A micro-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy study. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 101516. [Google Scholar]
- Rojas, J.C.; Gonzalez-Lima, F. Neurological and psychological applications of transcranial lasers and LEDs. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 86, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapchak, P.A. Taking a light approach to treating acute ischemic stroke patients: Transcranial near-infrared laser therapy translational science. Ann. Med. 2010, 42, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, V.; Atluri, V.; Tomitaka, A.; Shah, P.; Nagasetti, A.; Pilakka-Kanthikeel, S.; El-Hage, N.; McGoron, A.; Takemura, Y.; Nair, M. Coupling of transient near infrared photonic with magnetic nanoparticle for potential dissipation-free biomedical application in brain. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Takle, K.; Bilsel, O.; Li, Z.; Lee, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, D.; Fan, W.; Duan, C. Dye-sensitized core/active shell upconversion nanoparticles for optogenetics and bioimaging applications. ACS Nano. 2016, 10, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lai, P.; Ma, C.; Xu, X.; Grabar, A.A.; Wang, L.V. Optical focusing deep inside dynamic scattering media with near-infrared time-reversed ultrasonically encoded (TRUE) light. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, L.; Humayun, M.S. Monte Carlo analysis of the enhanced transcranial penetration using distributed near-infrared emitter array. J. Biomed. Opt. 2015, 20, 088001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, T.A.; Morries, L.D. Near-infrared photonic energy penetration: Can infrared phototherapy effectively reach the human brain? Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2015, 11, 2191–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morries, L.D.; Cassano, P.; Henderson, T.A. Treatments for traumatic brain injury with emphasis on transcranial near-infrared laser phototherapy. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2015, 11, 2159–2175. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Odekerken, V.J.; van Laar, T.; Staal, M.J.; Mosch, A.; Hoffmann, C.F.; Nijssen, P.C.; Beute, G.N.; van Vugt, J.P.; Lenders, M.W.; Contarino, M.F. Subthalamic nucleus versus globus pallidus bilateral deep brain stimulation for advanced Parkinson’s disease (NSTAPS study): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMauro, T.M.; Attawia, M.; Holy, C.; Lilienfeld, S.; Sutton, J.K.; Ward, M. Red Light Implant for Treating Parkinson’s Disease. U.S. Patent No. 7288108, 30 October 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Darlot, F.; Moro, C.; Massri, N.; Chabrol, C.; Johnstone, D.M.; Reinhart, F.; Agay, D.; Torres, N.; Bekha, D.; Auboiroux, V. Near-infrared light is neuroprotective in a monkey model of Parkinson disease. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 79, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tye, K.M.; Deisseroth, K. Optogenetic investigation of neural circuits underlying brain disease in animal models. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitzschke, A.; Lovisa, B.; Seydoux, O.; Zellweger, M.; Pfleiderer, M.; Tardy, Y.; Wagnieres, G. Red and NIR light dosimetry in the human deep brain. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 2921–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, C.; Massri, N.E.; Torres, N.; Ratel, D.; De Jaeger, X.; Chabrol, C.; Perraut, F.; Bourgerette, A.; Berger, M.; Purushothuman, S. Photobiomodulation inside the brain: A novel method of applying near-infrared light intracranially and its impact on dopaminergic cell survival in MPTP-treated mice: Laboratory investigation. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 120, 670–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnstone, D.; Coleman, K.; Moro, C.; Torres, N.; Eells, J.; Baker, G.; Ashkan, K.; Stone, J.; Benabid, A.; Mitrofanis, J. The potential of light therapy in Parkinson’s disease. Chrono Physiol. Ther. 2014, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Lapchak, P.A. Transcranial near-infrared laser therapy applied to promote clinical recovery in acute and chronic neurodegenerative diseases. Expert. Rev. Med. Devices. 2012, 9, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltmarche, A.E.; Naeser, M.A.; Ho, K.F.; Hamblin, M.R.; Lim, L. Significant Improvement in Cognition in Mild to Moderately Severe Dementia Cases Treated with Transcranial Plus Intranasal Photobiomodulation: Case Series Report. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2017, 35, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burchman, M.A. Using photobiomodulation on a severe Parkinson’s patient to enable extractions, root canal treatment, and partial denture fabrication. J. Laser Dent. 2011, 19, 297–300. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Guo, K.; Dan, J. Case analysis of Parkinson’s disease treated by endonasal low energy He-Ne laser. Acta Acad. Med. Qingdao Univ. 2003, 39, 398. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, L. The Potential of intranasal light therapy for brain stimulation. In Proceedings of the Presented, NAALTA Conference, Palm Beach Gardens, FL, USA, 20 February 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Peräkylä, J.; Kovalainen, A.; Ogawa, K.H.; Karhunen, P.J.; Hartikainen, K.M. Human brain reacts to transcranial extraocular light. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timonen, M.; Nissilä, J.; Liettu, A.; Jokelainen, J.; Jurvelin, H.; Aunio, A.; Räsänen, P.; Takala, T. Can transcranial brain-targeted bright light treatment via ear canals be effective in relieving symptoms in seasonal affective disorder?–A pilot study. Med. Hypotheses 2012, 78, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurvelin, H.; Takala, T.; Nissilä, J.; Timonen, M.; Rüger, M.; Jokelainen, J.; Räsänen, P. Transcranial bright light treatment via the ear canals in seasonal affective disorder: A randomized, double-blind dose-response study. BMC Psychiatry 2014, 14, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.; Dai, T.; Sharma, S.K.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Carroll, J.D.; Hamblin, M.R. The nuts and bolts of low-level laser (light) therapy. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 40, 516–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Bray, S.; Bryant, D.M.; Glover, G.H.; Reiss, A.L. A quantitative comparison of NIRS and fMRI across multiple cognitive tasks. Neuroimage 2011, 54, 2808–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haeussinger, F.B.; Heinzel, S.; Hahn, T.; Schecklmann, M.; Ehlis, A.C.; Fallgatter, A.J. Simulation of near-infrared light absorption considering individual head and prefrontal cortex anatomy: Implications for optical neuroimaging. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagdeo, J.R.; Adams, L.E.; Brody, N.I.; Siegel, D.M. Transcranial red and near infrared light transmission in a cadaveric model. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedford, C.E.; DeLapp, S.; Jacques, S.; Anders, J. Quantitative analysis of transcranial and intraparenchymal light penetration in human cadaver brain tissue. Lasers Surg. Med. 2015, 47, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapchak, P.A.; Boitano, P.D.; Butte, P.V.; Fisher, D.J.; Holscher, T.; Ley, E.J.; Nuno, M.; Voie, A.H.; Rajput, P.S. Transcranial near-infrared laser transmission (NILT) profiles (800 nm): Systematic comparison in four common research species. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitzschke, A.; Lovisa, B.; Seydoux, O.; Haenggi, M.; Oertel, M.F.; Zellweger, M.; Tardy, Y.; Wagnieres, G. Optical properties of rabbit brain in the red and near-infrared: Changes observed under in vivo, postmortem, frozen, and formalin-fixated conditions. J. Biomed. Opt. 2015, 20, 25006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaroslavsky, A.N.; Schulze, P.C.; Yaroslavsky, I.V.; Schober, R.; Ulrich, F.; Schwarzmaier, H.J. Optical properties of selected native and coagulated human brain tissues in vitro in the visible and near infrared spectral range. Phys. Med. Biol. 2002, 47, 2059–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, T.A. Multi-watt near-infrared light therapy as a neuroregenerative treatment for traumatic brain injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2016, 11, 563–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacke, W.; Schellinger, P.D.; Albers, G.W.; Bornstein, N.M.; Dahlof, B.L.; Fulton, R.; Kasner, S.E.; Shuaib, A.; Richieri, S.P.; Dilly, S.G.; et al. Investigators. Transcranial laser therapy in acute stroke treatment: Results of neurothera effectiveness and safety trial 3, a phase III clinical end point device trial. Stroke 2014, 45, 3187–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunnari, J.; Suomalainen, A. Mitochondria: In sickness and in health. Cell 2012, 148, 1145–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P.; Gleichmann, M.; Cheng, A. Mitochondria in neuroplasticity and neurological disorders. Neuron 2008, 60, 748–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezin, G.T.; Amboni, G.; Zugno, A.I.; Quevedo, J.; Streck, E.L. Mitochondrial dysfunction and psychiatric disorders. Neurochem. Res. 2009, 34, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong-Riley, M.T.; Liang, H.L.; Eells, J.T.; Chance, B.; Henry, M.M.; Buchmann, E.; Kane, M.; Whelan, H.T. Photobiomodulation directly benefits primary neurons functionally inactivated by toxins role of cytochrome c oxidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 4761–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong-Riley, M.T.; Bai, X.; Buchmann, E.; Whelan, H.T. Light-emitting diode treatment reverses the effect of TTX on cytochrome oxidase in neurons. Neuroreport 2001, 12, 3033–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, J.C.; Bruchey, A.K.; Gonzalez-Lima, F. Low-level light therapy improves cortical metabolic capacity and memory retention. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 32, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, J.C.; Lee, J.; John, J.M.; Gonzalez-Lima, F. Neuroprotective effects of near-infrared light in an in vivo model of mitochondrial optic neuropathy. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 13511–13521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Guo, X.; Yang, Y.; Tucker, D.; Lu, Y.; Xin, N.; Zhang, G.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Du, X.; et al. Low Level Laser Irradiation Improves Depression-Like Behaviors in Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 54, 4551–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, R.; Dong, Y.; Tucker, D.; Zhao, N.; Ahmed, M.E.; Zhu, L.; Liu, T.C.-Y.; Cohen, R.M.; Zhang, Q. Low-level laser therapy for beta amyloid toxicity in rat hippocampus. Neurobiol. Aging 2017, 49, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purushothuman, S.; Johnstone, D.M.; Nandasena, C.; Mitrofanis, J.; Stone, J. Photobiomodulation with near infrared light mitigates Alzheimer’s disease-related pathology in cerebral cortex–evidence from two transgenic mouse models. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2014, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Taboada, L.; Yu, J.; El-Amouri, S.; Gattoni-Celli, S.; Richieri, S.; McCarthy, T.; Streeter, J.; Kindy, M.S. Transcranial laser therapy attenuates amyloid-β peptide neuropathology in amyloid-β protein precursor transgenic mice. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 23, 521–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, A.P.; Bieschke, J.; Friedrich, R.P.; Zhu, D.; Wanker, E.E.; Fecht, H.J.; Mereles, D.; Hunstein, W. 670 nm laser light and EGCG complementarily reduce amyloid-β aggregates in human neuroblastoma cells: Basis for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease? Photomed. Laser Surg. 2012, 30, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trimmer, P.A.; Schwartz, K.M.; Borland, M.K.; De Taboada, L.; Streeter, J.; Oron, U. Reduced axonal transport in Parkinson’s disease cybrid neurites is restored by light therapy. Mol. Neurodegener. 2009, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki-Oda, N.; Kataoka, Y.; Cui, Y.; Yamada, H.; Heya, M.; Awazu, K. Effects of near-infrared laser irradiation on adenosine triphosphate and adenosine diphosphate contents of rat brain tissue. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 323, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapchak, P.A.; Boitano, P.D. A novel method to promote behavioral improvement and enhance mitochondrial function following an embolic stroke. Brain Res. 2016, 1646, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapchak, P.A.; De Taboada, L. Transcranial near infrared laser treatment (NILT) increases cortical adenosine-5′-triphosphate (ATP) content following embolic strokes in rabbits. Brain Res. 2010, 1306, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Zhang, Q.; Hamblin, M.R.; Wu, M.X. Low-level light in combination with metabolic modulators for effective therapy of injured brain. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2015, 35, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oron, U.; Ilic, S.; De Taboada, L.; Streeter, J. Ga-As (808 nm) laser irradiation enhances ATP production in human neuronal cells in culture. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2007, 25, 180–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraresi, C.; Kaippert, B.; Avci, P.; Huang, Y.Y.; Sousa, M.V.; Bagnato, V.S.; Parizotto, N.A.; Hamblin, M.R. Low-level Laser (Light) Therapy Increases Mitochondrial Membrane Potential and ATP Synthesis in C2C12 Myotubes with a Peak Response at 3–6 h. Photochem. Photobiol. 2015, 91, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mintzopoulos, D.; Gillis, T.E.; Tedford, C.E.; Kaufman, M.J. Effects of Near-Infrared Light on Cerebral Bioenergetics Measured with Phosphorus Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2017, 35, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, A.B.; O’Keefe, G.; Rowe, C.C.; Villemagne, V.L.; Gjedde, A. Cerebral blood flow and Aβ-amyloid estimates by WARM analysis of [11C] PiB uptake distinguish among and between neurodegenerative disorders and aging. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2016, 8, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghammer, P.; Cumming, P.; Østergaard, K.; Gjedde, A.; Rodell, A.; Bailey, C.J.; Vafaee, M.S. Cerebral oxygen metabolism in patients with early Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 313, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagafusa, Y.; Okamoto, N.; Sakamoto, K.; Yamashita, F.; Kawaguchi, A.; Higuchi, T.; Matsuda, H. Assessment of cerebral blood flow findings using 99mTc-ECD single-photon emission computed tomography in patients diagnosed with major depressive disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 140, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadigh-Eteghad, S.; Mahmoudi, J.; Babri, S.; Talebi, M. Effect of alpha-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor activation on beta-amyloid induced recognition memory impairment. Possible role of neurovascular function. Acta Cir. Bras. 2015, 30, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litscher, G.; Min, L.; Passegger, C.A.; Litscher, D.; Li, M.; Wang, M.; Ghaffari-Tabrizi-Wizsy, N.; Stelzer, I.; Feigl, G.; Gaischek, I. Transcranial Yellow, Red, and Infrared Laser and LED Stimulation: Changes of Vascular Parameters in a Chick Embryo Model. Integr. Med. Int. 2015, 2, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uozumi, Y.; Nawashiro, H.; Sato, S.; Kawauchi, S.; Shima, K.; Kikuchi, M. Targeted increase in cerebral blood flow by transcranial near-infrared laser irradiation. Lasers Surg. Med. 2010, 42, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.I.; Lee, S.-W.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, N.G.; Park, K.-J.; Choi, B.T.; Shin, Y.-I.; Shin, H.K. Pretreatment with light-emitting diode therapy reduces ischemic brain injury in mice through endothelial nitric oxide synthase-dependent mechanisms. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 486, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, K.A.; Castello, P.R.; Poyton, R.O. Low intensity light stimulates nitrite-dependent nitric oxide synthesis but not oxygen consumption by cytochrome c oxidase: Implications for phototherapy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B, Biol. 2011, 102, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawashiro, H.; Wada, K.; Nakai, K.; Sato, S. Focal increase in cerebral blood flow after treatment with near-infrared light to the forehead in a patient in a persistent vegetative state. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2012, 30, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, A.S.; Zângaro, R.A.; Parreira, R.B.; Kerppers, I.I. The effects of transcranial LED therapy (TCLT) on cerebral blood flow in the elderly women. J. Lasers Med. Sci. 2015, 30, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffer, F.; Johnston, A.L.; Ravichandran, C.; Polcari, A.; Teicher, M.H.; Webb, R.H.; Hamblin, M.R. Psychological benefits 2 and 4 weeks after a single treatment with near infrared light to the forehead: A pilot study of 10 patients with major depression and anxiety. Behav. Brain Funct. 2009, 5, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Hase, S.N.; Gonzalez-Lima, F.; Liu, H. Transcranial laser stimulation improves human cerebral oxygenation. Lasers Surg. Med. 2016, 48, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cury, V.; Moretti, A.I.; Assis, L.; Bossini, P.; Crusca, J.S.; Neto, C.B.; Fangel, R.; de Souza, H.P.; Hamblin, M.R.; Parizotto, N.A. Low level laser therapy increases angiogenesis in a model of ischemic skin flap in rats mediated by VEGF, HIF-1alpha and MMP-2. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2013, 125, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, B. Oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2013, 2013, 316523. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Rodriguez, A.; Jose Egea-Guerrero, J.; Murillo-Cabezas, F.; Carrillo-Vico, A. Oxidative stress in traumatic brain injury. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzanero, S.; Santro, T.; Arumugam, T.V. Neuronal oxidative stress in acute ischemic stroke: Sources and contribution to cell injury. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 62, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurya, P.K.; Noto, C.; Rizzo, L.B.; Rios, A.C.; Nunes, S.O.; Barbosa, D.S.; Sethi, S.; Zeni, M.; Mansur, R.B.; Maes, M. The role of oxidative and nitrosative stress in accelerated aging and major depressive disorder. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 65, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafur, J.; Mills, P.J. Low-intensity light therapy: Exploring the role of redox mechanisms. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2008, 26, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, G.; Dutta, A.; Mitra, K.; Grace, M.S.; Amat, A.; Romanczyk, T.B.; Wu, X.; Chakrabarti, K.; Anders, J.; Gorman, E. Effect of low intensity laser interaction with human skin fibroblast cells using fiber-optic nano-probes. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2007, 86, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Xing, D.; Chen, T.-S. High fluence laser irradiation induces reactive oxygen species generation in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Proc. SPIE 2006, 6047, 604736–604776. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, M.C.; Lo, S.C.; Siu, F.K.; So, K.F. Treatment of experimentally induced transient cerebral ischemia with low energy laser inhibits nitric oxide synthase activity and up-regulates the expression of transforming growth factor-beta 1. Lasers Surg. Med. 2002, 31, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutalangka, C.; Wattanathorn, J.; Muchimapura, S.; Thukham-mee, W.; Wannanon, P.; Tong-un, T. Laser acupuncture improves memory impairment in an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Acupunct. Meridian Stud. 2013, 6, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, W.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Karna, S.; Won, J.; Jeon, S.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Choi, Y.; Choi, H.; Kim, O. Modulation of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced NF-κB Signaling Pathway by 635 nm Irradiation via Heat Shock Protein 27 in Human Gingival Fibroblast Cells. Photochem. Photobiol. 2013, 89, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meredith, G.E.; Sonsalla, P.K.; Chesselet, M.-F. Animal models of Parkinson’s disease progression. Acta Neuropathol. 2008, 115, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloire, G.; Legrand-Poels, S.; Piette, J. NF-κB activation by reactive oxygen species: Fifteen years later. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 72, 1493–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.C.-H.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Sharma, S.K.; Hamblin, M.R. Effects of 810-nm laser on murine bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2011, 29, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamblin, M.R. Mechanisms and applications of the anti-inflammatory effects of photobiomodulation. AIMS Biophys. 2017, 4, 337–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Askarova, S.; Sheng, W.; Chen, J.K.; Sun, A.Y.; Sun, G.Y.; Yao, G.; Lee, J.M. Low energy laser light (632.8 nm) suppresses amyloid-β peptide-induced oxidative and inflammatory responses in astrocytes. Neuroscience 2010, 171, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Zhou, F.; Chen, W.R. Low-level laser therapy regulates microglial function through Src-mediated signaling pathways: Implications for neurodegenerative diseases. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachstetter, A.D.; Van Eldik, L.J. The p38 MAP kinase family as regulators of proinflammatory cytokine production in degenerative diseases of the CNS. Aging Dis. 2010, 1, 199–211. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, G.Y.; Chuang, D.Y.; Zong, Y.; Jiang, J.; Lee, J.C.M.; Gu, Z.; Simonyi, A. Role of cytosolic phospholipase A2 in oxidative and inflammatory signaling pathways in different cell types in the central nervous system. Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 50, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, W.; Huang, L.; Hamblin, M.R. Repeated transcranial low-level laser therapy for traumatic brain injury in mice: Biphasic dose response and long-term treatment outcome. J. Biophotonics 2016, 9, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desagher, S.; Martinou, J.-C. Mitochondria as the central control point of apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 2000, 10, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.-f.; Wang, H.; Yao, W.-b.; Gao, X.-d. Aqueous extract of the Chinese medicine, Danggui-Shaoyao-San, inhibits apoptosis in hydrogen peroxide-induced PC12 cells by preventing cytochrome c release and inactivating of caspase cascade. Cell Biol. Int. 2008, 32, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.L.; Whelan, H.T.; Eells, J.T.; Wong-Riley, M.T. Near-infrared light via light-emitting diode treatment is therapeutic against rotenone- and 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion-induced neurotoxicity. Neuroscience 2008, 153, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, R.; Liang, H.L.; Whelan, H.T.; Eells, J.T.; Wong-Riley, M.T. Pretreatment with near-infrared light via light-emitting diode provides added benefit against rotenone- and MPP+-induced neurotoxicity. Brain Res. 2008, 1243, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Whelan, H.; Eells, J.; Meng, H.; Buchmann, E.; Lerch-Gaggl, A.; Wong-Riley, M. Photobiomodulation partially rescues visual cortical neurons from cyanide-induced apoptosis. Neuroscience 2006, 139, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, N.; Jizhang, Y.; McCarthy, T.J.; Tedford, C.E.; Lo, E.H.; Wang, X. Near infrared radiation protects against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced neurotoxicity by down-regulating neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) activity in vitro. Metab. Brain Dis. 2015, 30, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanbari, A.; Ghareghani, M.; Zibara, K.; Delaviz, H.; Ebadi, E.; Jahantab, M. Light-Emitting Diode (LED) therapy improves occipital cortex damage by decreasing apoptosis and increasing BDNF-expressing cells in methanol-induced toxicity in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavish, L.; Asher, Y.; Becker, Y.; Kleinman, Y. Low level laser irradiation stimulates mitochondrial membrane potential and disperses subnuclear promyelocytic leukemia protein. Lasers Surg. Med. 2004, 35, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musashi, M.; Ota, S.; Shiroshita, N. The role of protein kinase C isoforms in cell proliferation and apoptosis. Int. J. Hematol. 2000, 72, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Weinreb, O.; Bar-Am, O.; Amit, T.; Chillag-Talmor, O.; Youdim, M.B. Neuroprotection via pro-survival protein kinase C isoforms associated with Bcl-2 family members. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1471–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xing, D.; Zhu, D.; Chen, Q. Low-power laser irradiation inhibiting Aβ25–35-induced PC12 cell apoptosis via PKC activation. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 22, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, D. LPLI inhibits apoptosis upstream of Bax translocation via a GSK-3β-inactivation mechanism. J. Cell Physiol. 2010, 224, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, S.; Xing, D. Inhibition of Aβ 25–35-induced cell apoptosis by low-power-laser-irradiation (LPLI) through promoting Akt-dependent YAP cytoplasmic translocation. Cell Signal. 2012, 24, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Liu, L.; Xing, D. Photobiomodulation by low-power laser irradiation attenuates Aβ-induced cell apoptosis through the Akt/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 53, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; He, Z.; Xing, D. Low-level laser therapy rescues dendrite atrophy via upregulating BDNF expression: Implications for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 13505–13517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, W.; Sun, S.; Zhao, J.; Sun, H. Low-level laser irradiation modulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA transcription through calcium-dependent activation of the ERK/CREB pathway. Lasers Med. Sci. 2017, 32, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, J.C.; Park, J.A.; Kim, D.K.; Lee, J.H. Photobiomodulation (660 nm) therapy reduces oxidative stress and induces BDNF expression in the hippocampus. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Massri, N.; Lemgruber, A.P.; Rowe, I.J.; Moro, C.; Torres, N.; Reinhart, F.; Chabrol, C.; Benabid, A.-L.; Mitrofanis, J. Photobiomodulation-induced changes in a monkey model of Parkinson’s disease: Changes in tyrosine hydroxylase cells and GDNF expression in the striatum. Exp. Brain Res. 2017, 235, 1861–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oron, A.; Oron, U.; Chen, J.; Eilam, A.; Zhang, C.; Sadeh, M.; Lampl, Y.; Streeter, J.; DeTaboada, L.; Chopp, M. Low-level laser therapy applied transcranially to rats after induction of stroke significantly reduces long-term neurological deficits. Stroke 2006, 37, 2620–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.-C.; Jang, D.; Yoon, S.-B.; Kim, D.; Choi, D.-H.; Kwon, O.; Lee, Y.-M.; Youn, D. Laser Acupuncture Exerts Neuroprotective Effects via Regulation of Creb, Bdnf, Bcl-2, and Bax Gene Expressions in the Hippocampus. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2017, 2017, 7181637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, W.; Vatansever, F.; Huang, L.; Wu, Q.; Xuan, Y.; Dai, T.; Ando, T.; Xu, T.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Hamblin, M.R. Transcranial low-level laser therapy improves neurological performance in traumatic brain injury in mice: Effect of treatment repetition regimen. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, W.; Vatansever, F.; Huang, L.; Hamblin, M.R. Transcranial low-level laser therapy enhances learning, memory, and neuroprogenitor cells after traumatic brain injury in mice. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 108003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sporns, O. Structure and function of complex brain networks. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 15, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Yang, Y.; Xi, J.-H.; Chen, Z.-Q. Structural and functional connectivity in traumatic brain injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2015, 10, 2062–2071. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De la Plata, C.D.M.; Garces, J.; Kojori, E.S.; Grinnan, J.; Krishnan, K.; Pidikiti, R.; Spence, J.; Devous, M.D.; Moore, C.; McColl, R. Deficits in functional connectivity of hippocampal and frontal lobe circuits after traumatic axonal injury. Arch. Neurol. 2011, 68, 74–84. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, B.; Zhang, K.; Gay, M.; Horovitz, S.; Hallett, M.; Sebastianelli, W.; Slobounov, S. Alteration of brain default network in subacute phase of injury in concussed individuals: Resting-state fMRI study. Neuroimage 2012, 59, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naeser, M.A.; Martin, P.I.; Ho, M.D.; Krengel, M.H.; Bogdanova, Y.; Knight, J.A.; Yee, M.K.; Zafonte, R.; Frazier, J.; Hamblin, M.R. Transcranial, Red/Near-Infrared Light-Emitting Diode Therapy to Improve Cognition in Chronic Traumatic Brain Injury. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2016, 34, 610–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeser, M.A.; Zafonte, R.; Krengel, M.H.; Martin, P.I.; Frazier, J.; Hamblin, M.R.; Knight, J.A.; Meehan, W.P., 3rd; Baker, E.H. Significant improvements in cognitive performance post-transcranial, red/near-infrared light-emitting diode treatments in chronic, mild traumatic brain injury: Open-protocol study. J. Neurotrauma 2014, 31, 1008–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeser, M.; Ho, M.; Martin, P.; Treglia, E.; Krengel, M.; Hamblin, M.; Baker, E. Improved language after scalp application of red/near-infrared light-emitting diodes: Pilot study supporting a new, noninvasive treatment for chronic aphasia. Proc. Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 61, 138–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, D.M.; Mitrofanis, J.; Stone, J. Targeting the body to protect the brain: Inducing neuroprotection with remotely-applied near infrared light. Neural Regen. Res. 2015, 10, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrie, S.R.; Hamblin, M.R.; Ionescu, D.F.; Cusin, C.; Yeung, A.; Cassano, P. Photobiomodulation in Patients with Low Back Pain: A Case Control Series for the Effect on Depression. Qual. Prim. Care 2016, 24, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zalewska-Kaszubska, J.; Obzejta, D. Use of low-energy laser as adjunct treatment of alcohol addiction. Lasers Med. Sci. 2004, 19, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.H.; Chang, W.D.; Hsieh, C.W.; Jiang, J.A.; Fang, W.; Shan, Y.C.; Chang, Y.C. Effect of low-level laser stimulation on EEG. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnstone, D.; El Massri, N.; Moro, C.; Spana, S.; Wang, X.; Torres, N.; Chabrol, C.; De Jaeger, X.; Reinhart, F.; Purushothuman, S. Indirect application of near infrared light induces neuroprotection in a mouse model of parkinsonism–An abscopal neuroprotective effect. Neuroscience 2014, 274, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrnes, K.R.; Waynant, R.W.; Ilev, I.K.; Wu, X.; Barna, L.; Smith, K.; Heckert, R.; Gerst, H.; Anders, J.J. Light promotes regeneration and functional recovery and alters the immune response after spinal cord injury. Lasers Surg. Med. 2005, 36, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muili, K.A.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Meyer, S.L.; Eells, J.T.; Lyons, J.-A. Amelioration of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in C57BL/6 mice by photobiomodulation induced by 670 nm light. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuby, H.; Maltz, L.; Oron, U. Induction of autologous mesenchymal stem cells in the bone marrow by low-level laser therapy has profound beneficial effects on the infarcted rat heart. Lasers Surg. Med. 2011, 43, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uccelli, A.; Benvenuto, F.; Laroni, A.; Giunti, D. Neuroprotective features of mesenchymal stem cells. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. 2011, 24, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oron, A.; Oron, U. Low-level laser therapy to the bone marrow ameliorates neurodegenerative disease progression in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease: A minireview. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2016, 34, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farfara, D.; Tuby, H.; Trudler, D.; Doron-Mandel, E.; Maltz, L.; Vassar, R.J.; Frenkel, D.; Oron, U. Low-level laser therapy ameliorates disease progression in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 55, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.-H.; Lim, J.H.; Lee, K.-H.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Shin, C.Y.; Han, S.-H.; Lee, J. Effect of 710-nm visible light irradiation on neuroprotection and immune function after stroke. Neuroimmunomodulation 2012, 19, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeo, S.; Vitale, F.; Viaggi, C.; di Marco, S.; Aloisi, G.; Fasciani, I.; Pardini, C.; Pietrantoni, I.; Di Paolo, M.; Riccitelli, S. Fluorescent light induces neurodegeneration in the rodent nigrostriatal system but near infrared LED light does not. Brain Res. 2017, 1662, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalikova, S.; Ennaceur, A.; van Rensburg, R.; Chazot, P. Emotional responses and memory performance of middle-aged CD1 mice in a 3D maze: Effects of low infrared light. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2008, 89, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grillo, S.; Duggett, N.; Ennaceur, A.; Chazot, P. Non-invasive infra-red therapy (1072 nm) reduces β-amyloid protein levels in the brain of an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model, TASTPM. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2013, 123, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murdock, M.H.; Yang, C.Y.; Sun, N.; Pao, P.C.; Blanco-Duque, C.; Kahn, M.C.; Tsai, L.H. Multisensory gamma stimulation promotes glymphatic clearance of amyloid. Nature 2024, 627, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampl, Y.; Zivin, J.A.; Fisher, M.; Lew, R.; Welin, L.; Dahlof, B.; Borenstein, P.; Andersson, B.; Perez, J.; Caparo, C. Infrared laser therapy for ischemic stroke: A new treatment strategy. Stroke 2007, 38, 1843–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ab Boonswang, N.; Chicchi, M.; Lukachek, A.; Curtiss, D. A new treatment protocol using photobiomodulation and muscle/bone/joint recovery techniques having a dramatic effect on a stroke patient’s recovery: A new weapon for clinicians. BMJ Case Rep. 2012, 2012, bcr0820114689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesse, S.; Werner, C.; Byhahn, M. Transcranial Low-Level Laser Therapy May Improve Alertness and Awareness in Traumatic Brain Injured Subjects with Severe Disorders of Consciousness: A Case Series. Int. Arch. Med. 2015, 6, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Maksimovich, I.V. Dementia and Cognitive Impairment Reduction after Laser Transcatheter Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. World J. Neurosci. 2015, 5, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, R.; Shanks, S.; Maloney, J. The application of low-level laser therapy for the symptomatic care of late stage Parkinson’s disease: A non-controlled, non-randomized study. Lasers Surg. Med. 2010, 185, 61. [Google Scholar]
- Cassano, P.; Cusin, C.; Mischoulon, D.; Hamblin, M.R.; De Taboada, L.; Pisoni, A.; Chang, T.; Yeung, A.; Ionescu, D.F.; Petrie, S.R. Near-infrared transcranial radiation for major depressive disorder: Proof of concept study. Psychiatr. J. 2015, 2015, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Disner, S.G.; Beevers, C.G.; Gonzalez-Lima, F. Transcranial laser stimulation as neuroenhancement for attention bias modification in adults with elevated depression symptoms. Brain Stimul. 2016, 9, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, D.; Gonzalez-Lima, F. Transcranial infrared laser stimulation produces beneficial cognitive and emotional effects in humans. Neuroscience 2013, 230, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinovi, L.M.; Jeli, M.B.; Jeremi, A.; Stevanovi, V.B.; Milanovi, S.D.; Filipovi, S.R. Transcranial application of near-infrared low-level laser can modulate cortical excitability. Lasers Surg. Med. 2013, 45, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaieb, L.; Antal, A.; Masurat, F.; Paulus, W. Neuroplastic effects of transcranial near-infrared stimulation (tNIRS) on the motor cortex. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tian, F.; Reddy, D.D.; Nalawade, S.S.; Barrett, D.W.; Gonzalez-Lima, F.; Liu, H. Up-regulation of cerebral cytochrome-c-oxidase and hemodynamics by transcranial infrared laser stimulation: A broadband near-infrared spectroscopy study. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2017, 37, 3789–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivin, J.A.; Sehra, R.; Shoshoo, A.; Albers, G.W.; Bornstein, N.M.; Dahlof, B.; Kasner, S.E.; Howard, G.; Shuaib, A.; Streeter, J.; et al. NeuroThera(R) Efficacy and Safety Trial-3 (NEST-3): A double-blind, randomized, sham-controlled, parallel group, multicenter, pivotal study to assess the safety and efficacy of transcranial laser therapy with the NeuroThera(R) Laser System for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke within 24 h of stroke onset. Int. J. Stroke 2014, 9, 950–955. [Google Scholar]
- Lapchak, P.A.; Boitano, P.D. Transcranial Near-Infrared Laser Therapy for Stroke: How to Recover from Futility in the NEST-3 Clinical Trial. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2016, 121, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, M.H.; Halper, J.P.; Nichols, T.W. Photobiomodulation with Near Infrared Light Helmet in a Pilot, Placebo Controlled Clinical Trial in Dementia Patients Testing Memory and Cognition. J. Neurol. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeser, M.A.; Saltmarche, A.; Krengel, M.H.; Hamblin, M.R.; Knight, J.A. Improved cognitive function after transcranial, light-emitting diode treatments in chronic, traumatic brain injury: Two case reports. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2011, 29, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duch, W.; Oentaryo, R.J.; Pasquier, M. Cognitive Architectures: Where do we go from here? AGI 2008, 171, 122–136. [Google Scholar]
- Newson, R.S.; Kemps, E.B.; Luszcz, M.A. Cognitive mechanisms underlying decrements in mental synthesis in older adults. Aging Neuropsychol. Cogn. 2003, 10, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, E.; Barrett, D.W.; Saucedo, C.L.; Huang, L.-D.; Abraham, J.A.; Tanaka, H.; Haley, A.P.; Gonzalez-Lima, F. Beneficial neurocognitive effects of transcranial laser in older adults. Lasers Med. Sci. 2017, 32, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Castelli, D.M.; Gonzalez-Lima, F. Cognitive enhancement by transcranial laser stimulation and acute aerobic exercise. Lasers Med. Sci. 2016, 31, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, N.J.; Saucedo, C.L.; Gonzalez-Lima, F. Transcranial infrared laser stimulation improves rule-based, but not information-integration, category learning in humans. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2017, 139, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, H.; Prakash, A.; Medhi, B. Drug therapy in stroke: From preclinical to clinical studies. Pharmacology 2013, 92, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, A.I.; Roozenbeek, B.; Manley, G.T. Clinical trials in traumatic brain injury: Past experience and current developments. Neurotherapeutics 2010, 7, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulshreshtha, A.; Piplani, P. Current pharmacotherapy and putative disease-modifying therapy for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 37, 1403–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givens, C.J. Adverse Drug Reactions Associated with Antipsychotics, Antidepressants, Mood Stabilizers, and Stimulants. Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 51, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Subjects (n) | Parameters | Major Findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acute stroke (120) | 808 nm; 10 mW/cm2, 1.2 J/cm2 laser applied at cortex, 2 min for each site, CW | Induced positive neuroprotective effects within 24 h of irradiation after stroke onset. | [149] |
| Chronic stroke (1) | 660 and 850 nm; 1400 mW, 2.95 J/cm2 LEDs delivered to multiple areas (32 sites), 1 min for each site, spot size of 0.196 cm2, 1/week for 8 weeks | Significant changes across all areas of deficits and notable enhancements in clinical manifestations of physical symptoms. | [150] |
| Chronic TBI (2 with depression) (11) | 633 and 870 nm; 500 mW, 22.48 mW/cm2, 13 J/cm2 LEDs administered at 11 sites of midline and bilateral forehead, 10 min per site, 3×/week for 6 weeks, CW | Enhanced sleep patterns, diminished symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder, and heightened proficiency across social, interpersonal, and occupational domains. | [131] |
| Chronic TBI (6 with MDD) (10) | 810 and 980 nm; 10 and 15 W, 14.8–28.3 J/cm2 laser applied in unilateral (forehead) and bilateral areas (prefrontal and temporal), 8–12 min per site, 2–3×/week for 8 weeks, with PW at 10 Hz | Reduced headache, sleep disruption, mood instability, anxiety levels, irritability, and cognitive symptoms. | [26] |
| TBI with disorders of consciousness (5) | 785 nm; 10 mW/cm2 laser delivered on the superior crest level of the fossa sphenoidale on the forehead, 10 min, 5×/week for 6 weeks, CW | Increased consciousness and alertness; as an adverse effect, epileptic episodes occur. | [151] |
| Alzheimer’s disease (89) | Visible region of spectrum; 20 mw laser conjugated with an optic fiber with a diameter of 25–100 μm inserted through a catheter into the femoral artery, navigated to reach the distal sites of the anterior and middle cerebral arteries, 20–40 min, CW or PW, or combined modes. | Reduced irreversible dementia; enhanced microcirculation within the cerebral region, leading to cognitive rehabilitation. | [152] |
| Parkinson’s disease (8) | Laser applied 2 weeks daily in several areas (bilateral occipital, parietal, temporal, frontal lobes and along sagittal sutures) | Enhanced stability, walking pattern, mitigation of freezing episodes, cognitive capabilities, movement while in bed, and speech challenges. | [153] |
| Major depressive disorder (10) | 810 nm; 250 mW/cm2, 60 J/cm2 LEDs applied at right and left forehead, 4 min, one irradiation session, CW | Reduced rates of depression and anxiety for two weeks after irradiation; no significant impacts on cerebral blood flow. | [82] |
| Major depressive disorder (4) | 808 nm; 5 W, 700 mW/cm2, 84 J/cm2 laser administered at right and left forehead center at 20 and 40 mm from the sagittal line, 2 min per site, 2×/week for 3 weeks, CW | Occurrence of depression exhibited a notable decrease around six to seven weeks following the irradiation. | [154] |
| Patients with elevated depression symptoms (51) | 1064 nm; 250 mW/cm2, 60 J/cm2 laser delivered to the medial and lateral parts of the left or right side of the forehead, 4 min per site, for 2 sessions, CW | Prefrontal irradiation on the right side enhanced the efficacy of attention bias modification interventions and alleviated symptoms of depression. | [155] |
| Healthy volunteers (40) | 1064 nm; 250 mW/cm2, 60 J/cm2 laser applied at right frontal pole 4 cm medially and laterally, 4 min, one irradiation session, CW | Enhancements in reaction time during the Psychomotor Vigilance Task and performance in a delayed match-to-sample memory task; sustained positive emotional states evident even two weeks after the treatment. | [156] |
| Healthy volunteers (14) | 905 nm; 50 mW/cm2 laser applied over the primary motor cortex (M1) areas, 3 J/cm2 per site, 60 s, PW at 3000 Hz | Temporary decrease in motor cortex excitability. | [157] |
| Healthy volunteers (55) | 810 nm, 500 mW/cm2 at scalp via 4 laser needles applied over the primary motor cortex (M1) area, 10 min, one irradiation session, CW | Reduced magnitude of motor-evoked potentials, heightened short-interval cortical inhibition, and diminished facilitation. | [158] |
| Healthy volunteers (11) | 1064 nm; 250 mW/cm2 laser applied at right forehead, 13.75 J/cm2 per 1 min for 8 min, one irradiation session, CW | During and after irradiation, cerebral levels of oxidized CCO, oxygenated hemoglobin, and total hemoglobin were elevated. | [159] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nairuz, T.; Sangwoo-Cho; Lee, J.-H. Photobiomodulation Therapy on Brain: Pioneering an Innovative Approach to Revolutionize Cognitive Dynamics. Cells 2024, 13, 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13110966
Nairuz T, Sangwoo-Cho, Lee J-H. Photobiomodulation Therapy on Brain: Pioneering an Innovative Approach to Revolutionize Cognitive Dynamics. Cells. 2024; 13(11):966. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13110966
Chicago/Turabian StyleNairuz, Tahsin, Sangwoo-Cho, and Jong-Ha Lee. 2024. "Photobiomodulation Therapy on Brain: Pioneering an Innovative Approach to Revolutionize Cognitive Dynamics" Cells 13, no. 11: 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13110966
APA StyleNairuz, T., Sangwoo-Cho, & Lee, J.-H. (2024). Photobiomodulation Therapy on Brain: Pioneering an Innovative Approach to Revolutionize Cognitive Dynamics. Cells, 13(11), 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13110966







