Temporal Analysis of OMI-Observed Tropospheric NO2 Columns over East Asia during 2006–2015
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. OMI Retrieved NO2 Columns
2.2. Bottom-Up NOx Emissions
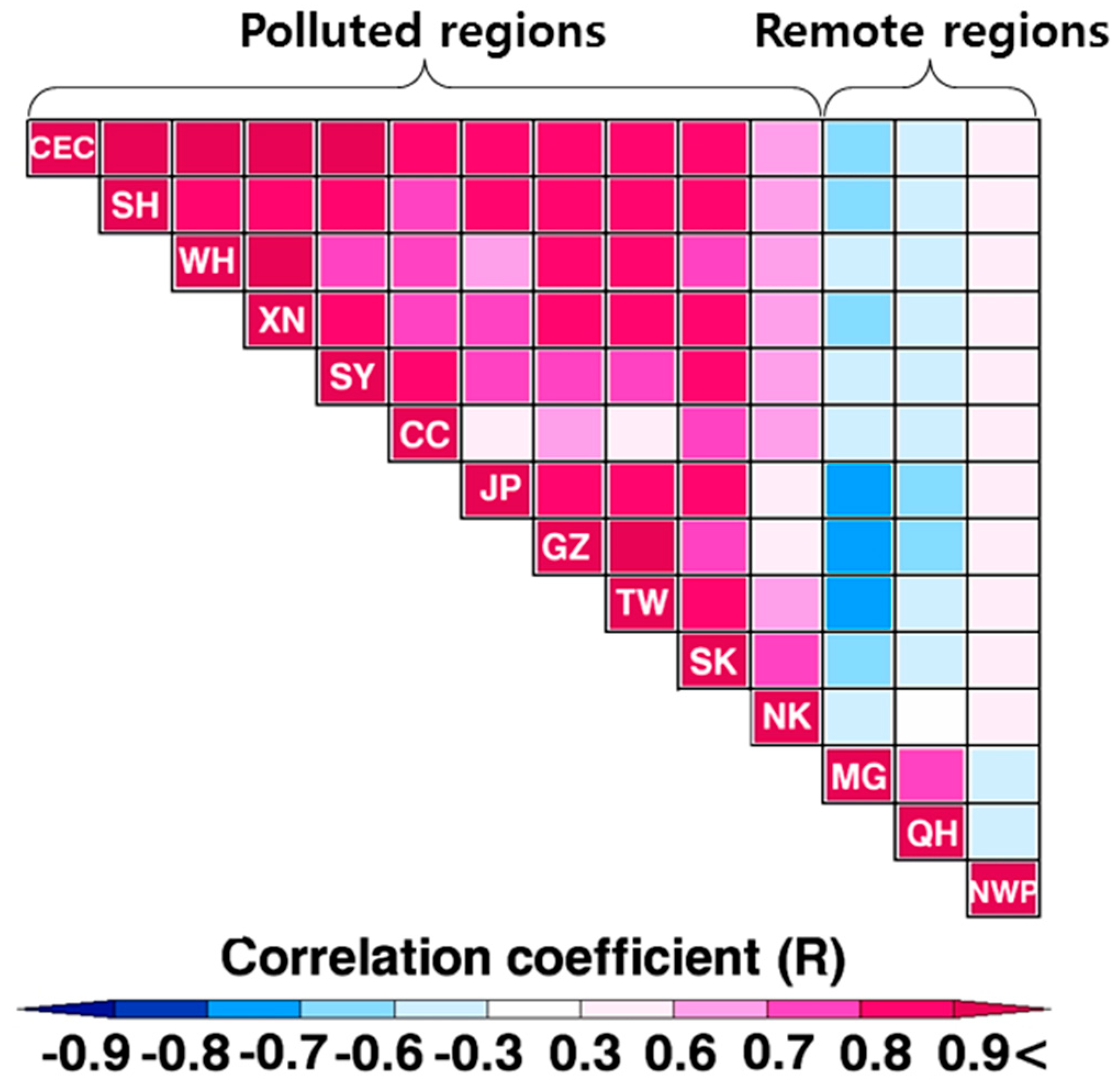
2.3. Target Areas
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Trend and Monthly Variations of Tropospheric NO2 Columns
3.2. Year-to-Year Variations of Tropospheric NO2 Columns with Bottom-Up NOx Emissions
3.3. Weekly Variations of Tropospheric NO2 Columns
4. Summaries and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Environment Agency (EEA). Annual European Community LRTAP Convention Emissions Inventory Report 1990–2006; No 7/2008; EEA: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2008; pp. 1–79. [Google Scholar]
- US Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). 2008 National Emissions Inventory: Review, Analysis and Highlights; EPA-454/R-13-005; US EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; pp. 1–70.
- Yienger, J.I.; Levy, H., II. Empirical model of global soil-biogenic NOx emissions. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 11447–11464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinken, G.C.M.; Boersma, K.F.; Maasakkers, J.D.; Adon, M.; Martin, R.V. Worldwide biogenic soil NOx emissions inferred from OMI NO2 observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 10363–10381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.V.; Chance, K.; Jacob, D.J.; Kurosu, T.P.; Spurr, R.J.D.; Bucsela, E.; Gleason, J.F.; Palmer, P.I.; Bey, I.; Fiore, A.M.; et al. An improved retrieval of tropospheric nitrogen dioxide from GOME. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, ACH-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeglé, L.; Steinberger, L.; Martin, R.V.; Chance, K. Global partitioning of NOx sources using satellite observations: Relative roles of fossil fuel combustion, biomass burning and soil emissions. Faraday Discuss. 2005, 130, 407–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Noije, T.P.C.; Eskes, H.J.; Dentener, F.J.; Stevenson, D.S.; Ellingsen, K.; Schultz, M.G.; Wild, O.; Amann, M.; Atherton, C.S.; Bergmann, D.J.; et al. Multi-model ensemble simulations of tropospheric NO2 compared with GOME retrievals for the year 2000. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 2943–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.M.; Song, C.H.; Ahn, H.J.; Park, R.S.; Woo, J.H.; Lee, C.K.; Richter, A.; Burrows, J.P.; Kim, J.Y.; Hong, J.H. Investigation of NOx emissions and NOx-related chemistry in East Asia using CMAQ-predicted and GOME-derived NO2 columns. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 1017–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.M.; Lee, S.; Chang, L.S.; Song, C.H. A comparison study between CMAQ-simulated and OMI-retrieved NO2 columns over East Asia for evaluation of NOx emission fluxes of INTEX-B, CAPSS, and REAS inventories. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 1913–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McLinden, C.A.; Fioletov, V.; Krotkov, N.A.; Li, C.; Boersma, K.F.; Adams, C. A decade of change in NO2 and SO2 over the Canadian oil sands as seen from space. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, A.; val Martin, M.; Lamsal, L.N.; Duncan, B.N. A decade of changes in nitrogen oxides over regions of oil and natural gas activity in the United States. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2017, 5, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.V.; Sioris, C.E.; Chance, K.; Ryerson, T.B.; Bertram, T.H.; Wooldridge, P.J.; Cohen, R.C.; Neuman, J.A.; Swanson, A.; Flocke, F.M. Evaluation of space-based constraints on global nitrogen oxide emissions with regional aircraft measurements over and downwind of eastern North America. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D15308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, Y. Assimilated inversion of NOx emissions over east Asia using OMI NO2 column measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L06805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamsal, L.N.; Martin, R.V.; van Donkelaar, A.; Celarier, E.A.; Bucsela, E.J.; Boersma, K.F.; Dirksen, R.; Luo, C.; Wang, Y. Indirect validation of tropospheric nitrogen dioxide retrieved from the OMI satellite instrument: Insight into the seasonal variation of nitrogen oxides at northern midlatitudes. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D05302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.T.; McElroy, M.B.; Boersma, K.F. Constraint of anthropogenic NOx emissions in China from different sectors: A new methodology using multiple satellite retrievals. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijling, B.; van der A, R.J. Using daily satellite observations to estimate emissions of short-lived air pollutants on a mesoscopic scale. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Henze, D.K.; Capps, S.L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Keller, M. Monthly top-down NOx emissions for China (2005–2012): A hybrid inversion method and trend analysis. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 4600–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, K.; Eskes, H.; Sudo, K.; Boersma, K.F.; Bowman, K.; Kanaya, Y. Decadal changes in global surface NOx emissions from multi-constituent satellite data assimilation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 807–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.W.; Brioude, J.; Cooper, O.R.; Frost, G.J.; Kim, C.H.; Park, R.J.; Trainer, M.; Woo, J.H. Transport of NOx in East Asia identified by satellite and in situ measurements and Lagrangian particle dispersion model simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 2574–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schere, K.; Flemming, J.; Vautard, R.; Chemel, C.; Colette, A.; Hogrefe, C.; Bessagnet, B.; Meleux, F.; Mathur, R.; Roselle, S.; et al. Trace gas/aerosol boundary concentrations and their impacts on continental-scale AQMEII modeling domains. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 53, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Giordano, L.; Brunner, D.; Flemming, J.; Hogrefe, C.; Im, U.; Bianconi, R.; Badia, A.; Balzarini, A.; Barò, R.; Chemel, C.; et al. Assessment of the MACC reanalysis and its influence as chemical boundary conditions for regional air quality modeling in AQMEII-2. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 115, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GlobEmission. Available online: http://www.globemission.eu/data.php (accessed on 11 September 2019).
- Beirle, S.; Platt, U.; Wenig, M.; Wagner, T. Weekly cycle of NO2 by GOME measurements: A signature of anthropogenic sources. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2003, 3, 2225–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der A, R.J.; Eskes, H.J.; Boersma, K.F.; van Noije, T.P.C.; van Roozendael, M.; de Smedt, I.; Peters, D.H.M.U.; Meijer, E.W. Trends, seasonal variability and dominant NOx source derived from a ten year record of NO2 measured from space. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D04302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valin, L.C.; Russell, A.R.; Cohen, R.C. Chemical feedback effects on the spatial patterns of the NOx weekend effect: A sensitivity analysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Lin, J.; Song, C.; Liu, M.; Yan, Y.; Xu, Y.; Huang, B. Rapid growth in nitrogen dioxide pollution over Western China, 2005–2013. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 6207–6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, Q.; van der A, R.J.; Zheng, B.; Tong, D.; Yan, L.; Zheng, Y.; He, K. Recent reduction in NOx emissions over China; synthesis of satellite observations and emission inventories. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 114002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lee, C.S.; Zhang, R.; Chen, L. Spatial and temporal evaluation of long term trend (2005–2014) of OMI retrieved NO2 and SO2 concentrations in Henan Province, China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 154, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; McDonald, B.C.; Worden, H.; Worden, J.R.; Miyazaki, K.; Qu, Z.; Henze, D.K.; Jones, D.B.A.; Arellano, A.F.; Fischer, E.V.; et al. Unexpected slowdown of US pollutant emission reduction in the past decade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 5099–5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Zhao, C.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, K.; Gao, J.; Qiao, Q.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chai, F. Spatial and temporal distribution of NO2 and SO2 in Inner Mongolia urban agglomeration obtained from satellite remote sensing and ground observations. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 188, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.M.; Lee, S.; Yoon, Y.J.; Lee, B.Y.; Song, C.H. A model investigation into the atmospheric NOy chemistry in remote continental Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 214, 116817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, W.S.; Graedel, T.E.; Kleiner, B.; Warner, J.L. Sunday and workday variations in photochemical air pollutions in New Jersey and New York. Science 1974, 186, 1037–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Foy, B.; Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G. Satellite NO2 retrievals suggest China has exceeded its NOx reduction goals from the twelfth Five-Year Plan. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, B.N.; Lamsal, L.N.; Thompson, A.M.; Yoshida, Y.; Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G.; Hurwitz, M.M.; Pickering, K.E. A space-based, high-resolution view of notable changes in urban NOx pollution around the world (2005–2014). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 976–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krotkov, N.A.; McLinden, C.A.; Li, C.; Lamsal, L.N.; Celarier, E.A.; Marchenko, S.V.; Swartz, W.H.; Bucsela, E.J.; Joiner, J.; Duncan, B.N.; et al. Aura OMI observations of regional SO2 and NO2 pollution changes from 2005 to 2015. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 4605–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levelt, P.F.; van den Oord, G.H.J.; Dobber, M.R.; Mälkki, A.; Visser, H.; de Vries, J.; Stammes, P.; Lundell, J.O.V.; Saari, H. The ozone monitoring instrument. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boersma, K.F.; Braak, R.; van der A, R.J. Dutch OMI NO2 (DOMINO) Data Product v2.0 HE5 Data File User Manual; Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (KNMI): De Bilt, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Boersma, K.F.; Eskes, H.J.; Dirksen, R.J.; van der A, R.J.; Veefkind, J.P.; Stammes, P.; Huijnen, V.; Kleipool, Q.L.; Sneep, M.; Claas, J.; et al. An improved tropospheric NO2 column retrieval algorithm for the Ozone Monitoring Instrument. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 1905–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropospheric Emission Monitoring Internet Service (TEMIS). Available online: http://www.temis.nl (accessed on 11 September 2019).
- Boersma, K.F.; Eskes, H.J.; Veefkind, J.P.; Brinksma, E.J.; van der A, R.J.; Sneep, M.; van den Oord, G.H.J.; Levelt, P.F.; Stammes, P.; Gleason, J.F.; et al. Near-real time retrieval of tropospheric NO2 from OMI. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 2103–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, U. Differential optical absorption spectroscopy (DOAS). Chem. Anal. Ser. 1994, 127, 27–83. [Google Scholar]
- Stammes, P. Spectral radiance modelling in the UV-Visible range. In IRS 2000: Current Problems in Atmospheric Radiation; Smith, W.L., Timofeyev, Y.M., Eds.; A. Deepak Publ.: Hampton, VA, USA, 2001; pp. 385–388. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Smeltzer, C.; Qu, H.; Koshak, W.; Boersma, K.F. Comparing OMI-based and EPA AQS in situ NO2 trends: Towards understanding surface NOx emission changes. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 3955–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-T.; Liu, M.-Y.; Xin, J.-Y.; Boersma, K.F.; Spurr, R.; Martin, R.; Zhang, Q. Influence of aerosols and surface reflectance on satellite NO2 retrieval: Seasonal and spatial characteristics and implications for NOx emission constraints. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 11217–11241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emissions of atmospheric Compounds and Compilation of Ancillary Data (ECCAD). Available online: https://eccad.aeris-data.fr/ (accessed on 11 September 2019).
- Clean Air Policy Support System (CAPSS). Available online: http://airemiss.nier.go.kr/ (accessed on 11 September 2019).
- Zheng, B.; Tong, D.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Hong, C.; Geng, G.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Peng, L.; Qi, J.; et al. Trends in China’s anthropogenic emissions since 2010 as the consequence of clean air actions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 14095–14111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granier, C.; Darras, S.; van der Gon, H.D.; Doubalova, J.; Elguindi, N.; Galle, B.; Gauss, M.; Guevara, M.; Jalkanen, J.P.; Kuenen, J.; et al. The Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service global and regional emissions (April 2019 version). CAMS Rep. 2019, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilboll, A.; Richter, A.; Burrows, J.P. Long-term changes of tropospheric NO2 over megacities derived from multiple satellite instruments. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4145–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaya, Y.; Irie, H.; Takashima, H.; Iwabuchi, H.; Akimoto, H.; Sudo, K.; Gu, M.; Chong, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, H.; et al. Long-term MAX-DOAS network observations of NO2 in Russia and Asia (MADRAS) during the period 2007–2012: Instrumentation, elucidation of climatology, and comparisons with OMI satellite observations and global model simulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 7909–7927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, T.; Wang, P. The spatial-temporal variation of tropospheric NO2 over China during 2005 to 2018. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.M.; Lee, C.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Song, C.H. A comparison study between model-predicted and OMI-retrieved tropospheric NO2 columns over the Korean peninsula. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2962–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.T.; Nielsen, C.P.; Zhao, Y.; Lei, Y.; Liu, Y.; McElroy, M.B. Recent changes in particulate air pollution over China observed from space and the ground: Effectiveness of emission control. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7771–7776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijling, B.; van der A, R.J.; Boersma, K.F.; van Roozendael, M.; de Smedt, I.; Kelder, H.M. Reductions of NO2 detected from space during the 2008 Beijing Olympic Games. Geophy. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L13801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, N.; Valk, P.; Loyola, D.; Cheng, Y.F.; Zimmer, W. Space-based measurements of air quality during the World Expo 2010 in Shanghai. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 044004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itahashi, S.; Uno, I.; Irie, H.; Kurokawa, J.I.; Ohara, T. Regional modeling of tropospheric NO2 vertical column density over East Asia during the period 2000–2010: Comparison with multisatellite observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 3623–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Chang, K.H.; Kim, H. Long-term (2005–2015) trend analysis of OMI retrieved NO2 columns in Taiwan. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 960–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.D.; Mills, S.P.; Elvidge, C.D.; Lindsey, D.T.; Lee, T.F.; Hawkins, J.D. Suomi satellite brings to light a unique frontier of nighttime environmental sensing capabilities. PNAS 2012, 109, 15706–15711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenig, M.; Spichtinger, N.; Stohl, A.; Held, G.; Beirle, S.; Wagner, T.; Jähne, B.; Platt, U. Intercontinental transport of nitrogen oxide pollution plumes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2003, 3, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Zhu, M.; Chen, S.; Sperling, D. Pollution: Three steps to a green shipping industry. Nature 2016, 230, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudman, R.C.; Russell, A.R.; Valin, L.C.; Cohen, R.C. Interannual variability in soil nitric oxide emissions over the United States as viewed from space. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 9943–9952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, P.Y.; Ge, C.; Wang, J.; Eberwein, J.R.; Liang, L.L.; Allsman, L.A.; Grantz, D.A.; Jenerette, G.D. Unusually high soil nitrogen oxide emissions influence air quality in a high-temperature agricultural region. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der A, R.J.; Peters, D.H.M.U.; Eskes, E.; Boersma, K.F.; van Roozendael, M. Detection of the trend and seasonal variation in tropospheric NO2 over China. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D12317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, E.; Dentener, F.J.; Braswell, B.H.; Sulzman, J.M. Contemporary and pre-industrial global reactive nitrogen budgets. Biogeochemistry 1999, 46, 7–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.V.; Jacob, D.J.; Chance, K.; Kurosu, T.P.; Palmer, P.I.; Evans, M.J. Global inventory of nitrogen oxide emissions constrained by space-based observations of NO2 columns. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, A.; Burrows, J.P.; Nüß, H.; Granier, C.; Niemeier, U. Increase in tropospheric nitrogen dioxide over China observed from space. Nature 2005, 437, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvern, R.F.; Jacob, D.J.; Mickley, L.J.; Sulprizio, M.P.; Travis, K.R.; Marais, E.A.; Cohen, R.C.; Laughner, J.L.; Choi, S.; Joiner, J.; et al. Using satellite observations of tropospheric NO2 columns to infer long-term trends in US NOx emissions: The importance of accounting for the free tropospheric NO2 background. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 8863–8878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, S.X.; Liu, H.; Xu, J.Y.; Fu, K.; Klimont, Z.; Hao, J.M.; He, K.B.; Cofala, J.; Amann, M. NOx emissions in China: Historical trends and future perspectives. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 9869–9897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Louie, P.K.K.; Zheng, J.; Wai, K.M.; Ho, J.W.K.; Yuan, Z.; Lau, A.K.H.; Yue, D.; Zhou, Y. The Pearl River Delta regional air quality monitoring network—Regional collaborative efforts on joint air quality management. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 1582–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.S.; Kim, Y.P. Characteristics of energy usage and emissions of air pollutants in North Korea. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 35, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, L.M.; Al-Saadi, J.A.; Valin, L.C.; Pierce, R.B.; Yang, K.; Janz, S.J.; Kowalewski, M.G.; Szykman, J.J.; Tiefengraber, M.; Mueller, M. The dawn of geostationary air quality monitoring: Case studies from Seoul and Los Angeles. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Foy, B.; Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G. Impacts of control strategies, the great recession and weekday variations on NO2 columns above North American cities. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 138, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ialongo, I.; Herman, J.; Krotkov, N.; Lamsal, L.; Boersma, K.F.; Hovila, J.; Tamminen, J. Comparison of OMI NO2 observations and their seasonal and weekly cycles with ground-based measurements in Helsinki. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 5203–5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jeong, U.; Ahn, M.; Kim, J.H.; Park, R.J.; Lee, H.; Song, C.H.; Choi, Y.S.; Lee, K.H.; Yoo, J.M.; et al. New era of air quality monitoring from space: Geostationary Environment Monitoring Spectrometer (GEMS). Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



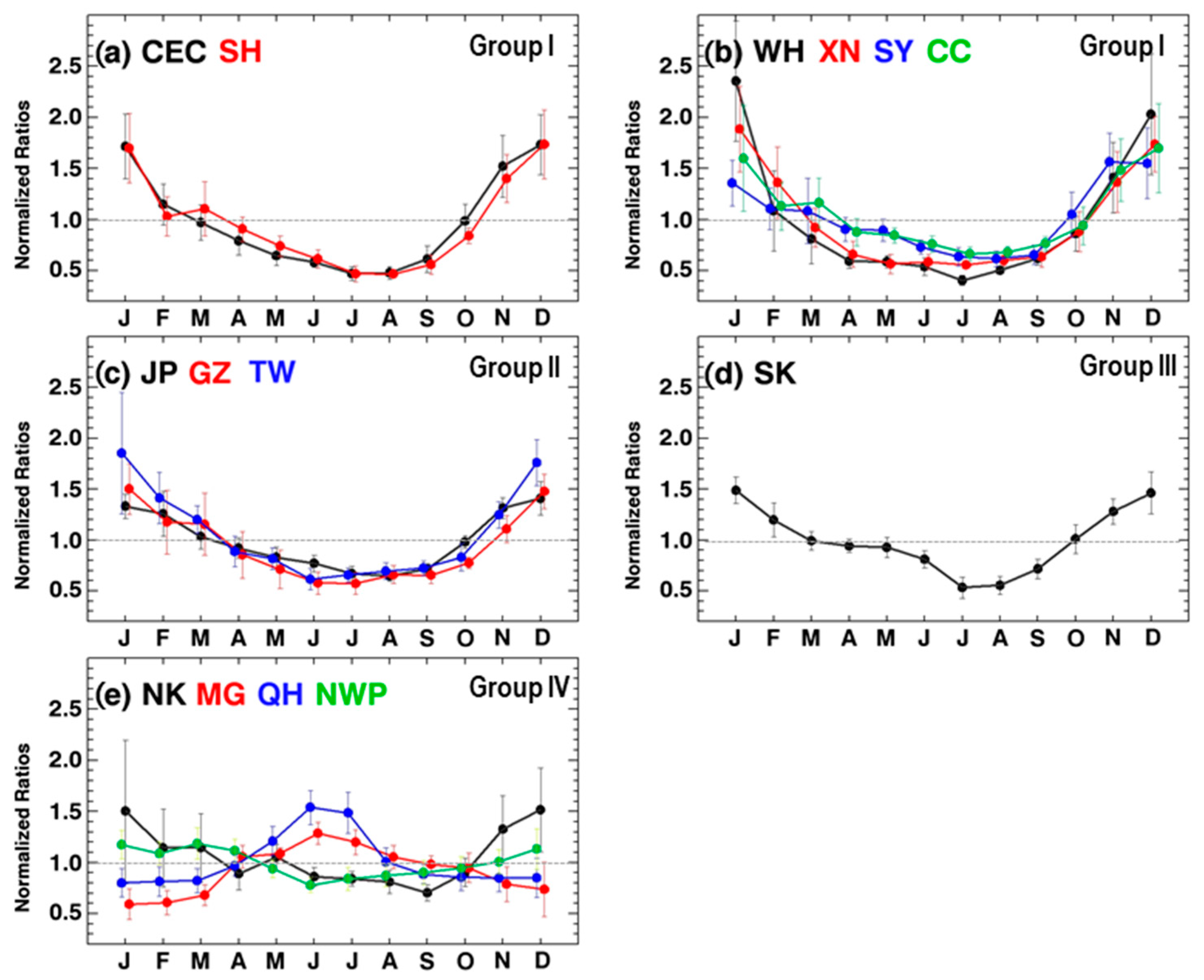


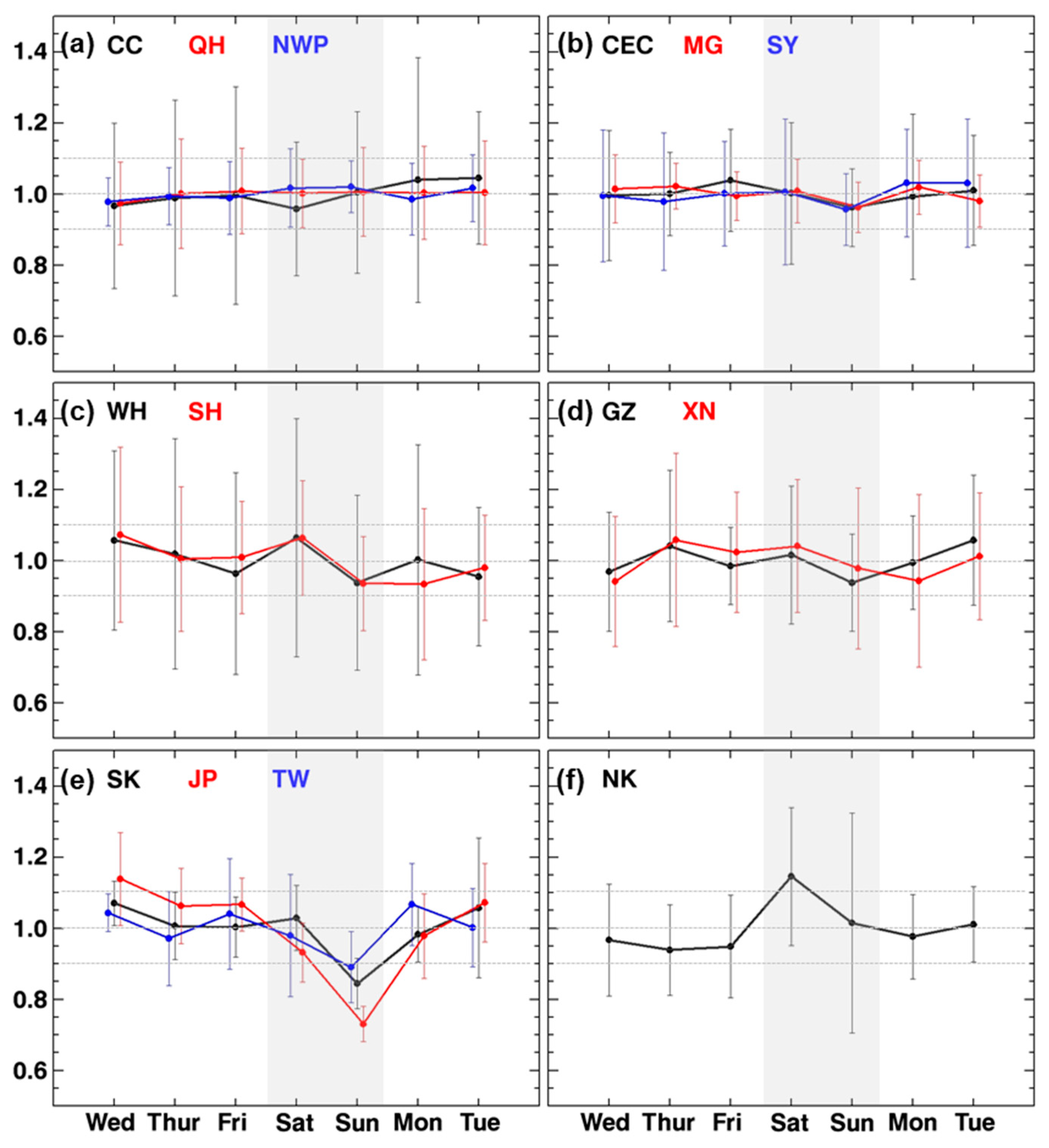
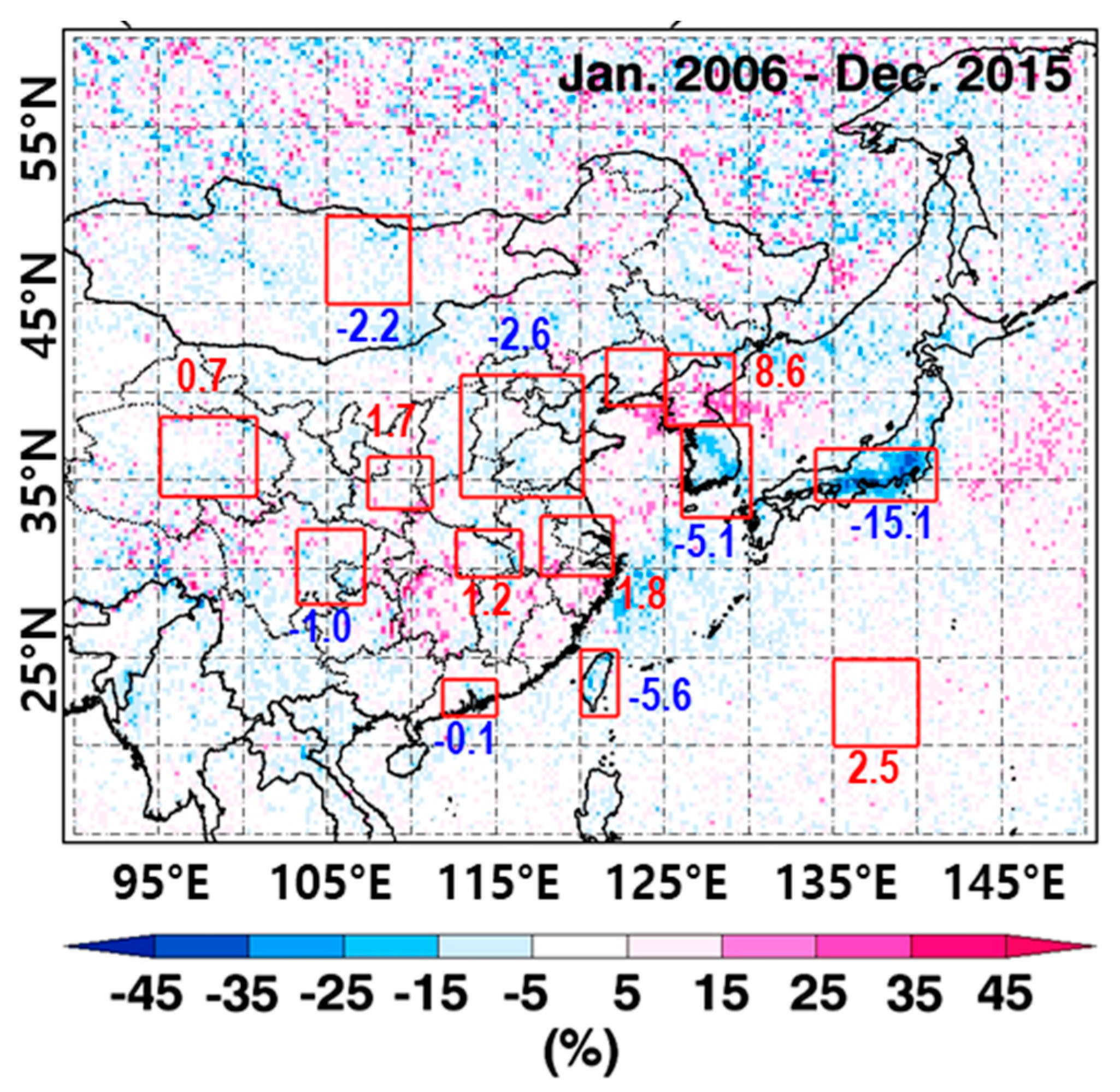
| Groups | Regions | Increasing or Decreasing Rates 1 (×1015 Molecules cm−2 year−1) | Remark (Turning Point) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I. Upward and downward trend | CEC | 0.75 ± 0.08 (R2 = 0.80) | −2.10 ± 0.13 (R2 = 0.97)2 | Nov. 2012 |
| SH | 0.50 ± 0.11 (R2 = 0.62) | −0.64 ± 0.07 (R2 = 0.85) | Jan. 2011 | |
| WH | 0.52 ± 0.08 (R2 = 0.72) | −0.54 ± 0.09 (R2 = 0.77) | Jun. 2011 | |
| XN | 0.40 ± 0.07 (R2 = 0.68) | −0.64 ± 0.04 (R2 = 0.96) | Aug. 2011 | |
| SY | 0.29 ± 0.04 (R2 = 0.77) | −0.14 ± 0.05 (R2 = 0.38) | Aug. 2011 | |
| CC | 0.20 ± 0.02 (R2 = 0.79) | −0.50 ± 0.09 (R2 = 0.85) | May 2013 | |
| II. Downward trend | GZ | - | −0.16 ± 0.03 (R2 = 0.58) | - |
| JP | - | −0.09 ± 0.01 (R2 = 0.73) | - | |
| TW | - | −0.05 ± 0.01 (R2 = 0.49) | - | |
| III. Stagnant trend | SK | 0.06 ± 0.02 (R2 = 0.23) | - | - |
| IV. Upward trend | NK | 0.06 ± 0.01 (R2 = 0.43) | - | - |
| MG | 0.02 ± 0.002 (R2 = 0.87) | - | - | |
| QH | 0.02 ± 0.002 (R2 = 0.96) | - | - | |
| NWP | 0.01 ± 0.001 (R2 = 0.31) | - | - | |
| Sector 1 | CC | QH | NWP | CEC | MG | SY | WH | SH | GZ | XN | SK | JP | TW | NK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENE | 31.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 46.6 | 40.0 | 21.8 | 27.7 | 45.4 | 43.9 | 54.8 | 24.0 | 32.3 | 28.3 | 29.4 |
| IND | 40.5 | 3.2 | 0.0 | 30.7 | 17.4 | 64.0 | 48.1 | 35.6 | 29.8 | 21.8 | 18.2 | 27.6 | 23.2 | 47.3 |
| RES | 7.6 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 4.1 | 3.2 | 2.4 | 4.4 | 2.5 | 3.9 | 4.3 | 4.9 | 10.0 | 1.2 | 9.7 |
| SWD | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| FEF | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 |
| TRO | 13.0 | 27.9 | 0.0 | 12.1 | 12.9 | 8.1 | 9.0 | 12.3 | 16.5 | 12.0 | 48.0 | 20.4 | 41.3 | 8.4 |
| TNR | 1.1 | 11.4 | 0.0 | 2.1 | 22.4 | 2.3 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 1.4 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.0 |
| SHP | 3.7 | 39.3 | 100.0 | 2.2 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 7.2 | 2.7 | 4.4 | 2.8 | 3.3 | 6.3 | 5.1 | 2.7 |
| AGR | 2.2 | 17.5 | 0.0 | 1.7 | 3.8 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 2.4 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 2.3 |
| MMA | 0.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| Total | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, K.M. Temporal Analysis of OMI-Observed Tropospheric NO2 Columns over East Asia during 2006–2015. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10110658
Han KM. Temporal Analysis of OMI-Observed Tropospheric NO2 Columns over East Asia during 2006–2015. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(11):658. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10110658
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Kyung M. 2019. "Temporal Analysis of OMI-Observed Tropospheric NO2 Columns over East Asia during 2006–2015" Atmosphere 10, no. 11: 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10110658
APA StyleHan, K. M. (2019). Temporal Analysis of OMI-Observed Tropospheric NO2 Columns over East Asia during 2006–2015. Atmosphere, 10(11), 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10110658





