Measuring the Vertical Profiles of Aerosol Extinction in the Lower Troposphere by MAX-DOAS at a Rural Site in the North China Plain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Site and Instrument
2.2. Spectral Analysis
2.3. Retrieval of the Vertical Profiles of Aerosol Extinction
2.4. Light Detection and Ranging (Lidar) Observation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Time Series of the Vertical Distribution of Aerosol Extinction
3.2. Diurnal Variations
3.3. Average Vertical Profile of Aerosol Extinction and Comparison with Lidar
4. Conclusions
- The average AOD and near-surface AE were 0.51 ± 0.26 and 0.33 ± 0.18 km−1 during the effective observation period, respectively. The time series of AODs and near-surface AEs presented similar variation trends, with several high value events occurring simultaneously. From the time series of AE profile, elevated AE layers were found to occur frequently. Both AODs and near-surface AEs were positively correlated with the relative humidity (correlation coefficient R = 0.32, 0.42, respectively).
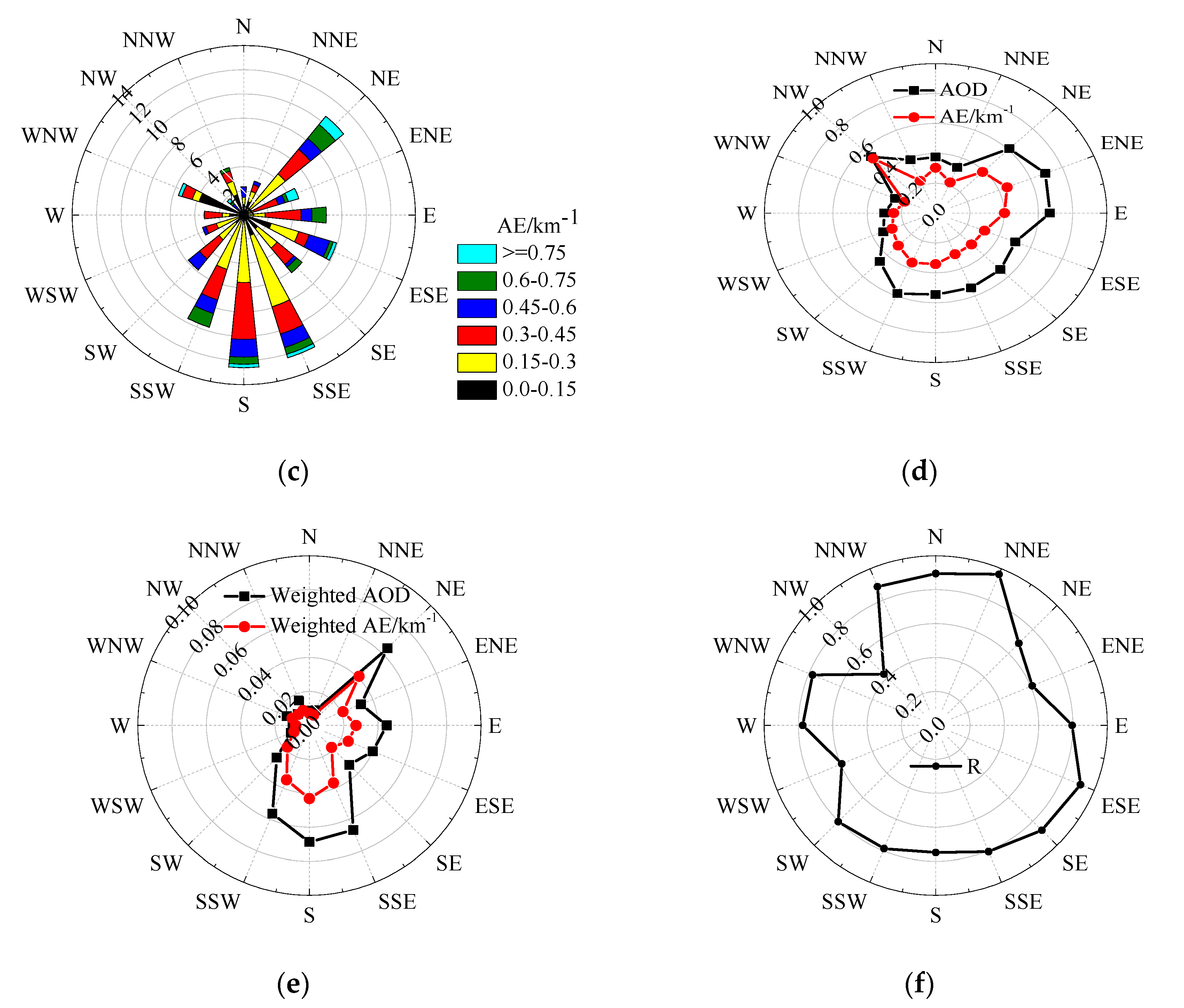
- The AOD and near-surface AE roses show that there are significant differences for averages of AODs and near-surface AEs in 16 wind sectors, with higher AOD or AE means often occurring in the upstream directions of cities. The weighted AOD and AE indicated that pollutant transport from the northeast and south contributes significantly to the AE level at the Raoyang station. The correlation coefficient between AODs and near-surface AEs depends on the wind direction. The low correlation in NE sector implies heterogeneous distribution of AE in the vertical direction. Therefore, the wind field and spatio-temporal distribution of emission sources significantly impact the near-surface AE, AOD, and AE profile.
- The average diurnal variations of AE profile, AODs and near-surface AE were significantly correlated, due to synchronized effects of the source emission and meteorological condition. The correlation coefficients between the AOD and near-surface AE presented the minimum at 10:00 LT. This was due to the influence of lifted AE layers. The AODs were sustained at a high level of ~0.5 during 11:00–18:00 LT, while near-surface AE gradually decreases after 11:00 LT. The differences can be attributed to the development of the convective boundary layer.
- The shape of the AE profiles derived by the MAX-DOAS and the lidar were in agreement. The two quantities revealed the lifted AE layers. However, the height of the lifted layer, the absolute AE level, and the AE vertical gradient were different between the two methods (MAX-DOAS and lidar). The differences were probably connected with the lidar and MAX-DOAS retrievals of the AE profiles, such as the use of a default lidar ratio and the possible uncertainties related to the application (or not) of a scaling factor for the O4 dSCDs. Based on the correlation of hourly AE profiles between MAX-DOAS and lidar, we also found that high correlation appeared when the AOD from MAX-DOAS and RH were higher. As a whole, MAX-DOAS can serve as a supplement to provide AE vertical profiles in the lower troposphere (0–2 km).
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, X.; Zhang, S.; Xing, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Ding, D.; Wu, Y.; Wang, S.; Duan, L.; Hao, J. Progress of Air Pollution Control in China and Its Challenges and Opportunities in the Ecological Civilization Era. Engineering 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Zhang, X.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Che, H. Feedback effects of boundary-layer meteorological factors on cumulative explosive growth of PM2.5 during winter heavy pollution episodes in Beijing from 2013 to 2016. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2018, 18, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Yan, P.; Liu, H.; Yang, S.; Hu, Z.; Lelieveld, J. Strong air pollution causes widespread haze-clouds over China. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, T.F.; Qin, D.; Plattner, G.-K.; Alexander, L.V.; Allen, S.K.; Bindoff, N.L.; Bréon, F.-M.; Church, J.A.; Cubasch, U.; Emori, S.; et al. Technical Summary. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Zhou, T. Health risk assessment of China’s main air pollutants. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Ding, A.; Liao, H.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, T.; Xue, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, B. Aerosol and boundary-layer interactions and impact on air quality. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 4, 810–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Zhang, L.; Cao, J.; Zhang, R. A review of current knowledge concerning PM2.5 chemical composition, aerosol optical properties and their relationships across China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2017, 17, 9485–9518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Xia, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, Z.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.; Goloub, P.; Estellés, V.; Cuevas-Agulló, E.; Blarel, L.; et al. Column aerosol optical properties and aerosol radiative forcing during a serious haze-fog month over North China Plain in 2013 based on ground-based sunphotometer measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2014, 14, 2125–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Che, H.; Yang, L.; Liu, C.; Xia, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Lu, X.; Zhang, X. Long-term validation of MODIS C6 and C6.1 Dark Target aerosol products over China using CARSNET and AERONET. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Xia, X.; Zhao, H.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.N.; Goloub, P.; Cuevas-Agulló, E.; Estelles, V.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; et al. Spatial distribution of aerosol microphysical and optical properties and direct radiative effect from the China Aerosol Remote Sensing Network. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2019, 19, 11843–11864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Li, J.; Dubovik, O.; Zeng, Z.-C.; Yung, Y.L. Impact of Aerosol Vertical Distribution on Aerosol Optical Depth Retrieval from Passive Satellite Sensors. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, J.; Fan, W.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, D. Review of aerosol optical depth retrieval using visibility data. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 200, 102986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xu, X.; Zhao, C.; Yan, P. A review of atmospheric chemistry research in China: Photochemical smog, haze pollution, and gas-aerosol interactions. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 29, 1006–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Che, H.; Xia, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Tao, J.; Zhao, H.; An, L.; Li, L.; et al. Five-year observation of aerosol optical properties and its radiative effects to planetary boundary layer during air pollution episodes in North China: Intercomparison of a plain site and a mountainous site in Beijing. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 674, 140–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Che, H.; Zhu, J.; Chen, H.; Cong, Z.; Deng, X.; Fan, X.; Fu, Y.; Goloub, P.; Jiang, H.; et al. Ground-based remote sensing of aerosol climatology in China: Aerosol optical properties, direct radiative effect and its parameterization. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Xia, X.; Goloub, P.; Holben, B.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Blarel, L.; Damiri, B.; et al. Ground-based aerosol climatology of China: Aerosol optical depths from the China Aerosol Remote Sensing Network (CARSNET) 2002–2013. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2015, 15, 7619–7652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, P.; Tang, J.; Huang, J.; Mao, J.T.; Zhou, X.J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.F.; Zhou, H.G. The measurement of aerosol optical properties at a rural site in Northern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2008, 8, 2229–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Yan, P.; Mao, J.; Zhang, X.; Tian, P.; Chang, H. Observational Study on Aerosol Scattering Phase Function at Raoyang of Hebei, China. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2017, 28, 436–446. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yan, P.; Zhang, L.; Tao, J.; Liu, X.; Tian, P.; Han, Z.; Zhang, R. Investigation of hygroscopic growth effect on aerosol scattering coefficient at a rural site in the southern North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Ren, X.; Jiang, Q.; He, H.; Dickerson, R.R.; Dong, X.; Lv, F. Vertical distributions of aerosol optical properties during the spring 2016 ARIAs airborne campaign in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2018, 18, 8995–9010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, P.; Liu, D.; Zhao, D.; Yu, C.; Liu, Q.; Huang, M.; Deng, Z.; Ran, L.; Wu, Y.; Ding, S.; et al. In situ vertical characteristics of optical properties and heating rates of aerosol over Beijing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2020, 20, 2603–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, R.; Xu, X.; Jia, S.; Ma, R.; Ran, L.; Deng, Z.; Lin, W.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Z. Lower tropospheric distributions of O3 and aerosol over Raoyang, a rural site in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2017, 17, 3891–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, D.; Gao, Q.; Tian, P.; Wang, F.; Zhao, D.; Bi, K.; Wu, Y.; Ding, S.; Hu, K.; et al. Vertical characteristics of aerosol hygroscopicity and impacts on optical properties over the North China Plain during winter. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2020, 20, 3931–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, C.; Liu, W.; Zhang, T.; Xu, J. A synchronous observation of enhanced aerosol and NO2 over Beijing, China, in winter 2015. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 575, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesche, M.; Ansmann, A.; Müller, D.; Althausen, D.; Engelmann, R.; Hu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Müller, D. Particle backscatter, extinction, and lidar ratio profiling with Raman lidar in south and north China. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 6302–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, D.; Tang, G.; Chen, P.; Du, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Vertical characterization of aerosol optical properties and brown carbon in winter in urban Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2019, 19, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Xu, W.; Du, W.; Zhou, L.; Tang, G.; Chen, C.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, X.; Ji, D.; et al. Vertically resolved characteristics of air pollution during two severe winter haze episodes in urban Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2018, 18, 2495–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bian, Y.; Xu, W.; Hu, Y.; Tao, J.; Kuang, Y.; Zhao, C. Method to retrieve aerosol extinction profiles and aerosol scattering phase functions with a modified CCD laser atmospheric detection system. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 6631–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hönninger, G.; Von Friedeburg, C.; Platt, U. Multi axis differential optical absorption spectroscopy (MAX-DOAS). Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2004, 4, 231–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halla, J.D.; Wagner, T.; Beirle, S.; Brook, J.R.; Hayden, K.L.; O’Brien, J.M.; Ng, A.; Majonis, D.; Wenig, M.O.; McLaren, R. Determination of tropospheric vertical columns of NO2 and aerosol optical properties in a rural setting using MAX-DOAS. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2011, 11, 12475–12498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Härtl, A.; Wenig, M.O. Regularisation model study for the least-squares retrieval of aerosol extinction time series from UV/VIS MAX-DOAS observations for a ground layer profile parameterisation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1959–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Brauers, T.; Shao, M.; Garland, R.M.; Wagner, T.; Deutschmann, T.; Wahner, A. MAX-DOAS measurements in southern China: Retrieval of aerosol extinctions and validation using ground-based in-situ data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2010, 10, 2079–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ortega, I.; Coburn, S.; Berg, L.K.; Lantz, K.; Michalsky, J.; Ferrare, R.A.; Hair, J.W.; Hostetler, C.A.; Volkamer, R. The CU 2-D-MAX-DOAS instrument—Part 2: Raman scattering probability measurements and retrieval of aerosol optical properties. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 3893–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, T.; Dix, B.; Von Friedeburg, C.; Fries, U.; Sanghavi, S.; Sinreich, R.; Platt, U. MAX-DOAS O4 measurements: A new technique to derive information on atmospheric aerosols-Principles and information content. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clémer, K.; Van Roozendael, M.; Fayt, C.; Hendrick, F.; Hermans, C.; Pinardi, G.; Spurr, R.; Wang, P.; De Mazière, M. Multiple wavelength retrieval of tropospheric aerosol optical properties from MAXDOAS measurements in Beijing. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 863–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fries, U.; Monks, P.S.; Remedios, J.J.; Rozanov, A.; Sinreich, R.; Wagner, T.; Platt, U. MAX-DOAS O4 measurements: A new technique to derive information on atmospheric aerosols: 2. Modeling studies. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irie, H.; Kanaya, Y.; Akimoto, H.; Iwabuchi, H.; Shimizu, A.; Aoki, K. First retrieval of tropospheric aerosol profiles using MAX-DOAS and comparison with lidar and sky radiometer measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2008, 8, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, S.; Hu, Q.; Liu, H.; Tan, W.; Zhang, W.; Li, B.; Liu, J. A new method to determine the aerosol optical properties from multiple-wavelength O4 absorptions by MAX-DOAS observation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 3289–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gratsea, M.; Bösch, T.; Kokkalis, P.; Richter, A.; Vrekoussis, M.; Kazadzis, S.; Tsekeri, A.; Papayannis, A.; Mylonaki, M.; Amiridis, V.; et al. Retrieval and evaluation of tropospheric aerosol extinction profiles using MAX-DOAS measurements over Athens, Greece. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 2020, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, Z.Y.W.; Friess, U.; Strawbridge, K.B.; Aggarwaal, M.; Baray, S.; Schnitzler, E.G.; Lobo, A.; Fioletov, V.E.; Abboud, I.; McLinden, C.A.; et al. Validation of MAX-DOAS retrievals of aerosol extinction, SO2, and NO2 through comparison with lidar, sun photometer, active DOAS, and aircraft measurements in the Athabasca oil sands region. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 1129–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, K.; Wiegner, M.; Wenig, M.; Pöhler, D. Observations of tropospheric aerosols and NO2 in Hong Kong over 5 years using ground based MAX-DOAS. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 1545–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irie, H.; Takashima, H.; Kanaya, Y.; Boersma, K.F.; Gast, L.; Wittrock, F.; Brunner, D.; Zhou, Y.; Van Roozendael, M. Eight-component retrievals from ground-based MAX-DOAS observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 1027–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mou, F.; Luo, J.; Li, S.; Shan, W.; Hu, L. Vertical profile of aerosol extinction based on the measurement of O4 of multi-elevation angles with MAX-DOAS. Chin. Phys. B 2019, 28, 084212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, A.; Xie, P.-H.; Chen, H.; Xu, J.; Wu, F.-C.; Liu, J.-G.; Liu, W.-Q. Retrieving vertical profile of aerosol extinction by multi-axis differential optical absorption spectroscopy. Acta Phys. Sin. 2013, 62, 180705. [Google Scholar]
- Fries, U.; Baltink, H.K.; Beirle, S.; Clémer, K.; Hendrick, F.; Henzing, B.; Irie, H.; De Leeuw, G.; Li, A.; Moerman, M.M.; et al. Intercomparison of aerosol extinction profiles retrieved from MAX-DOAS measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 3205–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gielen, C.; Hendrick, F.; Pinardi, G.; De Smedt, I.; Fayt, C.; Hermans, C.; Stavrakou, T.; Bauwens, M.; Müller, J.-F.; Ndenzako, E.; et al. Characterisation of Central-African aerosol and trace-gas emissions based on MAX-DOAS measurements and model simulations over Bujumbura, Burundi. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2017, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, T.; Beirle, S.; Brauers, T.; Deutschmann, T.; Fries, U.; Hak, C.; Halla, J.D.; Heue, K.-P.; Junkermann, W.; Li, X.; et al. Inversion of tropospheric profiles of aerosol extinction and HCHO and NO2 mixing ratios from MAX-DOAS observations in Milano during the summer of 2003 and comparison with independent data sets. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 2685–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Cuevas, C.A.; Fries, U.; Saiz-Lopez, A. MAX-DOAS retrieval of aerosol extinction properties in Madrid, Spain. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 5089–5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Wang, P.C. Assessment of MAX-DOAS aerosol retrieval over North China. Chin. J. Geophys. 2018, 61, 494–503. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Dörner, S.; Donner, S.; Böhnke, S.; De Smedt, I.; Dickerson, R.R.; Dong, Z.; He, H.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; et al. Vertical profiles of NO2, SO2, HONO, HCHO, CHOCHO and aerosols derived from MAX-DOAS measurements at a rural site in the central western North China Plain and their relation to emission sources and effects of regional transport. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2019, 19, 5417–5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, W.; Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Jia, S.; Xu, X.; Cheng, H.; Meng, Z. Characteristics of Ambient Formaldehyde at Two Rural Sites in the North China Plain in Summer. Res. Environ. Sci. 2016, 29, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, L.; Deng, Z.; Xu, X.; Yan, P.; Lin, W.; Wang, Y.; Tian, P.; Wang, P.; Pan, W.; Lu, D. Vertical profiles of black carbon measured by a micro-aethalometer in summer in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2016, 16, 10441–10454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, J.; Ma, J.; Lin, W.; Zhao, H.; Shaiganfar, R.; Beirle, S.; Wagner, T. MAX-DOAS measurements and satellite validation of tropospheric NO2 and SO2 vertical column densities at a rural site of North China. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 133, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Ma, J.; Cheng, W.; Yan, P.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, L.; Yang, P. Tropospheric NO2 vertical column densities retrieved from ground-based MAX-DOAS measurements at Shangdianzi regional atmospheric background station in China. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 80, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Beirle, S.; Jin, J.L.; Shaiganfar, R.; Yan, P.; Wagner, T. Tropospheric NO2 vertical column densities over Beijing: Results of the first three years of ground-based MAX-DOAS measurements (2008–2011) and satellite validation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2013, 13, 1547–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Dörner, S.; Donner, S.; Jin, J.; Cheng, S.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, P.; Zhang, G.; et al. MAX-DOAS measurements of NO2, SO2, HCHO, and BrO at the Mt. Waliguan WMO GAW global baseline station in the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2020, 20, 6973–6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinksma, E.J.; Pinardi, G.; Volten, H.; Braak, R.; Richter, A.; Schönhardt, A.; Van Roozendael, M.; Fayt, C.; Hermans, C.; Dirksen, R.J.; et al. The 2005 and 2006 DANDELIONS NO2and aerosol intercomparison campaigns. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piters, A.J.M.; Boersma, K.F.; Kroon, M.; Hains, J.C.; Van Roozendael, M.; Wittrock, F.; Abuhassan, N.; Adams, C.; Akrami, M.; Allaart, M.A.F.; et al. The Cabauw Intercomparison campaign for Nitrogen Dioxide measuring Instruments (CINDI): Design, execution, and early results. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 457–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Platt, U.; Stutz, J. Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy: Principles and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Lampel, J.; Xie, P.; Beirle, S.; Li, A.; Wu, D.; Wagner, T. Ground-based MAX-DOAS observations of tropospheric aerosols, NO2, SO2 and HCHO in Wuxi, China, from 2011 to 2014. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2017, 17, 2189–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; De Vries, M.J.M.P.; Xie, P.H.; Beirle, S.; Dörner, S.; Remmers, J.; Li, A.; Wagner, T. Cloud and aerosol classification for 2.5 years of MAX-DOAS observations in Wuxi (China) and comparison to independent data sets. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 5133–5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, T.; Apituley, A.; Beirle, S.; Dörner, S.; Fries, U.; Remmers, J.; Shaiganfar, R. Cloud detection and classification based on MAX-DOAS observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 1289–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Miao, S.; Zhang, X. Study on atmospheric pollution characteristics before a snowfall event in autumn in the Beijing urban area using lidar. Clim. Environ. Res. 2014, 19, 659–669. [Google Scholar]
- Bove, M.; Brotto, P.; Calzolai, G.; Cassola, F.; Cavalli, F.; Fermo, P.; Hjorth, J.; Massabò, D.; Nava, S.; Piazzalunga, A.; et al. PM10 source apportionment applying PMF and chemical tracer analysis to ship-borne measurements in the Western Mediterranean. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 125, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdoba-Jabonero, C.; Andrey-Andrés, J.; Gómez-Martín, L.; Adame, J.A.; Sorribas, M.; Navarro-Comas, M.; Puentedura, O.; Cuevas-Agulló, E.; Gil-Ojeda, M. Vertical mass impact and features of Saharan dust intrusions derived from ground-based remote sensing in synergy with airborne in-situ measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 142, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasano, Y.; Browell, E.V.; Ismail, S. Error caused by using a constant extinction/backscattering ratio in the lidar solution. Appl. Opt. 1985, 24, 3929–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, T.; Beirle, S.; Benavent, N.; Bösch, T.; Chan, K.L.; Donner, S.; Dörner, S.; Fayt, C.; Fries, U.; García-Nieto, D.; et al. Is a scaling factor required to obtain closure between measured and modelled atmospheric O4 absorptions? An assessment of uncertainties of measurements and radiative transfer simulations for 2 selected days during the MAD-CAT campaign. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 2745–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, S.; Jin, J.; Ma, J.; Xu, X.; Ran, L.; Ma, Z.; Chen, J.; Guo, J.; Yang, P.; Wang, Y.; et al. Measuring the Vertical Profiles of Aerosol Extinction in the Lower Troposphere by MAX-DOAS at a Rural Site in the North China Plain. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101037
Cheng S, Jin J, Ma J, Xu X, Ran L, Ma Z, Chen J, Guo J, Yang P, Wang Y, et al. Measuring the Vertical Profiles of Aerosol Extinction in the Lower Troposphere by MAX-DOAS at a Rural Site in the North China Plain. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(10):1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101037
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Siyang, Junli Jin, Jianzhong Ma, Xiaobin Xu, Liang Ran, Zhiqiang Ma, Junming Chen, Junrang Guo, Peng Yang, Yang Wang, and et al. 2020. "Measuring the Vertical Profiles of Aerosol Extinction in the Lower Troposphere by MAX-DOAS at a Rural Site in the North China Plain" Atmosphere 11, no. 10: 1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101037
APA StyleCheng, S., Jin, J., Ma, J., Xu, X., Ran, L., Ma, Z., Chen, J., Guo, J., Yang, P., Wang, Y., & Wagner, T. (2020). Measuring the Vertical Profiles of Aerosol Extinction in the Lower Troposphere by MAX-DOAS at a Rural Site in the North China Plain. Atmosphere, 11(10), 1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101037






