Screening Discriminating SNPs for Chinese Indigenous Pig Breeds Identification Using a Random Forests Algorithm
Highlights
- This paper describes a method based on the Random Forest algorithm to screen a collection of SNPs for the genetic identification of various pig breeds.
- The method was tested on a real dataset of more than 1000 individuals from 23 breeds and showed an identification accuracy of 99.3%.
- The method can be applied to whole genome resequencing data or SNP microarray datasets for the efficient screening of SNPs.
- The method provides an efficient way to analyze the genomic breed composition of pig breeds.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Information
2.2. LD Pruning
2.3. Random Forest Analysis
3. Results
3.1. LD Pruning
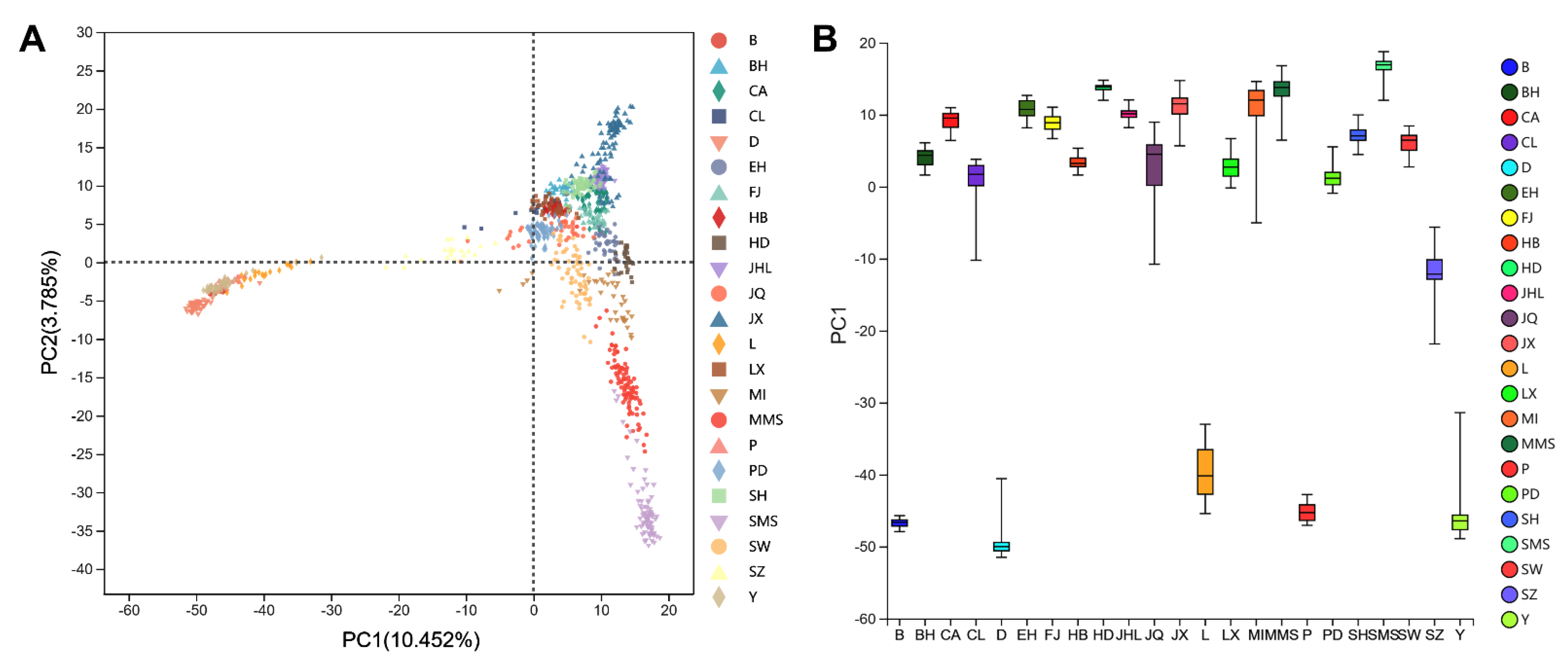
3.2. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3.3. The Number of Decision Trees in RF Model
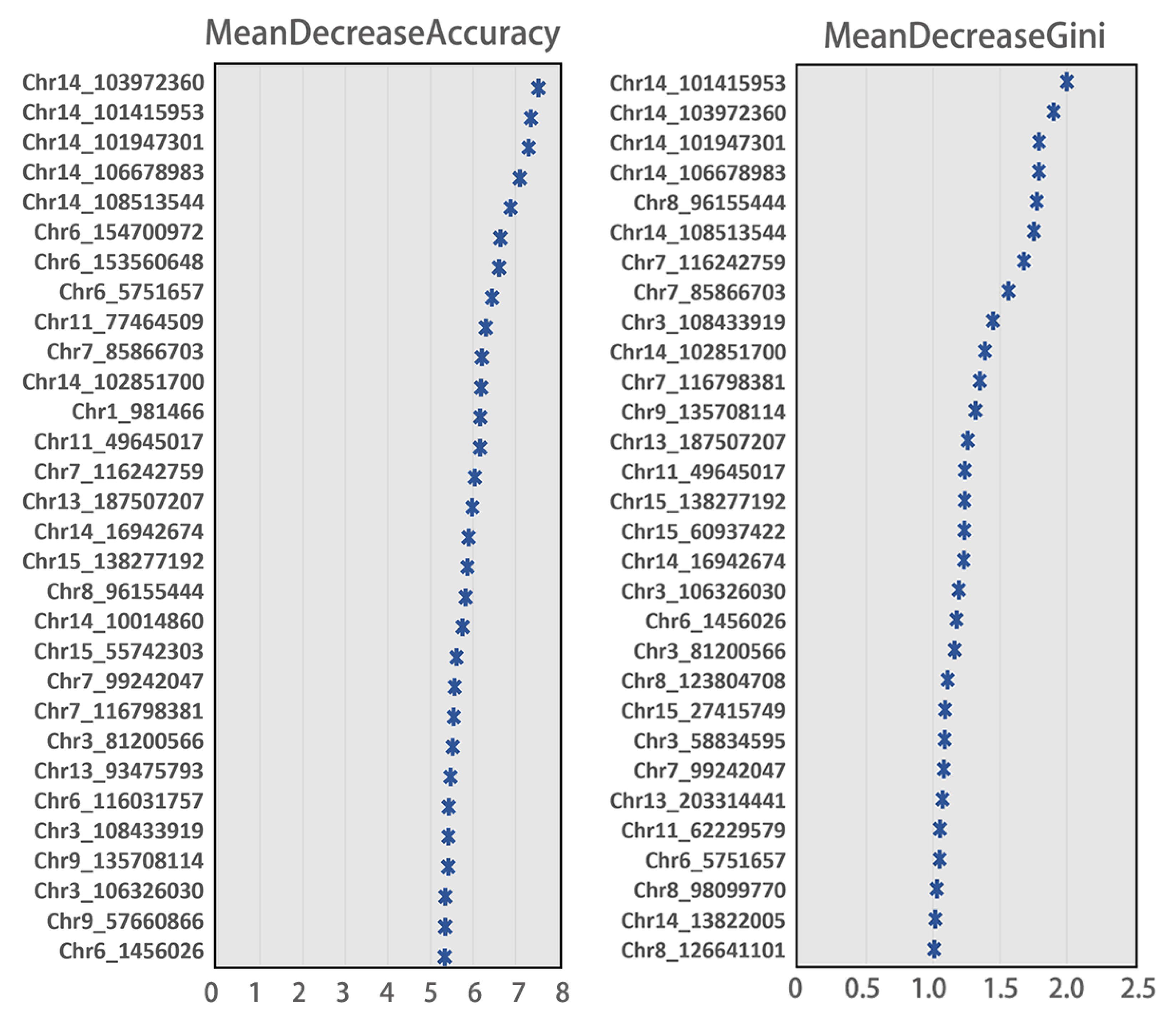
3.4. The Most Discriminating SNPs
3.5. Correlation between the Number of SNPs and Error Rate
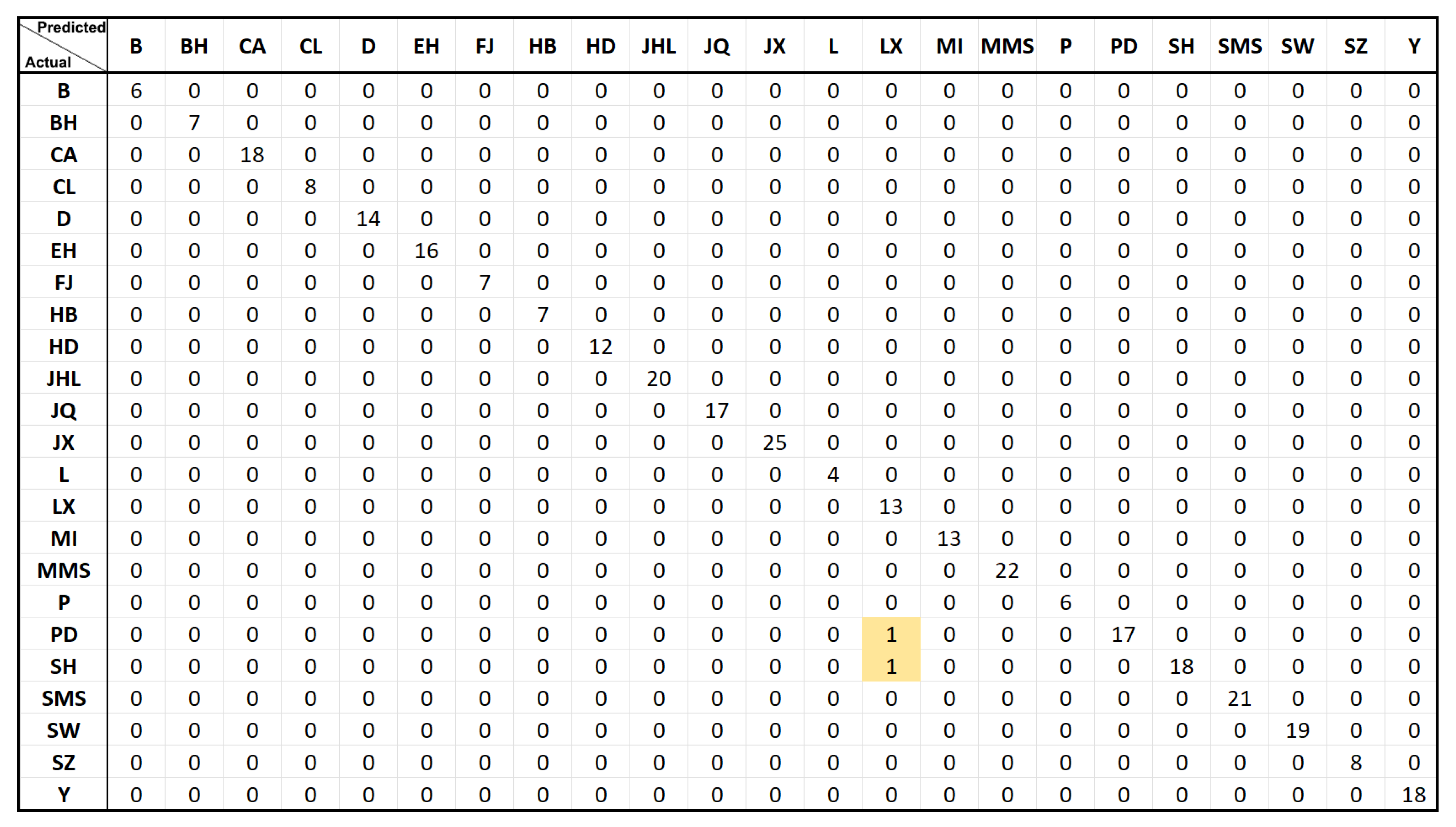
3.6. Classification Evaluation of a Panel of 1000 SNPs and 100 SNPs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Q.-b.; Oyelami, F.O.; Qadri, Q.R.; Sun, H.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Q.-S.; Pan, Y.-C. Identifying the unique characteristics of the Chinese indigenous pig breeds in the Yangtze River Delta region for precise conservation. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolini, F.; Galimberti, G.; Calò, D.; Schiavo, G.; Matassino, D.; Fontanesi, L. Combined use of principal component analysis and random forests identify population-informative single nucleotide polymorphisms: Application in cattle breeds. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2015, 132, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurgul, A.; Semik, E.; Pawlina, K.; Szmatoła, T.; Jasielczuk, I.; Bugno-Poniewierska, M. The application of genome-wide SNP genotyping methods in studies on livestock genomes. J. Appl. Genet. 2014, 55, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferdosi, M.H.; Kinghorn, B.P.; Van der Werf, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Gondro, C. hsphase: An R package for pedigree reconstruction, detection of recombination events, phasing and imputation of half-sib family groups. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, L.F.; McEwan, J.C.; Miller, S.P.; Pickering, N.K.; Bain, W.E.; Dodds, K.G.; Schenkel, F.S.; Clarke, S.M. Genetic diversity of a New Zealand multi-breed sheep population and composite breeds’ history revealed by a high-density SNP chip. BMC Genet. 2017, 18, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and regression by randomForest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Fang, L.; Cui, L.; Bai, S. Application of data mining for predicting hemodynamics instability during pheochromocytoma surgery. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2020, 20, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ishwaran, H. Random forests for genomic data analysis. Genomics 2012, 99, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavo, G.; Bertolini, F.; Galimberti, G.; Bovo, S.; Dall’Olio, S.; Costa, L.N.; Gallo, M.; Fontanesi, L. A machine learning approach for the identification of population-informative markers from high-throughput genotyping data: Application to several pig breeds. Animal 2020, 14, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, B.L.; Zhou, Y.; Browning, S.R. A one-penny imputed genome from next-generation reference panels. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 103, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Levine, D.; Shen, J.; Gogarten, S.M.; Laurie, C.; Weir, B.S. A high-performance computing toolset for relatedness and principal component analysis of SNP data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3326–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Yu, G.; Shi, C.; Liu, L.; Guo, Q.; Han, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, L.; Liu, B.; Gao, H. Majorbio Cloud: A one-stop, comprehensive bioinformatic platform for multiomics analyses. iMeta 2022, 1, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warr, A.; Affara, N.; Aken, B.; Beiki, H.; Bickhart, D.M.; Billis, K.; Chow, W.; Eory, L.; Finlayson, H.A.; Flicek, P. An improved pig reference genome sequence to enable pig genetics and genomics research. Gigascience 2020, 9, giaa051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Z.; Xu, J.; Yin, D.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, X.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, S.; Li, X. rMVP: A memory-efficient, visualization-enhanced, and parallel-accelerated tool for genome-wide association study. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2021, 19, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, A.; Megens, H.; Crooijmans, R.; Schook, L.; Groenen, M. Identification of high utility SNPs for population assignment and traceability purposes in the pig using high-throughput sequencing. Anim. Genet. 2011, 42, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, S.; Wiener, P.; Archibald, A.L.; Law, A.; Schnabel, R.D.; McKay, S.D.; Taylor, J.F.; Ogden, R. Evaluation of approaches for identifying population informative markers from high density SNP chips. BMC Genet. 2011, 12, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.; Abas, Z.; Dadousis, C.; Lykidis, D.; Paschou, P.; Drineas, P. Tracing cattle breeds with principal components analysis ancestry informative SNPs. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, D.; Cho, S.; Manjula, P.; Choi, N.; Kim, Y.-K.; Koh, Y.J.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.-Y.; Lee, J.H. Identification of Target Chicken Populations by Machine Learning Models Using the Minimum Number of SNPs. Animals 2021, 11, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulsegge, B.; Calus, M.; Windig, J.; Hoving-Bolink, A.; Maurice-van Eijndhoven, M.; Hiemstra, S. Selection of SNP from 50K and 777K arrays to predict breed of origin in cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 5128–5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Region | Breeds | Code | Number of Individuals |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cosmopolitan | Western Duroc | D | 49 |
| Landrace | L | 21 | |
| Yorkshire | Y | 53 | |
| Pietrain | P | 20 | |
| Berkshire | B | 16 | |
| Jiangsu, China | Small Meishan | SMS | 75 |
| Mi | MI | 36 | |
| Erhualian | EH | 42 | |
| Huaibei | HB | 34 | |
| Hongdenglong | HD | 30 | |
| Jiangquhai | JQ | 38 | |
| Shan | SZ | 20 | |
| Zhejiang, China | Bihu | BH | 30 |
| Chunan | CA | 59 | |
| Chalu | CL | 22 | |
| Jinhualiangtouwu | JHL | 57 | |
| Lanxi | LX | 40 | |
| Shengxianhua | SH | 64 | |
| Jiangxing Black | JX | 91 | |
| Shanghai, China | Middel Meishan | MMS | 97 |
| Shawutou | SW | 65 | |
| Fengjing | FJ | 32 | |
| Pudong White | PD | 68 | |
| Total | 23 breeds | / | 1059 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, J.; Sun, L.; Zhang, S.; Xu, J.; He, M.; Zhang, D.; Wu, C.; Dai, J. Screening Discriminating SNPs for Chinese Indigenous Pig Breeds Identification Using a Random Forests Algorithm. Genes 2022, 13, 2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122207
Gao J, Sun L, Zhang S, Xu J, He M, Zhang D, Wu C, Dai J. Screening Discriminating SNPs for Chinese Indigenous Pig Breeds Identification Using a Random Forests Algorithm. Genes. 2022; 13(12):2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122207
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Jun, Lingwei Sun, Shushan Zhang, Jiehuan Xu, Mengqian He, Defu Zhang, Caifeng Wu, and Jianjun Dai. 2022. "Screening Discriminating SNPs for Chinese Indigenous Pig Breeds Identification Using a Random Forests Algorithm" Genes 13, no. 12: 2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122207
APA StyleGao, J., Sun, L., Zhang, S., Xu, J., He, M., Zhang, D., Wu, C., & Dai, J. (2022). Screening Discriminating SNPs for Chinese Indigenous Pig Breeds Identification Using a Random Forests Algorithm. Genes, 13(12), 2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122207






