Analysis of Selected Eye Disorders in a Group of Predisposed Breeds of Dogs: Molecular Diagnostics of Collie Eye Anomaly and Progressive Retinal Atrophy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and DNA Isolation
2.2. Primers for CEA
2.3. Primers for PRA (RCD3)
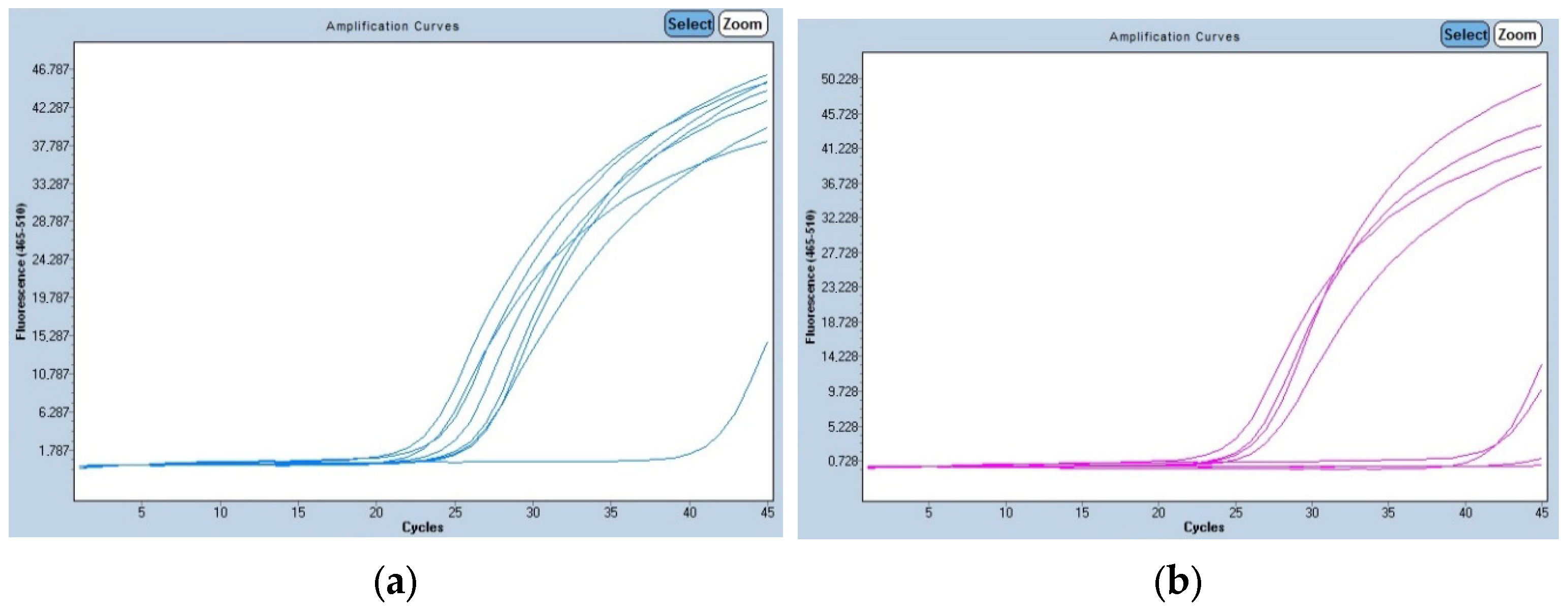
2.4. RealTime PCR
3. Results
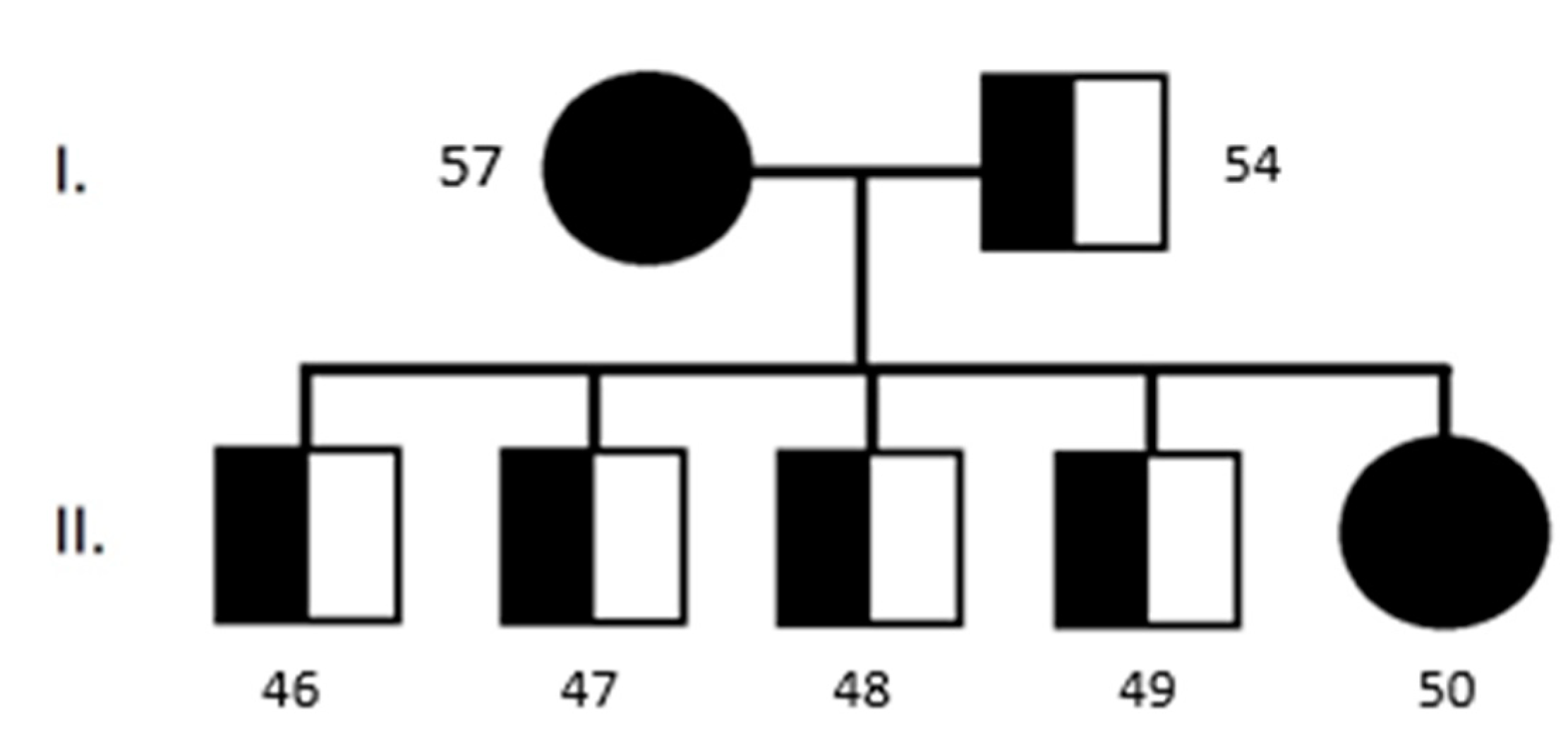
3.1. Collie Eye Anomaly
3.2. Progressive Retinal Atrophy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- OMIA—Online Mendelian Inheritance in Animals. Available online: https://www.omia.org/home/ (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Bunel, M.; Chaudieu, G.; Hamel, C.; Lagoutte, L.; Manes, G.; Botherel, N.; Quignon, P. Natural models for retinitis pigmentosa: Progressive retinal atrophy in dog breeds. Hum. Gen. 2019, 138, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowend, K.L.; Starr-Moss, A.N.; Murphy, K.E. The function of dog models in developing gene therapy strategies for human health. Mamm. Genome 2011, 22, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubrický, P.; Trbolová, A. Hereditary eye diseases in German shepherd dog. Fol. Vet. 2022, 66, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balicki, I.; Goleman, M.; Balicka, A. Ocular abnormalities in Polish Hunting Dogs. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0258636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.S.; Kadhim, N.A.; Rasool, E.M.A.; Al-Erjan, M.; Lahhob, Q.R.; Mudhafar, M. Harnessing CRISPR-CAS9 gene editing for the eradication of inherited retinal diseases in purebred dogs: A path to preservation and health. J. Anim. Health Prod. 2024, 12, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dostál, J.; Horák, P.; Hrdlicová, A.; Stratil, A. Simplified PCR analysis of a mutation in the NHEJ1 gene causing ollie eye anomaly in some dog breeds. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 55, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-S.; Mizukami, K.; Yabuki, A.; Hossain, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Uddin, M.M.; Arai, T.; Yamato, O. A Novel Rapid Genotyping Technique for Collie Eye Anomaly: SYBR Green–Based Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Method Applicable to Blood and Saliva Specimens on Flinders Technology Associates Filter Paper. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2010, 22, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampazzo, A.; D’Angelo, A.; Capucchio, M.T.; Sereno, S.; Peruccio, C. Collie eye anomaly in a mixed-breed dog. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2005, 8, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedford, P.G. Collie eye anomaly in the Lancashire heeler. Vet. Rec. 1998, 143, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marelli, S.P.; Rizzi, R.; Paganelli, A.; Bagardi, M.; Minozzi, G.; Brambilla, P.G.; Polli, M. Genotypic and allelic frequency of a mutation in the NHEJ1 gene associated with collie eye anomaly in dogs in Italy. Vet. Rec. Open 2022, 9, e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuntivanich, N.; Pittler, S.J.; Fischer, A.J.; Omar, G.; Kiupel, M.; Weber, A.; Yao, S.; Steibel, J.P.; Khan, N.K.; Petersen-Jones, S.P. Characterization of a Canine Model of Autosomal Recessive Retinitis Pigmentosa due to a PDE6A Mutation. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekomien, G.; Epplen, J.T. Analysis of PDE6D and PDE6G genes for generalised progressive retinal atrophy (gPRA) mutations in dogs. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2003, 35, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clements, P.J.M.; Gregory, C.Y.; Peterson-Jones, S.M.; Sargan, D.R.; Bhattacharya, S.S. Confirmation of the rod cGMP phosphodiesterase β subunit (PDEβ) nonsense mutation in affected rcd-1 Irish setters in the UK and development of a diagnostic test. Curr. Eye Res. 1993, 12, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chader, G.; Liu, Y.; O’Brien, P.; Fletcher, R.; Krishna, G.; Aguirre, G.; Farber, D.; Lolley, R. Cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase activator: Involvement in a hereditary retinal degeneration. Neurochem. Int. 1980, 1, 441–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen-Jones, S.M.; Zhu, F.X. Development and use of a polymerase chain reaction-based diagnostic test for the causal mutation of progressive retinal atrophy in Cardigan Welsh Corgis. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2000, 61, 844–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, H.G.; Kukekova, A.V.; Akey, D.T.; Goldstein, O.; Kirkness, E.F.; Baysac, K.C.; Mosher, D.S.; Aguirre, G.D.; Acland, G.M.; Ostrander, E.A. Breed relationships facilitate fine-mapping studies: A 7.8-kb deletion cosegregates with Collie eye anomaly across multiple dog breeds. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 1562–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, J.K.; Kukekova, A.V.; Kirkness, E.F.; Langlois, M.C.; Aguirre, G.D.; Acland, G.M.; Ostrander, E.A. Linkage mapping of the primary disease locus for collie eye anomaly. Genomics 2003, 82, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanova, A. Collie eye anomaly: A review. Vet. Med. 2015, 60, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stades, F.C.; Barnett, K.C. Collie eye anomaly in Collies in the Netherlands. Vet. Q. 1981, 3, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedford, P.G. Collie eye anomaly in the United Kingdom. Vet. Rec. 1982, 111, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walser-Reinhardt, L.; Hässig, M.; Spiess, B.M. Collie eye anomaly in Switzerland. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilkd. 2009, 151, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lerdkrai, C.; Phungphosop, N. A novel multiplex polymerase chain reaction assay for the genotypic survey of the non-homologous end-joining factor 1 gene associated with Collie eye anomaly in Thailand. Vet. World 2022, 15, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munyard, K.A.; Sherry, C.R.; Sherry, L. A retrospective evaluation of congenital ocular defects in Australian Shepherd dogs in Australia. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2007, 10, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucharczyk, N.; Cislo-Pakuluk, A.; Bedford, P. Collie eye anomaly in Australian Kelpie dogs in Poland. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majchrakova, Z.; Hrckova Turnova, E.; Bielikova, M.; Turna, J.; Dudas, A. The incidence of genetic disease alleles in Australian Shepherd dog breed in European countries. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.A.; Anderson, H.; Donner, J.; Pearce-Kelling, S.; Ekenstedt, K.J. Global Frequency Analyses of Canine Progressive Rod-Cone Degeneration–Progressive Retinal Atrophy and Collie Eye Anomaly Using Commercial Genetic Testing Data. Genes 2023, 14, 2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrigan, M.; Duignan, E.; Malone, C.; Stephenson, K.; Saad, T.; McDermott, C.; Green, A.; Keegan, D.; Humphries, P.; Kenna, P.F.; et al. Panel-Based Population Next-Generation Sequencing for Inherited Retinal Degenerations. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukovic, D.; Artero Castro, A.; Delgado, A.; Bernal, M.A.M.; Pelaez, A.D.; Lloret, R.P.; Espejo, R.P.; Kamenarova, K.; Sánchez, L.F.; Cuenca, N.; et al. Human iPSC derived disease model of MERTK-associated retinitis pigmentosa. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, J.L.; Pierce, E.A.; Laster, A.M.; Daiger, S.P.; Birch, D.G.; Ash, J.D.; Iannaccone, A.; Flannery, J.G.; Sahel, J.A.; Zack, D.J.; et al. Inherited Retinal Degenerations: Current Landscape and Knowledge Gaps. Trans. Vis. Sci. Tech. 2018, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanks, M.; Downes, S.M.; Copley, R.R.; Lise, S.; Broxholme, J.; Hudspith, K.A.Z.; Kwasniewska, A.; Davies, W.I.L.; Hankins, M.W.; Packham, E.; et al. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) as a diagnostic tool for retinal degeneration reveals a much higher detection rate in early-onset disease. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 21, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, M.F.; Faucz, F.R.; Bimpaki, E.; Horvath, A.; Levy, I.; De Alexandre, R.B.; Ahmad, F.; Manganiello, V.; Stratakis, C.A. Clinical and Molecular Genetics of the phosphodiesterases (PDES). Endocr. Rev. 2013, 35, 195–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghilardi, S.; Bagardi, M.; Frattini, S.; Barbariga, G.E.; Brambilla, P.G.; Giulietta, M.; Polli, M. Genotypic and allelic frequencies of progressive rod-cone degeneration and other main variants associated with progressive retinal atrophy in Italian dogs. Vet. Rec. Open 2023, 10, e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinho, L.F.L.P.; Occelli, L.M.; Bortolini, M.; Sun, K.; Winkler, P.A.; Montiani-Ferreira, F.; Petersen-Jones, S.M. Development of retinal bullae in dogs with progressive retinal atrophy. Vet. Ophthal. 2021, 25, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downs, L.M.; Hite, R.; Pregnolato, S.; Mellersh, C.S. Genetic screening for PRA-associated mutations in multiple dog breeds shows that PRA is heterogeneous within and between breeds. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2014, 17, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Name | Sequence | Expected Amplicon Size |
|---|---|---|
| NHEJ1-F17 | 5′-TCTCACAGGCAGAAAGCTCA-3′ | 636 bp |
| NHEJ1-R17 | 5′-CCATTCATTCCTTTGCCAGT-3′ | |
| NHEJ1-F20 | 5′-TGGGCTGGTGAACATTTGTA-3′ | 941 bp |
| NHEJ1-R23 | 5′-CCTTTTTGTTTGCCCTCAGA-3′ | |
| NHEJ1-FW | 5′-AGGGTTACCATTTGGGAACTGTCTT-3′ | - |
| NHEJ1-RW | 5′-AGCTTCTGACAGGCCACAATTATCTA-3′ | 120 bp |
| NHEJ1-RM | 5′-ACCAATCATCATCCAGCCCAGCAGCATTTAA-3′ | 68 bp |
| SPJn-F | 5′-TCCCATTCAGGTCCCAGAA-3′ | 212 bp |
| SPJn-R | 5′-TGATGACCTCTGACCTCTG-3′ | |
| SPJm-F | 5′-TTCCCATTCAGGTCCCAGAC-3′ | 213 bp |
| SPJm-R | 5′-GATGACCTCTGACCTCTGAT-3′ |
| Sample No. | Breed | Gender | Age | Sample Type | CEA RT-PCR | CEA | RCD3-PRA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Australian Shepherd | male | 4 years | Buccal swab | Aa | Aa | AA |
| 2. | Australian Shepherd | male | 7 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 3. | Australian Shepherd | female | 10 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 4. | Australian Shepherd | female | 3 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 5. | Australian Shepherd | female | 12 years | Blood/EDTA | AA | AA | AA |
| 6. | Australian Shepherd | female | 9 years | Blood/EDTA | AA | AA | AA |
| 7. | Australian Shepherd | female | 6 years | Blood/EDTA | AA | AA | AA |
| 8. | Australian Shepherd | female | 5 years | Blood/EDTA | AA | AA | AA |
| 9. | Australian Shepherd | male | 7 years | Blood/EDTA | AA | AA | AA |
| 10. | Australian Shepherd | female | 3 years | Blood/EDTA | AA | AA | AA |
| 11. | Australian Shepherd | female | 3 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 12. | Australian Shepherd | male | 4 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 13. | Australian Shepherd | female | 3 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 14. | Australian Shepherd | female | 6 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 15. | Australian Shepherd | male | 7 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 16. | Australian Shepherd | female | 8 years | Buccal swab | Aa | Aa | AA |
| 17. | Australian Shepherd | male | 13 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 18. | Australian Shepherd | male | 3 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 19. | Australian Shepherd | male | 7 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 20. | Australian Shepherd | male | 4 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 21. | Australian Shepherd | male | 4 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 22. | Australian Shepherd | female | 6 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 23. | Australian Shepherd | male | 2 years | Blood/EDTA | AA | AA | AA |
| 24. | Australian Shepherd | female | 2 years | Blood/EDTA | AA | AA | AA |
| 25. | Australian Shepherd | female | 2 years | Blood/EDTA | AA | AA | AA |
| 26. | Australian Shepherd | female | 6 years | Blood/EDTA | AA | AA | AA |
| 27. | Australian Shepherd | female | 2 years | Blood/EDTA | AA | AA | AA |
| 28. | Australian Shepherd | female | 2 years | Blood/EDTA | AA | AA | AA |
| 29. | Australian Shepherd | female | 3 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 30. | Border Collie | male | 8 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 31. | Border Collie | female | 7 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 32. | Border Collie | male | 4 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 33. | Border Collie | female | 3 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 34. | Border Collie | male | 7 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 35. | Border Collie | female | 7 years | Buccal swab | Aa | Aa | AA |
| 36. | Border Collie | female | 3 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 37. | Border Collie (mixed) | male | 3 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 38. | Border Collie (mixed) | male | 6 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 39. | Longhaired Collie | female | 6 years | Buccal swab | aa | aa | AA |
| 40. | Longhaired Collie | male | 4 years | Buccal swab | aa | aa | AA |
| 41. | Longhaired Collie | male | 10 years | Buccal swab | aa | aa | AA |
| 42. | Longhaired Collie | female | 8 years | Buccal swab | aa | aa | AA |
| 43. | Longhaired Collie | female | 5 years | Buccal swab | aa | aa | AA |
| 44. | Longhaired Collie | male | 4 years | Buccal swab | aa | aa | AA |
| 45. | Longhaired Collie | female | 6 years | Blood/EDTA | aa | aa | AA |
| 46. | Longhaired Collie | female | 1 years | Buccal swab | aa | aa | AA |
| 47. | Longhaired Collie | male | 1 years | Buccal swab | Aa | Aa | AA |
| 48. | Longhaired Collie | male | 1 years | Buccal swab | Aa | Aa | AA |
| 49. | Longhaired Collie | male | 1 years | Buccal swab | Aa | Aa | AA |
| 50. | Longhaired Collie | male | 1 years | Buccal swab | Aa | Aa | AA |
| 51. | Longhaired Collie | female | 11 years | Buccal swab | aa | aa | AA |
| 52. | Longhaired Collie | female | 8 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 53. | Longhaired Collie | female | 1 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 54. | Longhaired Collie | male | 4 years | Buccal swab | Aa | Aa | AA |
| 55. | Longhaired Collie | male | 4 years | Buccal swab | Aa | Aa | AA |
| 56. | Longhaired Collie | male | 4 years | Buccal swab | Aa | Aa | AA |
| 57. | Longhaired Collie | female | 4 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 58. | Longhaired Collie | female | 1 years | Buccal swab | aa | aa | AA |
| 59. | Longhaired Collie | male | 1 years | Buccal swab | Aa | Aa | AA |
| 60. | Longhaired Collie | male | 1 years | Buccal swab | aa | aa | AA |
| 61. | Longhaired Collie | male | 1 years | Buccal swab | aa | aa | AA |
| 62. | Longhaired Collie | male | 3 years | Buccal swab | aa | aa | AA |
| 63. | Longhaired Collie | female | 7 years | Buccal swab | aa | aa | AA |
| 64. | Longhaired Collie | female | 3 years | Buccal swab | Aa | Aa | AA |
| 65. | Longhaired Collie | female | 2 years | Buccal swab | aa | aa | AA |
| 66. | Shetland Sheepdog | female | 9 years | Buccal swab | Aa | Aa | AA |
| 67. | Shetland Sheepdog | female | 12 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 68. | Shetland Sheepdog | male | 10 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 69. | Shetland Sheepdog | female | 2 years | Buccal swab | Aa | Aa | AA |
| 70. | Shetland Sheepdog | female | 6 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 71. | Shetland Sheepdog | female | 3 years | Buccal swab | AA | AA | AA |
| 72. | Shetland Sheepdog | female | 4 years | Blood/EDTA | Aa | Aa | AA |
| 73. | Shetland Sheepdog | male | 3 years | Blood/EDTA | AA | AA | AA |
| 74. | Shetland Sheepdog | male | 5 years | Buccal swab | Aa | Aa | AA |
| 75. | Shetland Sheepdog | female | 5 years | Buccal swab | aa | aa | AA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bučan, J.; Holečková, B.; Galdíková, M.; Halušková, J.; Schwarzbacherová, V. Analysis of Selected Eye Disorders in a Group of Predisposed Breeds of Dogs: Molecular Diagnostics of Collie Eye Anomaly and Progressive Retinal Atrophy. Genes 2025, 16, 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16050474
Bučan J, Holečková B, Galdíková M, Halušková J, Schwarzbacherová V. Analysis of Selected Eye Disorders in a Group of Predisposed Breeds of Dogs: Molecular Diagnostics of Collie Eye Anomaly and Progressive Retinal Atrophy. Genes. 2025; 16(5):474. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16050474
Chicago/Turabian StyleBučan, Jaroslav, Beáta Holečková, Martina Galdíková, Jana Halušková, and Viera Schwarzbacherová. 2025. "Analysis of Selected Eye Disorders in a Group of Predisposed Breeds of Dogs: Molecular Diagnostics of Collie Eye Anomaly and Progressive Retinal Atrophy" Genes 16, no. 5: 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16050474
APA StyleBučan, J., Holečková, B., Galdíková, M., Halušková, J., & Schwarzbacherová, V. (2025). Analysis of Selected Eye Disorders in a Group of Predisposed Breeds of Dogs: Molecular Diagnostics of Collie Eye Anomaly and Progressive Retinal Atrophy. Genes, 16(5), 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16050474






