Complete Mitochondrial DNA Genome of Nine Species of Sharks and Rays and Their Phylogenetic Placement among Modern Elasmobranchs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue Sampling and DNA Extraction
2.2. Sequencing and Mitogenome Assembly
2.3. Annotation and Sequence Analysis
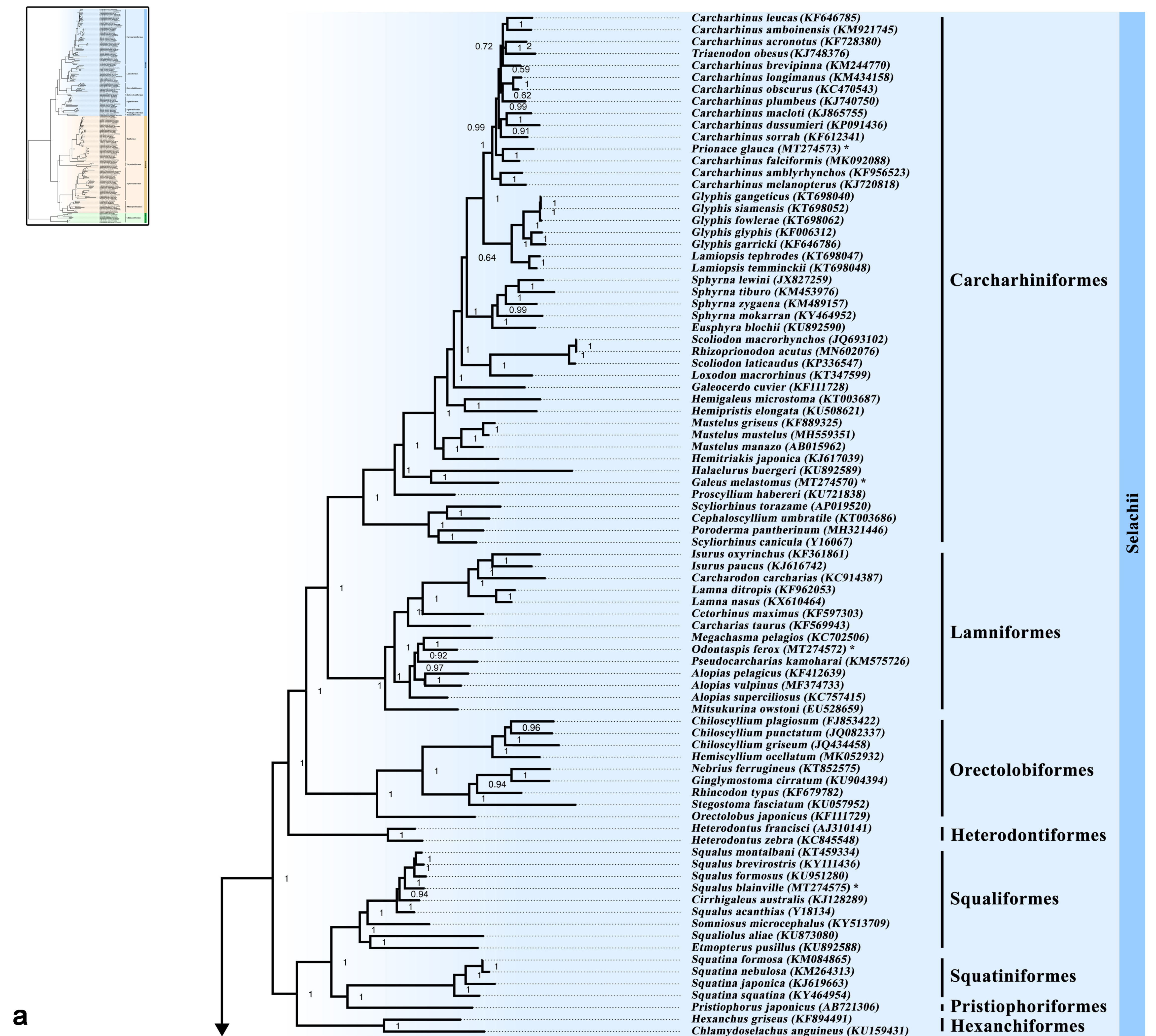
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Genome Organization
3.2. Protein-Coding Genes and Codon Usage
3.3. rRNA and tRNA Genes
3.4. Noncoding Regions
3.5. Phylogenetic Inference
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raup, D.; Sepkoski, J. Mass extinctions in the marine fossil record. Science 1982, 215, 1501–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stein, R.W.; Mull, C.G.; Kuhn, T.S.; Aschliman, N.C.; Davidson, L.N.K.; Joy, J.B.; Smith, G.J.; Dulvy, N.K.; Mooers, A.O. Global priorities for conserving the evolutionary history of sharks, rays and chimaeras. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grogan, E.; Lund, R. The origin and relationships of early Chondrichthyes. In Biology of Sharks and their Relatives; Carrier, J., Musick, J., Heithaus, M., Eds.; CRC Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; pp. 3–31. [Google Scholar]
- Musick, J.A.; Ellis, J.K. Reproductive evolution of chondrichthyans. In Reproductive Biology and Phylogeny of Chondrichthyes: Sharks, Rays and Chimaeras; Hamlett, W.C., Ed.; Science Publishers: Endfield, UK, 2005; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kousteni, V.; Megalofonou, P. Aging and life history traits of the longnose spiny dogfish in the Mediterranean: New insights into conservation and management needs. Fish. Res. 2015, 168, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousteni, V.; Megalofonou, P. Reproductive strategy of Scyliorhinus canicula (L., 1758): A holistic approach based on macroscopic measurements and microscopic observations of the reproductive organs. Mar. Freshwater Res. 2019, 71, 596–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metochis, C.P.; Carmona-Antoñanzas, G.; Kousteni, V.; Damalas, D.; Megalophonou, P. Population structure and aspects of the reproductive biology of the blackmouth catshark, Galeus melastomus Rafinesque, 1810 (Chondrichthyes: Scyliorhinidae) caught accidentally off the Greek coasts. J. Mar. Biolog. Assoc. U.K. 2016, 98, 909–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinicke, M.P.; Naylor, G.J.P.; Hedges, S.B. Cartilaginous fishes (Chondrichthyes). In The Time Tree of Life; Hedges, S.B., Kumar, S., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; p. 320. [Google Scholar]
- Ebert, D.A.; Fowler, S.L.; Compagno, L.J.V. Sharks of the World: A Fully Illustrated Guide; Wild Nature Press: Plymouth, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Weigmann, S. Annotated checklist of the living sharks, batoids and chimaeras (Chondrichthyes) of the world, with a focus on biogeographical diversity. J. Fish Biol. 2016, 88, 837–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetherbee, B.M.; Cortés, E. Food consumption and feeding habits. In Biology of Sharks and Their Relatives; Carrier, J.C., Musick, J.A., Heithaus, M.R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 223–244. [Google Scholar]
- Kousteni, V.; Karachle, P.K.; Megalofonou, P. Diet and trophic level of the longnose spurdog Squalus blainville (Risso, 1826) in the deep waters of the Aegean Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part I 2017, 124, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousteni, V.; Karachle, P.K.; Megalofonou, P. Diet of the small-spotted catshark Scyliorhinus canicula in the Aegean Sea (eastern Mediterranean). Mar. Biol. Res. 2017, 13, 161–173. [Google Scholar]
- Matich, P.; Heithaus, M.R.; Layman, C.A. Contrasting patterns of individual specialization and trophic coupling in two marine apex predators. J. Anim. Ecol. 2011, 80, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Da Cunha, D.B.; da Silva Rodrigues-Filho, L.F.; de Luna Sales, J.B. A review of the mitogenomic phylogeny of the Chondrichthyes. In Chondrichthyes-Multidisciplinary Approach; Da Cunha, D.B., da Silva Rodrigues-Filho, L.F., de Luna Sales, J.B., Eds.; TechOpen: London, UK, 2017; pp. 114–126. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh, B.; Kirkness, E.F.; Loh, Y.H.; Halpern, A.L.; Lee, A.P.; Johnson, J.; Dandona, N.; Viswanathan, L.D.; Tay, A.; Venter, J.C.; et al. Survey sequencing and comparative analysis of the elephant shark (Callorhinchus milii) genome. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, 932–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, S.L.; Reed, T.M.; Dipper, F.A. Elasmobranch Biodiversity, Conservation and Management; IUCN Species Survival Commission Shark Specialist Group: Gland, Switzerland; Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, S.C.; McAllister, M.K.; Milner-Gulland, E.J.; Kirkwood, G.P.; Michielsens, C.G.J.; Agnew, D.J.; Pikitch, E.K.; Nakano, H.; Shivji, M.S. Global estimates of shark catches using trade records from commercial markets. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 1115–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J.D.; Bonfil, R.; Dulvy, N.K.; Walker, P. The effects of fishing on sharks, rays and chimaeras (chondrichthyans), and the implications for marine ecosystems. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2000, 57, 476–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, S.F.J.; Simpfendorfer, C.A. Population status of 14 shark species caught in the protective gillnets off KwaZulu-Natal beaches, South Africa, 1978–2003. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2006, 57, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, F.; Worm, B.; Britten, G.L.; Heithaus, M.R.; Lotze, H.K. Patterns and ecosystem consequences of shark declines in the ocean. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 13, 1055–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, R.A.; Worm, B. Extinction, survival or recovery of large predatory fishes. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 2005, 360, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dulvy, N.K.; Fowler, S.L.; Musick, K.A.; Cavanagh, R.D.; Kyne, P.M.; Harrison, L.R.; Carlson, J.K.; Davidson, L.N.K.; Fordham, S.V.; Francis, M.P.; et al. Extinction risk and conservation of the world’s sharks and rays. eLife 2014, 3, e00590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Díaz-Jaimes, P.; Bayona-Vásquez, N.J.; Adams, D.H.; Uribe-Alcocer, M. Complete mitochondrial DNA genome of bonnethead shark, Sphyrna tiburo, and phylogenetic relationships among main superorders of modern elasmobranchs. Meta Gene 2016, 7, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglésias, S.P.; Toulhout, L.; Sellos, D.P. Taxonomic confusion and market mislabelling of threatened skates: Important consequences for their conservation status. Aquat. Conserv. 2010, 20, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.T.; Last, P.R. A review of the taxonomy of chondrichthyan fishes: A modern perspective. J. Fish Biol. 2012, 80, 901–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, S. Phylogenetic relationships of the angel sharks, with comments on elasmobranch phylogeny (Chondrichthyes, Squatinidae). Copeia 1992, 2, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, S. Phylogenetic interrelationships of neoselachians (Chondrichthyes: Euselachii). In Interrelationships of Fishes; Stiassny, M.L.J., Parenti, L.R., Johnson, G.D., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1996; pp. 9–34. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, M.R. Higher-level elasmobranch phylogeny, basal squaleans, and paraphyly. In Interrelationships of Fishes; Stiassny, M.L.J., Parenti, L.R., Johnson, G.D., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1996; pp. 35–62. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, M.R.; Maisey, J.G. Phylogenetic relationships of the late jurassic shark Protospinax Woodward 1919 (Chondrichthyes: Elasmobranchii). In Mesozoic Fishes: Systematics and Paleoecology; Arratia, G., Viohl, G., Eds.; Verlag Dr Friedrich Pfeil: Munich, Germany, 1996; pp. 9–46. [Google Scholar]
- Douady, C.J.; Dosay, M.; Shivji, M.S.; Stanhope, M.J. Molecular phylogenetic evidence refuting the hypothesis of Batoidea (rays and skates) as derived sharks. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 26, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Human, B.A.; Owen, E.P.; Compagno, L.J.V.; Harley, E.H. Testing morphologically based phylogenetic theories within the cartilaginous fishes with molecular data, with special reference to the catshark family (Chondrichthyes; Scyliorhinidae) and the interrelationships within them. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2006, 39, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vélez-Zuazo, X.; Agnarsson, I. Shark tales: A molecular species-level phylogeny of sharks (Selachimorpha, Chondrichthyes). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2011, 58, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, G.J.P.; Ryburn, J.A.; Fedrigo, O.; López, J.A. Phylogenetic relationships among the major lineages of modern elasmobranchs. In Reproductive Biology and Phylogeny; Hamlett, W.C., Jamieson, B.G.M., Eds.; Science Publishers: Endfield, UK, 2005; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Kousteni, V.; Bakiu, R.; Benhmida, A.; Crocetta, F.; Di Martino, V.; Dogrammatzi, A.; Doumpas, N.; Durmishaj, S.; Giovos, I.; Gökoğlu, M.; et al. New Mediterranean Biodiversity Records. Med. Mar. Sci. 2019, 20, 230–247. [Google Scholar]
- Kousteni, V.; Kasapidis, P.; Kotoulas, G.; Megalofonou, P. Strong population genetic structure and contrasting demographic histories for the small-spotted catshark (Scyliorhinus canicula) in the Mediterranean Sea. Heredity 2015, 114, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kousteni, V.; Kasapidis, P.; Kotoulas, G.; Megalofonou, P. Evidence of high genetic connectivity for the longnose spurdog Squalus blainville in the Mediterranean Sea. Med. Mar. Sci. 2016, 17, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, W.M. The mitochondrial genome of animals. In Molecular Evolutionary Genetics; MacIntyre, R.D., Ed.; Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 95–130. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Ai, W.; Ye, L.; Wang, X.; Lin, C.; Yang, S. The complete mitochondrial genome of the grey bamboo shark (Chiloscyllium griseum) (Orectolobiformes: Hemiscylliidae): Genomic characterization and phylogenetic application. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2013, 32, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc (accessed on 14 November 2019).
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, W.; Fukunaga, T.; Isagozawa, R.; Yamada, K.; Maeda, Y.; Satoh, T.P.; Sado, T.; Mabuchi, K.; Takeshima, H.; Miya, M.; et al. MitoFish and MitoAnnotator: A mitochondrial genome database of fish with an accurate and automatic annotation pipeline. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2531–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagesen, K.; Hallin, P.F.; Rødland, E.; Stærfeldt, H.H.; Rognes, T.; Ussery, D.W. RNammer: Consistent annotation of rRNA genes in genomic sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 3100–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, P.P.; Lowe, T. M. tRNAscan-SE: Searching for tRNA genes in genomic sequences. Methods Mol Biol. 2019, 1962, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Bernt, M.; Donath, A.; Jühling, F.; Externbrink, F.; Florentz, C.; Fritzsch, G.; Pütz, J.; Middendorf, M.; Stadler, P.F. MITOS: Improved de novo metazoan mitochondrial genome annotation. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 69, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, G. Tandem repeats finder: A program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Nei, M.; Dudley, J.; Tamura, K. MEGA: A biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences. Brief Bioinform. 2008, 9, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perna, N.T.; Kocher, T.D. Patterns of nucleotide composition at fourfold degenerate sites of animal mitochondrial genomes. J. Mol. Evol. 1995, 41, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stothard, P. The Sequence Manipulation Suite: JavaScript programs for analyzing and formatting protein and DNA sequences. Biotechniques 2000, 28, 1102–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharp, P.M.; Tuohy, T.M.F.; Mosurski, K.R. Codon usage in yeast: Cluster analysis clearly differentiates highly and lowly expressed genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986, 14, 5125–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, D.G. CLUSTAL V: Multiple alignment of DNA and protein sequences. Methods Mol. Biol. 1994, 25, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MRBAYES 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree v1.4, A Graphical Viewer of Phylogenetic Trees. 2014. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 26 October 2020).
- Vargas Caro, C.A. Skate-ing on thin ice: Molecular Ecology of Longnose Skates in the Southeast Pacific Ocean. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, J.G.; Miya, M.; Lam, K.; Tay, B.H.; Danks, J.A.; Bell, J.; Walker, T.I.; Venkatesh, B. Evolutionary origin and phylogeny of the modern holocephalans (Chondrichthyes: Chimaeriformes): A mitogenomic perspective. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 2576–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boore, J.L. Animal mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 1767–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ojala, D.; Montoya, J.; Attardi, G. tRNA punctuation model of RNA processing in human mitochondria. Nature 1981, 290, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hester, J.; Atwater, K.; Bernard, A.; Francis, M.; Shivji, M.S. The complete mitochondrial genome of the basking shark Cetorhinus maximus (Chondrichthyes, Cetorhinidae). Mitochondr. DNA 2015, 26, 730–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boore, J.L.; Macey, J.R.; Medina, M. Sequencing and comparing whole mitochondrial genomes of animals. Methods Enzymol. 2005, 395, 311–348. [Google Scholar]
- Satoh, T.P.; Miya, M.; Mabuchi, K.; Nishida, M. Structure and variation of the mitochondrial genome of fishes. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitamura, T.; Takemura, A.; Watabe, S.; Taniuchi, T.; Shimizu, M. Mitochondrial DNA analysis for the cytochrome b gene and D-loop from the bull shark Carcharhinus leucas. Fish. Sci. 1996, 62, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castro, A.L.F.; Stewart, B.S.; Wilson, S.G.; Hueter, R.E.; Meekan, M.G.; Motta, P.J.; Bowen, B.W.; Karl, S.A. Population genetic structure of Earth’s largest fish, the whale shark (Rhincodon typus). Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 5183–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Macías, D.; Vázquez-Juárez, R.; Galván-Magaña, F.; Munguía-Vega, A. Variations of the mitochondrial control region sequence in whale sharks (Rhincodon typus) from the Gulf of California, Mexico. Fish. Res. 2007, 84, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.J.; Conroy, J.; Howell, W.H.; Kocher, T.D. Structure and evolution of teleost mitochondrial control region. J. Mol. Evol. 1995, 41, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.R.; Beckenbach, K.; Beckenbach, A.T.; Smith, M.J. Length variation, heteroplasmy and sequence divergence in the mitochondrial DNA of four species of sturgeon (Acipenser). Genetics 1996, 142, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoarau, G.; Rijnsdorp, A.D.; Van Der Veer, H.W.; Stam, W.T.; Olsen, J.L. Population structure of plaice (Pleuronectes platessa L.) in northern Europe: Microsatellites revealed large scale spatial and temporal homogeneity. Mol. Ecol. 2002, 11, 1165–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maisey, J.G. Higher elasmobranch phylogeny and biostratigraphy. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 1984, 82, 33–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigelow, H.W.; Schroeder, W.C. Sharks. In Fishes of Western North Atlantic, Part 1; Tee-Van, J., Breder, C.M., Hildebrand, S.F., Parr, A.E., Schroeder, W.C., Eds.; Yale University: New Haven, CT, USA, 1948; pp. 59–576. [Google Scholar]
- Bigelow, H.W.; Schroeder, W.C. Sawfishes, guitarfishes, skates, and rays. In Fishes of Western North Atlantic, Part 2; Tee-Van, J., Breder, C.M., Hildebrand, S.F., Parr, A.E., Schroeder, W.C., Eds.; Yale University: New Haven, CT, USA, 1953; pp. 1–514. [Google Scholar]
- Winchell, C.J.; Martin, A.P.; Mallatt, J. Phylogeny of elasmobranchs based on LSU and SSU ribosomal RNA genes. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2004, 31, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavan-Kumar, A.; Gireesh-Babu, P.; Babu, P.P.; Jaiswar, A.K.; Hari Krishna, V.; Prasasd, K.P. Molecular phylogeny of elasmobranchs inferred from mitochondrial and nuclear markers. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, C.R.L.; Pereira, F.; Silva, D.A.; Amorim, A.; de Carvalho, E.F. The mitogenomic phylogeny of the Elasmobranchii (Chondrichthyes). Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 2018, 29, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, R.G. Reproductive biology of lamnoid sharks. Environ. Biol. Fishes. 1993, 38, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcock, A. On the utero-gestation in Trygon bleekeri. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. 1892, 9, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dulvy, N.K.; Reynolds, J.D. Evolutionary transitions among egg-laying, live-bearing and maternal inputs in sharks and rays. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 1997, 264, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rolim, F.A.; Rotundo, M.M.; Vaske-Júnior, T. Notes on the reproductive biology of the Brazilian electric ray Narcine brasiliensis (Elasmobranchii: Narcinidae). J. Fish Biol. 2015, 89, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, K.L.; Maduna, S.N.; Bester-van der Merwe, A.E. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of the common smoothhound shark, Mustelus mustelus (Carcharhiniformes: Triakidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2018, 3, 962–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teshima, K.; Koga, S. Studies on sharks. V. Taxonomic characteristics of reproductive organs in Japanese. Mustelus. Mar. Biol. 1973, 23, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smale, M.J.; Compagno, L.J.V. Life history and diet of two southern African smoothhound sharks, Mustelus mustelus (Linnaeus, 1758) and Mustelus palumbes Smith, 1957 (Pisces: Triakidae). S. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 1997, 18, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wourms, J.P. Reproduction and development in chondrichthyan fishes. Am. Zool. 1977, 17, 379–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wourms, J.P.; Lombardi, J. Reflections on the evolution of piscine viviparity. Am. Zool. 1992, 32, 276–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallatt, J.; Winchell, C.J. Ribosomal RNA genes and deuterostome phylogeny revisited: More cyclostomes, elasmobranchs, reptiles, and a brittle star. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 43, 1005–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagno, L.J.V. Interrelationships of living elasmobranchs. Zoolog. J. Linnean Soc. 1973, 53, 15–61. [Google Scholar]
- McEachran, J.D.; Dunn, K.A.; Miyake, T. Interrelationships within the batoid fishes (Chondrichthyes: Batoidea). In Interrelationship of Fishes; Stiassney, M.L.J., Parenti, L.R., Johnson, G.D., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 63–84. [Google Scholar]
- Compagno, L.J.V. Phylogenetic relationships of living sharks and rays. Am. Zool. 1977, 17, 303–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Regan, C.T. A classification of the selachian fishes. Proc. Zool. Soc. London. 1906, 1906, 722–758. [Google Scholar]
- White, E.G. Interrelationships of the elasmobranchs with a key to the order Galea. Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 1937, 74, 25–138. [Google Scholar]
- White, E.G. A classification and phylogeny of the elasmobranch fishes. Am. Mus. Novit. 1936, 837, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Compagno, L.J.V. Relationships of the megamouth shark, Megachasma pelagios (Lamniformes, Megachasmidae), with comments on its feeding habits. NOAA Tech. Rep. NMFS 1990, 90, 357–379. [Google Scholar]
- Naylor, G.J.P.; Martin, A.P.; Mattison, E.; Brown, W.M. The inter-relationships of lamniform sharks: Testing phylogenetic hypotheses with sequence data. In Molecular Systematics of Fishes; Kocher, T.D., Stepien, C., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 199–218. [Google Scholar]
- Naylor, G.J.P.; Caira, J.N.; Jensen, K.; Rosana, K.A.M.; Straube, N.; Lakner, C. Elasmobranch phylogeny: A mitochondrial estimate based on 595 species. In Biology of Sharks and Their Relatives, 2nd ed.; Carrier, J.C., Musick, J.A., Heithaus, M.R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 31–56. [Google Scholar]
- Iglésias, S.P.; Lecointre, G.; Sellos, D.Y. Extensive paraphylies within sharks of the order Carcharhiniformes inferred from nuclear and mitochondrial genes. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2005, 34, 569–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues-Filho, L.F.S.; Rocha, T.C.; Rêgo, P.S.; Schneider, H.; Sampaio, I.; Vallinoto, M. Identification and phylogenetic inferences on stocks of sharks affected by the fishing industry off the Northern coast of Brazil. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2009, 32, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaitáan-Espitia, J.D.; Solano-Iguaran, J.J.; Tejada-Martinez, D.; Quintero-Galvis, J.F. Mitogenomics of electric rays: Evolutionary considerations within Torpediniformes (Batoidea; Chondrichthyes). Zoolog. J. Linnean Soc. 2016, 178, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Species | Common Name | IUCN Conservation Status | GenBank Accession Number | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Globally | Mediterranean Sea | |||
| Bathytoshia centroura | Roughtail stingray | VU | Not evaluated | MT274568 |
| Dasyatis tortonesei | Tortonese’s stingray | DD | VU | MT274569 |
| Galeus melastomus | Blackmouth catshark | LC | LC | MT274570 |
| Gymnura altavela | Spiny butterfly ray | VU | CR | MT274571 |
| Odontaspis ferox | Smalltooth sand tiger | VU | CR | MT274572 |
| Prionace glauca | Blue shark | NT | CR | MT274573 |
| Raja undulata | Undulate ray | EN | NT | MT274574 |
| Squalus blainville | Longnose spurdog | DD | DD | MT274575 |
| Torpedo marmorata | Marbled electric ray | DD | LC | MT274576 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kousteni, V.; Mazzoleni, S.; Vasileiadou, K.; Rovatsos, M. Complete Mitochondrial DNA Genome of Nine Species of Sharks and Rays and Their Phylogenetic Placement among Modern Elasmobranchs. Genes 2021, 12, 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12030324
Kousteni V, Mazzoleni S, Vasileiadou K, Rovatsos M. Complete Mitochondrial DNA Genome of Nine Species of Sharks and Rays and Their Phylogenetic Placement among Modern Elasmobranchs. Genes. 2021; 12(3):324. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12030324
Chicago/Turabian StyleKousteni, Vasiliki, Sofia Mazzoleni, Katerina Vasileiadou, and Michail Rovatsos. 2021. "Complete Mitochondrial DNA Genome of Nine Species of Sharks and Rays and Their Phylogenetic Placement among Modern Elasmobranchs" Genes 12, no. 3: 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12030324
APA StyleKousteni, V., Mazzoleni, S., Vasileiadou, K., & Rovatsos, M. (2021). Complete Mitochondrial DNA Genome of Nine Species of Sharks and Rays and Their Phylogenetic Placement among Modern Elasmobranchs. Genes, 12(3), 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12030324








