BnPLP1 Positively Regulates Flowering Time, Plant Height, and Main Inflorescence Length in Brassica napus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
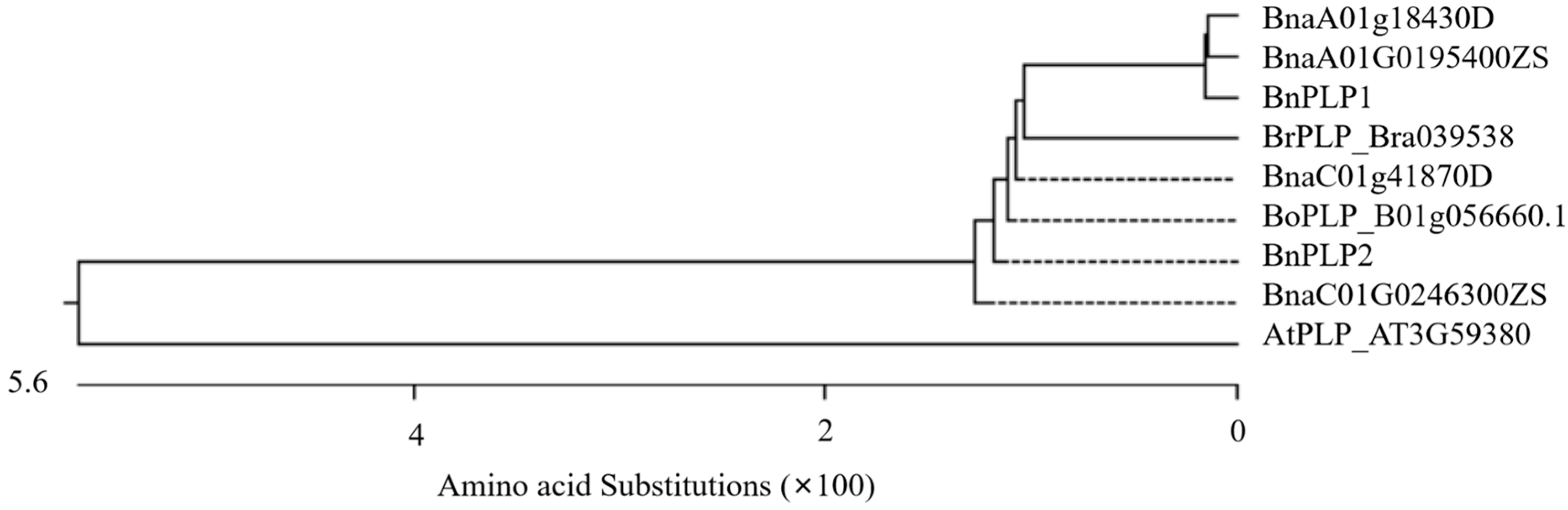
2.1. Gene Cloning and Sequence Analysis of BnPLPs
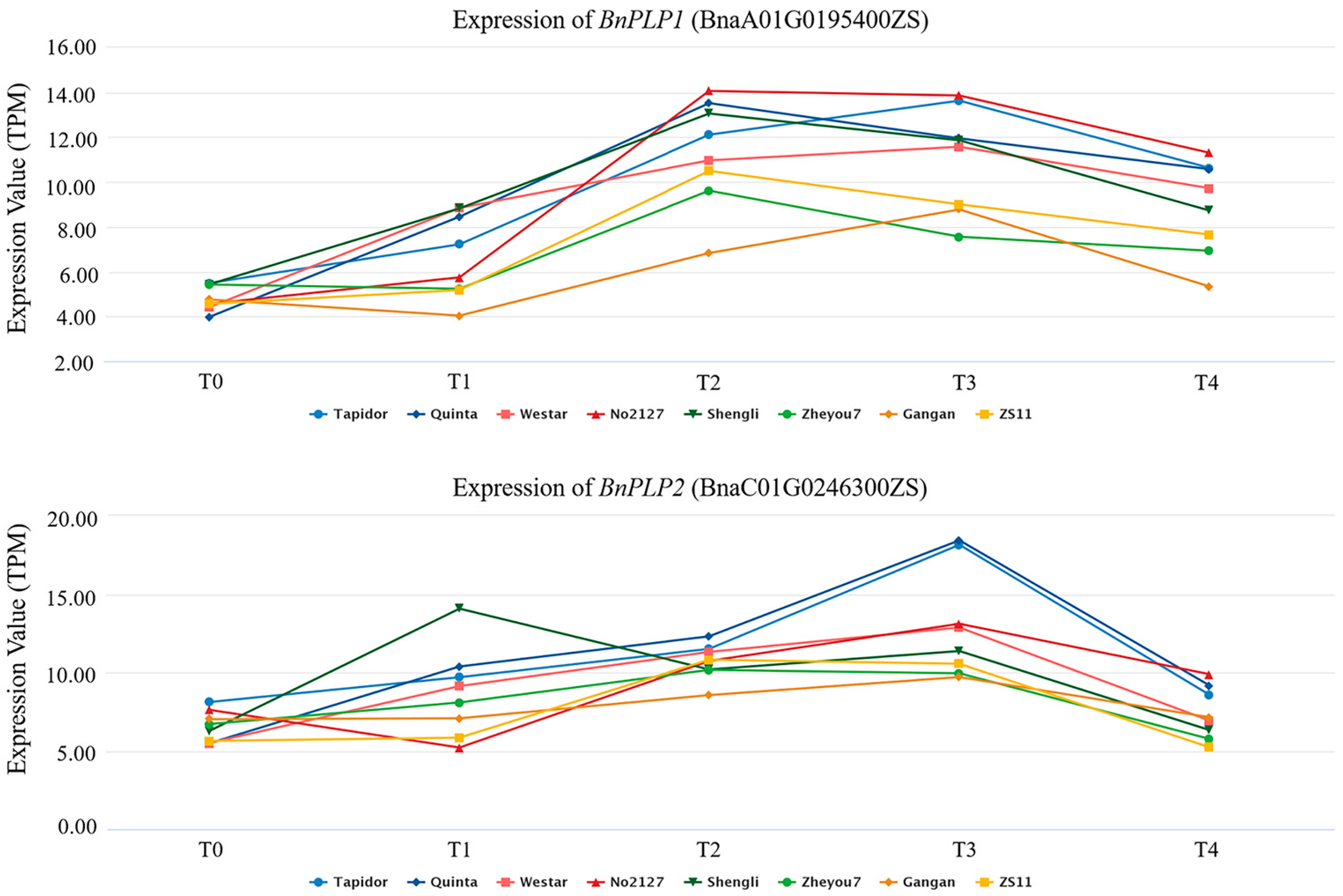
2.2. Gene Expression Analysis of BnPLPs
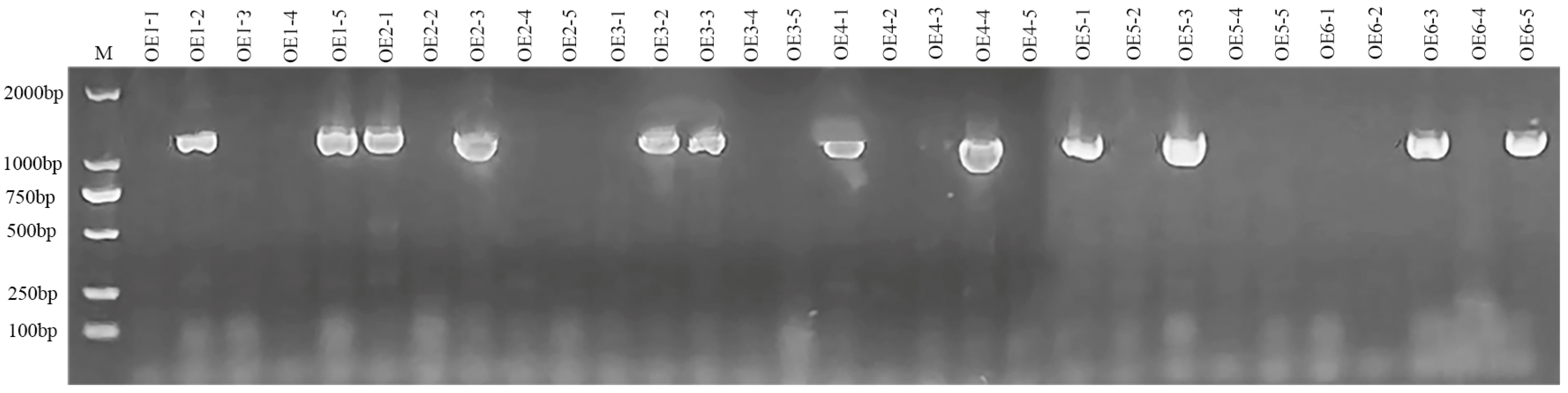
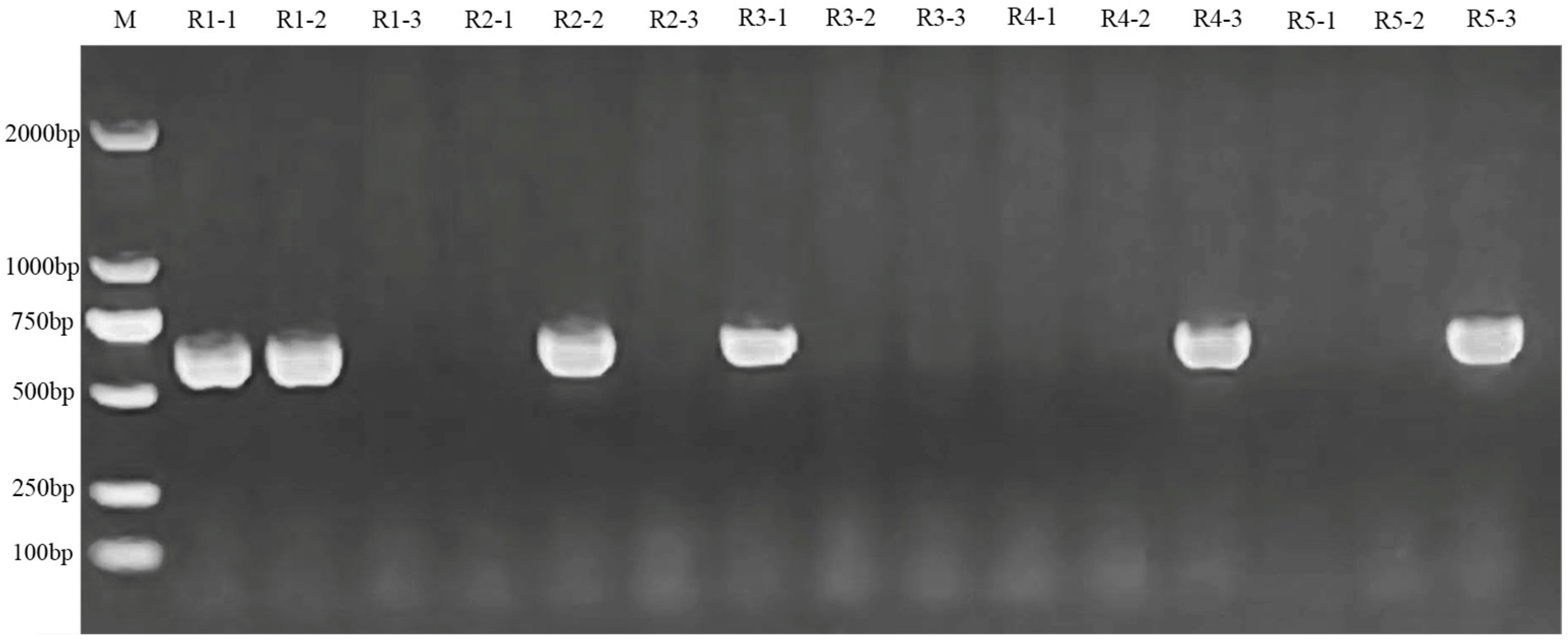
2.3. Overexpression and Knockout Plants Construction of BnPLP1 Gene
2.4. BnPLP1 Positively Regulates Early Flowering in Arabidopsis and Rapeseed, but Prolongs the Flowering Period
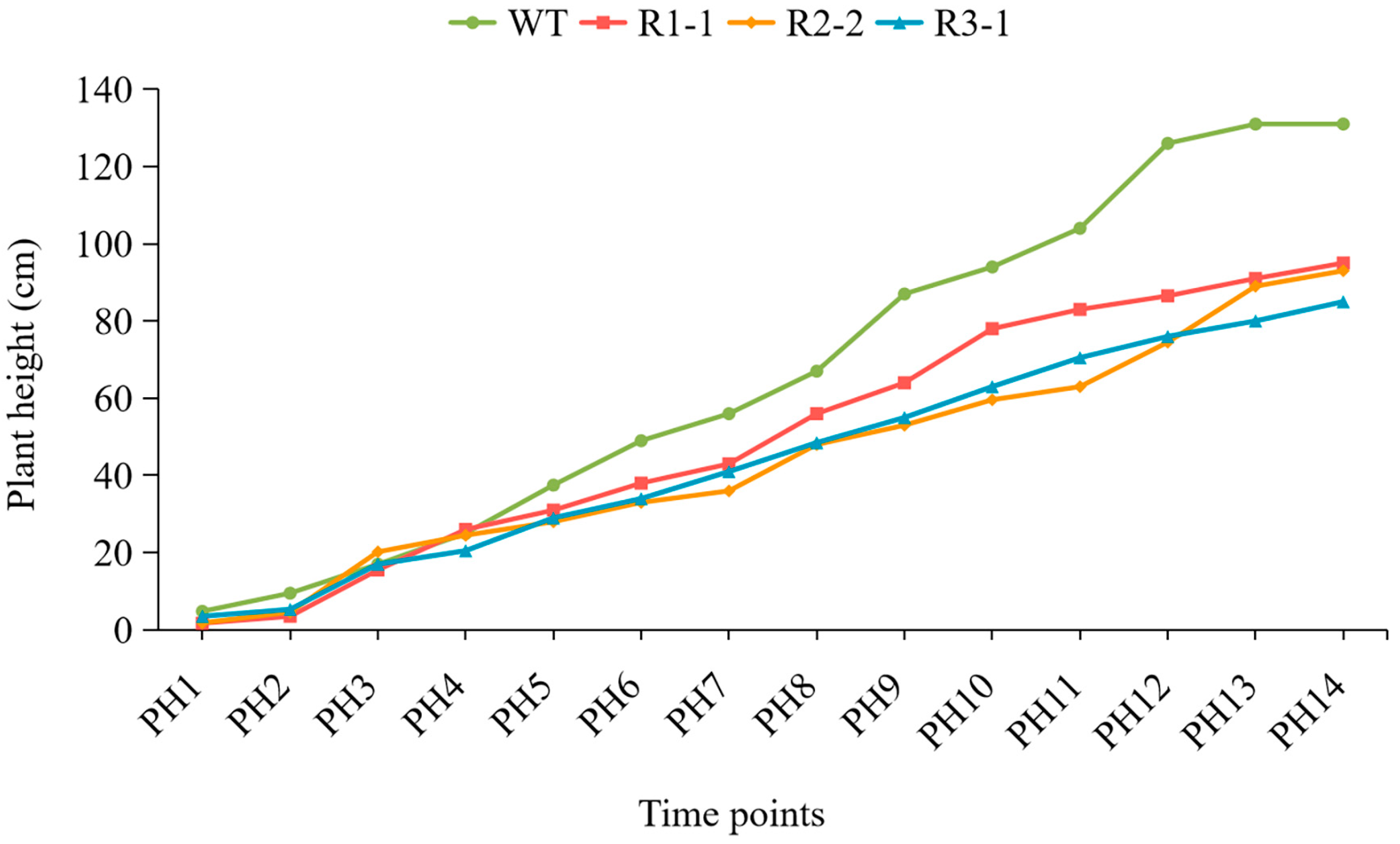
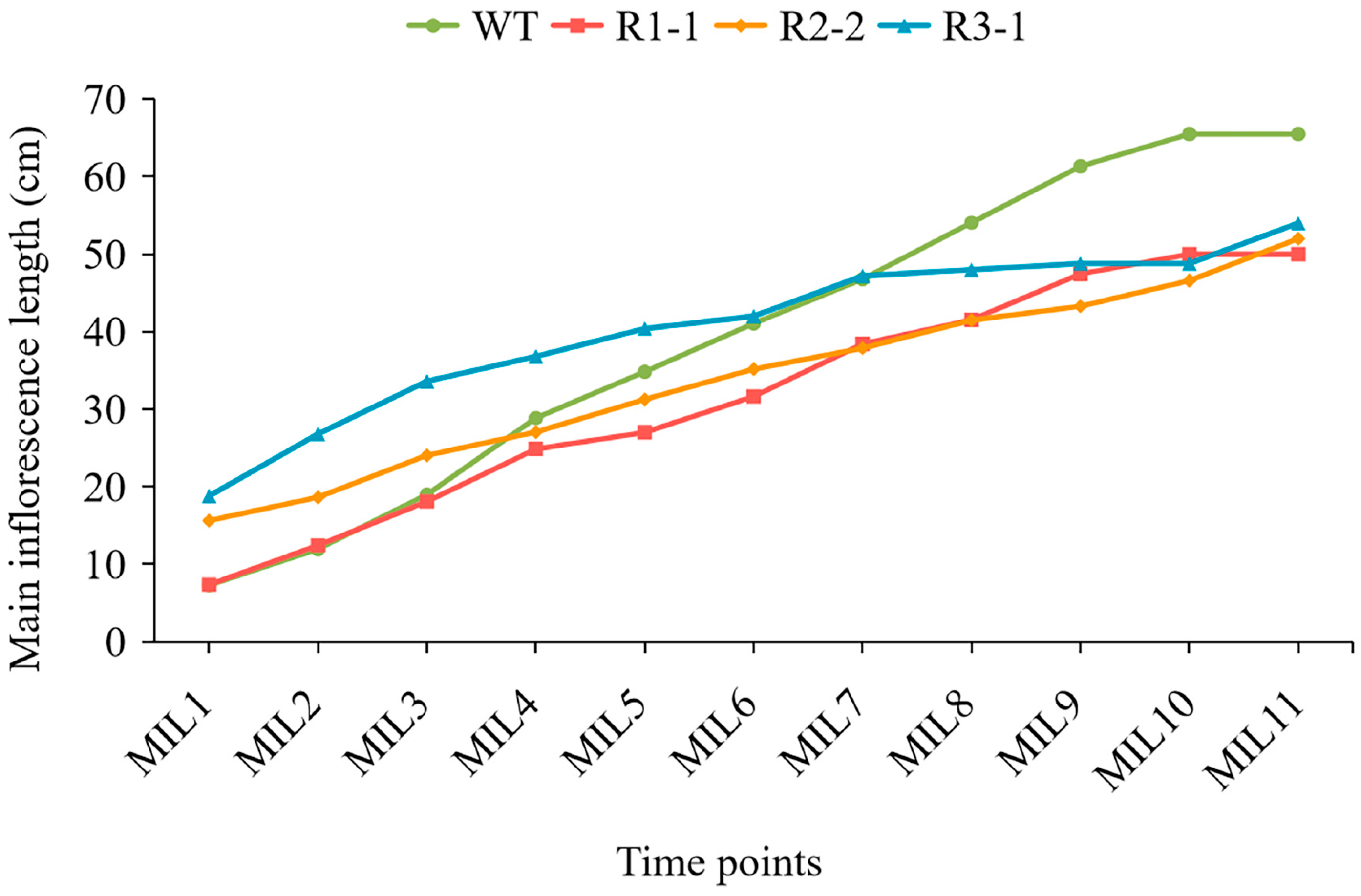
2.5. BnPLP1 Positively Regulates Plant Height and Main Inflorescence Length of Rapeseed
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. DNA, Total RNA Extraction, and cDNA Synthesis
4.3. Sequence Analysis
4.4. Gene Cloning and Plasmid Construction
4.5. Plant Transformation and Positive Plant Identification
4.6. Gene Expression Analysis
4.7. Phenotypic Determination
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, M.; Chang, W.; Yu, M.; Fan, Y.; Shang, G.; Xu, Y.; Niu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhu, H.; Dai, L.; et al. Overexpression of DEFECTIVE IN ANTHER DEHISCENCE 1 increases rapeseed silique length through crosstalk between JA and auxin signaling. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 168, 113576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalhoub, B.; Denoeud, F.; Liu, S.; Parkin, I.A.P.; Tang, H.; Wang, X.; Chiquet, J.; Belcram, H.; Tong, C.; Samans, B.; et al. Early allopolyploid evolution in the post-Neolithic Brassica napus oilseed genome. Science 2014, 345, 950–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaels, S.D. Flowering time regulation produces much fruit. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2009, 12, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T. On research and application of heterosis in rapeseed. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 2008, 30, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, T.; Zhou, Y. Progress and future development of hybrid rapeseed in China. Eng. Sci. 2013, 11, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Cai, L.; Yu, K. Variation and correlation analysis of six agronomic traits in Brassica napus germplasm population. J. Mt. Agric. Biol. 2022, 5, 84–87. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Anwar, S.; Kuai, J.; Noman, A.; Shahid, M.; Din, M.; Ali, A.; Zhou, G. Alteration in yield and oil quality traits of winter rapeseed by lodging at different planting density and nitrogen rates. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellmer, F.; Riechmann, J.L. Gene networks controlling the initiation of flower development. Trends Genet. 2010, 26, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amasino, R. Seasonal and developmental timing of flowering. Plant J. 2010, 61, 1001–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geraldo, N.; Baurle, I.; Kidou, S.; Hu, X.; Dean, C. FRIGIDA delays flowering in Arabidopsis via a cotranscriptional mechanism involving direct interaction with the nuclear cap-binding complex. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 1611–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Doyle, M.R.; Sung, S.; Amasino, R.M. Vernalization: Winter and the timing of flowering in plants. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2009, 25, 277–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Long, Y.; Wu, B.; Liu, J.; Jiang, C.; Shi, L.; Zhao, J.; King, G.J.; Meng, J. The evolution of Brassica napus FLOWERING LOCUS T paralogues in the context of inverted chromosomal duplication blocks. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Long, Y.; Raman, H.; Zou, X.; Wang, J.; Dai, S.; Xiao, Q.; Li, C.; Fan, L.; Liu, B.; et al. A Tourist-like MITE insertion in the upstream region of the BnFLC.A10 gene is associated with vernalization requirement in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.; Suppanz, I.; Raman, H.; Hou, J.; Wang, J.; Long, Y.; Jung, C.; Meng, J. Comparative analysis of FLC homologues in Brassicaceae provides insight into their role in the evolution of oilseed rape. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadege, M.; Sheldon, C.C.; Helliwell, C.A.; Stoutjesdijk, P.; Dennis, E.S.; Peacock, W.J. Control of flowering time by FLC orthologues in Brassica napus. Plant J. 2001, 5, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, L.S.; Robson, F.; Sharpe, A.; Lydiate, D.; Coupland, G. Conserved structure and function of the Arabidopsis flowering time gene CONSTANS in Brassica napus. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998, 5, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadina, O.; Pankin, A.; Khavkin, E. Molecular characterization of the flowering time gene FRIGIDA in Brassica genomes A and C. Russ. J. Plant Physl. 2013, 60, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Chen, C.; Yin, S.; Li, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, B.; King, G.J.; Wang, J.; Liu, K. Sequence variation and functional analysis of a FRIGIDA orthologue (BnaA3.FRI) in Brassica napus. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, L.; Chen, H.; Cai, W. BnNAC485 is involved in abiotic stress responses and flowering time in Brassica napus. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2014, 79, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Dai, H. Brassica napus Cycling Dof Factor1 (BnCDF1) is involved in flowering time and freezing tolerance. Plant Growth Regul. 2016, 80, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiessl, S. Regulation and subfunctionalization of flowering time genes in the allotetraploid oil crop Brassica napus. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 605155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, E.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Jia, Z.; Wang, X.; Wen, J.; Shen, J.; Fu, T.; Yi, B. Identification and characterization of the MIKC-Type MADS-Box gene family in Brassica napus and its role in floral transition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treccarichi, S.; Di Gaetano, C.; Di Stefano, F.; Gasparini, M.; Branca, F. Using simple sequence repeats in 9 Brassica complex species to assess hypertrophic curd induction. Agriculture 2021, 11, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treccarichi, S.; Di Gaetano, C.; Di Stefano, F.; Gasparini, M.; Branca, F. Molecular markers for detecting inflorescence size of Brassica oleracea L. crops and B. oleracea complex species (n = 9) useful for breeding of broccoli (B. oleracea var. italica) and cauliflower (B. oleracea var. botrytis). Plants 2023, 12, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Song, J.; Zhao, B.; Guo, C.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; King, G.J.; Liu, K. An auxin signaling gene BnaA3.IAA7 contributes to improved plant architecture and yield heterosis in rapeseed. New Phytol. 2019, 222, 837–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J. Molecular basis of plant architecture. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 253–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T. Gibberellin metabolism, perception and signaling pathways in Arabidopsis. Arab. Book 2008, 6, e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazuka, T.; Kamiya, N.; Nishimura, T.; Ohmae, K.; Sato, Y.; Imamura, K.; Nagato, Y.; Koshiba, T.; Nagamura, Y.; Ashikari, M.; et al. A rice tryptophan deficient dwarf mutant, tdd1, contains a reduced level of indole acetic acid and develops abnormal flowers and organless embryos. Plant J. 2009, 60, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, X.; Xiong, G.; Liu, H.; Chen, F.; Wang, L.; Meng, X.; Liu, G.; Yu, H.; Yuan, Y.; et al. DWARF 53 acts as a repressor of strigolactone signalling in rice. Nature 2013, 504, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Lin, Q.; Zhu, L.; Ren, Y.; Zhou, K.; Shabek, N.; Wu, F.; Mao, H.; Dong, W.; Gan, L.; et al. D14-SCFD3-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling. Nature 2013, 7480, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Y.; Qi, L.; Pu, Y.; Wen, J.; Yi, B.; Shen, J.; Ma, C.; Tu, J.; et al. Identification, fine mapping and characterisation of a dwarf mutant (bnaC.dwf) in Brassica napus. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2011, 122, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Xu, E.; Ge, X.; Li, Z. Major co-localized QTL for plant height, branch initiation height, stem diameter, and flowering time in an alien introgression derived Brassica napus DH population. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; He, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Wan, S.; Chu, P.; Guan, R. Fine mapping of a major locus controlling plant height using a high-density single-nucleotide polymorphism map in Brassica napus. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2016, 129, 1479–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Chu, P.; Wan, S.; Yang, M.; Wang, M.; Guan, R. Mapping a major QTL responsible for dwarf architecture in Brassica napus using a single-nucleotide polymorphism marker approach. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Wang, B.; Yan, L.; Hu, K.; Liu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Guan, C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. Genome-wide association study provides insight into the genetic control of plant height in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quijada, P.A.; Udall, J.A.; Lambert, B.; Osborn, T.C. Quantitative trait analysis of seed yield and other complex traits in hybrid spring rapeseed (Brassica napus L.): 1. Identification of genomic regions from winter germplasm. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 113, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basunanda, P.; Radoev, M.; Ecke, W.; Friedt, W.; Becker, H.C.; Snowdon, R.J. Comparative mapping of quantitative trait loci involved in heterosis for seedling and yield traits in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2010, 120, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Li, R.; Qiu, D.; Jiang, C.; Long, Y.; Morgan, C.; Bancroft, I.; Zhao, J.; Meng, J. Unraveling the complex trait of crop yield with quantitative trait loci mapping in Brassica napus. Genetics 2009, 182, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, W.; Ye, W.; Wang, B.; Younas, M.; Wu, J.; Liu, K. Association mapping of six yield-related traits in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Peng, C.; Liu, H.; Tang, M.; Yang, H.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; et al. Genome-Wide association study reveals candidate genes for control of plant height, branch initiation height and branch number in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Chen, B.; Xu, K.; Gao, G.; Yan, G.; Qiao, J.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Li, L.; Xiao, X.; et al. A genome-wide association study of plant height and primary branch number in rapeseed (Brassica napus). Plant Sci. 2016, 242, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.P.; Chen, B.Y.; Tu, J.X.; Fu, T. Detection of QTL for six yield-related traits in oilseed rape (Brassica napus) using DH and immortalized F2 populations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2007, 115, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Tian, J.; Li, B.; Chen, L.; Chao, H.; Long, Y.; Xiang, J.; Gan, J.; et al. Genome-Wide identification of QTL for seed yield and yield-related traits and construction of a high-density consensus map for QTL comparison in Brassica napus. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Wang, M.; Long, Y.; Huang, Y.; Shi, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Fitt, B.; Xiang, J.; Mason, A.S.; et al. Correction to: Incorporating pleiotropic quantitative trait loci in dissection of complex traits: Seed yield in rapeseed as an example. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2018, 131, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Hu, M.; Yang, H.; Tang, M.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, X.; Fan, S.; et al. Three BnaIAA7 homologs are involved in auxin/brassinosteroid-mediated plant morphogenesis in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Plant Cell Rep. 2019, 38, 883–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Huang, T.; Wang, F.; Yuan, F.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, S.; Wu, J.; Liu, K. A missense mutation in the VHYNP motif of a DELLA protein causes a semi-dwarf mutant phenotype in Brassica napus. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2010, 121, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Wang, B.; Dai, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, K. Brassica napus DS-3, encoding a DELLA protein, negatively regulates stem elongation through gibberellin signaling pathway. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2017, 130, 727–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Running, M.P.; Lavy, M.; Sternberg, H.; Galichet, A.; Gruissem, W.; Hake, S.; Ori, N.; Yalovsky, S. Enlarged meristems and delayed growth in plp mutants result from lack of CaaX prenyltransferases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 7815–7820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer-Stroh, S.; Washietl, S.; Eisenhaber, F. Protein prenyltransferases. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McTaggart, S.J. Isoprenylated proteins. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Running, M.P. The role of lipid post-translational modification in plant developmental processes. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemsley, P.A. The importance of lipid modified proteins in plants. New Phytol. 2014, 205, 476–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galichet, A.; Gruissem, W. Protein farnesylation in plants—Conserved mechanisms but different targets. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2003, 6, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Beaith, M.; Chalifoux, M.; Ying, J.; Uchacz, T.; Sarvas, C.; Griffiths, R.; Kuzma, M.; Wan, J.; Huang, Y. Shoot-specific down-regulation of protein farnesyltransferase (α-subunit) for yield protection against drought in canola. Mol. Plant 2009, 2, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Liang, C.; Wei, L.; Wang, S.; Yin, F.; Liu, D.; Guo, L.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Q. BnVIR: Bridging the genotype-phenotype gap to accelerate mining of candidate variations underlying agronomic traits in Brassica napus. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.; Wang, X.; Chen, F.; Chen, S.; Peng, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Hu, M.; Chu, P.; Zhang, J.; et al. Genome-wide transcriptomic analysis uncovers the molecular basis underlying early flowering and apetalous characteristic in Brassica napus L. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Sun, L.; Peng, Q.; Chen, F.; Zhang, W.; Guan, R.; Zhang, J. Identification and physical mapping of QTLs associated with flowering time in Brassica napus L. Euphytica 2019, 215, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Min, Y.; Schiessl, S.; Xiong, X.; Jan, H.U.; He, X.; Qian, W.; Guan, C.; Snowdon, R.J.; Hua, W.; et al. Integrative analysis of GWAS and transcriptome to reveal novel loci regulation flowering time in semi-winter rapeseed. Plant Sci. 2021, 310, 110980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, H.; Miura, H. Gene dosage effect of the wheat Wx alleles and their interaction on amylose synthesis in the endosperm. Euphytica 2003, 132, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, K.; Li, H.; Peng, Q.; Chen, F.; Zhang, W.; Chen, S.; Hu, M.; Zhang, J. High-density SNP map construction and QTL identification for the apetalous character in Brassica napus L. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.M.; Guan, Z.; Hu, J.; Guo, C.; Yang, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, D.; Wang, B.; Lu, S.; Zhou, R.; et al. Eight high-quality genomes reveal pan-genome architecture and ecotype differentiation of Brassica napus. Nat. Plants 2020, 6, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Sun, R.; Wu, J.; Liu, S.; Bai, Y.; Mun, J.H.; Bancroft, I.; Cheng, F.; et al. The genome of the mesopolyploid crop species Brassica rapa. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Tong, C.; Edwards, D.; Parkin, I.A.; Zhao, M.; Ma, J.; Yu, J.; Huang, S.; et al. The Brassica oleracea genome reveals the asymmetrical evolution of polyploid genomes. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Dudley, J.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; He, J.; Liu, L.; Xie, R.; Qiu, L.; Li, X.; Yuan, W.; Chen, K.; Yin, Y.; Kyaw, M.; et al. A convenient, rapid and efficient method for establishing transgenic lines of Brassica napus. Plant Methods 2020, 16, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, S.J.; Bent, A.F. Floral dip: A simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 1998, 16, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Yang, Q.; Fu, T.; Zhou, Y. Overexpression of the Brassica napus BnLAS gene in Arabidopsis affects plant development and increases drought tolerance. Plant Cell Rep. 2011, 30, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broun, P.; Poindexter, P.; Osborne, E.; Jiang, C.Z.; Riechmann, J.L. WIN1, a transcriptional activator of epidermal wax accumulation in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4706–4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.; Schmittgen, T. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Long, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, J.; Zhao, W.; Li, B.; Chen, L.; Chao, H.; et al. Dynamic and comparative QTL analysis for plant height in different developmental stages of Brassica napus L. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 1175–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.; Zhang, W.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, M.; Chen, F.; Sun, C.; Hu, M.; Tian, E.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J. Integrating unconditional and conditional QTLs to dissect the genetic basis of stem mechanical strength in Brassica napus L. Euphytica 2021, 217, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Genotype | Onset of Flowering | End of Flowering | Flowering Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 26.2 ± 0.4 a | 50.4 ± 0.5 a | 24.2 ± 0.4 a |
| OE1-5 | 21.6 ± 0.5 b | 50.8 ± 0.5 a | 29.2 ± 0.4 b |
| OE2-3 | 21.4 ± 0.5 b | 48.0 ± 0.7 b | 26.6 ± 0.5 b |
| OE5-1 | 24.4 ± 0.5 b | 52.6 ± 0.5 b | 28.2 ± 0.4 b |
| OE5-3 | 21.2 ± 0.5 b | 50.4 ± 0.5 a | 29.2 ± 0.4 b |
| OE6-5 | 22.8 ± 0.8 b | 52.0 ± 0.7 b | 29.2 ± 0.4 b |
| OE_mean | 22.3 ± 1.3 b | 50.8 ± 1.8 a | 28.5 ± 1.1 b |
| Genotype | Onset of Flowering | End of Flowering | Flowering Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 23.8 ± 0.8 a | 53.2 ± 1.3 a | 29.4 ± 1.1 a |
| R1-1 | 27.8 ± 0.8 b | 55.2 ± 0.8 b | 27.4 ± 0.8 b |
| R2-2 | 27.6 ± 1.1 b | 54.8 ± 0.8 a | 27.2 ± 0.9 b |
| R3-1 | 28.0 ± 0.7 b | 54.0 ± 0.7 a | 26.0 ± 0.7 b |
| R_mean | 27.8 ± 0.2 b | 54.7 ± 0.6 a | 26.9 ± 0.8 b |
| Genotype | Plant Height | Main Inflorescence Length | Number of Primary Branches |
|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 27.9 ± 1.4 a | 16.4 ± 1.1 a | 3.2 ± 0.4 a |
| OE1-5 | 36.0 ± 1.6 b | 24.0 ± 1.6 b | 3.8 ± 0.4 a |
| OE2-3 | 34.8 ± 1.3 b | 23.8 ± 1.3 b | 2.8 ± 0.4 a |
| OE5-1 | 35.4 ± 1.7 b | 23.4 ± 1.5 b | 3.0 ± 0.4 a |
| OE5-3 | 35.0 ± 1.6 b | 23.8 ± 1.3 b | 3.2 ± 0.4 a |
| OE6-5 | 37.6 ± 1.1 b | 25.6 ± 2.1 b | 3.2 ± 0.4 a |
| OE_mean | 35.8 ± 1.1 b | 24.1 ± 0.9 b | 3.2 ± 0.4 a |
| Genotype | Plant Height | Main Inflorescence Length | Number of Primary Branches | Stem Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 131.6 ± 2.7 a | 65.4 ± 1.1 a | 6.2 ± 0.4 a | 1.3 ± 0.1 a |
| R1-1 | 91.4 ± 2.1 b | 50.0 ± 1.5 b | 6.8 ± 0.4 a | 1.2 ± 0.1 a |
| R2-2 | 92.8 ± 1.3 b | 52.0 ± 0.7 b | 7.0 ± 0.7 a | 1.3 ± 0.1 a |
| R3-1 | 86.6 ± 2.1 b | 54.0 ± 1.6 b | 7.2 ± 0.8 a | 1.2 ± 0.1 a |
| R_mean | 90.3 ± 3.3 b | 52.0 ± 2.0 b | 7.0 ± 0.2 a | 1.2 ± 0.1 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, T.; Cai, L.; He, Y.; Li, Y.; Tian, E.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Yu, K.; Shen, X. BnPLP1 Positively Regulates Flowering Time, Plant Height, and Main Inflorescence Length in Brassica napus. Genes 2023, 14, 2206. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14122206
Ding T, Cai L, He Y, Li Y, Tian E, Zhou Q, Zhou X, Wang X, Yu K, Shen X. BnPLP1 Positively Regulates Flowering Time, Plant Height, and Main Inflorescence Length in Brassica napus. Genes. 2023; 14(12):2206. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14122206
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Ting, Lei Cai, Yuqi He, Yuanhong Li, Entang Tian, Qianhui Zhou, Xufan Zhou, Xiaodong Wang, Kunjiang Yu, and Xinjie Shen. 2023. "BnPLP1 Positively Regulates Flowering Time, Plant Height, and Main Inflorescence Length in Brassica napus" Genes 14, no. 12: 2206. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14122206
APA StyleDing, T., Cai, L., He, Y., Li, Y., Tian, E., Zhou, Q., Zhou, X., Wang, X., Yu, K., & Shen, X. (2023). BnPLP1 Positively Regulates Flowering Time, Plant Height, and Main Inflorescence Length in Brassica napus. Genes, 14(12), 2206. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14122206






