Variation of the 3’RR1 HS1.2 Enhancer and Its Genomic Context
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. HS1.2-Length Typing
2.2. Handling of the 1000 Genomes Data
2.3. DNA Sequencing
2.4. Search for Putative Transcription Factor Binding Sites and Other Elements
3. Results
3.1. HS1.2-Length Allele Contributions to Haplotype Blocks
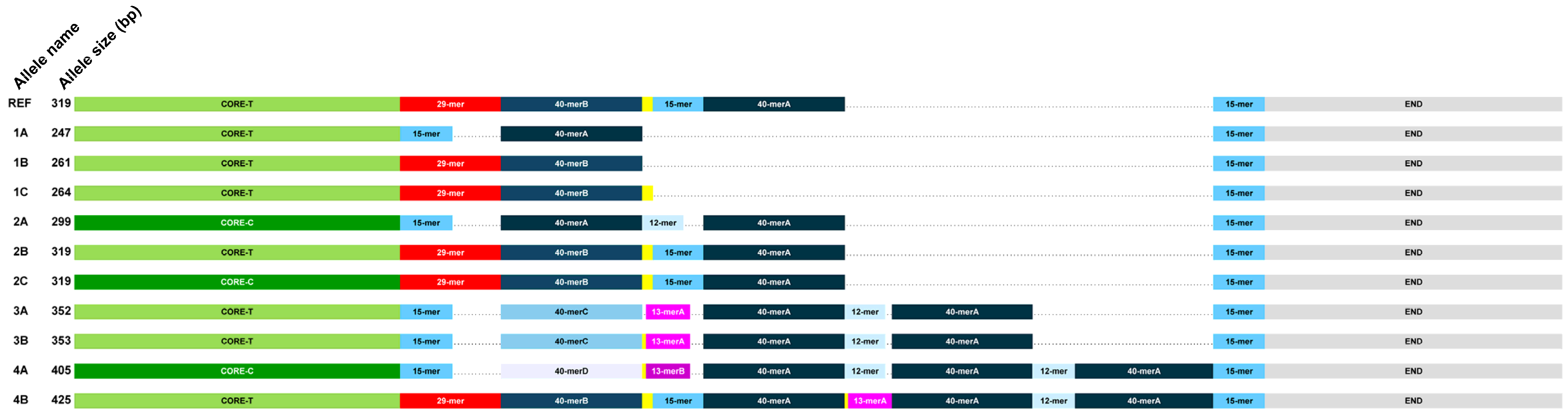
3.2. Internal Sequence Heterogeneity of HS1.2 Alleles
3.3. Single Nucleotide Variation in the CORE and the Modules
3.4. Putative Impact of HS1.2 Diversity on Transcription Factor Binding Sites and Other Elements
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cianci, R.; Mancino, G.; Galli, E.; Serone, E.; Massoud, R.; D’Addabbo, P.; Poscia, A.; Borghetti, A.; Porzio, O.; Marmo, R.; et al. New insight of human-IgH 3′regulatory regions in immunoglobulins switch. Gene 2023, 862, 147254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda, M.A.; Garrett, F.E.; Price-Whelan, A.; Birshtein, B.K. Comparative analysis of human and mouse 3′ Igh regulatory regions identifies distinctive structural features. Mol. Immunol. 2005, 42, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hnisz, D.; Abraham, B.J.; Lee, T.I.; Lau, A.; Saint-André, V.; Sigova, A.A.; Hoke, H.A.; Young, R.A. Super-Enhancers in the control of cell identity and disease. Cell 2013, 155, 934–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinaud, E.; Marquet, M.; Fiancette, R.; Péron, S.; Vincent-Fabert, C.; Denizot, Y.; Cogné, M. The IgH Locus 3′ Regulatory Region: Pulling the Strings from Behind. In Advances in Immunology; Alt, F.W., Austen, K.F., Honj, T., Melchers, F., Uhr, J.W., Unanue, E.R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; Volume 110, pp. 27–70. [Google Scholar]
- Pinaud, E.; Aupetit, C.; Chauveau, C.; Cogné, M. Identification of a homolog of the Cα3′/hs3 enhancer and of an allelic variant of the 3′IgH/hs1,2 enhancer downstream of the human immunoglobulin α1 gene. Eur. J. Immunol. 1997, 27, 2981–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Addabbo, P.; Scascitelli, M.; Giambra, V.; Rocchi, M.; Frezza, D. Position and sequence conservation in Amniota of polymorphic enhancer HS1.2 within the palindrome of IgH 3′Regulatory Region. BMC Evol. Biol. 2011, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garot, A.; Marquet, M.; Saintamand, A.; Bender, S.; Le Noir, S.; Rouaud, P.; Carrion, C.; Oruc, Z.; Bébin, A.-G.; Moreau, J.; et al. Sequential activation and distinct functions for distal and proximal modules within the IgH 3′ regulatory region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1618–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denizot, Y.; Pinaud, E.; Aupetit, C.; Le Morvan, C.; Magnoux, E.; Aldigier, J.C.; Cogné, M. Polymorphism of the human α1 immunoglobulin gene 3′ enhancer hs1,2 and its relation to gene expression. Immunology 2001, 103, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giambra, V.; Fruscalzo, A.; Giufre’, M.; Martinez-Labarga, C.; Favaro, M.; Rocchi, M.; Frezza, D. Evolution of human IgH3′EC duplicated structures: Both enhancers HS1,2 are polymorphic with variation of transcription factor’s consensus sites. Gene 2005, 346, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giambra, V.; Martìnez-Labarga, C.; Giufre’, M.; Modiano, D.; Simpore’, J.; Gisladottir, B.K.; Francavilla, R.; Zhelezova, G.; Kilic, S.S.; Crawford, M.; et al. Immunoglobulin enhancer HS1,2 polymorphism: A new powerful anthropogenetic marker. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2006, 70, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giambra, V.; Cianci, R.; Lolli, S.; Mattioli, C.; Tampella, G.; Cattalini, M.; Kilic, S.S.; Pandolfi, F.; Plebani, A.; Frezza, D. Allele *1 of HS1.2 enhancer associates with selective IgA deficiency and IgM concentration. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 8280–8285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Labarga, C.; Lelli, R.; Tarsi, T.; Babalini, C.; De Angelis, F.; Ottoni, C.; Giambra, V.; Pepe, G.; Azzebi, E.; Frezza, D.; et al. Polymorphisms of the COL1A2, CYP1A1 and HS1,2 Ig enhancer genes in the Tuaregs from Libya. Ann. Hum. Biol. 2007, 34, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frezza, D.; Giambra, V.; Cianci, R.; Fruscalzo, A.; Giufrè, M.; Cammarota, G.; Martìnez-Labarga, C.; Rickards, O.; Scibilia, G.; Sferlazzas, C.; et al. Increased frequency of the immunoglobulin enhancer HS1,2 allele 2 in coeliac disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 39, 1083–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frezza, D.; Giambra, V.; Mattioli, C.; Piccoli, K.; Massoud, R.; Siracusano, A.; Di Giannantonio, M.; Birshtein, B.K.; Rubino, I.A. Allelic frequencies of 3′ Ig heavy chain locus enhancer HS1,2-A associated with Ig levels in patients with schizophrenia. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2009, 22, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serone, E.; Daleno, C.; Principi, N.; Porretti, L.; Iacoacci, V.; Gargioli, C.; Magrini, A.; Massoud, R.; D’Addabbo, P.; Cattalini, M.; et al. The change in Ig regulation from children to adults disconnects the correlation with the 3′RR hs1.2 polymorphism. BMC Immunol. 2014, 15, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colucci, M.; Frezza, D.; Gambassi, G.; De Vito, F.; Iaquinta, A.; Massaro, M.G.; Di Giambenedetto, S.; Borghetti, A.; Lombardi, F.; Panzironi, N.; et al. Functional associations between polymorphic regions of the human 3′IgH locus and COVID-19 disease. Gene 2022, 838, 146698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cianci, R.; D’Addabbo, P.; Gambassi, G.; Lolli, S.; Serone, E.; Rizzi, A.; Pitocco, D.; Pandolfi, F.; Frezza, D. Association between IgH enhancer hs1.2 and type 1 diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2018, 55, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Addabbo, P.; Serone, E.; Esposito, M.; Vaccari, G.; Gargioli, C.; Frezza, D.; Bianchi, L. Association between Psoriasis and haplotypes of the IgH 3′ Regulatory Region 1. Gene 2018, 669, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frezza, D.; Martinez-Labarga, C.; Giambra, V.; Serone, E.; Scano, G.; Rickards, O.; D’Addabbo, P.; Novelletto, A. Concerted variation of the 3′ regulatory region of Ig heavy chain and Gm haplotypes across human continental populations. Am. J. Phys. Anthrop. 2020, 171, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefranc, M.P.; Lefranc, G. (Eds.) Human Gm, Km, and Am Allotypes and Their Molecular Characterization: A Remarkable Demonstration of Polymorphism; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; Volume 882. [Google Scholar]
- The 1000 Genomes Project Consortium. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015, 526, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferis, R.; Lefranc, M.-P. Human immunoglobulin allotypes. mAbs 2009, 1, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GTEx Consortium. Genetic effects on gene expression across human tissues. Nature 2017, 550, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, D.; Albrecht, E.; Aslam, M.; Goris, A.; Hauenstein, N.; Jochim, A.; International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Consortium; Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium; Cepok, S.; Grummel, V.; et al. Genetic variants in the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus are associated with the IgG index in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 73, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsson, S.; Sveinbjornsson, G.; de Lapuente Portilla, A.L.; Swaminathan, B.; Plomp, R.; Dekkers, G.; Ajore, R.; Ali, M.; Bentlage, A.E.H.; Elmér, E.; et al. Identification of sequence variants influencing immunoglobulin levels. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, B.G.; Penkert, R.R.; Xu, B.; Fan, Y.; Neale, G.; Gearhart, P.J.; Hurwitz, J.L. Binding of estrogen receptors to switch sites and regulatory elements in the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus of activated B cells suggests a direct influence of estrogen on antibody expression. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 77, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.G.; Sealy, R.E.; Penkert, R.R.; Surman, S.L.; Maul, R.W.; Neale, G.; Xu, B.; Gearhart, P.J.; Hurwitz, J.L. Complex sex-biased antibody responses: Estrogen receptors bind estrogen response elements centered within immunoglobulin heavy chain gene enhancers. Int. Immunol. 2019, 31, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurwitz, J.L.; Penkert, R.R.; Xu, B.; Fan, Y.; Partridge, J.F.; Maul, R.W.; Gearhart, P.J. Hotspots for vitamin-steroid-thyroid hormone response elements within switch regions of immunoglobulin Heavy Chain loci predict a direct influence of vitamins and hormones on B Cell class switch recombination. Viral Immunol. 2016, 29, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guglielmi, L.; Truffinet, V.; Magnoux, E.; Cogné, M.; Denizot, Y. The polymorphism of the locus control region lying downstream the human IgH locus is restricted to hs1,2 but not to hs3 and hs4 enhancers. Immunol. Lett. 2004, 94, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, M.; Smith, N.J.; Donnelly, P. A new statistical method for haplotype reconstruction from population data. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 68, 978–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J.C.; Fry, B.; Maller, J.; Daly, M.J. Haploview: Analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunoda, T.; Takagi, T. Estimating transcription factor bindability on DNA. Bioinformatics 1999, 15, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingender, E.; Dietze, P.; Karas, H.; Knüppel, R. TRANSFAC: A database on transcription factors and their DNA binding sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996, 24, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, A.D.; Ochs, S.D.; Johnson, B.E.; Sulentic, C.E.W. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-induced activation of the human IGH hs1.2 enhancer: Mutational analysis of putative regulatory binding motifs. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 120, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli-Sforza, L.L.; Menozzi, P.; Piazza, A. The History and Geography of Human Genes; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jodice, C.; Malaspina, P.; Ciminelli, B.M.; Martinez-Labarga, C.; Biancolella, M.; Novelli, G.; Novelletto, A. Variation of the 3’RR1 HS1.2 Enhancer and Its Genomic Context. Genes 2024, 15, 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15070856
Jodice C, Malaspina P, Ciminelli BM, Martinez-Labarga C, Biancolella M, Novelli G, Novelletto A. Variation of the 3’RR1 HS1.2 Enhancer and Its Genomic Context. Genes. 2024; 15(7):856. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15070856
Chicago/Turabian StyleJodice, Carla, Patrizia Malaspina, Bianca Maria Ciminelli, Cristina Martinez-Labarga, Michela Biancolella, Giuseppe Novelli, and Andrea Novelletto. 2024. "Variation of the 3’RR1 HS1.2 Enhancer and Its Genomic Context" Genes 15, no. 7: 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15070856
APA StyleJodice, C., Malaspina, P., Ciminelli, B. M., Martinez-Labarga, C., Biancolella, M., Novelli, G., & Novelletto, A. (2024). Variation of the 3’RR1 HS1.2 Enhancer and Its Genomic Context. Genes, 15(7), 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15070856







