Role of IgG4 Antibodies in Human Health and Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
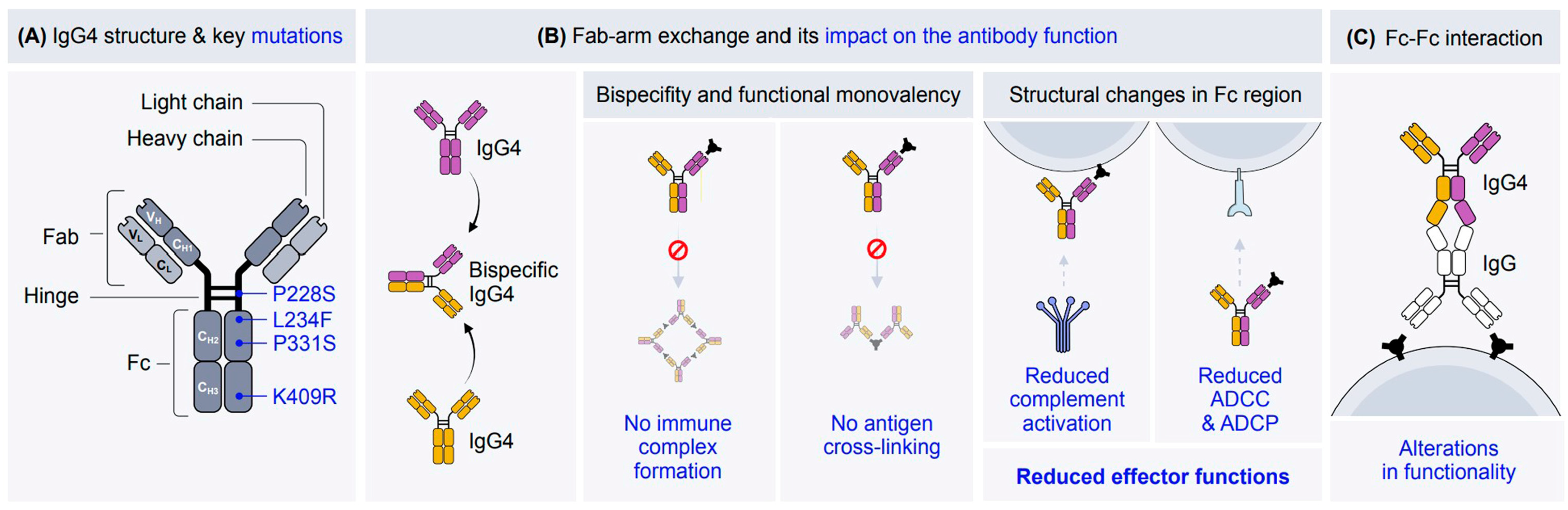
2. The Structure of IgG4
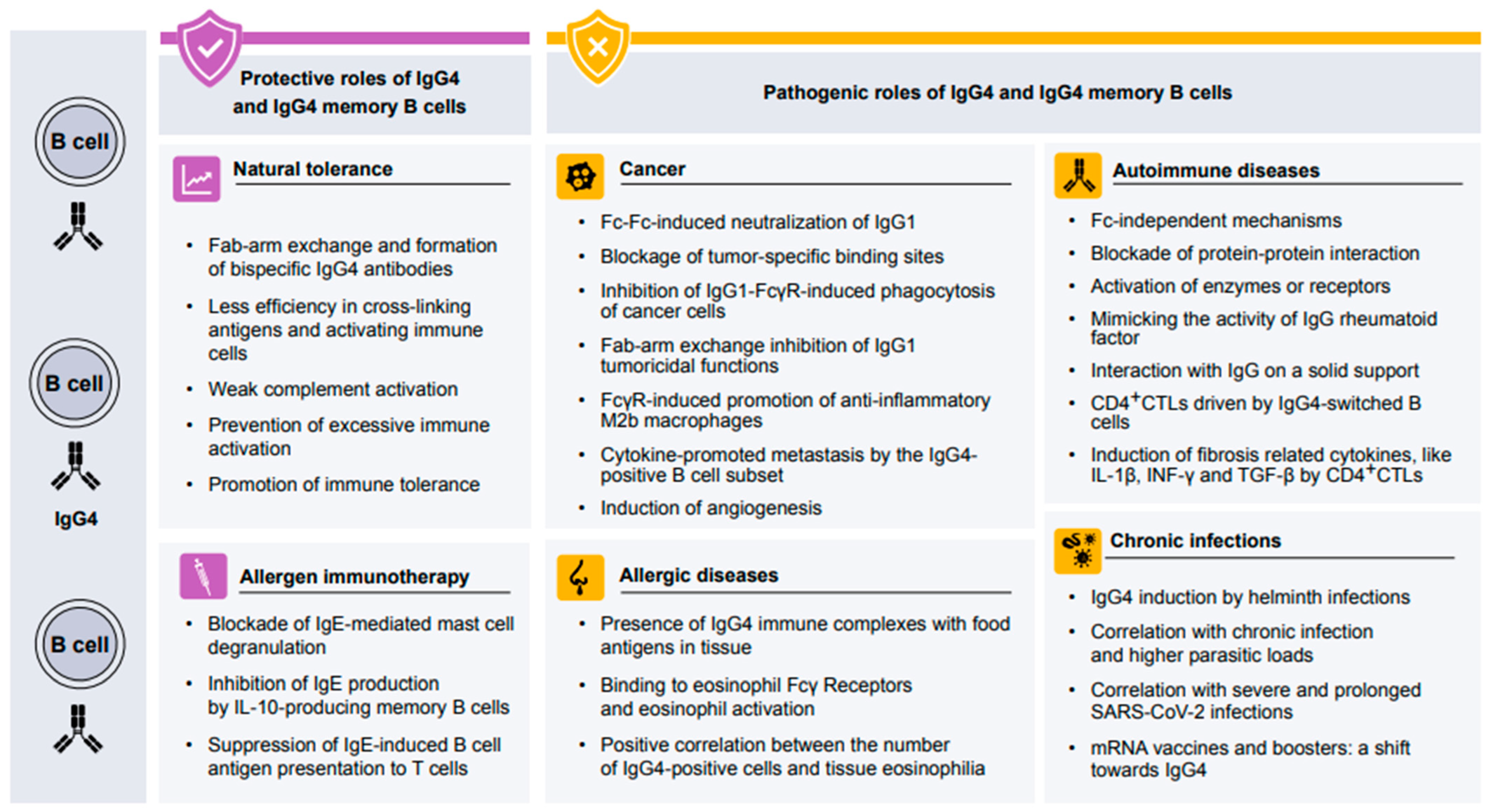
3. Protective Role of IgG4 in Human Health
4. Protective Role of IgG4 in Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy
5. Pathogenic Role of IgG4 in Human Diseases
5.1. Pathogenic Role of IgG4 in Allergic Diseases
5.2. Pathogenic Role of IgG4 in Autoimmune Diseases
5.3. Role of IgG4 in Chronic Infection Disease
5.4. Role of IgG4 in Neoplasms
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aalberse, R.C.; Stapel, S.O.; Schuurman, J.; Rispens, T. Immunoglobulin G4: An odd antibody. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2009, 39, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temming, A.R.; Bentlage, A.E.H.; de Taeye, S.W.; Bosman, G.P.; Lissenberg-Thunnissen, S.N.; Derksen, N.I.L.; Brasser, G.; Mok, J.Y.; van Esch, W.J.E.; Howie, H.L.; et al. Cross-reactivity of mouse IgG subclasses to human Fc gamma receptors: Antibody deglycosylation only eliminates IgG2b binding. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 127, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Neut Kolfschoten, M.; Schuurman, J.; Losen, M.; Bleeker, W.K.; Martínez-Martínez, P.; Vermeulen, E.; den Bleker, T.H.; Wiegman, L.; Vink, T.; Aarden, L.A.; et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of human IgG4 antibodies by dynamic Fab arm exchange. Science 2007, 317, 1554–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjobimey, T.; Hoerauf, A. Induction of immunoglobulin G4 in human filariasis: An indicator of immunoregulation. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2010, 104, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagiannis, P.; Gilbert, A.E.; Josephs, D.H.; Ali, N.; Dodev, T.; Saul, L.; Correa, I.; Roberts, L.; Beddowes, E.; Koers, A.; et al. IgG4 subclass antibodies impair antitumor immunity in melanoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1457–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babayev, H.; Sahin, A.; Ardicli, S.; Akdis, M.; Akdis, C.A. Tracing the evolutionary pathway of IgG4: Implications for immune tolerance and regulation. Allergy 2025, 80, 346–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rispens, T.; Huijbers, M.G. The unique properties of IgG4 and its roles in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 763–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiler, F.; Zumkehr, J.; Klunker, S.; Rückert, B.; Akdis, C.A.; Akdis, M. In vivo switch to IL-10-secreting T regulatory cells in high dose allergen exposure. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 2887–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdis, M.; Verhagen, J.; Taylor, A.; Karamloo, F.; Karagiannidis, C.; Crameri, R.; Thunberg, S.; Deniz, G.; Valenta, R.; Fiebig, H.; et al. Immune responses in healthy and allergic individuals are characterized by a fine balance between allergen-specific T regulatory 1 and T helper 2 cells. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoerauf, A.; Satoguina, J.; Saeftel, M.; Specht, S. Immunomodulation by filarial nematodes. Parasite Immunol. 2005, 27, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satitsuksanoa, P.; van de Veen, W.; Tan, G.; Lopez, J.F.; Wirz, O.; Jansen, K.; Sokolowska, M.; Mirer, D.; Globinska, A.; Boonpiyathad, T.; et al. Allergen-specific B cell responses in oral immunotherapy-induced desensitization, remission, and natural outgrowth in cow’s milk allergy. Allergy 2025, 80, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motta, R.V.; Culver, E.L. IgG4 autoantibodies and autoantigens in the context of IgG4-autoimmune disease and IgG4-related disease. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1272084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Ye, J.; Pan, X. Isolated IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis with normal serum IgG4 levels-A case report. Clin. Case Rep. 2020, 8, 2186–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, F.A.G.; Pereira, I.A.; de Souza, A.W.S.; Giardini, H.A.M.; Cordeiro, R.A. IgG4-related disease—Rare but you should not forget it. Adv. Rheumatol. 2024, 64, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, T.; Kariya, S.; Sato, Y.; Gion, Y.; Higaki, T.; Haruna, T.; Fujiwara, T.; Minoura, A.; Takao, S.; Orita, Y.; et al. Significance of IgG4-positive cells in severe eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergol. Int. 2019, 68, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, A.; Ninomiya, T.; Fujiwara, T.; Takao, S.; Sato, Y.; Gion, Y.; Minoura, A.; Haruna, S.I.; Yoshida, N.; Sakuma, Y.; et al. Serum IgG4 as a biomarker reflecting pathophysiology and post-operative recurrence in chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergol. Int. 2020, 69, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, R.; Karagiannis, S.N.; Jordakieva, G.; Jensen-Jarolim, E. The Role of IgG4 in the Fine Tuning of Tolerance in IgE-Mediated Allergy and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koneczny, I. Update on IgG4-mediated autoimmune diseases: New insights and new family members. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescioli, S.; Correa, I.; Karagiannis, P.; Davies, A.M.; Sutton, B.J.; Nestle, F.O.; Karagiannis, S.N. IgG4 Characteristics and Functions in Cancer Immunity. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lighaam, L.C.; Rispens, T. The Immunobiology of Immunoglobulin G4. Semin Liver Dis. 2016, 36, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gon, Y.; Kandou, T.; Tsuruyama, T.; Iwasaki, T.; Kitagori, K.; Murakami, K.; Nakashima, R.; Akizuki, S.; Morinobu, A.; Hikida, M.; et al. Increased number of T cells and exacerbated inflammatory pathophysiology in a human IgG4 knock-in MRL/lpr mouse model. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0279389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestas, J.; Hughes, C.C. Of mice and not men: Differences between mouse and human immunology. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 2731–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koneczny, I. A new classification system for IgG4 autoantibodies. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidarsson, G.; Dekkers, G.; Rispens, T. IgG subclasses and allotypes: From structure to effector functions. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Song, Y.; Tian, W. How to select IgG subclasses in developing anti-tumor therapeutic antibodies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damelang, T.; Rogerson, S.J.; Kent, S.J.; Chung, A.W. Role of IgG3 in infectious diseases. Trends Immunol. 2019, 40, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Tang, L.-F.; Cheng, L.; Wang, H.-Y. The clinical significance of allergen-specific IgG4 in allergic diseases. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1032909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rispens, T.; Meesters, J.; den Bleker, T.H.; Ooijevaar-De Heer, P.; Schuurman, J.; Parren, P.W.; Labrijn, A.; Aalberse, R.C. Fc-Fc interactions of human IgG4 require dissociation of heavy chains and are formed predominantly by the intra-chain hinge isomer. Mol. Immunol. 2013, 53, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Yan, X.; Zha, H.; Ma, X.; Zhao, C.; Su, M.; et al. Fc-Fc interactions and immune inhibitory effects of IgG4: Implications for anti-PD-1 immunotherapies. J. Immunother. Cancer. 2024, 12, e009034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Veen, W.; Akdis, M. Role of IgG(4) in IgE-mediated allergic responses. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1434–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, M.; Persson, U.; Larsson, P.; Magnusson, C.; Smith, C.I.; Hammarström, L.; Severinson, E. Interleukin 4 induces synthesis of IgE and IgG4 in human B cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 1989, 19, 1311–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suprun, M.; Getts, R.; Grishina, G.; Tsuang, A.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Sampson, H.A. Ovomucoid epitope-specific repertoire of IgE, IgG(4), IgG(1), IgA(1), and IgD antibodies in egg-allergic children. Allergy 2020, 75, 2633–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figo, D.D.; Cordeiro Macedo, P.R.; Gadermaier, G.; Remuzgo, C.; Castro, F.F.M.; Kalil, J.; Galvão, C.E.S.; Santos, K.S. IgE and IgG4 Epitopes of Dermatophagoides and Blomia Allergens before and after Sublingual Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeannin, P.; Lecoanet, S.; Delneste, Y.; Gauchat, J.F.; Bonnefoy, J.Y. IgE versus IgG4 production can be differentially regulated by IL-10. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 3555–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevhertas, L.; Ma, S.; Stanic, B.; Ochsner, U.; Jansen, K.; Ferstl, R.; Frei, R.; Chijioke, O.; Münz, C.; Zhang, L.; et al. IL-10 induces IgG4 production in NOD-scid Il2rγ(null) mice humanized by engraftment of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Allergy 2021, 76, 3525–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonpiyathad, T.; Meyer, N.; Moniuszko, M.; Sokolowska, M.; Eljaszewicz, A.; Wirz, O.F.; Tomasiak-Lozowska, M.M.; Bodzenta-Lukaszyk, A.; Ruxrungtham, K.; van de Veen, W. High-dose bee venom exposure induces similar tolerogenic B-cell responses in allergic patients and healthy beekeepers. Allergy 2017, 72, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, E.M.; Kausar, F.; Aberer, W.; Zach, M.; Eber, E.; Durham, S.R.; Shamji, M.H. Tolerant beekeepers display venom-specific functional IgG4 antibodies in the absence of specific IgE. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 1419–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas, A.; Ruiz-Leon, B.; Serrano, P.; Martí, M.; Espinazo, M.L.; Blanco, N.; Molina, J.; Alonso, C.; Jurado, A.; Moreno-Aguilar, C. Natural and Induced Tolerance to Hymenoptera Venom: A Single Mechanism? Toxins 2022, 14, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Veen, W.; Stanic, B.; Yaman, G.; Wawrzyniak, M.; Söllner, S.; Akdis, D.G.; Rückert, B.; Akdis, C.A.; Akdis, M. IgG4 production is confined to human IL-10-producing regulatory B cells that suppress antigen-specific immune responses. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schopf, L.R.; Hoffmann, K.F.; Cheever, A.W.; Urban, J.F.; Wynn, T.A., Jr. IL-10 is critical for host resistance and survival during gastrointestinal helminth infection. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 2383–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perzanowski, M.S.; Rönmark, E.; Platts-Mills, T.A.; Lundbäck, B. Effect of cat and dog ownership on sensitization and development of asthma among preteenage children. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renand, A.; Archila, L.D.; McGinty, J.; Wambre, E.; Robinson, D.; Hales, B.J.; Thomas, W.R.; Kwok, W.W. Chronic cat allergen exposure induces a TH2 cell-dependent IgG4 response related to low sensitization. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 1627–1635.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, M.; Wegienka, G.; Havstad, S.; Kim, H.; Johnson, C.C.; Ownby, D.; Zoratti, E. Relationship of dog- and cat-specific IgE and IgG4 levels to allergic symptoms on pet exposure. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2013, 1, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portengen, L.; de Meer, G.; Doekes, G.; Heederik, D. Immunoglobulin G4 antibodies to rat urinary allergens, sensitization and symptomatic allergy in laboratory animal workers. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2004, 34, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krop, E.J.; Doekes, G.; Heederik, D.J.; Aalberse, R.C.; van der Zee, J.S. IgG4 antibodies against rodents in laboratory animal workers do not protect against allergic sensitization. Allergy 2011, 66, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, E.C.; Diette, G.B.; Krop, E.J.; Aalberse, R.C.; Smith, A.L.; Curtin-Brosnan, J.; Eggleston, P.A. Mouse allergen-specific immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin G4 and allergic symptoms in immunoglobulin E-sensitized laboratory animal workers. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2005, 35, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.; Jeal, H.; Schofield, S.; Harris, J.M.; Shamji, M.H.; Francis, J.N.; Durham, S.R.; Cullinan, P. Rat-specific IgG and IgG4 antibodies associated with inhibition of IgE-allergen complex binding in laboratory animal workers. Occup. Environ. Med. 2014, 71, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caubet, J.C.; Lin, J.; Ahrens, B.; Gimenez, G.; Bardina, L.; Niggemann, B.; Sampson, H.A.; Beyer, K. Natural tolerance development in cow’s milk allergic children: IgE and IgG4 epitope binding. Allergy 2017, 72, 1677–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akdis, C.A. Therapies for allergic inflammation: Refining strategies to induce tolerance. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 736–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, L.K.; Till, S.J. Potential Mechanisms for IgG4 Inhibition of Immediate Hypersensitivity Reactions. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016, 16, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jutel, M.; Jaeger, L.; Suck, R.; Meyer, H.; Fiebig, H.; Cromwell, O. Allergen-specific immunotherapy with recombinant grass pollen allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 116, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckl-Dorna, J.; Weber, M.; Stanek, V.; Linhart, B.; Ristl, R.; Waltl, E.E.; Villazala-Merino, S.; Hummel, A.; Focke-Tejkl, M.; Froeschel, R.; et al. Two years of treatment with the recombinant grass pollen allergy vaccine BM32 induces a continuously increasing allergen-specific IgG(4) response. EBioMedicine 2019, 50, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinkhan, S.; Thoms, F.; Augusto, G.; Vogel, M.; Bachmann, M.F. On the role of allergen-specific IgG subclasses for blocking human basophil activation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 892631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobl, M.R.; Demir, H.; Sánchez Acosta, G.; Drescher, A.; Kitzmüller, C.; Möbs, C.; Pfützner, W.; Bohle, B. The role of IgG(1) and IgG(4) as dominant IgE-blocking antibodies shifts during allergen immunotherapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, 1371–1378.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koneczny, I.; Tzartos, J.; Mané-Damas, M.; Yilmaz, V.; Huijbers, M.G.; Lazaridis, K.; Höftberger, R.; Tüzün, E.; Martinez-Martinez, P.; Tzartos, S.; et al. IgG4 Autoantibodies in Organ-Specific Autoimmunopathies: Reviewing Class Switching, Antibody-Producing Cells, and Specific Immunotherapies. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 834342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Zee, J.S.; van Swieten, P.; Aalberse, R.C. Inhibition of complement activation by IgG4 antibodies. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1986, 64, 415–422. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, O.T.; Logsdon, S.L.; Zhou, J.S.; Medina-Tamayo, J.; Abdel-Gadir, A.; Noval Rivas, M.; Koleoglou, K.J.; Chatila, T.A.; Schneider, L.C.; Rachid, R.; et al. Oral immunotherapy induces IgG antibodies that act through FcγRIIb to suppress IgE-mediated hypersensitivity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 1310–1317.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.F.; James, L.K.; Bahnson, H.T.; Shamji, M.H.; Couto-Francisco, N.C.; Islam, S.; Houghton, S.; Clark, A.T.; Stephens, A.; Turcanu, V.; et al. IgG4 inhibits peanut-induced basophil and mast cell activation in peanut-tolerant children sensitized to peanut major allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamji, M.H.; Layhadi, J.A.; Scadding, G.W.; Cheung, D.K.M.; Calderon, M.A.; Turka, L.A.; Phippard, D.; Durham, S.R. Basophil expression of diamine oxidase: A novel biomarker of allergen immunotherapy response. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 913–921.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scadding, G.W.; Shamji, M.H.; Jacobson, M.R.; Lee, D.I.; Wilson, D.; Lima, M.T.; Pitkin, L.; Pilette, C.; Nouri-Aria, K.; Durham, S.R. Sublingual grass pollen immunotherapy is associated with increases in sublingual Foxp3-expressing cells and elevated allergen-specific immunoglobulin G4, immunoglobulin A and serum inhibitory activity for immunoglobulin E-facilitated allergen binding to B cells. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2010, 40, 598–606. [Google Scholar]
- Vickery, B.P.; Lin, J.; Kulis, M.; Fu, Z.; Steele, P.H.; Jones, S.M.; Scurlock, A.M.; Gimenez, G.; Bardina, L.; Sampson, H.A.; et al. Peanut oral immunotherapy modifies IgE and IgG4 responses to major peanut allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 128–134.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djurup, R.; Malling, H.J. High IgG4 antibody level is associated with failure of immunotherapy with inhalant allergens. Clin. Allergy 1987, 17, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, Q.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Ma, D.; Lin, X.; Sun, B.; et al. Specific IgE and IgG4 Profiles of House Dust Mite Components in Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 786738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, M.; Su, Q.; Lai, X.; Xian, M.; Shi, X.; Wurtzen, P.A.; Qin, R.; Zeng, X.; Li, J. Functional and Immunoreactive Levels of IgG4 Correlate with Clinical Responses during the Maintenance Phase of House Dust Mite Immunotherapy. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 3897–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hu, M.; Tao, X.; He, J.; Wang, J.; Song, Z.; Wu, L.; Tang, L.; Chen, Z.; Xu, X. Salivary IgG4 Levels Contribute to Assessing the Efficacy of Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus Subcutaneous Immunotherapy in Children with Asthma or Allergic Rhinitis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orengo, J.M.; Radin, A.R.; Kamat, V.; Badithe, A.; Ben, L.H.; Bennett, B.L.; Zhong, S.; Birchard, D.; Limnander, A.; Rafique, A.; et al. Treating cat allergy with monoclonal IgG antibodies that bind allergen and prevent IgE engagement. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapel, S.O.; Asero, R.; Ballmer-Weber, B.K.; Knol, E.F.; Strobel, S.; Vieths, S.; Kleine-Tebbe, J.; EAACI Task Force. Testing for IgG4 against foods is not recommended as a diagnostic tool: EAACI Task Force Report. Allergy 2008, 63, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AAAI Board of Directors. Measurement of specific and nonspecific IgG4 levels as diagnostic and prognostic tests for clinical allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1995, 95, 652–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeekens, J.M.; Baloh, C.; Lim, N.; Larson, D.; Qin, T.; Wheatley, L.; Kim, E.H.; Jones, S.M.; Burks, A.W.; Kulis, M.D. Peanut-Specific IgG4 and IgA in Saliva Are Modulated by Peanut Oral Immunotherapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2022, 10, 3270–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keswani, T.; LaHood, N.A.; Marini-Rapoport, O.; Karmakar, B.; Andrieux, L.; Reese, B.; Sneed, S.L.; Pedersen, L.C.; Mueller, G.A.; Patil, S.U. Neutralizing IgG(4) antibodies are a biomarker of sustained efficacy after peanut oral immunotherapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, 153, 1611–1620.e1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamji, M.H.; Kappen, J.H.; Akdis, M.; Jensen-Jarolim, E.; Knol, E.F.; Kleine-Tebbe, J.; Bohle, B.; Chaker, A.M.; Till, S.J.; Valenta, R.; et al. Biomarkers for monitoring clinical efficacy of allergen immunotherapy for allergic rhinoconjunctivitis and allergic asthma: An EAACI Position Paper. Allergy 2017, 72, 1156–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarkvist, J.; Salehi, C.; Akin, C.; Gülen, T. Venom immunotherapy in patients with clonal mast cell disorders: IgG4 correlates with protection. Allergy 2020, 75, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.; Deng, X.; Song, Z.; Darsow, U.; Chen, W.; Chen, S.; Luo, N.; Hao, F. Immunological changes after ASIT in AD allergen-specific immunotherapy and their potential correlation with clinical response in patients with atopic dermatitis patients sensitized to house dust mite. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 29, 1318–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aalberse, R.C.; Platts-Mills, T.A.; Rispens, T. The Developmental History of IgE and IgG4 Antibodies in Relation to Atopy, Eosinophilic Esophagitis, and the Modified TH2 Response. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016, 16, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, F.; Fang, J.C.; Gleich, G.J.; Lucendo, A.J.; Olalla, J.M.; Vinson, L.A.; Lowichik, A.; Chen, X.; Emerson, L.; Cox, K.; et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis in adults is associated with IgG4 and not mediated by IgE. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inage, E.; Furuta, G.T.; Menard-Katcher, C.; Masterson, J.C. Eosinophilic esophagitis: Pathophysiology and its clinical implications. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018, 315, G879–G886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medernach, J.G.; Li, R.C.; Zhao, X.Y.; Yin, B.; Noonan, E.A.; Etter, E.F.; Raghavan, S.S.; Borish, L.C.; Wilson, J.M.; Barnes, B.H.; et al. Immunoglobulin G4 in eosinophilic esophagitis: Immune complex formation and correlation with disease activity. Allergy 2023, 78, 3193–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuyler, A.J.; Wilson, J.M.; Tripathi, A.; Commins, S.P.; Ogbogu, P.U.; Kruzsewski, P.G.; Barnes, B.H.; McGowan, E.C.; Workman, L.J.; Lidholm, J.; et al. Specific IgG(4) antibodies to cow’s milk proteins in pediatric patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 139–148.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, E.C.; Platts-Mills, T.A.E.; Wilson, J.M. Food allergy, eosinophilic esophagitis, and the enigma of IgG4. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019, 122, 563–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezanpour, M.; Hu, H.; Lau, A.; Liu, S.; De Silva, A.; Bolt, H.; Patterson, K.; Rischmueller, M.; Psaltis, A.J.; Wormald, P.J.; et al. Increased Serum IgG4 Associates with Asthma and Tissue Eosinophilia in Chronic Rhinosinusitis Patients. Pathogens 2020, 9, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flament, T.; Marchand-Adam, S.; Gatault, P.; Dupin, C.; Diot, P.; Guilleminault, L. What are the characteristics of asthma patients with elevated serum IgG4 levels? Respir. Med. 2016, 112, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orfali, R.L.; Sato, M.N.; Santos, V.G.; Titz, T.O.; Brito, C.A.; Duarte, A.J.; Takaoka, R.; Aoki, V. Staphylococcal enterotoxin B induces specific IgG4 and IgE antibody serum levels in atopic dermatitis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2015, 54, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesari Crnković, H.; Bendelja, K.; Gjergja Juraški, R.; Turkalj, M. Respiratory syncytial virus specific immunoglobulin G4 antibodies and atopic diseases in children. Minerva Pediatr. 2025, 77, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchheit, K.M.; Dwyer, D.F.; Ordovas-Montanes, J.; Katz, H.R.; Lewis, E.; Vukovic, M.; Lai, J.; Bankova, L.G.; Bhattacharyya, N.; Shalek, A.K.; et al. IL-5Rα marks nasal polyp IgG4- and IgE-expressing cells in aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platts-Mills, T.A.; Keshavarz, B.; Wilson, J.M.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Ailsworth, S.M.; Sordillo, J.E.; Workman, L.; Chapman, M.; Lidholm, J.; Oken, E.; et al. High risk of asthma among early teens is associated with quantitative differences in mite and cat allergen specific IgE and IgG4: A modified Th2 related antibody response revisited. EBioMedicine 2025, 112, 105556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valk, A.M.; Keijser, J.B.D.; van Dam, K.P.J.; Stalman, E.W.; Wieske, L.; Steenhuis, M.; Kummer, L.Y.L.; Spuls, P.I.; Bekkenk, M.W.; Musters, A.H.; et al. Suppressed IgG4 class switching in dupilumab- and TNF inhibitor-treated patients after mRNA vaccination. Allergy 2024, 79, 1952–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.S.; Jang, J.H.; Lee, Y.; Park, H.S. Long-term efficacy of anti-IL-4 receptor antibody in a patient with aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease and IgG4-related disease. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2023, 19, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Boo, J.; Jang, H.; Jung, Y.W.; Kim, J.; Zhang, K.; Park, C.O. Combined Dupilumab and Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy in Severe Refractory Atopic Dermatitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2024, 16, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sindher, S.B.; Nadeau, K.C.; Chinthrajah, R.S.; Leflein, J.G.; Bégin, P.; Ohayon, J.A.; Ponda, P.; Wambre, E.; Liu, J.; Khokhar, F.A.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Dupilumab in Children With Peanut Allergy: A Multicenter, Open-Label, Phase II Study. Allergy 2025, 80, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munemura, R.; Maehara, T.; Murakami, Y.; Koga, R.; Aoyagi, R.; Kaneko, N.; Doi, A.; Perugino, C.A.; Della-Torre, E.; Saeki, T.; et al. Distinct disease-specific Tfh cell populations in 2 different fibrotic diseases: IgG(4)-related disease and Kimura disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 150, 440–455.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisetsky, D.S. Pathogenesis of autoimmune disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, T.; Silva, S. IgG4-related disease: How to place it in the spectrum of immune-mediated and rheumatologic disorders? Mod. Rheumatol. 2020, 30, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perugino, C.A.; Stone, J.H. IgG4-related disease: An update on pathophysiology and implications for clinical care. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 702–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattoo, H.; Mahajan, V.S.; Maehara, T.; Deshpande, V.; Della-Torre, E.; Wallace, Z.S.; Kulikova, M.; Drijvers, J.M.; Daccache, J.; Carruthers, M.N.; et al. Clonal expansion of CD4+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in patients with IgG4-related disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wang, M.; Sun, R.; Nie, Y.; Zhang, N.; He, X.; Sun, B.; Peng, L.; Fei, Y.; Zhou, J.; et al. Revealing the distinct clinical patterns and relapse risk factors in seronegative IgG4-RD patients: A retrospective cohort study over a decade. J. Intern. Med. 2024, 296, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, K.C.J.; Moloney, K.J.; Mercado, J.U.; Rostad, S.; McCullough, B.J.; Litvack, Z.N.; Delashaw, J.B.; Mayberg, M.R. A case series of atypical features of patients with biopsy-proven isolated IgG4-related hypophysitis and normal serum IgG4 levels. Pituitary 2018, 21, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perugino, C.A.; AlSalem, S.B.; Mattoo, H.; Della-Torre, E.; Mahajan, V.; Ganesh, G.; Allard-Chamard, H.; Wallace, Z.; Montesi, S.B.; Kreuzer, J.; et al. Identification of galectin-3 as an autoantigen in patients with IgG(4)-related disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 736–745.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löhr, J.M.; Faissner, R.; Koczan, D.; Bewerunge, P.; Bassi, C.; Brors, B.; Eils, R.; Frulloni, L.; Funk, A.; Halangk, W.; et al. Autoantibodies against the exocrine pancreas in autoimmune pancreatitis: Gene and protein expression profiling and immunoassays identify pancreatic enzymes as a major target of the inflammatory process. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 2060–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manral, P.; Caza, T.N.; Storey, A.J.; Beck, L.H., Jr.; Borza, D.B. The Alternative Pathway Is Necessary and Sufficient for Complement Activation by Anti-THSD7A Autoantibodies, Which Are Predominantly IgG4 in Membranous Nephropathy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 952235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Xiao, H.; Shi, L.; He, Y.; Cai, J.; Wu, J.; Li, A.; Ye, L.; Yang, C.; Liu, H.F. IgG4 Autoantibodies Attenuate Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Progression by Suppressing Complement Consumption and Inflammatory Cytokine Production. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brglez, V.; Boyer-Suavet, S.; Seitz-Polski, B. Complement Pathways in Membranous Nephropathy: Complex and Multifactorial. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 572–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldas, I.R.; Campi-Azevedo, A.C.; Oliveira, L.F.; Silveira, A.M.; Oliveira, R.C.; Gazzinelli, G. Human schistosomiasis mansoni: Immune responses during acute and chronic phases of the infection. Acta Trop. 2008, 108, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chayé, M.A.M.; Gasan, T.A.; Ozir-Fazalalikhan, A.; Scheenstra, M.R.; Zawistowska-Deniziak, A.; van Hengel, O.R.J.; Gentenaar, M.; Manurung, M.D.; Harvey, M.R.; Codée, J.D.C.; et al. Schistosoma mansoni egg-derived thioredoxin and Sm14 drive the development of IL-10 producing regulatory B cells. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomides, T.A.R.; de Souza, M.L.M.; de Figueiredo, A.B.; Lima, M.R.; Silveira, A.M.S.; de Assis, G.F.M.; Fraga, L.A.O.; Silveira-Nunes, G.; Martucci, L.; Garcia, J.D.; et al. Expression of SmATPDases 1 and 2 in Schistosoma mansoni eggs favours IL-10 production in infected individuals. Parasite Immunol. 2024, 46, e13017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, A.; Bohnacker, S.; Esser-von Bieren, J. Macrophage regulation & function in helminth infection. Semin. Immunol. 2021, 53, 101526. [Google Scholar]
- Maizels, R.M.; McSorley, H.J. Regulation of the host immune system by helminth parasites. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagel, I.; Cabrera, M.; Buvat, E.; Gutiérrez, L.; Santaella, C.; Borges, R.; Infante, B.; Salas, M.C.; Barrios, Y. Antibody responses and resistance against Ascaris lumbricoides infection among Venezuelan rural children: The influence of ethnicity. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2008, 54, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, S.D.; Magalhaes, F.C.; Rodrigues-Oliveira, J.L.; Castro, V.N.; Souza, C.S.A.; Oliveira, E.J.; Carneiro, M.; Geiger, S.M.; Negrão-Corrêa, D.A. Modulation of Allergic Reactivity in Humans Is Dependent on Schistosoma mansoni Parasite Burden, Low Levels of IL-33 or TNF-alpha and High Levels of IL-10 in Serum. Front. Immunol. 2019, 9, 3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, S.E.; Huang, Y.; Curtis, K.C.; King, C.L.; Fischer, P.U.; Weil, G.J. IgG4 antibodies to the recombinant filarial antigen Wb-Bhp-1 decrease dramatically following treatment of lymphatic filariasis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Casillas, A.; Redwan, E.M.; Uversky, V.N. Does SARS-CoV-2 Induce IgG4 Synthesis to Evade the Immune System? Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della-Torre, E.; Lanzillotta, M.; Strollo, M.; Ramirez, G.A.; Dagna, L.; Tresoldi, M.; COVID-BioB Study Group. Serum IgG4 level predicts COVID-19 related mortality. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 93, 107–109. [Google Scholar]
- Satoguina, J.S.; Weyand, E.; Larbi, J.; Hoerauf, A. T regulatory-1 cells induce IgG4 production by B cells: Role of IL-10. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 4718–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xia, T.; Shin, W.J.; Yu, K.M.; Jung, W.; Herrmann, A.; Foo, S.S.; Chen, W.; Zhang, P.; Lee, J.S.; et al. Viral Mimicry of Interleukin-17A by SARS-CoV-2 ORF8. mBio 2022, 13, e0040222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvan-Pena, S.; Leon, J.; Chowdhary, K.; Michelson, D.A.; Vijaykumar, B.; Yang, L.; Magnuson, A.M.; Chen, F.; Manickas-Hill, Z.; Piechocka-Trocha, A.; et al. Profound Treg perturbations correlate with COVID-19 severity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2021, 118, e2111315118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irrgang, P.; Gerling, J.; Kocher, K.; Lapuente, D.; Steininger, P.; Habenicht, K.; Wytopil, M.; Beileke, S.; Schäfer, S.; Zhong, J.; et al. Class switch toward noninflammatory, spike-specific IgG4 antibodies after repeated SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination. Sci. Immunol. 2023, 8, eade2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.; Islam, M.R.; Khaton, F.; Soltana, U.H.; Jafrin, S.A.; Rahman, S.I.A.; Tauheed, I.; Ahmed, T.; Khan, I.I.; Akter, A.; et al. Appearance of tolerance-induction and non-inflammatory SARS-CoV-2 spike-specific IgG4 antibodies after COVID-19 booster vaccinations. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1309997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinig, S.; Shih, S.R. Non-neutralizing functions in anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies. Biomed. J. 2024, 47, 100666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.F.; Mo, Y.Q.; Ma, J.D.; Luo, L.; Zheng, D.H.; Dai, L. Elevated serum IgG4 defines specific clinical phenotype of rheumatoid arthritis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 635293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalberse, R.C.; van der Gaag, R.; van Leeuwen, J. Serologic aspects of IgG4 antibodies. I. Prolonged immunization results in an IgG4-restricted response. J. Immunol. 1983, 130, 722–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodgers, C.B.; Mustard, C.J.; McLean, R.T.; Hutchison, S.; Pritchard, A.L. A B-cell or a key player? The different roles of B-cells and antibodies in melanoma. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2022, 35, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egbuniwe, I.U.; Karagiannis, S.N.; Nestle, F.O.; Lacy, K.E. Revisiting the role of B cells in skin immune surveillance. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trampert, D.C.; Hubers, L.M.; van de Graaf, S.F.J.; Beuers, U. On the role of IgG4 in inflammatory conditions: Lessons for IgG4-related disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864 Pt B, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiannis, P.; Gilbert, A.E.; Nestle, F.O.; Karagiannis, S.N. IgG4 antibodies and cancer-associated inflammation: Insights into a novel mechanism of immune escape. Oncoimmunology 2013, 2, e24889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punnonen, J.; Aversa, G.; Cocks, B.G.; McKenzie, A.N.; Menon, S.; Zurawski, G.; de Waal Malefyt, R.; de Vries, J.E. Interleukin 13 induces interleukin 4-independent IgG4 and IgE synthesis and CD23 expression by human B cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 3730–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathaliyawala, T.; Kubota, M.; Yudanin, N.; Turner, D.; Camp, P.; Thome, J.J.; Bickham, K.L.; Lerner, H.; Goldstein, M.; Sykes, M.; et al. Distribution and compartmentalization of human circulating and tissue-resident memory T cell subsets. Immunity 2013, 38, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellyard, J.I.; Simson, L.; Parish, C.R. Th2-mediated anti-tumour immunity: Friend or foe? Tissue Antigens 2007, 70, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Monte, L.; Clemente, F.; Ruggiero, E.; Pini, R.; Ceraolo, M.G.; Schiavo Lena, M.; Balestrieri, C.; Lazarevic, D.; Belfiori, G.; Crippa, S.; et al. Pro-tumor Tfh2 cells induce detrimental IgG4 production and PGE(2)-dependent IgE inhibition in pancreatic cancer. EBioMedicine 2023, 97, 104819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harshyne, L.A.; Nasca, B.J.; Kenyon, L.C.; Andrews, D.W.; Hooper, D.C. Serum exosomes and cytokines promote a T-helper cell type 2 environment in the peripheral blood of glioblastoma patients. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, T.; Zhang, B.; Li, J.; et al. An immune evasion mechanism with IgG4 playing an essential role in cancer and implication for immunotherapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Quan, Y.; Ma, X.; Zeng, L.; Li, J.; Chen, S.; Su, M.; Hong, L.; Li, P.; Wang, H.; et al. Synergistic effect of glutathione and IgG4 in immune evasion and the implication for cancer immunotherapy. Redox Biol. 2023, 60, 102608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordakieva, G.; Bianchini, R.; Reichhold, D.; Piehslinger, J.; Groschopf, A.; Jensen, S.A.; Mearini, E.; Nocentini, G.; Crevenna, R.; Zlabinger, G.J.; et al. IgG4 induces tolerogenic M2-like macrophages and correlates with disease progression in colon cancer. Oncoimmunology 2021, 10, 1880687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swisher, J.F.; Haddad, D.A.; McGrath, A.G.; Boekhoudt, G.H.; Feldman, G.M. IgG4 can induce an M2-like phenotype in human monocyte-derived macrophages through FcγRI. MAbs 2014, 6, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Veen, W.; Globinska, A.; Jansen, K.; Straumann, A.; Kubo, T.; Verschoor, D.; Wirz, O.F.; Castro-Giner, F.; Tan, G.; Rückert, B.; et al. A novel proangiogenic B cell subset is increased in cancer and chronic inflammation. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daveau, M.; Pavie-Fischer, J.; Rivat, L.; Rivat, C.; Ropartz, C.; Peter, H.H.; Cesarini, J.P.; Kourilsky, F.M. IgG4 subclass in malignant melanoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1977, 58, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagiannis, P.; Villanova, F.; Josephs, D.H.; Correa, I.; Van Hemelrijck, M.; Hobbs, C.; Saul, L.; Egbuniwe, I.U.; Tosi, I.; Ilieva, K.M.; et al. Elevated IgG4 in patient circulation is associated with the risk of disease progression in melanoma. Oncoimmunology 2015, 4, e1032492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saul, L.; Ilieva, K.M.; Bax, H.J.; Karagiannis, P.; Correa, I.; Rodriguez-Hernandez, I.; Josephs, D.H.; Tosi, I.; Egbuniwe, I.U.; Lombardi, S.; et al. IgG subclass switching and clonal expansion in cutaneous melanoma and normal skin. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Qing, J.; Zhang, K.; Peng, H. Lung adenocarcinoma misdiagnosed as IgG4-related lung disease: A case report and literature review. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2021, 46, 767–773. [Google Scholar]
- Caturegli, P.; Kuppers, R.C.; Mariotti, S.; Burek, C.L.; Pinchera, A.; Ladenson, P.W.; Rose, N.R. IgG subclass distribution of thyroglobulin antibodies in patients with thyroid disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1994, 98, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, S.D.; Karlsson-Parra, A.; Nilsson, B.; Grimelius, L.; Akerström, G.; Rastad, J.; Juhlin, C. Tumor-specific deposition of immunoglobulin G and complement in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 1996, 27, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyatani, K.; Saito, H.; Murakami, Y.; Watanabe, J.; Kuroda, H.; Matsunaga, T.; Fukumoto, Y.; Osaki, T.; Nakayama, Y.; Umekita, Y.; et al. A high number of IgG4-positive cells in gastric cancer tissue is associated with tumor progression and poor prognosis. Virchows Arch. 2016, 468, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamisawa, T.; Chen, P.Y.; Tu, Y.; Nakajima, H.; Egawa, N.; Tsuruta, K.; Okamoto, A.; Hishima, T. Pancreatic cancer with a high serum IgG4 concentration. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 6225–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, M.; Inada, H.; Kanayama, K.; Shiraishi, T. A case of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with marked infiltration with IgG4-positive cells. J. Cytol. 2013, 30, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Niu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Pan, B.; Lu, Z.; Liao, Q.; Zhao, Y. Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)-positive plasma cell infiltration is associated with the clinicopathologic traits and prognosis of pancreatic cancer after curative resection. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2016, 65, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.Y.L.; Chua, W.M.; Cheng, L.T.J.; Fong, W.; Zaheer, S.; Lam, W.W. (18)F-FDG PET/CT Manifestations of IgG4-related Disease. Br. J. Radiol. 2021, 94, 20210105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ma, X.L.; Tian, L.; Zhang, C.Y.; Wang, B.L.; Hu, Y.Y.; Gao, X.H.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, M.N.; Peng, Y.F.; et al. Serum IgG4:IgG Ratio Predicts Recurrence of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Curative Resection. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 1338–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, Y.; Harada, K.; Nakanuma, Y. Pathologic significance of immunoglobulin G4-positive plasma cells in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2012, 43, 2149–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, K.; Shimoda, S.; Kimura, Y.; Sato, Y.; Ikeda, H.; Igarashi, S.; Ren, X.S.; Sato, H.; Nakanuma, Y. Significance of immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)-positive cells in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Molecular mechanism of IgG4 reaction in cancer tissue. Hepatology 2012, 56, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, K.; Nakanuma, Y. Cholangiocarcinoma with respect to IgG4 Reaction. Int. J. Hepatol. 2014, 2014, 803876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, T.; Uehara, T.; Iwaya, M.; Asaka, S.; Nakajima, T.; Kinugawa, Y.; Shimizu, A.; Kubota, K.; Notake, T.; Masuo, H.; et al. IgG4 expression and IgG4/IgG ratio in the tumour invasion front predict long-term outcomes for patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Pathology 2023, 55, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaitre, S.; Esquerda, G.M.; Guardiola, A.C.; Agustin, J.T.; Sanda, N.; González-Candial, M. Colon cancer and IgG4-related disease with orbital inflammation and bilateral optic perineuritis: A case report. Medicine 2018, 97, e12197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, A.; Krasinskas, A.M.; Greer, J.B.; Lamb, J.; Fink, E.; Moser, A.J.; Zeh, H.J., 3rd; Slivka, A.; Whitcomb, D.C. Serum immunoglobulin G fraction 4 levels in pancreatic cancer: Elevations not associated with autoimmune pancreatitis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2008, 132, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohyama, K.; Tanaka, M.; Nosaki, Y.; Yokoi, T.; Iwai, K. IgG4-related Inflammatory Pseudotumor with Imaging Findings Similar to Meningioma. Intern. Med. 2023, 62, 1665–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seip, T.; Calderón Novoa, F.; Valeo Chulvi, M.P.; Smith, D.; Dietrich, A. IgG4 inflammatory pseudotumor mimicking primary lung cancer. Rev. Fac. Cienc. Médicas 2023, 80, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itazaki, Y.; Einama, T.; Konno, F.; Fujinuma, I.; Takihata, Y.; Iwasaki, T.; Ogata, S.; Tsujimoto, H.; Ueno, H.; Kishi, Y. IgG4-related hepatic inflammatory pseudotumor mimicking cholangiolocellular carcinoma. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 14, 1733–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Heerde, M.J.; Biermann, K.; Zondervan, P.E.; Kazemier, G.; van Eijck, C.H.; Pek, C.; Kuipers, E.J.; van Buuren, H.R. Prevalence of autoimmune pancreatitis and other benign disorders in pancreatoduodenectomy for presumed malignancy of the pancreatic head. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 2458–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, N.L.; Negmeldin, M. IgG4-related disease: A great mimicker of lung cancer. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e239976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazale, A.; Chari, S.T.; Smyrk, T.C.; Levy, M.J.; Topazian, M.D.; Takahashi, N.; Clain, J.E.; Pearson, R.K.; Pelaez-Luna, M.; Petersen, B.T.; et al. Value of serum IgG4 in the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis and in distinguishing it from pancreatic cancer. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 1646–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhall, D.; Suriawinata, A.A.; Tang, L.H.; Shia, J.; Klimstra, D.S. Use of immunohistochemistry for IgG4 in the distinction of autoimmune pancreatitis from peritumoral pancreatitis. Hum. Pathol. 2010, 41, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, K.; Suzuki, S.; Yokoi, Y.; Ota, S.; Nakamura, T.; Konno, H.; Baba, S.; Takehara, Y.; Nakamura, S. Hepatic inflammatory pseudotumor mimicking intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Report of a case. Surg. Today 2003, 33, 714–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamano, A.; Yamada, R.; Kurata, K.; Tsuboi, J.; Inoue, H.; Tanaka, K.; Horiki, N.; Takei, Y. Difficulty in differentiating between IgG4-related hepatic inflammatory pseudotumor and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 14, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwa, T.; Law, R.; Hart, P.; Smyrk, T.C.; Chari, S.T. Serum IgG4 elevation in pancreatic cancer: Diagnostic and prognostic significance and association with autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreas 2015, 44, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, T.; Huang, X.; Fang, J.; Huang, L.; Yan, X.; Chen, J. Differential Diagnosis of IgG4-related Pancreatitis and Pancreatic Cancer by MRI Features and Its Correlation with Serum IgG4 Level. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2023, 69, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | IgG1 | IgG2 | IgG3 | IgG4 | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Human, mouse | Human, mouse | Human, mouse | Human | [21,22,23] |
| % of antibodies within the IgG class | Most (~60–70%) | Moderate (~20–30%) | Low (~5%) | Lowest (<5%) | [7,19,21,24] |
| Molecular mass (kD) | 146 | 146 | 170 | 146 | [19,24] |
| Hinge region | 15 aa | 12 aa | 62 aa | 12 aa | [24] |
| Fab-arm exchange | No | No | No | Yes | [7,19] |
| Complement activation | High | Moderate | Very high | Low | [25] |
| Fcγ receptor binding | Very high | Moderate | High | Low | [7,21,24] |
| Antibody (Ab)-mediated phagocytosis | High | Low | Very high | Low | [19,24,26] |
| Ab-mediated cellular cytotoxicity | High | Low | Very high | Low | [19,24,26] |
| Anti-inflammatory role | Limited | Low | Limited | Prominent | [7,12] |
| Dominance in allergies | Rare | None | Rare | Common | [7,27] |
| Role in autoimmunity | Common | Rare | Limited | Often associated with tolerance | [7,12] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, L.-l.; Xiong, P.; Yang, M.; Ardicli, O.; Schneider, S.R.; Funch, A.B.; Kiykim, A.; Lopez, J.; Akdis, C.A.; Akdis, M. Role of IgG4 Antibodies in Human Health and Disease. Cells 2025, 14, 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14090639
Shi L-l, Xiong P, Yang M, Ardicli O, Schneider SR, Funch AB, Kiykim A, Lopez J, Akdis CA, Akdis M. Role of IgG4 Antibodies in Human Health and Disease. Cells. 2025; 14(9):639. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14090639
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Li-li, Peng Xiong, Minglin Yang, Ozge Ardicli, Stephan Raphael Schneider, Anders Boutrup Funch, Ayca Kiykim, Juan Lopez, Cezmi A. Akdis, and Mübeccel Akdis. 2025. "Role of IgG4 Antibodies in Human Health and Disease" Cells 14, no. 9: 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14090639
APA StyleShi, L.-l., Xiong, P., Yang, M., Ardicli, O., Schneider, S. R., Funch, A. B., Kiykim, A., Lopez, J., Akdis, C. A., & Akdis, M. (2025). Role of IgG4 Antibodies in Human Health and Disease. Cells, 14(9), 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14090639







