High-Efficiency Enrichment of Megakaryocytes and Identification of Micromegakaryocytes from Human Bone Marrow by Imaging Flow Cytometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bone Marrow Samples
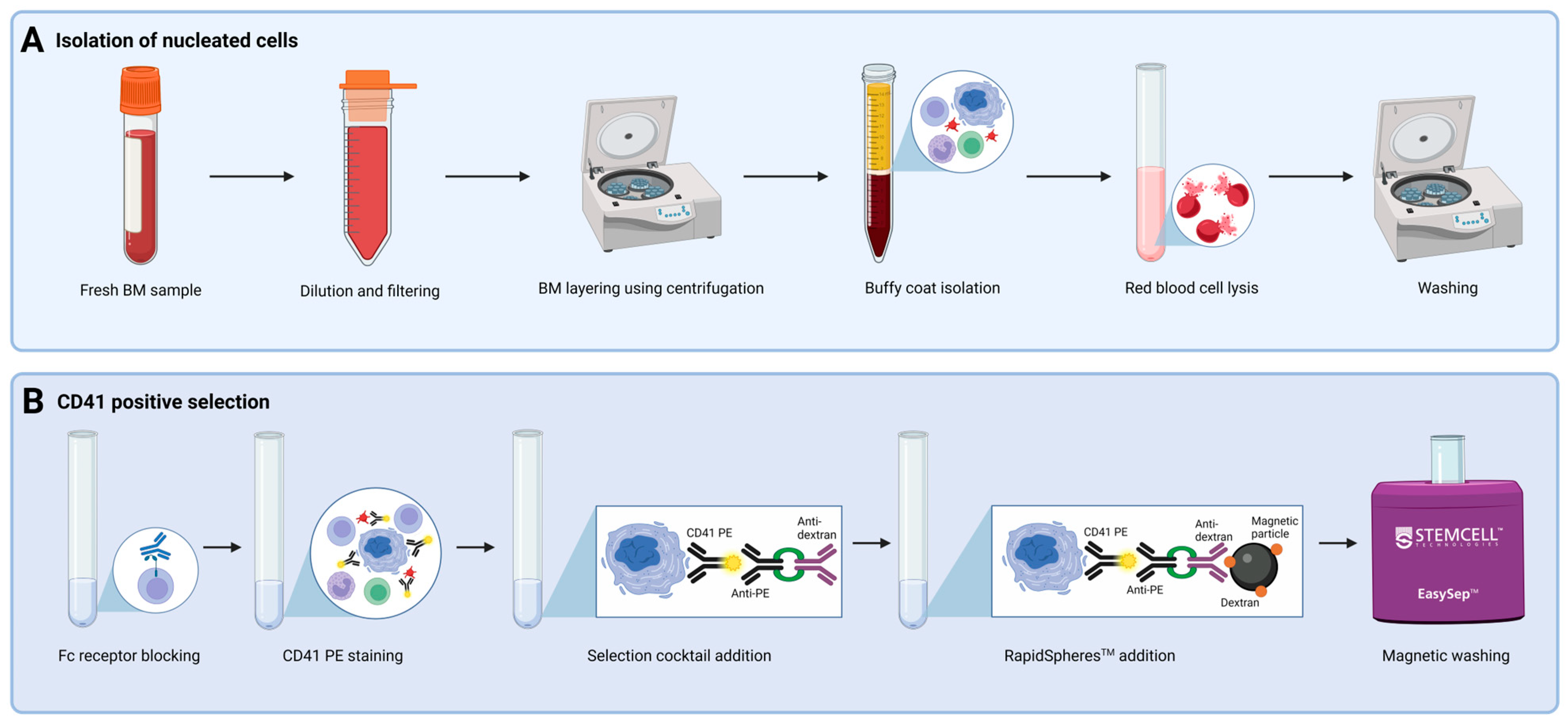
2.2. Selection of CD41+ Cells
2.3. Morphological Examination of CD41 Positive Enrichment Efficiency
2.4. Evaluation of CD41 Positive Enrichment Efficiency Using IFC
2.5. Staining Protocol for the MK-Specific IFC Panel
2.6. IFC Configuration and Acquisition
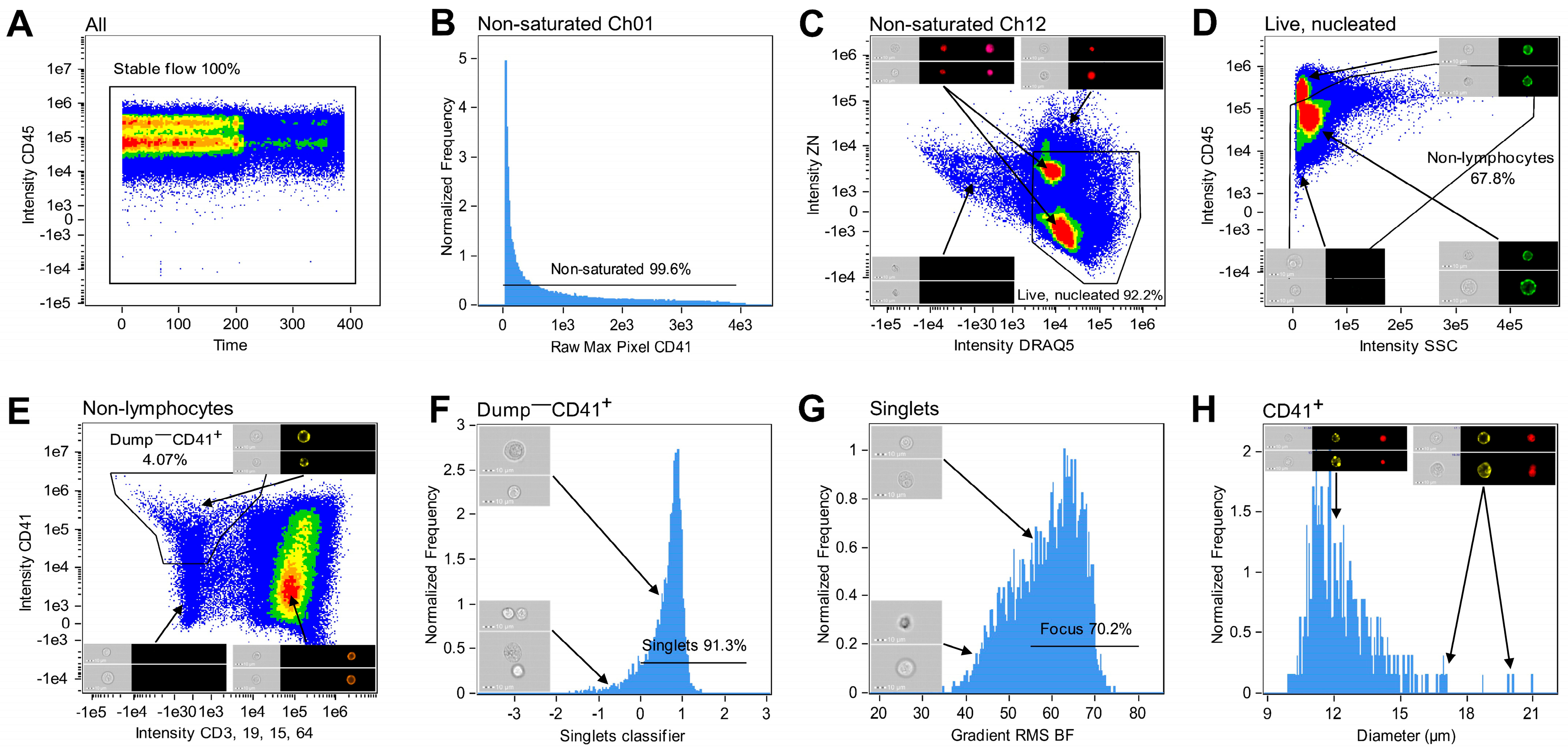
2.7. Gating Strategy
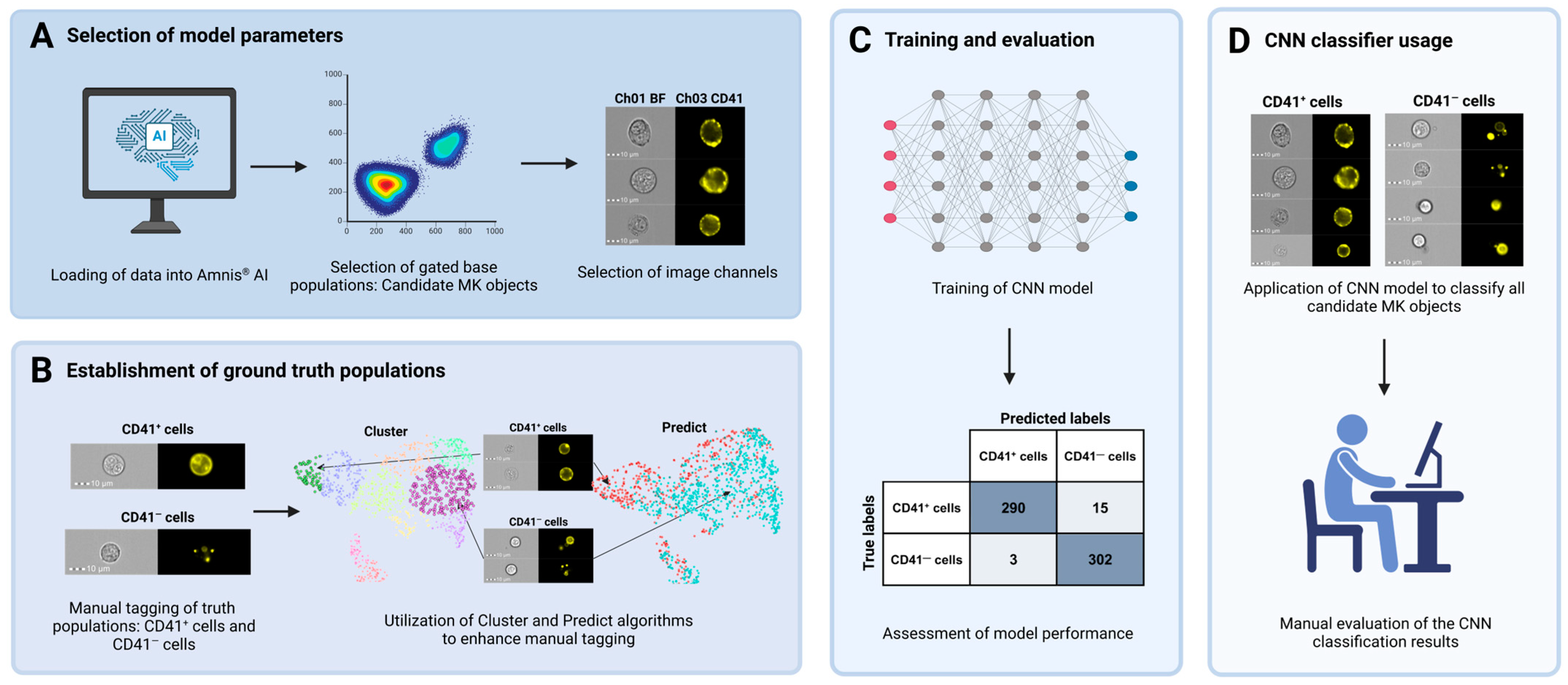
2.8. Image-Based MK Classification Using Artificial Intelligence
3. Results
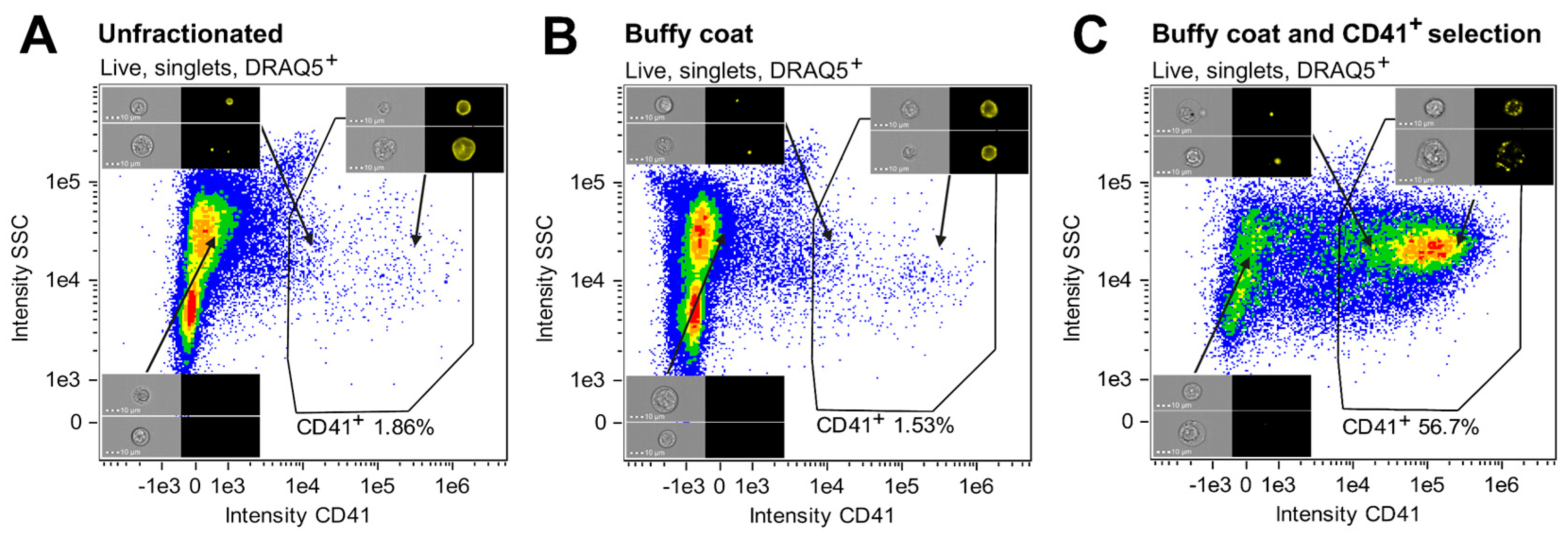
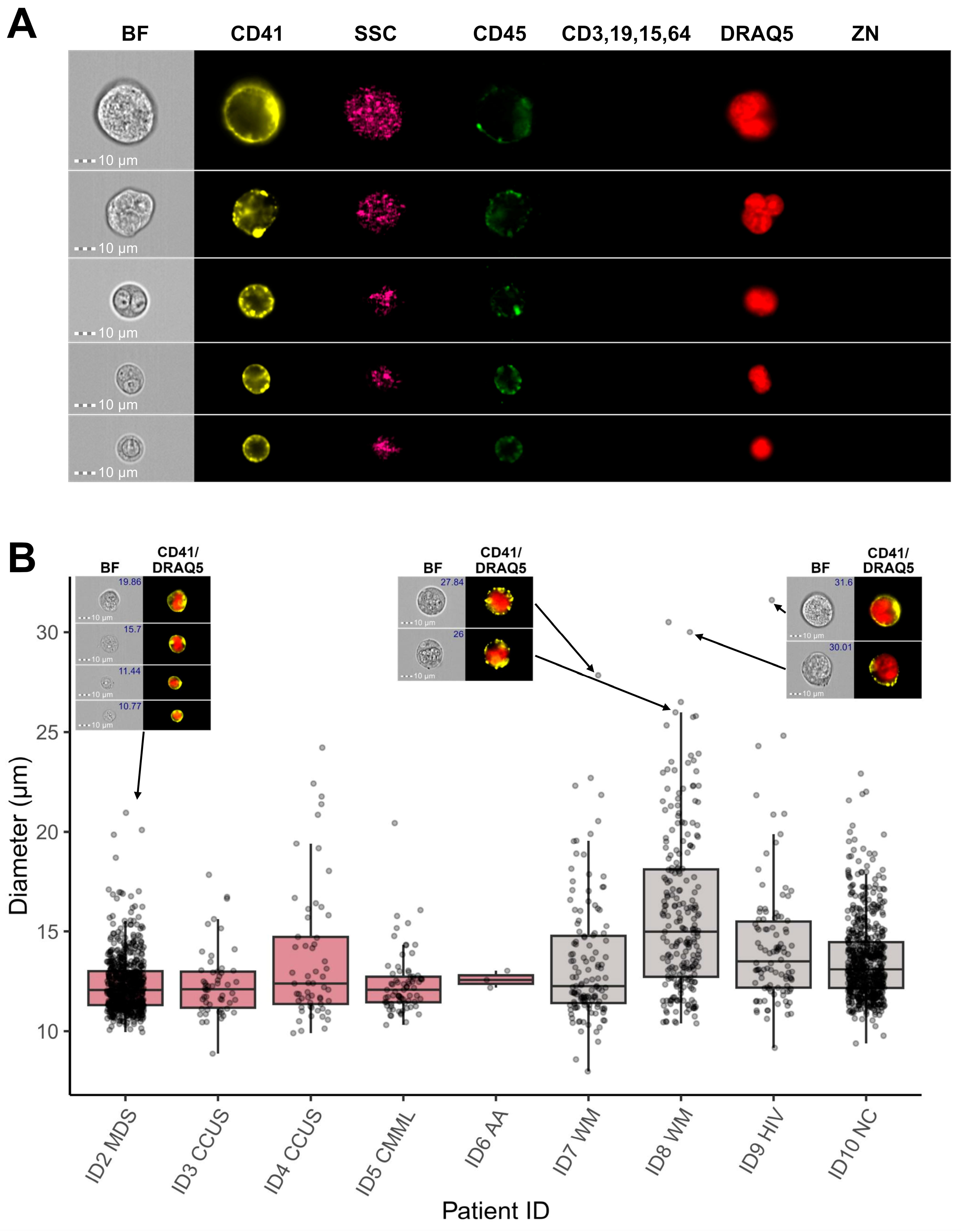
3.1. CD41 Positive Selection Ensured Enrichment of Megakaryocytic Cells
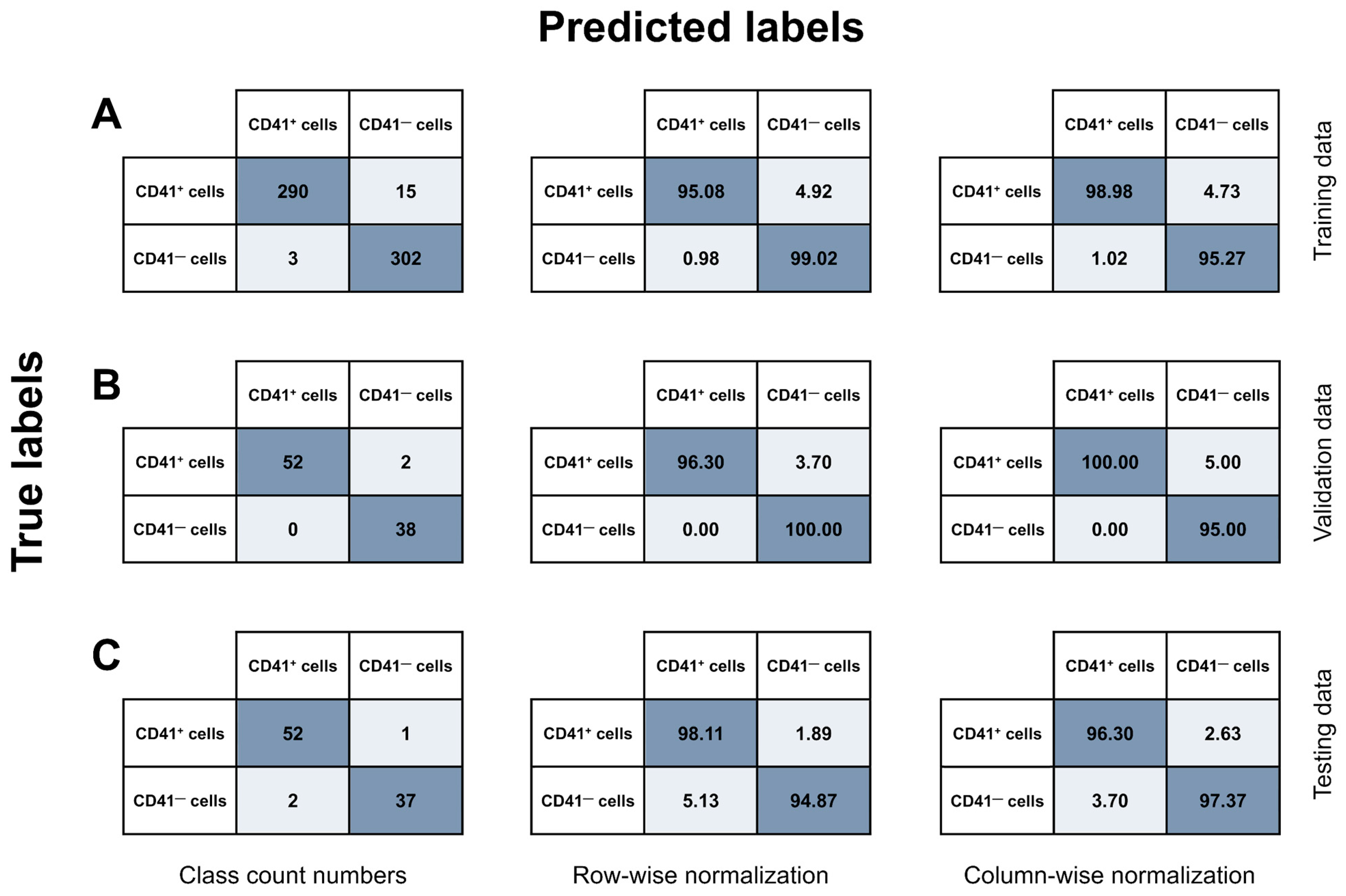
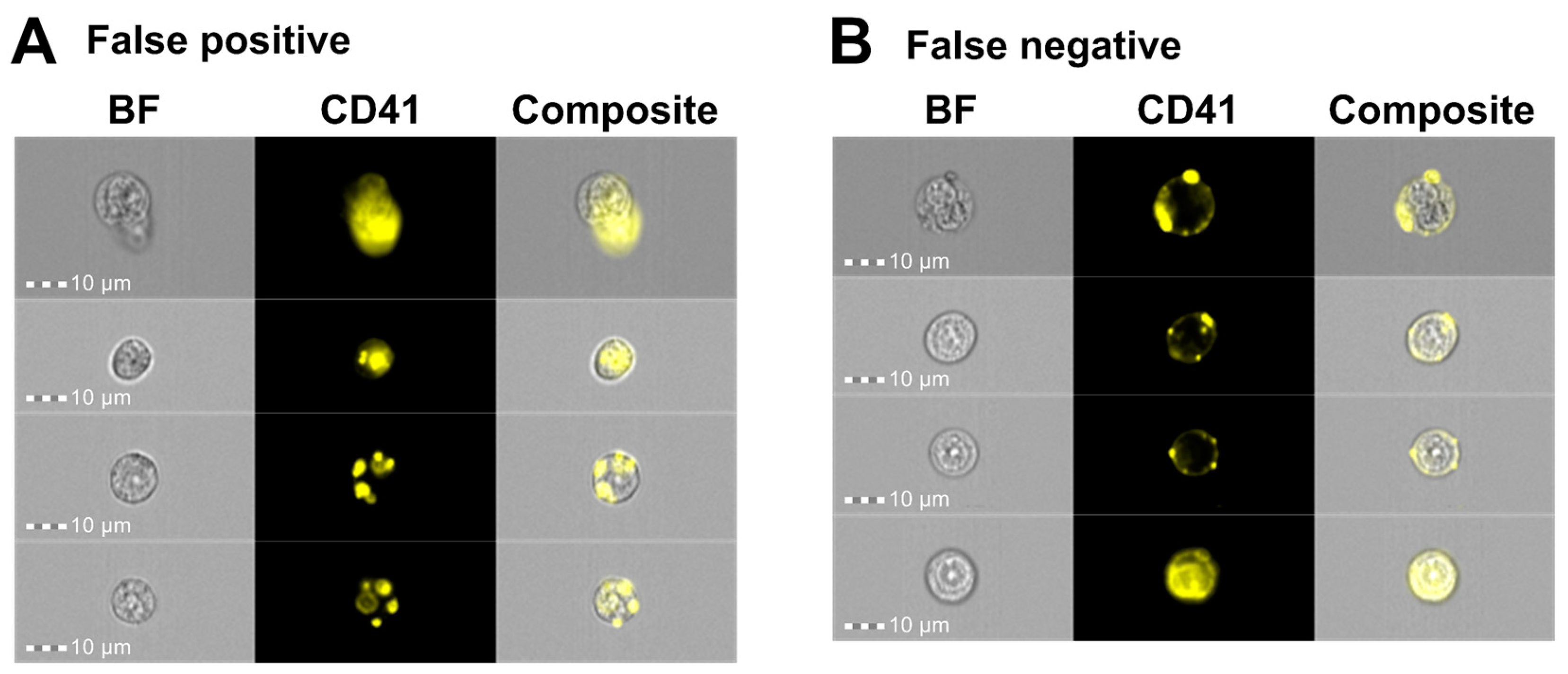
3.2. Combination of IFC and Image-Based Classification Enabled Effective Identification of MKs
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holinstat, M. Normal platelet function. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017, 36, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Q.; Goldenson, B.; Crispino, J.D. Normal and malignant megakaryopoiesis. Expert. Rev. Mol. Med. 2011, 13, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomer, A. Human marrow megakaryocyte differentiation: Multiparameter correlative analysis identifies von Willebrand factor as a sensitive and distinctive marker for early (2N and 4N) megakaryocytes. Blood 2004, 104, 2722–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomer, A.; Harker, L.A.; Burstein, S.A. Purification of human megakaryocytes by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Blood 1987, 70, 1735–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomer, A.; Harker, L.A.; Burstein, S.A. Flow cytometric analysis of normal human megakaryocytes. Blood 1988, 71, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabellino, E.M.; Levene, R.B.; Leung, L.L.; Nachman, R.L. Human megakaryocytes. II. Expression of platelet proteins in early marrow megakaryocytes. J. Exp. Med. 1981, 154, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.R.; Charo, I.F.; Parise, L.V.; Fitzgerald, L.A. The platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex. Blood 1988, 71, 831–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levene, R.B.; Lamaziere, J.M.; Broxmeyer, H.E.; Lu, L.; Rabellino, E.M. Human megakaryocytes. V. Changes in the phenotypic profile of differentiating megakaryocytes. J. Exp. Med. 1985, 161, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, J.D.; Solary, E.; Abla, O.; Akkari, Y.; Alaggio, R.; Apperley, J.F.; Bejar, R.; Berti, E.; Busque, L.; Chan, J.K.C.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Myeloid and Histiocytic/Dendritic Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1703–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arber, D.A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.; Thiele, J.; Borowitz, M.J.; Le Beau, M.M.; Bloomfield, C.D.; Cazzola, M.; Vardiman, J.W. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood 2016, 127, 2391–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, E.; Tuechler, H.; Greenberg, P.L.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Ossa, J.E.A.; Nannya, Y.; Devlin, S.M.; Creignou, M.; Pinel, P.; Monnier, L.; et al. Molecular International Prognostic Scoring System for Myelodysplastic Syndromes. NEJM Evid. 2022, 1, EVIDoa2200008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Manero, G.; Chien, K.S.; Montalban-Bravo, G. Myelodysplastic syndromes: 2021 update on diagnosis, risk stratification and management. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 1399–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasserjian, R.P.; Orazi, A.; Orfao, A.; Rozman, M.; Wang, S.A. The International Consensus Classification of myelodysplastic syndromes and related entities. Virchows Arch. 2023, 482, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, F.; Fernández-Ferrero, S.; Suárez, D.; Barbón, M.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Gil, S.; Megido, M.; Ciudad, J.; López, N.; del Cañizo, C.; et al. Myelodysplastic syndrome: A search for minimal diagnostic criteria. Leuk. Res. 1999, 23, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naqvi, K.; Jabbour, E.; Bueso-Ramos, C.; Pierce, S.; Borthakur, G.; Estrov, Z.; Ravandi, F.; Faderl, S.; Kantarjian, H.; Garcia-Manero, G. Implications of discrepancy in morphologic diagnosis of myelodysplastic syndrome between referral and tertiary care centers. Blood 2011, 118, 4690–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font, P.; Loscertales, J.; Benavente, C.; Bermejo, A.; Callejas, M.; Garcia-Alonso, L.; Garcia-Marcilla, A.; Gil, S.; Lopez-Rubio, M.; Martin, E.; et al. Inter-observer variance with the diagnosis of myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) following the 2008 WHO classification. Ann. Hematol. 2013, 92, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font, P.; Loscertales, J.; Soto, C.; Ricard, P.; Novas, C.M.; Martín-Clavero, E.; López-Rubio, M.; Garcia-Alonso, L.; Callejas, M.; Bermejo, A.; et al. Interobserver variance in myelodysplastic syndromes with less than 5% bone marrow blasts: Unilineage vs. multilineage dysplasia and reproducibility of the threshold of 2% blasts. Ann. Hematol. 2015, 94, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcovati, L.; Hellström-Lindberg, E.; Bowen, D.; Adès, L.; Cermak, J.; del Cañizo, C.; Della Porta, M.G.; Fenaux, P.; Gattermann, N.; Germing, U.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of primary myelodysplastic syndromes in adults: Recommendations from the European LeukemiaNet. Blood 2013, 122, 2943–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Porta, M.G.; Travaglino, E.; Boveri, E.; Ponzoni, M.; Malcovati, L.; Papaemmanuil, E.; Rigolin, G.M.; Pascutto, C.; Croci, G.; Gianelli, U.; et al. Minimal morphological criteria for defining bone marrow dysplasia: A basis for clinical implementation of WHO classification of myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia 2015, 29, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goasguen, J.E.; Bennett, J.M.; Bain, B.J.; Brunning, R.D.; Vallespí, M.-T.; Tomonaga, M.; Zini, G.; Renault, A. Quality control initiative on the evaluation of the dysmegakaryopoiesis in myeloid neoplasms: Difficulties in the assessment of dysplasia. Leuk. Res. 2016, 45, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Stetler-Stevenson, M.; Arthur, D.C.; Jabbour, N.; Xie, X.Y.; Molldrem, J.; Barrett, A.J.; Venzon, D.; Rick, M.E. Diagnostic utility of flow cytometric immunophenotyping in myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 2001, 98, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, W.; Westers, T.M.; Bellos, F.; Bene, M.C.; Bettelheim, P.; Brodersen, L.E.; Burbury, K.; Chu, S.; Cullen, M.; Della Porta, M.; et al. Multicenter prospective evaluation of diagnostic potential of flow cytometric aberrancies in myelodysplastic syndromes by theELN iMDSflow working group. Cytom. Part B Clin. Cytom. 2023, 104, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Loosdrecht, A.A.; Kern, W.; Porwit, A.; Valent, P.; Kordasti, S.; Cremers, E.; Alhan, C.; Duetz, C.; Dunlop, A.; Hobo, W.; et al. Clinical application of flow cytometry in patients with unexplained cytopenia and suspected myelodysplastic syndrome: A report of the European LeukemiaNet International MDS-Flow Cytometry Working Group. Cytom. Part B Clin. Cytom. 2023, 104, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, W.; Haferlach, C.; Schnittger, S.; Haferlach, T. Clinical utility of multiparameter flow cytometry in the diagnosis of 1013 patients with suspected myelodysplastic syndrome: Correlation to cytomorphology, cytogenetics, and clinical data. Cancer 2010, 116, 4549–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Porta, M.G.; Malcovati, L.; Invernizzi, R.; Travaglino, E.; Pascutto, C.; Maffioli, M.; Gallì, A.; Boggi, S.; Pietra, D.; Vanelli, L.; et al. Flow cytometry evaluation of erythroid dysplasia in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia 2006, 20, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malcovati, L.; Della Porta, M.G.; Lunghi, M.; Pascutto, C.; Vanelli, L.; Travaglino, E.; Maffioli, M.; Bernasconi, P.; Lazzarino, M.; Invernizzi, R.; et al. Flow cytometry evaluation of erythroid and myeloid dysplasia in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia 2005, 19, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Matarraz, S.; López, A.; Barrena, S.; Fernandez, C.; Jensen, E.; Flores-Montero, J.; Rasillo, A.; Sayagues, J.M.; Sánchez, M.L.; Bárcena, P.; et al. Bone marrow cells from myelodysplastic syndromes show altered immunophenotypic profiles that may contribute to the diagnosis and prognostic stratification of the disease: A pilot study on a series of 56 patients. Cytom. Part B Clin. Cytom. 2010, 78, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremers, E.M.; Westers, T.M.; Alhan, C.; Cali, C.; Visser-Wisselaar, H.A.; Chitu, D.A.; van der Velden, V.H.; Marvelde, J.G.T.; Klein, S.K.; Muus, P.; et al. Implementation of erythroid lineage analysis by flow cytometry in diagnostic models for myelodysplastic syndromes. Haematologica 2017, 102, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westers, T.M.; Saft, L.; van der Velden, V.H.J.; Marvelde, J.G.T.; Dunlop, A.; Ireland, R.; Valent, P.; Porwit, A.; Béné, M.C.; van de Loosdrecht, A.A. A series of case studies illustrating the role of flow cytometry in the diagnostic work-up of myelodysplastic syndromes. Cytom. Part B Clin. Cytom. 2023, 104, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westers, T.M.; Cremers, E.M.; Oelschlaegel, U.; Johansson, U.; Bettelheim, P.; Matarraz, S.; Orfao, A.; Moshaver, B.; Brodersen, L.E.; Loken, M.R.; et al. Immunophenotypic analysis of erythroid dysplasia in myelodysplastic syndromes. A report from the IMDSFlow working group. Haematologica 2017, 102, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, A.; Hong, Y.; Wang, G.; Erusalimsky, J.D. Assays of megakaryocyte development: Surface antigen expression, ploidy, and size. Methods Mol. Biol. 2004, 272, 309–322. [Google Scholar]
- Duetz, C.; Westers, T.M.; van de Loosdrecht, A.A. Clinical Implication of Multi-Parameter Flow Cytometry in Myelodysplastic Syndromes. Pathobiology 2019, 86, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalina, T.; Fišer, K.; Pérez-Andrés, M.; Kuzílková, D.; Cuenca, M.; Bartol, S.J.W.; Blanco, E.; Engel, P.; van Zelm, M.C.; on Behalf of the Human Cell Differentiation Molecules (HCDM) Organization. CD Maps—Dynamic Profiling of CD1–CD100 Surface Expression on Human Leukocyte and Lymphocyte Subsets. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, G.; Gale, R.P.; Cui, W.; Cai, W.; Huang, G.; Xu, Z.; Qin, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Fang, L.; et al. A systematic classification of megakaryocytic dysplasia and its impact on prognosis for patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriyama, K.; Tomonaga, M.; Matsuo, T.; Glnnai, I.; Ichimaru, M. Diagnostic significance of detecting pseudo-Pelger-Huet anomalies and micro-megakaryocytes in myelodysplastic syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 1986, 63, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bain, B.J. The bone marrow aspirate of healthy subjects. Br. J. Haematol. 1996, 94, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niswander, L.M.; Palis, J.; McGrath, K.E. Imaging Flow Cytometric Analysis of Primary Bone Marrow Megakaryocytes. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1389, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Niswander, L.M.; McGrath, K.E.; Kennedy, J.C.; Palis, J. Improved quantitative analysis of primary bone marrow megakaryocytes utilizing imaging flow cytometry. Cytom. Part A 2014, 85, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, K.E. Utilization of imaging flow cytometry to define intermediates of megakaryopoiesis in vivo and in vitro. J. Immunol. Methods 2015, 423, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basiji, D.A.; Ortyn, W.E.; Liang, L.; Venkatachalam, V.; Morrissey, P. Cellular Image Analysis and Imaging by Flow Cytometry. Clin. Lab. Med. 2007, 27, 653–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.A.; Probst, C.E.; Zayats, A.; Davidson, B.; Riedel, M.; Li, Y.; Venkatachalam, V. The in vitro micronucleus assay using imaging flow cytometry and deep learning. NPJ Syst. Biol. Appl. 2021, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porwit, A.; McCullough, J.; Erber, W.N. Section A: Normal Blood and Bone Marrow Cells; Elsevier Health Sciences: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Wood, B.L. Monitoring minimal residual disease in acute leukemia: Technical challenges and interpretive complexities. Blood Rev. 2017, 31, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dongen, J.J.M.; Lhermitte, L.; Böttcher, S.; Almeida, J.; van der Velden, V.H.J.; Flores-Montero, J.; Rawstron, A.; Asnafi, V.; Lécrevisse, Q.; Lucio, P.; et al. EuroFlow antibody panels for standardized n-dimensional flow cytometric immunophenotyping of normal, reactive and malignant leukocytes. Leukemia 2012, 26, 1908–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, L.M.; Healy, C.P.; Marvin, J.E.; Deans, T.L. High-throughput enrichment and isolation of megakaryocyte progenitor cells from the mouse bone marrow. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ortega, L.; Morales-Camacho, R.M. Nuclear protrusion in dysplastic micromegakaryocytes. Blood 2019, 133, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, R.F.; Hazzard, K.C.; Lamberg, J.D. The significance of megakaryocyte size. Blood 1982, 60, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hybel, T.E.; Jensen, S.H.; Rodrigues, M.A.; Hybel, T.E.; Pedersen, M.N.; Qvick, S.H.; Enemark, M.H.; Bill, M.; Rosenberg, C.A.; Ludvigsen, M. Imaging Flow Cytometry and Convolutional Neural Network-Based Classification Enable Discrimination of Hematopoietic and Leukemic Stem Cells in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, C.A.; Rodrigues, M.A.; Bill, M.; Ludvigsen, M. Comparative analysis of feature-based ML and CNN for binucleated erythroblast quantification in myelodysplastic syndrome patients using imaging flow cytometry data. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probst, C.; Zayats, A.; Venkatachalam, V.; Davidson, B. Advanced Characterization of Silicone Oil Droplets in Protein Therapeutics Using Artificial Intelligence Analysis of Imaging Flow Cytometry Data. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 2996–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, S.; Brandsma, E.T.; Mul, F.P.J.; Kuijpers, T.W.; Matlung, H.L.; van Bruggen, R. An AI-based imaging flow cytometry approach to study erythrophagocytosis. Cytom. Part A 2024, 105, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.A.; Mendoza, M.G.G.; Kong, R.; Sutton, A.; Pugsley, H.R.; Li, Y.; Hall, B.E.; Fogg, D.; Ohl, L.; Venkatachalam, V. Automation of the Micronucleus Assay Using Imaging Flow Cytometry and Artificial Intelligence. J. Vis. Exp. 2023, e64549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, J.M.; Orazi, A. Diagnostic criteria to distinguish hypocellular acute myeloid leukemia from hypocellular myelodysplastic syndromes and aplastic anemia: Recommendations for a standardized approach. Haematologica 2009, 94, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Patient ID | Age | Gender | Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 71 | M | MDS |
| 2 | 79 | M | MDS |
| 3 | 81 | M | CCUS |
| 4 | 44 | M | CCUS |
| 5 | 75 | M | CMML |
| 6 | 54 | M | AA |
| 7 | 74 | M | WM |
| 8 | 77 | F | WM |
| 9 | 59 | M | HIV |
| 10 | 87 | M | NC |
| 11 | 24 | M | Infection |
| Specificity | Fluorophore/Stain | Clone | Vendor | Cat # | Titer | Quantity * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD41 | PE | MWReg30 | BioLegend | 133905 | 1:20 | 5 µL |
| CD45 | KrO | J33 | Beckman Coulter | PN A966416 | 1:40 | 2.5 µL |
| DNA | DRAQ5 | NA | eBioScience | 65-0880-92 | NA | 2.5 µM |
| Viability | ZG | NA | BioLegend | 423112 | 1:200 | 0.5 µL |
| Specificity | Fluorophore/Stain | Clone | Vendor | Cat # | Titer | Quantity * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD41 | PE | HIP8 | BioLegend | 303706 | NA | 3 µg/mL |
| CD45 | SBV515 | F10-89-4 | Bio-Rad Laboratories | MCA87SBV515 | 1:20 | 5 µL |
| CD3 | BV605 | SK7 | BioLegend | 344836 | 1:80 | 1.25 µL |
| CD19 | BV605 | HIB19 | BioLegend | 302244 | 1:160 | 0.625 µL |
| CD15 | BV605 | W6D3 | BioLegend | 323032 | 1:40 | 2.5 µL |
| CD64 | BV605 | 10.1 | BioLegend | 305034 | 1:40 | 2.5 µL |
| DNA | DRAQ5 | NA | eBioScience | 65-0880-92 | NA | 1.25 µM |
| Viability | ZN | NA | BioLegend | 423105 | 1:400 | 0.25 µL |
| Model Class | Training Data | Validation Data | Testing Data | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Objects (N) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 (%) | Objects (N) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 (%) | Objects (N) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 (%) | |
| CD41+ cells | 305 | 99.0 | 95.1 | 97.0 | 54 | 100.0 | 96.3 | 98.1 | 53 | 96.3 | 98.1 | 97.2 |
| CD41− cells | 305 | 95.3 | 99.0 | 97.1 | 38 | 95.0 | 100.0 | 97.4 | 39 | 97.4 | 94.9 | 96.1 |
| Weighted average | 610 | 97.1 | 97.0 | 97.0 | 92 | 97.9 | 97.8 | 97.8 | 92 | 96.8 | 96.7 | 96.7 |
| Model Class | Manual Evaluation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID5 CMML | ID7 WM | |||||||
| Objects (N) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 (%) | Objects (N) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 (%) | |
| CD41+ cells | 83 | 89.2 | 90.4 | 89.8 | 123 | 84.3 | 87.0 | 85.6 |
| CD41− cells | 102 | 93.1 | 92.2 | 92.6 | 133 | 87.6 | 85.0 | 86.3 |
| Weighted average | 185 | 91.1 | 91.3 | 91.2 | 256 | 85.9 | 86.0 | 85.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pedersen, M.N.; Hybel, T.E.; Bjerre, J.H.; Hammer, A.S.B.; Bohn, A.B.; Bill, M.; Rosenberg, C.A.; Ludvigsen, M. High-Efficiency Enrichment of Megakaryocytes and Identification of Micromegakaryocytes from Human Bone Marrow by Imaging Flow Cytometry. Cells 2025, 14, 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080588
Pedersen MN, Hybel TE, Bjerre JH, Hammer ASB, Bohn AB, Bill M, Rosenberg CA, Ludvigsen M. High-Efficiency Enrichment of Megakaryocytes and Identification of Micromegakaryocytes from Human Bone Marrow by Imaging Flow Cytometry. Cells. 2025; 14(8):588. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080588
Chicago/Turabian StylePedersen, Maya Nautrup, Trine Engelbrecht Hybel, Jens Haugbølle Bjerre, Anne Sofie Borg Hammer, Anja Bille Bohn, Marie Bill, Carina Agerbo Rosenberg, and Maja Ludvigsen. 2025. "High-Efficiency Enrichment of Megakaryocytes and Identification of Micromegakaryocytes from Human Bone Marrow by Imaging Flow Cytometry" Cells 14, no. 8: 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080588
APA StylePedersen, M. N., Hybel, T. E., Bjerre, J. H., Hammer, A. S. B., Bohn, A. B., Bill, M., Rosenberg, C. A., & Ludvigsen, M. (2025). High-Efficiency Enrichment of Megakaryocytes and Identification of Micromegakaryocytes from Human Bone Marrow by Imaging Flow Cytometry. Cells, 14(8), 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080588







