Differentiation of the Athens Fine PM Profile during Economic Recession (March of 2008 Versus March of 2013): Impact of Changes in Anthropogenic Emissions and the Associated Health Effect
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Campaign
2.2. Data Analysis
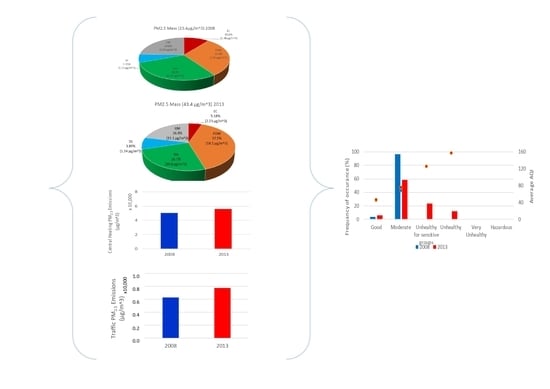
2.2.1. Mass Closure
2.2.2. Emissions
2.2.3. Health Risk
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Data Overview
3.2. Influence of the Emissions
3.3. Health Impact of the Aerosol Levels
4. Conclusions
- An enhanced input from the anthropogenic emissions and in full compliance with the emission data, was observed in 2013 for both the PM load and the POM component.
- The obtained PM chemical profile scheme was the result of both local and regional sources with POM and SIA, being the main constituents of the particles’ mass.
- When moving from 2008 to 2013, the sector of residential heating seemed to drive the changes to the configuration of the PM burden.
- In 2013, the EC input from the domestic heating was almost double of the one from traffic while the POM contribution from the traffic sector was decreased at about 7%.
- The changes to the air quality were mainly driven by PM2.5.
- From the health perspective, the considerable deterioration of the air quality in 2013, appeared to coincide with low average wind values (avg ws ≤ 0.69 m/s).
- Despite the position of the monitoring location next to the most trafficked avenues of the capital, the EC input from the heating sector was double compared to the traffic in 2013.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paglione, M.; Gilardoni, S.; Rinaldi, M.; Decesari, S.; Zanca, N.; Sandrini, S.; Giulianelli, L.; Bacco, D.; Ferrari, S.; Poluzzi, V.; et al. The impact of biomass burning and aqueous-phase processing on air quality: A multi-year source apportionment study in the Po Valley, Italy. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 1233–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Squizzato, S.; Masiol, M.; Agostini, C.; Visin, F.; Formenton, G.; Harrison, R.M.; Rampazzo, G. Factors, origin and sources affecting PM1 concentrations and composition at an urban background site. Atmos. Res. 2016, 180, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vecchi, R.; Chiari, M.; D’Alessandro, A.; Fermo, P.; Lucarelli, F.; Mazzei, F.; Navab, S.; Piazzalungac, A.; Pratie, P.; Silvania, F.; et al. A mass closure and PMF source apportionment study on the sub-micron sized aerosol fraction at urban sites in Italy. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2240–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, N.; Gil-Molto, J.; Varea, M.; Chofre, C.; Yubero, E. Seasonal and interanual trends in PM levels and associated inorganic ions in southeastern Spain. Microchem. J. 2013, 110, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, N.; Yubero, E.; Clemente, A.; Nicolas, J.F.; Varea, M.; Crespo, J. PM events and changes in the chemical composition of urban aerosols: A case study in the western Mediterranean. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzeghar, V.; Sarbakhsh, P.; Hassanvand, M.S.; Faridi, S.; Gholampour, A. Long-term trend of ambient air PM10, PM2.5, and O3 and their health effects in Tabriz city, Iran, during 2006–2017. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 54, 101988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Wang, S.; Xing, J.; Chang, X.; Ding, D.; Zheng, H. Regional transport in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and its changes during 2014–2017: The impacts of meteorology and emission reduction. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Ding, X.; Hang, J.; Ge, J. Characteristics of urban air pollution in different regions of China between 2015 and 2019. Build. Environ. 2020, 180, 107048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gu, X.; Cheng, C.; Yang, D. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of PM2.5 and its relationship with urbanization in North China from 2000 to 2017. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, J.; Liao, H.; Yang, Y.; Yue, X. Meteorological influences on PM2.5 and O3 trends and associated health burden since China’s clean air actions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Carmichael, G.R.; Saide, P.E.; Lu, Z.; Yu, M.; Streets, D.G.; Wang, Z. Response of winter fine particulate matter concentrations to emission and meteorology changes in North China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 11837–11851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; Yi, S.-M.; Heo, J. Fifteen-year trends in carbon species and PM2.5 in Seoul, South Korea (2003–2017). Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevopoulou, D.; Liakakou, E.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Mihalopoulos, N. Sources of atmospheric aerosol from long-term measurements (5 years) of chemical composition in Athens, Greece. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 527, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Jolleys, M.D.; Fu, T.-M.; Palmer, P.I.; Ma, Y.; Tian, H.; Li, J.; Yang, X. Spatiotemporal and probability variations of surface PM2.5 over China between 2013 and 2019 and the associated changes in health risks: An integrative observation and model analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 137896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Tong, D.; Shao, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; He, H.; Liu, W.; et al. Drivers of improved PM2.5 air quality in China from 2013 to 2017. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24463–24469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, M.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, B.; Ji, D.; Sherman, P.; Song, S.; Xin, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; et al. China’s emission control strategies have suppressed unfavorable influences of climate on wintertime PM2.5 concentrations in Beijing since 2002. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Pandolfi, M.; Reche, C.; Pérez, N.; Minguillón, M.C.; Moreno, T.; Viana, M.; Escudero, M.; Orio, A.; et al. 2001–2012 trends on air quality in Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 957–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pateraki, S.; Asimakopoulos, D.N.; Maggos, T.; Assimakopoulos, V.D.; Bougiatioti, A.; Bairachtari, K.; Vasilakos, C.; Mihalopoulos, N. Chemical characterization, sources and potential health risk of PM2.5 and PM1 pollution across the Greater Athens Area. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fameli, K.M.; Assimakopoulos, V.D. The new open Flexible Emission Inventory for Greece and the Greater Athens Area (FEI-GREGAA): Account of pollutant sources and their importance from 2006 to 2012. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 137, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crilley, L.R.; Bloss, W.J.; Yin, J.; Beddows, D.C.S.; Harrison, R.M.; Allan, J.D.; Young, D.E.; Flynn, M.; Williams, P.; Zotter, P.; et al. Sources and contributions of wood smoke during winter in London: Assessing local and regional influences. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 3149–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mueller, W.; Loh, M.; Vardoulakis, S.; Johnston, H.J.; Steinle, S.; Precha, N.; Kliengchuay, W.; Tantrakarnapa, K.; Cherrie, J.W. Ambient particulate matter and biomass burning: An ecological time series study of respiratory and cardiovascular hospital visits in northern Thailand. Environ. Health 2020, 19, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourtziou, L.; Liakakou, E.; Stavroulas, I.; Theodosi, C.; Zarmpas, P.; Psiloglou, B.; Sciare, J.; Maggos, T.; Bairachtari, K.; Bougiatioti, A.; et al. Multi-tracer approach to characterize domestic wood burning in Athens (Greece) during wintertime. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 148, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pateraki, S. Experimental and Arithmetic Study of the Particulate Matter (ΡΜ10, ΡΜ2.5, ΡΜ1) Concentrations and Their Chemical Composition (PAHs, Ions, Organic/Elemental Carbon) over the Greater Athens Area. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Physics, National Kapodistrian of Athens, Athens, Greece, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Stavraka, T. A Study of PM2.5 and PM1 in the Atmosphere of a Suburban Area within the Athens Basin. Bachelor’s Thesis, Department of Physics, National Kapodistrian of Athens, Athens, Greece, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zagkos, A. A Study of the Temporal Evolution of Particulate Pollution in Different Types of Environment across the Greater Athens Area: Concentrations, Chemical Composition and the Role of the Meteorology. Master’s Thesis, Department of Physics, National Kapodistrian of Athens, Athens, Greece, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pateraki, S.; Assimakopoulos, V.D.; Bougiatioti, A.; Kouvarakis, G.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Vasilakos, C. Carbonaceous and ionic compositional patterns of fine particles over an urban Mediterranean area. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 424, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocak, M.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Kubilay, N. Chemical composition of the fine and coarse fraction of aerosols in the northeastern Mediterranean. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 7351–7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodosi, C.; Grivas, G.; Zarmpas, P.; Chaloulakou, A.; Mihalopoulos, N. Mass and chemical composition of size-segregated aerosols (PM1, PM2.5, PM10) over Athens, Greece: Local versus regional sources. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 11895–11911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liakakou, E.; Stavroulas, I.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Grivas, G.; Paraskevopoulou, D.; Dumka, U.C.; Tsagkaraki, M.; Bougiatioti, A.; Oikonomou, K.; Sciare, J.; et al. Long-term variability, source apportionment and spectral properties of black carbon at an urban background site in Athens, Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 222, 117137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzi, E.; Argyropoulos, G.; Bougatioti, A.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Nikolaou, K.; Samara, C. Chemical composition and mass closure of ambient PM10 at urban sites. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2231–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pateraki, S.; Asimakopoulos, D.N.; Bougiatioti, A.; Maggos, T.; Vasilakos, C.; Mihalopoulos, N. Assessment of PM2.5 and PM1 Chemical Profile in a Multiple-Impacted Mediterranean Urban Area: Origin, Sources and Meteorological Dependence. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 479, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odysseee Mure Project. Available online: https://www.odyssee-mure.eu/ (accessed on 15 March 2019).
- Fameli, K.M.; Assimakopoulos, V.D. Development of a road transport emission inventory for Greece and the Greater Athens Area: Effects of important parameters. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 770–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaap, M.; Roemer, M.; Sauter, F.; Boersen, G.; Timmermans, R.; Builtjes, P.J.H.; Vermeulen, A.T. Lotos-Euros: Documentation; TNO-Report B&O-A R 2005/297; TNO: Apeldoorn, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gorai, A.K.; Tchounwou, P.B.; Biswal, S.S.; Francis Tuluri, F. Spatio-Temporal Variation of Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Concentrations and Its Health Impacts in a Mega City, Delhi in India. Environ. Health Insights 2018, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EPA. Guideline for Reporting of Daily Air Quality—Air Quality Index (AQI); EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitriou, K.; Liakakou, E.; Lianou, M.; Psiloglou, B.; Kassomenos, P.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Gerasopoulos, E. Implementation of an aggregate index to elucidate the influence of atmospheric synoptic conditions on air quality in Athens, Greece. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2020, 13, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shooter, D. Coarse–fine and day–night differences of water-soluble ions in atmospheric aerosols collected in Christchurch and Auckland, New Zealand. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 3519–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.Z.; Sun, L.; Tian, Y.; Shi, G.; Feng, Y. Chemical characterization and source apportionment of PM1 and PM2.5 in Tianjin, China: Impacts of biomass burning and primary biogenic sources. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 99, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phairuang, W.; Inerb, M.; Furuuchi, M.; Hata, M.; Tekasakul, S.; Tekasakul, P. Size-fractionated carbonaceous aerosols down to PM0.1 in southern Thailand: Local and long-range transport effects. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-L.; Huang, R.-J.; El Haddad, I.; Ho, K.-F.; Cao, J.-J.; Han, Y.; Zotter, P.; Bozzetti, C.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Canonaco, F.; et al. Fossil vs. non-fossil sources of fine carbonaceous aerosols in four Chinese cities during the extreme winter haze episode of 2013. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 1299–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zotter, P.; Herich, H.; Gysei, M.; El-Haddad, I.; Zhang, Y.; Mocnik, G.; Hüglin, C.; Baltensperger, U.; Szidat, S.; Prévôt, A.S.H. Evaluation of the absorption Ångström exponents for traffic and wood burning in the Aethalometer-based source apportionment using radiocarbon measurements of ambient aerosol. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 4229–4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lonati, G.; Giugliano, M.; Butelli, P.; Romele, L.; Tardivo, R. Major chemical components of PM2.5 in Milan (Italy). Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 1925–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillanpaa, M.; Hillamoa, R.; Saarikoskia, S.; Frey, A.; Pennanen, A.; Makkonen, U.; Spolnik, Z.; Van Grieken, R.; Branis, M.; Brunekreef, B.; et al. Chemical composition and mass closure of particulate matter at six urban sites in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, S212–S223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattigan, O.V.; Felton, H.D.; Bae, M.-S.; Schwab, J.J.; Demerjian, K.L. Multi-year hourly PM2.5 carbon measurements in New York: Diurnal, day of week and seasonal patterns. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2043–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, C.D.; Oanh, N.T.K. Effects of local, regional meteorology and emission sources on mass and compositions of particulate matter in Hanoi. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 78, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jia, C.; Tao, J.; Zhang, L.; Liang, X.; Ma, J.; Gao, H.; Huang, T.; Zhang, K. Chemical characterization and source apportionment of PM2.5 in a semi-arid and petrochemical-industrialized city, Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Tian, H.; Cheng, K.; Lu, L.; Zheng, M.; Wang, S.; Hao, J.; Wang, K.; Hua, S.; Zhu, C.; et al. The variation of chemical characteristics of PM2.5 and PM10 and formation causes during two haze pollution events in urban Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 107, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.K.; Khoder, M.I. Chemical characteristics of atmospheric PM2.5 loads during air pollution episodes in Giza, Egypt. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 150, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pateraki, S.; Fameli, K.-M.; Assimakopoulos, V.; Bairachtari, K.; Zagkos, A.; Stavraka, T.; Bougiatioti, A.; Maggos, T.; Mihalopoulos, N. Differentiation of the Athens Fine PM Profile during Economic Recession (March of 2008 Versus March of 2013): Impact of Changes in Anthropogenic Emissions and the Associated Health Effect. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101121
Pateraki S, Fameli K-M, Assimakopoulos V, Bairachtari K, Zagkos A, Stavraka T, Bougiatioti A, Maggos T, Mihalopoulos N. Differentiation of the Athens Fine PM Profile during Economic Recession (March of 2008 Versus March of 2013): Impact of Changes in Anthropogenic Emissions and the Associated Health Effect. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(10):1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101121
Chicago/Turabian StylePateraki, Styliani, Kyriaki-Maria Fameli, Vasiliki Assimakopoulos, Kyriaki Bairachtari, Alexandros Zagkos, Theodora Stavraka, Aikaterini Bougiatioti, Thomas Maggos, and Nikolaos Mihalopoulos. 2020. "Differentiation of the Athens Fine PM Profile during Economic Recession (March of 2008 Versus March of 2013): Impact of Changes in Anthropogenic Emissions and the Associated Health Effect" Atmosphere 11, no. 10: 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101121
APA StylePateraki, S., Fameli, K.-M., Assimakopoulos, V., Bairachtari, K., Zagkos, A., Stavraka, T., Bougiatioti, A., Maggos, T., & Mihalopoulos, N. (2020). Differentiation of the Athens Fine PM Profile during Economic Recession (March of 2008 Versus March of 2013): Impact of Changes in Anthropogenic Emissions and the Associated Health Effect. Atmosphere, 11(10), 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101121