Genome-Wide Screening of the MYB Genes in Coptis chinensis and Their Roles in Growth, Development, and Heavy Metal Resistance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification and Sequence Analysis of CcMYB Sequences
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. Chromosomal Localization and Synteny Analysis of CcMYB
2.4. Expression Analysis of CcMYB Genes
2.5. qRT-PCR Procedures
3. Results
3.1. Identification of MYB in C. chinensis
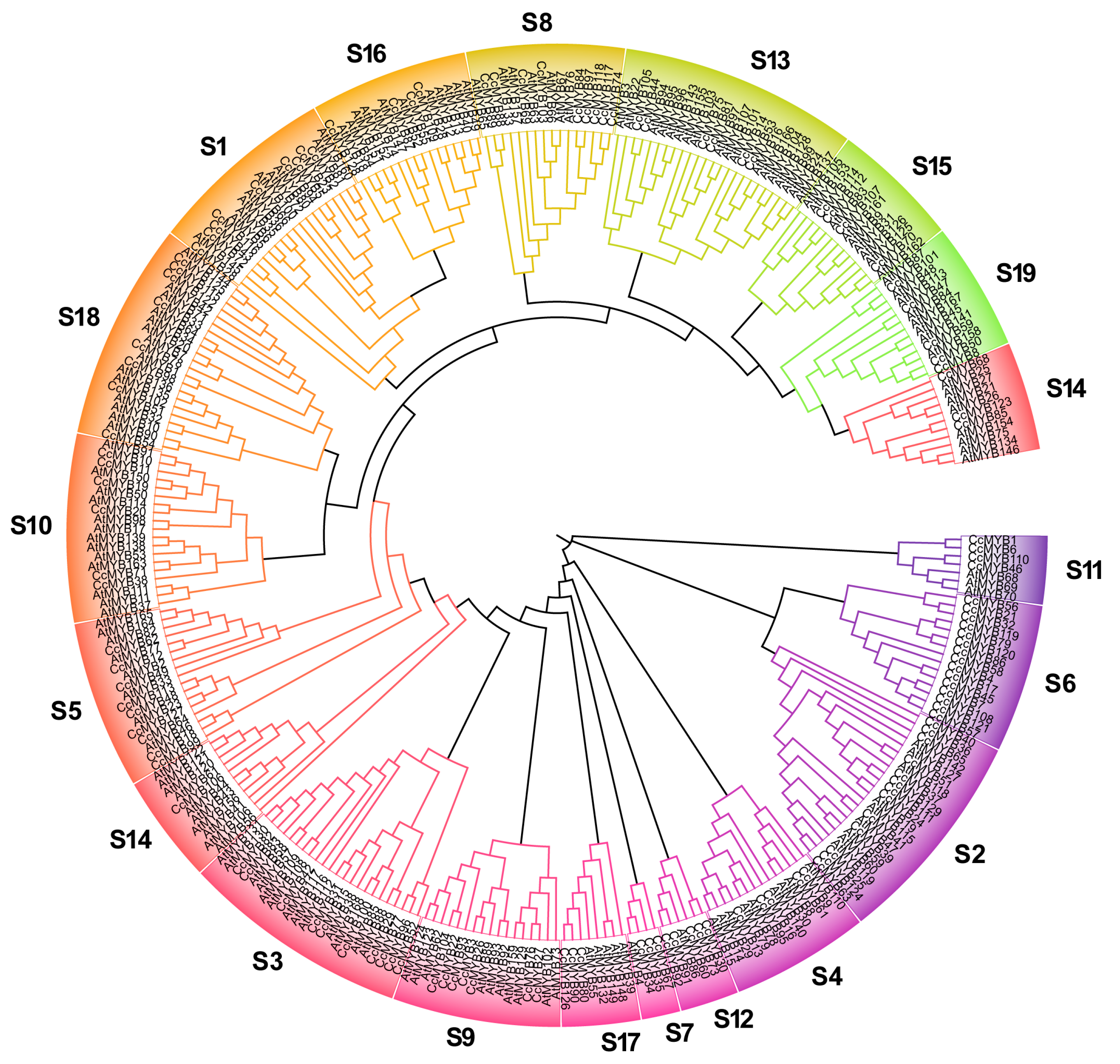
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of CcMYB Gene Family
3.3. Exon/Intron Organization and Motif Composition Analysis of CcMYB Genes
3.4. Cis-Acting Elements Analysis of CcMYB Genes
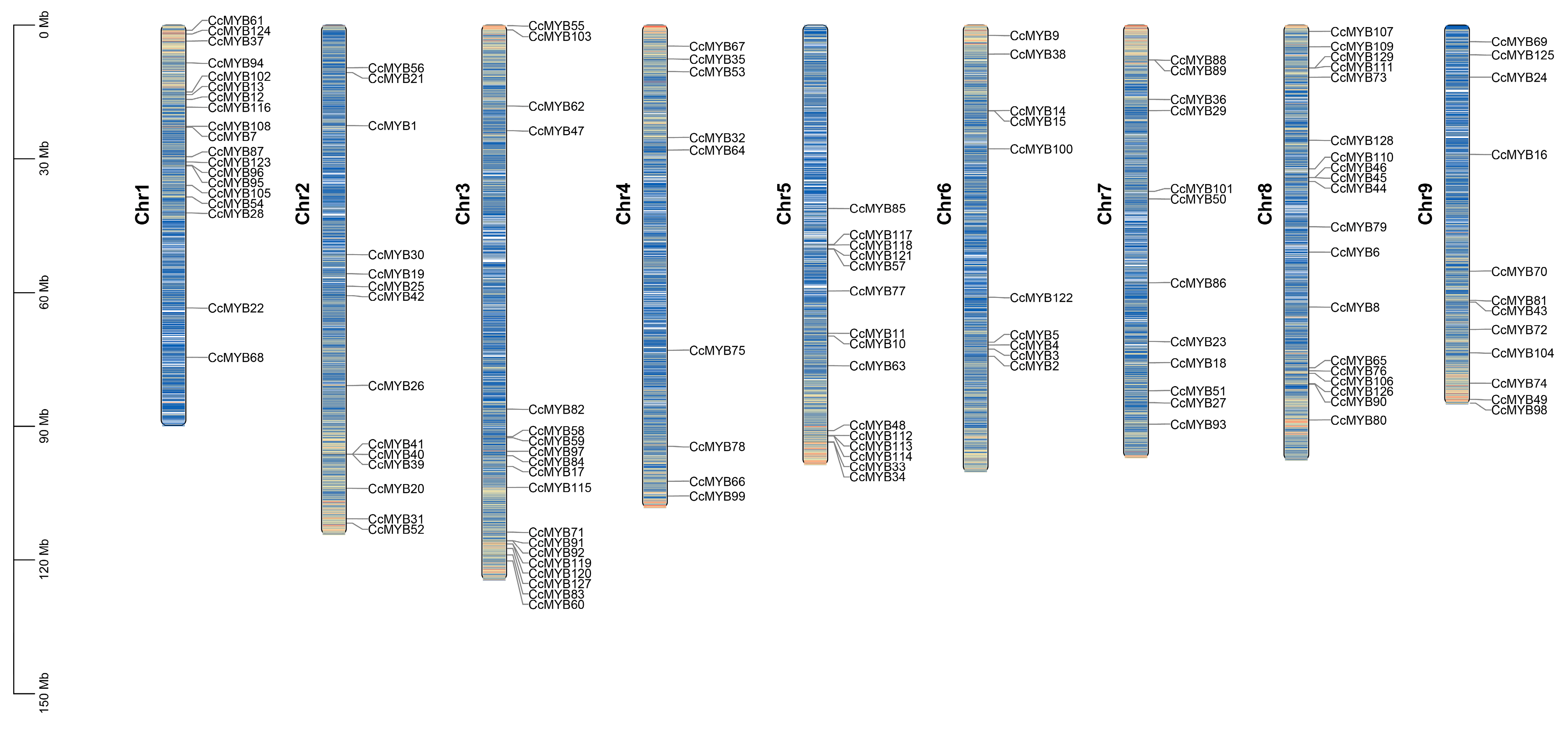
3.5. Chromosomal Distribution and Synteny Analysis of CcMYB Genes
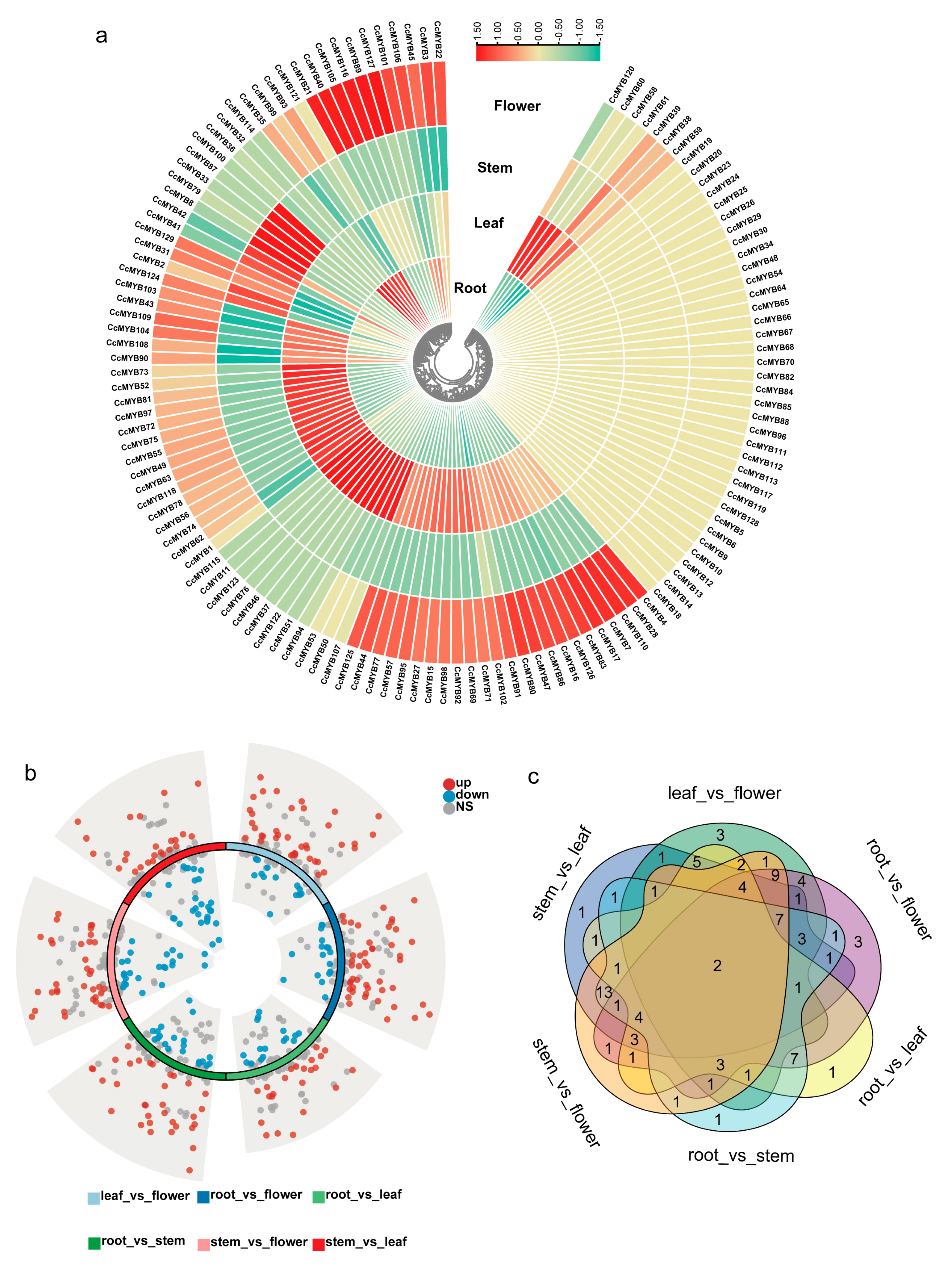
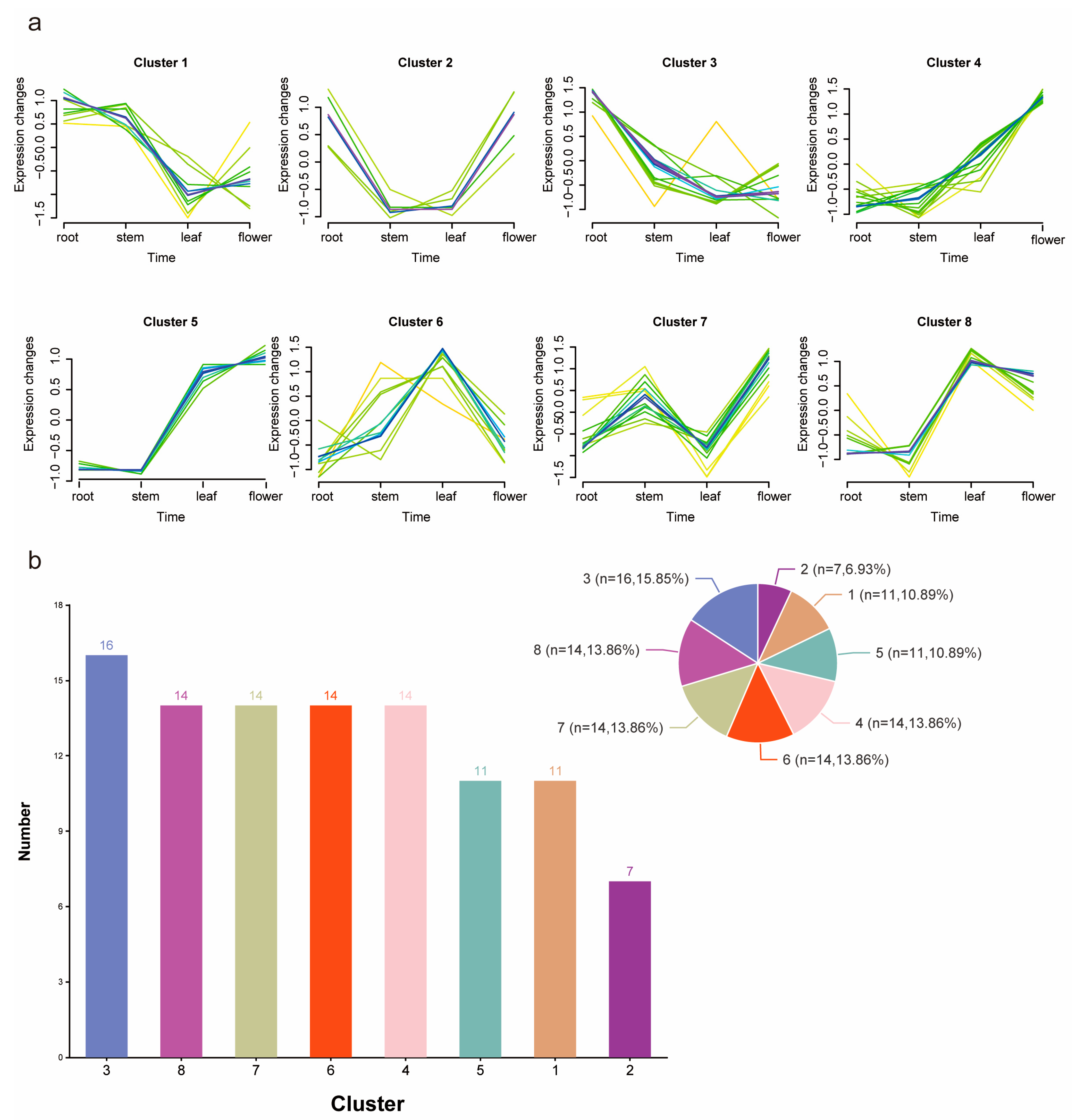
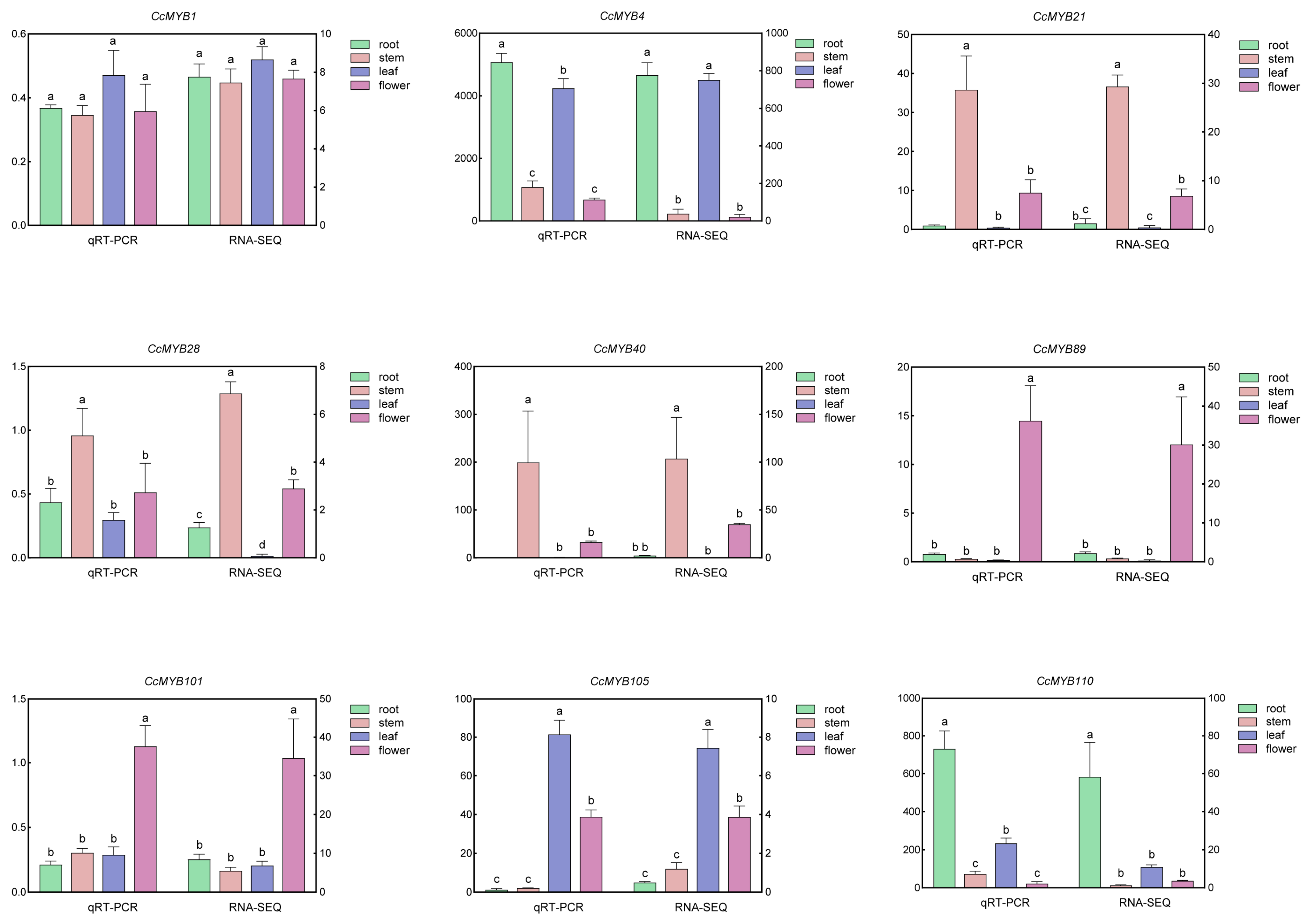
3.6. Expression Patterns of CcMYB in Different Tissues
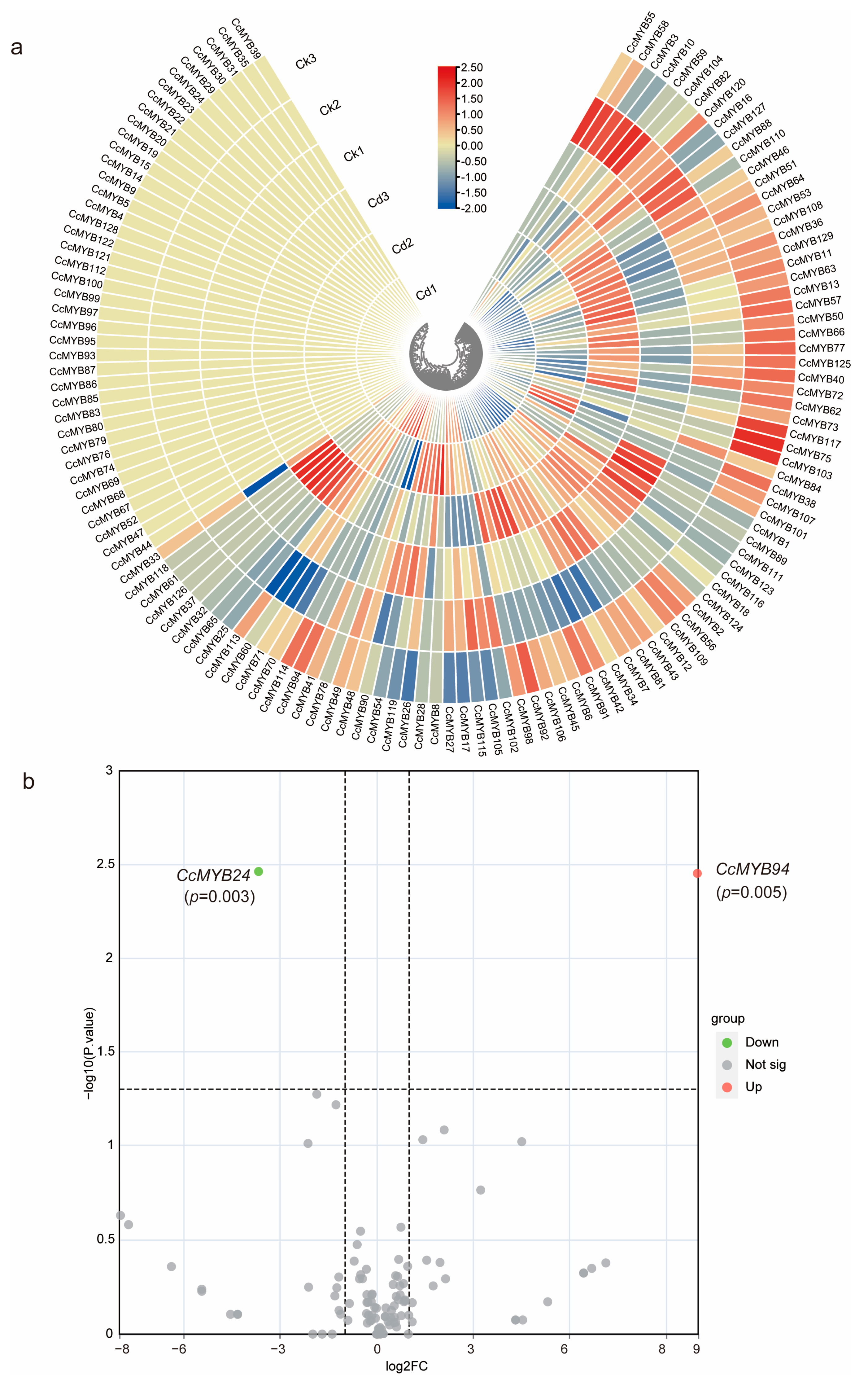
3.7. Identification of CcMYB Genes Conferring Resistance to Metal Stress
3.8. qRT-PCR Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, J.; Luo, Y.; Deng, D.; Su, S.; Li, S.; Xiang, L.; Hu, Y.; Wang, P.; Meng, X. Coptisine from Coptis chinensis exerts diverse beneficial properties: A concise review. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 7946–7960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Vong, C.T.; Zeng, S.; Gao, C.; Chen, Z.; Fu, C.; Wang, S.; Zou, L.; Wang, A.; Wang, Y. Tracking evidences of Coptis chinensis for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease from pharmacological, pharmacokinetic to clinical studies. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 268, 113573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Tian, F.; Guo, J.; Li, X.; Ma, L.; Jiang, M.; Zhao, J. Therapeutic potential of Coptis chinensis for arthritis with underlying mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1243820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D.; Jin, C.; Xiao, X.-H.; Dong, X.-P. Antimicrobial properties of berberines alkaloids in Coptis chinensis Franch by microcalorimetry. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2008, 70, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Piao, X.-L.; Piao, X.-S.; Lu, T.; Wang, D.; Kim, S.W. Preventive effect of Coptis chinensis and berberine on intestinal injury in rats challenged with lipopolysaccharides. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Ng, L.T.; Hsu, F.F.; Shieh, D.E.; Chiang, L.C. Cytotoxic effects of Coptis chinensis and Epimedium sagittatum extracts and their major constituents (berberine, coptisine and icariin) on hepatoma and leukaemia cell growth. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2004, 31, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Du, P.; An, L.; Yuan, G.; Sun, Z. Anti-diabetic effect of Coptis Chinensis polysaccharide in high-fat diet with STZ-induced diabetic mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 55, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.; Paz-Ares, J. MYB transcription factors in plants. Trends Genet. 1997, 13, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Martin, C. Multifunctionality and diversity within the plant MYB-gene family. Plant Mol. Biol. 1999, 41, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Tang, X.-F.; Yang, W.-J.; Wu, Y.-M.; Huang, Y.-B.; Tang, Y.-X. Biochemical and molecular characterization of plant MYB transcription factor family. Biochemistry 2009, 74, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubos, C.; Stracke, R.; Grotewold, E.; Weisshaar, B.; Martin, C.; Lepiniec, L. MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stracke, R.; Werber, M.; Weisshaar, B. The R2R3-MYB gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2001, 4, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Xu, X.; Yang, L.; Zhu, X.; Du, Y.; Fang, Z. A R2R3-MYB transcription factor, FeR2R3-MYB, positively regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis and drought tolerance in common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 217, 109254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Lei, D.; Yao, W.; Li, S.; Wang, H.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, W. A novel R2R3-MYB transcription factor PbMYB1L of Pyrus bretschneideri regulates cold tolerance and anthocyanin accumulation. Plant Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, T.; Hou, S.; Ma, J.; Li, D.; Chen, S.; Gao, X.; Zhao, Y.; He, Y.; Yang, G. A R2R3-MYB, BpMYB1, from paper mulberry interacts with DELLA protein BpGAI1 in soil cadmium phytoremediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 463, 132871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Constabel, C.P. MYB repressors as regulators of phenylpropanoid metabolism in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2019, 24, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zheng, M.; Zhu, S.; Pei, T.; Cui, M.; Chang, L.; Xiao, H.; Yang, J.; Martin, C. SbMYB3 transcription factor promotes root-specific flavone biosynthesis in Scutellaria baicalensis. Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, uhac266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xia, E.; Fu, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Tong, W.; Tang, Q.; Tadege, M.; Fernie, A.R.; Zhao, J. Diverse roles of MYB transcription factors in regulating secondary metabolite biosynthesis, shoot development, and stress responses in tea plants (Camellia sinensis). Plant J. 2022, 110, 1144–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lei, D.; He, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Y. R2R3-MYB transcription factor PbMYB5-like positively regulates the biosynthesis of phenylalanine-related metabolites in pear (Pyrus bretschneideri). J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 18, 101328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Kong, F.; Liu, Q.; Lan, T.; Liu, F.; Wang, X.; Du, X.; Chen, X.; Yuan, J. Identification of key enzymes in lignocellulose biosynthesis from dynamic observations in maize stalks. Crop J. 2024, 12, 1754–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Chae, S.; Jo, J.E.; Do Kim, K.; Song, S.-I.; Park, S.H.; Choi, S.-B.; Jun, K.M.; Shim, S.-H.; Jeon, J.-S. OsMYB14, an R2R3-MYB transcription factor, regulates plant height through the control of hormone metabolism in rice. Mol. Cells 2024, 47, 100093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaud, S.e.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. Proteom. Protoc. Handb. 2005, 112, 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, T.L.; Johnson, J.; Grant, C.E.; Noble, W.S. The MEME suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W39–W49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; DeBarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.-h.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. KaKs_Calculator 3.0: Calculating selective pressure on coding and non-coding sequences. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2022, 20, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.; Pirrung, M.; McCue, L.A. FQC Dashboard: Integrates FastQC results into a web-based, interactive, and extensible FASTQ quality control tool. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3137–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Paggi, J.M.; Park, C.; Bennett, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, M.-C.; Konaté, M.M.; Chen, L.; Das, B.; Karlovich, C.; Williams, P.M.; Evrard, Y.A.; Doroshow, J.H.; McShane, L.M. TPM, FPKM, or normalized counts? A comparative study of quantification measures for the analysis of RNA-seq data from the NCI patient-derived models repository. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Futschik, M.E. Mfuzz: A software package for soft clustering of microarray data. Bioinformation 2007, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.-x.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cui, Y.-Z.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Mo, R.-y.; Wu, X.-l.; Tan, J.; Zhang, J.; Guo, L.-a. The chromosome-level reference genome of Coptis chinensis provides insights into genomic evolution and berberine biosynthesis. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, B.; Shu, S.; Li, Z.; Song, C.; Liu, D.; Niu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H. Analysis of the Coptis chinensis genome reveals the diversification of protoberberine-type alkaloids. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiyar, A.; Smita, S.; Lenka, S.K.; Rajwanshi, R.; Chinnusamy, V.; Bansal, K.C. Genome-wide classification and expression analysis of MYB transcription factor families in rice and Arabidopsis. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Yang, S.-S.; Liang, Z.; Feng, B.-R.; Liu, L.; Huang, Y.-B.; Tang, Y.-X. Genome-wide analysis of the MYB transcription factor superfamily in soybean. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Yang, J.; Zou, M. Identification of MYB transcription factor genes and their expression during abiotic stresses in maize. Biol. Plant. 2018, 62, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Ma, Z.; Chen, H.; Liu, M. MYB gene family in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.): Genome-wide identification of hormone-responsive reveals their potential functions in growth and development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Duan, S.; Shua, Z.; Li, K.; Xiang, G.; Baldwin, T.C.; Lu, Y.; Liang, Y. R2R3-MYB Gene Family in Coptis teeta Wall.: Genome-Wide Identification, Phylogeny, Evolutionary Expansion, and Expression Analyses during Floral Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phukela, B.; Leonard, H.; Sapir, Y. In silico analysis of R2R3-MYB transcription factors in the basal eudicot model, Aquilegia coerulea. 3 Biotech 2024, 14, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.W.; Donoghue, P.C. Whole-genome duplication and plant macroevolution. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 933–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, S.B.; Mitra, A.; Baumgarten, A.; Young, N.D.; May, G. The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2004, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Z.; Wang, L.; Ji, Z.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, K.; Qiao, Y. Comparative analysis of the MYB gene family in seven Ipomoea species. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1155018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhang, Q.; Hou, S.; Chen, J.; Meng, J.; Wang, C.; Liang, D.; Wu, R.; Guo, Y. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the R2R3-MYB gene family in Theobroma cacao. Genes 2022, 13, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wen, X.; Wei, M.; Huang, X.; Dai, S.; Ruan, L.; Yu, Y. Genome-Wide identification, characterization, and expression pattern of MYB gene family in Melastoma candidum. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorjee, T.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Sumbur, B.; Yan, H.; Bing, J.; Geng, Y.; Zhou, Y. Characterization of NAC gene family in Ammopiptanthus mongolicus and functional analysis of AmNAC24, an osmotic and cold-stress-induced NAC gene. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Guo, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Yu, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J. Genome-wide identification, evolution, and expression analysis of the NAC gene family in chestnut (Castanea mollissima). Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1337578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnaiah, D.; Sarbatly, R.; Nithyanandam, R. A review of the antioxidant potential of medicinal plant species. Food Bioprod. Process. 2011, 89, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, X.; Lin, H. Diverse roles of MYB transcription factors in plants. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2025, 67, 539–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C. A review on heavy metal contamination in the soil worldwide: Situation, impact and remediation techniques. Environ. Skept. Crit. 2014, 3, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Ghori, N.-H.; Ghori, T.; Hayat, M.; Imadi, S.; Gul, A.; Altay, V.; Ozturk, M. Heavy metal stress and responses in plants. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 1807–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Chen, Q.; Guo, L.; Deng, S.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, S.; Cong, X.; Xu, F. Genome-wide identification of MYB gene family and exploration of selenium metabolism-related candidates in paper mulberry (Broussonetia papyrifera). Plant Cell Rep. 2025, 44, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Lee, J.; Rhee, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lim, S.-H. Loss of the R2R3 MYB transcription factor RsMYB1 shapes anthocyanin biosynthesis and accumulation in Raphanus sativus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Shi, W.; Jie, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Song, C. A MYB transcription factor, BnMYB2, cloned from ramie (Boehmeria nivea) is involved in cadmium tolerance and accumulation. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, R.; Ju, Q.; Li, W.; Tran, L.-S.P.; Xu, J. The R2R3-MYB transcription factor MYB49 regulates cadmium accumulation. Plant Physiol. 2019, 180, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; You, J.; Hu, X. Genome-Wide Screening of the MYB Genes in Coptis chinensis and Their Roles in Growth, Development, and Heavy Metal Resistance. Genes 2025, 16, 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16050476
Yang Y, You J, Hu X. Genome-Wide Screening of the MYB Genes in Coptis chinensis and Their Roles in Growth, Development, and Heavy Metal Resistance. Genes. 2025; 16(5):476. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16050476
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yang, Jingmao You, and Xuebo Hu. 2025. "Genome-Wide Screening of the MYB Genes in Coptis chinensis and Their Roles in Growth, Development, and Heavy Metal Resistance" Genes 16, no. 5: 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16050476
APA StyleYang, Y., You, J., & Hu, X. (2025). Genome-Wide Screening of the MYB Genes in Coptis chinensis and Their Roles in Growth, Development, and Heavy Metal Resistance. Genes, 16(5), 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16050476





