Neuregulin-1 (NRG1) Binds to the Allosteric Binding Site (Site 2) and Suppresses Allosteric Integrin Activation by Inflammatory Cytokines: A Potential Mechanism of Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Fibrosis Action of NRG1
Abstract
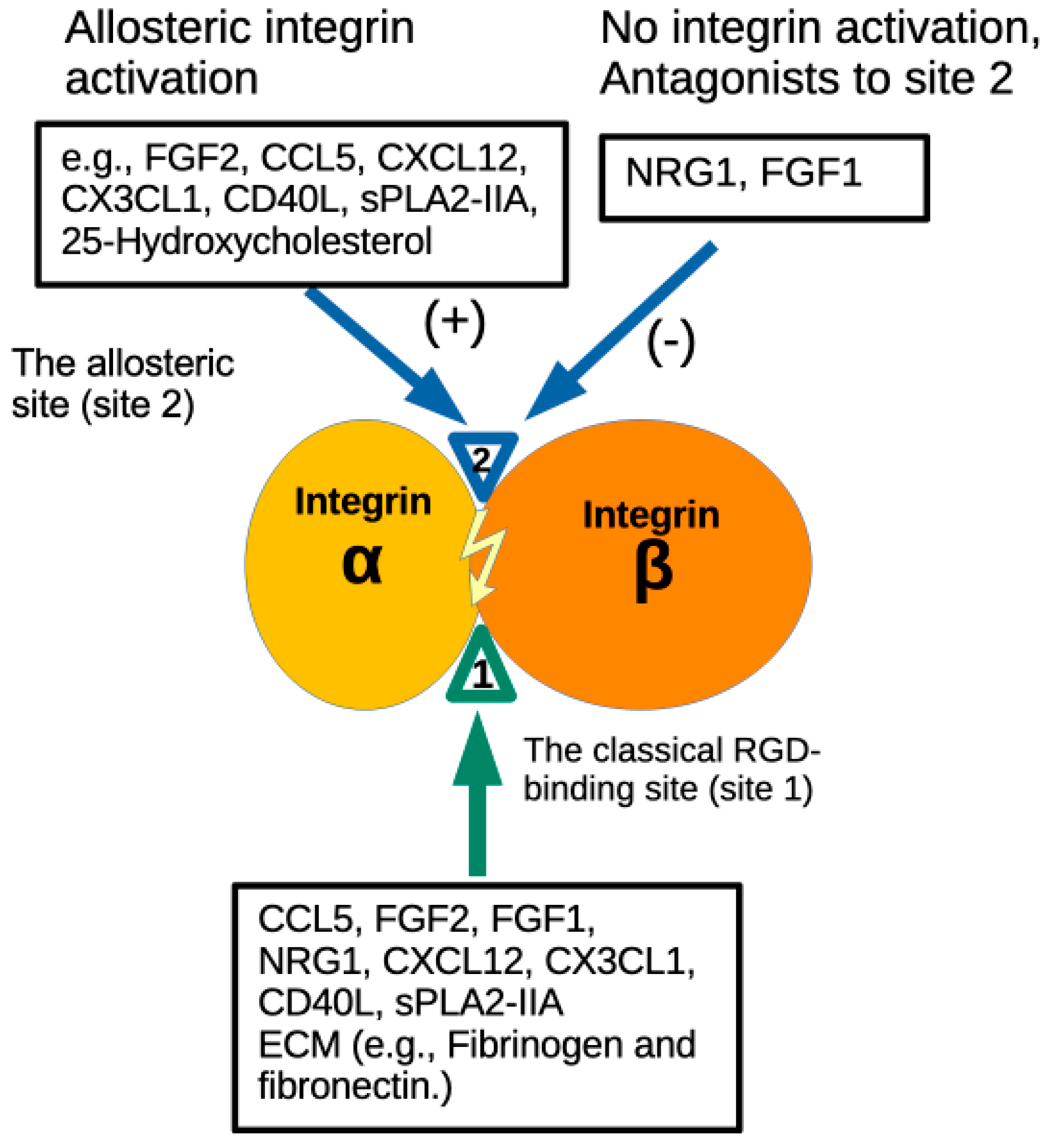
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protein Expression
2.2. Docking Simulation
2.3. Statistical Analyses
2.4. Site 2 and SDL Peptide Binding to NRG1
2.5. Blocking Activation of Cell-Surface αIIbβ3 by NRG1 3KE
3. Results
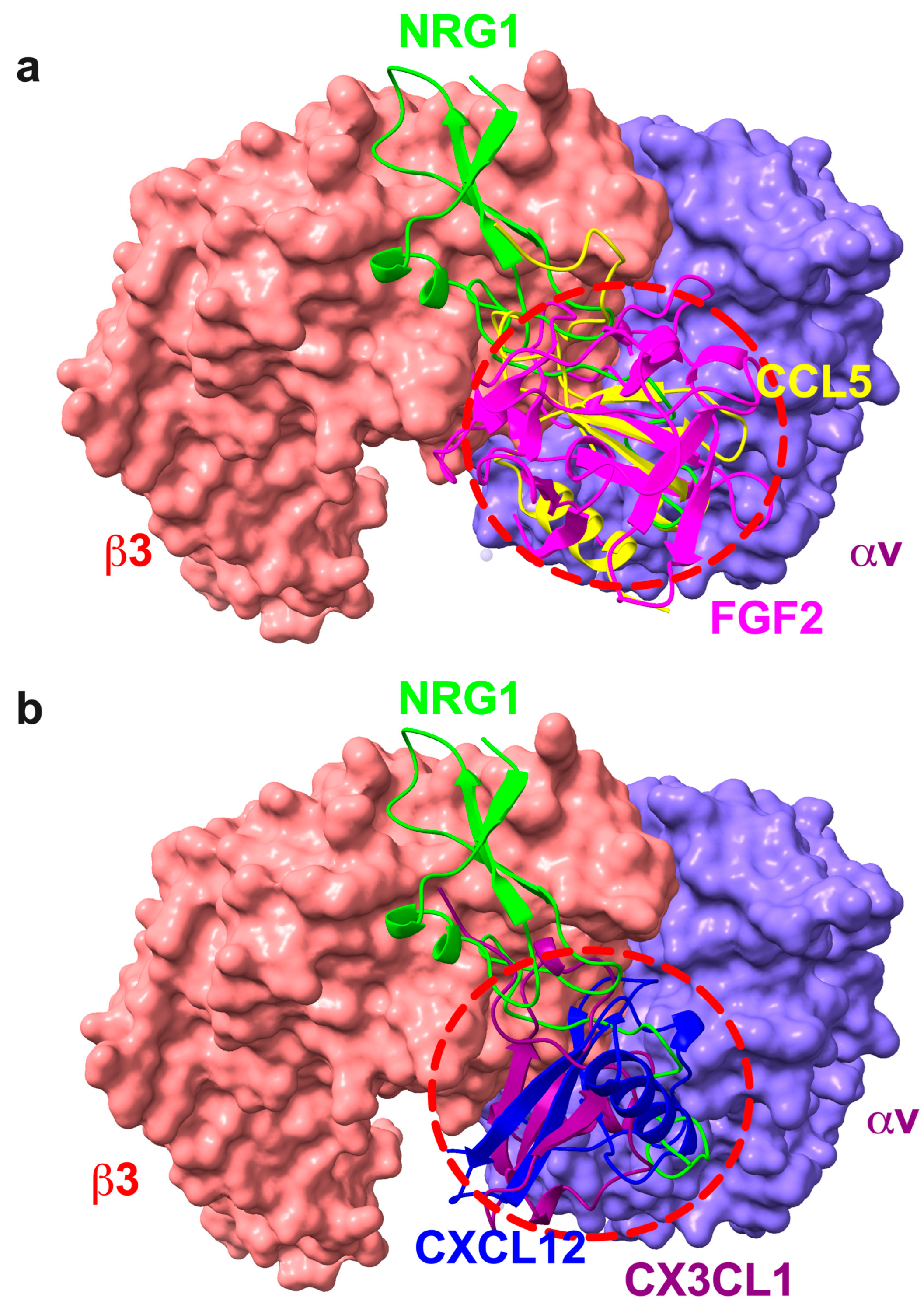
3.1. Docking Simulation Predicts That NRG1 Binds to Site 2
3.2. Site 2-Derived Peptide and Specificity-Determining Loop (SDL) Peptide Bind to NRG1
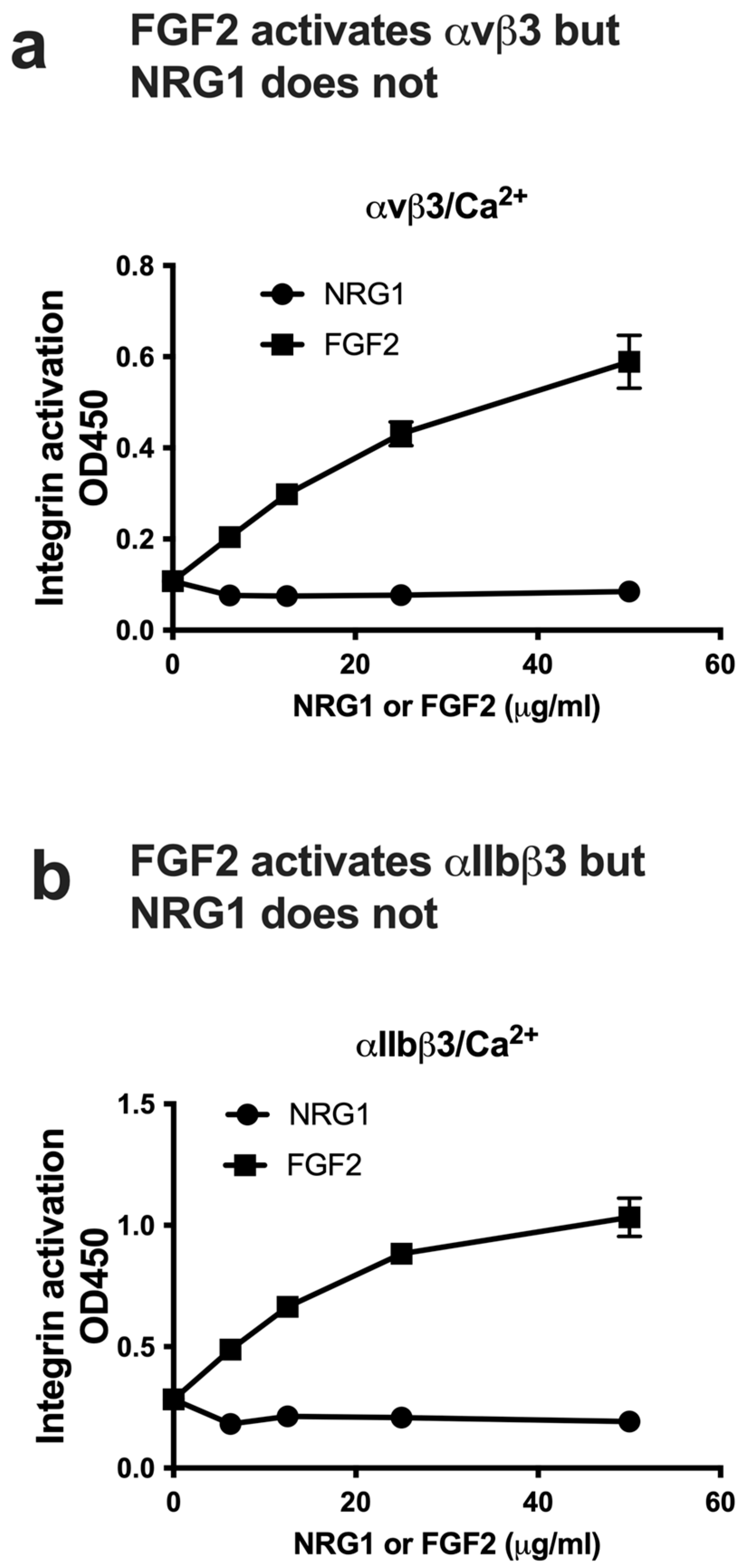
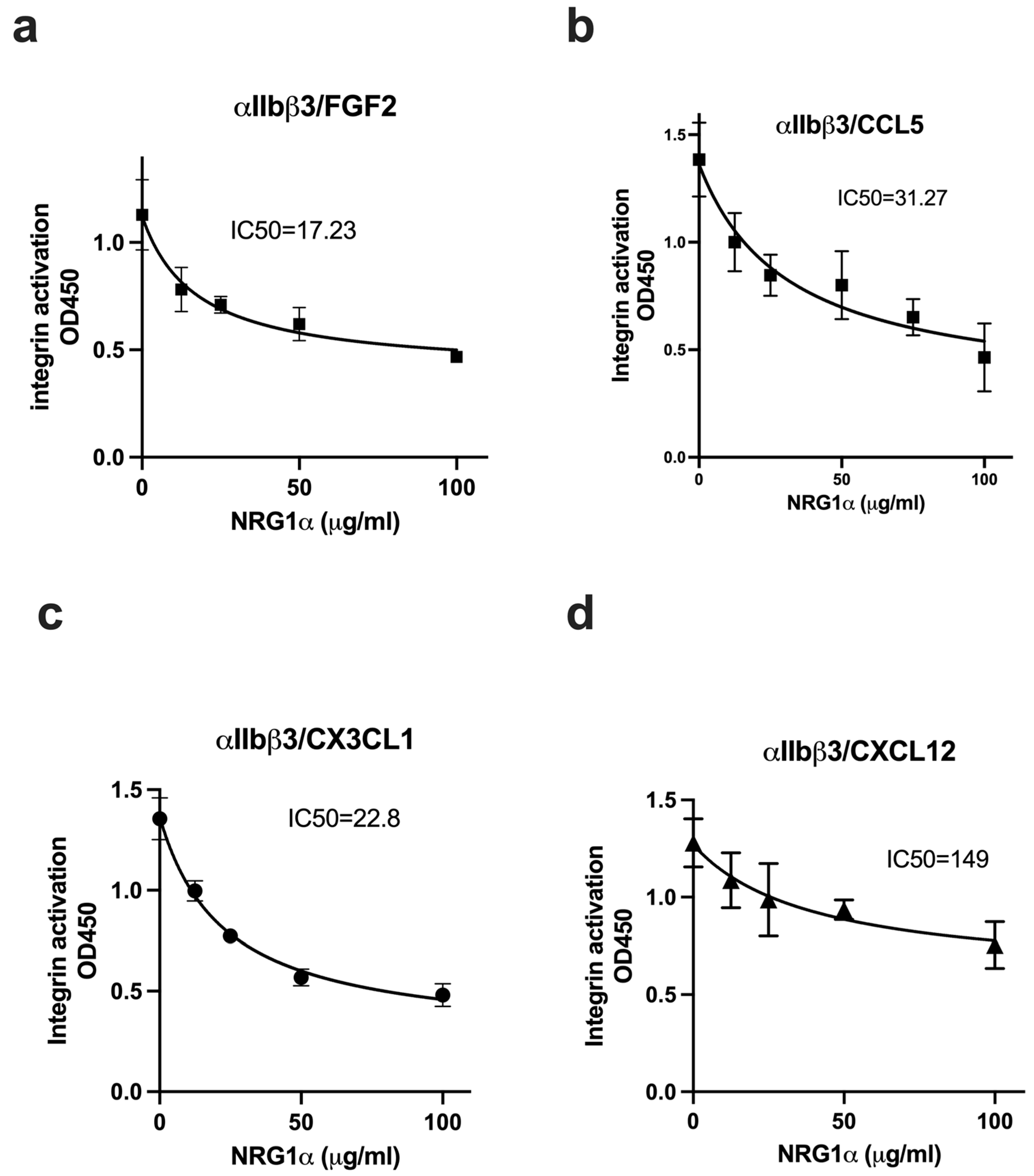
3.3. NRG1 Does Not Activate β3 Integrins and Instead Suppresses Activation Induced by Inflammatory Cytokines
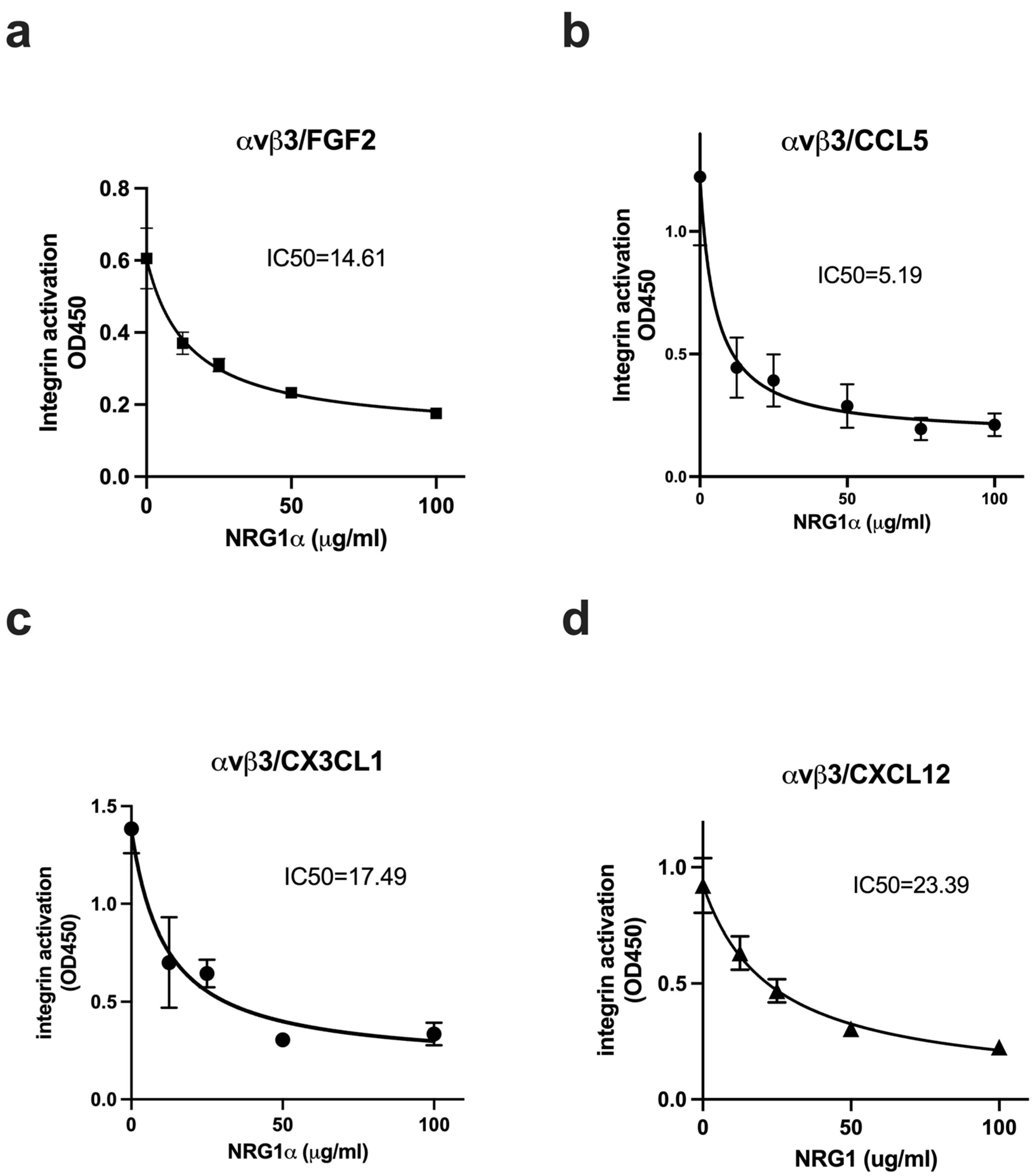
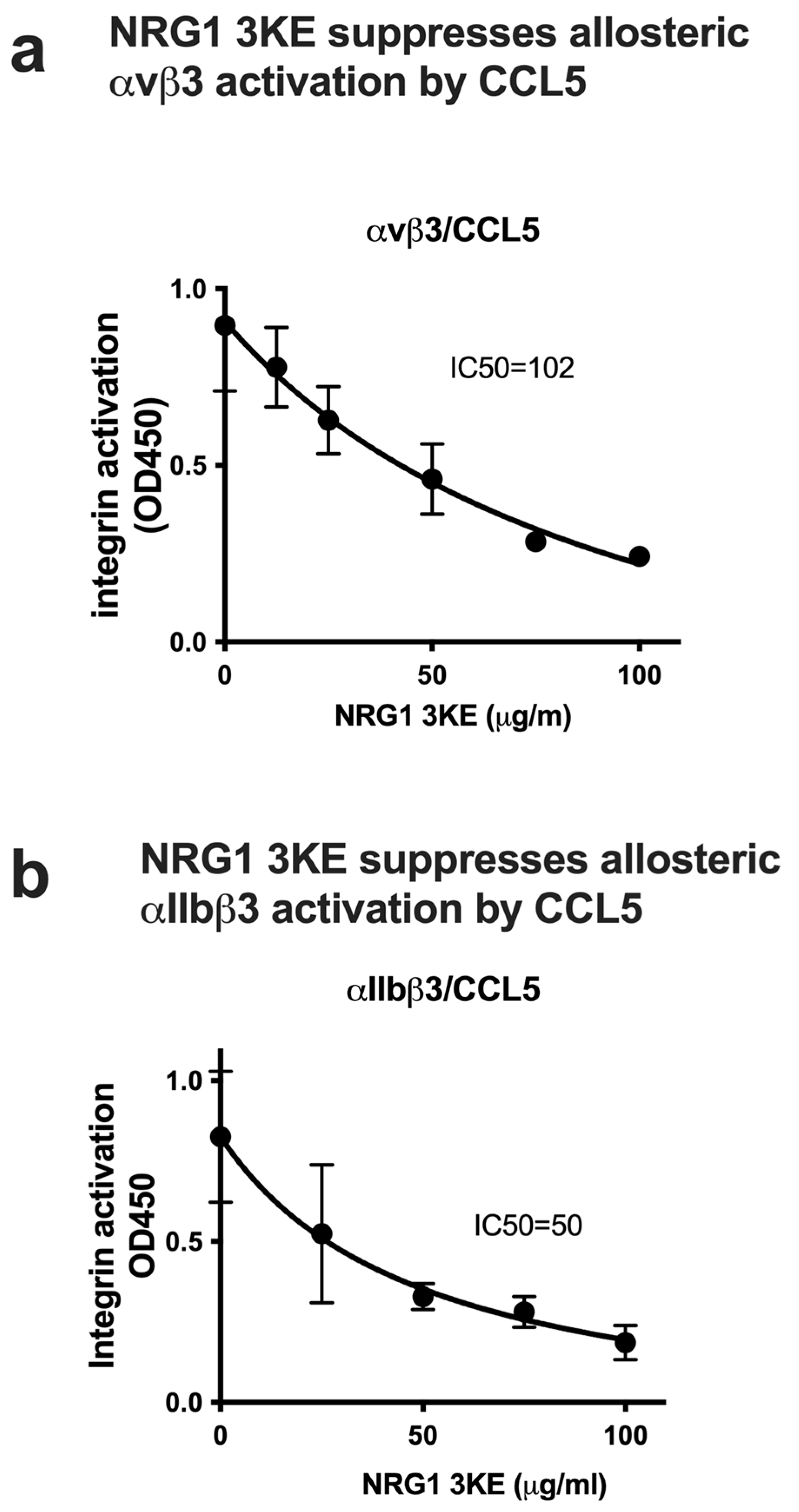
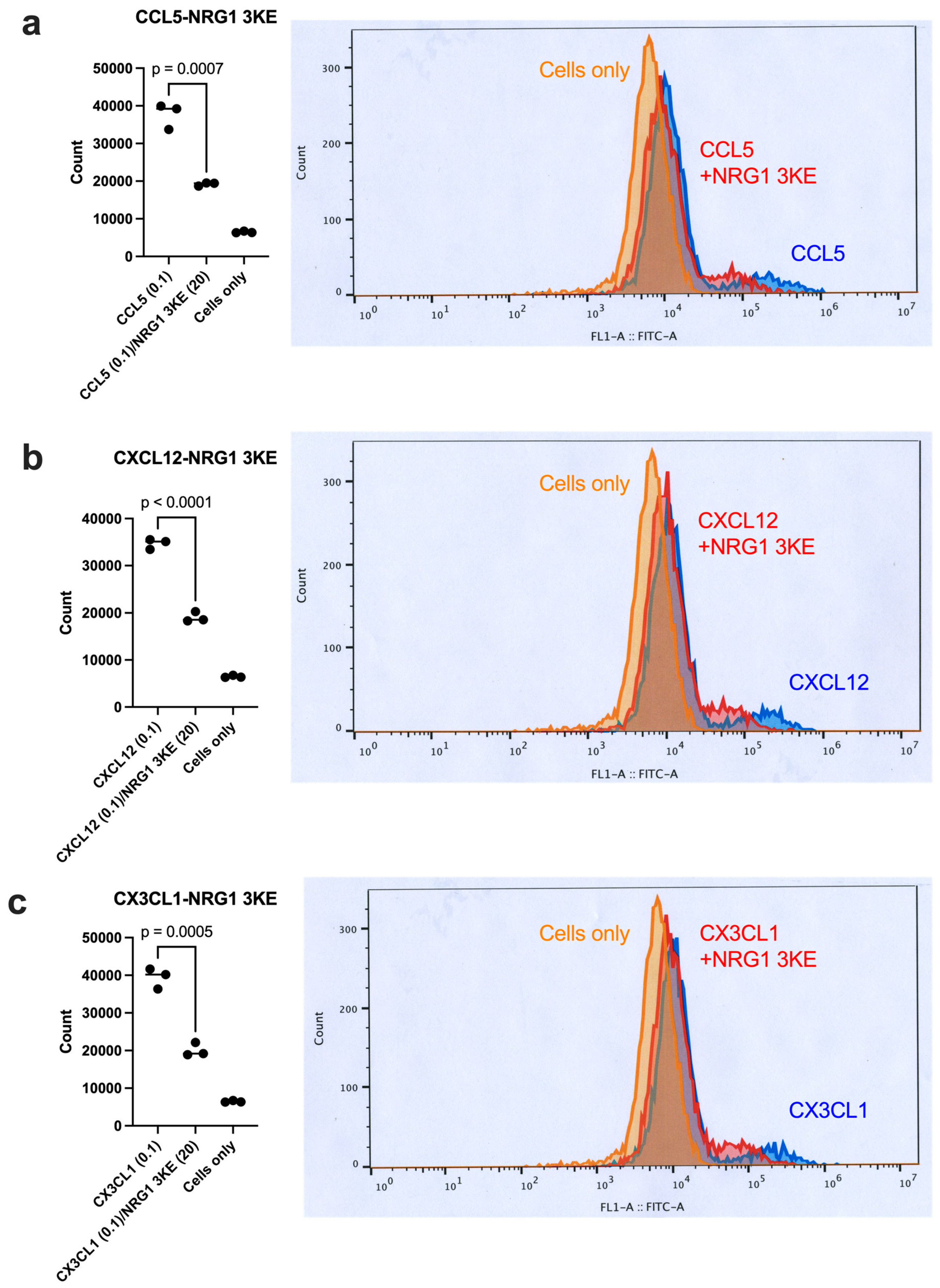
3.4. Non-Mitogenic NRG1 3KE Mutant Suppresses Integrin Activation Induced by Inflammatory Cytokines Through Site 2 Binding
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NRG1 | Neuregulin-1 |
References
- Takada, Y.; Ye, X.; Simon, S. The integrins. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliceiri, B.P. Integrin and growth factor receptor crosstalk. Circ. Res. 2001, 89, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.I.; Prevette, T.; Gockerman, A.; Clemmons, D.R. Ligand occupancy of the alpha-V-beta3 integrin is necessary for smooth muscle cells to migrate in response to insulin-like growth factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 2482–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, P.C.; Clark, R.A.; Cheresh, D.A. Requirement of vascular integrin alpha v beta 3 for angiogenesis. Science 1994, 264, 569–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Wu, C.Y.; Yamaji, S.; Saegusa, J.; Shi, B.; Ma, Z.; Kuwabara, Y.; Lam, K.S.; Isseroff, R.R.; Takada, Y.K.; et al. Direct binding of integrin alphavbeta3 to FGF1 plays a role in FGF1 signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 18066–18075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaji, S.; Saegusa, J.; Ieguchi, K.; Fujita, M.; Mori, S.; Takada, Y.K.; Takada, Y. A novel fibroblast growth factor-1 (FGF1) mutant that acts as an FGF antagonist. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saegusa, J.; Yamaji, S.; Ieguchi, K.; Wu, C.-Y.; Lam, K.S.; Liu, F.-T.; Takada, Y.K.; Takada, Y. The direct binding of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) to integrin alphavbeta3 is involved in IGF-1 signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 24106–24114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Ieguchi, K.; Cedano-Prieto, D.M.; Fong, A.; Wilkerson, C.; Chen, J.Q.; Wu, M.; Lo, S.-H.; Cheung, A.T.W.; Wilson, M.D.; et al. An integrin binding-defective mutant of insulin-like growth factor-1 (R36E/R37E IGF1) acts as a dominant-negative antagonist of the IGF1 receptor (IGF1R) and suppresses tumorigenesis but still binds to IGF1R. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 19593–19603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ieguchi, K.; Fujita, M.; Ma, Z.; Davari, P.; Taniguchi, Y.; Sekiguchi, K.; Wang, B.; Takada, Y.K.; Takada, Y. Direct binding of the EGF-like domain of neuregulin-1 to integrins ({alpha}v{beta}3 and {alpha}6{beta}4) is involved in neuregulin-1/ErbB signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 31388–31398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saegusa, J.; Akakura, N.; Wu, C.Y.; Hoogland, C.; Ma, Z.; Lam, K.S.; Liu, F.-T.; Takada, Y.K.; Takada, Y. Pro-inflammatory secretory phospholipase A2 type IIA binds to integrins alphavbeta3 and alpha4beta1 and induces proliferation of monocytic cells in an integrin-dependent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 26107–26115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, Y.K.; Yu, J.; Shimoda, M.; Takada, Y. Integrin Binding to the Trimeric Interface of CD40L Plays a Critical Role in CD40/CD40L Signaling. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginsberg, M.H. Integrin activation. BMB Rep. 2014, 47, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shattil, S.J.; Kim, C.; Ginsberg, M.H. The final steps of integrin activation: The end game. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, M.; Takada, Y.K.; Izumiya, Y.; Takada, Y. The binding of monomeric C-reactive protein (mCRP) to Integrins alphavbeta3 and alpha4beta1 is related to its pro-inflammatory action. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Zhu, K.; Fujita, C.K.; Zhao, M.; Lam, K.S.; Kurth, M.J.; Takada, Y.K.; Takada, Y. Proinflammatory secreted phospholipase A2 type IIA (sPLA-IIA) induces integrin activation through direct binding to a newly identified binding site (site 2) in integrins alphavbeta3, alpha4beta1, and alpha5beta1. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Davari, P.; Takada, Y.K.; Takada, Y. Stromal cell-derived factor-1 (CXCL12) activates integrins by direct binding to an allosteric ligand-binding site (site 2) of integrins without CXCR4. Biochem. J. 2018, 475, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, Y.K.; Shimoda, M.; Maverakis, E.; Felding, B.H.; Cheng, R.H.; Takada, Y. Soluble CD40L activates soluble and cell-surface integrins alphavbeta3, alpha5beta1 and alpha4beta1 by binding to the allosteric ligand-binding site (site 2). J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, Y.K.; Fujita, M.; Takada, Y. Pro-Inflammatory Chemokines CCL5, CXCL12, and CX3CL1 Bind to and Activate Platelet Integrin alphaIIbbeta3 in an Allosteric Manner. Cells 2022, 11, 3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, Y.K.; Shimoda, M.; Takada, Y. CD40L Activates Platelet Integrin alphaIIbbeta3 by Binding to the Allosteric Site (Site 2) in a KGD-Independent Manner and HIGM1 Mutations Are Clustered in the Integrin-Binding Sites of CD40L. Cells 2023, 12, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokharel, S.M.; Shil, N.K.; Gc, J.B.; Colburn, Z.T.; Tsai, S.-Y.; Segovia, J.A.; Chang, T.-H.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Natesan, S.; Jones, J.C.R.; et al. Integrin activation by the lipid molecule 25-hydroxycholesterol induces a proinflammatory response. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Ding, L.; Lan, J.; Niu, J.; He, Y.; Song, L. Fibroblast Growth Factor-1 Improves Insulin Resistance via Repression of JNK-Mediated Inflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.M.; Jonker, J.W.; Ahmadian, M.; Goetz, R.; Lackey, D.; Osborn, O.; Huang, Z.; Liu, W.; Yoshihara, E.; van Dijk, T.H.; et al. Endocrinization of FGF1 produces a neomorphic and potent insulin sensitizer. Nature 2014, 513, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Qin, J. LINC00659 exacerbates endothelial progenitor cell dysfunction in deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities by activating DNMT3A-mediated FGF1 promoter methylation. Thromb. J. 2023, 21, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, Y.K.; Wu, X.; Wei, D.; Hwang, S.; Takada, Y. FGF1 Suppresses Allosteric Activation of beta3 Integrins by FGF2: A Potential Mechanism of Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Thrombotic Action of FGF1. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataria, H.; Hart, C.G.; Alizadeh, A.; Cossoy, M.; Kaushik, D.K.; Bernstein, C.N.; Marrie, R.A.; Yong, V.W.; Karimi-Abdolrezaee, S. Neuregulin-1 beta 1 is implicated in pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Brain 2021, 144, 162–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viehover, A.; Miller, R.H.; Park, S.-K.; Fischbach, G.; Vartanian, T. Neuregulin: An oligodendrocyte growth factor absent in active multiple sclerosis lesions. Dev. Neurosci. 2001, 23, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataria, H.; Alizadeh, A.; Shahriary, G.M.; Rizi, S.S.; Henrie, R.; Santhosh, K.T.; Thliveris, J.A.; Karimi-Abdolrezaee, S. Neuregulin-1 promotes remyelination and fosters a pro-regenerative inflammatory response in focal demyelinating lesions of the spinal cord. Glia 2018, 66, 538–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannella, B.; Hoban, C.J.; Gao, Y.-L.; Garcia-Arenas, R.; Lawson, D.; Marchionni, M.; Gwynne, D.; Raine, C.S. The neuregulin, glial growth factor 2, diminishes autoimmune demyelination and enhances remyelination in a chronic relapsing model for multiple sclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 10100–10105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Honarmand, K.; Taheri, M. A comprehensive review on the role of chemokines in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Metab. Brain Dis. 2021, 36, 375–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Fan, P.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Cui, W. Neuregulin-1 regulates the conversion of M1/M2 microglia phenotype via ErbB4-dependent inhibition of the NF-kappaB pathway. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 3975–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupte, M.; Lal, H.; Ahmad, F.; Sawyer, D.B.; Hill, M.F. Chronic Neuregulin-1beta Treatment Mitigates the Progression of Postmyocardial Infarction Heart Failure in the Setting of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus by Suppressing Myocardial Apoptosis, Fibrosis, and Key Oxidant-Producing Enzymes. J. Card. Fail. 2017, 23, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Kuang, H.; He, Y.; Idiga, S.O.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Z.; Cai, X.; Zhang, K.; Potthoff, M.J. NRG1-Fc improves metabolic health via dual hepatic and central action. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e98522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, K.; Zhang, X.P.; Medved, L.; Takada, Y. Specific binding of integrin alpha v beta 3 to the fibrinogen gamma and alpha E chain C-terminal domains. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 5872–5877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, S.; Hatori, N.; Kawaguchi, N.; Hamada, Y.; Shih, T.-C.; Wu, C.-Y.; Lam, K.S.; Matsuura, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Takada, Y.K.; et al. The integrin-binding defective FGF2 mutants potently suppress FGF2 signaling and angiogenesis. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37, BSR20170173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, D.B.; Dombkowski, A.A. Disulfide by Design 2.0: A web-based tool for disulfide engineering in proteins. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Malcolm, B.A. Two-stage polymerase chain reaction protocol allowing introduction of multiple mutations, deletions, and insertions, using QuikChange site-directed mutagenesis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2002, 182, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Fujita, M.; Takada, Y.K.; Takada, Y. The chemokine fractalkine can activate integrins without CX3CR1 through direct binding to a ligand-binding site distinct from the classical RGD-binding site. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
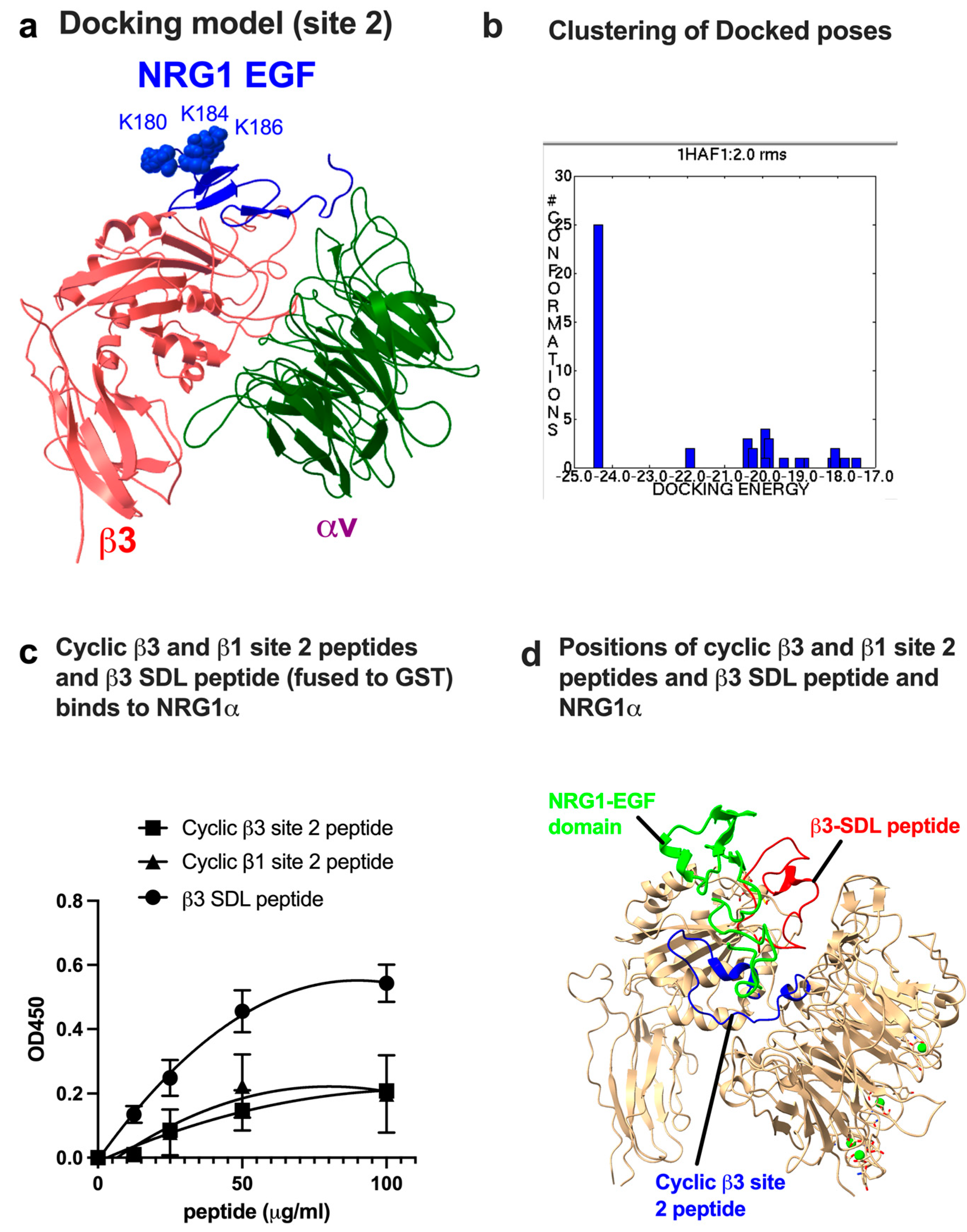

| NRG1 (1HAF.pdb) | αv (1JV2.pdb) | β3 (1JV2.pdb) |
|---|---|---|
| Leu3, Glu10, Phe13, Cys14, Met22, Val23, Ser27, Asn28, Pro29, Ser30, Arg31, Tyr32, Leu33, Cys34, Lys35, Cys36, Gln37, Pro38, Phe40, Thr41, Gly42, Ala43, Arg44, Cys45, Thr46, Glu47, Pro50, Val53, Asn55, Gln56 | His91 | Tyr122, Lys125, Leu128, Trp129, Gln132, Pro160, Met165, Glu171, Glu174, Asn175, Pro176, Cys177, Lys181, Thr182, Thr183, Cys184, Leu185, Pro186, Met187, Phe188, Lys191, Val207, Lys208, Lys209, Gln210, Ser211, Val212, Asp278, His280, Tyr281, Ser282, Thr285 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takada, Y.K.; Takada, Y. Neuregulin-1 (NRG1) Binds to the Allosteric Binding Site (Site 2) and Suppresses Allosteric Integrin Activation by Inflammatory Cytokines: A Potential Mechanism of Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Fibrosis Action of NRG1. Cells 2025, 14, 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080617
Takada YK, Takada Y. Neuregulin-1 (NRG1) Binds to the Allosteric Binding Site (Site 2) and Suppresses Allosteric Integrin Activation by Inflammatory Cytokines: A Potential Mechanism of Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Fibrosis Action of NRG1. Cells. 2025; 14(8):617. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080617
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakada, Yoko K., and Yoshikazu Takada. 2025. "Neuregulin-1 (NRG1) Binds to the Allosteric Binding Site (Site 2) and Suppresses Allosteric Integrin Activation by Inflammatory Cytokines: A Potential Mechanism of Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Fibrosis Action of NRG1" Cells 14, no. 8: 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080617
APA StyleTakada, Y. K., & Takada, Y. (2025). Neuregulin-1 (NRG1) Binds to the Allosteric Binding Site (Site 2) and Suppresses Allosteric Integrin Activation by Inflammatory Cytokines: A Potential Mechanism of Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Fibrosis Action of NRG1. Cells, 14(8), 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080617







