Spatiotemporal Change of Plum Rains in the Yangtze River Delta and Its Relation with EASM, ENSO, and PDO During the Period of 1960–2012
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition
2.2.2. The Empirical Orthogonal Function
3. Results
3.1. The Time Variation of Plum Rainfall
3.2. Spatial Pattern of Plum Rainfall
3.3. The Relation among EASM, ENSO, PDO, and Plum Rainfall
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ninomiya, K. Characteristics of Baiu front as a predominant subtropical front in the summer Northern Hemisphere. J. Meteor. Soc. Jpn. 1984, 62, 880–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, T. The large-scale aspects of the characteristic features of the Baiu front. Meteor. Geophys. 1973, 24, 157–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, Y.-M. Large-scale common features of subtropical precipitation zones (the Baiu frontal zone, the SPCZ, and the SACZ). Part I: Characteristics of subtropical frontal zones. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1992, 70, 813–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampe, T.; Xie, S.P. Large-scale dynamics of the Meiyu-Baiu rainband: Environmental forcing by the westerly jet. J. Climatol. 2010, 23, 113–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, H.; Hu, J. Review and Discussion on the Plum Rain Research in China. Meteorol. Environ. Res. 2011, 2, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.H.; Lee, D.I.; Jang, S.M.; Jang, M.; Uyeda, H.; Shinoda, T.; Kobayashi, F. Characteristics of rainfall systems accompanied with Changma front at Chujado in Korea. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 46, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.Z. The southeast summer monsoon and precipitation of China. J. Geogr. Sci. 1934, 1, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, C.W. Chinese air mass properties. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1939, 65, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A. Precipitation in the South Chinese-Tibetan Borderland. Geogr. Rev. 1947, 37, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, I.S.; Ho, C.H.; Lim, Y.K. Principle modes of climatological seasonal and intraseasonal variations of the Asian summer monsoon. Mon. Weather Rev. 1999, 127, 322–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H. Study on the mesoscale structure of the heavy rainfall on Meiyu front with dual-Doppler RADAR. Atmos. Res. 2009, 93, 335–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.Q.; Qian, Y.F.; Zhu, J. The heterogeneity of Meiyu rainfall over Yangtze-Huaihe River vally and its relationship with oceanic surface heating and intraseasonal variability. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2012, 108, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Sun, Y.; You, Q. The northward shift of Meiyu rain belt and its possible association with rainfall intensity changes and the Pacific-Japan pattern. Dyn. Atmos. Ocean. 2016, 76, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, J. Heavy rainfall over East Asia. Int. J. Climatol. 1988, 9, 407–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.K.; Kim, Y.A. Variability of the East Asian summer monsoon during the period of 1980–1989. J. Korean Meteorol. Soc. 1992, 28, 315–331. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C. Investigation of a heavy rainfall event over southwestern Taiwan associated with a sub-synoptic cyclone during the 2003 Mei-Yu season. Atmos. Res. 2010, 95, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.Y.; Xie, Y. Interannual and interdecadal oscillations of Meiyu over the middle-lower reaches of the Changjiang River for 1885–2000. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climtol. 2005, 16, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Chen, Z.S.; Zhao, B.F. Application of Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition Method in Multiscale analysis of Meiyu in Middle-Lower Reaches of Yangtze River. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2015, 24, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.Y.; Ni, Y.Q. Diagnostic study on the structural characteristics of a typical Meiyu front system and its maintenance mechanism. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 21, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoda, T.; Uyeda, H.; Yoshimura, K. Structure of moist layer and sources of water over the southern region far from the Meiyu/Baiu front. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2005, 83, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.J.; Zha, P.; Liu, G.; Zhou, T.J. Characteristics of decadal-centennial-scale changes in East Asian summer monsoon circulation and precipitation during the medieval warm period and little ice age and in the present day. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 3003–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.N.; He, J.H.; Yao, Y.H.; Qi, L. Characteristics and Evolution of Atmospheric Circulation Patterns during Meiyu over the Jianghuai valley. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 48, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.T.; Shaw, T.A. The Impact of the Asian Summer Monsoon Circulation on the Tropopause. J. Climatol. 2016, 8, 8689–8701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Huang, X.; Yu, Y.; Guo, X.; Dong, B.; Lu, T.; Wang, H. Analysis on the new index of plum rains intensity and its spatio-temporal characteristics: A case study on the reaches of the region along Huaihe River in Anhui Province. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2009, 42, 1325–1330. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.J.; Kuo, Y.W.; Wang, W.; Tao, Z.Y.; Cui, B. A Modeling Case Study of Heavy Rainstorms along the Mei-Yu Front. Mon. Weather Rev. 1998, 126, 2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhai, P.; Qian, Y. Variations of Meiyu indicators in the Yangtze-Huaihe River basin during 1954–2003. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2005, 19, 479–484. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Wu, Z.; He, J. Anomalous Meiyu onset averaged over the Yangtze River valley. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2008, 94, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Huang, D.Q.; Zhang, Y.C.; Huang, A.N.; Kuang, X.Y.; Huang, Y. Decadal changes of Meiyu rainfall around 1991 and its relationship with two types of ENSO. J. Geophys Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9766–9777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Liu, C.Z. The influence of moderate ENSO on summer rainfall in eastern China and its comparison with strong ENSO. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yao, J.Q.; Shi, C.H.; Chen, B.M. The relationship between Meiyu and the intensity of East Asian Summer Monsoon. Plateau Meteorol. 2008, 27, 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Gao, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y. Modeling the impact of urbanization on the local and regional climate in Yangtze River Delta, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2010, 102, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Jin, M.; Zhang, F.; Huang, Y. Effects of ground-level ozone (O3) pollution on the yields of rice and winter wheat in the Yangtze River Delta. J. Environ. Sci. China 2003, 15, 360–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Gemmer, M.; Chen, J. Climate changes and flood/drought risk in the Yangtze Delta, China, during the past millennium. Quat. Int. 2008, 176, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lei, C.; Li, G.; Han, L.; Song, S.; Yang, L.; Deng, X. Spatio-temporal characteristics of precipitation and dryness/wetness in Yangtze River Delta, eastern China, during 1960–2012. Atmos. Res. 2016, 172, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Cutter, S.L.; Emrivh, C.T.; Shi, P. Measuring social vulnerability to natural hazards in the Yangtze River Delta region, China. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2013, 4, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Xu, J.; Li, W.; Li, K.; Zhou, C. A Comprehensive Approach to Assess the Hydrological Drought of Inland River Basin in Northwest China. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Sixth Census Commission. The Main Data Bulletin for the Sixth National Census in 2010 (No. 1); Sixth Census Commission: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China and China National Standardization Management Committee. Mei-Yu Monitoring Indicators; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.P.; Zeng, Q.C. A new monsoon index and the geographical distribution of the global monsoons. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 20, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.P.; Zeng, Q.C. A unified monsoon index. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.; Qiu, S.; Xu, J. Temperature change of Shanghai and its response to global warming and urbanization. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Bai, L.; Xu, Y. A hybrid model to simulate the annual runoff of the Kaidu River in northwest China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 1447–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Xu, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, B.; Wang, Z. The regional features of temperature variation trends over Xinjiang in China by the ensemble empirical mode decomposition method. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 3229–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.H.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adap. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A: Mathematical. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Xu, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, Z.; Luo, Y. Modeling the multiple time scale response of hydrological drought to climate change in the data-scarce inland river basin of Northwest China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xoplaki, E.; Luterbacher, J.; Burkard, R.; Patrikas, I.; Maheras, P. Connection between the large-scale 500 hPa geopotential height fields and precipitation over Greece during wintertime. Climatol. Res. 2000, 14, 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, K.; Wang, B. Diurnal precipitation regimes in the global tropics. J. Climate 2008, 21, 2680–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.N. Empirical orthogonal functions and statistical weather prediction. In Technical Report; Statistical Forecast Project Report 1; Dept. of Meteor. MIT: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1956; p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, C. Potential impacts of human-induced land cover change on East Asia monsoon. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2003, 37, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayenu-Prah, A.Y.; Attoh-Okine, N.O. Comparative study of Hilbert-Huang transform, Fourier transform and wavelet transform in pavement profile analysis. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2009, 47, 437–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, T. A method of trend extraction using singular spectrum analysis. Rev. Stat. J. 2009, 7, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.H.; Wu, Z.W.; Jiang, Z.H.; Miao, C.S.; Han, G.R. “Climate effect” of the northeast cold vortex and its influences on Meiyu. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2007, 52, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, G.R.; Bell, T.L.; Cahalan, R.F. Sampling errors in the estimation of the empirical orthogonal functions. Mon. Weather Rev. 1982, 110, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Zheng, J.; Ge, Q. Variations in the summer monsoon rainbands across eastern China over the past 300 years. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 26, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Jiang, W.; Li, W.J. Changed Relationships Between the East Asian Summer Monsoon Circulations and the Summer Rainfall in Eastern China. Acta Meteorol. Sin. (Engl. Ed.) 2014, 28, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Wang, S. Impacts of ENSO on rainfall of global land and China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1999, 44, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Z.; Wang, H.J.; Jiang, D.B. The Configurable Relationships between Summer Monsoon and Precipitation over East Asia. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 28, 700–712. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Q.S.; Guo, X.F.; Zheng, J.Y.; He, Z.X. Meiyu in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River since 1736. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2007, 52, 2792–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.S.; Xu, Y.P.; Han, L.F.; Yang, L. Long-term trends in daily precipitation over the Yangtze River Delta region during 1960–2012, Eastern China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 125, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Gao, H. New features of Meiyu over middle-lower reaches of Yangtze River in the 21st century and the possible causes. Meteorol. Mon. 2013, 39, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, L.; Xiong, K. Climate characteristics and influential systems of Meiyu to the south of the Yangtze River based on the new monitoring rules. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2018, 76, 680–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, D. The features of Meiyu under the new standard. J. Meteorol. Sci. 2016, 36, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, J.; Zhuang, Y. Abnormal distribution of Meiyu precipitation over Jianghuai region and its relation with East Asia subtropical westerly jet. J. Meteorol. Sci. 2018, 38, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


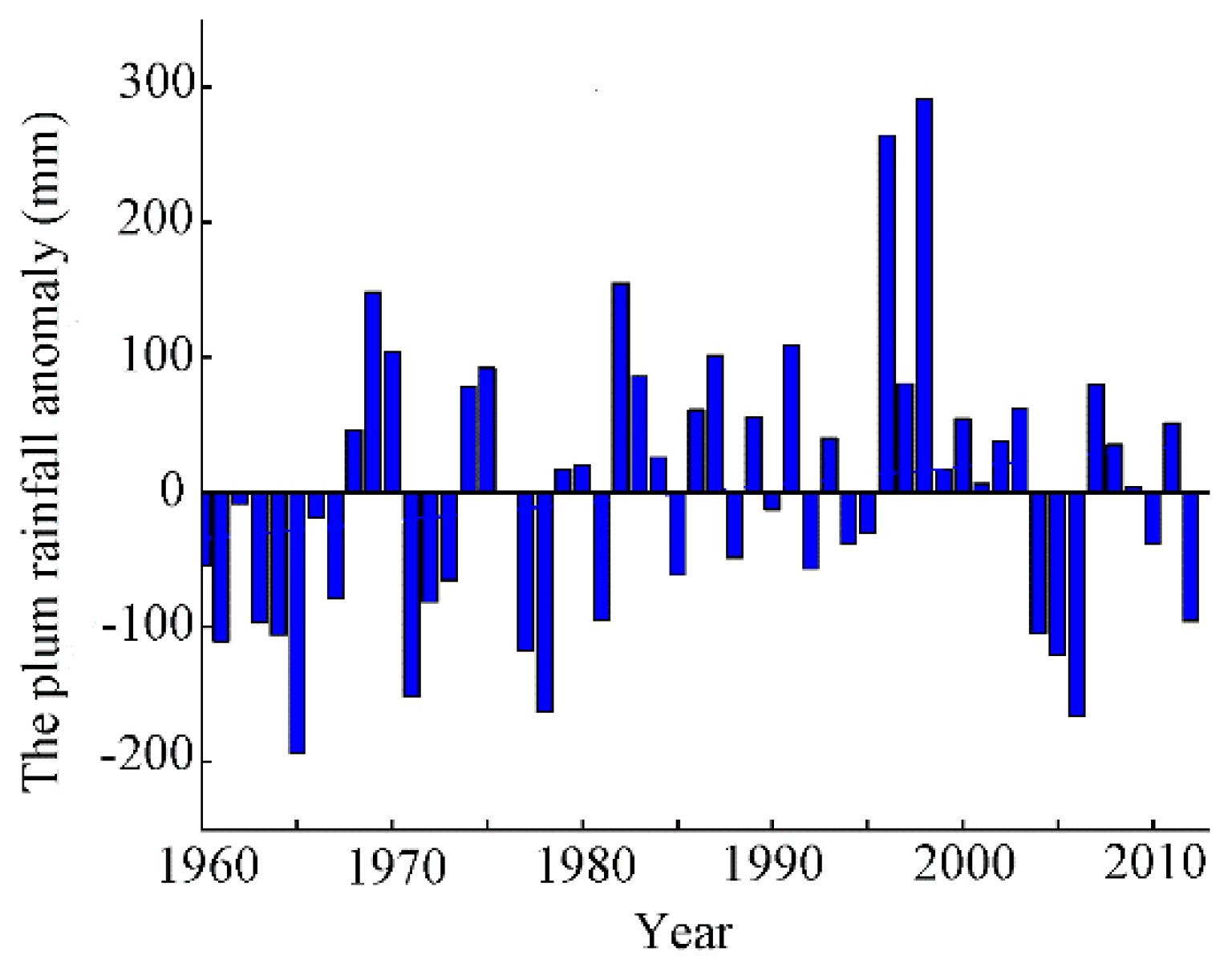

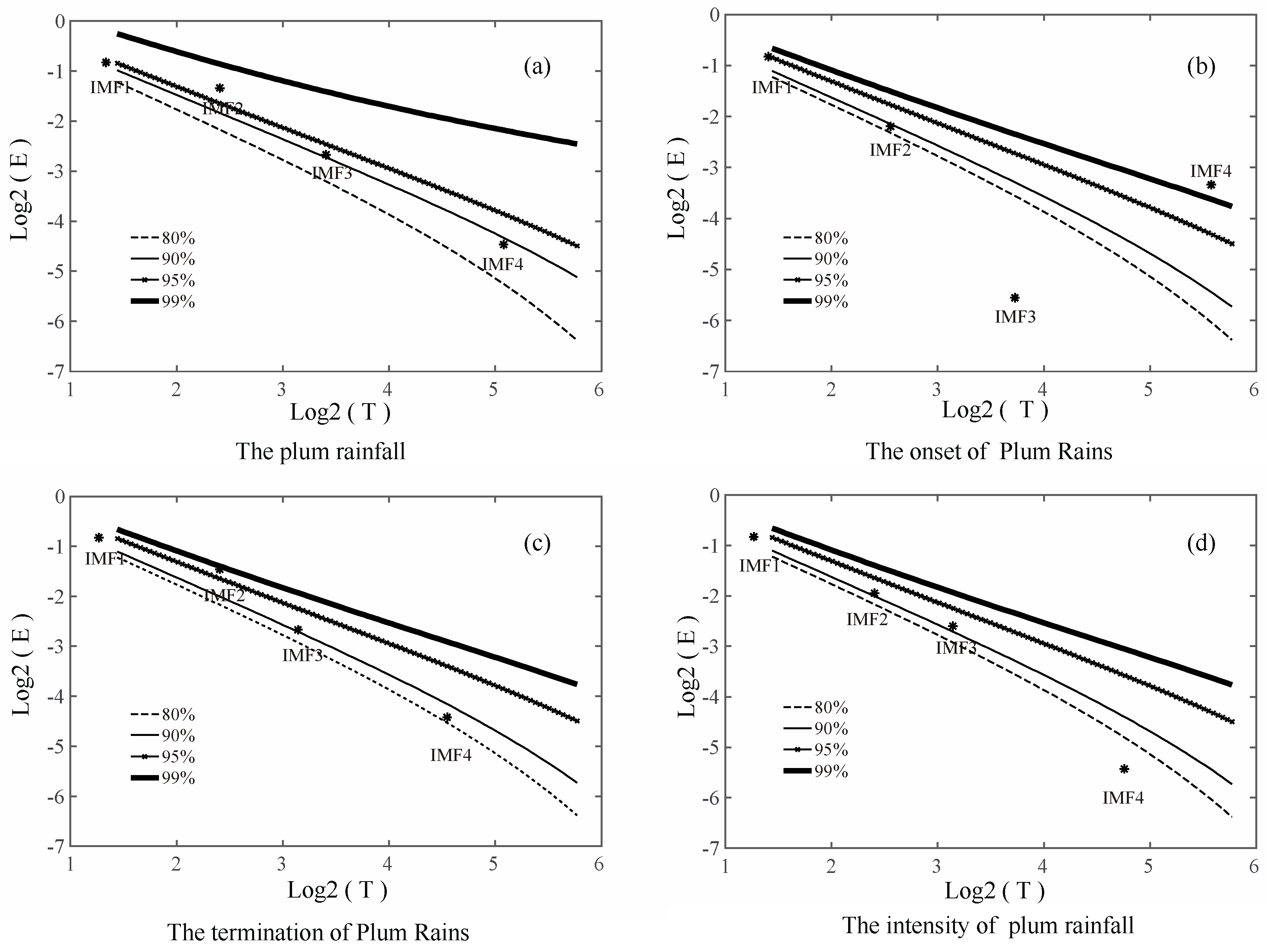


| Variance Contribution Rate (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMF1 | IMF2 | IMF3 | IMF4 | RES | |
| The plum rainfall | 41.04 | 28.33 | 14.20 | 2.63 | 16.14 |
| The onset of Plum Rains | 55.91 | 21.21 | 2.23 | 9.17 | 9.22 |
| The termination of Plum Rains | 51.91 | 33.85 | 15.20 | 4.19 | 3.12 |
| The intensity of plum rainfall | 43.61 | 20.43 | 12.80 | 1.93 | 14.31 |
| Principal Component | Variance Contribution Rate (%) | Cumulative Variance Contribution Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 50.48 | 50.48 |
| 2 | 18.57 | 69.05 |
| 3 | 8.05 | 77.10 |
| 4 | 5.23 | 82.33 |
| 5 | 3.72 | 86.05 |
| 6 | 1.53 | 87.58 |
| Cycle (Year) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMF1 | IMF2 | IMF3 | IMF4 | |
| Plum rainfall | 3 | 6 | 14 | 33 |
| EASM | 3 | 6 | 14 | 48 |
| ENSO | 4 | 6 | 11 | 49 |
| PDO | 4 | 7 | 14 | 28 |
| IMF1 | IMF2 | IMF3 | IMF4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EASM | 0.05 | −0.18 | −0.18 | 0.11 |
| (0.37) | (0.09) | (0.10) | (0.21) | |
| ENSO | 0.24 | 0.04 | 0.16 | −0.00 |
| (0.09) | (0.78) | (0.26) | (0.98) | |
| PDO | 0.07 | −0.01 | −0.24 | 0.24 |
| (0.60) | (0.96) | (0.08) | (0.08) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, N.; Xu, J.; Li, K.; Luo, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhou, C. Spatiotemporal Change of Plum Rains in the Yangtze River Delta and Its Relation with EASM, ENSO, and PDO During the Period of 1960–2012. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10050258
Zhu N, Xu J, Li K, Luo Y, Yang D, Zhou C. Spatiotemporal Change of Plum Rains in the Yangtze River Delta and Its Relation with EASM, ENSO, and PDO During the Period of 1960–2012. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(5):258. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10050258
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Nina, Jianhua Xu, Kaiming Li, Yang Luo, Dongyang Yang, and Cheng Zhou. 2019. "Spatiotemporal Change of Plum Rains in the Yangtze River Delta and Its Relation with EASM, ENSO, and PDO During the Period of 1960–2012" Atmosphere 10, no. 5: 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10050258
APA StyleZhu, N., Xu, J., Li, K., Luo, Y., Yang, D., & Zhou, C. (2019). Spatiotemporal Change of Plum Rains in the Yangtze River Delta and Its Relation with EASM, ENSO, and PDO During the Period of 1960–2012. Atmosphere, 10(5), 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10050258






