The Influence of the COVID-19 Pandemic in NK Cell Subpopulations from CML Patients Enrolled in the Argentina Stop Trial
Abstract
1. Background
2. Materials and Methods
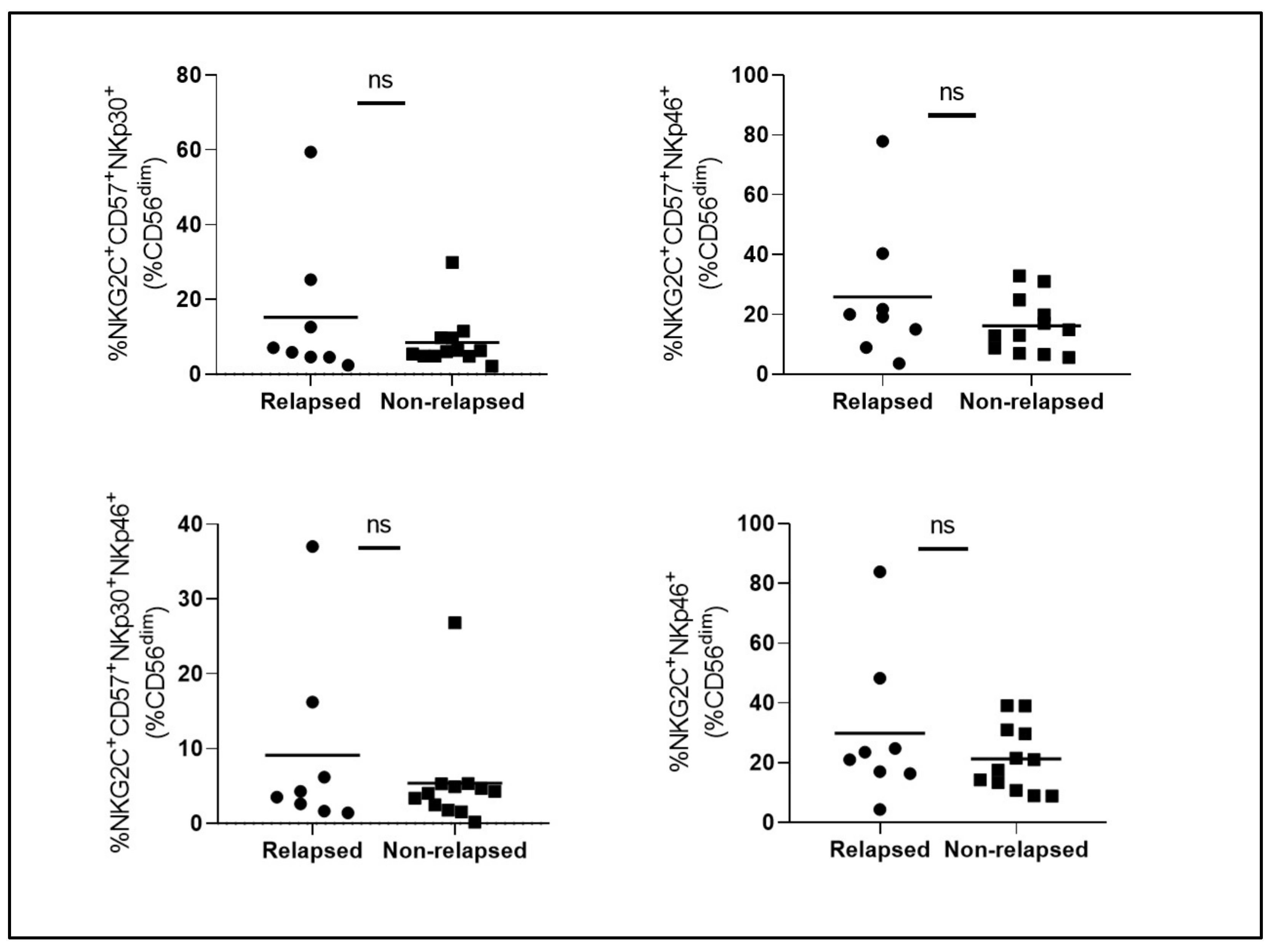
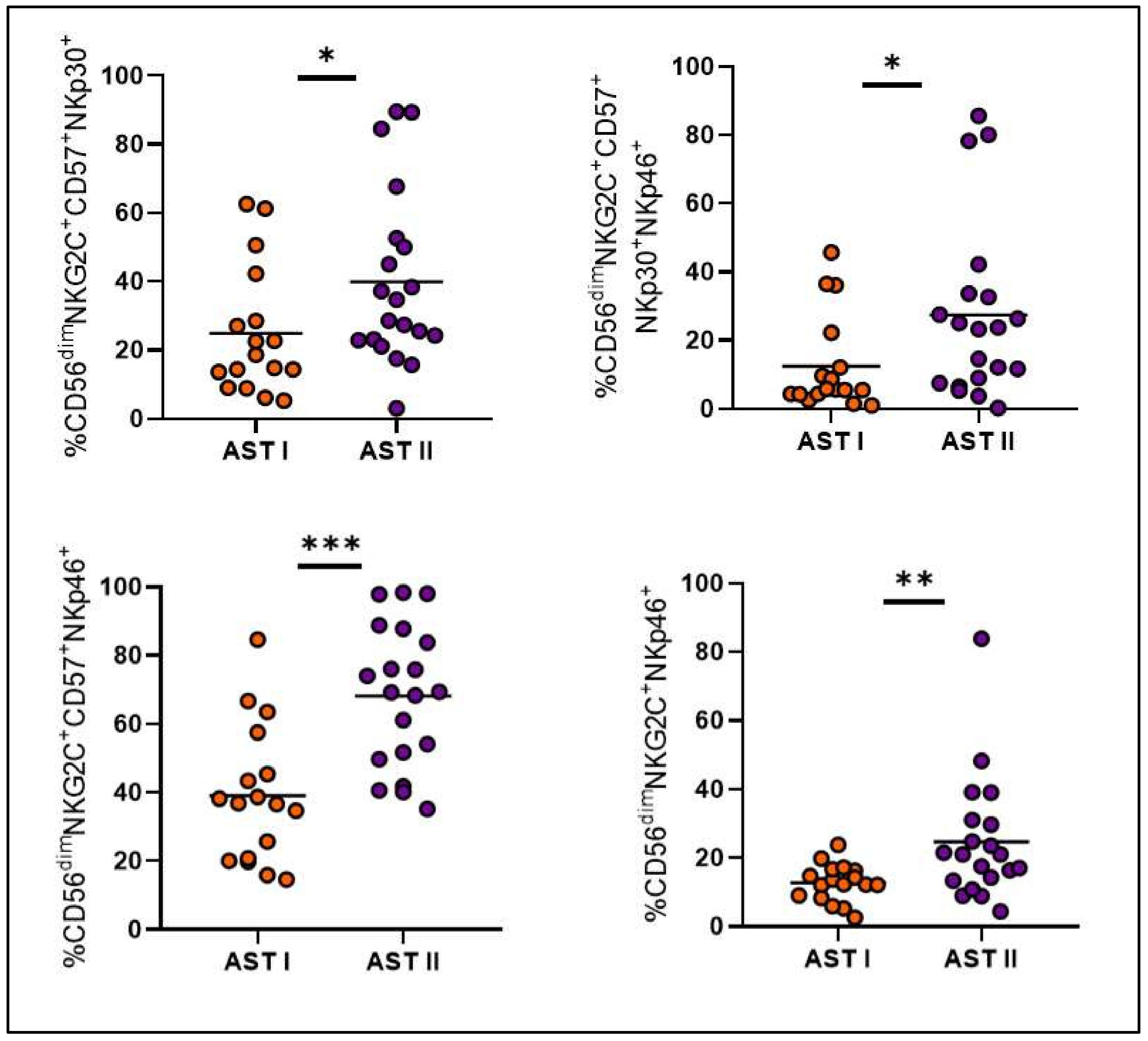
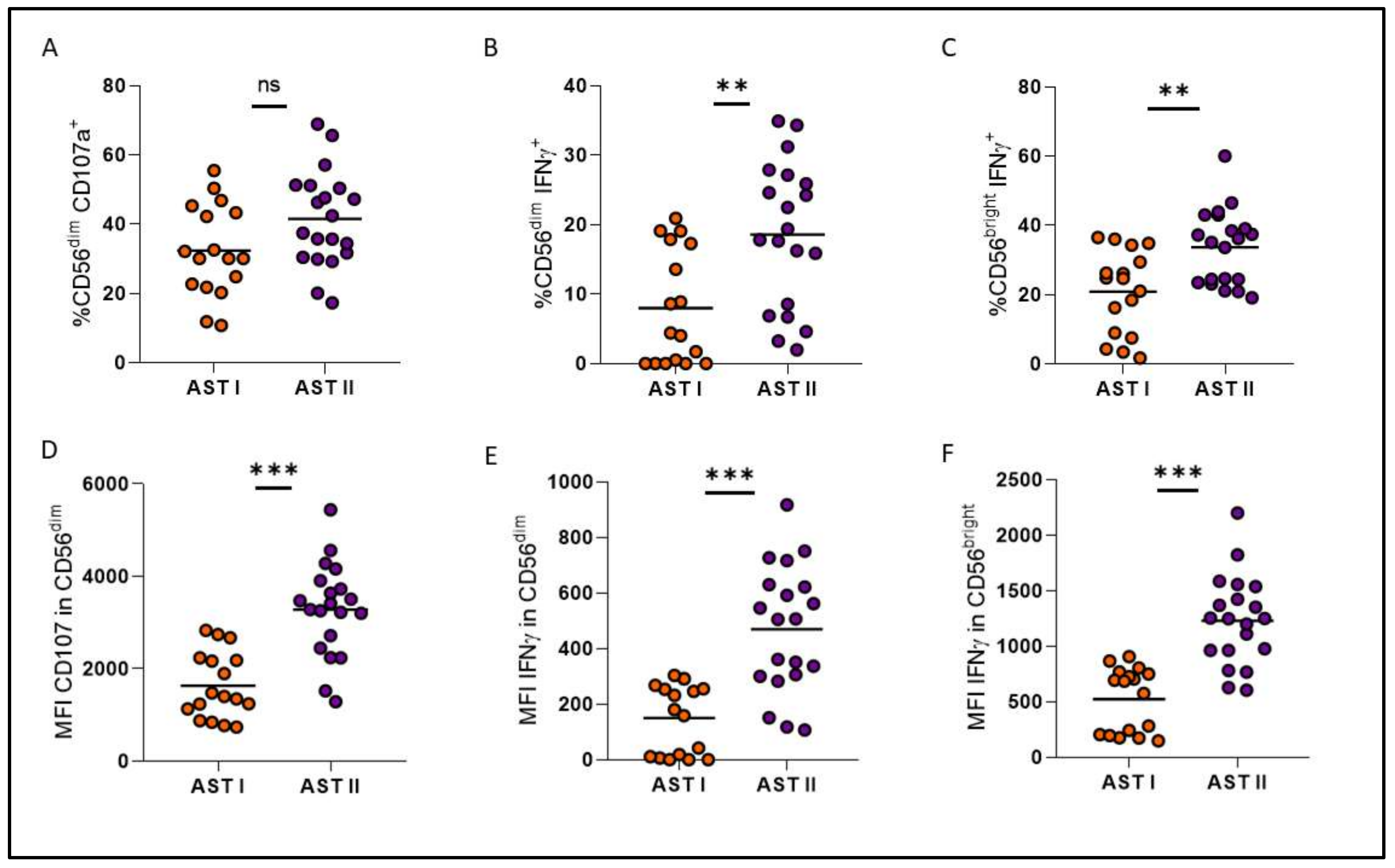
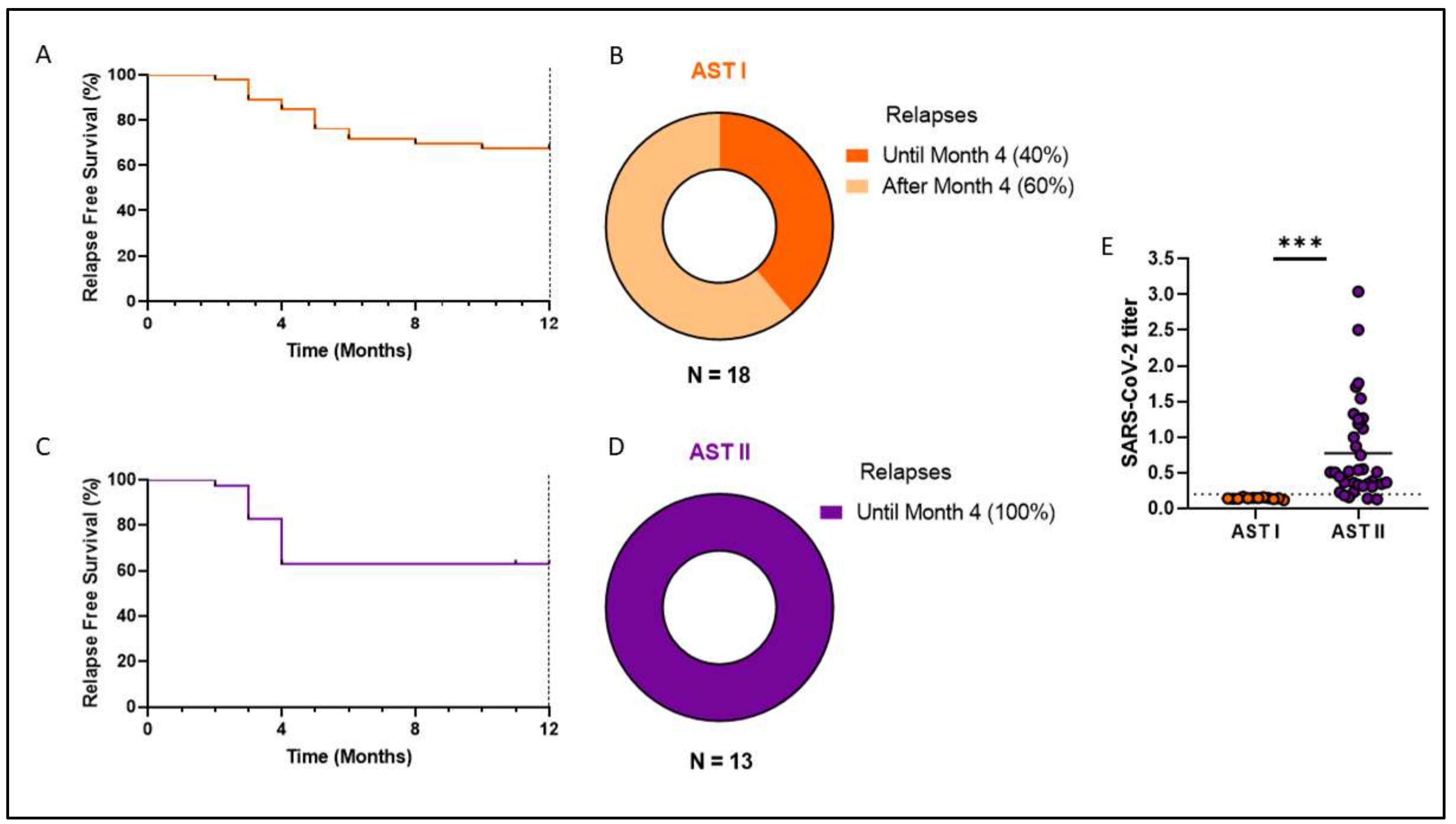
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rowley, J.D. A new consistent chromosomal abnormality in chronic myelogenous leukaemia identified by quinacrine fluorescence and Giemsa staining cromosomal abnormality in CML. Nature 1973, 243, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahon, F.X.; Delbrel, X.; Cony-Makhoul, P.; Fabè, C.; Boiron, J.M.; Barthe, C.; Bilhou-Nabéra, C.; Pigneux, A.; Marit, G.; Reiffers, J. Follow-Up of Complete Cytogenetic Remission in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia After Cessation of Interferon Alfa. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantarjian, H.; Shah, N.P.; Hochhaus, A.; Cortes, J.; Shah, S.; Ayala, M.; Moiraghi, B.; Shen, Z.; Mayer, J.; Pasquini, R.; et al. Dasatinib versus Imatinib in Newly Diagnosed Chronic-Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2260–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saglio, G.; Kim, D.-W.; Issaragrisil, S.; le Coutre, P.; Etienne, G.; Lobo, C.; Pasquini, R.; Clark, R.E.; Hochhaus, A.; Hughes, T.P.; et al. Nilotinib versus Imatinib for Newly Diagnosed Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2251–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.E.; Kim, D.W.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Brümmendorf, T.H.; Dyagil, I.; Griskevicius, L.; Malhotra, H.; Powell, C.; Gogat, K.; Countouriotis, A.M.; et al. Bosutinib versus imatinib in newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia: Results from the BELA trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3486–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahon, F.X.; Réa, D.; Guilhot, J.; Guilhot, F.; Huguet, F.; Nicolini, F.; Legros, L.; Charbonnier, A.; Guerci, A.; Varet, B.; et al. Discontinuation of imatinib in patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia who have maintained complete molecular remission for at least 2 years: The prospective, multicentre Stop Imatinib (STIM) trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imagawa, J.; Tanaka, H.; Okada, M.; Nakamae, H.; Hino, M.; Murai, K.; Ishida, Y.; Kumagai, T.; Sato, S.; Ohashi, K.; et al. Discontinuation of dasatinib in patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia who have maintained deep molecular response for longer than 1 year (DADI trial): A multicentre phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2015, 2, e528–e535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochhaus, A.; Masszi, T.; Giles, F.J.; Radich, J.P.; Ross, D.M.; Gómez Casares, M.T.; Hellmann, A.; Stentoft, J.; Conneally, E.; García-Gutiérrez, V.; et al. Treatment-free remission following frontline nilotinib in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase: Results from the ENESTfreedom study. Leukemia 2017, 31, 1525–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saussele, S.; Richter, J.; Guilhot, J.; Gruber, F.X.; Hjorth-Hansen, H.; Almeida, A.; Janssen, J.J.W.M.; Mayer, J.; Koskenvesa, P.; Panayiotidis, P.; et al. Discontinuation of tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy in chronic myeloid leukaemia (EURO-SKI): A prespecified interim analysis of a prospective, multicentre, non-randomised, trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.M.; Jørgensen, H.G.; Allan, E.; Pearson, C.; Alcorn, M.J.; Richmond, L.; Holyoake, T.L. Primitive, quiescent, Philadelphia-positive stem cells from patients with chronic myeloid leukemia are insensitive to STI571 in vitro. Blood 2002, 99, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, D.; Henry, G.; Khaznadar, Z.; Etienne, G.; Guilhot, F.; Nicolini, F.; Guilhot, J.; Rousselot, P.; Huguet, F.; Legros, L.; et al. Natural killer-cell counts are associated with molecular relapse-free survival after imatinib discontinuation in chronic myeloid leukemia: The IMMUNOSTIM study. Haematologica 2017, 102, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilander, M.; Olsson-Strömberg, U.; Schlums, H.; Guilhot, J.; Brück, O.; Lähteenmäki, H.; Kasanen, T.; Koskenvesa, P.; Söderlund, S.; Höglund, M.; et al. Increased proportion of mature NK cells is associated with successful imatinib discontinuation in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2017, 31, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, M.; Imagawa, J.; Tanaka, H.; Nakamae, H.; Hino, M.; Murai, K.; Ishida, Y.; Kumagai, T.; Sato, S.; Ohashi, K.; et al. Final 3-year Results of the Dasatinib Discontinuation Trial in Patients With Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Who Received Dasatinib as a Second-line Treatment. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018, 18, 353–360.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumá, M.; Angulo, A.; Vilches, C.; Gómez-Lozano, N.; Malats, N.; López-Botet, M. Imprint of human cytomegalovirus infection on the NK cell receptor repertoire. Blood 2004, 104, 3664–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlums, H.; Cichocki, F.; Tesi, B.; Theorell, J.; Beziat, V.; Holmes, T.D.; Han, H.; Chiang SC, C.; Foley, B.; Mattsson, K.; et al. Cytomegalovirus infection drives adaptive epigenetic diversification of NK cells with altered signaling and effector function. Immunity 2015, 42, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Zhang, T.; Hwang, I.; Kim, A.; Nitschke, L.; Kim, M.J.; Scott, J.M.; Kamimura, Y.; Lanier, L.L.; Kim, S. Epigenetic modification and antibody-dependent expansion of memory-like NK cells in human cytomegalovirus-infected individuals. Immunity 2015, 42, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.L.; Leisenring, W.M.; Xie, H.; Walter, R.B.; Mielcarek, M.; Sandmaier, B.M.; Riddell, S.R.; Boeckh, M. CMV reactivation after allogeneic HCT and relapse risk: Evidence for early protection in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2013, 122, 1316–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Pophali, P.; Co, W.; Koklanaris, E.K.; Superata, J.; Fahle, G.A.; Childs, R.; Battiwalla, M.; Barrett, A.J. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) reactivation is associated with a lower incidence of relapse after allogeneic stem cell transplantation (SCT) for chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013, 48, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Foley, B.; Cooley, S.; Verneris, M.R.; Pitt, M.; Curtsinger, J.; Luo, X.; Lopez-Vergès, S.; Lanier, L.L.; Weisdorf, D.; Miller, J.S. Cytomegalovirus reactivation after allogeneic transplantation promotes a lasting increase in educated NKG2C+ natural killer cells with potent function. Blood 2012, 119, 2665–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichocki, F.; Davis, Z.B.; DeFor, T.E.; Cooley, S.A.; Bryceson, Y.T.; Diamond, D.J.; Blazar, B.R.; Brunstein, C.; Wagner, J.E.; Verneris, M.R.; et al. CMV Reactivation is Associated with Reduced Relapse Risk, Better Disease-Free Survival and Expansion of Adaptive NK Cells after Reduced Intensity Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Blood 2014, 124, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, M.B.; Vasconcelos Cordoba, B.; Pavlovsky, C.; Moiraghi, B.; Varela, A.; Custidiano, R.; Fernandez, I.; Freitas, M.J.; Ventriglia, M.V.; Bendek, G.; et al. In-depth characterization of NK cell markers from CML patients who discontinued tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1241600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zafarani, A.; Razizadeh, M.H.; Pashangzadeh, S.; Amirzargar, M.R.; Taghavi-Farahabadi, M.; Mahmoudi, M. Natural killer cells in COVID-19: From infection, to vaccination and therapy. Future Virol. 2023, 18, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demaria, O.; Carvelli, J.; Batista, L.; Thibult, M.L.; Morel, A.; André, P.; Morel, Y.; Vély, F.; Vivier, E. Identification of druggable inhibitory immune checkpoints on Natural Killer cells in COVID-19. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 995–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, L.; Martin-Inaraja, M.; Santos, S.; Inglés-Ferrándiz, M.; Azkarate, A.; Perez-Vaquero, M.A.; Vesga, M.A.; Vicario, J.L.; Soria, B.; Solano, C.; et al. Identifying SARS-CoV-2 ‘memory’ NK cells from COVID-19 convalescent donors for adoptive cell therapy. Immunology 2022, 165, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentili, V.; Bortolotti, D.; Morandi, L.; Rizzo, S.; Schiuma, G.; Beltrami, S.; Casciano, F.; Papi, A.; Contoli, M.; Zauli, G.; et al. Natural Killer Cells in SARS-CoV-2-Vaccinated Subjects with Increased Effector Cytotoxic CD56dim Cells and Memory-Like CD57+NKG2C+CD56dim Cells. Front. Biosci. 2023, 28, 156-1–156-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.Z.; Claus, M.; Krüger, N.; Reusing, S.; Gall, E.; Bade-Döding, C.; Braun, A.; Watzl, C.; Uhrberg, M.; Walter, L. SARS-CoV-2 infection induces adaptive NK cell responses by spike protein-mediated induction of HLA-E expression. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2024, 13, 2361019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanchez, M.B.; Cordoba, B.V.; Pavlovsky, C.; Moiraghi, B.; Varela, A.I.; Giere, I.; Juni, M.; Flaibani, N.; Mordoh, J.; Avalos, J.C.S.; et al. The Influence of the COVID-19 Pandemic in NK Cell Subpopulations from CML Patients Enrolled in the Argentina Stop Trial. Cells 2025, 14, 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14090628
Sanchez MB, Cordoba BV, Pavlovsky C, Moiraghi B, Varela AI, Giere I, Juni M, Flaibani N, Mordoh J, Avalos JCS, et al. The Influence of the COVID-19 Pandemic in NK Cell Subpopulations from CML Patients Enrolled in the Argentina Stop Trial. Cells. 2025; 14(9):628. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14090628
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanchez, María Belén, Bianca Vasconcelos Cordoba, Carolina Pavlovsky, Beatriz Moiraghi, Ana Ines Varela, Isabel Giere, Mariana Juni, Nicolas Flaibani, José Mordoh, Julio Cesar Sanchez Avalos, and et al. 2025. "The Influence of the COVID-19 Pandemic in NK Cell Subpopulations from CML Patients Enrolled in the Argentina Stop Trial" Cells 14, no. 9: 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14090628
APA StyleSanchez, M. B., Cordoba, B. V., Pavlovsky, C., Moiraghi, B., Varela, A. I., Giere, I., Juni, M., Flaibani, N., Mordoh, J., Avalos, J. C. S., Levy, E. M., & Bianchini, M. (2025). The Influence of the COVID-19 Pandemic in NK Cell Subpopulations from CML Patients Enrolled in the Argentina Stop Trial. Cells, 14(9), 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14090628





