Genome-Wide Mapping Defines a Role for C/EBPβ and c-Jun in Non-Canonical Cyclic AMP Signalling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture and mRNA Extraction
2.3. RNA Sequencing (RNA-SEQ)
2.4. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation and Sequencing (ChIP-SEQ) Analysis
2.5. ChIP-SEQ Data Analysis
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.7. siRNA Procedures
2.8. Western Blotting
2.9. Densitometry and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
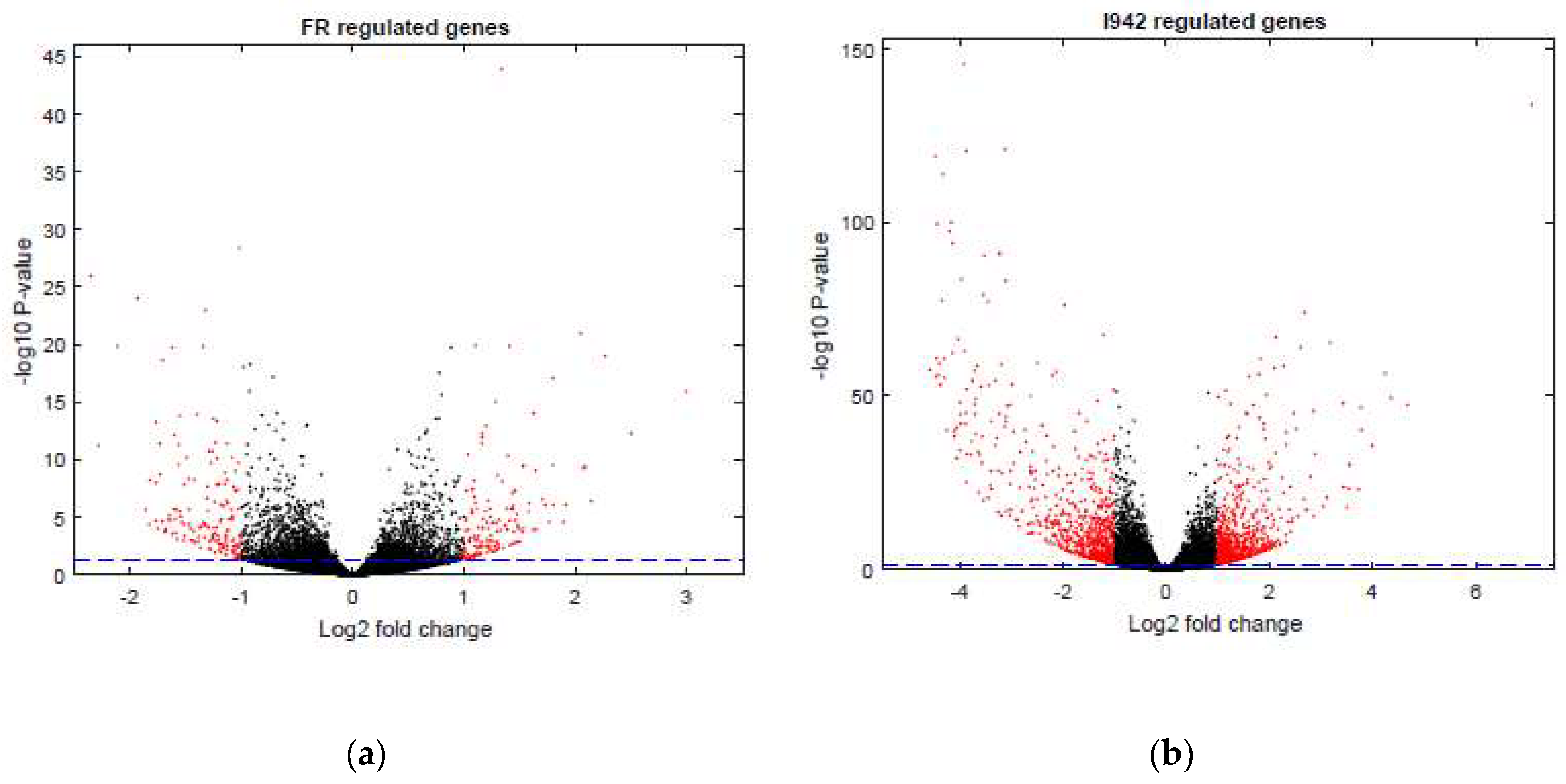
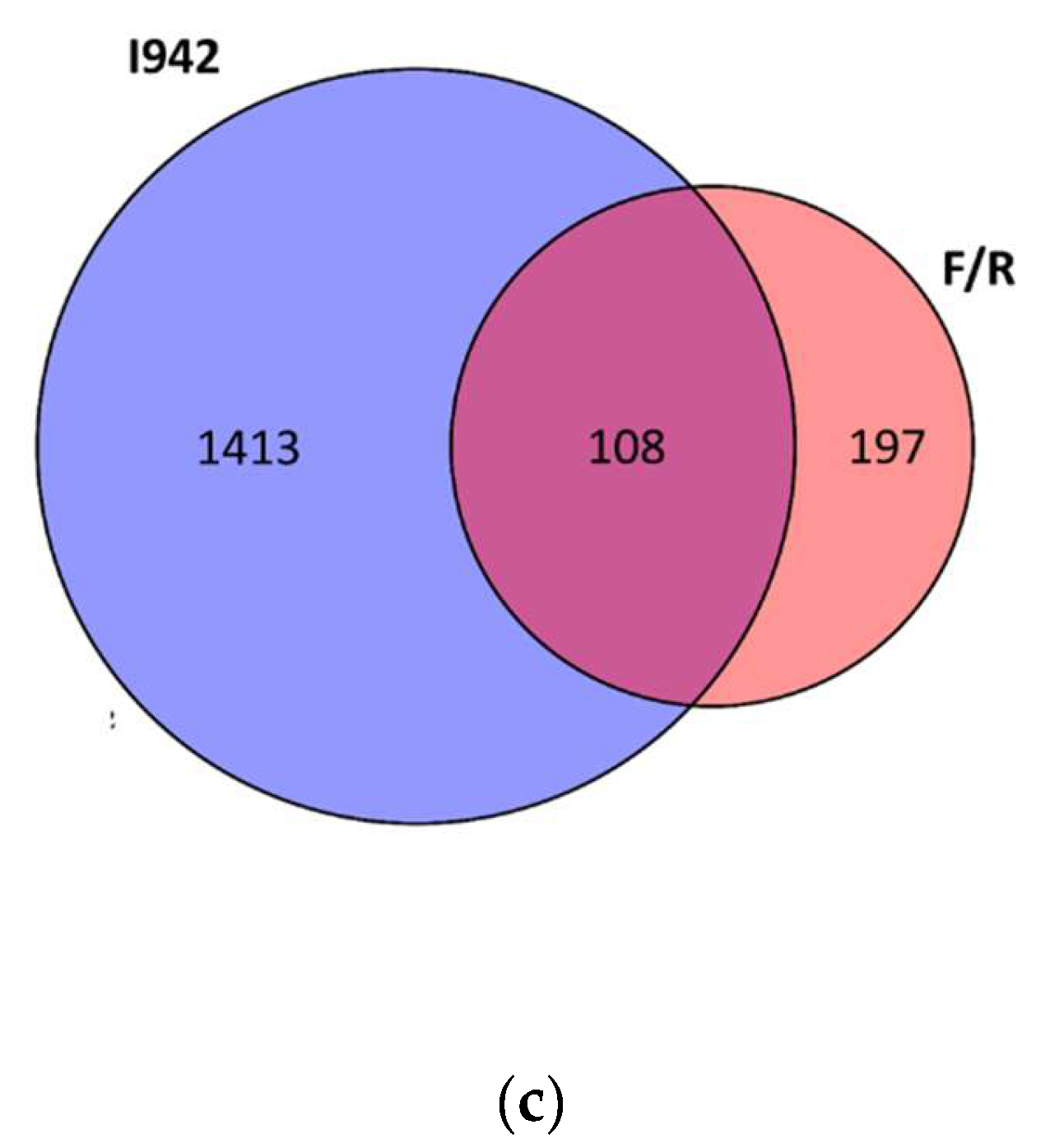
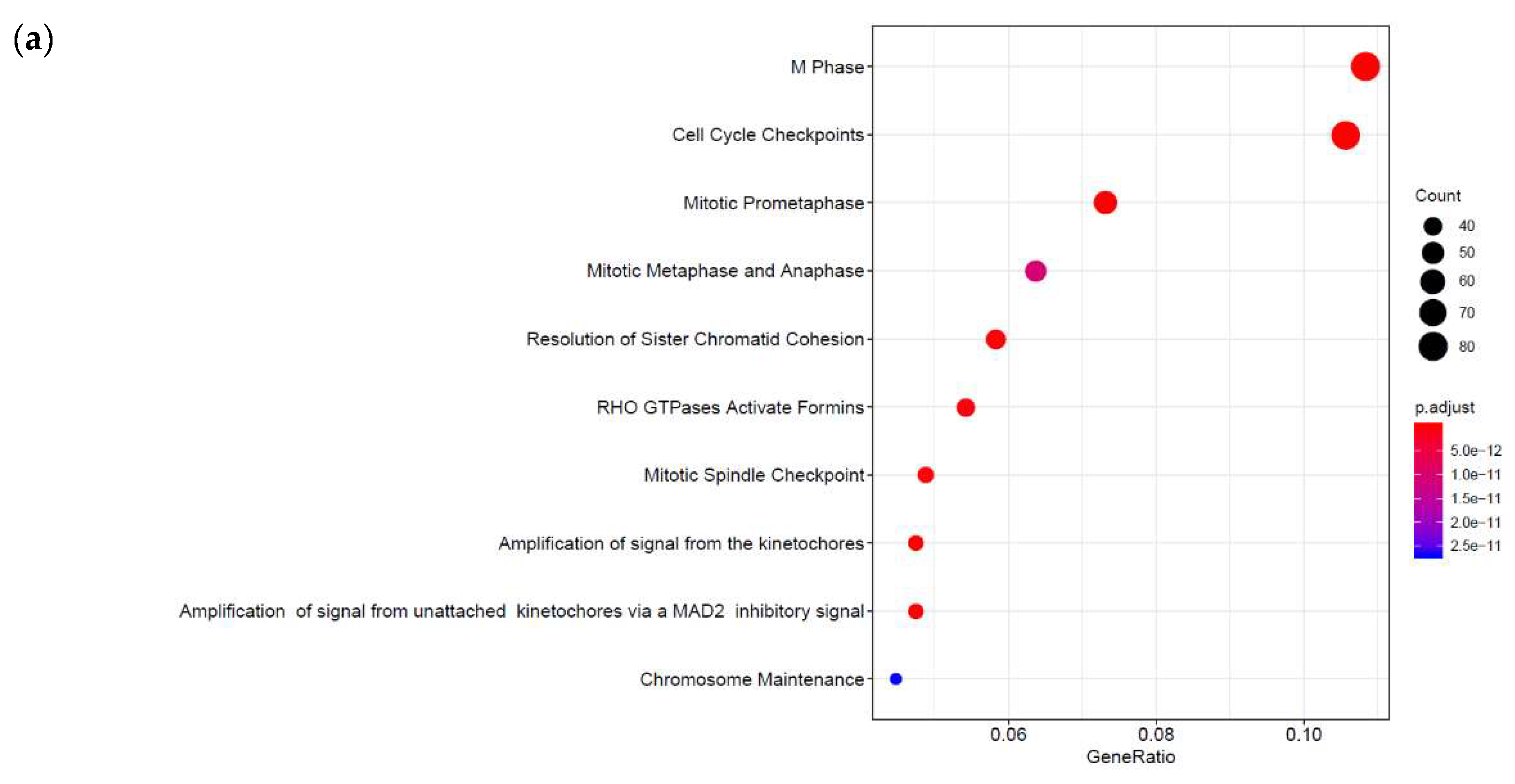
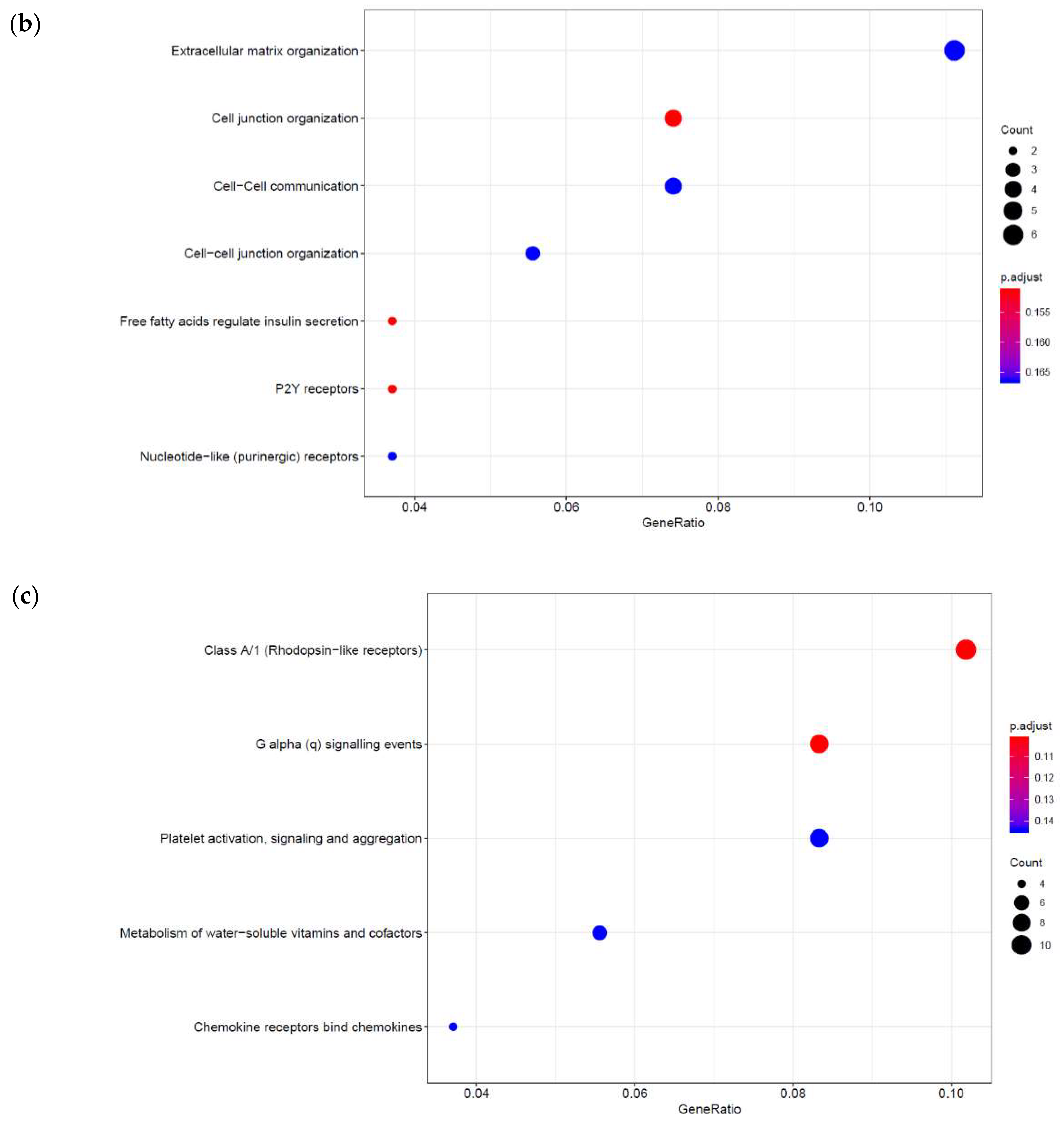
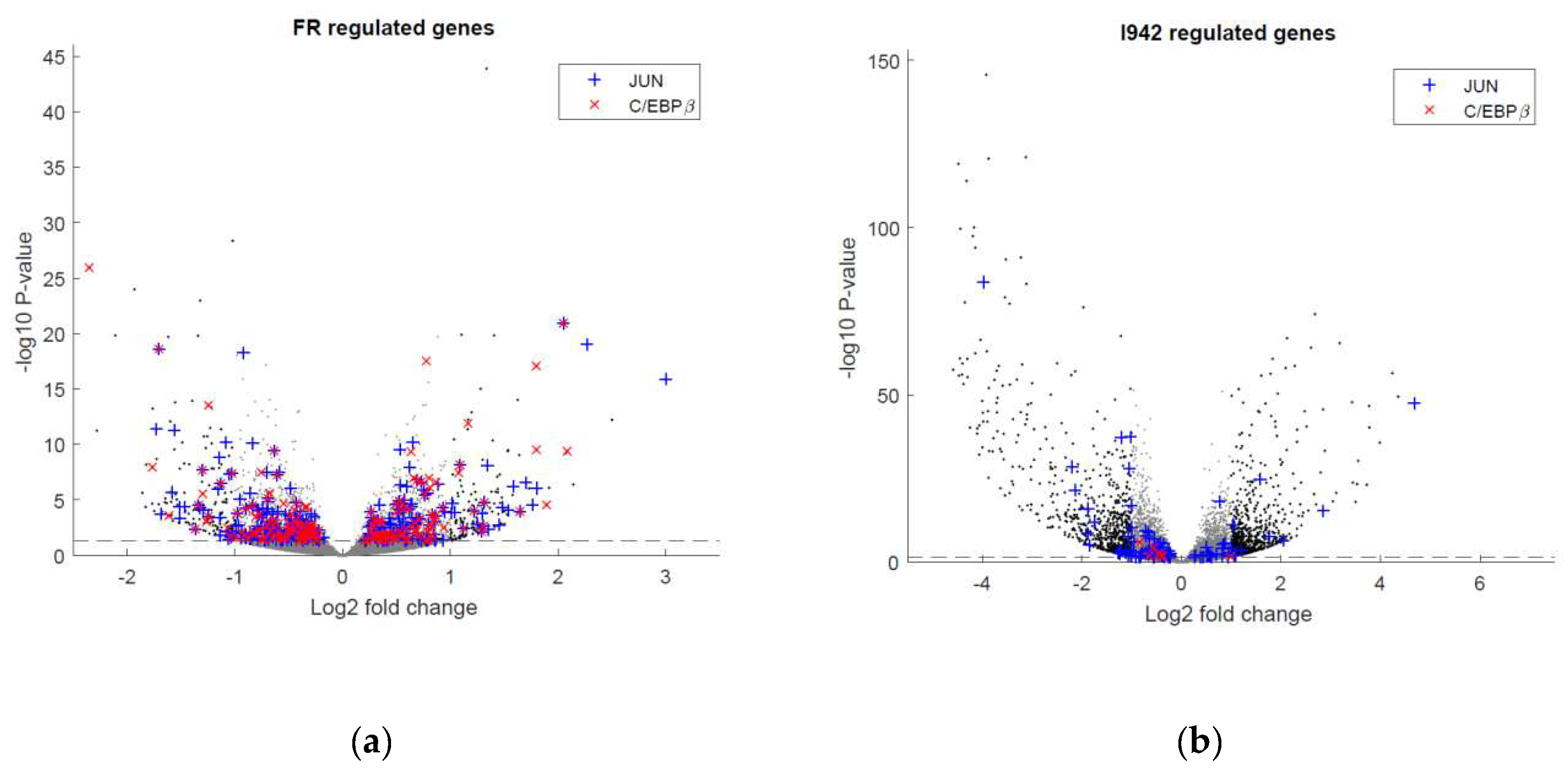
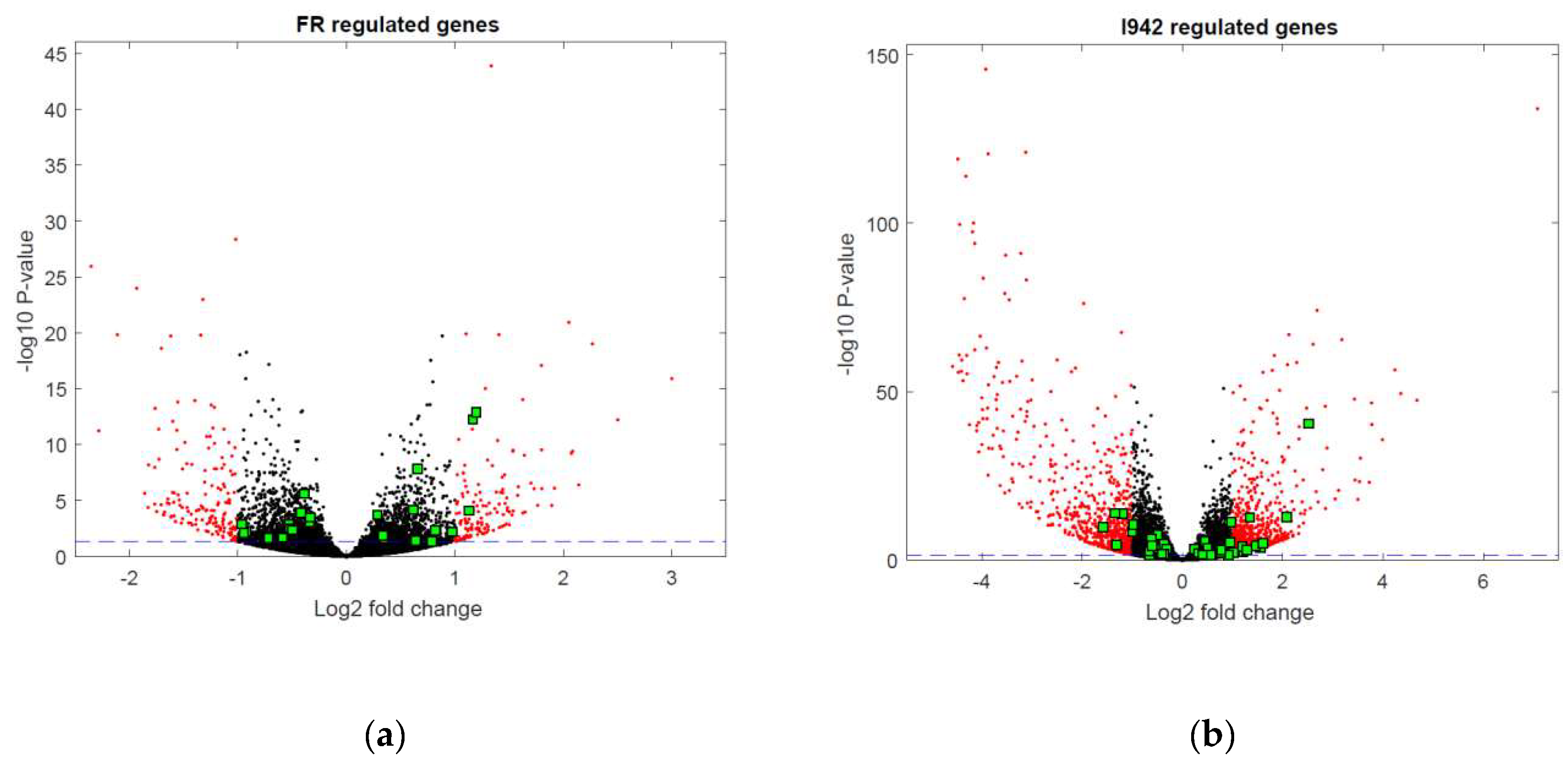
3.1. Identification of Genes Regulated by Cyclic AMP and I942 in HUVECs
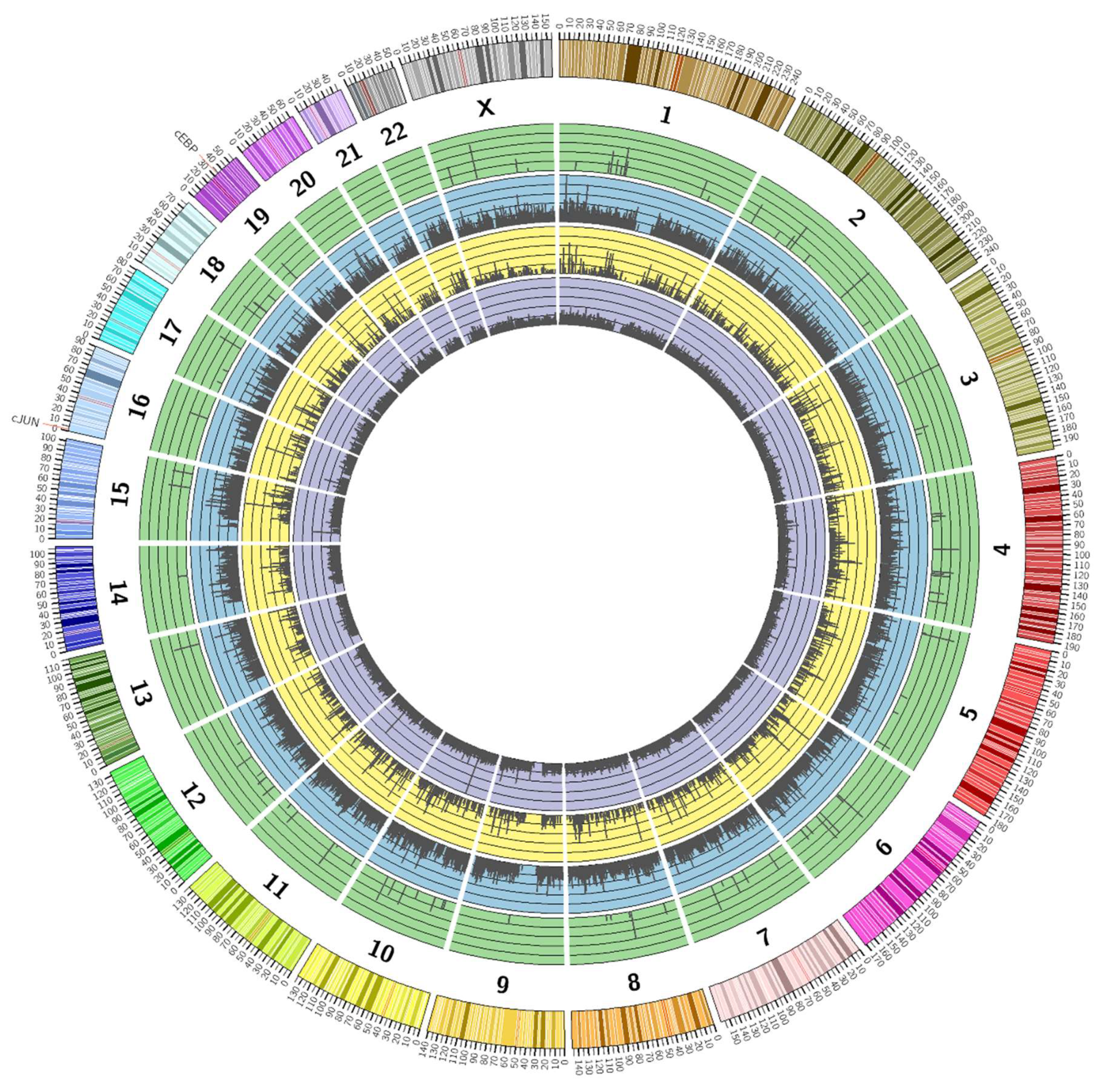
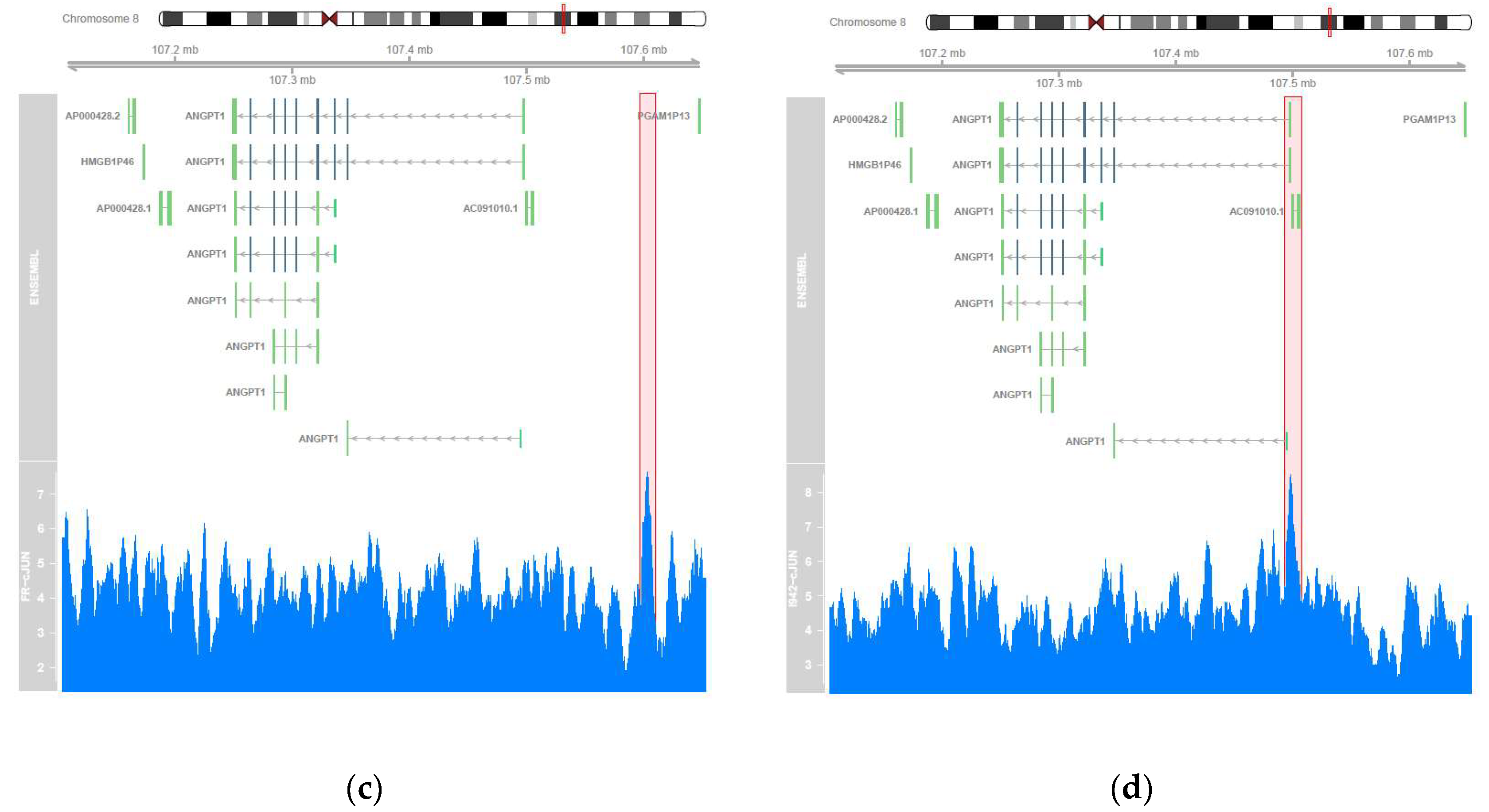
3.2. Genome-Wide Mobilisation of c-Jun and C/EBPβ Transcription Factors by Cyclic AMP and I942
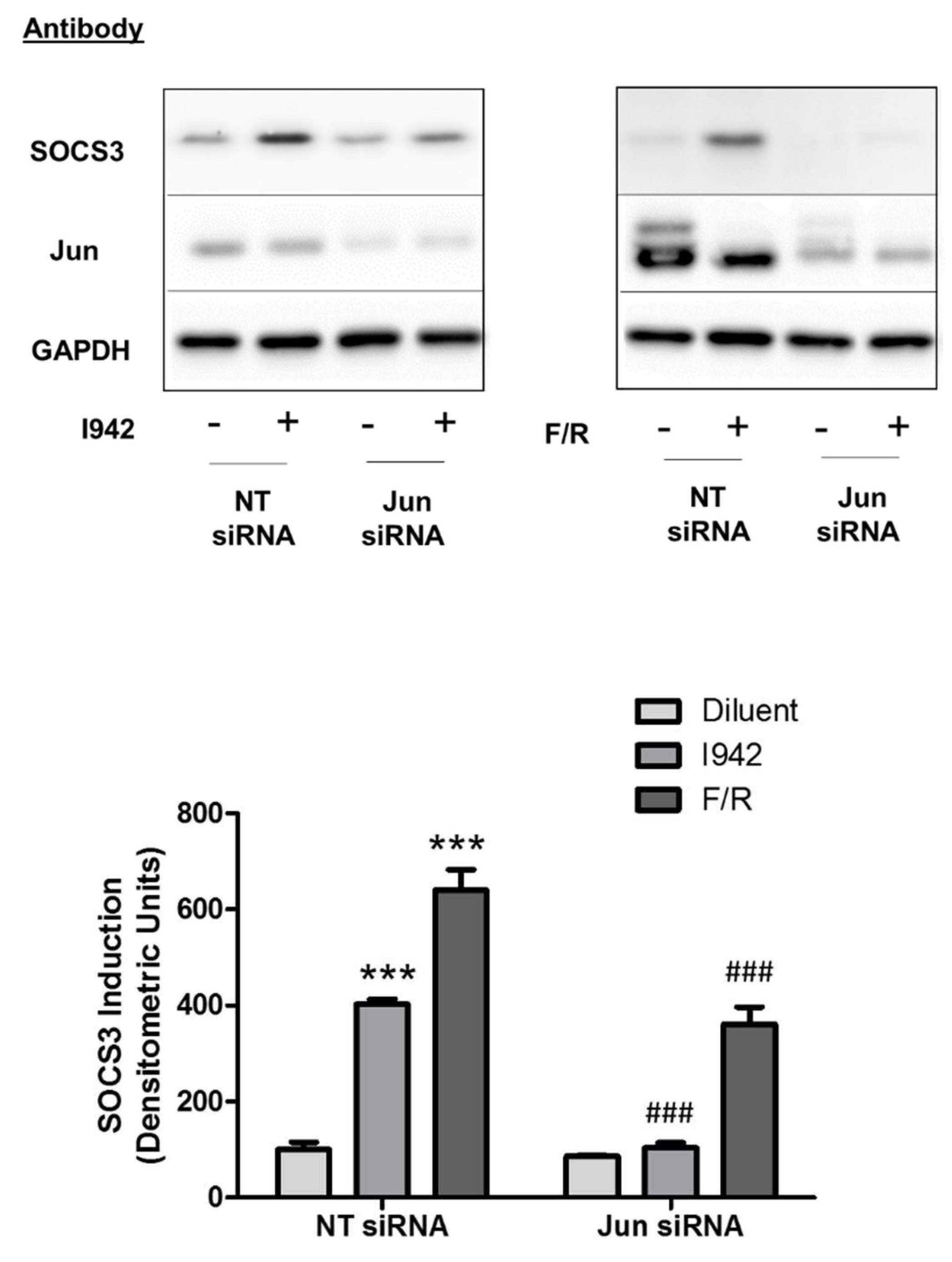
3.3. c-Jun Is Required for SOCS3 Induction and Suppression of IL6 Signalling by I942 in HUVECs
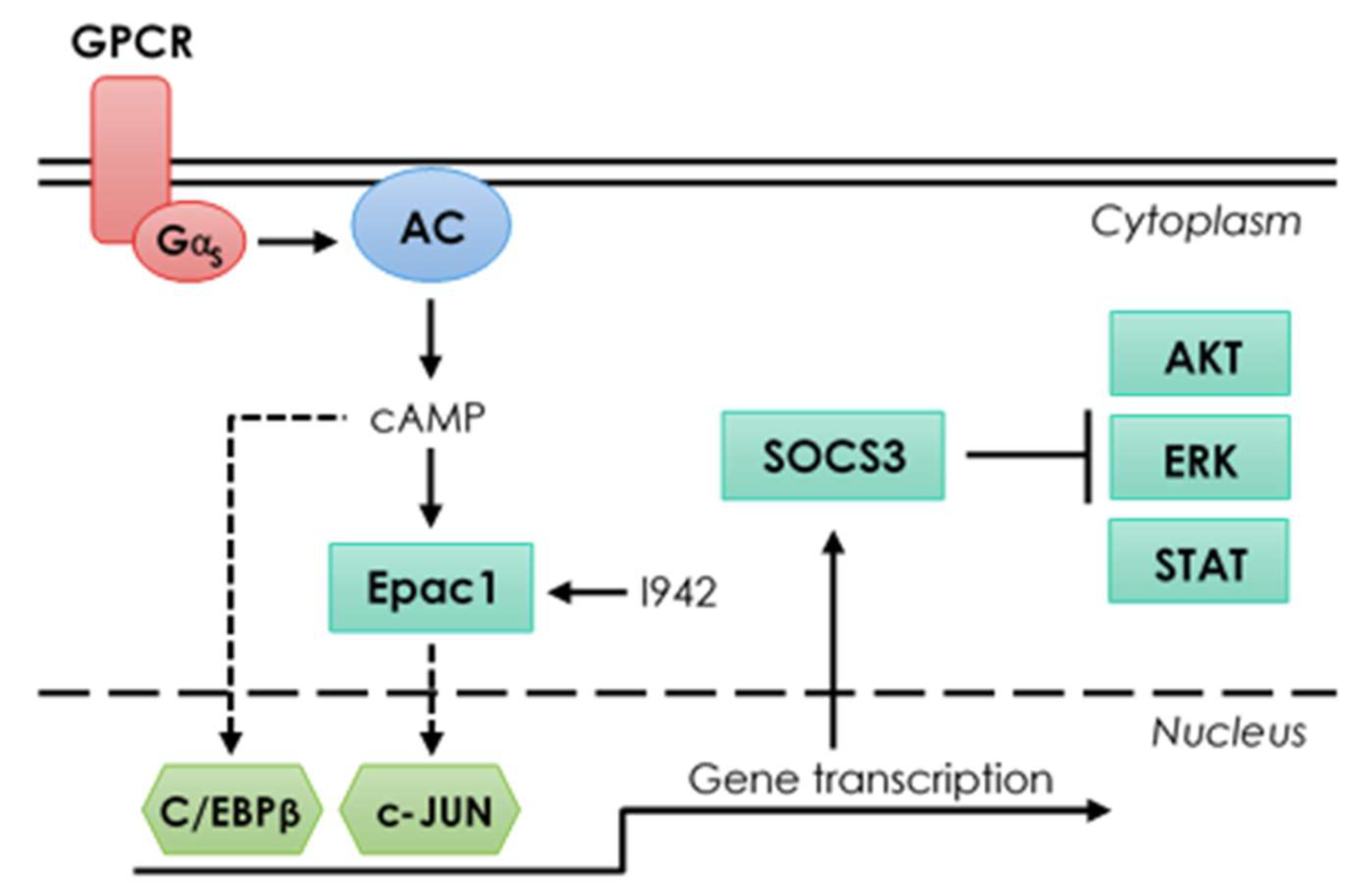
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Montminy, M. Transcriptional regulation by cyclic AMP. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1997, 66, 807–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayr, B.; Montminy, M. Transcriptional regulation by the phosphorylation-dependent factor CREB. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Boil. 2001, 2, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stork, P.J.S.; Schmitt, J.M. Crosstalk between cAMP and MAP kinase signaling in the regulation of cell proliferation. Trends Cell Boil. 2002, 12, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sands, W.A.; Woolson, H.D.; Milne, G.R.; Rutherford, C.; Palmer, T.M. Exchange protein activated by cyclic AMP (Epac)-mediated induction of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS-3) in vascular endothelial cells. Mol. Cell. Boil. 2006, 26, 6333–6346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piessevaux, J.; Lavens, D.; Peelman, F.; Tavernier, J. The many faces of the SOCS box. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008, 19, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, J.L. Epac proteins: Multi-purpose cAMP targets. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2006, 31, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnell, E.; O Smith, B.; Palmer, T.M.; Terrin, A.; Zaccolo, M.; Yarwood, S.J. Regulation of the inflammatory response of vascular endothelial cells by EPAC1. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 166, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borland, G.; Bird, R.J.; Palmer, T.M.; Yarwood, S.J. Activation of protein kinase Calpha by EPAC1 is required for the ERK- and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta-dependent induction of the SOCS-3 gene by cyclic AMP in COS1 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 17391–17403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarwood, S.; Borland, G.; Sands, W.A.; Palmer, T.M. Identification of CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins as exchange protein activated by cAMP-activated transcription factors that mediate the induction of the SOCS-3 gene. J. Boil. Chem. 2008, 283, 6843–6853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarwood, S. Microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) regulate cAMP signalling through exchange protein directly activated by cAMP (EPAC). Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2005, 33, 1327–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woolson, H.D.; Thomson, V.S.; Rutherford, C.; Yarwood, S.J.; Palmer, T.M. Selective inhibition of cytokine-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase by cyclic AMP via Epac1-dependent induction of suppressor of cytokine signalling-3. Cell. Signal. 2009, 21, 1706–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiejak, J.; Dunlop, J.; Gao, S.; Borland, G.; Yarwood, S.J. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent SOCS-3 gene induction requires c-Jun, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, and specificity protein 3 transcription factors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2012, 81, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiejak, J.; Dunlop, J.; Stoyle, C.; Lappin, G.; McIlroy, A.; Pediani, J.D.; Gao, S.; Yarwood, S.J. The protein kinase C inhibitor, Ro-31-7459, is a potent activator of ERK and JNK MAP kinases in HUVECs and yet inhibits cyclic AMP-stimulated SOCS-3 gene induction through inactivation of the transcription factor c-Jun. Cell. Signal. 2012, 24, 1690–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eid, A.H.; Chotani, M.A.; Mitra, S.; Miller, T.J.; Flavahan, N.A. Cyclic AMP acts through Rap1 and JNK signaling to increase expression of cutaneous smooth muscle alpha2C-adrenoceptors. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2008, 295, H266–H272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochbaum, D.; Tanos, T.; Ribeiro-Neto, F.; Altschuler, D.; Coso, O.A. Activation of JNK by Epac is independent of its activity as a rap guanine nucleotide exchanger. J. Boil. Chem. 2003, 278, 33738–33746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnell, E.; McElroy, S.P.; Wiejak, J.; Baillie, G.L.; Porter, A.; Adams, D.R.; Rehmann, H.; Smith, B.O.; Yarwood, S.J. Identification of a novel, small molecule partial agonist for the cyclic AMP sensor, EPAC1. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet.J. 2011, 17, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fastqc. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 14 October 2019).
- Bray, N.L.; Pimentel, H.; Melsted, P.; Pachter, L. Near-optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- I Love, M.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Boil. 2014, 15, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowtie Aligner. Available online: bowtie-bio.sourceforge.net/index.shtml (accessed on 14 October 2019).
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Boil. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homer (Version 3.9). Available online: http://homer.ucsd.edu/homer/ngs/ (accessed on 14 October 2019).
- PCR Array Data Analysis. Available online: http://pcrdataanalysis.sabiosciences.com/pcr/arrayanalysis.php (accessed on 14 October 2019).
- Image, J. Available online: http://rsbweb.nih.gov/ij/ (accessed on 14 October 2019).
- Wiejak, J.; van Basten, B.; Luchowska-Stanska, U.; Hamilton, G.; Yarwood, S.J. The novel exchange protein activated by cyclic AMP 1 (EPAC1) agonist, I942, regulates inflammatory gene expression in human umbilical vascular endothelial cells (HUVECs). Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2019, 1866, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avanzato, D.; Genova, T.; Pla, A.F.; Bernardini, M.; Bianco, S.; Bussolati, B.; Mancardi, D.; Giraudo, E.; Maione, F.; Cassoni, P.; et al. Activation of P2X7 and P2Y11 purinergic receptors inhibits migration and normalizes tumor-derived endothelial cells via cAMP signaling. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, C.J.; Lin, C.; Liu, X.; Antonetti, D.A. The EPAC-Rap1 pathway prevents and reverses cytokine-induced retinal vascular permeability. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 717–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, C.W.; Parker, L.H.; Hall, C.J.; Smyczek, T.; Mak, J.; Crow, A.; Posthuma, G.; De Mazière, A.; Sagolla, M.; Chalouni, C.; et al. Rasip1 regulates vertebrate vascular endothelial junction stability through Epac1-Rap1 signaling. Blood 2013, 122, 3678–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
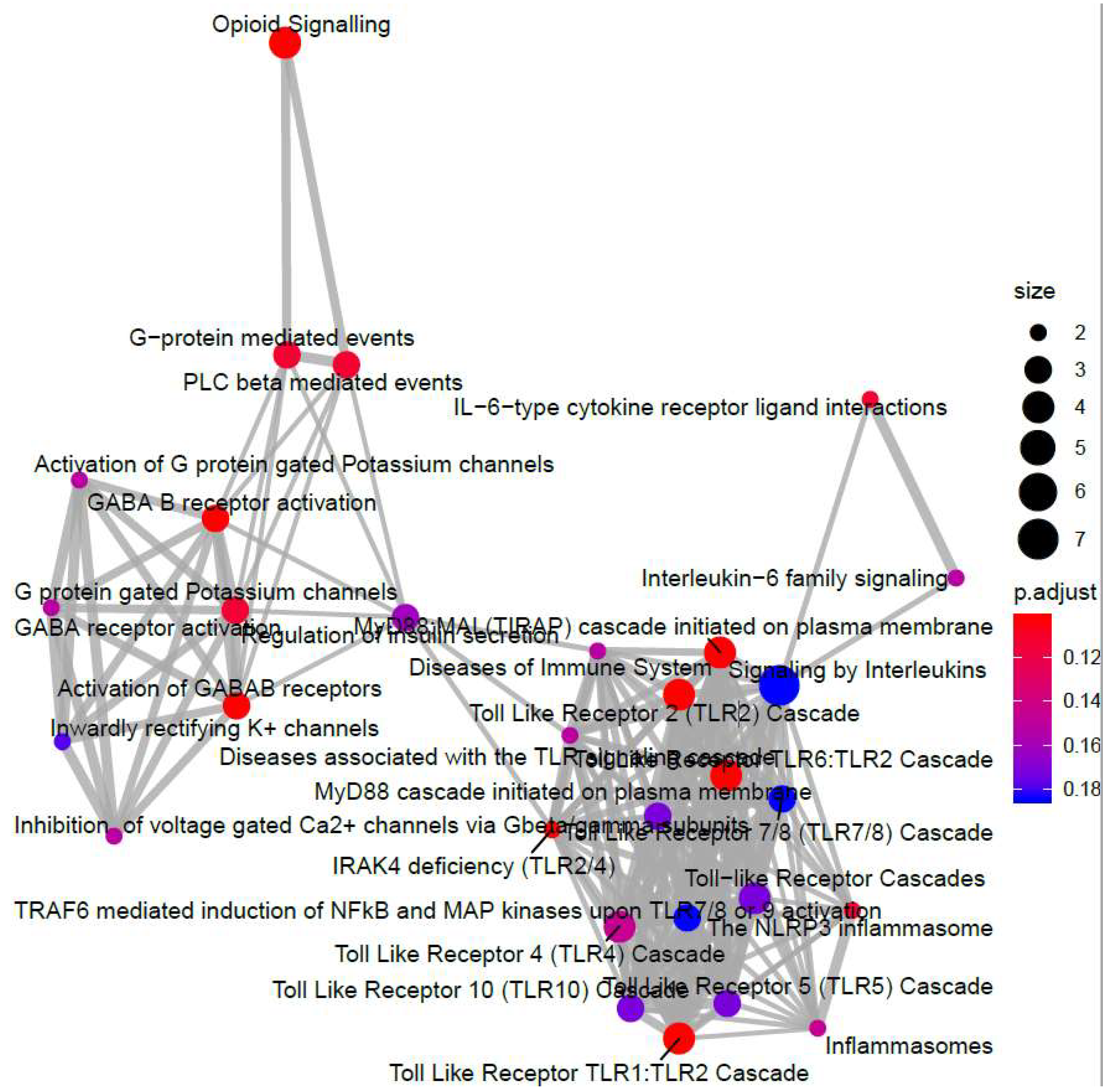
- Yu, G.; He, Q.-Y. ReactomePA: An R/Bioconductor package for reactome pathway analysis and visualization. Mol. Biosyst. 2016, 12, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiejak, J.; Dunlop, J.; Yarwood, S.J. The role of c-Jun in controlling the EPAC1-dependent induction of the SOCS3 gene in HUVECs. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 1556–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angel, P.; Imagawa, M.; Chiu, R.; Stein, B.; Imbra, R.J.; Rahmsdorf, H.J.; Jonat, C.; Herrlich, P.; Karin, M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell 1987, 49, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.; Shuman, J.D.; Sebastian, T.; Dauter, Z.; Johnson, P.F. Structural basis for DNA recognition by the basic region leucine zipper transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein. J. Boil. Chem. 2003, 278, 15178–15184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borland, G.; O Smith, B.; Yarwood, S.J. EPAC proteins transduce diverse cellular actions of cAMP. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 158, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Endothelial Cell Biology. Available online: https://geneglobe.qiagen.com/product-groups/rt2-profiler-pcr-arrays (accessed on 14 October 2019).
- Schindler, R.F.; Brand, T. The Popeye domain containing protein family--A novel class of cAMP effectors with important functions in multiple tissues. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Boil. 2016, 120, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehrawat, S.; Ernandez, T.; Cullere, X.; Takahashi, M.; Ono, Y.; Komarova, Y.; Mayadas, T.N. AKAP9 regulation of microtubule dynamics promotes Epac1-induced endothelial barrier properties. Blood 2011, 117, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sehrawat, S.; Cullere, X.; Patel, S.; Italiano, J., Jr.; Mayadas, T.N. Role of Epac1, an exchange factor for rap GTPases, in endothelial microtubule dynamics and barrier function. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiStefano, P.V.; Smrcka, A.V.; Glading, A.J. Phospholipase cepsilon modulates Rap1 activity and the endothelial barrier. PloS One 2016, 11, e0162338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gregorio, C.; Heras, M.L.; Meinohl, C.; Noorman, K.; Boddeke, E.; Cheng, X.; Lezoualc’H, F.; Schmidt, M.; Muñoz-Llancao, P.; Gonzalez-Billault, C.; et al. Microtubule-regulating proteins and cAMP-dependent signaling in neuroblastoma differentiation. Cytoskeleton 2017, 74, 143–158. [Google Scholar]
- Fuld, S.; Borland, G.; Yarwood, S.J. Elevation of cyclic AMP in Jurkat T-cells provokes distinct transcriptional responses through the protein kinase A (PKA) and exchange protein activated by cyclic AMP (EPAC) pathways. Exp. Cell Res. 2005, 309, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Mei, F.C.; Johnson, B.H.; Thompson, E.B.; Cheng, X. Protein kinase A, not Epac, suppresses Hedgehog activity and regulates glucocorticoid sensitivity in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 37370–37377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Ma, Y.; Bast, R.C., Jr.; Li, Y.; Wan, L.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; et al. Epac1 knockdown inhibits the proliferation of ovarian cancer cells by inactivating AKT/Cyclin D1/CDK4 pathway in vitro and in vivo. Med. Oncol. 2016, 33, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochbaum, D.; Barila, G.; Ribeiro-Neto, F.; Altschuler, D.L. Radixin assembles cAMP effectors Epac and PKA into a functional cAMP compartment: Role in cAMP-dependent cell proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassel, K.M.; Wyatt, T.A.; Panettieri, R.A., Jr.; Toews, M.L. Inhibition of human airway smooth muscle cell proliferation by beta 2-adrenergic receptors and cAMP is PKA independent: Evidence for EPAC involvement. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2008, 294, L131–L138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiermayer, S.; Biondi, R.M.; Imig, J.; Plotz, G.; Haupenthal, J.; Zeuzem, S.; Piiper, A. Epac activation converts cAMP from a proliferative into a differentiation signal in PC12 cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 5639–5648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roscioni, S.S.; Prins, A.G.; Elzinga, C.R.; Menzen, M.H.; Dekkers, B.G.; Halayko, A.J.; Meurs, H.; Maarsingh, H.; Schmidt, M. Protein kinase A and the exchange protein directly activated by cAMP (Epac) modulate phenotype plasticity in human airway smooth muscle. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 958–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hewer, R.C.; Sala-Newby, G.B.; Wu, Y.J.; Newby, A.C.; Bond, M. PKA and Epac synergistically inhibit smooth muscle cell proliferation. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2011, 50, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, M.; Yarwood, S.J. MAP1A light chain 2 interacts with exchange protein activated by cyclic AMP 1 (EPAC1) to enhance Rap1 GTPase activity and cell adhesion. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 8109–8116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, F.C.; Cheng, X. Interplay between exchange protein directly activated by cAMP (Epac) and microtubule cytoskeleton. Mol. Biosyst. 2005, 1, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Mei, F.C.; Popov, V.L.; Vergara, L.A.; Cheng, X. Cell cycle-dependent subcellular localization of exchange factor directly activated by cAMP. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 26581–26586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borland, G.; Gupta, M.; Magiera, M.M.; Rundell, C.J.; Fuld, S.; Yarwood, S.J. Microtubule-associated protein 1B-light chain 1 enhances activation of Rap1 by exchange protein activated by cyclic AMP but not intracellular targeting. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 69, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiera, M.M.; Gupta, M.; Rundell, C.J.; Satish, N.; Ernens, I.; Yarwood, S.J. Exchange protein directly activated by cAMP (EPAC) interacts with the light chain (LC) 2 of MAP1A. Biochem. J. 2004, 382, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parnell, E.; Koschinski, A.; Zaccolo, M.; Cameron, R.T.; Baillie, G.S.; Baillie, G.L.; Porter, A.; McElroy, S.P.; Yarwood, S.J. Phosphorylation of ezrin on Thr567 is required for the synergistic activation of cell spreading by EPAC1 and protein kinase A in HEK293T cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Bioenerg. 2015, 1853, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boyle, W.J.; Smeal, T.; Defize, L.H.; Angel, P.; Woodgett, J.R.; Karin, M.; Hunter, T. Activation of protein kinase C decreases phosphorylation of c-Jun at sites that negatively regulate its DNA-binding activity. Cell 1991, 64, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, A.; Yasukawa, H.; Suzuki, A.; Kamizono, S.; Syoda, T.; Kinjyo, I.; Sasaki, M.; Johnston, J.A.; Yoshimura, A. Cytokine-inducible SH2 protein-3 (CIS3/SOCS3) inhibits Janus tyrosine kinase by binding through the N-terminal kinase inhibitory region as well as SH2 domain. Genes Cells 1999, 4, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.J.; Palmer, T.M. Unbiased identification of substrates for the Epac1-inducible E3 ubiquitin ligase component SOCS-3: Figure 1. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2012, 40, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croker, B.A.; Kiu, H.; Pellegrini, M.; Toe, J.; Preston, S.; Metcalf, D.; O’Donnell, J.A.; Cengia, L.H.; McArthur, K.; Nicola, N.A.; et al. IL-6 promotes acute and chronic inflammatory disease in the absence of SOCS3. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2012, 90, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, A.; Joyal, J.-S.; Chen, J.; Sapieha, P.; Juan, A.M.; Hatton, C.J.; Pei, D.T.; Hurst, C.G.; Seaward, M.R.; Krah, N.M.; et al. SOCS3 is an endogenous inhibitor of pathologic angiogenesis. Blood 2012, 120, 2925–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| ChIP | Treatment | Motif | Alignment | Name | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C/EBPβ | F/R |  | RTGTTGCAA--TTNNNCAAY | CEBP/AP1 | 0.001 |
| C/EBPβ | I942 |  | TGACGTCATGACGTCA | CREB/ATF | 0.001 |
| c-Jun | F/R |  | RTGTTGCAA--TTNNNCAAY | CEBP/AP1 | 0.001 |
| c-Jun | I942 |  | TGASTCATGAGTCA | Jun/AP1 | 0.001 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wiejak, J.; van Basten, B.; Hamilton, G.; Yarwood, S.J. Genome-Wide Mapping Defines a Role for C/EBPβ and c-Jun in Non-Canonical Cyclic AMP Signalling. Cells 2019, 8, 1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101253
Wiejak J, van Basten B, Hamilton G, Yarwood SJ. Genome-Wide Mapping Defines a Role for C/EBPβ and c-Jun in Non-Canonical Cyclic AMP Signalling. Cells. 2019; 8(10):1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101253
Chicago/Turabian StyleWiejak, Jolanta, Boy van Basten, Graham Hamilton, and Stephen J. Yarwood. 2019. "Genome-Wide Mapping Defines a Role for C/EBPβ and c-Jun in Non-Canonical Cyclic AMP Signalling" Cells 8, no. 10: 1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101253
APA StyleWiejak, J., van Basten, B., Hamilton, G., & Yarwood, S. J. (2019). Genome-Wide Mapping Defines a Role for C/EBPβ and c-Jun in Non-Canonical Cyclic AMP Signalling. Cells, 8(10), 1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101253






