YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA Binding Protein 1 Inhibits Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Modulation and Neointimal Hyperplasia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. m6A Level Quantification
2.3. m6A-Specific RNA Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.4. Electroporation
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Lentivirus Package
2.7. Animals
2.8. Rat Carotid Artery Injury Model and Lentivirus Transduction
2.9. Histomorphometric Analyses and Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Staining
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
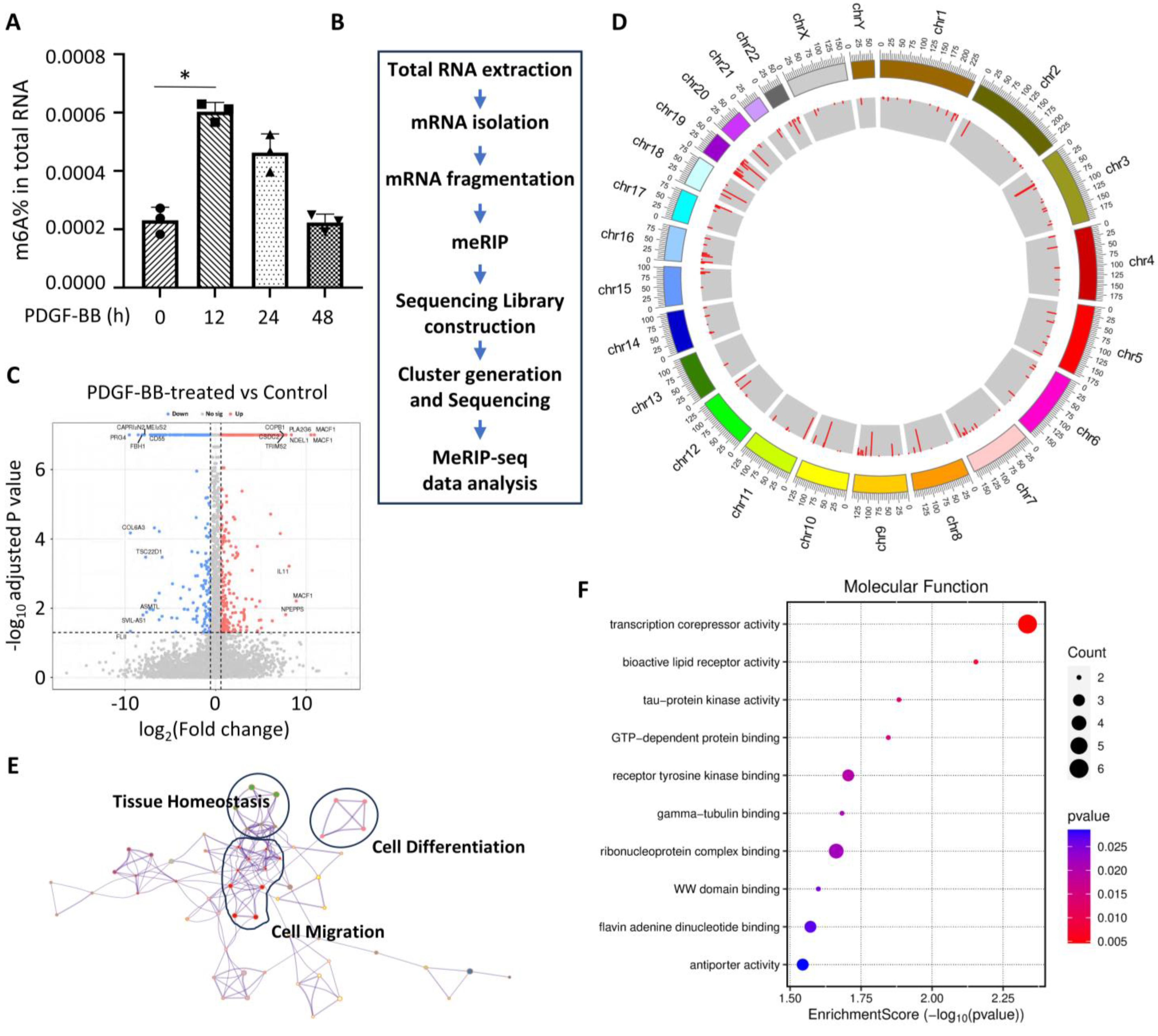
3.1. m6A Modification Is Altered During PDGF-BB-Induced SMC Phenotypic Modulation
3.2. PDGF-BB Regulates the Expression of Genes Involved in m6A Modification
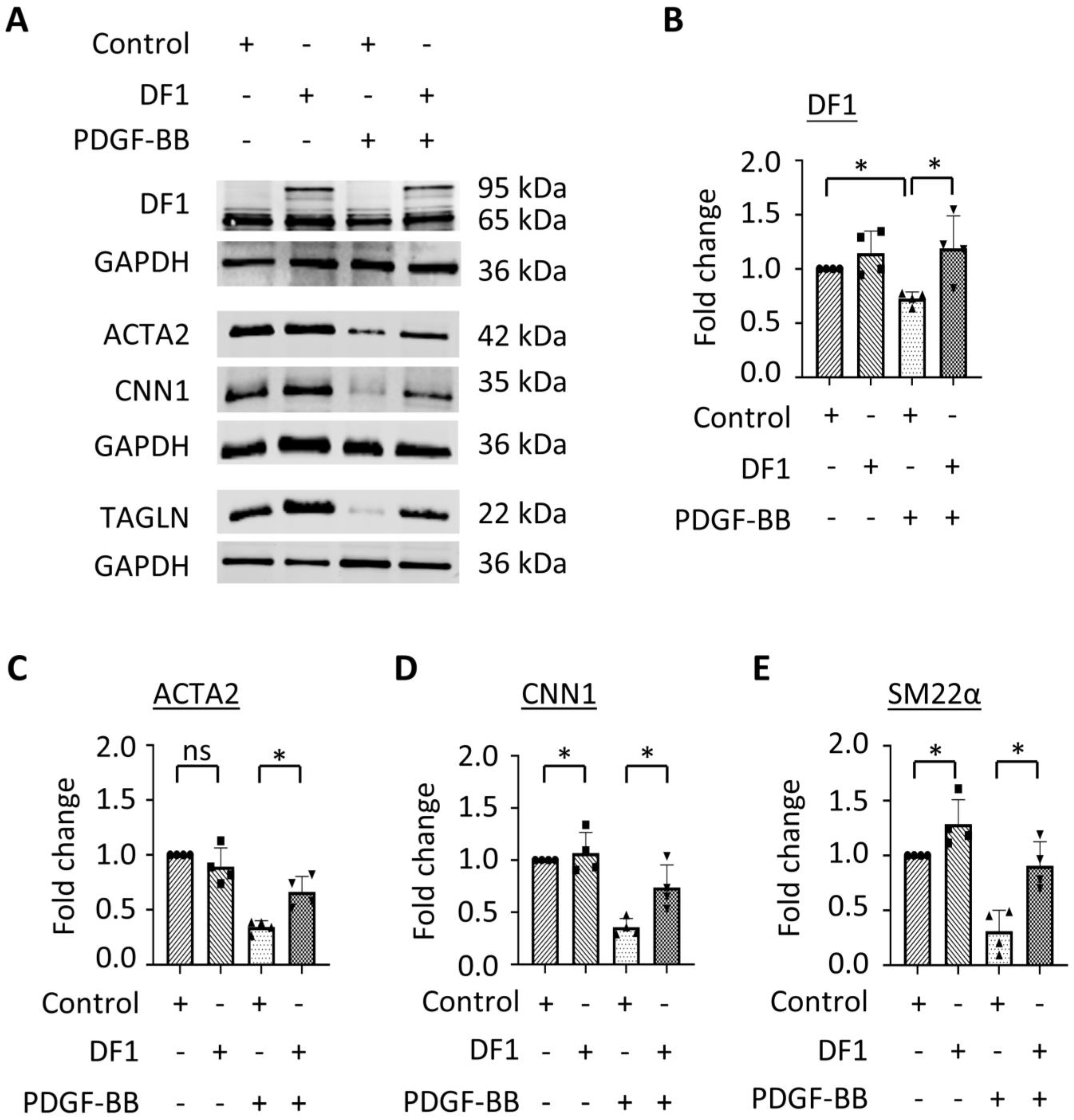
3.3. Overexpression of YTHDF1 Restores SMC Contractile Protein Expression Downregulated During SMC Phenotypic Modulation
3.4. YTHDF1 Attenuates Injury-Induced Neointimal Formation/Vascular Remodeling
3.5. YTHDF1 Inhibits SMC Phenotypic Modulation In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, N.; Mei, X.; Chen, S.-Y. Smooth Muscle Cells in Vascular Remodeling. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, e247–e252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.H.; Campbell, G.R. Smooth Muscle Phenotypic Modulation—A Personal Experience. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 1784–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, R.; Chatterjee, P.; Dave, J.M.; Ostriker, A.C.; Greif, D.M.; Rzucidlo, E.M.; Martin, K.A. Targeting smooth muscle cell phenotypic switching in vascular disease. JVS-Vasc. Sci. 2021, 2, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Yang, Y.; Wei, H.; Xie, X.; Lu, J.; Zeng, Q.; Peng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, S.; Peng, J. Zfp217 mediates m6A mRNA methylation to orchestrate transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation to promote adipogenic differentiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 6130–6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, X.-B.; Lei, S.-F.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Zhang, H. Examination of the associations between m6A-associated single-nucleotide polymorphisms and blood pressure. Hypertens. Res. 2019, 42, 1582–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathiyalagan, P.; Adamiak, M.; Mayourian, J.; Sassi, Y.; Liang, Y.; Agarwal, N.; Jha, D.; Zhang, S.; Kohlbrenner, E.; Chepurko, E.; et al. FTO-Dependent N6-Methyladenosine Regulates Cardiac Function During Remodeling and Repair. Circulation 2019, 139, 518–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.-B.; Lei, S.-F.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Zhang, H. Detection of m6A-associated SNPs as potential functional variants for coronary artery disease. Epigenomics 2018, 10, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, D.; Sun, C.; Zhang, G.; Que, X.; Fujise, K.; Weintraub, N.L.; Chen, S.-Y. A Novel Mechanism Underlying Inflammatory Smooth Muscle Phenotype in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. Circ. Res. 2021, 129, e202–e214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhuang, X. m6A-binding YTHDF proteins promote stress granule formation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, X.; Cui, X.-B.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.-Y. CircSOD2: A Novel Regulator for Smooth Muscle Proliferation and Neointima Formation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 2961–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutner, R.H.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Reiser, J. Production, concentration and titration of pseudotyped HIV-1-based lentiviral vectors. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinet, P.; Milewicz, D.M.; Cassis, L.A.; Leeper, N.J.; Lu, H.S.; Smith, J.D. Consideration of Sex Differences in Design and Reporting of Experimental Arterial Pathology Studies-Statement From ATVB Council. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Kuhel, D.G.; Witte, D.P.; Hui, D.Y. Apolipoprotein E Inhibits Neointimal Hyperplasia after Arterial Injury in Mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 1839–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, R.; Cai, D.; King, S.D.; Que, X.; Bath, J.M.; Chen, S.-Y. Surfactant Protein A, a Novel Regulator for Smooth Muscle Phenotypic Modulation and Vascular Remodeling—Brief Report. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Shi, N.; Cui, X.-B.; Wang, J.-N.; Fukui, Y.; Chen, S.-Y. Dedicator of Cytokinesis 2, A Novel Regulator for Smooth Muscle Phenotypic Modulation and Vascular Remodeling. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, e71–e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Fan, S.; Wu, M.; Zuo, Z.; Li, X.; Jiang, L.; Shen, Q.; Xu, P.; Zeng, L.; Zhou, Y.; et al. YTHDF1 links hypoxia adaptation and non-small cell lung cancer progression. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Cui, Y.; Liu, L.; Ma, X.; Qi, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ma, S.; Liu, J.; Wu, J. METTL3 Facilitates Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Tumorigenesis by Enhancing c-Myc Stability via YTHDF1-Mediated m6A Modification. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Liu, J.; Chen, C.; Dong, L.; Liu, Y.; Chang, R.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Dougherty, U.; et al. Anti-tumour immunity controlled through mRNA m6A methylation and YTHDF1 in dendritic cells. Nature 2019, 566, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, M.; Li, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, J.; Niu, F.; Liang, F.; Chen, M.; Li, D.; Han, P.; Ji, S.-J. The m6A reader YTHDF1 regulates axon guidance through translational control of Robo3.1 expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 4765–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W. Regulation of Virus Replication and T Cell Homeostasis by N6-Methyladenosine. Virol. Sin. 2019, 34, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Cao, Y.; Gong, R.; Yu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Guo, X.; Liu, S.; Yu, M.; et al. ALKBH5 regulates cardiomyocyte proliferation and heart regeneration by demethylating the mRNA of YTHDF1. Theranostics 2021, 11, 3000–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; Lin, X.; Liu, X.-M.; Zhou, J. Differential roles of YTHDF1 and YTHDF3 in embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocyte differentiation. RNA Biol. 2021, 18, 1354–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Yu, Y.; Ding, J.; Yu, Y.; Li, K.; Wei, D.; Ye, Q.; Wang, F.; et al. YTHDF1 Regulates Pulmonary Hypertension through Translational Control of MAGED1. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 1158–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raguram, A.; Banskota, S.; Liu, D.R. Therapeutic in vivo delivery of gene editing agents. Cell 2022, 185, 2806–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishizawa, Y.; Konno, M.; Asai, A.; Koseki, J.; Kawamoto, K.; Miyoshi, N.; Takahashi, H.; Nishida, N.; Haraguchi, N.; Sakai, D.; et al. Oncogene c-Myc promotes epitranscriptome m6A reader YTHDF1 expression in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 7476–7486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pi, J.; Wang, W.; Ji, M.; Wang, X.; Wei, X.; Jin, J.; Liu, T.; Qiang, J.; Qi, Z.; Li, F.; et al. YTHDF1 Promotes Gastric Carcinogenesis by Controlling Translation of FZD7. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 2651–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Yuan, B.; He, T.; Ding, B.; Li, S. Prognostic values of YTHDF1 regulated negatively by mir-3436 in Glioma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 7538–7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Tian, X.; Luo, L. N6-methyladenosine reader YTHDF1 regulates the proliferation and migration of airway smooth muscle cells through m6A/cyclin D1 in asthma. PeerJ 2023, 11, e14951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.; Liu, L.; Tan, F.; Zhang, D.; Yu, L.; Jiang, H.; Qian, W.; Hua, J.; Zheng, Z. Inhibition of YTHDF1 prevents hypoxia-induced pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation by regulating Foxm1 translation in an m6A-dependent manner. Exp. Cell Res. 2023, 424, 113505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, K.; Cai, D.; Yang, S.; Zhao, W.; Mei, X.; Chen, S.-Y. YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA Binding Protein 1 Inhibits Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Modulation and Neointimal Hyperplasia. Cells 2025, 14, 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14030160
Tian K, Cai D, Yang S, Zhao W, Mei X, Chen S-Y. YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA Binding Protein 1 Inhibits Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Modulation and Neointimal Hyperplasia. Cells. 2025; 14(3):160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14030160
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Kai, Dunpeng Cai, Shuang Yang, Wen Zhao, Xiaohan Mei, and Shi-You Chen. 2025. "YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA Binding Protein 1 Inhibits Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Modulation and Neointimal Hyperplasia" Cells 14, no. 3: 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14030160
APA StyleTian, K., Cai, D., Yang, S., Zhao, W., Mei, X., & Chen, S.-Y. (2025). YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA Binding Protein 1 Inhibits Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Modulation and Neointimal Hyperplasia. Cells, 14(3), 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14030160






