Observation-Based Summer O3 Control Effect Evaluation: A Case Study in Chengdu, a Megacity in Sichuan Basin, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Field Measurement
2.2. VOC Reactivity and Contribution to O3 Formation
2.3. Source Apportionment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Ambient Air Pollutants before and during the Control Campaign
3.2. Contributions of Different Volatile Organic Compounds to Ozone Formation
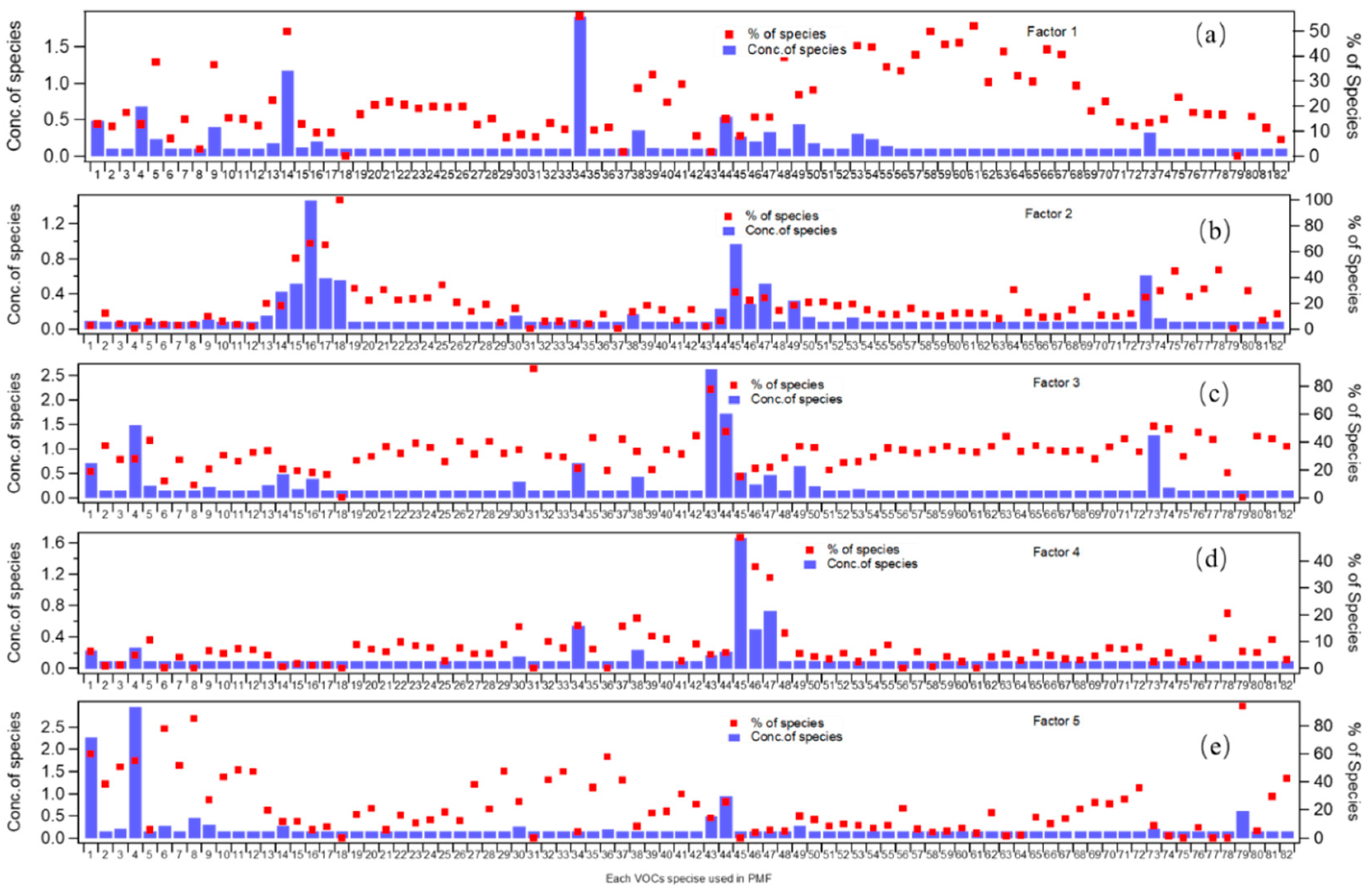
3.3. Comparison of VOC Sources before and during Control Period
3.4. Contributions of VOC Sources to O3 Formation before and during the Performed Control Measures
4. Conclusions and Long-Term Countermeasures
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, T.; Xue, L.; Brimblecombe, P.; Lam, Y.F.; Li, L.; Zhang, L. Ozone pollution in China: A review of concentrations, meteorological influences, chemical precursors, and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1582–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.Y.; Bi, J.; Liu, Q.; Ling, Z.H.; Shen, G.F.; Chen, F.; Qiao, Y.Z.; Li, C.Y.; Ma, Z.W. Sources of volatile organic compounds and policy implications for regional ozone pollution control in an urban location of Nanjing, East China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 3905–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Z.R.; Wang, X.M.; Ling, Z.H.; Zhao, J.; Guo, H.; Shao, M.; Wang, Z. Contributions of different anthropogenic volatile organic compound sources to ozone formation at a receptor site in the Pearl River Delta region and its policy implications. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 8801–8816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, G.; Yang, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, T.; Hu, J. Impact of Atmospheric Circulation and Meteorological Parameters on Wintertime Atmospheric Extinction in Chengdu and Chongqing of Southwest China during 2001–2016. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 1538–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.Y.; Wu, K.; Wang, H.L.; Liu, Y.M.; Gu, S.; Lu, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.L.; Hu, Y.S.; Ou, Y.H.; Wang, S.G.; et al. Summertime ozone pollution in Sichuan Basin, China: Meteorological conditions, sources and process analysis. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 226, 117392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Tan, J.; Zhao, Q.; Du, Z.; He, K.; Ma, Y.; Duan, F.; Chen, G.; Zhao, Q. Characteristics of PM2.5 speciation in representative megacities and across China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 5207–5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, J.; Luo, M. Seasonal and spatial variability of surface ozone over China: Contributions from background and domestic pollution. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 3511–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, R.; Xie, S. Characteristics of volatile organic compounds, NO2, and effects on ozone formation at a site with high ozone level in Chengdu. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 75, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Fan, Z.Y.; Pu, M.; Zhang, J.L.; Yang, Z.Z.; Wu, D. Pollution Characteristics and Health Risk Assessment of Atmospheric VOCs in Chengdu. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.X.; Han, L.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.Q. Analyses of Pollution Characteristics, Ozone Formation Potential and Sources of VOCs Atmosphere in Chengdu City in Summer 2017. Res. Environ. Sci. 2019, 32, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Q.; Liu, H.; Xie, S.; Zhou, L.; Song, T.; Shi, G.; Jiang, W.; Yang, F.; Wei, F. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and source origins of volatile organic compounds in a megacity of Sichuan Basin, China. Environ. Res. 2020, 185, 109478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Z.; Lu, K.; Jiang, M.; Su, R.; Dong, H.; Zeng, L.; Xie, S.; Tan, Q.; Zhang, Y. Exploring ozone pollution in Chengdu, southwestern China: A case study from radical chemistry to O-3-VOC-NOx sensitivity. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Tan, Q.; Feng, M.; Qu, Y.; Liu, X.; An, J.; Zhang, Y. Source Apportionment and Secondary Transformation of Atmospheric Nonmethane Hydrocarbons in Chengdu, Southwest China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 9741–9763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Liu, X.; Tan, Q.; Feng, M.; Qu, Y.; An, J.; Zhang, Y. Characteristics and formation mechanism of persistent extreme haze pollution events in Chengdu, southwestern China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 251, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Ho, S.S.H.; Gong, S.; Ni, J.; Li, H.; Han, L.; Yang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Zhao, D. Characterization of VOCs and their related atmospheric processes in a central Chinese city during severe ozone pollution periods. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 617–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Yuan, B.; Shao, M.; Wang, X.; Lu, S.; Lu, K.; Wang, M.; Chen, L.; Chang, C.C.; Liu, S.C. Variations of ground-level O-3 and its precursors in Beijing in summertime between 2005 and 2011. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 6089–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Carlo, P.; Brune, W.H.; Martinez, M.; Harder, H.; Lesher, R.; Ren, X.R.; Thornberry, T.; Carroll, M.A.; Young, V.; Shepson, P.B.; et al. Missing OH reactivity in a forest: Evidence for unknown reactive biogenic VOCs. Science 2004, 304, 722–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, L.; Huang, L.; Wang, Y.J.; Huo, J.T.; Duan, Y.S.; Wang, Y.H.; Fu, Q.Y. The impact of volatile organic compounds on ozone formation in the suburban area of Shanghai. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Shao, M.; Lu, S.H.; Yuan, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, S.Q.; Wu, D. Variation of ambient non-methane hydrocarbons in Beijing city in summer 2008. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 5911–5923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, B.; Xu, H.; Deng, J.; Yi, Z.; Chen, J.; Xu, L.; Hong, Z.; Chen, X.; Hong, Y. Characteristics and Source Apportionment of Volatile Organic Compounds for Different Functional Zones in a Coastal City of Southeast China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 2840–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Bi, F.; Chai, F.; Gao, J.; Meng, L.; et al. Atmospheric Volatile Organic Compounds in a Typical Urban Area of Beijing: Pollution Characterization, Health Risk Assessment and Source Apportionment. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Xie, S.; Zeng, L.; Wu, R.; Li, J. Characteristics of volatile organic compounds and their role in ground-level ozone formation in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 113, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Xue, L.; Sui, X.; Wen, L.; Xu, C.; Yao, L.; Zhang, J.; et al. Characteristics of ambient volatile organic compounds and the influence of biomass burning at a rural site in Northern China during summer 2013. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, W.P.L. Development of the SAPRC-07 chemical mechanism. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 5324–5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhai, C.; Yu, J.; Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Zeng, L.; Xie, S. Spatiotemporal variations of ambient volatile organic compounds and their sources in Chongqing, a mountainous megacity in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 1442–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Acciai, C.; Zhong, Z.; Huang, Z.; Lonati, G. An Integrated Method for Factor Number Selection of PMF Model: Case Study on Source Apportionment of Ambient Volatile Organic Compounds in Wuhan. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.S.; Hsieh, C.C. Ambient volatile organic compound presence in the highly urbanized city: Source apportionment and emission position. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 206, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, L.R.; Liu, X.G.; Tan, Q.W.; Feng, M.; An, J.L.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Jiang, M.Q. Characteristics, source apportionment and contribution of VOCs to ozone formation in Wuhan, Central China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 192, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Kong, S.F.; Xing, X.L.; Mao, Y.; Hu, T.P.; Ding, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, D.T.; Li, S.L.; Qi, S.H. Monitoring of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from an oil and gas station in northwest China for 1 year. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 4567–4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, P.; An, J.; Xin, J.; Wu, F.; Wang, J.; Ji, D.; Wang, Y. Source apportionment of VOCs and the contribution to photochemical ozone formation during summer in the typical industrial area in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Res. 2016, 176, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Chen, T.Y.; Chou, C.; Liu, S.C. Assessment of traffic contribution to hydrocarbons using 2,2-dimethylbutane as a vehicular indicator. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2004, 15, 697–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Lu, K.; Lv, W.; Li, J.; Zhong, L.; Ou, Y.; Chen, D.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y. Fast increasing of surface ozone concentrations in Pearl River Delta characterized by a regional air quality monitoring network during 2006–2011. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.T.; Shao, M.; Lu, S.H.; Wang, M.; Zeng, L.M.; Yuan, B.; Liu, Y. Understanding primary and secondary sources of ambient carbonyl compounds in Beijing using the PMF model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 3047–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mo, Z.; Shao, M.; Lu, S.; Qu, H.; Zhou, M.; Sun, J.; Gou, B. Process-specific emission characteristics of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from petrochemical facilities in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 533, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudic, A.; Gros, V.; Sauvage, S.; Locoge, N.; Sanchez, O.; Sarda-Estève, R.; Kalogridis, C.; Petit, J.E.; Bonnaire, N.; Baisnée, D.; et al. Seasonal variability and source apportionment of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the Paris megacity (France). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 11961–11989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| JPJ | SL | XD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | During | Before | During | Before | During | |
| O3 (μg/m3) | 88.5 | 66.7 | 95.1 | 75.9 | 93.6 | 67.9 |
| NO2 (μg/m3) | 45.0 | 34.2 | 32.7 | 24.5 | 23.9 | 21.2 |
| CO (μg/m3) | 0.680 | 0.570 | 0.910 | 0.790 | 0.880 | 0.760 |
| TVOCs (ppbv) | 14.4 | 11.8 | 52.8 | 34.9 | 60.6 | 47.0 |
| Alkanes (ppbv) | 10.0 | 6.28 | 16.5 | 12.3 | 18.4 | 23.7 |
| Alkenes (ppbv) | 0.89 | 2.57 | 3.77 | 2.79 | 4.46 | 3.12 |
| Acetylene (ppbv) | 2.44 | 2.13 | 3.26 | 2.40 | 2.81 | 2.59 |
| Aromatics(ppbv) | 1.01 | 0.79 | 7.85 | 4.41 | 7.27 | 3.32 |
| OVOCs (ppbv) | - | - | 13.3 | 7.68 | 20.5 | 9.81 |
| Halohydrocarbons(ppbv) | - | - | 7.70 | 4.90 | 6.70 | 4.14 |
| Serial Number | VOC Species | Serial Number | VOC Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Acetaldehyde | 42 | 1,4-Dichlorobenzene |
| 2 | Acrolein | 43 | Acetylene |
| 3 | Propanal | 44 | Ethane |
| 4 | Acetone | 45 | Propane |
| 5 | MTBE | 46 | Isobutane |
| 6 | Methacrolein | 47 | n-Butane |
| 7 | n-Butanal | 48 | Cyclopentane |
| 8 | Methylvinylketone | 49 | Isopentane |
| 9 | Methylethylketone | 50 | n-Pentane |
| 10 | 2-pentanone | 51 | 2,2-dimethylbutane |
| 11 | n-Pentanal | 52 | 2,3-dimethylbutane |
| 12 | 3-pentanone | 53 | 2-methylpentane |
| 13 | Benzene | 54 | 3-methylpentane |
| 14 | Toluene | 55 | n-hexane |
| 15 | Ethylbenzene | 56 | 2,4-dimethylpentane |
| 16 | m/p-xylene | 57 | methylcyclopentane |
| 17 | o-xylene | 58 | 2-methylhexane |
| 18 | Styrene | 59 | Cyclohexane |
| 19 | isopropylbenzene | 60 | 2,3-dimethylpentane |
| 20 | n-Propylbenzene | 61 | 3-methylhexane |
| 21 | 3-ethyltoluene | 62 | 2,2,4-trimethylpentane |
| 22 | 4-ethyltoluene | 63 | n-heptane |
| 23 | 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene | 64 | Methylcyclohexane |
| 24 | 2-ethyltoluene | 65 | 2,3,4-trimethylpentane |
| 25 | 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene | 66 | 2-methylheptane |
| 26 | 1,2,3-trimethylbenzene | 67 | 3-methylheptane |
| 27 | 1,3-diethylbenzene | 68 | Octane |
| 28 | 1,4-diethylbenzene | 69 | n-Nonane |
| 29 | Freon114 | 70 | n-decane |
| 30 | Chloromethane | 71 | Udecane |
| 31 | Vinylchloride | 72 | Dodecane |
| 32 | Freon11 | 73 | Ethylene |
| 33 | Freon113 | 74 | Propene |
| 34 | Dichloromethane | 75 | trans-2-Butene |
| 35 | 1,1-Dichloroethane | 76 | 1-Butene |
| 36 | Chloroform | 77 | 1,3-Butadiene |
| 37 | tetrachloromethane | 78 | trans-2-pentene |
| 38 | 1,2-Dichloroethane | 79 | Isoprene |
| 39 | 1,2-Dichloropropane | 80 | 1-hexene |
| 40 | trans-1,3-Dichloropropene | 81 | Trichloroethylene |
| 41 | Tetrachloroethylene | 82 | Acetonitrile |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, Q.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Feng, M.; Qiu, Y.; Yang, F.; Jiang, W.; Wei, F. Observation-Based Summer O3 Control Effect Evaluation: A Case Study in Chengdu, a Megacity in Sichuan Basin, China. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11121278
Tan Q, Zhou L, Liu H, Feng M, Qiu Y, Yang F, Jiang W, Wei F. Observation-Based Summer O3 Control Effect Evaluation: A Case Study in Chengdu, a Megacity in Sichuan Basin, China. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(12):1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11121278
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Qinwen, Li Zhou, Hefan Liu, Miao Feng, Yang Qiu, Fumo Yang, Wenju Jiang, and Fusheng Wei. 2020. "Observation-Based Summer O3 Control Effect Evaluation: A Case Study in Chengdu, a Megacity in Sichuan Basin, China" Atmosphere 11, no. 12: 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11121278
APA StyleTan, Q., Zhou, L., Liu, H., Feng, M., Qiu, Y., Yang, F., Jiang, W., & Wei, F. (2020). Observation-Based Summer O3 Control Effect Evaluation: A Case Study in Chengdu, a Megacity in Sichuan Basin, China. Atmosphere, 11(12), 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11121278






