Formation of Multilayered Sporadic E under an Influence of Atmospheric Gravity Waves (AGWs)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theory of Sporadic E Formation under the Influence of AGWs and Background Horizontal Wind
2.1. Equation for Ion/Electron Density Height Profile Behavior under Influence of Horizontal Wind with AGWs
2.2. Analytical Approach for Ion/Electron Density Height Profile Behavior and Condition of Sporadic E Formation under Influence of Horizontal Wind
2.3. Vertical Motion of Es Layers and Their Localization during Presence of Homogeneous Wind and AGWs
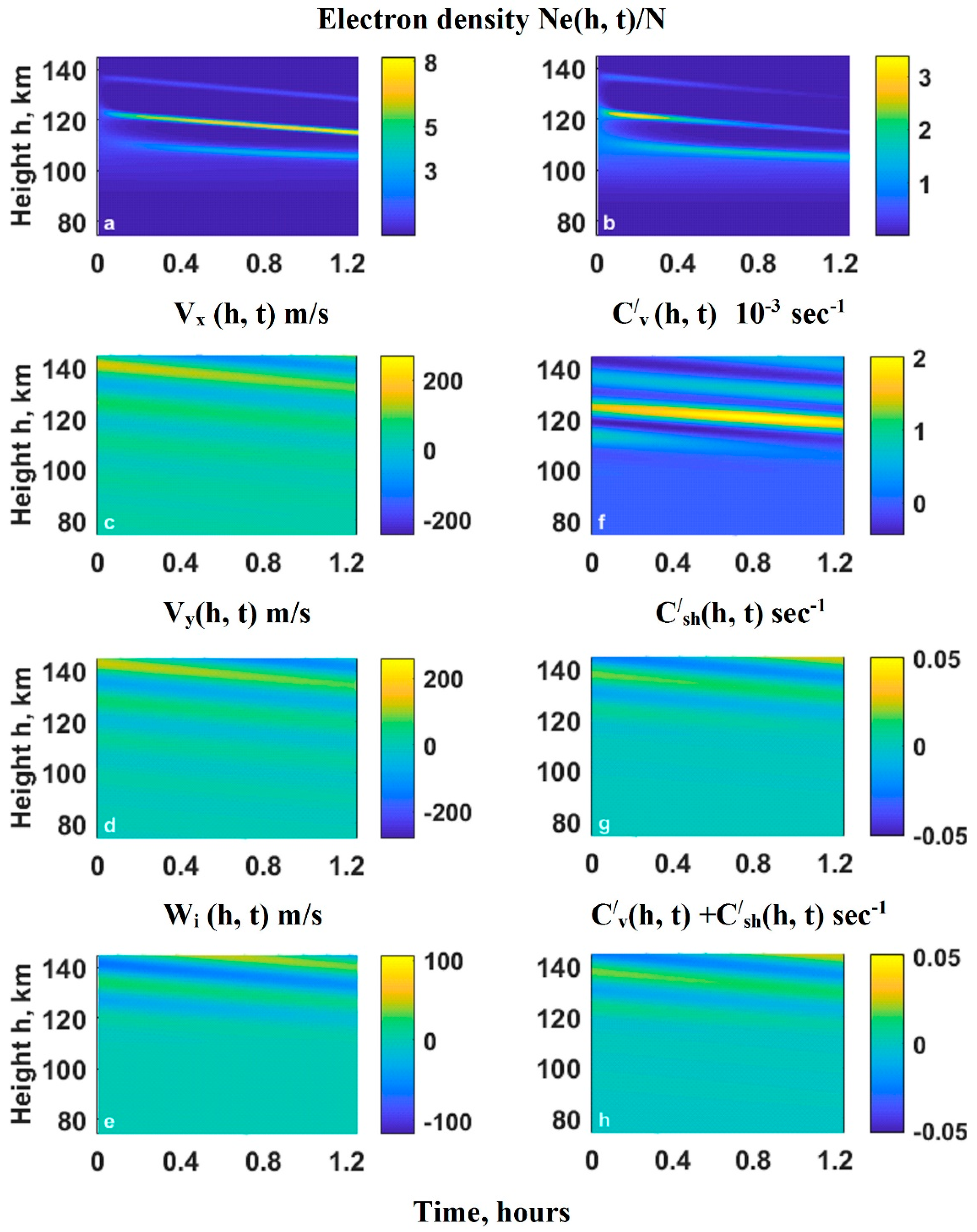
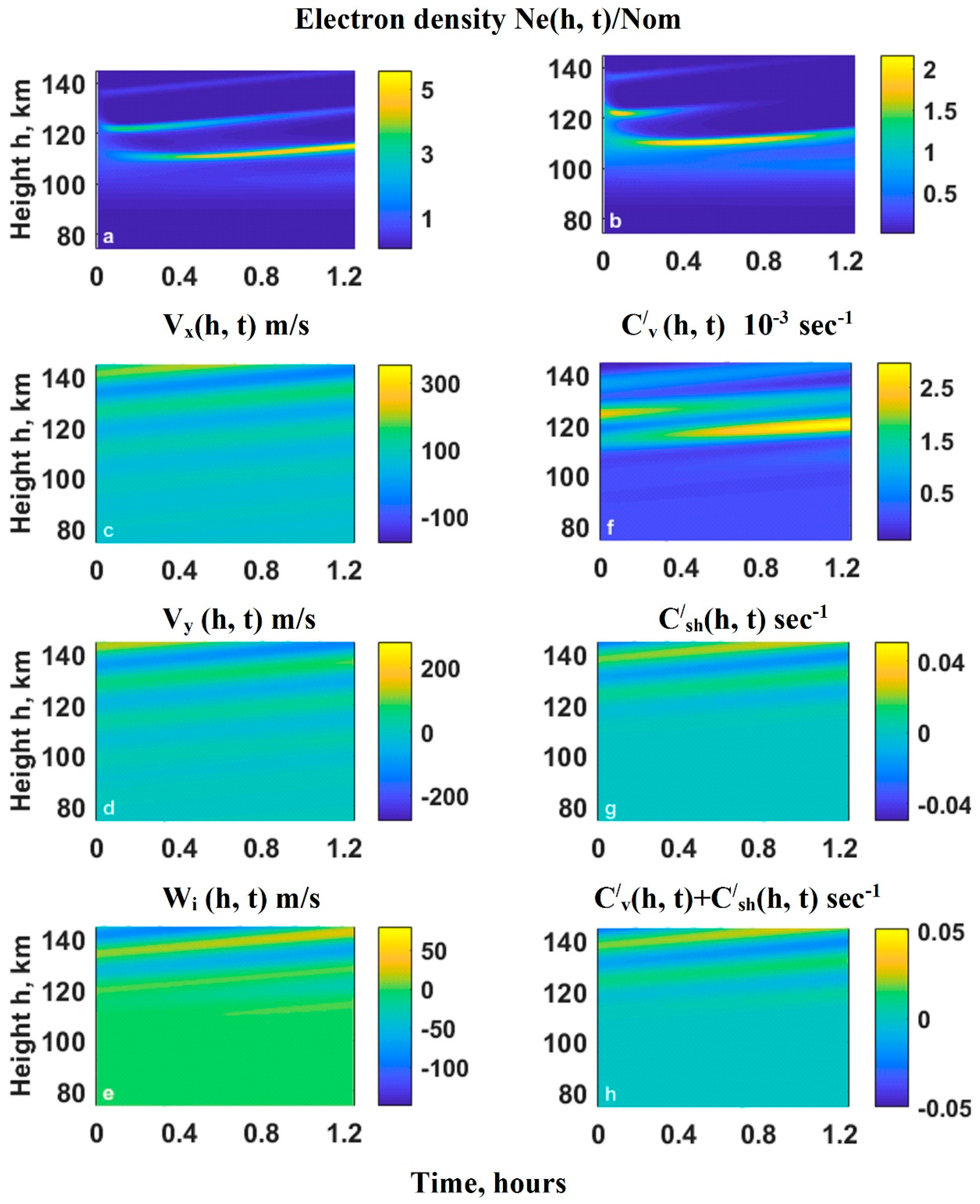
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Formation of Es Layers at the Fixed Heights by Stationary AGWs
3.2. Descending Es Layers Formed by Oblique Downward Propagating AGWs
3.3. Upward Motion of Es Layers Formed by Oblique Upward Propagating AGWs
3.4. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drob, D.P.; Emmert, J.T.; Meriwether, J.W.; Makela, J.J.; Doornbos, E.; Conde, M.; Hernandez, G.; Noto, J.; Zawdie, K.A.; McDonald, S.E.; et al. An update to the Horizontal Wind Model (HWM): The quiet time thermosphere. Earth Space Sci. 2015, 2, 301–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiğit, E.; Koucká Knížová, P.; Georgieva, K.; Ward, W. A review of vertical coupling in the Atmosphere–Ionosphere system: Effects of waves, sudden stratospheric warmings, space weather, and of solar activity. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2016, 141, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygrén, T.; Jalonen, L.; Oksman, J.; Turunen, T. The role of electric field and neutral wind direction in the formation of sporadic E-layers. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1984, 46, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldoupis, C.; Pancheva, D. Planetary waves and midlatitude sporadic E layers: Strong experimental evidence for a close relationship. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didebulidze, G.G.; Lomidze, L. The formation of sporadic E layers by a vortical perturbation excited in the horizontal wind shear flow. Ann. Geophys. 2008, 26, 1741–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Didebulidze, G.G.; Lomidze, L.N. Double atmospheric gravity wave frequency oscillations of sporadic E formed in a horizontal shear flow. Phys. Lett. A 2010, 374, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hysell, D.L.; Munk, J.; McCarrick, M. Sporadic E ionization layers observed with radar imaging and ionospheric modification. Geophys.Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 6987–6993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, R.L.; Earle, G.D.; Larsen, M.F.; Swenson, C.M.; Carlson, C.G.; Roddy, P.A.; Fish, C.; Bullett, T.W. Sequential observations of the local neutral wind field structure associated with E region plasma layers. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, A04309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, M.; Ono, T. Multi-layer structure of mid-latitude sporadic-E observed during the SEEK-2 campaign. Ann. Geophys. 2005, 23, 2347–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roddy, P.A.; Earle, G.D.; Swenson, C.M.; Carlson, C.G.; Bullett, T.W. The composition and horizontal homogeneity of E region plasma layers. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, A06312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimonas, G. Enhancement of sporadic-E by horizontal transport within the layer. J. Geophys. Res. 1971, 76, 4578–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodman, R.F.; Yamamoto, M.; Fukao, S. Gravity wave modulation of gradient drift instabilities in mid-latitude sporadic E irregularities. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1991, 18, 1197–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didebulidze, G.G.; Dalakishvili, G.; Lomidze, L.; Matiashvili, G. Formation of sporadic-E(Es) layers under the influence of AGWs evolving in a horizontal shear flow. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2015, 136, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collinson, G.A.; McFadden, J.; Grebowsky, J.; Mitchell, D.; Lillis, R.; Withers, P.; Vogt, M.F.; Benna, M.; Espley, J.; Jakosky, B. Constantly forming sporadic E-like layers and rifts in the Martian ionosphere and their implications for Earth. Nat. Astron. 2020, 4, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, J.D. The formation of the sporadic E layer in the temperate zone. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1961, 51, 20–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, J.D. Recent work on mid-latitude and equatorial sporadic-E. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1989, 51, 401–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axford, W.I. The formation and vertical movement of dense ionized layers in the ionosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1963, 68, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, J.D. Sporadic E: Current views and recent progress. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 1998, 60, 413–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldoupis, C. Midlatitude sporadic E. A typical paradigm of atmosphere-ionosphere coupling. Space Sci. Rev. 2012, 168, 441–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, W.-H.; Liu, J.-Y.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chen, S.-P. Explanation of the sporadic-E layer formation by comparing FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC data with meteor and wind shear information. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 4568–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Tang, Q.; Li, Z.; Song, Y.; Qing, H.; Ni, B.; Zhao, Z. The seasonal distribution of sporadic E layers observed from radio occultation measurements and its relation with wind shear measured by TIMED/TIDI. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 62, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, M.F. Winds and shears in the mesosphere and lower thermosphere: Results from four decades of chemical release wind measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huba, J.D.; Krall, J.; Drob, D. Global ionospheric metal ion transport with SAMI3. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 7937–7944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Xue, X.; Kuo, C.; Lu, G.; Scott, C.J.; Wu, J.; Ma, J.; Dou, X.; Gao, Q.; Qie, X.; et al. The intensification of metallic layered phenomena above thunderstorms through the modulation of atmospheric tides. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, C.O. Internal atmospheric gravity waves at ionospheric heights. Can. J. Phys. 1960, 38, 1441–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossard, E.E.; Hooke, W.H. Waves in the Atmosphere; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1975; p. 456. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.-S.; Kelly, M.C. Numerical solution of gravity wave modulation of midlatitude sporadic E layer. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 24533–24543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Fukao, S. Computer simulation of polarization electric fields as a source of midlatitude field-aligned irregularities. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, P.M.; Kockarts, G. Aeronomy; Part A; Academic: New York, NY, USA, 1973; pp. 217–232. [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock, K.R.S.; Vondrak, T.; Meech, S.R.; Plane, J.M.C. A kinetic study of the reactions FeO+ + O, Fe+∙N2 + O, Fe+∙O2 + O and FeO+ + CO: Implications for sporadic E layers in the upper atmosphere. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Fort, E.C.; Frankel, S.P. Stability conditions in the numerical treatment of parabolic differential equations. MTAC 1953, 7, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lanser, D.; Verwer, G.J. Analysis of operator splitting for advection-diffusion-reaction problems from air pollution modelling. J. Com. Appl. Math. 1999, 111, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hundsdorfer, W.; Verwer, G.J. Numerical Solution of Time-Dependent Advection-Diffusion-Reaction Equations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 325–417. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.C.; Chu, Y.H. Model simulations of ion and electron density profiles in ionospheric E and F regions. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 2505–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picone, J.M.; Hedin, A.E.; Drob, D.P.; Aikin, A.C. NRLMSISE00 empirical model of the atmosphere: Statistical comparisons and scientific issues. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, L.C.A.; Batista, I.S.; Denardini, C.M.; Batista, P.P.; Carrasco, A.J.; Andrioli, V.F.; Moro, J. Simulations of blanketing sporadic E-layer over the Brazilian sector driven by tidal winds. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2017, 154, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Jin, H.; Huang, X.; Zhong, D.; Yan, C.; Yang, G. Strong correlation between quasiperiodic echoes and plasma drift in the E region. J. Geophys. Res. Space Physics 2015, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yokoyama, T. A review on the numerical simulation of equatorial plasma bubbles toward scintillation evaluation and forecasting. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2017, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulinets, S.A.; Boyarchuk, K.A. Ionospheric Precursors of Earthquakes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; p. 315. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, W.; Marsh, D.R.; Chipperfield, M.P.; Janches, D.; Höffner, J.; Yi, F.; Plane, J.M.C. A global atmospheric model of meteoric iron. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9456–9474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, R.B.; Tsunoda, R.T. A direction-dependent instability of sporadic-E layers in the nighttime midlatitude ionosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Didebulidze, G.G.; Dalakishvili, G.; Todua, M. Formation of Multilayered Sporadic E under an Influence of Atmospheric Gravity Waves (AGWs). Atmosphere 2020, 11, 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060653
Didebulidze GG, Dalakishvili G, Todua M. Formation of Multilayered Sporadic E under an Influence of Atmospheric Gravity Waves (AGWs). Atmosphere. 2020; 11(6):653. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060653
Chicago/Turabian StyleDidebulidze, Goderdzi G., Giorgi Dalakishvili, and Maya Todua. 2020. "Formation of Multilayered Sporadic E under an Influence of Atmospheric Gravity Waves (AGWs)" Atmosphere 11, no. 6: 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060653
APA StyleDidebulidze, G. G., Dalakishvili, G., & Todua, M. (2020). Formation of Multilayered Sporadic E under an Influence of Atmospheric Gravity Waves (AGWs). Atmosphere, 11(6), 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11060653




