Molecular Characterization and Expression Analysis of YABBY Genes in Chenopodium quinoa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials, Growth Conditions, and Stress Treatments
2.2. Identification of YABBY Genes
2.3. Chromosomal Location
2.4. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Tree Construction
2.5. Gene Structure and Conserved Motif Prediction
2.6. Promoter Analysis
2.7. Isolation of RNA and qRT-PCR
2.8. Vector Construction, Plant Transformation, and Imaging
2.9. Statistical Analysis of Data
3. Results
3.1. Chromosomal Location and Molecular Features of Quinoa YABBY Genes
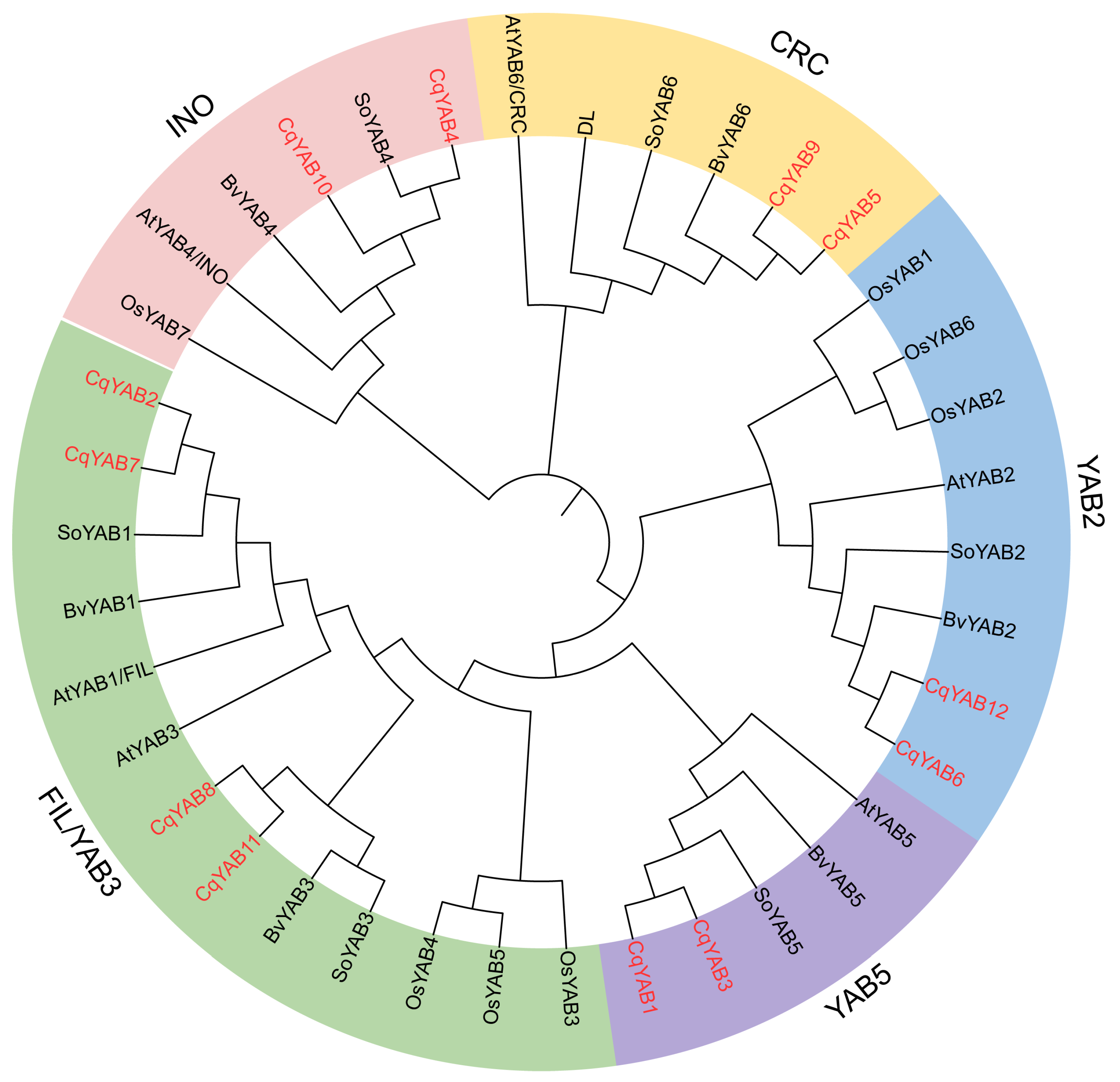
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of YABBY Family Genes
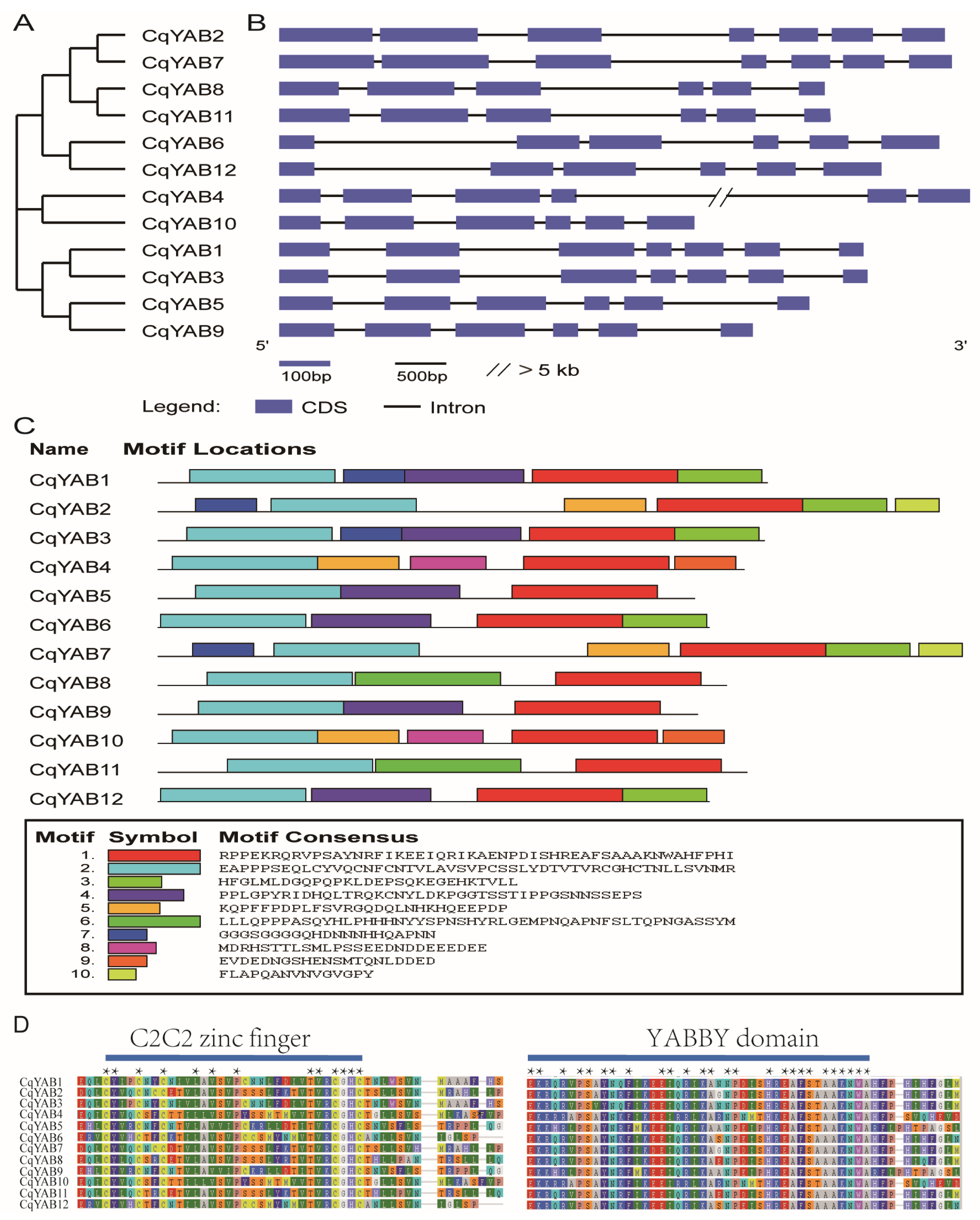
3.3. Gene Structure, Protein Motif, and Domain Analyses
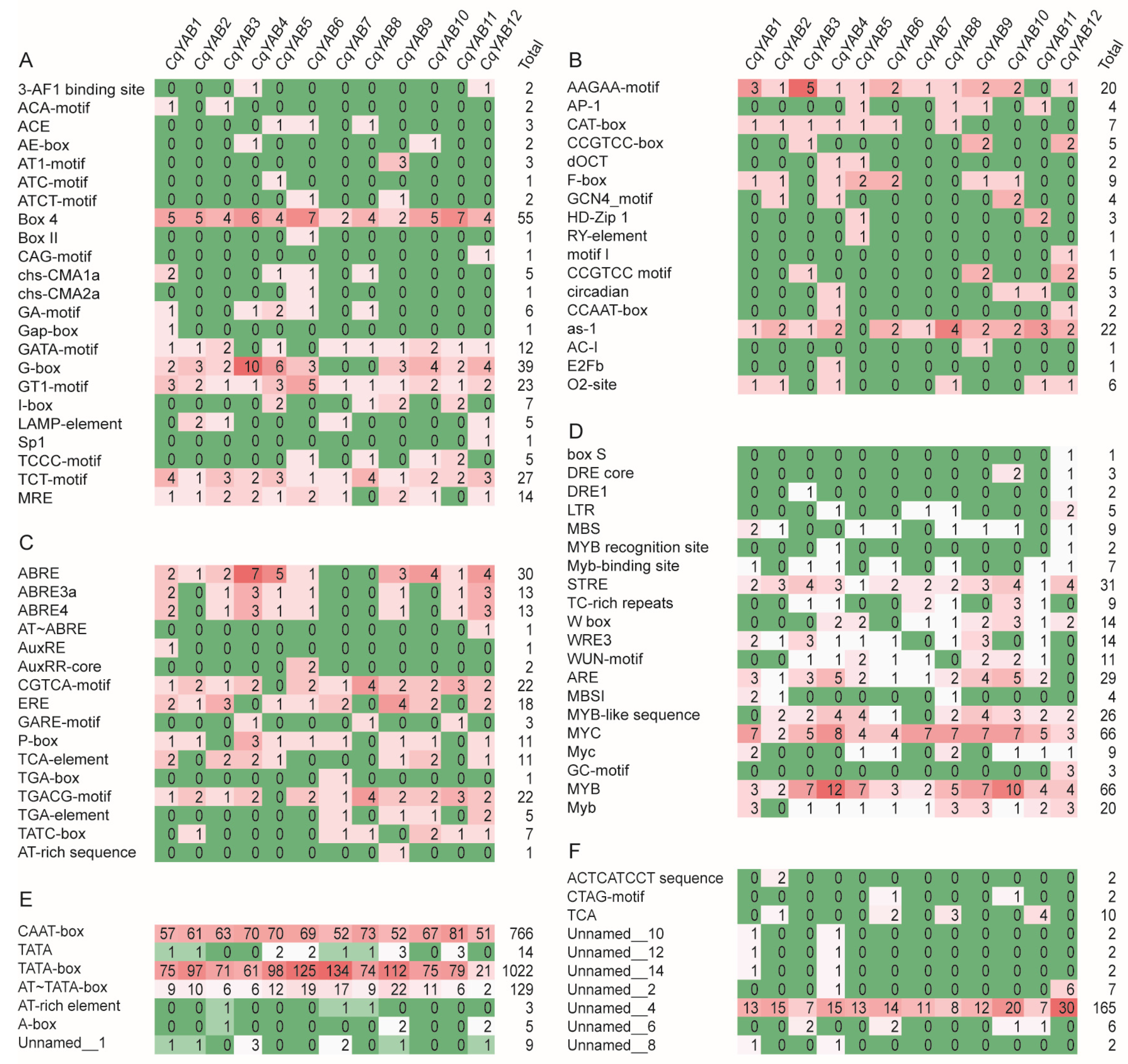
3.4. Analysis of Cis-Regulatory Elements in CqYAB Promoters
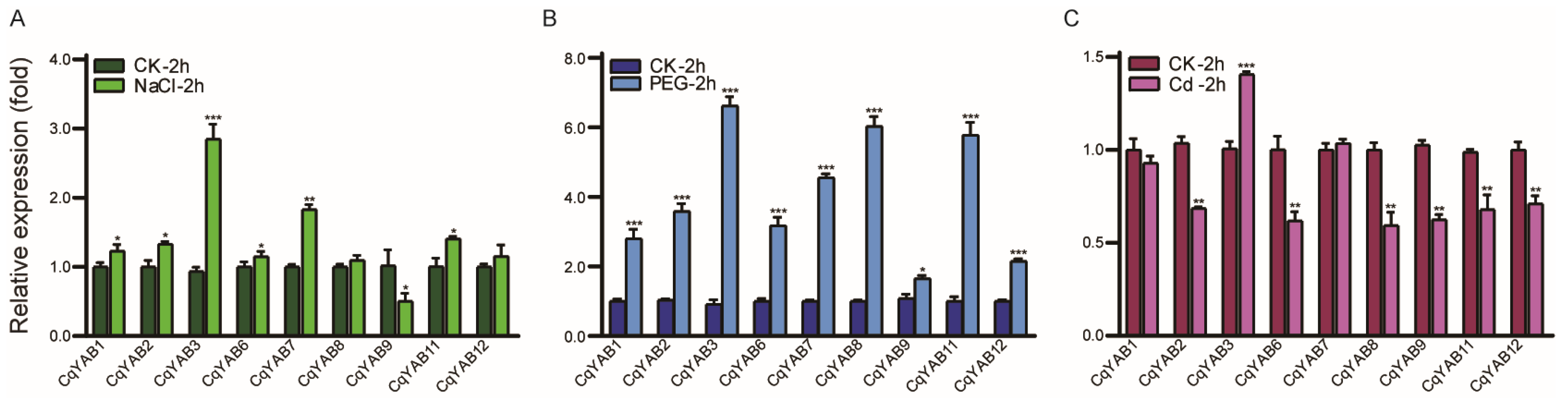
3.5. Expression Responses of CqYAB Genes under Salt, Drought, and Cd Stresses
3.6. Tissue Expression Profiles of CqYAB Genes
3.7. Functional Analysis of CqYAB4 and CqYAB10 in Arabidopsis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ballegaard, A.R.; Larsen, J.M.; Rasmussen, P.H.; Untersmayr, E.; Pilegaard, K.; Bogh, K.L. Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) Seeds Increase Intestinal Protein Uptake. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, e2100102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazile, D.; Jacobsen, S.E.; Verniau, A. The Global Expansion of Quinoa: Trends and Limits. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirzadah, T.B.; Malik, B. Pseudocereals as super foods of 21st century: Recent technological interventions. J. Agric. Food Res. 2020, 2, 100052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathan, S.; Siddiqui, R.A. Nutritional Composition and Bioactive Components in Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) Greens: A Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liu, J.; Guo, X.; Yin, L.; Zhang, H.; Wen, R. Genome-wide survey, characterization, and expression analysis of bZIP transcription factors in Chenopodium quinoa. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurita-Silva, A.; Fuentes, F.; Zamora, P.; Jacobsen, S.-E.; Schwember, A.R. Breeding quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.): Potential and perspectives. Mol. Breed. 2014, 34, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Marques, R.L.; Norrevang, A.F.; Ache, P.; Moog, M.; Visintainer, D.; Wendt, T.; Osterberg, J.T.; Dockter, C.; Jorgensen, M.E.; Salvador, A.T.; et al. Prospects for the accelerated improvement of the resilient crop quinoa. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 5333–5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, V.; Du, J.; Charrondiere, U.R. Assessment of the nutritional composition of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Food Chem. 2016, 193, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golicz, A.A.; Steinfort, U.; Arya, H.; Singh, M.B.; Bhalla, P.L. Analysis of the quinoa genome reveals conservation and divergence of the flowering pathways. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2020, 20, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojosa, L.; Sanad, M.; Jarvis, D.E.; Steel, P.; Murphy, K.; Smertenko, A. Impact of heat and drought stress on peroxisome proliferation in quinoa. Plant J. 2019, 99, 1144–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, K.B.; Maldonado, J.; Biondi, S.; Silva, H. RNA-seq Analysis of Salt-Stressed Versus Non Salt-Stressed Transcriptomes of Chenopodium quinoa Landrace R49. Genes 2019, 10, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariotti, L.; Huarancca Reyes, T.; Ramos-Diaz, J.M.; Jouppila, K.; Guglielminetti, L. Hormonal Regulation in Different Varieties of Chenopodium quinoa Willd. Exposed to Short Acute UV-B Irradiation. Plants 2021, 10, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Qu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Geng, Y.; Li, Y.; Shao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Ma, C. Transcriptome and Small RNA Sequencing Reveals the Basis of Response to Salinity, Alkalinity and Hypertonia in Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.S.; Ramezanpour, S.S.; Soltanloo, H.; Seifati, S.E. RNA-seq analysis and reconstruction of gene networks involved in response to salinity stress in quinoa (cv. Titicaca). Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaikishun, S.; Li, W.; Yang, Z.; Song, S. Quinoa: In Perspective of Global Challenges. Agronomy 2019, 9, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, D.E.; Ho, Y.S.; Lightfoot, D.J.; Schmockel, S.M.; Li, B.; Borm, T.J.; Ohyanagi, H.; Mineta, K.; Michell, C.T.; Saber, N.; et al. The genome of Chenopodium quinoa. Nature 2017, 542, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, W.; Xu, R.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Li, A.; Liang, Y.; Ou, S.; et al. Genomic basis of geographical adaptation to soil nitrogen in rice. Nature 2021, 590, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Tian, F.; Yang, D.C.; Meng, Y.Q.; Kong, L.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. PlantTFDB 4.0: Toward a central hub for transcription factors and regulatory interactions in plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D1040–D1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Guo, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H.; Cao, H.; Su, H.; Wen, R. Genome-Wide Identification, Characterization, and Expression Analysis of the NAC Transcription Factor in Chenopodium quinoa. Genes 2019, 10, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, H.; Chang, X.; Zhi, Y.; Wang, L.; Xing, G.; Song, W.; Nie, X. Evolution and Identification of the WRKY Gene Family in Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa). Genes 2019, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Ma, R.; Fan, Y.; Zhao, B.; Cheng, P.; Fan, Y.; Wang, B. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the SPL transcription factor family and its response to abiotic stress in Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa). BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Cao, H.; Zhang, M.; Deng, S.; Li, T.; Xing, S. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of SPL Family Genes in Chenopodium quinoa. Genes 2022, 13, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.; Fan, Y.; Zheng, C.; Yang, H.; Feng, L.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y.; Yao, X.; Weng, W.; Kong, L.; et al. bHLH transcription factor family identification, phylogeny, and its response to abiotic stress in Chenopodium quinoa. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1171518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, G.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Chang, X.; Wu, W.; Duan, L.; Yao, M.; Wang, R.; et al. Genome-wide identification, phylogenetic analysis, and expression profiles of trihelix transcription factor family genes in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) under abiotic stress conditions. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, P.; Qian, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L. Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of R2R3-MYB Genes Response to Saline-Alkali Stress in Quinoa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuefen, D.; Wei, X.; Wang, B.; Xiaolin, Z.; Xian, W.; Jincheng, L. Genome-wide identification and expression pattern analysis of quinoa BBX family. PeerJ 2022, 10, e14463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Yu, H.; Ma, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, S.; Yan, J.; Xu, X.; Chen, H. Molecular Evolution and Local Root Heterogeneous Expression of the Chenopodium quinoa ARF Genes Provide Insights into the Adaptive Domestication of Crops in Complex Environments. J. Mol. Evol. 2021, 89, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Jiang, R.; Li, B.; Wang, D.; Fang, D.; Yin, M.; Yin, M.; Gu, M. Genome-Wide Analysis and Expression Profiles of the VOZ Gene Family in Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa). Genes 2022, 13, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, B.; Wei, X. Genome wide identification and expression pattern analysis of the GRAS family in quinoa. Funct. Plant Biol. 2021, 48, 948–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholmes, C.; Hidalgo, O.; Gleissberg, S. Evolution of the YABBY gene family with emphasis on the basal eudicot Eschscholzia californica (Papaveraceae). Plant Biol. 2012, 14, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawa, S.; Watanabe, K.; Goto, K.; Liu, Y.G.; Shibata, D.; Kanaya, E.; Morita, E.H.; Okada, K. FILAMENTOUS FLOWER, a meristem and organ identity gene of Arabidopsis, encodes a protein with a zinc finger and HMG-related domains. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldshmidt, A.; Alvarez, J.P.; Bowman, J.L.; Eshed, Y. Signals derived from YABBY gene activities in organ primordia regulate growth and partitioning of Arabidopsis shoot apical meristems. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 1217–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahle, M.I.; Kuehlich, J.; Staron, L.; von Arnim, A.G.; Golz, J.F. YABBYs and the transcriptional corepressors LEUNIG and LEUNIG_HOMOLOG maintain leaf polarity and meristem activity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 3105–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, J.L.; Smyth, D.R. CRABS CLAW, a gene that regulates carpel and nectary development in Arabidopsis, encodes a novel protein with zinc finger and helix-loop-helix domains. Development 1999, 126, 2387–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva, J.M.; Broadhvest, J.; Hauser, B.A.; Meister, R.J.; Schneitz, K.; Gasser, C.S. INNER NO OUTER regulates abaxial- adaxial patterning in Arabidopsis ovules. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 3160–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarojam, R.; Sappl, P.G.; Goldshmidt, A.; Efroni, I.; Floyd, S.K.; Eshed, Y.; Bowman, J.L. Differentiating Arabidopsis shoots from leaves by combined YABBY activities. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 2113–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toriba, T.; Harada, K.; Takamura, A.; Nakamura, H.; Ichikawa, H.; Suzaki, T.; Hirano, H.Y. Molecular characterization the YABBY gene family in Oryza sativa and expression analysis of OsYABBY1. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2007, 277, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttar, Z.A.; Yang, Y.; Sharif, R.; Nan Wu, S.; Xie, Y.; Wang, C. Genome Wide Identification, Characterization, and Expression Analysis of YABBY-Gene Family in WHEAT (Triticum aestivum L.). Agronomy 2020, 10, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Zhang, J.; Shi, S.; Li, P.; Li, D.; Zhang, T.; Guo, H. Identification and expression profiles of the YABBY transcription factors in wheat. PeerJ 2022, 10, e12855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wu, A.; Hu, X.; Deng, Q.; Ma, Z.; Su, L. Comprehensive study of rice YABBY gene family: Evolution, expression and interacting proteins analysis. PeerJ 2023, 11, e14783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Nagasawa, N.; Kawasaki, S.; Matsuoka, M.; Nagato, Y.; Hirano, H.Y. The YABBY gene DROOPING LEAF regulates carpel specification and midrib development in Oryza sativa. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.L.; Xu, Y.Y.; Xu, Z.H.; Chong, K. A rice YABBY gene, OsYABBY4, preferentially expresses in developing vascular tissue. Dev. Genes Evol. 2007, 217, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juarez, M.T.; Twigg, R.W.; Timmermans, M.C. Specification of adaxial cell fate during maize leaf development. Development 2004, 131, 4533–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Su, H.Y.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhang, X.S. Ectopic expression of TaYAB1, a member of YABBY gene family in wheat, causes the partial abaxialization of the adaxial epidermises of leaves and arrests the development of shoot apical meristem in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci. 2006, 170, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strable, J.; Wallace, J.G.; Unger-Wallace, E.; Briggs, S.; Bradbury, P.J.; Buckler, E.S.; Vollbrecht, E. Maize YABBY Genes drooping leaf1 and drooping leaf2 Regulate Plant Architecture. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 1622–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strable, J.; Vollbrecht, E. Maize YABBY genes drooping leaf1 and drooping leaf2 regulate floret development and floral meristem determinacy. Development 2019, 146, dev171181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, W.; Toriba, T.; Ohmori, Y.; Yoshida, A.; Kawai, A.; Mayama-Tsuchida, T.; Ichikawa, H.; Mitsuda, N.; Ohme-Takagi, M.; Hirano, H.Y. The YABBY gene TONGARI-BOUSHI1 is involved in lateral organ development and maintenance of meristem organization in the rice spikelet. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 80–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, W.; Toriba, T.; Hirano, H.Y. Three TOB1-related YABBY genes are required to maintain proper function of the spikelet and branch meristems in rice. New Phytol. 2017, 215, 825–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Li, X.; Shannon, L.M.; Yeh, C.T.; Wang, M.L.; Bai, G.; Peng, Z.; Li, J.; Trick, H.N.; Clemente, T.E.; et al. Parallel domestication of the Shattering1 genes in cereals. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Hu, H.; Voytas, D.F.; Doust, A.N.; Kellogg, E.A. The YABBY gene SHATTERING1 controls activation rather than patterning of the abscission zone in Setaria viridis. New Phytol. 2023, 240, 846–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, Q.; Hu, Y.; Hedden, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, D.X. The rice YABBY1 gene is involved in the feedback regulation of gibberellin metabolism. Plant Physiol. 2007, 144, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.P.; Lu, D.; Yu, T.F.; Ji, Y.J.; Zheng, W.J.; Zhang, S.X.; Chai, S.C.; Chen, Z.Y.; Cui, X.Y. Genome-wide analysis of the YABBY family in soybean and functional identification of GmYABBY10 involvement in high salt and drought stresses. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 119, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, G.; Cai, M.; Priyadarshani, S.; Aslam, M.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Qin, Y. Genome-Wide Analysis of the YABBY Transcription Factor Family in Pineapple and Functional Identification of AcYABBY4 Involvement in Salt Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhar, H.S.; Shafiq, M.; Ali, H.; Ashfaq, M.; Anwar, A.; Tabassum, J.; Ali, Q.; Jilani, G.; Awais, M.; Sahu, R.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification, and In-Silico Expression Analysis of YABBY Gene Family in Response to Biotic and Abiotic Stresses in Potato (Solanum tuberosum). Genes 2023, 14, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Gong, Q.; Wang, L.; Jin, Y.; Xi, J.; Li, Z.; Qin, W.; Yang, Z.; Lu, L.; Chen, Q.; et al. Genome-Wide Study of YABBY Genes in Upland Cotton and Their Expression Patterns under Different Stresses. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegfried, K.R.; Eshed, Y.; Baum, S.F.; Otsuga, D.; Drews, G.N.; Bowman, J.L. Members of the YABBY gene family specify abaxial cell fate in Arabidopsis. Development 1999, 126, 4117–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, J.L. The YABBY gene family and abaxial cell fate. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2000, 3, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Van Houten, J.; Gonzalez, G.; Xiao, H.; van der Knaap, E. Genome-wide identification, phylogeny and expression analysis of SUN, OFP and YABBY gene family in tomato. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2013, 288, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, C.; Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X. Roles of YABBY transcription factors in the modulation of morphogenesis, development, and phytohormone and stress responses in plants. J. Plant Res. 2020, 133, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Yao, J.; van Nocker, S.; Wang, X. Genome-Wide Analysis of the YABBY Gene Family in Grapevine and Functional Characterization of VvYABBY4. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ye, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Li, M.; Wang, G.; Hou, N.; Zhao, P. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of YABBY Gene Family in Juglans regia and Juglans mandshurica. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Yokota, S.; Hirayama, Y.; Imaichi, R.; Kato, M.; Gasser, C.S. Ancestral expression patterns and evolutionary diversification of YABBY genes in angiosperms. Plant J. 2011, 67, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finet, C.; Floyd, S.K.; Conway, S.J.; Zhong, B.; Scutt, C.P.; Bowman, J.L. Evolution of the YABBY gene family in seed plants. Evol. Dev. 2016, 18, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckardt, N.A. YABBY genes and the development and origin of seed plant leaves. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evkaikina, A.I.; Berke, L.; Romanova, M.A.; Proux-Wera, E.; Ivanova, A.N.; Rydin, C.; Pawlowski, K.; Voitsekhovskaja, O.V. The Huperzia selago Shoot Tip Transcriptome Sheds New Light on the Evolution of Leaves. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 2444–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Nukazuka, A.; Tsukaya, H. Leaf adaxial-abaxial polarity specification and lamina outgrowth: Evolution and development. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012, 53, 1180–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelaz, S.; Tapia-Lopez, R.; Alvarez-Buylla, E.R.; Yanofsky, M.F. Conversion of leaves into petals in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 2001, 11, 182–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hou, J.; Fu, Y.; Li, H. Genome-wide identification of YABBY transcription factors in Brachypodium distachyon and functional characterization of Bd DROOPING LEAF. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 185, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Wu, P.; Gao, L.; Zhang, C.; Hou, X. Characterization and expression profile analysis of YABBY family genes in Pak-choi (Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis) under abiotic stresses and hormone treatments. Plant Growth Regul. 2019, 87, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inal, B.; Buyuk, I.; Ilhan, E.; Aras, S. Genome-wide analysis of Phaseolus vulgaris C2C2-YABBY transcription factors under salt stress conditions. 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, M.; Jiao, J.; Zhang, C.; Wu, P.; Feng, K.; Li, L. Identification of YABBY Transcription Factors and Their Function in ABA and Salinity Response in Nelumbo nucifera. Plants 2023, 12, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Chen, G.Z.; Ahmad, S.; Wang, Q.; Tu, S.; Shi, X.L.; Hao, Y.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Lan, S.R.; Liu, Z.J.; et al. Identification, Molecular Characteristics, and Evolution of YABBY Gene Family in Melastoma dodecandrum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Sun, J.; Jiang, Z.; Ren, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Ma, W.; Xu, J. Identification and expression analysis of YABBY family genes in Platycodon grandiflorus. Plant Signal. Behav. 2023, 18, 2163069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Wang, D.; Peng, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, K.; Li, J.; Xu, X. Genome-Wide Analysis of the YABBY Transcription Factor Family in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Genes 2021, 12, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene Name | Gene ID | CDS (bp) | Exon | Protein (aa) | MW (kDa) | pI | Subcellular Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CqYAB1 | XP_021760782.1 | 633 | 7 | 210 | 23.53 | 8.44 | Nucleus/extracellular |
| CqYAB2 | XP_021748608.1 | 810 | 7 | 269 | 29.53 | 7.78 | Nucleus |
| CqYAB3 | XP_021741749.1 | 630 | 7 | 209 | 23.51 | 8.44 | Nucleus/extracellular |
| CqYAB4 | XP_021727415.1 | 609 | 6 | 202 | 23.15 | 4.67 | Nucleus/chloroplast |
| CqYAB5 | XP_021729181.1 | 558 | 6 | 185 | 20.51 | 8.76 | Nucleus |
| CqYAB6 | XP_021720585.1 | 573 | 6 | 190 | 21.23 | 7.64 | Nucleus |
| CqYAB7 | XP_021756313.1 | 834 | 7 | 277 | 30.44 | 7.39 | Nucleus |
| CqYAB8 | AUR62007472 | 591 | 6 | 196 | 21.94 | 9.40 | Nucleus |
| CqYAB9 | XP_021717873.1 | 561 | 6 | 186 | 20.73 | 8.76 | Nucleus |
| CqYAB10 | XP_021742940.1 | 588 | 6 | 195 | 22.25 | 4.90 | Nucleus/chloroplast |
| CqYAB11 | AUR62039930 | 612 | 6 | 203 | 22.71 | 9.37 | Nucleus |
| CqYAB12 | XP_021715646.1 | 573 | 6 | 190 | 21.21 | 7.66 | Nucleus |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Zhang, M.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Xing, S. Molecular Characterization and Expression Analysis of YABBY Genes in Chenopodium quinoa. Genes 2023, 14, 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14112103
Li T, Zhang M, Li M, Wang X, Xing S. Molecular Characterization and Expression Analysis of YABBY Genes in Chenopodium quinoa. Genes. 2023; 14(11):2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14112103
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Tingting, Mian Zhang, Mengyao Li, Xinxin Wang, and Shuping Xing. 2023. "Molecular Characterization and Expression Analysis of YABBY Genes in Chenopodium quinoa" Genes 14, no. 11: 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14112103
APA StyleLi, T., Zhang, M., Li, M., Wang, X., & Xing, S. (2023). Molecular Characterization and Expression Analysis of YABBY Genes in Chenopodium quinoa. Genes, 14(11), 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14112103






