Population Genetics and Anastomosis Group’s Geographical Distribution of Rhizoctonia solani Associated with Soybean
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Characterization of the Distribution and Frequency of Anastomosis Groups Assoiated with Soybean
2.3. Sequences Alignments
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Principal Coordinate Analysis (PCoA) and Sequence Similarities
3. Results
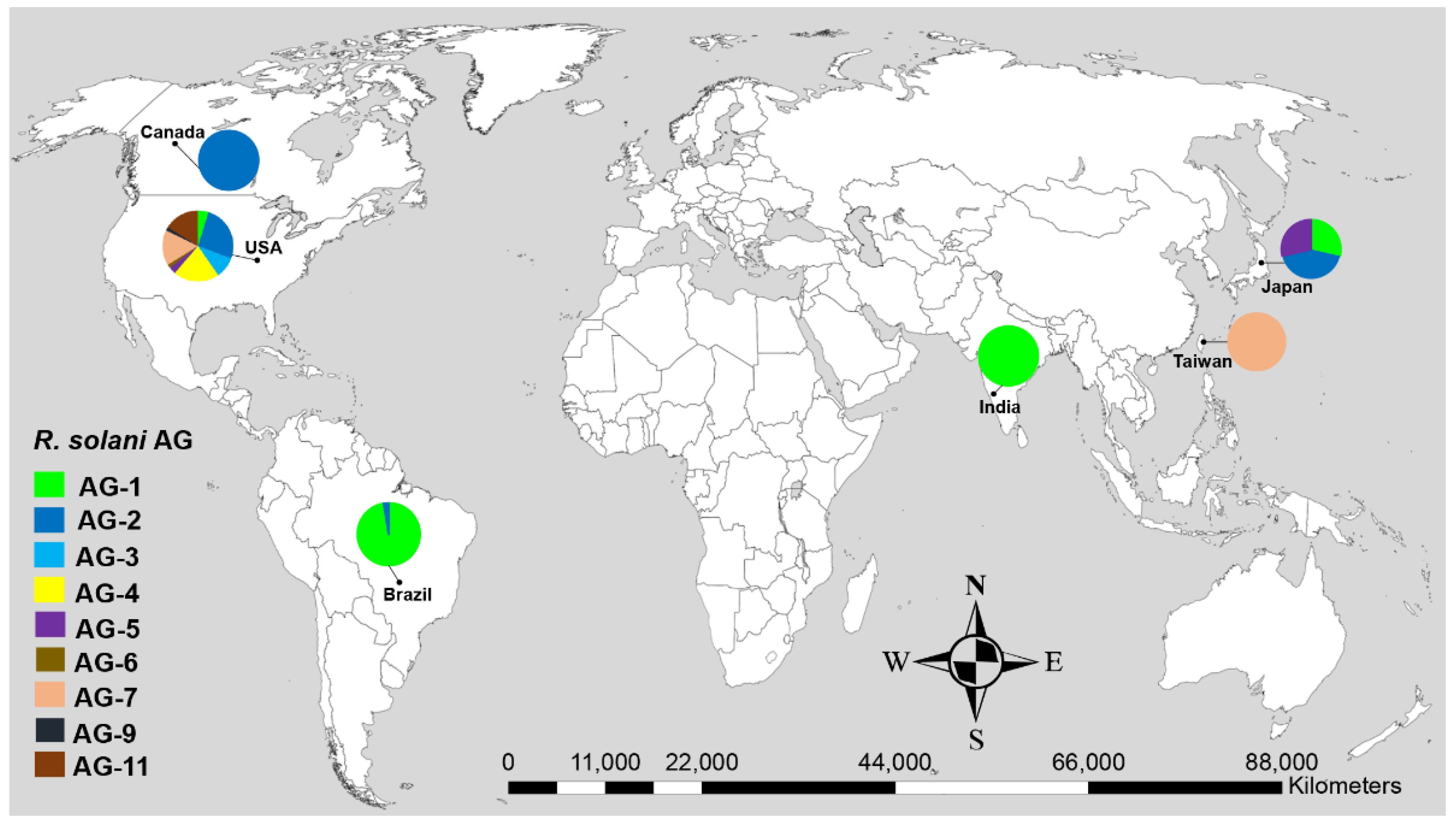
3.1. Distribution of Anastomosis Groups
3.2. Genetic Diversity of Anastomosis Groups
3.3. Relationship between Genetic Diversity of Anastomosis Groups and Their Geographic Origin
3.4. Genetic Relatedness among and within Clades and Subclades Representing Anast Mosis Groups
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions, Limitations and Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Surbhi, K.; Singh, K.P.; Singh, N.K.; Aravind, T. Assessment of genetic diversity among soybean genotypes differing in response to aerial blight (Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn) using SSR markers. J. Phytopathol. 2021, 169, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowska, S.; Łoziński, M.; Marczewski, K.; Kozak, M.; Schmidtke, K. Influence of priming on germination, development, and yield of soybean varieties. Open Agric. 2020, 5, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, I.; Lewandowska, S.; Niemczyk, K.; Detyna, J.; Bujak, H.; Arik, P.; Bartniczak, A. Germination of soybean seeds exposed to the static/alternating magnetic field and algal extract. Eng. Life Sci. 2019, 19, 986–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi-Oyetunde, O.; Bradley, C. Rhizoctonia solani: taxonomy, population biology and management of Rhizoctonia seedling disease of soybean. Plant pathol. 2018, 67, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi-Oyetunde, O.O.; Bradley, C.A. Identification and characterization of Rhizoctonia species associated with soybean seedling disease. Plant Dis. 2017, 101, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenille, R.C.; De Souza, N.L.; Kuramae, E.E. Characterization of Rhizoctonia solani associated with soybean in Brazil. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2002, 108, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetina, K.C.; Stetina, S.R.; Russin, J.S. Comparison of severity assessment methods for predicting yield loss to Rhizoctonia foliar blight in soybean. Plant Dis. 2006, 90, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampi, M.B.; Meyer, M.C.; Costa, M.J.; Zala, M.; McDonald, B.A.; Ceresini, P.C. Genetic structure of populations of Rhizoctonia solani anastomosis group-1 IA from soybean in Brazil. Phytopathol. 2008, 98, 932–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copley, T.R.; Duggavathi, R.; Jabaji, S. The transcriptional landscape of Rhizoctonia solani AG1-IA during infection of soybean as defined by RNA-seq. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0184095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Heuvel, J. Rhizoctonia Species: Taxonomy, Molecular Biology, Ecology, Pathology and Disease Control; Sneh, B., Jabaji-Hare, S., Neate, S.M., Dijst, G.N., Eds.; Kluwer Academic: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. XVI + 577. [Google Scholar]
- Urrea, K.; Rupe, J.C.; Rothrock, C.S. Effect of fungicide seed treatments, cultivars, and soils on soybean stand establishment. Plant Dis. 2013, 97, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, S.; Bowen, C.R.; Slaminko, T.L.; Hobbs, H.A.; Hartman, G.L.; Nachilima, C.; Chigeza, G.; Chibanda, M.; Mushoriwa, H.; Diers, B.D.; et al. A public program to evaluate commercial soybean cultivars for pathogen and pest resistance. Plant Dis. 2013, 97, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogoshi, A. Ecology and pathogenicity of anastomosis and intraspecific groups of Rhizoctoniasolani Kuhn. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1987, 25, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy-Lutz, G.; Steadman, J.R.; Higgins, B.; Powers, K. Genetic variation among isolates of the web blight pathogen of common bean based on PCR-RFLP of the ITS-rDNA region. Plant Dis. 2003, 87, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuninaga, S.; Natsuaki, T.; Takeuchi, T.; Yokosawa, R. Sequence variation of the rDNA ITS regions within and between anastomosis groups in Rhizoctonia solani. Curr. Genet. 1997, 32, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carling, D.E. Grouping in Rhizoctonia solani by hyphal anastomosis. In Rhizoctonia species: Taxonomy, molecular biology, ecology, pathology, and disease control; Sneh, B., Jabaji-Hare, S., Neate, S.M., Dijst, G.N., Eds.; Kluwer Academic: Dordrecht, the Netherlands, 1996; pp. 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Kuninaga, S.; Godoy-Lutz, G.; Yokosawa, R. rDNA-ITS nucleotide sequences analysis of Thanatephoruscucumeris AG-1 associated with web blight on common beans in Central America and Caribbean. Ann. Phytopathol. Soc. Japan. 2002, 68, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carling, D.E.; Kuninaga, S.; Brainard, K.A. Hyphal anastomosis reactions, rDNA-internal transcribed spacer sequences, and virulence levels among subsets of Rhizoctonia solani anastomosis group-2 (AG-2) and AG-BI. Phytopathol. 2002, 92, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Ablett, G.R.; Anderson, T.R.; Rajcan, I.; Schaafsma, A.W. Anastomosis groups of Rhizoctoniasolani associated with soybean root and hypocotyl rot in Ontario and resistance of accession PI 442031 to different anastomosis groups. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2005, 27, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carling, D.E.; Rothrock, C.S.; MacNish, G.C.; Sweetingham, M.W.; Brainard, K.A.; Winters, S.W. Characterization of anastomosis group 11 (AG-11) of Rhizoctonia solani. Phytopathol. 1994, 84, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, B.; Helms, T.; Christianson, T.; Kural, I. Characterization and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia from soybean. Plant Dis. 1996, 80, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, R.E.; Carling, D.E.; Mullinix, B.G. Characterization and comparison of isolates of Rhizoctonia solani AG-7 from Arkansas, Indiana, and Japan, and select AG-4 isolates. Plant Dis. 1996, 80, 1424–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guleria, S.; Aggarwal, R.; Thind, T.S.; Sharma, T.R. Morphological and pathological variability in rice isolates of Rhizoctoniasolani and molecular analysis of their genetic variability. JJ. Plant Pathol. 2007, 155, 654–661. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Vera, A.D.; Bernardes-de-Assis, J.; Zala, M.; McDonald, B.A.; Correa-Victoria, F.; Graterol-Matute, E.J.; Ceresini, P.C. Divergence between sympatric rice-and maize-infecting populations of Rhizoctonia solani AG-1 IA from Latin America. Phytopathol. 2010, 100, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padasht-Dehkaei, F.; Ceresini, P.C.; Zala, M.; Okhovvat, S.M.; Nikkhah, M.J.; McDonald, B.A. Population genetic evidence that basidiospores play an important role in the disease cycle of rice-infecting populations of Rhizoctonia solani AG-1 IA in Iran. Plant Pathol. 2013, 62, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampi, M.B.; Gale, L.R.; Lemos, E.G.; Ceresini, P.C. Distinctively variable sequence-based nuclear DNA markers for multilocusphylogeography of the soybean-and rice-infecting fungal pathogen Rhizoctonia solani AG-1 IA. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2009, 32, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, P.; Gnanamanickam, S.; Höfte, M. Characterization, genetic structure, and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia spp. associated with rice sheath diseases in India. Phytopathol. 2007, 97, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosewich, U.L.; Pettway, R.E.; McDonald, B.A.; Kistler, H.C. High levels of gene flow and heterozygote excess characterize Rhizoctonia solani AG-1 IA (Thanatephoruscucumeris ) from Texas. Fungal Genet. Biol. 1999, 28, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, L.M.; Wang, Z.G.; Huang, S.W. Genetic Structure and Aggressiveness of Rhizoctoniasolani AG 1-IA, the Cause of Sheath Blight of Rice in Southern C hina. J. Plant Pathol. 2013, 161, 753–762. [Google Scholar]
- Keijer, J.; Houterman, P.M.; Dullemans, A.M.; Korsman, M.G. Heterogeneity in electrophoretic karyotype within and between anastomosis groups of Rhizoctonia solani. Mycol. Res. 1996, 100, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carling, D.E.; Kuninaga, S. DNA base sequence homology in Rhizoctoniasolani Kuhn: Inter- and intragroup relatedness of anastomosis group-9. Phytopathol. 1990, 80, 1362–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenille, R.C.; Ciampi, M.B.; Kuramae, E.E.; Souza, N.L. Identification of Rhizoctonia solani associated with soybean in Brazil by rDNA-ITS sequences. Fitopatol. Bras. 2003, 28, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampi, M.B.; Kuramae, E.E.; Fenille, R.C.; Meyer, M.C.; Souza, N.L.; Ceresini, P.C. Intraspecific Evolution of Rhizoctonia solani AG-1 IA Associated with Soybean and Rice in Brazil based on Polymorphisms at the ITS-5.8S rDNA Operon. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2005, 113, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monazzah, M.; Esfahani, M.N.; Sattar, T.E. Genetic structure and proteomic analysis associated in potato to Rhizoctonia solani AG-3PT-stem canker and black scurf. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2022, 122, 101905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boysen, M.; Borja, M.; del Moral, C.; Salazar, O.; Rubio, V. Identification at strain level of Rhizoctonia solani AG4 isolates by direct sequence of asymmetric PCR products of the ITS regions. Curr. Genet. 1996, 29, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, O.; Julián, M.C.; Rubio, H.V. Phylogenetic Grouping of Cultural Types of Rhizoctonia solani AG 2-2 Based on Ribosomal ITS Sequences. Mycologia 2000, 92, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, D.; Carling, D.E.; Kuninaga, S.; Vilgalys, R.; Cubeta, M.A. Ribosomal DNA systematics of Ceratobasidium and Thanatephorus with Rhizoctonia anamorphs. Mycologia 2001, 93, 1138–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, M.; Kuninaga, S.; Hyakumachi, M.; Sneh, B. The advancing identification and classification of Rhizoctonia spp. using molecular and biotechnological methods compared with the classical anastomosis grouping. Mycoscience 2006, 47, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkura, M.; Abawi, G.S.; Smart, C.D.; Hodge, K.T. Diversity and aggressiveness of Rhizoctonia solani and Rhizoctonia -like fungi on vegetables in New York. Plant Dis. 2009, 93, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, I.; Wendel, J.F. Ribosomal ITS sequences and plant phylogenetic inference. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 29, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharon, M.; Sneh, B.; Kuninaga, S.; Hyakumachi, M.; Naito, S. Classification of Rhizoctonia spp. using rDNA-ITS sequence analysis supports the genetic basis of the classical anastomosis grouping. Mycoscience 2008, 49, 93–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Tseng, M.N.; Chang, H.X. First Report of Soybean Seedling Disease caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG-7 in Taiwan. Plant Dis. 2021, 106, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamta, M.; Singh, K.P. Prevalence and severity of Rhizoctonia aerial blight of soybean in Uttarakhand. Indian J. Ecol. 2017, 44, 417–419. [Google Scholar]
- Misawa, T.; Komatsu, T. Occurrence of Rhizoctonia root rot of soybean caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG-2-2IV and adzuki bean caused by R. solani AG-1 IB in commercial fields of Hokkaido. Annu. Rep. Soc. Plant Prot. North Jpn. 2011, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Arias, M.M.D.; Munkvold, G.P.; Ellis, M.L.; Leandro, L.F.S. Distribution and frequency of Fusarium species associated with soybean roots in Iowa. Plant Dis. 2013, 97, 1557–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A User-Friendly Biological Sequence Alignment Editor and Analysis Program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nuclc Acids Symposium Series 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharon, M.; Freeman, S.; Kuninaga, S.; Sneh, B. Genetic diversity, anastomosis groups and virulence of Rhizoctonia spp. from strawberry. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2007, 117, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods. 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neath, A.A.; Cavanaugh, J.E. The Bayesian information criterion: Background, derivation, and applications. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Comput. Stat. 2012, 4, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.C.; Chang, C.W.; Wang, C.J. First report of Rhizoctonia solani AG-4 HG-I causing leaf blight disease on Cattleya × hybrid in Taiwan. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M. Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1993, 10, 512–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar]
- Nei, M.; Kumar, S. Molecular Evolution and Phylogenetics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, J.J.; Bitincka, L.; Smalley, J. MatGAT: An application that generates similarity/identity matrices using protein or DNA sequences. BMC Bioinformatics 2003, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower, J.C. A general coefficient of similarity and some of its properties. Biometrics 1971, 22, 857–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, C.; Zheng, D.; Wei, L.; Dai, L.; Liu, S. Research Progress of Soybean Root Rot. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin 2016, 32, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Guo, R.J.; Dong, L.S. Control of soybean root rot disease with silver-carrying antimicrobial preparations. ActaPhytophylacica Sin. 2006, 36, 550–554. [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana, H. Rhizoctonia solani root rot epidemic of Soybeans in Central Iowa 1967. Plant Disease Reporter 1968, 52, 613–614. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Sinclair, J.B. Isolates of Rhizoctonia solani anastomosis group 2-2 pathogenic to soybean. Plant Dis. 1991, 75, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyolo, N.G.; Lipps, P.E.; Schmitthenner, A.F. Anastomosis grouping and variation in virulence among isolates of Rhizoctoniasolani associated with dry bean and soybean in Ohio and Zaire. Phytopathol 1993, 83, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavarro-Mesa, E.; Ceresini, P.; Pereira, D.; Vicentini, S.; Silva, T.; Ramos-Molina, L.; Negrisoli, M.; Schurt, D.; Vieira Júnior, J.R. A broad diversity survey of Rhizoctonia species from the Brazilian Amazon reveals the prevalence of R. solani AG-1 IA on signal grass and the new record of AG-1 IF on cowpea and soybeans. Plant Pathol 2020, 69, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.R.; Tenuta, A.U. Diseases of soybean in Ontario and estimated yield losses, 1994, 1996–2000. Can. Plant Dis. Surv. 2001, 81, 133–135. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, K.-F.; Hwang, S.-F.; Ahmed, H.U.; Strelkov, S.E.; Harding, M.W.; Conner, R.L.; McLaren, D.L.; Gossen, B.D.; Turnbull, G.D. Disease reaction to Rhizoctonia solani and yield losses in soybean. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2017, 98, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, D.; Pushpendra, K.S.; Adhikari, S.; Rani, S. Screening of soybean germplasm for important disease prevalent in North India. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2018, 6, 2731–2733. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, S.C.; Tripathi, A.; Upadhyay, B.K.; Deka, U.K. Diversity of Rhizoctoniasolani associated with pulse crops in different agro-ecological regions of India. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 1699–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy-Lutz, G.; Kuninaga, S.; Steadman, J.R.; Powers, K. Phylogenetic analysis of Rhizoctoniasolani subgroups associated with web blight symptoms on common bean based on ITS-5.8S rDNA. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2008, 74, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzhinji, N.; Truter, M.; Woodhall, J.W.; Van der Waals, J.E. Anastomosis groups and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia solani and binucleate Rhizoctonia from potato in South Africa. Plant Dis. 2015, 99, 1790–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budge, G.E.; Shaw, M.W.; Lambourne, C.; Jennings, P.; McPherson, M. Characterization and origin of infection of Rhizoctoniasolani associated with Brassica oleracea crops in the UK. Plant Pathol. 2010, 58, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, D.; Cubeta, M.A.; Vilgalys, R. Phylogenetic utility of indels within ribosomal DNA and β-tubulin sequences from fungi in the Rhizoctonia solani species complex. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2006, 40, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, T.; Hyakumachi, M.; Arora, D.K. Genetic relatedness among and within different Rhizoctoniasolani anastomosis groups as assessed by RAPD, ERIC and REP-PCR. Microbiol. Res. 1999, 154, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, T.; Mghalu, J.M.; Priyatomojo, A.; Hyakumachi, M. Comparison of sequences for the internal transcribed spacer region in Rhizoctoniasolani AG 1-ID and other subgroups of AG 1. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2004, 70, 270–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtonen, M.J.; Ahvenniemi, P.; Wilson, P.S.; German-Kinnari, M.; Valkonen, J.P.T. Biological diversity of Rhizoctonia solani (AG-3) in a northern potato-cultivation environment in Finland. Plant Pathol. 2008, 57, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broders, K.D.; Parker, M.L.; Melzer, M.S.; Boland, G.J. Phylogenetic diversity of Rhizoctoniasolani associated with canola and wheat in Alberta, Manitoba, and Saskatchewan. Plant Dis. 2014, 98, 1695–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, E.J.; Carter, D.A. Phylogenetic placement and host specificity of mycorrhizal isolates belonging to AG-6 and AG-12 in the Rhizoctonia solani species complex. Mycologia 2001, 93, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gónzalez, D.; Rodriguez-Carres, M.; Boekhout, T.; Stalpers, J.; Kuramae, E.E.; Nakatani, A.K.; Vilgalys, R.; Cubeta, M.A. Phylogenetic relationships of Rhizoctonia fungi within the Cantharellales. Fungal Biol. 2016, 120, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| AG | AG Subgroups | Geographical Origin | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA | Brazil | Canada | Taiwan | India | Japan | Total | aF | |||
| AG-1 | AG-1-IA | 1 | 36 | 2 | 39 | 33.91 | 40.00 | |||
| AG-1-IB | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2.61 | ||||||
| AG-1-IC | 1 | 1 | 0.87 | |||||||
| AG-1-IF | 1 | 1 | 0.87 | |||||||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.87 | |||||||
| AG-1-ID | 1 | 1 | 0.87 | |||||||
| AG-2 | AG-2-1 | 3 | 3 | 2.61 | 19.13 | |||||
| AG-2-2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1.74 | ||||||
| AG-2-3 | 3 | 3 | 2.61 | |||||||
| AG-2-2IIIB | 12 | 2 | 14 | 12.17 | ||||||
| AG-3 | 6 | 6 | 5.22 | 5.22 | ||||||
| AG-4 | AG-4 | 1 | 1 | 0.87 | 11.30 | |||||
| AG-4-HGI | 2 | 2 | 1.74 | |||||||
| AG-4-HGII | 5 | 5 | 4.35 | |||||||
| AG-4-HGIII | 5 | 5 | 4.35 | |||||||
| AG-5 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 3.48 | 3.48 | |||||
| AG-6 | 1 | 1 | 0.87 | 0.87 | ||||||
| AG-7 | 10 | 2 | 12 | 10.43 | 10.43 | |||||
| AG-9 | 1 | 1 | 0.87 | 0.87 | ||||||
| AG-11 | 10 | 10 | 8.70 | 8.70 | ||||||
| Total | 62 | 39 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 7 | ||||
| Clades and Subclades | Ia (AG-11 and AG-5) | Ib (AG-2) | Ic (AG-3) | Id (AG-4) | Ie (AG-7) | IIa (AG-1) | Outgroup | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ia-1 | Ia-2 | Ib-1 | Ib-2 | Ib-3 | Id-1 | Id-2 | Id-3 | Id-4 | IIa-1 | IIa-2 | |||||
| Ia (AG-11 and AG-5) | Ia-1 | 77–99.6 | |||||||||||||
| Ia-2 | 85.8–93 | 93–99.4 | |||||||||||||
| Ib (AG-2) | Ic-1 | 84.6–89.18 | 81.9–89 | 97.2–99.4 | |||||||||||
| Ib-2 | 80.7–85.1 | 76.1–84.6 | 83.7–86 | 90.9–96.5 | |||||||||||
| Ib-3 | 79.4–85.7 | 74–85.1 | 81.5–85.4 | 92–99.1 | 91.6–100 | ||||||||||
| Ic (AG-3) | 82.3–88.3 | 83.8–84.9 | 91.4–92.5 | 82.7–85.2 | 79.3–85.7 | 97.7–99.4 | |||||||||
| Id (AG-4) | Ie-1 | 80.7–84.6 | 80.1–80.2 | 85.1–85.9 | 82–82.8 | 77.2–83.8 | 81.8–84.9 | 99.4 * | |||||||
| Id-2 | 79.3–80.8 | 79.4–84.2 | 80.7–81.9 | 78.3–80.5 | 75.8–82.5 | 78.3–80.6 | 91.1–94 | 99.6–100 | |||||||
| Id-3 | 79.5–84.1 | 76–84.5 | 82.5–86 | 74.6–83.3 | 76.2–84.3 | 81.7–83.89 | 87.1–96.4 | 81.7–94.4 | 87.4–99.1 | ||||||
| Id-4 | 79.1–82.8 | 79.6–83.6 | 81.8–83.3 | 75.5–77.1 | 72.5–77.1 | 81.9–82.2 | 82.6–82.9 | 86.1–86.4 | 82.6–83.6 | 87.2 * | |||||
| Ie (AG-7) | 77.2–83.8 | 76–84.6 | 83.3–86.3 | 79.9–85.9 | 74.7–82.3 | 78.4–85.9 | 81.5–87.9 | 80–83.7 | 84.4–87.5 | 83.1–84.6 | 82.1–99.1 | ||||
| IIa (AG-1) | IIa-1 | 72.5–79.8 | 74–80.5 | 74.7–77.8 | 69.6–75.2 | 69.5–77.5 | 73.3–76.5 | 76.2–77.9 | 81.7–83.4 | 74.4–78.5 | 79.4–81.6 | 74.3–85.5 | 87.9–100 | ||
| IIa-2 | 72.8–79.4 | 73–83.7 | 75.8–80.6 | 69.5–80.5 | 70.4–80.2 | 73–79.8 | 77.9–82.9 | 81.9–88.8 | 75.7–83.3 | 81.7–82.8 | 74.7–83.6 | 76.3–92.2 | 89.5–100 | ||
| Outgroup | 47.4–51.3 | 46.2–49.1 | 50–51 | 47.3–52.7 | 48.4–52.5 | 51.5–52.5 | 51.5–51.9 | 46.6–48 | 51.1–53.1 | 48.3 * | 48.8–49.3 | 39.1–42.3 | 40.9–46 | 100 * | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbas, A.; Fang, X.; Iqbal, S.; Naqvi, S.A.H.; Mehmood, Y.; Rao, M.J.; Hassan, Z.; Ortiz, R.M.; Baazeem, A.; Moustafa, M.; et al. Population Genetics and Anastomosis Group’s Geographical Distribution of Rhizoctonia solani Associated with Soybean. Genes 2022, 13, 2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122417
Abbas A, Fang X, Iqbal S, Naqvi SAH, Mehmood Y, Rao MJ, Hassan Z, Ortiz RM, Baazeem A, Moustafa M, et al. Population Genetics and Anastomosis Group’s Geographical Distribution of Rhizoctonia solani Associated with Soybean. Genes. 2022; 13(12):2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122417
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbas, Aqleem, Xiangling Fang, Shehzad Iqbal, Syed Atif Hasan Naqvi, Yasir Mehmood, Muhammad Junaid Rao, Zeshan Hassan, Roberto Miño Ortiz, Alaa Baazeem, Mahmoud Moustafa, and et al. 2022. "Population Genetics and Anastomosis Group’s Geographical Distribution of Rhizoctonia solani Associated with Soybean" Genes 13, no. 12: 2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122417
APA StyleAbbas, A., Fang, X., Iqbal, S., Naqvi, S. A. H., Mehmood, Y., Rao, M. J., Hassan, Z., Ortiz, R. M., Baazeem, A., Moustafa, M., Alrumman, S., & Negm, S. (2022). Population Genetics and Anastomosis Group’s Geographical Distribution of Rhizoctonia solani Associated with Soybean. Genes, 13(12), 2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122417











