An Overview of the Integrated Meteorological Observations in Complex Terrain Region at Dali National Climate Observatory, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
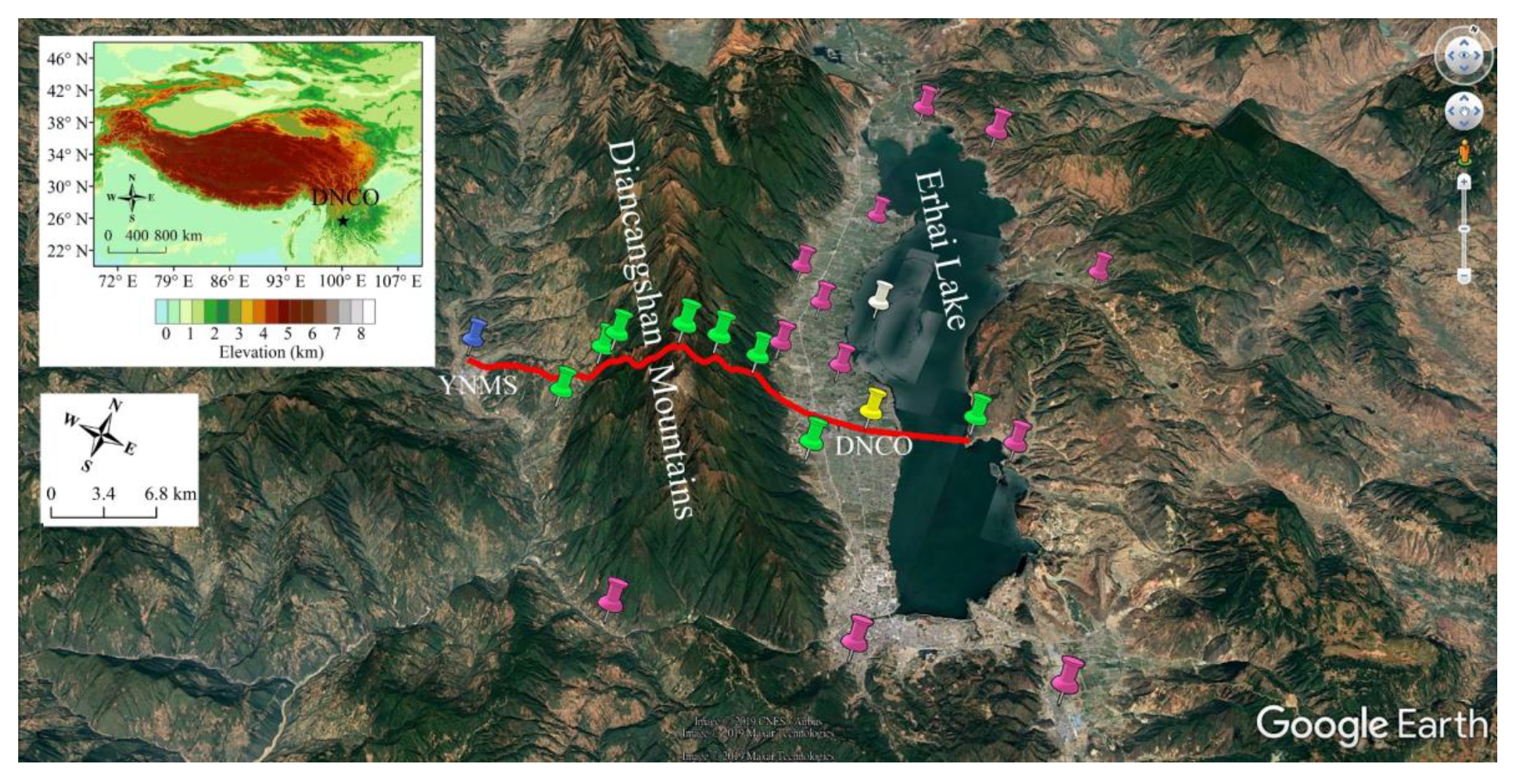
2. Observation Network Layout
2.1. Local Climatology
2.2. Scientific Objectives and Research Tasks
2.2.1. High-Resolution Observations and Fine-Scale Investigations of Meteorological Variables in Complex Terrain Region
2.2.2. Land–Atmosphere Interaction Observations and Investigations over the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau
2.2.3. Water Vapor Observations and Investigations of the Major Water Vapor Path in the Southwest China
2.2.4. Regional Eco-Meteorology Measurements and Services
2.3. Existing Observation Projects
2.3.1. Reference Climatological Observations
2.3.2. Comprehensive Observations for the Atmospheric Boundary Layer
2.3.3. Comprehensive Observations of Meteorology, Hydrology, and Water Quality at Erhai Lake
2.3.4. Typical Mountain Meteorological Observations
2.3.5. Baseline Surface Radiation Observations
2.3.6. Other Parameters Observations
3. Progress in Observation Research
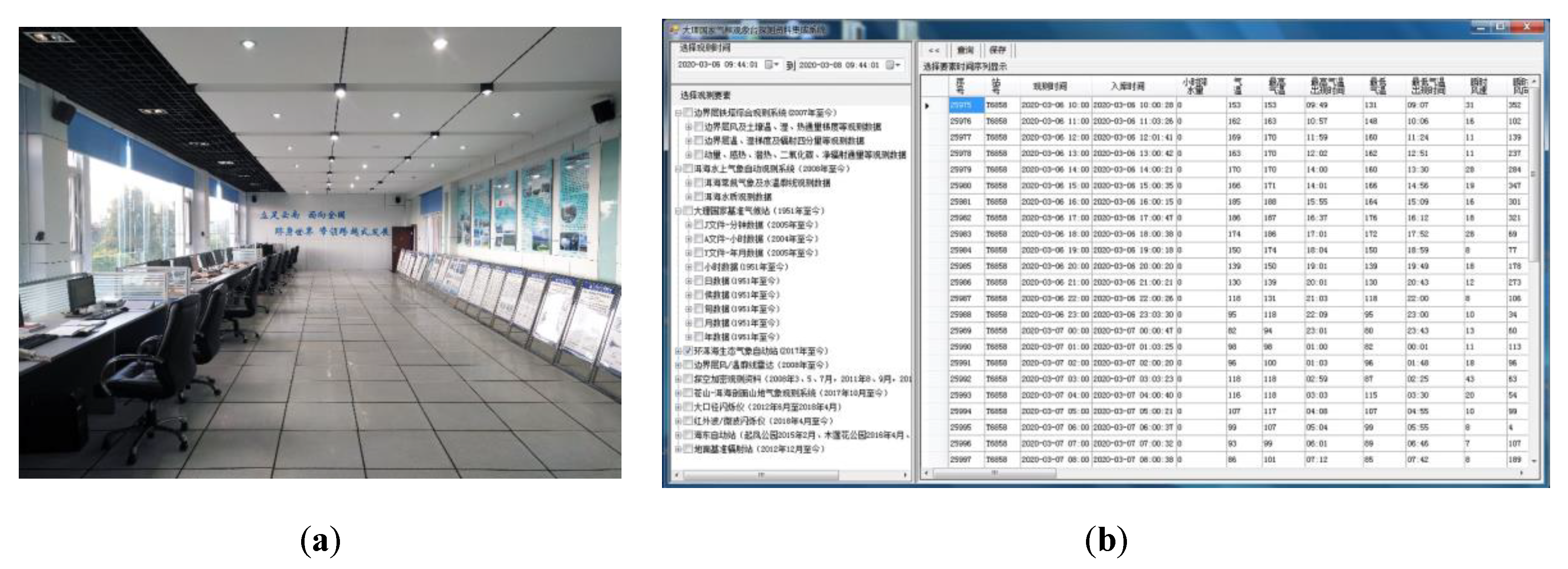
3.1. Data Quality, Controls, and Assessments
3.1.1. Data Quality
3.1.2. Quality Controls and Assessments
3.2. Observation Results
3.2.1. Spatial Representativeness of Weather Stations
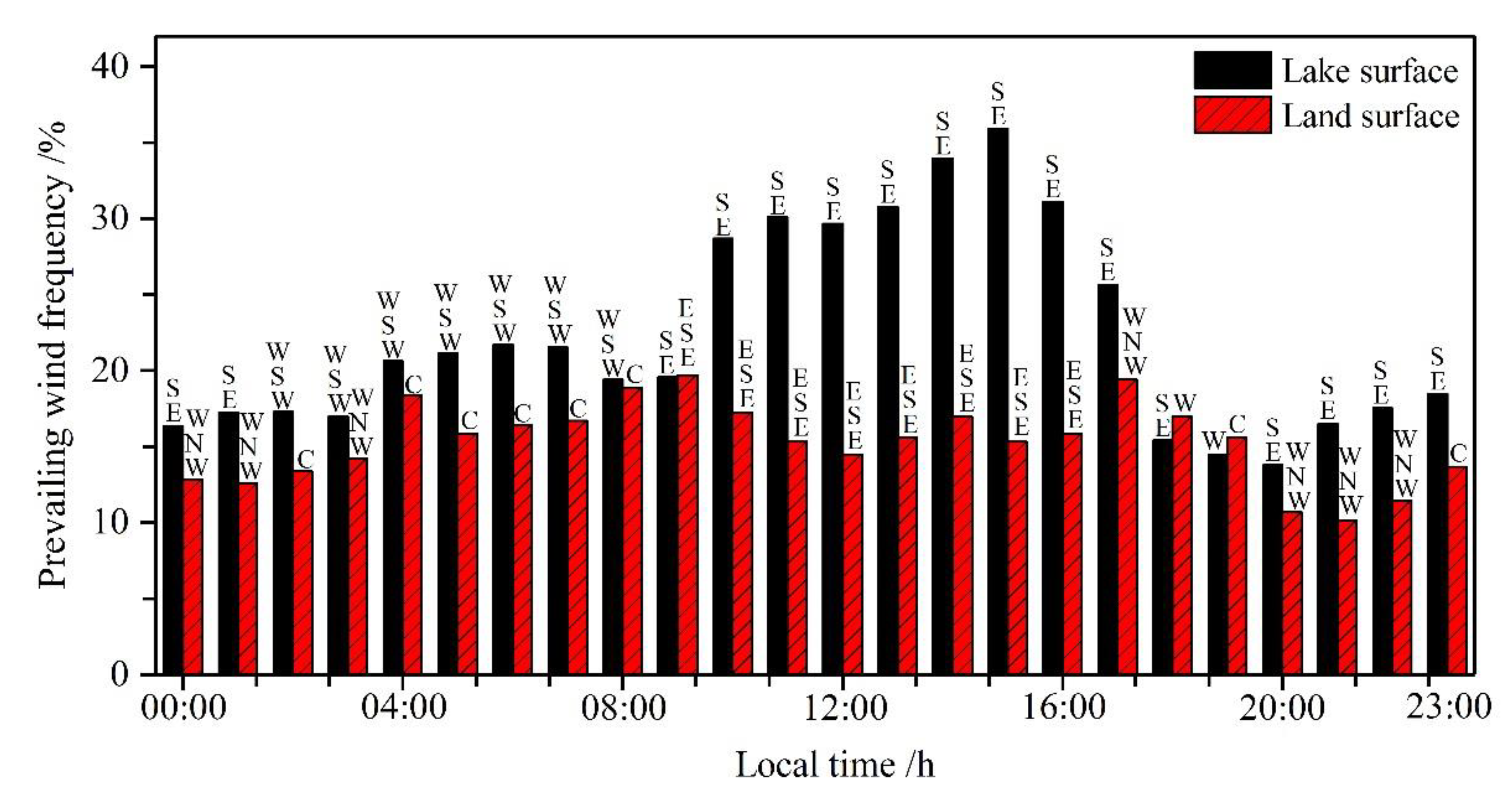
3.2.2. Local Circulation Characteristics
3.2.3. Atmospheric Vertical Structure Characteristics
3.2.4. Energy, Water Vapor, and CO2 Exchange Characteristics
3.2.5. Typical Weather Events Characteristics
4. Progress in Application Research
4.1. Observation Dataset Support for Numerical Simulations under Complex Terrain Conditions
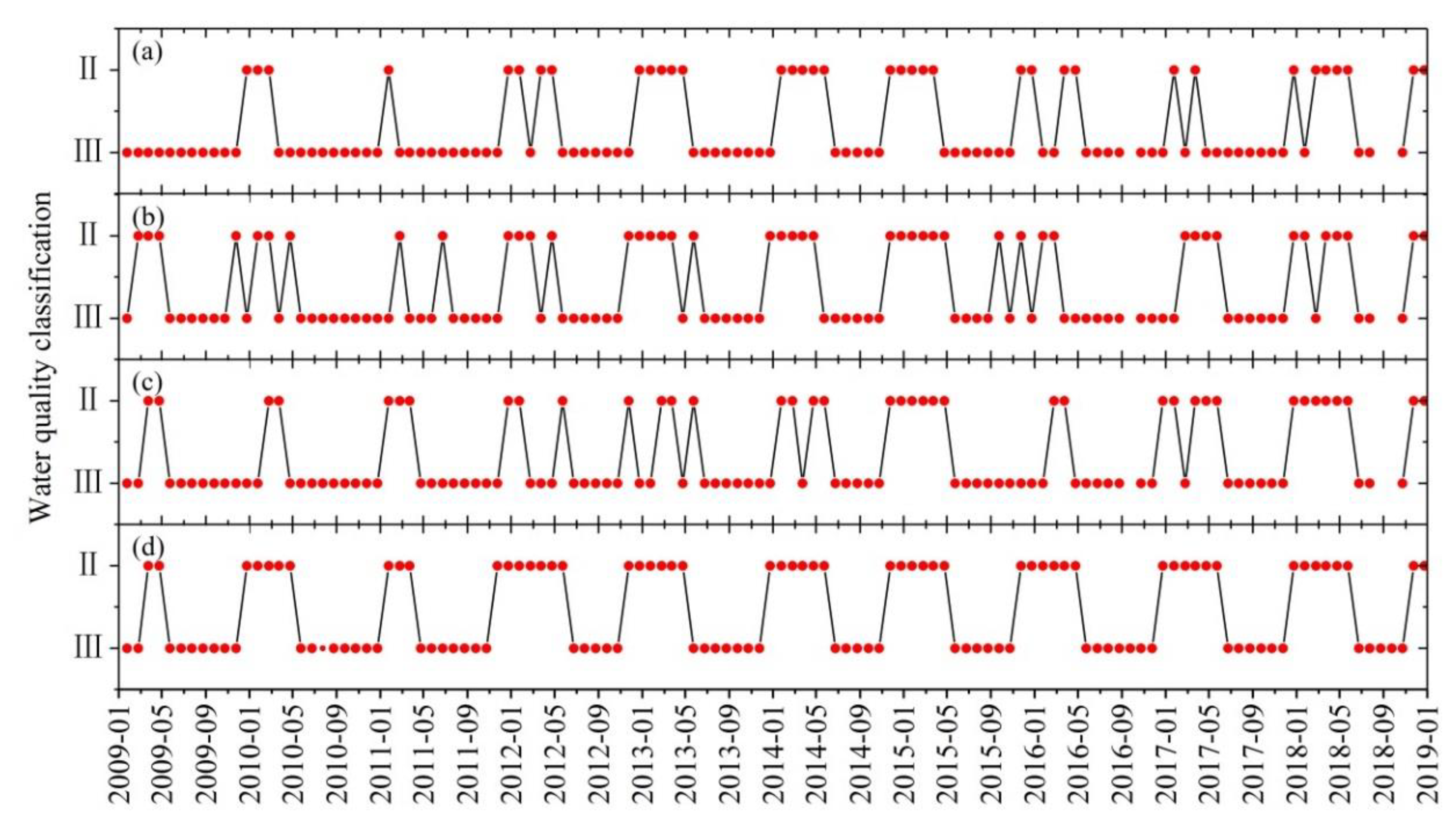
4.2. Influence of Meteorological Conditions on Water Quality Factors of Erhai Lake
5. Conclusions and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Colomon, S., Qin, D.H., Manning, M., Marquis, M., Averyt, K., Tignor, M., Miller, H.L., Chen, Z.L., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.H.; Xu, X.D. Chinese Climate Observing System; China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Houghton, J.; Townshend, J.; Dawson, K.; Mason, P.; Zillman, J.; Simmons, A. The GCOS at 20 years: The origin, achievement and future development of the Global Climate Observing System. Weather 2012, 67, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, P.W.; Diamond, H.J.; Goodison, B.; Harrigan, S.; Hausfather, Z.; Ingleby, N.B.; Jones, P.D.; Lawrimore, J.H.; Lister, D.H.; Merlone, A.; et al. Towards a global land surface climate fiducial reference measurements network. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 2760–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conover, J.H. Blue Hill Meteorological Observatory: The First 100 Years, 1885–1985; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 1–514. [Google Scholar]
- Magee, N.B.; Melaas, E.; Finocchio, P.M.; Jardel, M.; Noonan, A.; Iacono, M.J. Blue Hill Observatory Sunshine: Assessment of climate signals in the longest continuous meteorological record in North America. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 1741–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neisser, J.; Adam, W.; Beyrich, F.; Leiterer, U.; Steinhagen, H. Atmospheric boundary layer monitoring at the Meteorological Observatory Lindenberg as a part of the “Lindenberg Column”: Facilities and selected results. Meteorol. Z. 2002, 11, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, W.; Dier, H.; Leiterer, U. 100 years aerology in Lindenberg and first long-time observations in the free atmosphere. Meteorol. Z. 2005, 14, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, F.H.; Hantel, M. Meteorological Observatory Lindenberg 1905–2005. Meteorol. Z. 2005, 14, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, W.; Klaus, G. Long-term observations of aerosol optical depths at the Meteorological Observatory Lindenberg. Meteorol. Z. 2005, 14, 651–662. [Google Scholar]
- Overton, A.K. Jungfraujoch high altitude research station. Weather 2008, 63, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonasoni, P.; Laj, P.; Angelini, F.; Arduini, J.; Bonafetè, F.; Calzolari, F.; Cristofanelli, P.; Decesari, S.; Facchin, M.C.; Fuzzi, S.; et al. The ABC-Pyramid atmospheric research observatory in Himalaya for aerosol, ozone and halocarbon measurements. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 391, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonasoni, P.; Laj, P.; Marinoni, A.; Sprenger, M.; Angelini, F.; Arduini, J.; Bonafè, U.; Calzolari, F.; Colombo, T.; Decesari, S.; et al. Atmospheric brown clouds in the Himalayas: First two years of continuous observations at the Nepal Climate Observatory—Pyramid (5079 m). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 7515–7531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meybeck, M.; Green, P.; Vörösmarty, C. A new typology for mountains and other relief classes: An application to global continental water resources and population distribution. Mt. Res. Dev. 2001, 21, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lehner, M.; Whiteman, C.D.; Hoch, S.W.; Jensen, D.; Pardyjak, E.R.; Leo, L.S.; Sabation, S.D.; Fernando, H.J.S. A case study of the nocturnal boundary layer evolution on a slope at the foot of a desert mountain. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2015, 54, 732–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.B. 100 years of progress on mountain meteorology research. Meteorol. Monogr. 2018, 59, 20.1–20.73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, C.D. Mountain Meteorology: Fundamentals and Applications; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 171–202. [Google Scholar]
- Barry, R.G. Mountain Weather and Climate, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Boulder, CO, USA, 2008; pp. 186–250. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, P.L.; Mayr, G.; Vosper, S. Dynamically-driven winds. In Mountain Weather Research and Forecasting: Recent Progress and Current Challenges; Chow, F.K., De Weaker, S.F.J., Snyder, B.J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 121–218. [Google Scholar]
- Gultepe, I. Mountain Weather: Observation and Modeling. Adv. Geophys. 2015, 56, 229–312. [Google Scholar]
- Durán, L.; Rodríguez-Muñoz, I.; Sánchez, E. The Peñalara Mountain meteorological network (1999–2014): Description, preliminary results and lessons learned. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emeis, S.; Kalthoff, N.; Adler, B.; Pardyjak, E.; Paci, A.; Junkermann, W. High-resolution observations of transport and exchange processes in mountainous terrain. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, S.Y.; Luo, S.W.; Zhang, H.C. The Qinghai-Xizang Plateau Meteorological Experiment (QXPMEX) May-August 1979. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau and Mountain Meteorology; Xu, Y.G., Ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 1986; pp. 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.Y.; Xu, X.D.; Bian, L.G.; Chen, J.Y.; Liu, H.Z.; Zhang, H.S.; Li, S.M.; Zhao, Y.J. Observational Analysis and Dynamic Study of Atmospheric Boundary Layer on Tibetan Plateau: Tibetan Plateau Experiment of Atmospheric Sciences, (TIPEX) 1998; China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Xu, X.D.; Chen, F.; Guo, X.L.; Zheng, X.D.; Liu, L.P.; Hong, Y.; Li, Y.Q.; La, Z.; Peng, H.; et al. The third atmospheric scientific experiment for understanding the earth-atmosphere coupled system over the Tibetan Plateau and its effects. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, 757–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Li, Y.Q.; Guo, X.L.; Xu, X.D.; Liu, Y.M.; Tang, S.H.; Xiao, W.M.; Shi, C.X.; Ma, Y.M.; Yu, X.; et al. The Tibetan Plateau surface-atmosphere coupling system and its weather and climate effects: The Third Tibetan Plateau Atmospheric Science Experiment. J. Meteor. Res. 2019, 33, 375–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuettner, J.P.; O’Neill, T.H. ALPEX: The GARP mountain subprogram. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1981, 62, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bougeault, P.; Benech, B.; Bessemoulin, P.; Carissimo, B.; Clar, A.J.; Pelon, J.; Petitdidier, M.; Richard, E. PYREX: A summary of findings. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bougeault, P.; Binder, P.; Buzzi, A.; Dirks, R.; Houze, R.; Kuettner, J.; Smith, R.B.; Steinacker, R.; VoIkert, H. The MAP special observing period. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2001, 82, 433–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grubišić, V.; Doyle, J.D.; Kuettner, J.; Mobbs, S.; Smith, R.B.; Whiteman, C.D.; Dirks, R.; Czyzyk, S.; Cohn, S.A.; Vosper, S.; et al. The terrain-induced rotor experiment: A field campaign overview including observational highlights. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 89, 1513–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, H.J.; Pardyjak, E.R.; Di Sabatino, S.; Chow, F.K.; De Wekker, S.F.; Hoch, S.W.; Hacker, J.; Pace, J.C.; Pratt, T.; Pu, Z.; et al. The MATERHORN: Unraveling the intricacies of mountain weather. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 1945–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houze, R.A.; McMurdie, L.A.; Petersen, W.A.; Schwaller, M.R.; Baccus, W.; Lundquist, J.D.; Mass, C.F.; Nijssen, B.; Rutledge, S.A.; Hudak, D.R.; et al. The Olympic Mountains Experiment (OLYMPEX). Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 2167–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotach, M.W.; Stiperski, I.; Fuhrer, O.; Goger, B.; Gohm, A.; Obleitner, F.; Rau, G.; Sfyri, E.; Vergeiner, J. Investigating exchange processes over complex topography: The Innsbruck box (i-Box). Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 787–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udina, M.; Bech, J.; Gonzalez, S.; Soler, M.R.; Paci, A.; Miró, J.R.; Trapero, L.; Donier, J.M.; Douffet, T.; Codina, B.; et al. Multi-sensor observations of an elevated rotor during a mountain wave event in the Eastern Pyrenees. Atmos. Res. 2020, 234, 104698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, B.W.; Wagenbrenner, N.S.; Forthofer, J.M.; Lamb, B.K.; Shannon, K.S.; Finn, D.; Eckman, R.M.; Clawson, K.; Bradshaw, L.; Sopko, P.; et al. High-resolution observations of the near-surface wind field over an isolated mountain and in a steep river canyon. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 3785–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, Q.; Liu, H.Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, L.J.; Sun, J.H.; Xu, A.L. Factors controlling evaporation and the CO2 flux over an open water lake in southwest of China on multiple temporal scales. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.D.; Zhang, R.H.; Koike, T.; Lu, C.G.; Shi, X.H.; Zhang, S.J.; Bian, L.G.; Cheng, X.H.; Li, P.Y.; Ding, G.A. A new integrated observational system over the Tibetan Plateau. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 89, 1492–1496. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.H.; Koike, T.; Xu, X.D.; Ma, Y.M.; Yang, K. A China-Japan cooperative JICA atmospheric observing network over the Tibetan Plateau (JICA/Tibet Project): An overviews. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2012, 90, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burba, G. Eddy Covariance Method for Scientific, Industrial, Agricultural, and Regulatory Applications; LI-COR Biosciences: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2013; pp. 200–201. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, B.J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, A.L. Assessment of wind profiler radar data in plateau area. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2009, 37, 580–583. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, A.L.; Li, J.; Liu, H.Z.; Sun, J.H. Quality control of surface radiation data measured in Dali National Climate Observatory. Plateau Meteorol. 2013, 32, 1432–1441. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.H.; Wu, P.; Liu, J.Y. Calculation scheme and accuracy test of ground-based GPS atmospheric water vapour in Yunnan. J. Nanjing Univ. Inf. Sci. Technol. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2013, 5, 106–112. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.Z.; Sun, J.H.; Li, J.; Xu, K. Comparison of precipitation in Yunnan from GPS observation data and three reanalysis data. Plateau Meteorol. 2014, 33, 1480–1489. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, A.L.; Sun, J.H.; Li, J.; Feng, J.W.; Dong, B.J.; Liu, J.S. A study on the data processing and quality assessment of the eddy-covariance system at Dali National Climate Observatory. J. Yunnan Univ. 2014, 36, 224–232. [Google Scholar]
- Wilczak, J.M.; Oncley, S.P.; Stage, A. Sonic anemometer tilt correction algorithms. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2001, 99, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, E.K.; Pearman, G.I.; Leuning, R. Correction of the flux measurements for density effects due to heat and water vapour transfer. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1980, 106, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
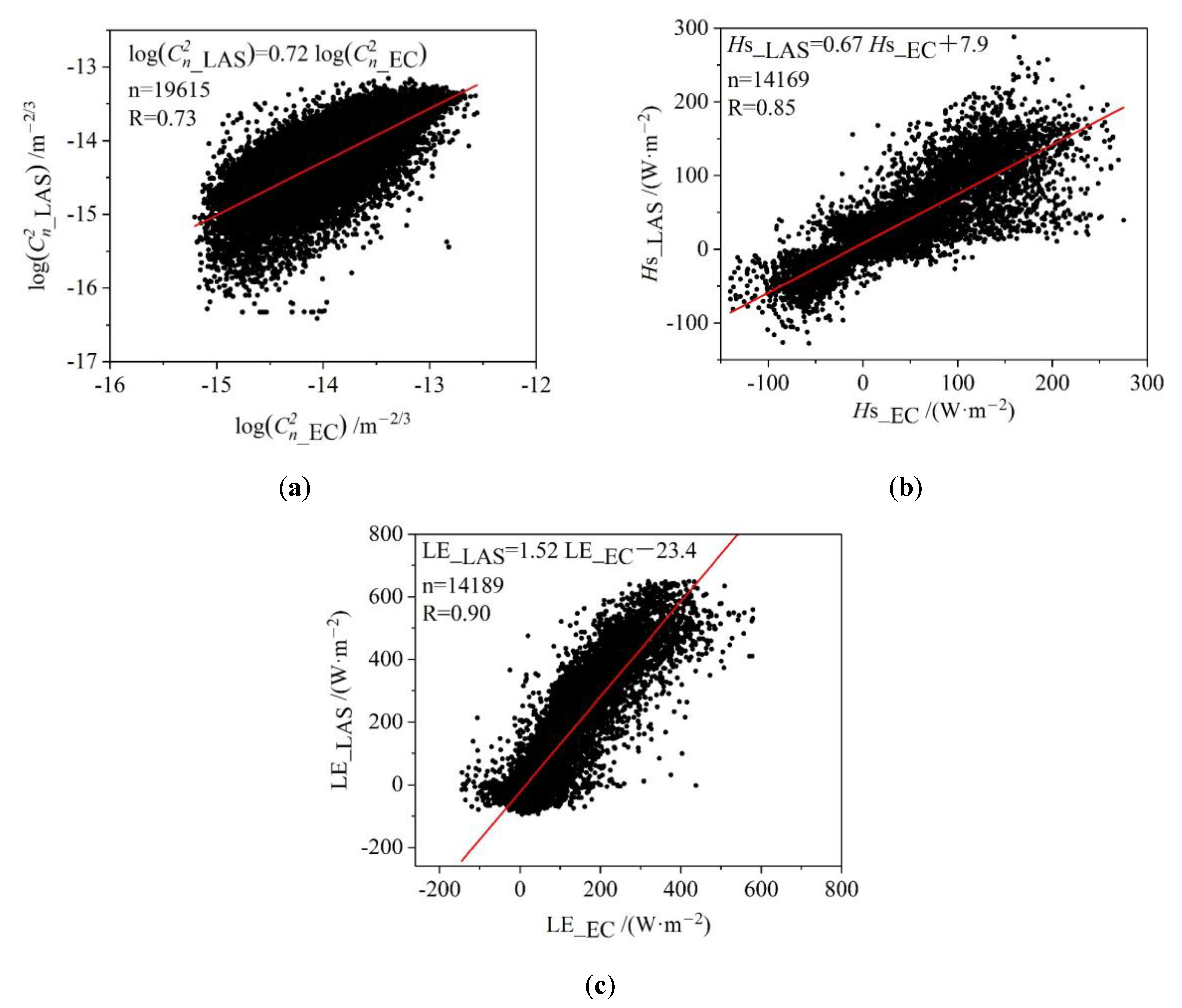
- Xu, A.L.; Peng, H.; Dong, B.J. Comparison of large aperture scintillometer and eddy-covariance system measurements with structure parameter of refractive index of air. Plateau Meteorol. 2015, 34, 935–941. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, A.L.; Li, J.; Peng, H.; Sun, J.H. Comparison of sensible and latent heat fluxes over farmland underlying surface of Erhai Lakeside region measured from large aperture scintillometer and eddy-covariance system. Plateau Meteorol. 2017, 36, 98–106. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.N.; Li, J. Preliminary analysis of representativeness of precipitation observation over Southwest China. Plateau Meteorol. 2017, 36, 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, J.S.; Sun, J.H. Lake-land breeze and turbulence characteristics in the surface layer of valley and basin in Dali, Yunnan province. J. Meteorol. Environ. 2008, 24, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, A.L.; Zhao, X.H.; Fu, Z.J.; Liu, J.S.; Sun, J.H. Comparison of meteorological elements over water and land surface in the Erhai Lake basin. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 34, 225–231. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, B.J.; Li, J.; Sun, J.H.; Xu, A.L.; Su, J.L. Vertical structure and variation characteristics of wind field in low-level atmosphere in the southeastern margin of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Plateau Meteorol. 2016, 35, 597–607. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, A.L.; Dong, B.J.; Liu, J.S.; Sun, J.H.; Zhu, Y.W. Structure and characteristic of the atmospheric boundary layer in Erhai Lakeside region of Dali. Plateau Meteorol. 2010, 29, 637–644. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.D.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhao, T.L.; Yao, W.Q. Relationship between turbulent energy in the near surface layer and atmospheric boundary layer thermodynamic structure over the southeastern side of Tibetan Plateau. Meteorol. Mon. 2014, 40, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.J.; Xu, X.D.; Zhao, T.L.; Sun, J.H.; Yao, W.Q.; Zhou, M.Y. Structures of convection and turbulent kinetic energy in boundary layer over the southeastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Chin. Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 1198–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.L.; Zhong, A.H.; Sun, J.H.; Yang, G.R. Vertical structure characteristic from troposphere to low stratosphere in Dali region over the southeastern margin of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Plateau Meteorol. 2016, 35, 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.H.; Liu, H.P.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, C.Y.; Liang, F.M.; Wang, J.H. Numerical simulations of land surface physical processes and land-atmosphere interactions over oasis-desert/Gobi region. Sci. Chin. Ser. D Earth Sci. 2007, 50, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, J.S.; Zhu, Y.W.; Dong, B.J. Comparative analyses of turbulent characteristics in near-surface layer in dry/wet periods at Dali. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2009, 37, 429–433. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, A.L.; Li, J.; Sun, J.H.; Liu, J.S.; Zhao, X.H. Analyses on micrometeorology characteristic and energy exchange in surface layer in Dali region of the southeastern margin of Tibetan Plateau. Plateau Meteorol. 2013, 32, 9–22. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, A.L.; Li, J. Long-term energy and CO2 flux observations over an agricultural field in southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2020. in review. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.W.; Liu, H.Z.; Sun, J.H.; Wang, L. The surface energy budget and interannual variation of the annual total evaporation over a highland lake in Southwest China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 126, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Z.; Feng, J.W.; Sun, J.H.; Wang, L.; Xu, A.L. Eddy covariance measurements of water vapour and CO2 fluxes above the Erhai Lake. Sci. Chin. Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Liu, H.Z.; Xu, L.J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L. The monsoon effect on energy and carbon exchange processes over a highland lake in the southwest of China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 15087–15104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, B.J.; Liu, J.S.; Gao, Y.Z. Case study of heavy rainfall based on wind profiler radar products. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2009, 37, 411–414. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, B.J.; Fu, Z.J.; Li, M.; Yang, Y.J. Feature analysis of a rain storm with wind profile radar data. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2012, 40, 74–78. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, B.J.; Gao, Y.Z.; Zhang, L.F. Application of new-type observational data to analysis of a rainstorm weather event in northwestern Yunnan plateau. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2014, 42, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.Y.; Gao, Y.Z.; Yin, L.Y.; Zhong, A.H.; Dong, B.J. Characteristics of extremes in WPR data during severe convective rainfall. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2016, 44, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Fu, Z.J.; Zhao, X.H. Diagnostic analysis of winter gale complex terrain in the southeast of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Plateau Meteorol. 2014, 33, 346–354. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, A.L.; Yang, Y.J.; Sun, J.H.; Liu, J.S.; Li, W.H. Case study of PBL characteristics before and after late frost in Dali. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2011, 39, 513–519. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Fu, Z.J. Applicability of the WRF model in complex topographic conditions: A case study on precipitation simulation in the western Yunnan region. Adv. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.J.; Liu, H.Z.; Du, Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.H. Differences of atmospheric boundary layer characteristics between pre-monsoon and monsoon period over the Erhai Lake. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 135, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.L.; Li, J.; Qian, T.T.; Gu, H.P. A 100-m-scale modeling study of a gale event on the lee side of a long narrow mountain. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2020, 59, 23–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Station Name | Location | Variables | Observing Time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dianshizhuanbotai | Peak of mountains | 100°05′32″ E, 25°40′13″ N, 4092 m | WS, WD, RH, Ta, Pa, PPT | Since December 2010 |
| Shansiting | East slope of mountains | 100°06′14″ E, 25°41′05″ N, 3520 m | WS, WD, RH, Ta, Pa, Ts, Ms, PPT | Since April 2011 |
| Baiquesi | 100°07′08″ E, 25°04′59″ N, 2660 m | WS, WD, RH, Ta, Pa, Ts, Ms, PPT | Since January 2011 | |
| Yanghe | 100°09′36″ E, 25°40′12″ N, 2130 m | WS, WD, RH, Ta, Pa, Ts, PPT | Since December 2010 | |
| Daduizi | West slope of mountains | 100°02′47″ E, 25°40′53″ N, 2980 m | Ta, PPT | From May 2011 to November 2013 |
| Qiutian | 100°02′12″ E, 25°40′57″ N, 2545 m | Ta, PPT | From May 2011 to April 2014 | |
| Shangyuan | 100°01′16″ E, 25°39′39″ N, 1920 m | Ta, PPT | From May 2011 to November 2013 | |
| Tianjingge | East shore of Erhai Lake | 100°14′12″ E, 25°42′50″ N, 2080 m | WS, WD, RH, Ta, Pa, Ts, PPT | Since December 2010 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, A.; Li, J. An Overview of the Integrated Meteorological Observations in Complex Terrain Region at Dali National Climate Observatory, China. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11030279
Xu A, Li J. An Overview of the Integrated Meteorological Observations in Complex Terrain Region at Dali National Climate Observatory, China. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(3):279. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11030279
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Anlun, and Jian Li. 2020. "An Overview of the Integrated Meteorological Observations in Complex Terrain Region at Dali National Climate Observatory, China" Atmosphere 11, no. 3: 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11030279
APA StyleXu, A., & Li, J. (2020). An Overview of the Integrated Meteorological Observations in Complex Terrain Region at Dali National Climate Observatory, China. Atmosphere, 11(3), 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11030279





