LncRNAs Regulate Vasculogenic Mimicry in Human Cancers
Abstract
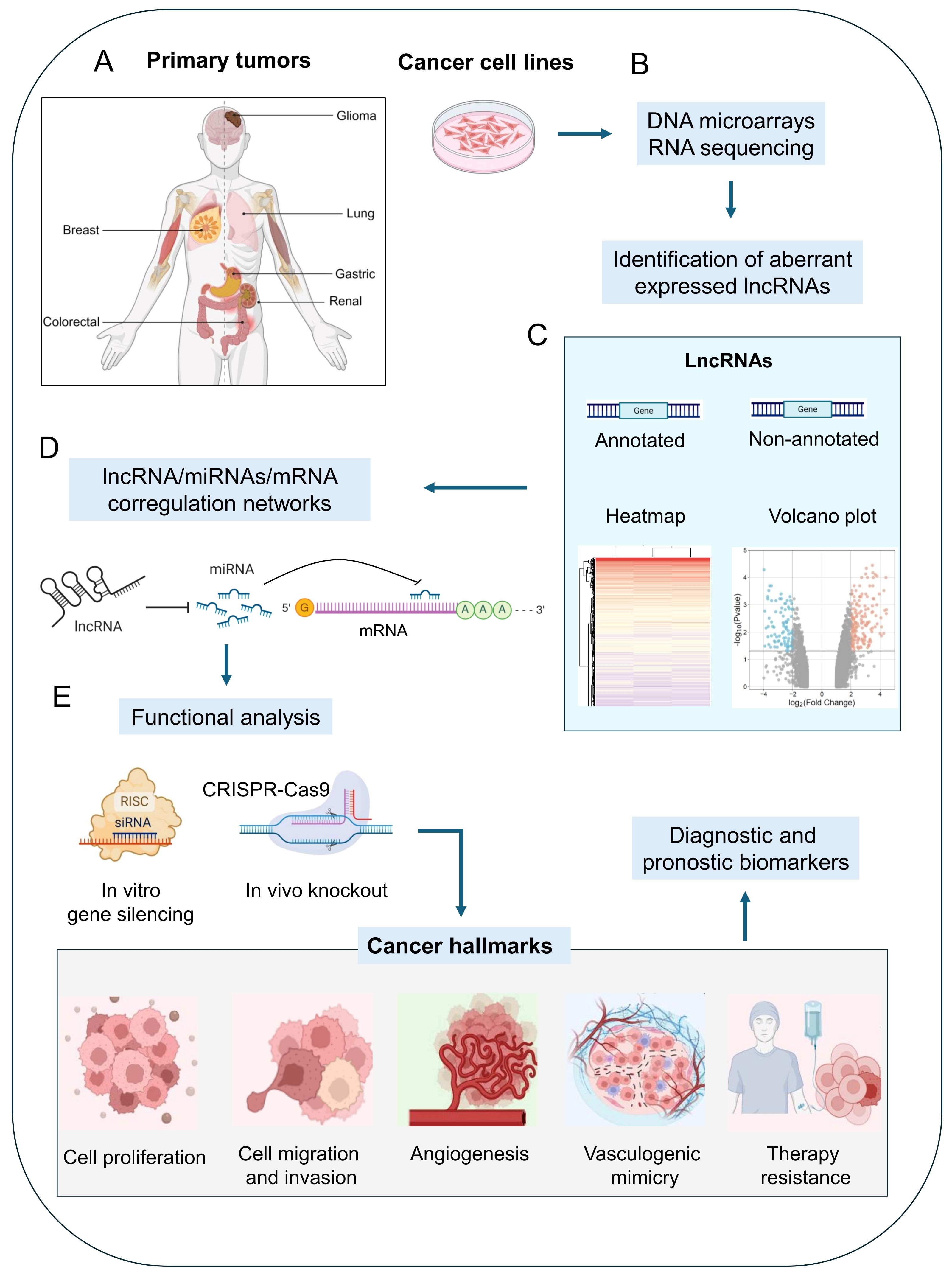
1. Introduction
2. LncRNAs Regulate Vasculogenic Mimicry in Human Cancers
2.1. LncRNA Functions in Glioma
LncRNAs Acting as ECM Remodeling Factors During VM in Glioma
2.2. LncRNA Functions in Lung Cancer
2.3. LncRNA Functions in Gastric Cancer
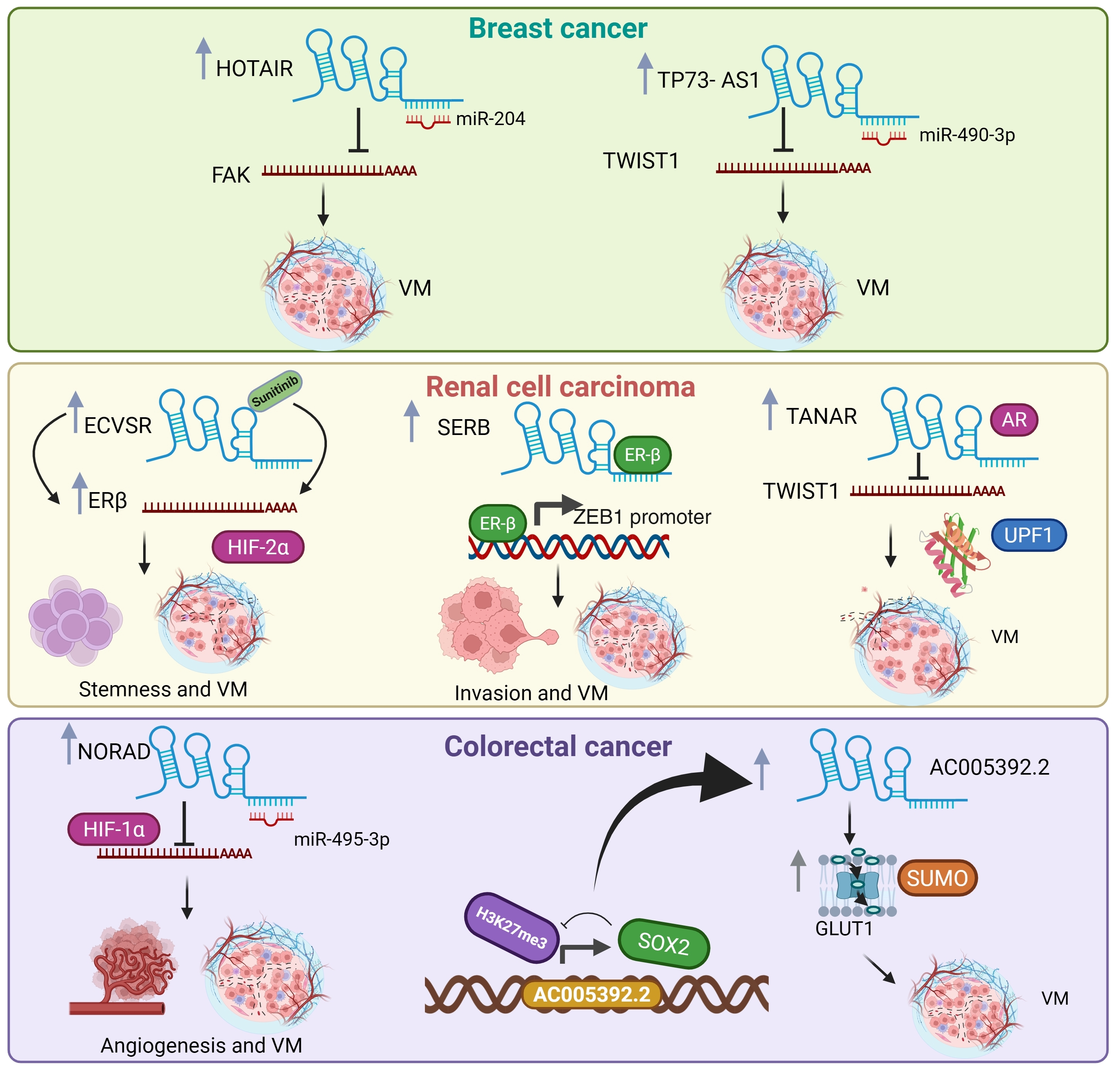
2.4. LncRNA Functions in Breast Cancer
2.5. LncRNA Functions in Renal Cell Carcinoma
2.6. LncRNA Functions in Colorectal Cancer
3. LncRNAs as Therapeutic Targets
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tahara, S.; Rentsch, S.; De Faria, F.C.C.; Sarchet, P.; Karna, R.; Calore, F.; Pollock, R.E. Three-dimensional models. Onco. Res. 2024, 33, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix, M.J.; Seftor, E.A.; Hess, A.R.; Seftor, R.E. Vasculogenic mimicry and tumour-cell plasticity: Lessons from melanoma. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzella, F.; Ribatti, D. Vascular co-option and vasculogenic mimicry mediate resistance to antiangiogenic strategies. Cancer Rep. 2022, 5, e1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Schaft, D.W.; Seftor, R.E.; Seftor, E.A.; Hess, A.R.; Gruman, L.M.; Kirschmann, D.A.; Yokoyama, Y.; Griffioen, A.W.; Hendrix, M.J. Effects of angiogenesis inhibitors on vascular network formation by human endothelial and melanoma cells. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2004, 96, 1473–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Hernández, A.P.; Sánchez-Sánchez, G.; Carlos-Reyes, A.; López-Camarillo, C. Functional roles of microRNAs in vasculogenic mimicry and resistance to therapy in human cancers: An update. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2024, 20, 913–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulitsky, I.; Bartel, D.P. lincRNAs: Genomics, evolution, and mechanisms. Cell 2013, 154, 26–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekulaeva, M.; Rajewsky, N. Roles of Long Noncoding RNAs and Circular RNAs in Translation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2019, 11, a032680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuska, B. Should scientists scrap the notion of junk DNA? J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1998, 90, 1032–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, F.; Mendell, J.T. Functional Classification and Experimental Dissection of Long Noncoding RNAs. Cell 2018, 172, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhu, W.; Dong, J.; Cheng, Y.; Yin, Z.; Shen, F. Mechanisms and Functions of Long Non-Coding RNAs at Multiple Regulatory Levels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamazaki, N.; Uesaka, M.; Nakashima, K.; Agata, K.; Imamura, T. Gene activation-associated long noncoding RNAs function in mouse preimplantation development. Development 2015, 142, 910–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.; Orom, U.A.; Cesaroni, M.; Beringer, M.; Taatjes, D.J.; Blobel, G.A.; Shiekhattar, R. Activating RNAs associate with Mediator to enhance chromatin architecture and transcription. Nature 2013, 494, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maamar, H.; Orom, U.A.; Cesaroni, M.; Beringer, M.; Taatjes, D.J.; Blobel, G.A.; Shiekhattar, R. linc-HOXA1 is a noncoding RNA that represses Hoxa1 transcription in cis. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 1260–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, I.C.; Kwak, H.; Chen, F.L.; Werner, M.; Shopland, L.S.; Danko, C.G.; Lis, J.T.; Zhang, M.; Martin, J.F.; Kurpios, N.A. Chromatin Architecture of the Pitx Locus Requires CTCF- and Pitx2-Dependent Asymmetry that Mirrors Embryonic Gut Laterality. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, T.; Subhash, S.; Vaid, R.; Enroth, S.; Uday, S.; Reinius, B.; Mitra, S.; Mohammed, A.; James, A.R.; Hoberg, E.; et al. MEG3 long noncoding RNA regulates the TGF-β pathway genes through formation of RNA–DNA triplex structures. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grote, P.; Herrmann, B.G. The long non-coding RNA Fendrr links epigenetic control mechanisms to gene regulatory networks in mammalian embryogenesis. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 1579–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinn, J.L.; Kertesz, M.; Wang, J.K.; Squazzo, S.L.; Xu, X.; Brugmann, S.A.; Goodnough, L.H.; Helms, J.A.; Farnham, P.J.; Segal, E.; et al. Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin domains in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell 2007, 129, 1311–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, B.; Wapinski, O.L.; Tsai, M.-C.; Qu, K.; Zhang, J.; Carlson, J.C.; Lin, M.; Fang, F.; Gupta, R.A.; et al. Targeted disruption of Hotair leads to homeotic transformation and gene derepression. Cell Rep. 2013, 5, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memczak, S.; Jens, M.; Elefsinioti, A.; Torti, F.; Krueger, J.; Rybak, A.; Maier, L.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Gregersen, L.H.; Munschauer, M. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 2013, 495, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapicavoli, N.A.; Qu, K.; Zhang, J.; Mikhail, M.; Laberge, R.M.; Chang, H.Y. A mammalian pseudogene lncRNA at the interface of inflammation and anti-inflammatory therapeutics. Elife 2013, 2, e00762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.D.; Andersen, R.E.; Liu, S.J.; Jan Nowakowski, T.; Hong, S.J.; Gertz, C.C.; Salinas, R.D.; Zarabi, H.; Kriegstein, A.R.; Lim, D.A. The long noncoding RNA Pnky regulates neuronal differentiation of embryonic and postnatal neural stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2015, 16, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprea, J.; Prenninger, S.; Dori, M.; Ghosh, T.; Monasor, L.S.; Wessendorf, E.; Zocher, S.; Massalini, S.; Alexopoulou, D.; Lesche, M. Transcriptome sequencing during mouse brain development identifies long non-coding RNAs functionally involved in neurogenic commitment. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 3145–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, A.M.; Chang, H.Y. Long Noncoding RNAs in Cancer Pathways. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Cai, H.; Liu, X.; Zheng, J.; Liu, Y.; Gong, W.; Chen, J.; Xi, Z.; Xue, Y. Long Non-coding RNA LINC00339 Stimulates Glioma Vasculogenic Mimicry Formation by Regulating the miR-539-5p/TWIST1/MMPs Axis. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 10, 170–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, D.; Yi, B.; Cai, H.; Wang, Y.; Lou, X.; Xi, Z.; Li, Z. SUMOylation of IGF2BP2 promotes vasculogenic mimicry of glioma via regulating OIP5-AS1/miR-495-3p axis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 2912–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, B.; Li, H.; Cai, H.; Lou, X.; Yu, M.; Li, Z. LOXL1-AS1 communicating with TIAR modulates vasculogenic mimicry in glioma via regulation of the miR-374b-5p/MMP14 axis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; Wu, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, M.; He, J. Long non-coding RNA HULC stimulates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition process and vasculogenic mimicry in human glioblastoma. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 5270–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Ruan, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, F.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Shao, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, L.; et al. HNRNPD interacts with ZHX2 regulating the vasculogenic mimicry formation of glioma cells via linc00707/miR-651-3p/SP2 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Ding, J.; He, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, R.; Han, Z.; Xing, E.Z.; Zhang, C.; Yeh, S. Estrogen receptor β promotes the vasculogenic mimicry (VM) and cell invasion via altering the lncRNA-MALAT1/miR-145-5p/NEDD9 signals in lung cancer. Oncogene 2019, 38, 1225–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Shen, Y.; Ren, H.; Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y. Repression of linc01555 up-regulates angiomotin-p130 via the microRNA-122-5p/clic1 axis to impact vasculogenic mimicry-mediated chemotherapy resistance in small cell lung cancer. Cell Cycle 2023, 22, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yang, B.; Shen, A.; Yu, K.; Ma, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, H. LncRNA UCA1 promotes vasculogenic mimicry by targeting miR-1-3p in gastric cancer. Carcinogenesis 2024, 45, 658–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano-Romero, A.; Astudillo-de la Vega, H.; Terrones-Gurrola, M.C.D.R.; Marchat, L.A.; Hernández-Sotelo, D.; Salinas-Vera, Y.M.; Ramos-Payan, R.; Silva-Cázares, M.B.; Nuñez-Olvera, S.I.; Hernández-de la Cruz, O.N. HOX Transcript Antisense RNA HOTAIR Abrogates Vasculogenic Mimicry by Targeting the AngiomiR-204/FAK Axis in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Non-Coding RNA 2020, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Sun, W.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA TP73-AS1 suppresses triple negative breast cancer cell vasculogenic mimicry by targeting miR-490-3p/TWIST1 axis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 504, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Chu, F.; Zhang, L. Induction of lncRNA NORAD accounts for hypoxia-induced chemoresistance and vasculogenic mimicry in colorectal cancer by sponging the miR-495-3p/hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α). Bioengineered 2022, 13, 950–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Q.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Chen, M.; Li, Q.; Ma, K.; Xiao, P.; Luo, C. Hypomethylation-associated LINC00987 downregulation induced lung adenocarcinoma progression by inhibiting the phosphorylation-mediated degradation of SND1. Mol. Carcinog. 2024, 63, 1260–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xue, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, J.; Shen, S.; Yang, C.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Ma, J.; et al. ZRANB2/SNHG20/FOXK1 Axis regulates Vasculogenic mimicry formation in glioma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, F.; Ruan, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, C.; Wang, D.; Zheng, J.; Xue, Y.; Shen, S.; Shao, L.; Yang, Y.; et al. The PABPC5/HCG15/ZNF331 Feedback Loop Regulates Vasculogenic Mimicry of Glioma via STAU1-Mediated mRNA Decay. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2020, 17, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wei, N. METTL3-mediated HOTAIRM1 promotes vasculogenic mimicry icontributionsn glioma via regulating IGFBP2 expression. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, J.; Shan, B.; Li, B.; Peng, W.; Dong, Y.; Shi, W.; Zhao, W.; He, D.; Duan, M.; et al. The long noncoding RNA LINC00312 induces lung adenocarcinoma migration and vasculogenic mimicry through directly binding YBX1. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yuan, J.; Sun, L.; Lin, L.; Huang, N.; Bin, J.; Liao, Y.; Liao, W. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes gastric cancer tumorigenicity and metastasis by regulating vasculogenic mimicry and angiogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2017, 395, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wu, J.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Huang, G.; Qin, L. LncRNA PVT1 induces aggressive vasculogenic mimicry formation through activating the STAT3/Slug axis and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer. Cell. Oncol. 2020, 43, 863–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Du, Y.; Gong, L.P.; Shao, Y.T.; Wen, J.Y.; Sun, L.P.; He, D.; Guo, J.R.; Chen, J.N.; Shao, C.K. EBV-Induced CXCL8 Upregulation Promotes Vasculogenic Mimicry in Gastric Carcinoma via NF-κB Signaling. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 780416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Yang, H.; Shi, H.; Hu, Y.; Chang, C.; Liu, S.; Yeh, S. Sunitinib increases the cancer stem cells and vasculogenic mimicry formation via modulating the lncRNA-ECVSR/ERβ/Hif2-α signaling. Cancer Lett. 2022, 524, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Chen, F.; Zhang, J.; Chang, F.; Lv, Z.; Li, K.; Li, S.; Hu, Y.; Yeh, S. LncRNA-SERB promotes vasculogenic mimicry (VM) formation and tumor metastasis in renal cell carcinoma. J. Biol. Chem. 2024, 300, 107297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, B.; Sun, Y.; Luo, J.; Wang, K.; Liu, Q.; Fang, R.; Liu, B.; Chou, F.; Wang, R.; Meng, J. Androgen receptor promotes renal cell carcinoma (RCC) vasculogenic mimicry (VM) via altering TWIST1 nonsense-mediated decay through lncRNA-TANAR. Oncogene 2021, 40, 1674–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zheng, H. SOX2 promotes vasculogenic mimicry by accelerating glycolysis via the lncRNA AC005392.2-GLUT1 axis in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Bauchet, L.; Davis, F.G.; Deltour, I.; Fisher, J.L.; Langer, C.E.; Pekmezci, M.; Schwartzbaum, J.A.; Turner, M.C.; Walsh, K.M.; et al. The epidemiology of glioma in adults: A “state of the science” review. Neuro-Oncology 2014, 16, 896–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Burke, A.P.; Marx, A.; Nicholson, A.G. Introduction to the 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus, and Heart. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2015, 10, 1240–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondov, B.; Milenkovikj, Z.; Kondov, G.; Petrushevska, G.; Basheska, N.; Bogdanovska-Todorovska, M.; Tolevska, N.; Ivkovski, L. Presentation of the Molecular Subtypes of Breast Cancer Detected by Immunohistochemistry in Surgically Treated Patients. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandpur, U.; Haile, B.; Makary, M.S. Early-Stage Renal Cell Carcinoma Locoregional Therapies: Current Approaches and Future Directions. Clin. Med. Insights Oncol. 2024, 18, 11795549241285390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, S.; Nandi, S.; Nayak, A. Unraveling the complexities of colorectal cancer and its promising therapies—An updated review. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 143 Pt 1, 113325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.J.; Lim, D. A Modulating the expression of long non-coding RNAs for functional studies. EMBO Rep. 2018, 19, e46955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, H.; Guo, M.; Liu, L.; Liu, C.; et al. CRISPR-CasRx Targeting LncRNA LINC00341 Inhibits Tumor Cell Growth in vitro and in vivo. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 638995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Tang, Y.; Fang, Z.; Wen, J.; Wicha, M.S.; Luo, M. Long Non-Coding RNAs: Key Regulators of Tumor Epithelial/Mesenchymal Plasticity and Cancer Stemness. Cells 2025, 14, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma ecology theory: Cancer as multidimensional spatiotemporal “unity of ecology and evolution” pathological ecosystem. Theranostics 2023, 13, 1607–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]


| lncRNA | Cancer | Target | Mechanisms of Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LINC00339 | Glioma | miR-539-5p | Promotes proliferation, invasion, and VM by sponging miR-539-5p and increasing TWIST1 expression | [24] |
| OIP5-AS1 | Glioma | miR-495-3p | Promotes angiogenesis, migration, and VM acting as a sponge for miR-495-3p, regulating HIF-1α and MMP14 | [25] |
| LOXL1-AS1 | Glioma | miR-374b-5p | Involved in ECM degradation; downregulates miR-374b-5p and increases MMP14 expression | [26] |
| HULC | Glioma | Unknown | Stimulates the EMT and tube formation | [27] |
| LINC00707 | Glioma | miR-651-3p | Induces ECM degradation and VM formation, reducing the expression of miR-651-3p and increasing its target gene SP2 | [28] |
| MALAT1 | Lung | miR-145-5p | Stimulates cell invasion and VM formation and acts as a competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) by sponging miR-145-5p | [29] |
| LINC01555 | Lung | miR-122-5p | Promotes angiogenesis and the chemoresistance miR-122-5p/CLIC1 axis in vivo | [30] |
| UCA1 | Gastric | miR-1-3p | Induces proliferation and metastasis, sponges miR-1-3p, and activates PI3K/AKT and AKT/GSK3-β signaling | [31] |
| HOTAIR | Breast | miR-204 | Promotes cell migration, is highly expressed under hypoxic conditions, and adsorbs miR-204; FAK is the target gene of miR-204 | [32] |
| TP73-AS1 | Breast | miR-490-3p | Involved in VM formation; acts as an miR-490-3p sponge by quenching TWIST1 | [33] |
| NORAD | Colorectal | miR-495-3p | Modulates VM and EMT, acting as a sponge for miR-495-3p, preventing binding to its target mRNA HIF-1α | [34] |
| LncRNA | Cancer | Validated Target | Function in VM | Mechanisms of Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Downregulated | |||||
| LINC00987 | Lung | SND1 | Inhibitor | Inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, promoting SND1 phosphorylation and degradation | [35] |
| Upregulated | |||||
| HCG15 | Glioma | ZNF331 | Promoter | Induces proliferation, migration, invasion, and VM formation and influences the degradation of ZNF331 mRNA, a PALB transcription inhibitor | [36] |
| SNHG20 | Glioma | FOXK1 | Promoter | Promotes proliferation, migration, invasion, VM, FOXK1 mRNA degradation, downregulating the MMP1, MMP9, and VE-cadherin levels | [37] |
| HOTAIRM1 | Glioma | IGFBP2 | Promoter | Induces proliferation, migration, invasion, and VM by regulating IGFBP2 expression | [38] |
| LINC00312 | Lung | YBX1 | Promoter | Promotes migration and invasion by directly binding to the YBX1 protein | [39] |
| MALAT1 | Gastric | Unknown | Promoter | Increases vascular permeability and angiogenesis by activating the VE-cadherin/β-catenin complex, ERK/MMP, and FAK/paxillin signaling | [40] |
| PVT1 | Gastric | STAT3 | Promoter | Promotes EMT and VM formation by interacting and recruiting STAT3 to the SLUG promoter to induce ETM gene expression | [41] |
| RPMS1 | Gastric | CXCL8 | Promoter | Increases CXCL8 expression by interfering with H3K27me at the promoter region to induce proliferation, migration, and VM formation | [42] |
| ECVSR | Renal cell carcinoma | ERβ | Promoter | Sunitinib binds to and upregulates ECVSR, increasing ERβ mRNA stability and promoting a cancer stem-like cell (CSC) phenotype | [43] |
| SERB | Renal cell carcinoma | ERβ | Promoter | Upregulates invasion and VM formation by binding to the Erβ promoter region, increasing its expression. ZEB1 is the transcriptional target of ERβ | [44] |
| TANAR | Renal cell carcinoma | Twist | Promoter | The androgen receptor (AR) upregulates TANAR, which in turn inhibits TWIST1 degradation by directly binding to its 5′UTR, thereby promoting E-cadherin expression to induce VM | [45] |
| AC005392.2 | Colorectal | GLUT1 | Promoter | Activates glycolysis by binding to GLUT1 and promoting its stability | [46] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibarra-Sierra, E.; Bermúdez, M.; Villegas-Mercado, C.E.; Silva-Cázares, M.B.; López-Camarillo, C. LncRNAs Regulate Vasculogenic Mimicry in Human Cancers. Cells 2025, 14, 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080616
Ibarra-Sierra E, Bermúdez M, Villegas-Mercado CE, Silva-Cázares MB, López-Camarillo C. LncRNAs Regulate Vasculogenic Mimicry in Human Cancers. Cells. 2025; 14(8):616. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080616
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbarra-Sierra, Eloísa, Mercedes Bermúdez, Carlos Esteban Villegas-Mercado, Macrina B. Silva-Cázares, and César López-Camarillo. 2025. "LncRNAs Regulate Vasculogenic Mimicry in Human Cancers" Cells 14, no. 8: 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080616
APA StyleIbarra-Sierra, E., Bermúdez, M., Villegas-Mercado, C. E., Silva-Cázares, M. B., & López-Camarillo, C. (2025). LncRNAs Regulate Vasculogenic Mimicry in Human Cancers. Cells, 14(8), 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080616









