Advancements in Utilizing Natural Compounds for Modulating Autophagy in Liver Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Molecular Mechanism of Autophagy in HCC
2.1. A Dual Role in HCC
2.2. Signaling Cascades of Autophagy in HCC
3. Natural Compounds Targeting Autophagy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
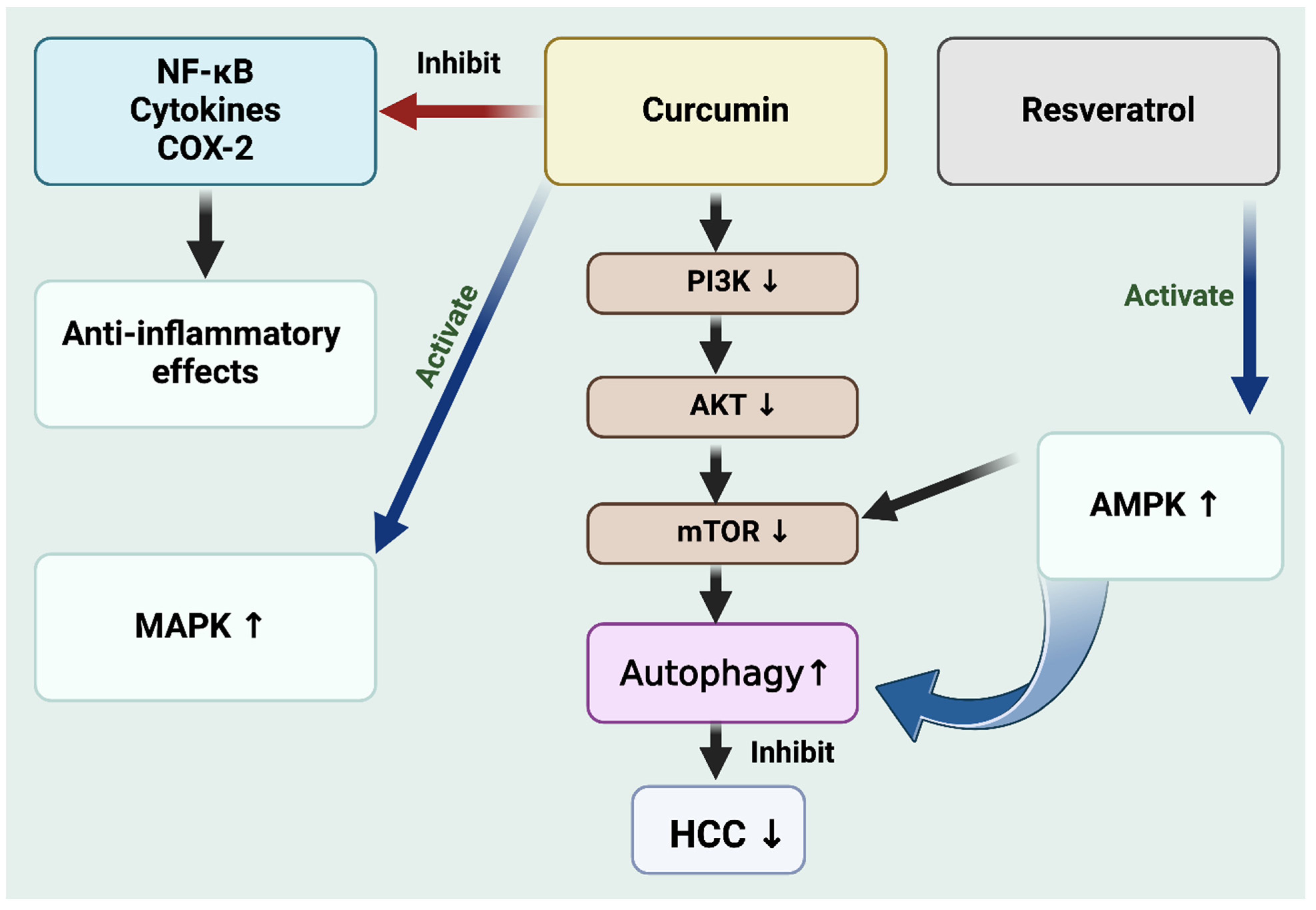
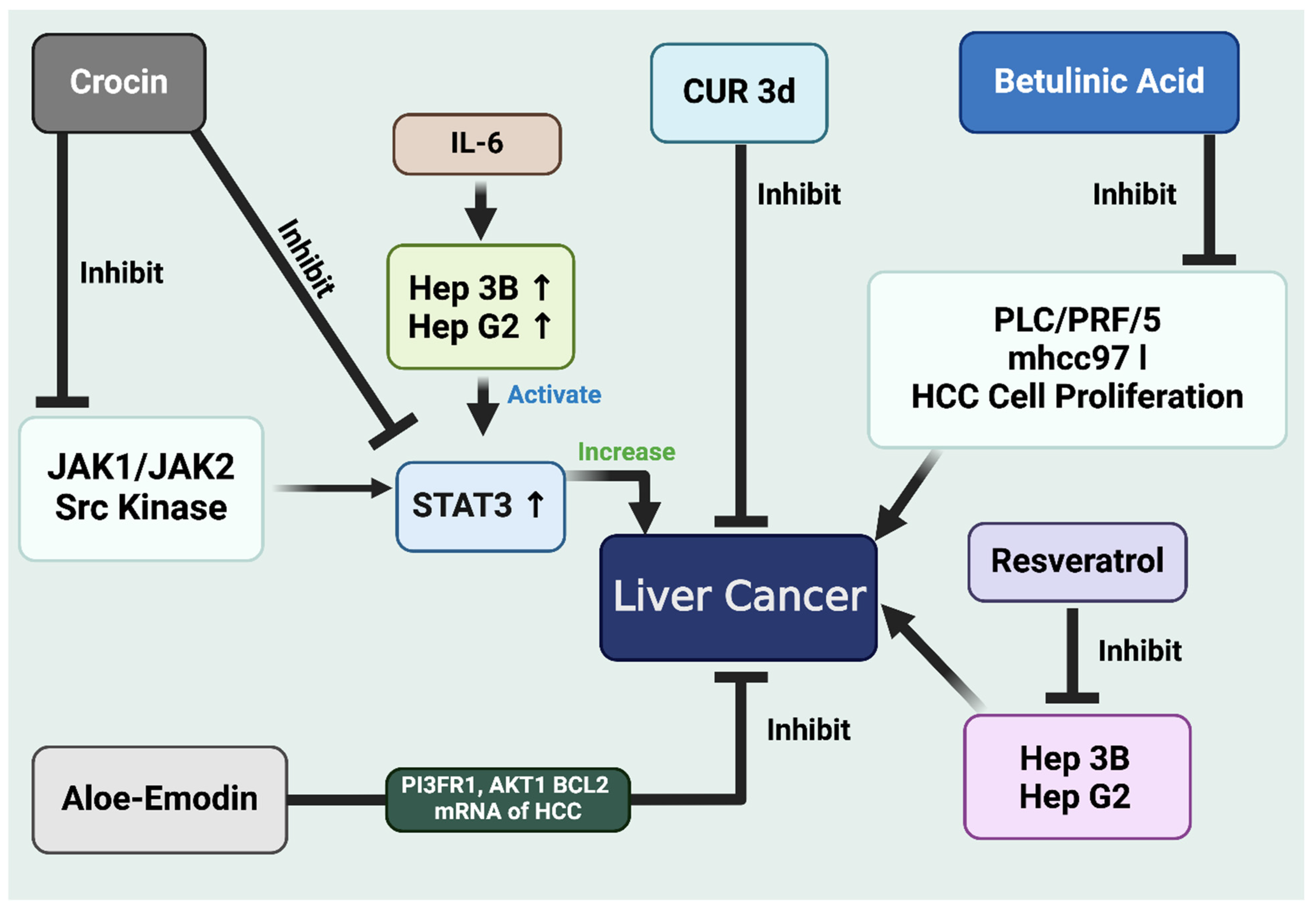
4. Recent Advances in the Use of Natural Compounds in Liver Cancer
5. Preclinical and Clinical Evidence of NCs Directing Liver Cancer via Autophagy
6. Current Challenges and Future Directions for the Use of Autophagy-Mediated Natural Compound in Liver Disease
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, Q.; Liu, M.; Rong, Z.; Liang, H.; Xu, X.; Sun, S.; Lei, Y.; Li, P.; Meng, H.; Zheng, R.; et al. Rebamipide attenuates alcohol-induced gastric epithelial cell injury by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress and activating autophagy-related proteins. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 922, 174891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.-X.; Al Mamun, A.; Lyu, A.-P.; Zhang, H.-J. Natural Compounds Targeting the Autophagy Pathway in the Treatment of Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Chen, Y.; Tan, H.; Liu, B.; Zheng, L.-L.; Mu, Y. Targeting Autophagy with Natural Compounds in Cancer: A Renewed Perspective from Molecular Mechanisms to Targeted Therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 748149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.N.; Rahman, A.; Rahman, H.; Kim, J.W.; Choi, M.; Kim, J.W.; Choi, J.; Moon, M.; Ahmed, K.R.; Kim, B. Potential therapeutic implication of herbal medicine in mitochondria-mediated oxidative stress-related liver diseases. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, M.; Nadafzadeh, N.; Imani, M.H.; Rajabi, R.; Ziaolhagh, S.; Bayanzadeh, S.D.; Norouzi, R.; Rafiei, R.; Koohpar, Z.K.; Raei, B.; et al. Targeting and regulation of autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma: Revisiting the molecular interactions and mechanisms for new therapy approaches. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xiong, X.; Hua, X.; Liu, W. Expression and Gene Regulation Network of Metabolic Enzyme Phosphoglycerate Mutase Enzyme 1 in Breast Cancer Based on Data Mining. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6670384. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.G.; Jeon, T.I. Modulation of the Autophagy-Lysosomal Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Small Molecules. Molecules 2020, 25, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Tan, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Deng, X.; Zeng, J.; Huang, L.; Ma, X. Natural products targeting macroautophagy signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma therapy: Recent evidence and perspectives. Phytother. Res. 2024, 38, 1623–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.A.; Hannan, M.A.; Dash, R.; Rahman, M.H.; Islam, R.; Uddin, M.J.; Sohag, A.A.; Rahman, M.H.; Rhim, H. Phytochemicals as a complement to cancer chemotherapy: Pharmacological modulation of the autophagy-apoptosis pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 639628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Cho, Y.; Nam, G.; Rhim, H. Antioxidant compound, oxyresveratrol, inhibits APP production through the AMPK/ULK1/mTOR-mediated autophagy pathway in mouse cortical astrocytes. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieghart, W.; Fuereder, T.; Schmid, K.; Cejka, D.; Werzowa, J.; Wrba, F.; Wang, X.; Gruber, D.; Rasoul-Rockenschaub, S.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M.; et al. Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Pathway Activity in Hepatocellular Carcinomas of Patients Undergoing Liver Transplantation. Transplantation 2007, 83, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Bishayee, K.; Sadra, A.; Huh, S.O. Oxyresveratrol activates parallel apoptotic and autophagic cell death pathways in neuroblastoma cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-General. Subj. 2017, 1861, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.W.; Jang, E.J.; Kim, C.-H.; Lee, J.-H. Sauchinone exerts anticancer effects by targeting AMPK signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2017, 261, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borlak, J.; Meier, T.; Halter, R.; Spanel, R.; Spanel-Borowski, K. Epidermal growth factor-induced hepatocellular carcinoma: Gene expression profiles in precursor lesions, early stage and solitary tumours. Oncogene 2005, 24, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, K.; Roberts, L.R.; Aderca, I.N.; Dong, X.; Qian, C.; Murphy, L.M.; Nagorney, D.M.; Burgart, L.J.; Roche, P.C.; Smith, D.I.; et al. Mutational spectrum of β-catenin, AXIN1, and AXIN2 in hepatocellular carcinomas and hepatoblastomas. Oncogene 2002, 21, 4863–4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunst, C.; Haderer, M.; Heckel, S.; Schlosser, S.; Müller, M. The p53 family in hepatocellular carcinoma. Transl. Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Park, M.N.; Rahman, M.H.; Rashid, M.M.; Islam, R.; Uddin, M.J.; Hannan, M.A.; Kim, B. p53 modulation of autophagy signaling in cancer therapies: Perspectives mechanism and therapeutic targets. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 761080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luedde, T.; Schwabe, R.F. NF-κB in the liver—Linking injury, fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Shen, H.-M.; Lim, L.H.K. The Role of Autophagy in Liver Cancer: Crosstalk in Signaling Pathways and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, G.A.; Elias, S.T.; Amorim, B.; de Lima, C.L.; Della Coletta, R.; Castilho, R.M.; Squarize, C.H.; Guerra, E.N.S. Curcumin downregulates the PI3K–AKT–mTOR pathway and inhibits growth and progression in head and neck cancer cells. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 3311–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, S.; Cheng, X.; Wu, J.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Bao, J.; Yu, H. Curcumin induces autophagic cell death in human thyroid cancer cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2022, 78, 105254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.A.; Kim, N.H.; Kim, S.H.; Oh, S.M.; Huh, S.O. Antiproliferative and cytotoxic effects of resveratrol in mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in rat b103 neuroblastoma cells. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2012, 16, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Dong, H.; Jia, S.; Yang, Z. Resveratrol as a modulatory of apoptosis and autophagy in cancer therapy. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 24, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahia, I.B.H.; Baccouri, O.; Jalouli, M.; Boujelbene, N.; Rahman, A.; Harrath, A.H.; Zidi, I. The small phytomolecule resveratrol: A promising role in boosting tumor cell chemosensitivity. Pharmacia 2024, 71, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Yu, D.; Peng, Y.; Yi, H.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, T.; Shi, B.; Yang, G.; Lai, W.; Wu, X.; et al. Resveratrol induces AMPK and mTOR signaling inhibition-mediated autophagy and apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2021, 53, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, K.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Tong, Y.; Li, X.; Yan, S.; Hu, P. Resveratrol Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression Through Regulating Exosome Secretion. Curr. Med. Chem. 2023, 31, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škubník, J.; Pavlíčková, V.S.; Ruml, T.; Rimpelová, S. Autophagy in cancer resistance to paclitaxel: Development of combination strategies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 161, 114458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.A.; Apu, E.H.; Rakib-Uz-Zaman, S.M.; Chakraborti, S.; Bhajan, S.K.; Taleb, S.A.; Shaikh, M.H.; Jalouli, M.; Harrath, A.H.; Kim, B. Exploring Importance and Regulation of Autophagy in Cancer Stem Cells and Stem Cell-Based Therapies. Cells 2024, 13, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, J.; Shen, K.; Wang, R.; Chen, C.; Liao, Z.; Zhou, J. Paclitaxel Suppresses Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tumorigenesis Through Regulating Circ-BIRC6/miR-877-5p/YWHAZ Axis. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 9377–9388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.-y.; Zheng, H.-M.; Xia, C.; Li, X.; Wang, G.; Zhao, T.; Cui, X.-N.; Wang, R.-Y.; Liu, Y. The Research Progress of Bufalin in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2022, 15, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Yu, F.; Wu, W.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Guo, F.; Xu, L.; Wang, F.; Cui, X. Bufalin enhances the killing efficacy of NK cells against hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting MICA shedding. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101, 108195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, E.; Bettuzzi, S.; Naponelli, V. The Potential of Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) in Targeting Autophagy for Cancer Treatment: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, S.; Xu, J.; Li, W.; Duan, G.; Wang, H.; Yang, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, R. A new molecular mechanism underlying the EGCG-mediated autophagic modulation of AFP in HepG2 cells. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Cao, D.; Cui, Y.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, J.; Cao, X. The potential of epigallocatechin gallate in the chemoprevention and therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1201085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.; Liu, B.-B.; Qian, X.-D.; Li, L.-Q.; Cao, H.-B.; Guo, Q.-S.; Zhou, G.-F. Crocin induces autophagic apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting Akt/mTOR activity. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 2017–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korani, S.; Korani, M.; Sathyapalan, T.; Sahebkar, A. Therapeutic effects of Crocin in autoimmune diseases: A review. Biofactors 2019, 45, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, B.; Hamza, A.A.; Al-Maktoum, A.; Al-Salam, S.; Amin, A. Combining Crocin and Sorafenib Improves Their Tumor-Inhibiting Effects in a Rat Model of Diethylnitrosamine-Induced Cirrhotic-Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Hu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Jia, R.; Zhang, H.; Xia, L. Advances on the anti-tumor mechanisms of the carotenoid Crocin. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aswathy, M.; Vijayan, A.; Daimary, U.D.; Girisa, S.; Radhakrishnan, K.V.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. Betulinic acid: A natural promising anticancer drug, current situation, and future perspectives. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2022, 36, e23206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Shangwen, J.; Ye, Z.J.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Peng, G.; Wang, Q.; Gu, W.; et al. Emodin inhibits invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via regulating autophagy-mediated degradation of snail and β-catenin. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Qaed, E.; Zhu, Y.; Tian, W.; Wang, Y.; Kang, L.; Ma, X.; Tang, Z. Research Progress and New Perspectives of Anticancer Effects of Emodin. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2023, 51, 1751–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Ma, Y.-X.; Li, W.-T.; Li, L.; Zhu, H.-Z.; Wu, M.-H.; Zhou, J.-R. Quercetin inhibits growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by apoptosis induction in part via autophagy stimulation in mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 69, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Cai, X.; Khan, G.J.; Cheng, J.; He, J.; Zhai, K.; Mao, Y. Exploring the molecular mechanism of Artemisia rupestris L. for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma via PI3K/AKT pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 322, 117572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y. Prunella vulgaris L.–A Review of its Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry, Quality Control and Pharmacological Effects. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 903171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norikura, T.; Fujiwara, K.; Narita, T.; Yamaguchi, S.; Morinaga, Y.; Kunihisa, I.; Matsue, H. Anticancer activities of thelephantin O and vialinin A isolated from Thelephora aurantiotincta. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 6974–6979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakib-Uz-Zaman, S.M.; Iqbal, A.; Mowna, S.A.; Khanom, M.G.; Al Amin, M.M.; Khan, K. Ethnobotanical study and phytochemical profiling of Heptapleurum hypoleucum leaf extract and evaluation of its antimicrobial activities against diarrhea-causing bacteria. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2020, 18, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakib-Uz-Zaman, S.M.; Apu, E.H.; Muntasir, M.N.; Mowna, S.A.; Khanom, M.G.; Jahan, S.S.; Akter, N.; Khan, M.A.R.; Shuborna, N.S.; Shams, S.M.; et al. Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Cymbopogon citratus Leaf Extract and Evaluation of Their Antimicrobial Properties. Challenges 2022, 13, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Kim, B. Anti-Cancer Natural Products and Their Bioactive Compounds Inducing ER Stress-Mediated Apoptosis: A Review. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.H.; Ng, T.B.; Chan, H.H.L.; Liu, Q.; Man, G.C.W.; Zhang, C.Z.; Guan, S.; Ng, C.C.W.; Fang, E.F.; Wang, H.; et al. Mushroom extracts and compounds with suppressive action on breast cancer: Evidence from studies using cultured cancer cells, tumor-bearing animals, and clinical trials. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 4675–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, J.; Sachan, P.; Wal, P.; Dwivedi, S.; Sharma, M.C.; Rao, S.P. Detailed review on phytosomal formulation attenuating new pharmacological therapies. Adv. Tradit. Med. 2023, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Singh, S.V.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, S.; Senapati, S.; Pandey, A.K. Current therapeutic modalities and chemopreventive role of natural products in liver cancer: Progress and promise. World J. Hepatol. 2023, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lao, Y.; Xu, N.; Xi, Z.; Wu, M.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Tan, H.; Sun, M.; Xu, H. Oblongifolin C inhibits metastasis by up-regulating keratin 18 and tubulins. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.R.; Qiu, H.-C.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.-T. Herbal Medicine Offered as an Initiative Therapeutic Option for the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aguanno, S.; Del Bufalo, D. Inhibition of Anti-Apoptotic Bcl-2 Proteins in Preclinical and Clinical Studies: Current Overview in Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, L.J.; Zhang, J.-H.; Gomez, H.; Murugan, R.; Hong, X.; Xu, D.; Jiang, F.; Peng, Z.-Y. Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced Lipid Peroxidation in Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Ferroptosis. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 2019, 5080843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Wang, C.; Xie, B.; Hu, L.; Chai, H.; Ding, L.; Tang, L.; Xia, Y.; Dou, X. Tanshinone IIA induced cell death via miR30b-p53-PTPN11/SHP2 signaling pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 796, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Xiong, J. Induction of apoptosis in human hepatocarcinoma SMMC-7721 cells in vitro by psoralen from Psoralea corylifolia. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 70, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisteau, X.; Caldez, M.J.; Kaldis, P. The Complex Relationship between Liver Cancer and the Cell Cycle: A Story of Multiple Regulations. Cancers 2014, 6, 79–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegfried, Z.; Bonomi, S.; Ghigna, C.; Karni, R. Regulation of the Ras-MAPK and PI3K-mTOR Signalling Pathways by Alternative Splicing in Cancer. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 2013, 568931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Wu, M.; Cao, K.; Jiang, F.; Chen, D.; Li, N.; Li, W. The significance of exosomes in the development and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.J.; Pan, W.W.; Liu, S.B.; Shen, Z.F.; Xu, Y.; Hu, L.L. ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhullar, K.S.; Jha, A.; Rupasinghe, H.P. Novel carbocyclic curcumin analog CUR3d modulates genes involved in multiple apoptosis pathways in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2015, 242, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Li, M.; Yang, W.; Sun, X.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Su, J.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Zhao, M. Resveratrol inhibits the malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via MARCH1-induced regulation of PTEN/AKT signaling. Aging 2020, 12, 11717–11731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Yin, X.; Sui, S. Resveratrol inhibited the progression of human hepatocellular carcinoma by inducing autophagy via regulating p53 and the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 2758–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, H.; Zheng, F.; Liu, H.; Qiu, F.; Chen, Y.; Liang, C.-L.; Dai, Z. Resveratrol exerts antitumor effects by downregulating CD8. Oncoimmunology 2020, 9, 1829346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Zhou, C.; Li, J.; Chen, K.; Wang, G.; Wei, G.; Chen, M.; Li, X. Resveratrol inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression driven by hepatic stellate cells by targeting Gli-1. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2017, 434, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, C.; Yin, D.; Zhao, F.; Yin, J.; Guo, M.; Zhang, L.; et al. Resveratrol represses estrogen-induced mammary carcinogenesis through NRF2-UGT1A8-estrogen metabolic axis activation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 155, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notas, G.; Nifli, A.-P.; Kampa, M.; Vercauteren, J.; Kouroumalis, E.; Castanas, E. Resveratrol exerts its antiproliferative effect on HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells, by inducing cell cycle arrest, and NOS activation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1760, 1657–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.S.; Pan, C.-E.; Yang, W.; Liu, X.-M. Antitumor and immunomodulatory activity of resveratrol on experimentally implanted tumor of H22 in Balb/c mice. World J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 9, 1474–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, D.; Rajasekaran, D.; Elavarasan, J.; Sivalingam, M.; Ganapathy, E.; Kumar, A.; Kalpana, K. Resveratrol interferes with N-nitrosodiethylamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma at early and advanced stages in male Wistar rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2011, 4, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Deng, G.; Liu, W.; Zhou, K.; Li, M. Resveratrol suppresses human hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting HGF-c-Met signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Ahn, K.S.; Kim, C.; Siveen, K.S.; Ong, T.H.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Li, F.; Shi, J.; Kumar, A.P.; Wang, L.Z.; et al. Ascochlorin, an isoprenoid antibiotic inhibits growth and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting STAT3 signaling cascade through the induction of PIAS3. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 818–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adesoye, T.; Tripathy, D.; Hunt, K.K.; Keyomarsi, K. Exploring Novel Frontiers: Leveraging STAT3 Signaling for Advanced Cancer Therapeutics. Cancers 2024, 16, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, A.; Hamza, A.A.; Daoud, S.; Khazanehdari, K.; Al Hrout, A.; Baig, B.; Chaiboonchoe, A.; Adrian, T.E.; Zaki, N.; Salehi-Ashtiani, K. Saffron-Based Crocin Prevents Early Lesions of Liver Cancer: In vivo, In vitro and Network Analyses. Recent Pat. Anti-Cancer Drug Discov. 2016, 11, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Park, B. Saffron carotenoids inhibit STAT3 activation and promote apoptotic progression in IL-6-stimulated liver cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 1883–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwanowycz, S.; Wang, J.; Altomare, D.; Hui, Y.; Fan, D. Emodin Bidirectionally Modulates Macrophage Polarization and Epigenetically Regulates Macrophage Memory. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 11491–11503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; He, Q.; Wang, Y.; Duan, L.; Rong, K.; Wu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Mi, Y.; Ge, X.; Yang, X.; et al. Exploring the mechanism of aloe-emodin in the treatment of liver cancer through network pharmacology and cell experiments. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1238841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Zhong, Z.; Tan, H.Y.; Guo, W.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, C.; Wang, N.; Ren, J.; Feng, Y. Suppression of lncRNA MALAT1 by betulinic acid inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression by targeting IAPs via miR-22-3p. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 10, e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Li, S.; Qu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Chen, R.; Wei, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q. Betulinic acid induces autophagy-mediated apoptosis through suppression of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 6952–6964. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, T.; Li, D.; Huang, Y.; Li, Q.; Bai, G.; Shi, L. Betulinic acid induces apoptosis and suppresses metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines in vitro and in vivo. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, H.; Feng, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhou, H.; Cai, Q.; Feng, Y. Exploring the mechanism of bioactive components of Prunella vulgaris L. in treating hepatocellular carcinoma based on network pharmacology. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2024, 103, e14413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Chen, Q.-X.; Li, P.; Yu, H.; Yu, L.; Lu, J.-L.; Yin, H.-Z.; Huang, B.-J.; Zhang, S.-J. Lobelia chinensis Lour inhibits the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via the regulation of the PTEN/AKT signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 318 Pt A, 116886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.P.; Hsiao, P.C.; Yang, S.F.; Hsieh, S.C.; Bau, D.T.; Ling, C.L.; Pai, C.L.; Hsieh, Y.H. Licochalcone A suppresses migration and invasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through downregulation of MKK4/JNK via NF-κB mediated urokinase plasminogen activator expression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xu, L.; Zhou, H.; Yuan, M.; Xu, H. Recent progress in understanding the action of natural compounds at novel therapeutic drug targets for the treatment of liver cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 11, 795548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Huang, H.; Ma, Y.; Wu, C.; Yang, X.; Choi, H.-Y. Davidone C induces the death of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by promoting apoptosis and autophagy. Molecules 2021, 26, 5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Tang, Z.-H.; Xu, W.-S.; Wu, G.-S.; Wang, Y.-F.; Chang, L.-L.; Zhu, H.; Chen, X.-P.; Wang, Y.-T.; Chen, Y.; et al. Platycodin D triggers autophagy through activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 749, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Gong, X.; Yin, X.-Y.; Hou, J.-X.; Chen, J.; Xie, B.; Chen, G.; Wang, L.-N.; Wang, X.-Y.; Wang, D.-C.; et al. Parthenolide and arsenic trioxide co-trigger autophagy-accompanied apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 988528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.Y.; Gao, G.B.; Zheng, Y.H.; Yu, N.N.; Ouyang, L.; Gao, X.; Li, N.; Wen, S.Y.; Huang, S.; et al. Polyphyllin D punctures hypertrophic lysosomes to reverse drug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting acid sphingomyelinase. Mol. Ther. 2023, 31, 2169–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, B.; Gamallat, Y.; Khan, M.F.; Din, S.R.; Israr, M.; Ahmad, M.; Tahir, N.; Azam, N.; Rahman, K.U.; Xin, W.; et al. Natural polyphyllins (I, II, D, VI, VII) reverses cancer through apoptosis, autophagy, mitophagy, inflammation, and necroptosis. OncoTargets Ther. 2021, 14, 1821–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Gao, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Han, Y.; Pan, J. Sarmentosin induces autophagy-dependent apoptosis via activation of Nrf2 in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2023, 11, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shang, L.; Jiang, W.; Wu, W. Shikonin induces apoptosis and autophagy via downregulation of pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 7904–7918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Jin, W.; Qiu, Y.; Fu, L.; Wang, T.; Yu, H. Solamargine induces hepatocellular carcinoma cell apoptosis and autophagy via inhibiting LIF/miR-192-5p/CYR61/Akt signaling pathways and eliciting immunostimulatory tumor microenvironment. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.R.; Rauf, A.; Akash, S.; Trisha, S.I.; Nasim, A.H.; Akter, M.; Dhar, P.S.; Ogaly, H.A.; Hemeg, H.A.; Wilairatana, P.; et al. Targeted therapies of curcumin focus on its therapeutic benefits in cancers and human health: Molecular signaling pathway-based approaches and future perspectives. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 170, 116034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinilla-González, V.; Rojas-Solé, C.; Gómez-Hevia, F.; González-Fernández, T.; Cereceda-Cornejo, A.; Chichiarelli, S.; Saso, L.; Rodrigo, R. Tapping into Nature’s Arsenal: Harnessing the Potential of Natural Antioxidants for Human Health and Disease Prevention. Foods 2024, 13, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malavolta, M.; Bracci, M.; Santarelli, L.; Sayeed, M.A.; Pierpaoli, E.; Giacconi, R.; Costarelli, L.; Piacenza, F.; Basso, A.; Cardelli, M.; et al. Inducers of senescence, toxic compounds, and senolytics: The multiple faces of Nrf2-activating phytochemicals in cancer adjuvant therapy. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 4159013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.-L.; Liu, P.-Y.; Yeh, S.-L.; Lee, H.-J. Effects of dried onion powder and quercetin on obesity-associated hepatic menifestation and retinopathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Qu, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, W. Role of natural products in tumor therapy from basic research and clinical perspectives. Acta Mater. Medica 2024, 3, 163–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinou, E.K.; Gioxari, A.; Dimitriou, M.; Panoutsopoulos, G.I.; Panagiotopoulos, A.A. Molecular Pathways of Genistein Activity in Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iweala, E.J.; Adurosakin, O.E.; Innocent, U.; Omonhinmin, C.A.; Dania, O.E.; Ugbogu, E.A. Anti-Aging Potential of Bioactive Phytoconstituents Found in Edible Medicinal Plants: A Review. Sci 2024, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allemailem, K.S.; Almatroudi, A.; Alharbi, H.O.A.; AlSuhaymi, N.; Alsugoor, M.H.; Aldakheel, F.M.; Khan, A.A.; Rahmani, A.H. Apigenin: A Bioflavonoid with a Promising Role in Disease Prevention and Treatment. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Guan, Y.; Hu, W.; Xu, Z.; Ishfaq, M. An overview of pharmacological activities of baicalin and its aglycone baicalein: New insights into molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways. Iran J. Basic Med. Sci. 2022, 25, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rauf, A.; Olatunde, A.; Imran, M.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Aljohani, A.S.; Khan, S.A.; Uddin, S.; Mitra, S.; Bin Emran, T.; Khayrullin, M.; et al. Honokiol: A review of its pharmacological potential and therapeutic insights. Phytomedicine 2021, 90, 153647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare Mehrjerdi, P.; Asadi, S.; Ehsani, E.; Askari, V.R.; Rahimi, V.B. Silibinin as a major component of milk thistle seed provides promising influences against diabetes and its complications: A systematic review. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2024, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurkiewicz, A.; Mądry, W.; Kołodziej, M.; Męczyńska, J.; Saiuk, N.; Kozicz, M.A.; Seredyński, T.; Wojciechowska, A.; Marcicka, J.; Salasa, W. Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera)—Its Antibacterial and Anticancer Activity. J. Educ. Health Sport 2024, 66, 50081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Feng, W.; Bu, J.; Lu, Z.; Wang, J. Emodin ameliorates acute radiation proctitis in mice by regulating AKT/MAPK/NF-κB/VEGF pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 132, 111945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tak, Y.; Kaur, M.; Chitranashi, A.; Samota, M.K.; Verma, P.; Bali, M.; Kumawat, C. Fenugreek derived diosgenin as an emerging source for diabetic therapy. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1280100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, W.; Jin, L.; Liu, S.; Liang, L.; Wei, Y. Plumbagin exhibits genotoxicity and induces G2/M cell cycle arrest via ROS-mediated oxidative stress and activation of ATM-p53 signaling pathway in hepatocellular cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cargnin, S.T.; Gnoatto, S.B. Ursolic acid from apple pomace and traditional plants: A valuable triterpenoid with functional properties. Food Chem. 2017, 220, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, T. The Role of the Central mTOR Signaling Pathway in Psoriasis Pathogenesis and Its Therapeutic Targeting with Fisetin. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Louisiana at Monroe, Monroe, LA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Almatroodi, S.A.; Almatroudi, A.; Alharbi, H.O.A.; Khan, A.A.; Rahmani, A.H. Effects and Mechanisms of Luteolin, a Plant-Based Flavonoid, in the Prevention of Cancers via Modulation of Inflammation and Cell Signaling Molecules. Molecules 2024, 29, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, F.; Jin, D. Ginsenosides are promising medicine for tumor and inflammation: A review. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2023, 51, 883–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Q.; Guo, W.; Tang, X.; Cui, S.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Mao, B.; Chen, W. Capsaicin—The spicy ingredient of chili peppers: A review of the gastrointestinal effects and mechanisms. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braicu, C.; Zanoaga, O.; Zimta, A.-A.; Tigu, A.B.; Kilpatrick, K.L.; Bishayee, A.; Nabavi, S.M.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. Natural compounds modulate the crosstalk between apoptosis-and autophagy-regulated signaling pathways: Controlling the uncontrolled expansion of tumor cells. In Seminars in Cancer Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, G.; Li, F.; Wang, P.; Jin, X.; Liu, R. Natural-product-mediated autophagy in the treatment of various liver diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Gong, Z.; Shen, H.-M. The role of autophagy in liver cancer: Molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Rev. Cancer 2013, 1836, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Kumar, A.P.; Yap, C.T.; Sethi, G.; Bishayee, A. Targeting autophagy using natural compounds for cancer prevention and therapy. Cancer 2019, 125, 1228–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; He, J.; Luo, L.; Wang, K. Targeting the Interplay of Autophagy and ROS for Cancer Therapy: An Updated Overview on Phytochemicals. Pharmaceuticals. 2023, 16, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Z.; Yang, P.; Shen, Y.; Bei, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, Y.; Newman, R.A.; Cohen, L.; Liu, L.; Thornton, B.; et al. Pilot study of huachansu in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, nonsmall-cell lung cancer, or pancreatic cancer. Cancer 2009, 115, 5309–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, A.; De, A.; Papasian, C.; Hentges, S.; Banerjee, S.; Haque, I.; Banerjee, S.K. Emblica officinalis extract induces autophagy and inhibits human ovarian cancer cell proliferation, angiogenesis, growth of mouse xenograft tumors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.H.; Sethi, G.; Um, J.-Y.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Arfuso, F.; Kumar, A.P.; Bishayee, A.; Ahn, K.S. The Role of Resveratrol in Cancer Therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2017, 18, 2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.R.; Brown, V.A.; Jones, D.J.; Britton, R.G.; Hemingway, D.; Miller, A.S.; West, K.P.; Booth, T.D.; Perloff, M.; Crowell, J.A.; et al. Clinical pharmacology of resveratrol and its metabolites in colorectal cancer patients. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 7392–7399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boocock, D.J.; Faust, G.E.S.; Patel, K.R.; Schinas, A.M.; Brown, V.A.; Ducharme, M.P.; Booth, T.D.; Crowell, J.A.; Perloff, M.; Gescher, A.J.; et al. Phase I dose, pharmacokinetic study in healthy volunteers of resveratrol, a potential cancer chemopreventive agent. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2007, 16, 1246–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.C.; Chen, Y.-F.; Hsu, W.-H.; Yang, C.-W.; Kao, C.-H.; Tsai, T.-F. Resveratrol helps recovery from fatty liver and protects against hepatocellular carcinoma induced by hepatitis B virus X protein in a mouse model. Cancer Prev. Res. 2012, 5, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, Y.H.; Kim, S.; Park, J.E.; Jeong, L.S.; Lee, S.K. Induction of quinone reductase activity by stilbene analogs in mouse Hepa 1c1c7 cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2001, 24, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Ouyang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, B. Plant natural compounds: Targeting pathways of autophagy as anti-cancer therapeutic agents. Cell Prolif. 2012, 45, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Deng, C.; Dang, F. Synergistic antitumor effect of resveratrol and sorafenib on hepatocellular carcinoma through PKA/AMPK/eEF2K pathway. Food Nutr. Res. 2021, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, C.T.; Li, W.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Tsai, T.-H. Preventive and therapeutic role of traditional Chinese herbal medicine in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2015, 78, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansouri, K.; Rasoulpoor, S.; Daneshkhah, A.; Abolfathi, S.; Salari, N.; Mohammadi, M.; Shabani, S. Clinical effects of curcumin in enhancing cancer therapy: A systematic review. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aja, I.; Ruiz-Larrea, M.B.; Courtois, A.; Krisa, S.; Richard, T.; Ruiz-Sanz, J.-I. Screening of Natural Stilbene Oligomers from. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Guo, H.; Zong, Y.; Zhao, X. Curcumin restrains hepatocellular carcinoma progression depending on the regulation of the circ_0078710/miR-378b/PRIM2 axis. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2022, 42, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, C.; Zhao, J.; Su, J.; Chen, J.; Cui, X.; Sun, M.; Zhang, X. Curcumin induces mitochondrial apoptosis in human hepatoma cells through BCLAF1-mediated modulation of PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β signaling. Life Sci. 2022, 306, 120804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Alsayed, A.M.M.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Q.; Shen, A.; Zhang, J.; Ye, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, K.; Zheng, X. Discovery of β-cyclocitral-derived mono-carbonyl curcumin analogs as anti-hepatocellular carcinoma agents via suppression of MAPK signaling pathway. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 132, 106358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Xiong, H. Chemotherapy-induced nephrotoxicity was improved by crocin in mouse model. Eur. J. Histochem. 2022, 66, 3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdu, S.; Juaid, N.; Amin, A.; Moulay, M.; Miled, N. Therapeutic Effects of Crocin Alone or in Combination with Sorafenib against Hepatocellular Carcinoma: In Vivo & In Vitro Insights. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Song, G.; Jin, N.; Fang, J.; Han, J.; et al. Betulinic acid inhibits growth of hepatoma cells through activating the NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy pathway. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 102, 105441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinzaru, I.; Sarau, C.; Coricovac, D.; Marcovici, I.; Utescu, C.; Tofan, S.; Popovici, R.A.; Manea, H.C.; Pavel, I.E.; Soica, C.; et al. Silver Nanocolloids Loaded with Betulinic Acid with Enhanced Antitumor Potential: Physicochemical Characterization and In Vitro Evaluation. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabolacci, C.; Oliverio, S.; Lentini, A.; Rossi, S.; Galbiati, A.; Montesano, C.; Mattioli, P.; Provenzano, B.; Facchiano, F.; Beninati, S. Aloe-emodin as antiproliferative and differentiating agent on human U937 monoblastic leukemia cells. Life Sci. 2011, 89, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Zhao, X.; Chen, X.; Shen, G. Emodin suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma growth by regulating macrophage polarization via microRNA-26a/transforming growth factor beta 1/protein kinase B. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 9548–9563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsico, M.; Santarsiero, A.; Pappalardo, I.; Convertini, P.; Chiummiento, L.; Sardone, A.; Di Noia, M.A.; Infantino, V.; Todisco, S. Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis of HCC Cells Triggered by Knockdown of Glutamate Dehydrogenase 1: Perspective for Its Inhibition through Quercetin and Permethylated Anigopreissin A. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.M.; Yang, L.; Geng, Y.-D.; Zhang, C.; Kong, L.-Y. Polyphyllin I induced-apoptosis is enhanced by inhibition of autophagy in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 1139–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.A.; Ahmed, K.R.; Haque, F.; Park, M.N.; Kim, B. Recent advances in cellular signaling interplay between redox metabolism and autophagy modulation in cancer: An overview of molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.A.; Ahmed, K.R.; Rahman, M.H.; Parvez, M.A.; Lee, I.S.; Kim, B. Therapeutic Aspects and Molecular Targets of Autophagy to Control Pancreatic Cancer Management. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, N.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Newman, R.A.; Wolff, R.A.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Ng, C.S.; Badmaev, V.; Kurzrock, R. Phase II trial of curcumin in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 4491–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoor, H.; Feehan, J.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Platat, C.; Al Dhaheri, A.S.; Ali, H.I.; Ismail, L.C.; Bosevski, M.; Stojanovska, L. Immunomodulatory Effects of Dietary Polyphenols. Nutrients 2021, 13, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirazimi, S.M.A.; Dashti, F.; Tobeiha, M.; Shahini, A.; Jafari, R.; Khoddami, M.; Sheida, A.H.; EsnaAshari, P.; Aflatoonian, A.H.; Elikaii, F.; et al. Application of Quercetin in the Treatment of Gastrointestinal Cancers. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 860209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Xu, H.-M.; Yu, F.; Wang, M.; Li, M.-Y.; Xu, T.; Gao, Y.-Y.; Wang, J.-X.; Li, P.-F. Crosstalk between MicroRNAs and Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors and Their Emerging Regulatory Roles in Cardiovascular Pathophysiology. PPAR Res. 2018, 2018, 8530371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wu, L.; Huang, Y.; Mao, Z.; Zhan, Z.; Chen, W.; Dai, F.; Cao, W.; Cao, Y.; et al. Metabolism and Toxicity of Emodin: Genome-Wide Association Studies Reveal Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4α Regulates UGT2B7 and Emodin Glucuronidation. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 33, 1798–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.Y.; Yiang, G.-T.; Liao, W.-T.; Tsai, A.P.Y.; Cheng, Y.-L.; Cheng, P.-W.; Li, C.-Y.; Li, C.J. Current Mechanistic Concepts in Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 46, 1650–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Su, D.; Shi, D.; Xiang, X. The improving strategies and applications of nanotechnology-based drugs in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1272850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaher, S.; Soliman, M.E.; Elsabahy, M.; Hathout, R.M. Protein nanoparticles as natural drugs carriers for cancer therapy. Adv. Tradit. Med. 2023, 23, 1035–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niture, S.; Tricoli, L.; Qi, Q.; Gadi, S.; Hayes, K.; Kumar, D. MicroRNA-99b-5p targets mTOR/AR axis, induces autophagy and inhibits prostate cancer cell proliferation. Tumour Biol. 2022, 44, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paskeh, M.D.A.; Entezari, M.; Clark, C.; Zabolian, A.; Ranjbar, E.; Farahani, M.V.; Saleki, H.; Sharifzadeh, S.O.; Far, F.B.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; et al. Targeted regulation of autophagy using nanoparticles: New insight into cancer therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2022, 1868, 166326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ma, X.; Chang, X.; Liang, Z.; Lv, L.; Shan, M.; Lu, Q.; Wen, Z.; Gust, R.; Liu, W. Recent development of gold(I) and gold(III) complexes as therapeutic agents for cancer diseases. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 5518–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadkhoda, J.; Tarighatnia, A.; Nader, N.D.; Aghanejad, A. Targeting mitochondria in cancer therapy: Insight into photodynamic and photothermal therapies. Life Sci. 2022, 307, 120898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Singh, A.K.; Raj, V.; Rai, A.; Keshari, A.K.; Kumar, D.; Maity, B.; Prakash, A.; Maiti, S.; Saha, S. Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid)-loaded nanoparticles of betulinic acid for improved treatment of hepatic cancer: Characterization, in vitro and in vivo evaluations. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 975–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saneja, A.; Kumar, R.; Mintoo, M.J.; Dubey, R.D.; Sangwan, P.L.; Mondhe, D.M.; Panda, A.K.; Gupta, P.N. Gemcitabine and betulinic acid co-encapsulated PLGA-PEG polymer nanoparticles for improved efficacy of cancer chemotherapy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 98, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Li, X.; Zeng, B.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Xing, H.R. Exosomal microRNA-4535 of Melanoma Stem Cells Promotes Metastasis by Inhibiting Autophagy Pathway. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2023, 19, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.X.; Sun, Y.R.; Peluso, I.; Zeng, Y.; Yu, X.; Lu, J.H.; Xu, Z.; Wang, M.Z.; Liu, L.F.; Huang, Y.Y.; et al. A novel curcumin analog binds to and activates TFEB in vitro and in vivo independent of MTOR inhibition. Autophagy 2016, 12, 1372–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Compounds | Source | Dosage | Administration Method | Mechanism of Action | Potential Side Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Curcumin | Turmeric | 100–200 mg/kg | Oral | Inhibits mTOR signaling | Gastrointestinal discomfort | [93] |
| Resveratrol | Grapes | 10–100 mg/kg | Oral | Activates AMPK pathway | Headache, dizziness | [94] |
| Berberine | Goldenseal | 5–50 mg/kg | Oral | Induces autophagic cell death | Nausea, constipation | [95] |
| Quercetin | Onions | 25–50 mg/kg | Oral | Inhibits PI3K/Akt pathway | Headache, upset stomach | [96] |
| Epigallocatechin | Green Tea | 50–200 mg/kg | Oral | Modulates Beclin-1 and Bcl-2 | Liver toxicity at high doses | [97] |
| Genistein | Soybeans | 10–50 mg/kg | Oral | Inhibits Akt/mTOR signaling | Gastrointestinal issues | [98] |
| Lycopene | Tomatoes | 10–50 mg/kg | Oral | Induces autophagy via AMPK | Low toxicity, rare allergic reactions | [99] |
| Apigenin | Parsley | 10–40 mg/kg | Oral | Inhibits PI3K/Akt pathway | Mild gastrointestinal discomfort | [100] |
| Baicalein | Scutellaria | 10–50 mg/kg | Oral | Modulates autophagy and apoptosis | Nausea, vomiting | [101] |
| Honokiol | Magnolia | 5–50 mg/kg | Oral, intravenous | Activates AMPK and inhibits mTOR | Sedation, drowsiness | [102] |
| Silibinin | Milk Thistle | 100–300 mg/kg | Oral | Inhibits mTOR and activates AMPK | Mild gastrointestinal issues | [103] |
| Withaferin A | Ashwagandha | 5–20 mg/kg | Oral | Modulates p62/SQSTM1 pathway | Nausea, skin rash | [104] |
| Emodin | Rhubarb | 10–40 mg/kg | Oral | Inhibits PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling | Diarrhea, abdominal pain | [105] |
| Diosgenin | Fenugreek | 10–50 mg/kg | Oral | Inhibits Akt/mTOR signaling | Mild gastrointestinal discomfort | [106] |
| Plumbagin | Black Walnut | 2–10 mg/kg | Oral | Induces autophagy via ROS | Hemolysis, nephrotoxicity | [107] |
| Ursolic Acid | Apple Peel | 10–50 mg/kg | Oral | Inhibits mTOR signaling | Mild gastrointestinal discomfort | [108] |
| Fisetin | Strawberries | 10–50 mg/kg | Oral | Inhibits PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway | Mild gastrointestinal issues | [109] |
| Luteolin | Celery | 10–50 mg/kg | Oral | Inhibits Akt/mTOR signaling | Mild gastrointestinal discomfort | [110] |
| Ginsenoside Rg3 | Ginseng | 5–30 mg/kg | Oral, intravenous | Inhibits mTOR and induces autophagy | Mild gastrointestinal discomfort | [111] |
| Capsaicin | Chili Peppers | 2–10 mg/kg | Oral | Activates AMPK pathway | Gastrointestinal irritation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahman, M.A.; Rakib-Uz-Zaman, S.M.; Chakraborti, S.; Bhajan, S.K.; Gupta, R.D.; Jalouli, M.; Parvez, M.A.K.; Shaikh, M.H.; Hoque Apu, E.; Harrath, A.H.; et al. Advancements in Utilizing Natural Compounds for Modulating Autophagy in Liver Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets. Cells 2024, 13, 1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13141186
Rahman MA, Rakib-Uz-Zaman SM, Chakraborti S, Bhajan SK, Gupta RD, Jalouli M, Parvez MAK, Shaikh MH, Hoque Apu E, Harrath AH, et al. Advancements in Utilizing Natural Compounds for Modulating Autophagy in Liver Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets. Cells. 2024; 13(14):1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13141186
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahman, Md Ataur, S M Rakib-Uz-Zaman, Somdeepa Chakraborti, Sujay Kumar Bhajan, Rajat Das Gupta, Maroua Jalouli, Md. Anowar Khasru Parvez, Mushfiq H. Shaikh, Ehsanul Hoque Apu, Abdel Halim Harrath, and et al. 2024. "Advancements in Utilizing Natural Compounds for Modulating Autophagy in Liver Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets" Cells 13, no. 14: 1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13141186
APA StyleRahman, M. A., Rakib-Uz-Zaman, S. M., Chakraborti, S., Bhajan, S. K., Gupta, R. D., Jalouli, M., Parvez, M. A. K., Shaikh, M. H., Hoque Apu, E., Harrath, A. H., Moon, S., & Kim, B. (2024). Advancements in Utilizing Natural Compounds for Modulating Autophagy in Liver Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets. Cells, 13(14), 1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13141186










