Abstract
Indian populations of the Pink Bollworm (PBW) are resistant to Bt (Bacillus thuringiensis) cotton hybrids containing Cry1Ac and Cry2Ab genes. Segregation of these Cry genes in F1 hybrids could subject PBW to sublethal concentrations. Moreover, planting hybrids with varying zygosities of Cry genes could produce diverse segregation patterns and expose PBW populations to highly variable toxin concentrations. This could potentially promote the rate of resistance development. Therefore, we studied the segregation patterns of Cry genes in different commercial Bt hybrids cultivated in India. Results showed that two hybrids segregated according to the Mendelian mono-hybrid ratio, three segregated according to the Mendelian di-hybrid ratio, and one showed a mixed segregation pattern. The assortment of seeds containing Cry genes varied between bolls of the same hybrid. In India, different Bt cotton hybrids are cultivated in small patches next to each other, exposing PBW populations to sublethal doses and wide variations in the occurrence of Cry genes. It is necessary to avoid segregation of Cry genes in the seeds produced by F1 hybrids. This study recommends using Bt parents homozygous for Cry genes in commercial Bt cotton hybrid development. This breeding strategy could be effective for similar transgenic crop hybrids as well.
1. Introduction
Bt (Bacillus thuringiensis) cotton refers to cotton plants that are genetically modified to contain Bt toxin-producing genes, which enhance their resistance against insects feeding on cotton bolls [1,2,3]. These insects are commonly known as bollworms, and the toxins produced by the Bt toxin-producing genes are called Bt toxins [1]. Since the past few years in India vast areas of the cotton crop are being destroyed by the pink bollworm (PBW, Pectinophora gossypiella) [4,5]. This situation has been prevailing despite 88% of the area being under the Bollgard® II Bt cotton containing Cry1Ac and Cry2Ab genes [6]. There are conclusive pieces of evidence that the Indian populations of the PBW are resistant to the two Bt toxins [4,5,7,8,9,10,11,12], which has prompted researchers to investigate the reasons for the development of resistance.
In India, Bt cotton has been available as hybrids [6,11,13], not varieties, and the Cry genes could be in hemizygous condition in the hybrids [14,15]. Genes in the hemizygous condition are expected to segregate in the progeny (F2 generation) of the hybrids (F1 generation) planted by the farmers [11,14,15]. As the embryo and endosperm of the seeds produced by the hybrids belong to the F2 generation [16], the Cry genes in hemizygous condition are expected to segregate in the F2 seeds [15,17,18]. This is important because seeds are the main food source for the PBW [6,19], and feeding on segregated seeds could lead to sublethal exposure and increase the survival of the individuals carrying resistance alleles [14,20,21]. It has been found that exposure of Helicoverpa zea [22] and Ostrinia nubilalis [23] individuals to both Bt and non-Bt tissues could accelerate the development of resistance in the respective species. Contrarily, Heuberger et al. [24] predicted that the rate of resistance development in PBW individuals to Cry1Ac may not increase when feeding on Bt and non-Bt seeds under total compliance of the refugia strategy. Their model tries to predict the development of resistance when a small proportion of the bolls on non-Bt refuge plants are contaminated by Bt pollen. This model might not be applicable to the present study. Here, segregation could produce a mixture of Bt (Cry1Ac and Cry2Ab) and non Bt seeds in every boll of the Bt plants. Furthermore, in India, millions of hectares are planted with potentially segregating Bt cotton hybrids, and there is a gross non-compliance of the refugia strategy.
Seed companies seem to focus on the expression, not on the zygosity, of the Cry genes in the hybrids. Therefore, commercial hybrids may have one or both genes in homozygous or hemizygous condition as the genes express under both conditions. However, the outcome of segregation shall vary with the zygosity of each Cry gene in the hybrids. Further, in India, there are a large number of farmers with small landholdings planting different commercially available Bt cotton hybrids [25]. Therefore, the variations between hybrids in the zygosity of the Cry genes, along with the farmers’ preferences for different hybrids, could result in a considerable spatial heterogeneity of the segregated seeds. Moreover, each cotton boll can contain up to ~40 seeds in them, and the assortment of the segregated seeds in each boll could differ within a hybrid, which increases the heterogeneity. As the segregation of the Cry genes could directly impact the toxicity of the seeds, the overall spatial heterogeneity would also represent the range of toxicities that different PBW individuals are exposed to at any given time. Therefore, segregation might influence the extent of not only the survival of the PBW on the Bt cotton, but also add to the variability in the surviving individuals with respect to their exposure to Bt toxins. Together, these could increase the rate of development of resistance in the PBW.
The segregation patterns of the Cry genes in seeds produced by different cultivated F1 hybrids has not been studied so far. Therefore, we investigated the segregation pattern of the Cry genes in the seeds produced by different Bollgard® II Bt cotton hybrids, and the influence of the segregation on the assortment of Cry genes within the bolls.
2. Materials and Methods
Six popular Bt cotton hybrids, with Bollgard® II technology, were purchased from open, commercial markets (names of the hybrids have been withheld due to potential conflict of interest with the manufacturers). The hybrids (sequentially numbered from Hybrid 1 to Hybrid 6) were planted in separate blocks. There was no cotton crop in the perimeter of more than two kilometres from the experimental plot.
Thirty days after the germination of seeds, leaf tissue samples were drawn from every plant and individually subjected to ELISA for determining the expression of the two Bt toxins [26]. The plants that were negative for the presence of either, or both, toxins were removed from the field (1.11, 2.22, 0.00, 6.67, 6.67 and 0.00 percent of plants were removed from Hybrids 1 to 6, respectively. There were 90 plants in each block before removal) and only those plants that were positive for both Bt toxins were retained. Several flowers on each plant were bagged one day before flower opening to avoid cross-pollination. The bags were removed one week later, and the developing squares were marked. Such marked bolls, when fully opened, were selected for further studies.
Three plants of Hybrids 1, 4, 5 and 6, and four plants of Hybrids 2 and 3 were randomly selected, and ten marked bolls from each plant of Hybrid 1 (30 bolls in total); eight bolls of Hybrids 2 and 3 (32 bolls per hybrid) and seven bolls of Hybrids 4, 5 and 6 (21 bolls per hybrid) were identified. All the seeds were extracted from these bolls and maintained boll-wise. Seeds were soaked overnight under ambient conditions. Later, the seed coat was discarded, and the endosperm was retained. In all, the endosperms of 4973 seeds were individually subjected to ELISA [26] for recording the expression of the Cry1Ac and Cry2Ab genes.
Data Analysis
The two Cry genes are known to segregate independently following the Mendelian Law of Independent Assortment [15]. The segregation pattern of seeds from each hybrid (positive for both genes (+ +); positive only for Cry1Ac (+ −); positive only for Cry2Ab (− +); and negative for both genes (− −)) was compared with the Mendelian mono- or di-hybrid ratios using Chi-square test. The proportion of seeds in a boll representing different gene combinations was plotted for each hybrid, and the Coefficient of Variance (CV%) was calculated for the observed variations across the sampled bolls for each combination of the Cry genes. The proportion of seeds in a plant representing different gene combinations was plotted for all the hybrids.
3. Results
3.1. Di-Hybrid Ratio
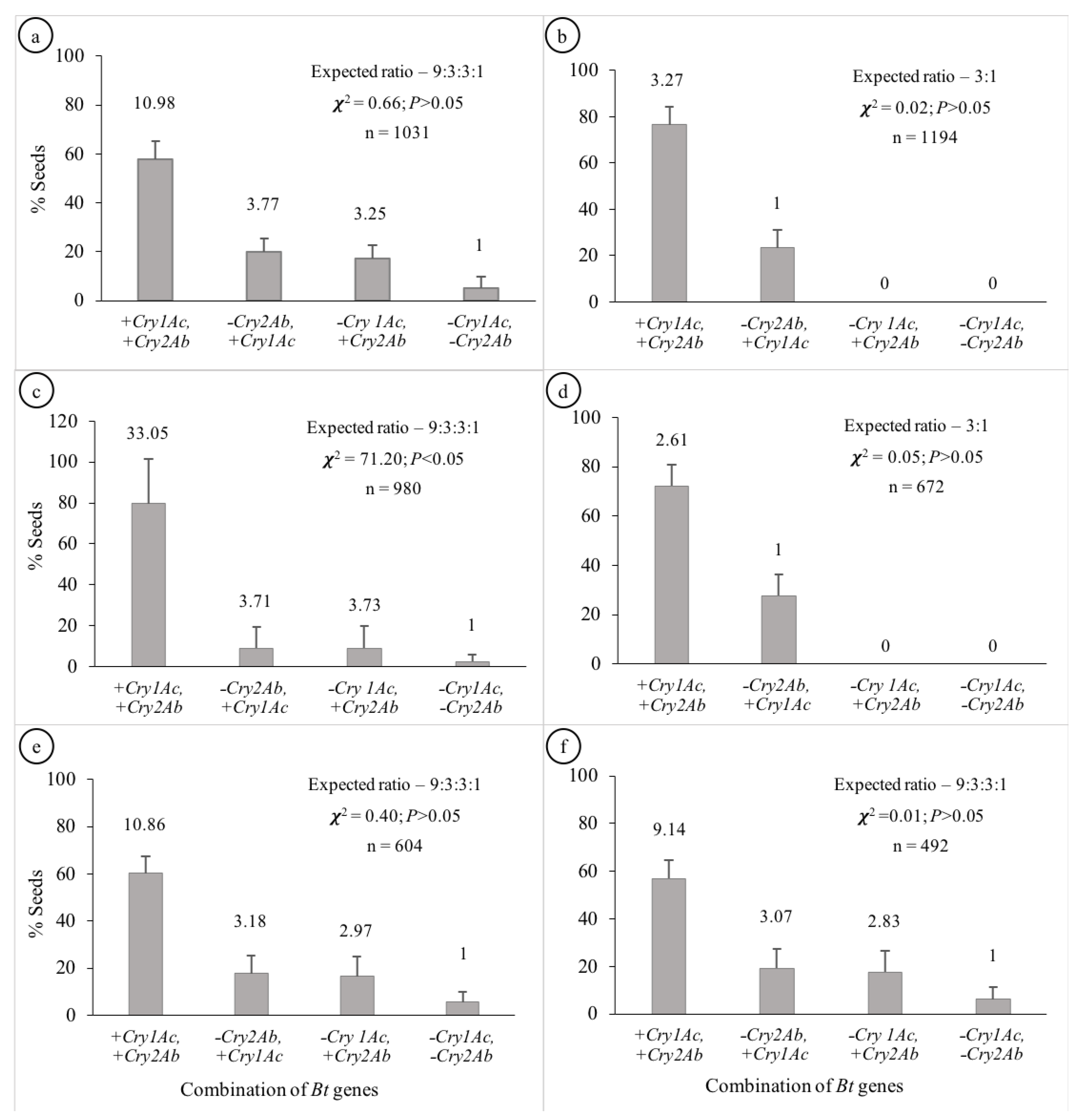
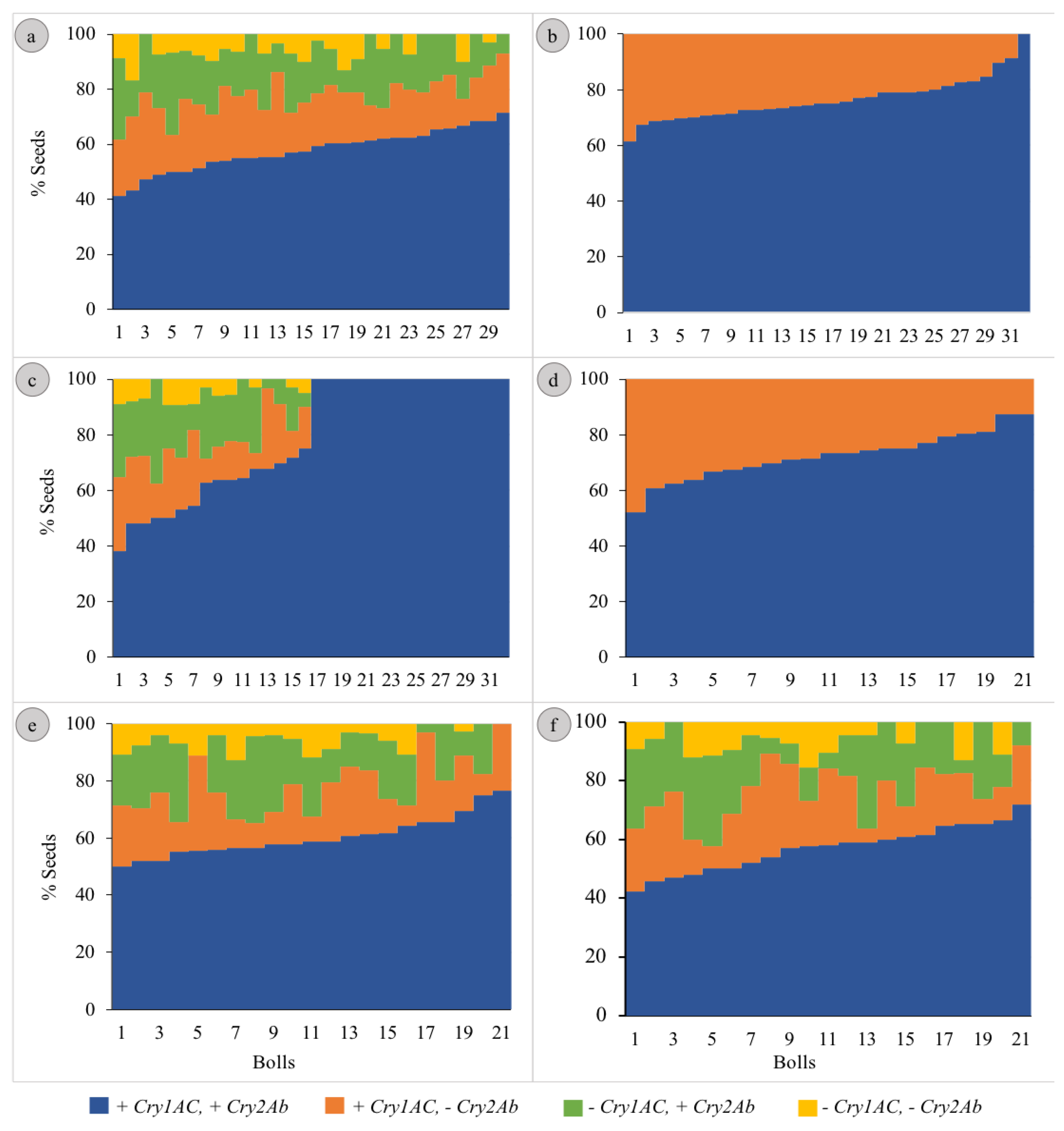
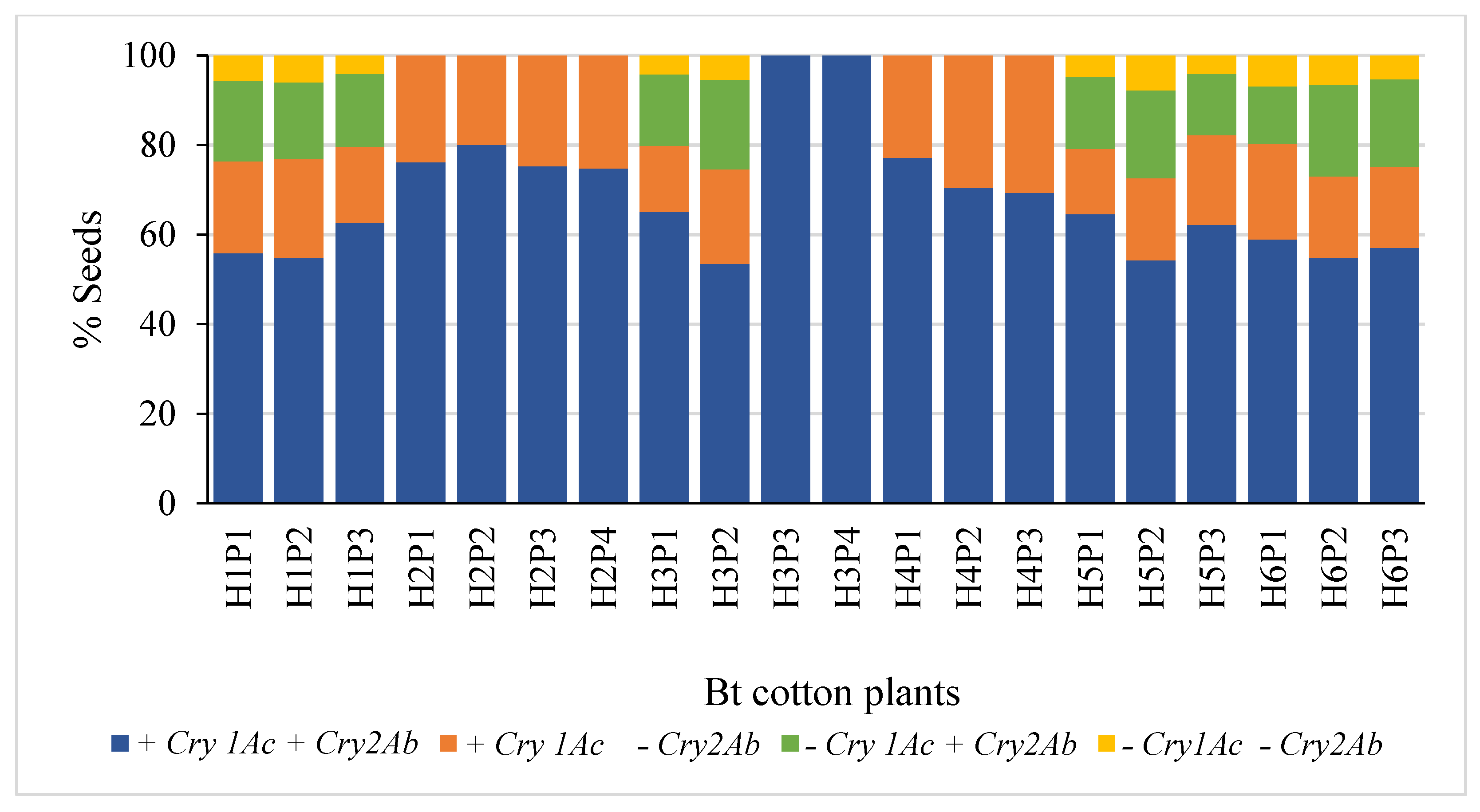
The segregation patterns of seeds in Hybrids 1, 5 and 6 followed the Mendelian di-hybrid ratio (Figure 1a,e,f, respectively). Chi-square test showed no significant differences between the observed ratios and 9:3:3:1 (+ +, + −, − + and − −) for the three hybrids (𝝌2 = 0.66, 0.40 and 0.01 for Hybrids 1, 5 and 6, respectively). Boll-wise variations in the proportion of seeds with different gene combinations have been represented in Figure 2a,e,f for Hybrids 1, 5 and 6, respectively. Among these three hybrids, the proportion of seeds in a boll containing both genes varied from ~41 to 76% with the Co-efficient of Variance (CV) varying from ~12 to ~14%. The CV ranged between ~27 and ~44% for seeds containing Cry1Ac only; it was between ~33 and ~51% for those containing Cry2Ab only; it was between ~75 and ~85% for those containing neither of the two genes (Table 1). All the plants that represented the three hybrids showed a similar segregation pattern (Figure 3).
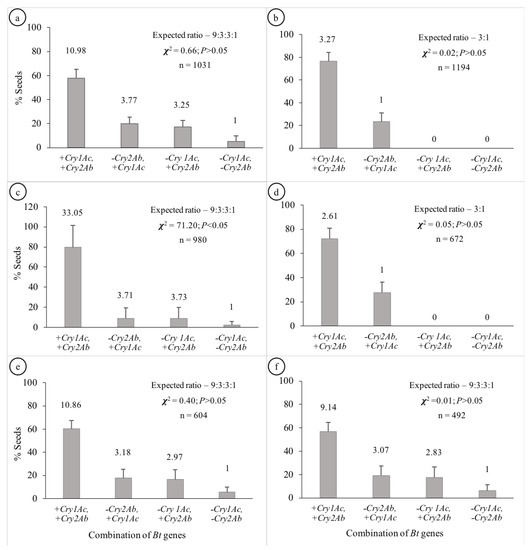
Figure 1.
Segregation pattern of Cry genes in the seeds of the Bt cotton hybrids. [Segregation ratios are mentioned above the respective columns; (a–f) represent Hybrids 1 to 6, respectively].
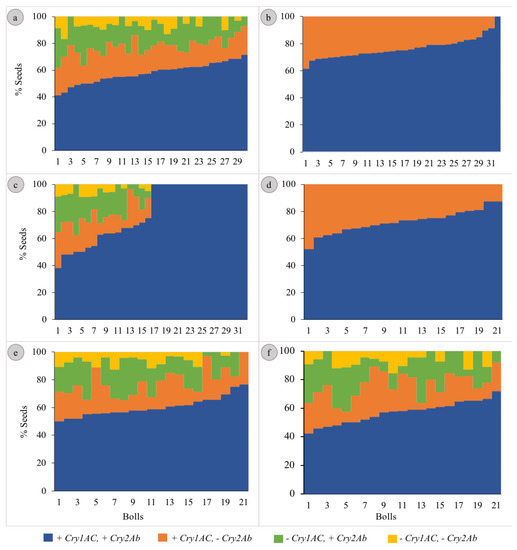
Figure 2.
Boll-wise segregation of the Cry genes in the seeds of Bt cotton hybrids. [(a–f) represent Hybrids 1 to 6, respectively. The bolls were ranked according to the proportion of + + seeds before plotting].

Table 1.
Expression of the Cry genes in the seeds produced by Bt cotton hybrids. The values represent percentage of seeds in a boll.
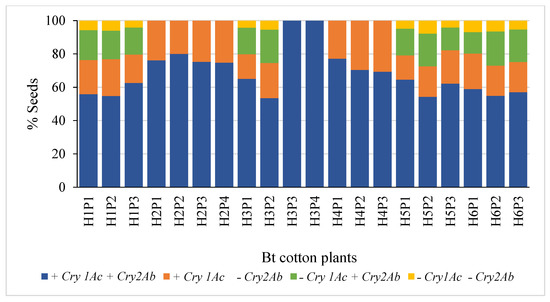
Figure 3.
Plant-wise segregation of Cry genes in the seeds of Bt cotton hybrids. [H represents the Hybrid number, and P represents the plant number].
3.2. Mono-Hybrid Ratio
The segregation patterns of seeds in Hybrids 2 and 4 followed the Mendelian mono-hybrid ratio (Figure 1b,d, respectively). Chi-square test showed no significant differences between the observed ratios and 3:1 (+ + and + −) for the two hybrids (𝝌2 = 0.02 and 0.05 for Hybrids 2 and 4, respectively). None of the seeds represented − + and − −. Boll-wise variations in the proportion of seeds with different gene combinations have been represented in Figure 2b,d for Hybrids 2 and 4, respectively. Among these two hybrids the proportion of seeds in a boll containing both genes varied from ~52 to 100% with a CV of ~10% for Hybrid 2 and ~12% for Hybrid 4. Similarly, the proportion of seeds in a boll containing Cry1Ac only varied from 0 to ~48% with a CV of ~33% for Hybrid 2 and ~31% for Hybrid 4 (Table 1). All the plants that represented the two Hybrids showed a similar segregation pattern (Figure 3).
3.3. Mixed Segregation
Although the seeds of Hybrid 3 represented all the four possible gene combinations (34.26:3.65:3.70:1 for + +, + −, − + and − −), the pattern did not conform with the di-hybrid ratio (Chi-square test; p < 0.05); + + was over-represented (Figure 1c). Boll-wise variations in the proportion of seeds with different gene combinations have been represented in Figure 2c. The proportion of seeds in a boll containing both genes varied from ~38 to 100% with a CV of ~28%. Similarly, the proportion varied from 0 to ~29% (CV = ~42%), from 0 to ~38% (CV = ~48%) and from 0 to ~9% (CV = ~75%) for + −, − + and − −, respectively (Table 1). Two of the four plants that represented Hybrid 3 showed no segregation in the F2 generation, while the segregation pattern in the other two plants was not different from 9:3:3:1 (Chi-square test; p > 0.05) (Figure 3).
4. Discussion
The PBW gaining resistance to the Bt toxins [4,5,7,8,9,10,11,12] has hinted towards critical weaknesses in the implementation of the Bt cotton technology. Therefore, finding reasons for the development of resistance has a global relevance. Presently, non-compliance of the refugia strategy is hypothesized to have led to the development of resistance [3,4,5,10,11,12,27,28]. However, the present findings suggest that segregation of the Cry genes in the seeds of the Bt cotton hybrids could potentially expose the PBW individuals to highly varying levels of toxicities, which could increase their survival on the Bt plants. Increased survival of the individuals with resistance alleles could enhance the rate of development of resistance in the PBW populations irrespective of the level of compliance to the refugia strategy.
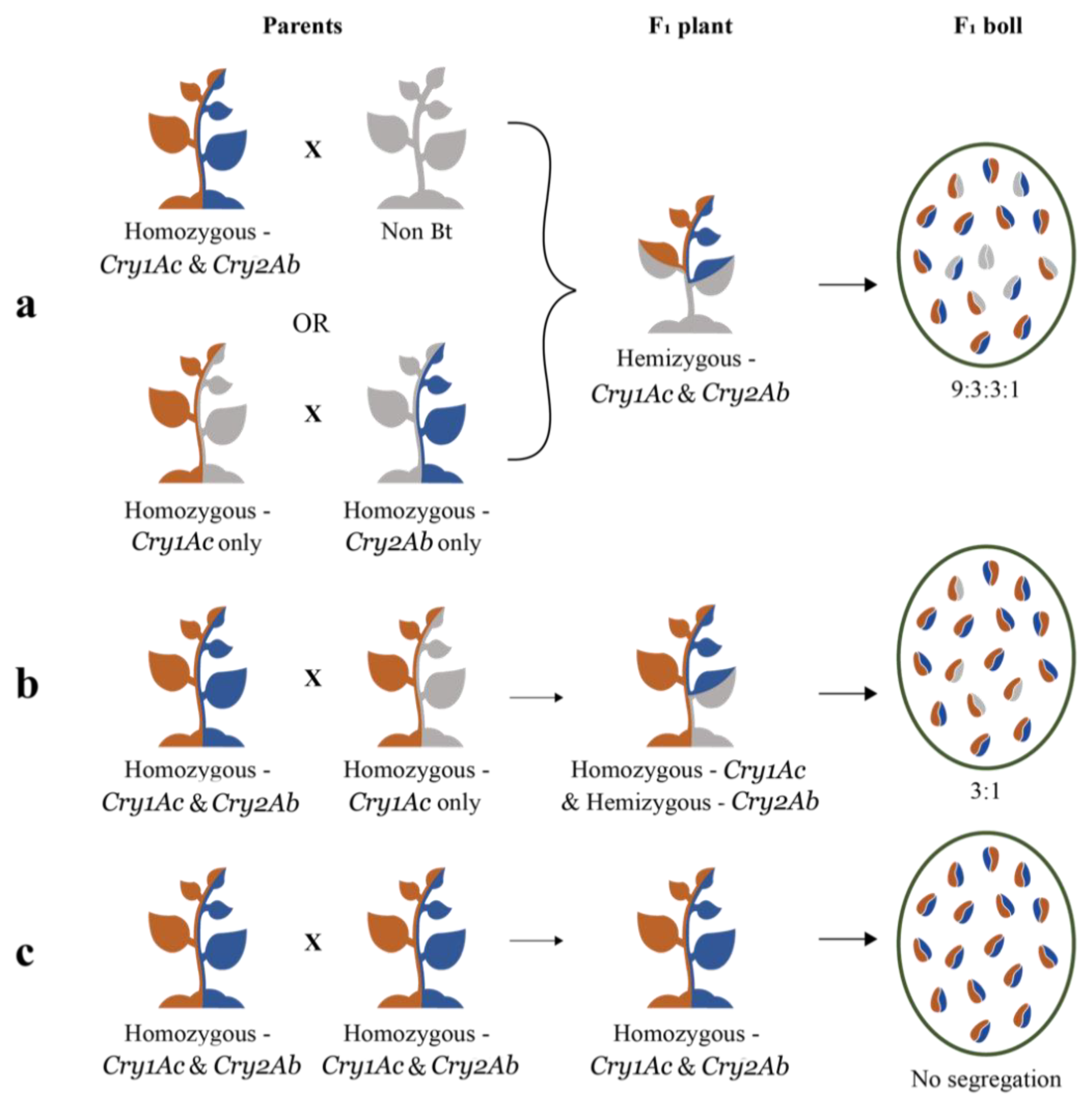
As the mere presence of a Cry gene could lead to its expression in the plant, the commercial hybrids could be homozygous, or hemizygous, to one, or both, Cry genes. Among the six hybrids studied here, the ones whose seeds segregated according to the Mendelian di-hybrid ratio (Hybrids 1, 5 and 6) were expected to be hemizygous to both genes (Figure 4a). There are two possible combinations of parental lines that could produce a hybrid with both Cry genes in hemizygous condition. In the first combination, one of the parental lines might be homozygous to both genes and the other might be a non-Bt plant. In the second combination, one parent might be homozygous for Cry1Ac while lacking in Cry2Ab, and the other might be homozygous for Cry2Ab while lacking in Cry1Ac (Figure 4a). Two other hybrids studied here (Hybrids 2 and 4) segregated in a typical Mendelian monohybrid ratio. This situation could occur when the hybrid is homozygous for Cry1Ac and hemizygous for Cry2Ab, which means that one of the parental lines was homozygous for both genes and the other was homozygous for Cry1Ac while lacking in Cry2Ab (Figure 4b). Two of the four plants that represented Hybrid 3 (Figure 3), segregated according to the di-hybrid ratio while the other two did not segregate. This meant that there were two types of F1 seeds in the same hybrid, one type was hemizygous, and the other was homozygous (Figure 4c), to both genes. As Hybrid 3 appears to originate from two different breeding programs, it could not be included in the mono or the di-hybrid groups.
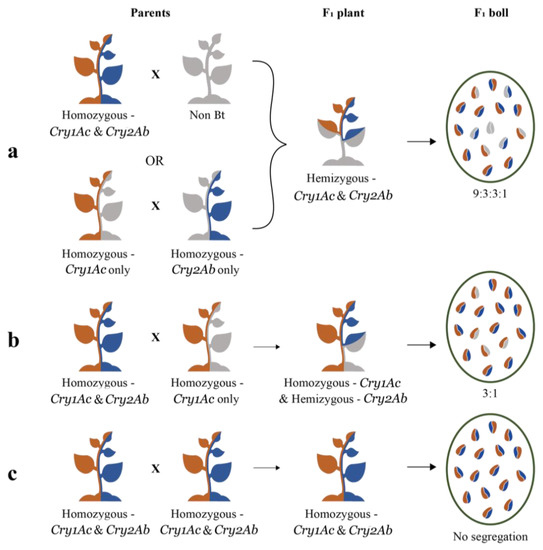
Figure 4.
Diagrammatic presentation of the zygosity of Cry genes in the parental lines (Parents), Bt cotton hybrid plants (F1 plant) and in the seeds occurring in the bolls produced by the hybrid plants (F1 boll). One half of the plant/seed represents Cry1Ac (orange), while the other half represents Cry2Ab (blue). The absence of any Cry gene is represented by grey colour. The full length of the plant represents homozygosity and half-length represents hemizygosity. (a) This represents a condition wherein any of the two different sets of parental lines could combine to produce a hybrid that is hemizygous to the two Cry genes. The seeds in the F1 boll segregate in the ratio of 9:3:3:1 (di-hybrid ratio). (b) This represents a condition where a parental line that is homozygous to the two Cry genes combines with a parent that is homozygous to any one of the Cry genes while lacking the other, to produce an F1 plant as depicted in the diagram. Here, the seeds in the F1 boll segregate in the ratio of 3:1 (monohybrid ratio). (c) This represents a condition where both parents are homozygous to the two Cry genes, which results in an F1 plant that is homozygous to the two genes and a non-segregating F1 boll.
The differences in the zygosity of the Cry genes among the six hybrids produced three segregation patterns—di-hybrid, monohybrid and mixed. Although the di-hybrid pattern was expected for the hybrids with two Cry genes segregating as per the law of independent assortment, the monohybrid was not; the mixed pattern of segregation in Hybrid 3 could not have been predicted. With more than a hundred Bt cotton hybrids available for the small landholder farmers to choose from, one can expect a substantial spatial heterogeneity of the segregated seeds. About 44% of the seeds contained one, or none, of the two Cry genes in the hybrids that followed the di-hybrid pattern, while ~25% of the seeds contained only one of the Cry genes in those that followed the monohybrid pattern of segregation. These also represented the proportion of seeds with lower toxicity than those with the two Cry genes. The results suggest that segregation could lower the mean and increase the variance in the toxicity of the bolls. Lowered mean toxicity is expected to increase the survival of the PBW individuals, while increased variance allows the PBW population to feed on bolls that display a wide range of Bt toxicities. Increased survival on a wide range of toxicities presented by the different Bt hybrids planted across a vast geographical area could potentially allow for the selection of multiple resistance-conferring alleles in different field populations of the PBW. The situation could contribute to the development of resistance. Feeding on Bt and non Bt plant tissues has been found to accelerate the development of resistance in different pest species [22,23].
Segregation of the Cry genes could produce bolls with variable Bt toxicities within a hybrid too. A PBW larva is generally confined to a boll for completing its development, and segregation could lead to differences between larvae of the same population for their exposure to Bt toxicity. Therefore, we studied segregation-induced variations between bolls of the same hybrid with respect to seeds containing Cry genes. As expected, the assortment of segregated seeds in a boll varied within each hybrid. These variations could produce small differences in the toxicity of the bolls to the PBW larvae feeding on them. The impact of subtle, within-hybrid, variations in toxicity on the development of resistance in the surviving PBW population has been rarely, if at all, addressed so far. Within-hybrid differences in the nature and extent of Bt toxicities could also lead to the selection of different resistance-conferring alleles within a given PBW population. Additionally, the observed pattern of assortment of the segregated seeds in a boll showed that the PBW larvae had only a rare chance, if any, of being selected for by individual Bt toxins.
The above discussion suggests that segregation could lower Bt toxicity and potentially increase the survival of the PBW on the Bt plants. Such an opportunity might not exist for the other bollworm species, especially the American bollworm (ABW, Helicoverpa armigera) that feeds on the F1 generation tissues such as the rind and lint of the bolls. The ABW feeds on several cultivated crop species in India [15,29,30] that are said to act as natural refuges for the resistant moths emerging from the Bt cotton fields [29,31,32]. This has been speculated to have reduced the rate of development of resistance in the ABW [29] despite non-compliance of refugia. On the other hand, as the PBW has a limited number of host plants [11,13,15], it has been said that non-compliance of refugia might have led to the observed resistance [4,5,11,12,27,28]. However, the earlier works failed to recognize that feeding on the F1 generation tissues would expose the ABW to a stronger and narrower range of Bt toxicity, than the PBW that feeds on the segregated F2 generation tissues. This could produce fewer ABW on the Bt plants than the PBW. Therefore, the expected rate of resistance development in the PBW might be greater than in the ABW even if the farmers complied with planting the refuge crop. Refugia could fail to manage the development of resistance in the PBW when the number of surviving individuals on the Bt plants increases [33]. Interestingly, a recent study suggested that the evidence for gross non-compliance of refugia in India were actually weak [34]. It noted that commercial hybrids sown by the farmers since the introduction of Bollgard® II might have contained about 5% non-Bt seeds in the seed packets, which equals the recommended refuge requirement in India (https://seednet.gov.in/SeedGO/2016/173355_2016.pdf, accessed on 10 October 2022).
5. Recommendation
The case of the PBW in India should be treated as an important benchmark for breeding transgenic insect-resistant hybrids of cultivated crops. Based on the current findings, we recommend that the parental lines involved in developing hybrids may be homozygous for the insect resistant transgenes [11]. This would perhaps be the only way to prevent segregation, which could be crucial for the success of the resistance management strategies such as the refugia. Presently, India has decided to mix a certain proportion of non-Bt along with the Bt cotton seeds to enforce compliance of the refugia strategy (https://seednet.gov.in/SeedGO/2016/173355_2016.pdf accessed on 10 October 2022). Through this study, we suggest the policymakers to implement refugia while ensuring that the cotton hybrids are homozygous for the Cry genes. This would justify the cultivation of artificial refuges for all bollworm species.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.M.; methodology, K.M.; formal analysis, H.M.M.; investigation, H.M.M.; writing—original draft preparation, H.M.M.; writing—review and editing, K.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to potential conflict of interest with the seed manufacturers.
Acknowledgments
We thank Y. B. Srinivasa for his guidance during the course of the study and for his help in preparing the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wu, K.M.; Lu, Y.H.; Feng, H.Q.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Zhao, J.Z. Suppression of Cotton Bollworm in Multiple Crops in China in Areas with Bt Toxin–Containing Cotton. Science 2008, 321, 1676–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, M.S.T. Genetically Engineered (Modified) Crops (Bacillus Thuringiensis Crops) and the World Controversy on Their Safety. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest. Control 2018, 28, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head, G.P.; Greenplate, J. The Design and Implementation of Insect Resistance Management Programs for Bt Crops. GM Crops Food 2012, 3, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, V.C.; Kumbhare, S.; Kranthi, S.; Satija, U.; Kranthi, K.R. Field-Evolved Resistance of Pink Bollworm, Pectinophora Gossypiella (Saunders) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae), to Transgenic Bacillus Thuringiensis (Bt) Cotton Expressing Crystal 1Ac (Cry1Ac) and Cry2Ab in India: Pink Bollworm Resistance to Cry Toxins. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 2544–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fand, B.B.; Nagrare, V.S.; Gawande, S.P.; Nagrale, D.T.; Naikwadi, B.V.; Deshmukh, V.; Gokte-Narkhedkar, N.; Waghmare, V.N. Widespread Infestation of Pink Bollworm, Pectinophora gossypiella (Saunders) (Lepidoptera: Gelechidae) on Bt Cotton in Central India: A New Threat and Concerns for Cotton Production. Phytoparasitica 2019, 47, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagrare, V.S.; Naik, V.C.B.; Fand, B.B.; Gawande, S.P.; Nagrale, D.T.; Gokte-Narkhedkar, N.; Waghmare, V.N. Cotton: Integrated Pest, Disease and Nematode Management; Technical Bulletin No 1/2019; ICAR-Central Institute for Cotton Research: Nagpur, India, 2019; pp. 9–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zafar, M.M.; Razzaq, A.; Farooq, M.A.; Rehman, A.; Firdous, H.; Shakeel, A.; Mo, H.; Ren, M. Insect Resistance Management in Bacillus thuringiensis Cotton by MGPS (Multiple Genes Pyramiding and Silencing). J. Cotton. Res. 2020, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhurua, S.; Gujar, G.T. Field-Evolved Resistance to Bt Toxin Cry1Ac in the Pink Bollworm, Pectinophora gossypiella (Saunders) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae), from India: Resistance of Pink Bollworm, Pectinophora gossypiella (Saunders), to Bt Toxin Cry1Ac. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, A.; Sree, K.S.; Sachdev, B.; Rashmi, M.; Ravi, K.; Suresh, P.; Mohan, K.S.; Bhatnagar, R.K. Analysis of Resistance to Cry1Ac in Field-Collected Pink Bollworm, Pectinophora gossypiella (Lepidoptera:Gelechiidae), Populations. GM Crops Food 2014, 5, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrick, J.A.; Unnithan, G.C.; Yelich, A.J.; DeGain, B.; Masson, L.; Zhang, J.; Carrière, Y.; Tabashnik, B.E. Multi-Toxin Resistance Enables Pink Bollworm Survival on Pyramided Bt Cotton. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranthi, K.R. Pink bollworm strikes Bt-cotton. Cotton Stat. News 2015, 35, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan, K.S.; Ravi, K.C.; Suresh, P.J.; Sumerford, D.; Head, G.P. Field Resistance to the Bacillus thuringiensis Protein Cry1Ac Expressed in Bollgard ® Hybrid Cotton in Pink Bollworm, Pectinophora gossypiella (Saunders), Populations in India: Field Resistance to Cry1Ac Protein in Indian Pink Bollworm. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kranthi, K.R.; Stone, G.D. Long-term impacts of Bt cotton in India. Nat Plants 2020, 6, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kranthi, K.R. Bt Cotton Q&A Questions and Answers; Indian society for Cotton Improvement: Mumbai, India, 2012; p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Edpuganti, S.L. Resistance Development in Pink Bollworm Pectinophora gossypiella (Saunders) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) to Bt Cotton and Resistance Management Strategies. Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 2018, 6, 1296–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhury, A.M.; Koltunow, A.; Payne, T.; Luo, M.; Tucker, M.R.; Dennis, E.S.; Peacock, W.J. Control of Early Seed Development. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2001, 17, 677–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Xu, D.; Cong, S.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Wang, L.; Wu, K.; Carrière, Y.; et al. Hybridizing Transgenic Bt Cotton with Non-Bt Cotton Counters Resistance in Pink Bollworm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 5413–5418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.H.; Guo, T.L.; Wang, Q.L. Inheritance and Segregation of Exogenous Genes in Transgenic Cotton. J. Genet. 2000, 79, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vennila, S.; Biradar, V.K.; Sabesh, M.; Bambawale, O.M. Know Your Cotton Insect Pest Pink Bollworm; Crop protection folder series 7 of 11; CICR: Nagpur, India, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mallet, J.; Porter, P. Preventing Insect Adaptation to Insect-Resistant Crops: Are Seed Mixtures or Refugia the Best Strategy? Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 1992, 250, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangila, D.S.; Leonard, B.R.; Ghimire, M.N.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Emfinger, K.D.; Head, G.P.; Yang, F.; Niu, Y.; et al. Occurrence and Larval Movement of Diatraea saccharalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) in Seed Mixes of Non- Bt and Bt Pyramid Corn: Larval Movement of D. saccharalis in Seed Mixes of Bt and Non- Bt Corn. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2013, 69, 1163–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brévault, T.; Tabashnik, B.E.; Carrière, Y. A Seed Mixture Increases Dominance of Resistance to Bt Cotton in Helicoverpa zea. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkness, E.C.; O’Rourke, P.K.; Hutchison, W.D. Cross-Pollination of Nontransgenic Corn Ears With Transgenic Bt Corn: Efficacy Against Lepidopteran Pests and Implications for Resistance Management. J. Econ. Entomol. 2011, 104, 1476–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuberger, S.; Ellers-Kirk, C.; Yafuso, C.; Gassmann, A.J.; Tabashnik, B.E.; Dennehy, T.J.; Carriere, Y. Effects of Refuge Contamination by Transgenes on Bt Resistance in Pink Bollworm (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2008, 101, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, B.; Gaur, K. Bt Cotton in India: A Country Profile; ISAAA Series of Biotech Crop Profiles; ISAAA: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dohare, A.; Tank, S.K. Identification of Cry1Ac and Cry2Ab proteins in transgenic cotton seeds available in Gujarat (India) by ELISA method. J. Exp. Biol. Agri. Sci. 2014, 2, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan, K.S. An area-wide approach to pink bollworm management on Bt cotton in India–A dire necessity with community participation. Curr. Sci. 2017, 112, 1988–1989. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, R.; Kamath, S.P.; Mohan, K.S.; Head, G.; Sumerford, D.V. Inheritance of Field-Relevant Resistance to the Bacillus thuringiensis Protein Cry1Ac in Pectinophora gossypiella (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) Collected from India: Inheritance of Cry1Ac Resistance in Pink Bollworm in India. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, K.C.; Mohan, K.S.; Manjunath, T.M.; Head, G.; Patil, B.V.; Greba, D.P.A.; Premalatha, K.; Peter, J.; Rao, N.G.V. Relative Abundance of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on Different Host Crops in India and the Role of These Crops as Natural Refuge for Bacillus thuringiensis Cotton. Environ. Entomol. 2005, 34, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behere, G.T.; Tay, W.T.; Russell, D.A.; Kranthi, K.R.; Batterham, P. Population Genetic Structure of the Cotton Bollworm Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in India as Inferred from EPIC-PCR DNA Markers. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Guo, Y.; Gao, S. Evaluation of the Natural Refuge Function for Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) within Bacillus Thuringiensis Transgenic Cotton Growing Areas in North China. J. Econ. Entomol. 2002, 95, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, K.; Tabashnik, B.E.; Wu, Y. Large-Scale Test of the Natural Refuge Strategy for Delaying Insect Resistance to Transgenic Bt Crops. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, F. Sustainability of Transgenic Insecticidal Cultivars: Integrating Pest Genetics and Ecology. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1998, 43, 701–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muralimohan, K.; Mahesh, H.M. Cry toxin expression in Bt cotton hybrid seeds: Impact on ‘Refuge-in-Bag’ strategy for managing resistance in bollworms. Curr. Sci. 2020, 118, 1494–1495. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).