Differential Influences of Teleconnections from the Indian and Pacific Oceans on Rainfall Variability in Southeast Asia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Anomalous Rainfall Distributions
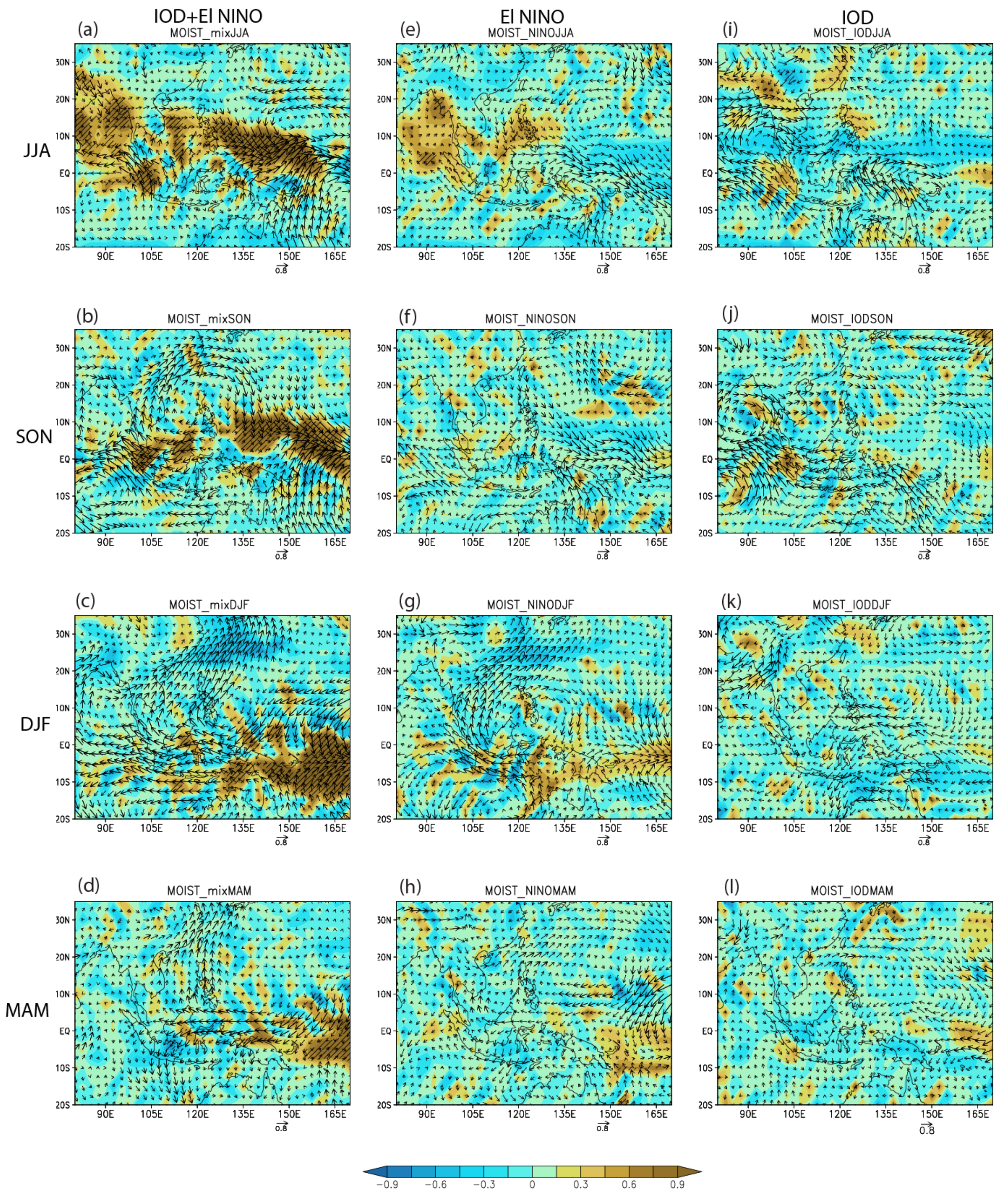
3.2. Sea Surface Temperature and Atmospheric Circulation
3.2.1. Anomalous Regional Sea Surface Temperature
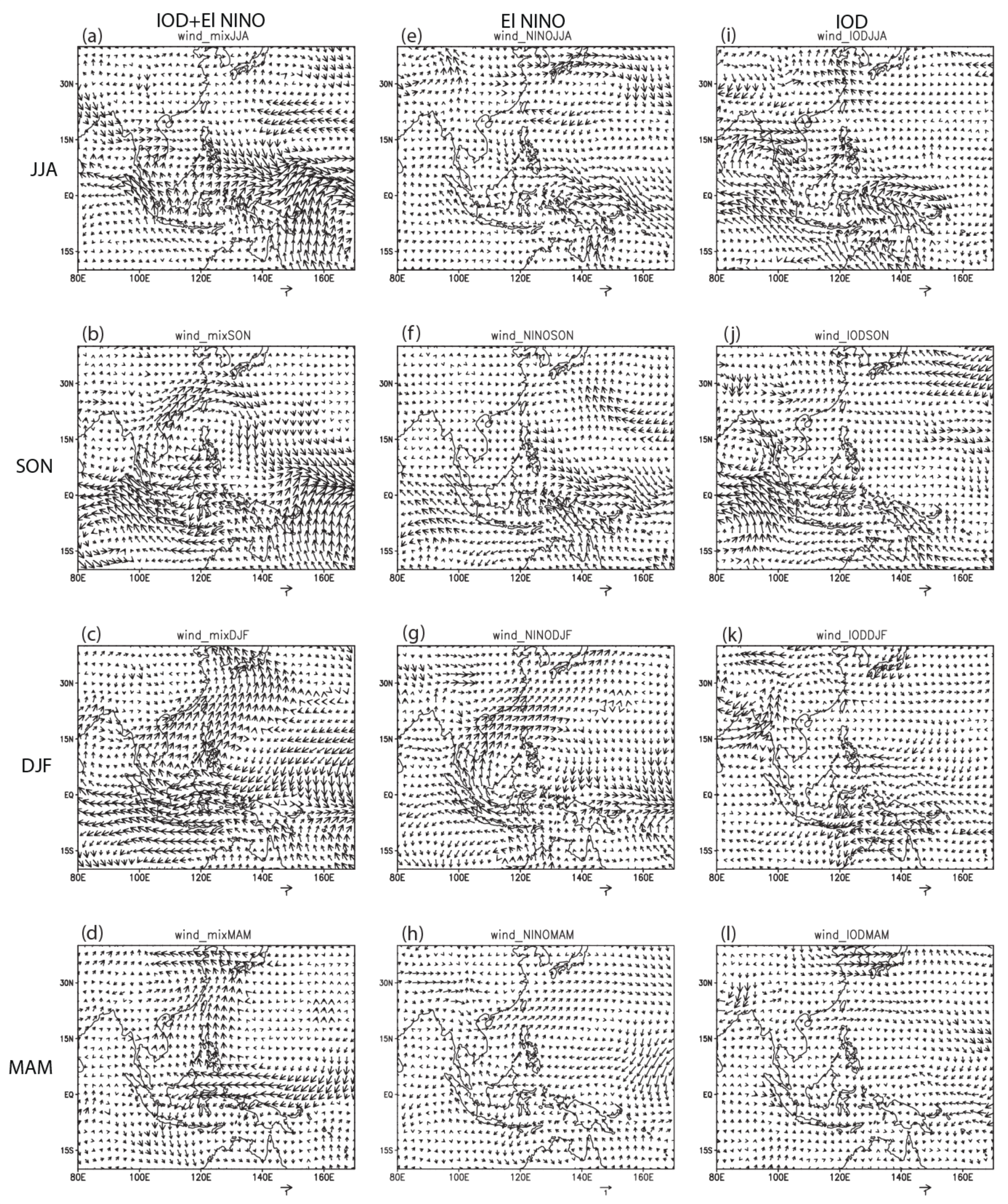
3.2.2. Anomalous Atmospheric Circulation
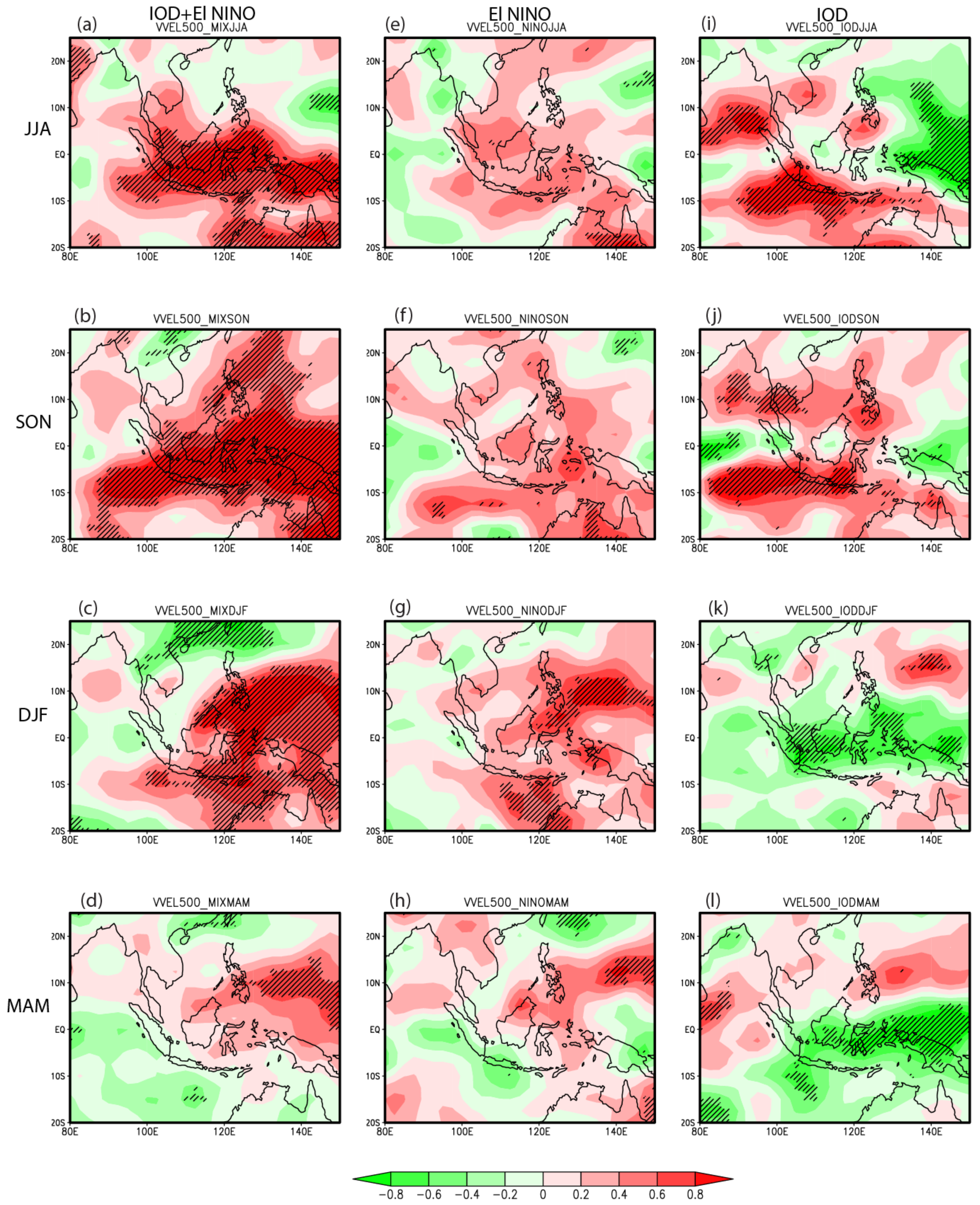
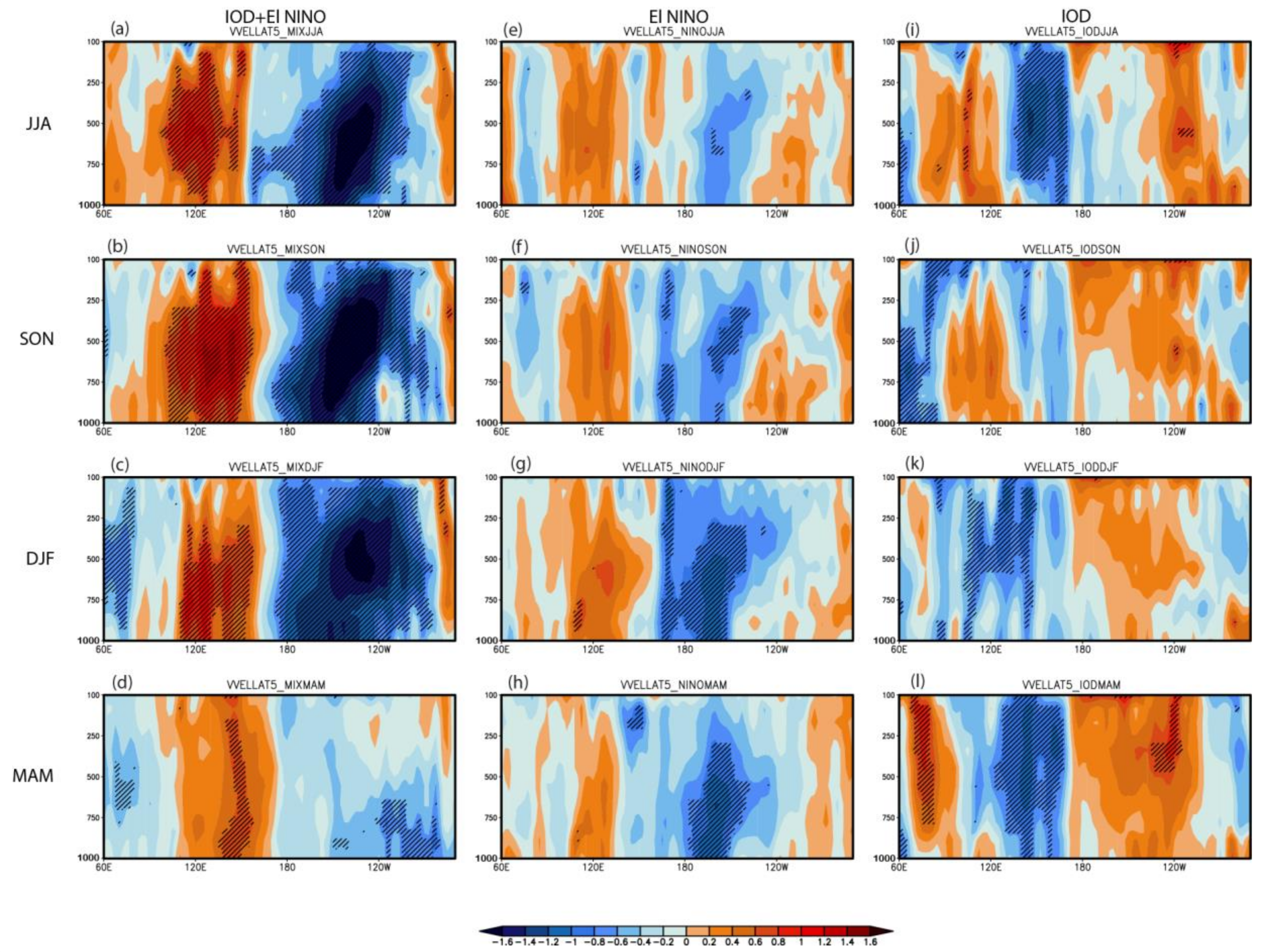
3.3. The Walker Circulation
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rasmusson, E.M.; Carpenter, T.H. Variations in tropical sea surface temperature and surface wind fields associated with the Southern Oscillation/El Niño. Mon. Weather Rev. 1982, 110, 354–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, N.; Kariko, A. East Australia rainfall events: Interannual variations, trends, and relationships with the Southern Oscillation. J. Clim. 1993, 6, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendon, H.H. Indonesian rainfall variability: Impacts of ENSO and local air–sea interaction. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 1775–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juneng, L.; Tangang, F.T. Evolution of ENSO-related rainfall anomalies in Southeast Asia region and its relationship with atmosphere–ocean variations in Indo-Pacific sector. Clim. Dyn. 2005, 25, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangang, F.; Latif, M.; Juneng, L. Climate Change: Is Southeast Asia up to the Challenge? The Roles of Climate Variability and Climate Change on Smoke Haze Occurrences in Southeast Asia Region. 2010. LSE IDEAS. Available online: eprints.lse.ac.uk/43571/1/Climate%20change_the%20roles%20of%20climate%20variability%28lsero%29.pdf (accessed on 27 April 2013).
- Salimun, E.; Tangang, F.; Juneng, L.; Behera, S.K.; Yu, W. Differential impacts of conventional El Niño versus El Niño Modoki on Malaysian rainfall anomaly during winter monsoon. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 2763–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangang, F.; Farzanmanesh, R.; Mirzaei, A.; Supari; Salimun, E.; Jamaluddin, A.F.; Juneng, L. Characteristics of precipitation extremes in Malaysia associated with El Niño and La Niña events. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 696–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangang, F.S.; Salimun, E.; Aldrian, E.; Sopaheluwakan, A.; Juneng, L. ENSO modulation of seasonal rainfall and extremes in Indonesia. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 51, 2559–2580. [Google Scholar]
- Behera, S.K.; Krishnan, R.; Yamagata, T. Unusual ocean–atmosphere conditions in the tropical Indian Ocean during 1994. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 3001–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saji, N.H.; Goswami, B.N.; Vinayachandran, P.N.; Yamagata, T. A dipole mode in the tropical Indian Ocean. Nature 1999, 401, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, P.J.; Moore, A.M.; Loschnigg, J.P.; Leben, R.R. Coupled ocean–atmosphere dynamics in the Indian Ocean during 1997–98. Nature 1999, 401, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagata, T.; Behera, S.K.; Rao, S.A.; Guan, Z.; Ashok, K.; Saji, H.N. Comments on “Dipoles, Temperature Gradient, and Tropical Climate Anomalies”. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 84, 1418–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saji, N.H.; Yamagata, T. Possible impacts of Indian Ocean Dipole Mode events on global climate. Clim. Res. 2003, 25, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, J.I.; Mori, S.; Kubota, H.; Yamanaka, M.D.; Haryoko, U.; Lestari, S.; Sulistyowati, R.; Syamsudin, F. Interannual rainfall variability over northwestern Jawa and its relation to the Indian Ocean Dipole and El Niño-Southern Oscillation events. SOLA 2012, 8, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, R.; Ando, K.; Masumoto, Y.; Luo, J.J. Interannual variability of rainfall over Indonesia: Impacts of ENSO and IOD and their predictability. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2016, 31, 012034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, K.; Guan, Z.; Saji, N.H.; Yamagata, T. Individual and combined influences of ENSO and the Indian Ocean dipole on the Indian summer monsoon. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 3141–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, K.; Nakamura, H.; Yamagata, T. Impacts of ENSO and Indian Ocean dipole events on the Southern Hemisphere storm-track activity during austral winter. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 3147–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, K.; Saji, N.H. On the impacts of ENSO and Indian Ocean dipole events on sub-regional Indian summer monsoon rainfall. Nat. Hazards 2007, 42, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, E.J. El Niño-Southern oscillation, Indian Ocean dipole mode, a relationship between the two phenomena, and their impact on the climate over the Korean peninsula. JKESS 2007, 28, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, P.A.; Mohankumar, K. Individual and combined influence of El Niño–Southern oscillation and Indian Ocean dipole on the tropospheric biennial oscillation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 136, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manatsa, D.; Matarira, C.H.; Mukwada, G. Relative impacts of ENSO and Indian Ocean dipole/zonal mode on east SADC rainfall. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 558–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, S.; Kumar, M.R.; Reason, C. On the relative roles of El Niño and Indian Ocean Dipole events on the Monsoon Onset over Kerala. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2011, 103, 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Van Rensch, P.; Cowan, T.; Hendon, H.H. An asymmetry in the IOD and ENSO teleconnection pathway and its impact on Australian climate. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 6318–6329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- As-syakur, A.R.; Adnyana, I.W.S.; Mahendra, M.S.; Arthana, I.W.; Merit, I.N.; Kasa, I.W.; Ekayanti, N.W.; Nuarsa, I.W.; Sunarta, I.N. Observation of spatial patterns on the rainfall response to ENSO and IOD over Indonesia using TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA). Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 3825–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaughan, A.E.; Staub, C.G.; Hoell, A.; Weaver, A.; Waylen, P.R. Inter-and Intra-annual precipitation variability and associated relationships to ENSO and the IOD in southern Africa. Int. J. Clim. 2016, 36, 1643–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestari, R.K.; Koh, T.Y. Statistical evidence for asymmetry in ENSO–IOD interactions. Atmos. Ocean 2016, 54, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Murtugudde, R.; Kumar, A. Evolution of Indian Ocean dipole and its forcing mechanisms in the absence of ENSO. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 47, 2481–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agilan, V.; Umamahesh, N.V. Changes in ENSO and IOD effects on the extreme rainfall of Hyderabad city, India. In Climate Change Impacts; Singh, V., Yadav, S., Yadava, R.N., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Chanda, A.; Das, S.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Ghosh, A.; Akhand, A.; Ghosh, P.; Ghosh, T.; Mitra, D.; Hazra, S. Sea surface temperature and rainfall anomaly over the Bay of Bengal during the El Niño-Southern Oscillation and the extreme Indian Ocean Dipole events between 2002 and 2016. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2018, 12, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, R.J.; Chambers, D.; Drosdowsky, W.; Hendon, H.; Latif, M.; Nicholls, N.; Smith, I.; Stone, R.; Tourre, Y. Is there an Indian Ocean dipole and is it independent of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation? Clivar Exch. 2001, 6, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Baquero-Bernal, A.; Latif, M.; Legutke, S. On dipole-like variability of sea surface temperature in the tropical Indian Ocean. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 1358–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagata, T.; Behera, S.K.; Luo, J.J.; Masson, S.; Jury, M.R.; Rao, S.A. Coupled ocean-atmosphere variability in the tropical Indian Ocean. In Earth’s Climate: The Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction; Wang, C., Xie, S.P., Carton, J.A., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; Volume 147, pp. 189–211. [Google Scholar]
- Vinayachandran, P.N.; Francis, P.A.; Rao, S.A. Indian Ocean Dipole: Processes and Impacts; Current Trends in Science: Platinum Jubilee Special; Indian Academy of Sciences: Bangalore, India, 2009; pp. 569–589. [Google Scholar]
- Ashok, K.; Guan, Z.; Yamagata, T. A look at the relationship between the ENSO and the Indian Ocean Dipole. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2003, 81, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoda, T.; Alexander, M.A.; Hendon, H.H. Remote response of the Indian Ocean to interannual SST variations in the tropical Pacific. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.K.; Luo, J.-J.; Masson, S.; Yamagata, T.; Delecluse, P.; Gualdi, S.; Navarra, A. Impact of the Indian Ocean Dipole on the East African short rains: A CGCM study. Clivar Exch. 2003, 27, 43–45. [Google Scholar]
- Behera, S.K.; Luo, J.J.; Masson, S.; Rao, S.A.; Sakumo, H.; Yamagata, T. A CGCM study on the interaction between IOD and ENSO. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 1688–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Hendon, H.H.; Meyers, G. Indian Ocean dipole-like variability in the CSIRO Mark 3 coupled climate model. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 1449–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Sullivan, A.; Cowan, T. Interactions of ENSO, the IOD, and the SAM in CMIP3 models. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 1688–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdain, N.C.; Gupta, A.S.; Taschetto, A.S.; Ummenhofer, C.C.; Moise, A.F.; Ashok, K. The Indo-Australian monsoon and its relationship to ENSO and IOD in reanalysis data and the CMIP3/CMIP5 simulations. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 41, 3073–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdain, N.C.; Lengaigne, M.; Vialard, J.; Izumo, T.; Gupta, A.S. Further insights on the influence of the Indian Ocean dipole on the following year’s ENSO from observations and CMIP5 models. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 637–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaswamy, J.; Vaidyanathan, S.; Rajagopalan, B.; Bonell, M.; Sankaran, M.; Bhalla, R.S.; Badiger, S. Non-stationary and non-linear influence of ENSO and Indian Ocean Dipole on the variability of Indian monsoon rainfall and extreme rain events. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 45, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, N.-C.; Nath, M.J. Coupled GCM simulation of atmosphere–ocean variability associated with zonally asymmetric SST changes in the tropical Indian Ocean. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 245–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Kumar, A.; Murtugudde, R.; Narapusetty, B.; Seip, K.L. Covariations between the Indian Ocean dipole and ENSO: A modeling study. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 5743–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Kirtman, B.P. Understanding the impacts of the Indian Ocean on ENSO variability in a coupled GCM. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 4019–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizuka, S.; Matsuura, T.; Yamagata, T. The Indian Ocean SST dipole simulated in a coupled general circulation model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 3369–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arrigo, R.; Wilson, R. El Niño and Indian Ocean influences on Indonesian drought: Implications for forecasting rainfall and crop productivity. Int. J. Climatol. 2008, 28, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Zhu, C.; Wang, W. The cooperative impacts of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation and the Indian Ocean Dipole on the interannual variability of autumn rainfall in China. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 1987–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.A.; Masson, S.; Luo, J.J.; Behera, S.K.; Yamagata, T. Termination of Indian Ocean dipole events in a coupled general circulation model. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 3018–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.K.; Luo, J.-J.; Masson, S.; Delecluse, P.; Gualdi, S.; Navarra, A.; Yamagata, T. Paramount impact of the Indian Ocean dipole on the East African short rains: A CGCM study. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 4514–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.K.; Luo, J.-J.; Yamagata, T. The unusual IOD event of 2007. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ummenhofer, C.C.; Gupta, A.S.; England, M.H.; Reason, C.J.C. Contributions of Indian Ocean sea surface temperatures to enhanced East African rainfall. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 993–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestari, D.O.; Sutriyono, E.; Kadir, S.; Iskandar, I. Severe drought event in Indonesia following 2015/16 El Niño/positive Indian dipole events. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1011, 012040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kistler, R.; Colloins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L.; Iredell, M.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Woolen, J.; et al. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 437–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, N.A.; Parker, D.E.; Horton, E.B.; Folland, C.K.; Alexander, L.V.; Rowell, D.P.; Kent, E.C.; Kaplan, A. Global analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J. Geophy. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Finger, P.; Meyer-Christoffer, A.; Rudolf, B.; Schamm, K.; Schneider, U.; Ziese, M. A description of the global land-surface precipitation data products of the Global Precipitation Climatology Centre with sample applications including centennial (trend) analysis from 1901–present. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2013, 5, 921–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverdin, G.; Cadet, D.L.; Gutzler, D. Interannual displacements of convection and surface circulation over the equatorial Indian Ocean. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1986, 112, 43–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastenrath, S.; Nicklis, A.; Greischar, L. Atmospheric–hydrospheric mechanisms of climate anomalies in the western equatorial Indian Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1993, 98, 20219–20235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtugudde, R.; McCreary, J.P.; Busalacchi, A.J. Oceanic processes associated with anomalous events in the Indian Ocean with relevance to 1997–1998. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans. 2000, 105, 3295–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horii, T.; Hanawa, K. A relationship between timing of El Niño onset and subsequent evolution. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chan, J.C.L. The role of the Asian-Australian monsoon system in the onset time of El Niño events. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 418–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, M. Peristiwa El Niño dan Pengaruh IOD Terhadap Hujan di Malaysia (El Niño Events and the Influence of IOD on Rainfall in Malaysia). J. Soc. Sci. Humanit. 2018, 13, 166–177. [Google Scholar]
- Ratna, S.B.; Ratnam, J.V.; Behera, S.K.; Tangang, F.T.; Yamagata, T. Validation of the WRF regional climate model over the subregions of Southeast Asia: Climatology and interannual variability. Clim. Res. 2017, 71, 263–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Clarke, A.J.; Liu, X. Interannual sea level in the northern and eastern Indian Ocean. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1994, 24, 1224–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, G. Variations of Indonesian through flow and the El Niño-Southern Oscillation. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1996, 101, 12255–12263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, R.; Li, T. Atmosphere-warm ocean interaction and its impacts on Asian-Australian monsoon variation. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 1195–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagata, T.; Behera, S.K.; Rao, S.A.; Guan, Z.; Ashok, K.; Saji, H.N. The Indian Ocean Dipole: A physical entity. Clivar Exch. 2002, 24, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, N.-C.; Nath, M.J. Atmosphere-ocean variations in the Indo-Pacific sector during ENSO episodes. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerknes, J. Atmospheric teleconnections from the equatorial Pacific. Mon. Weather Rev. 1969, 97, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.E. Some simple solutions for heat-induced tropical circulation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1980, 106, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
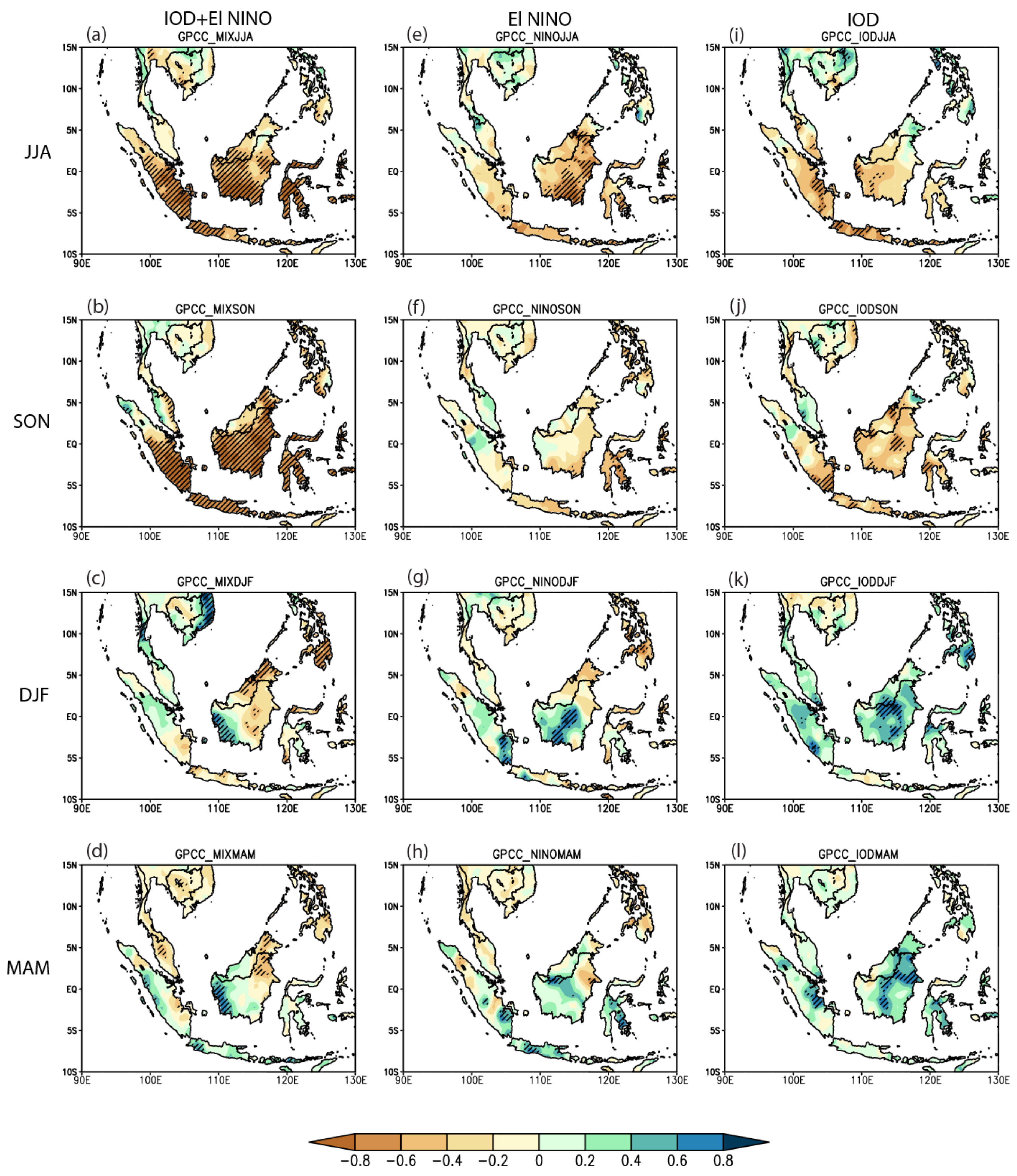
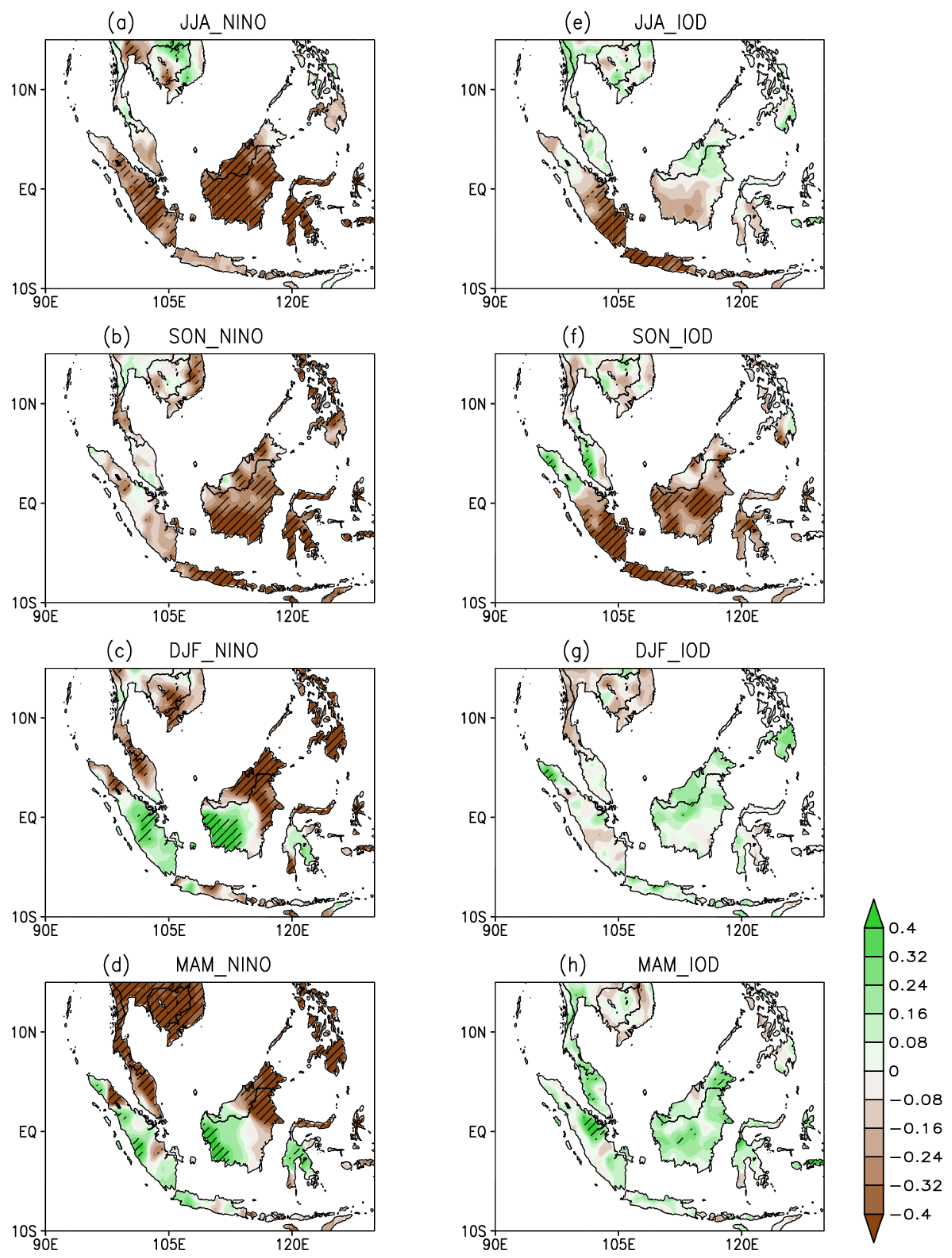
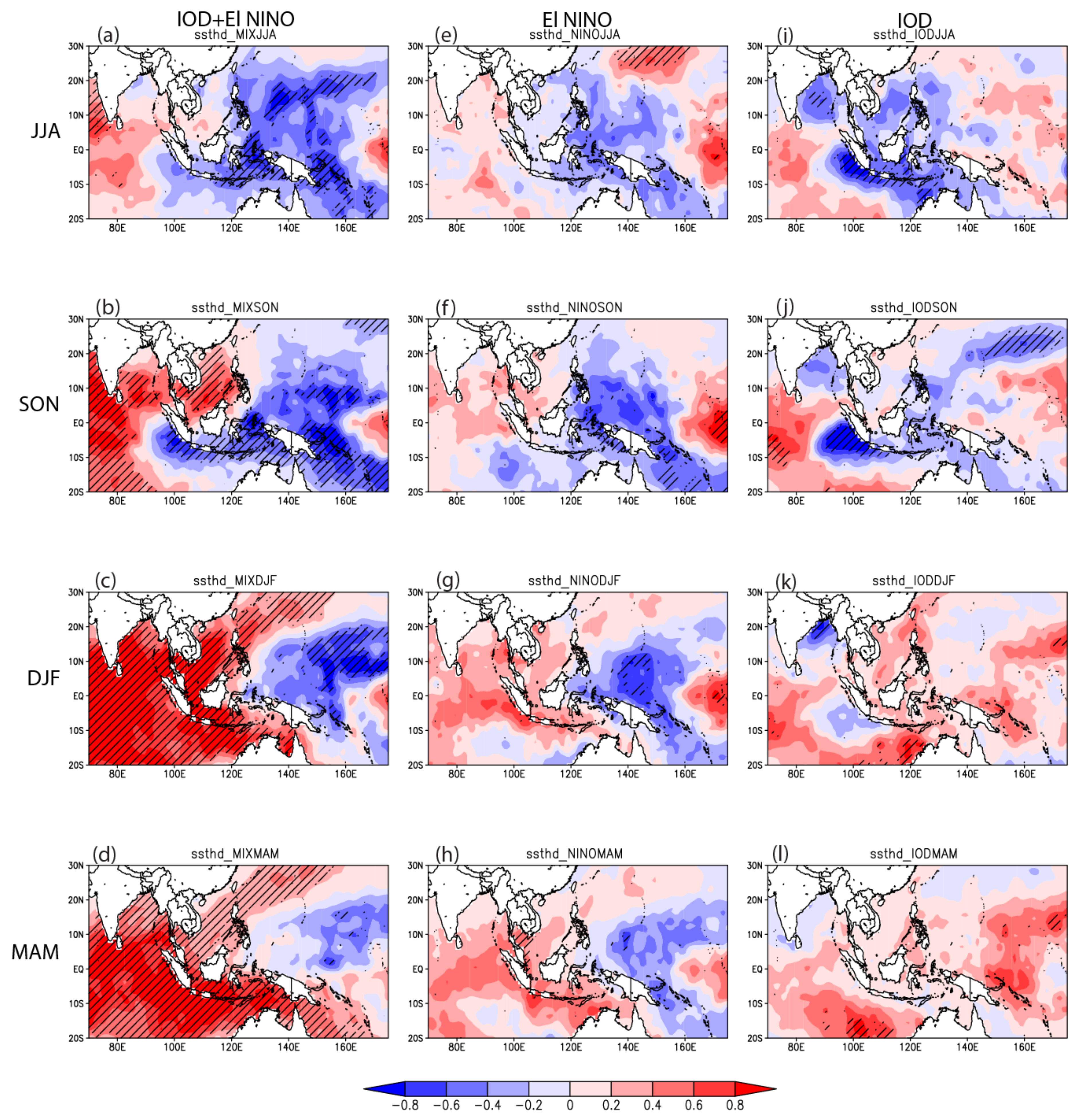
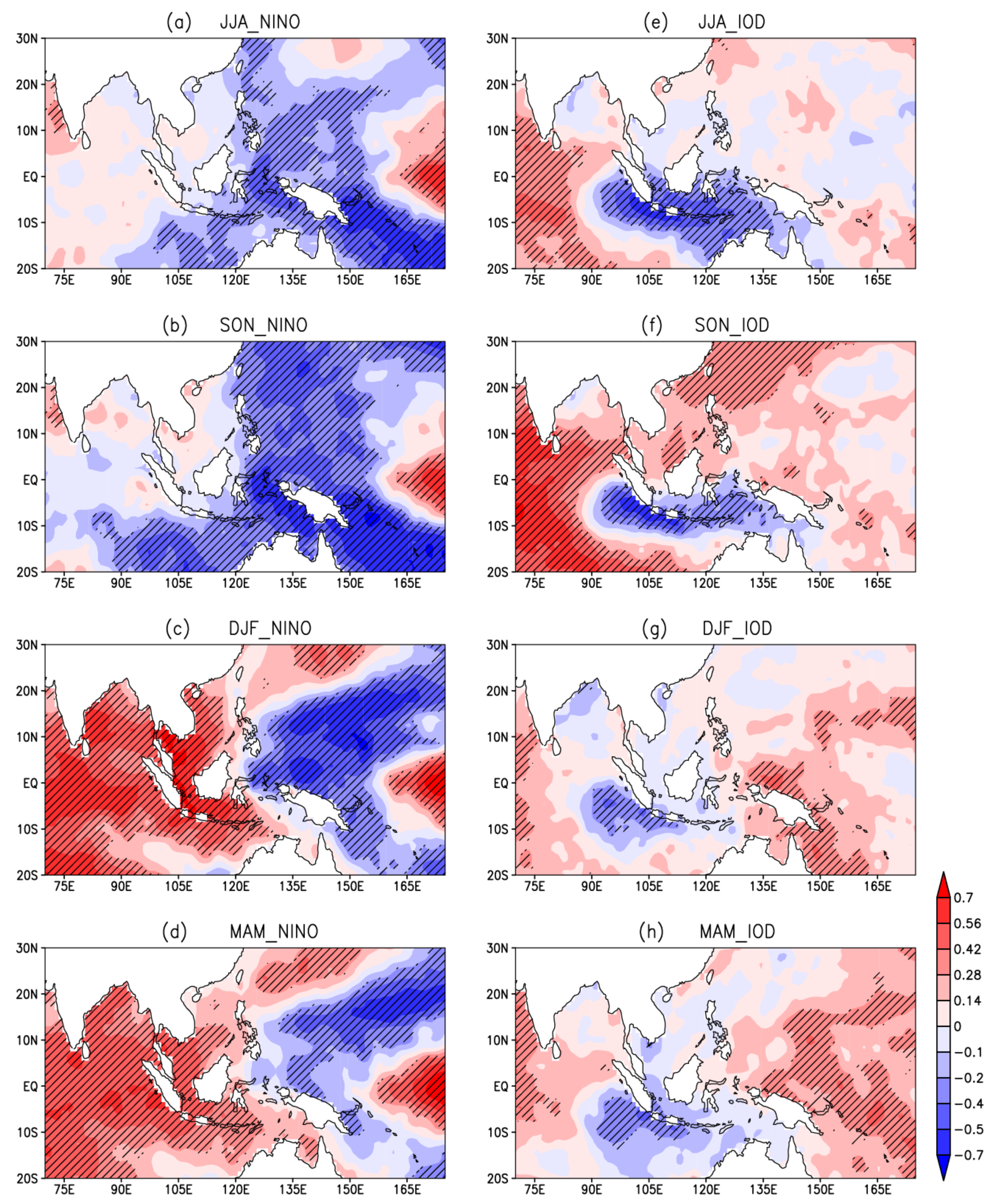
| Pure El Niño | Pure IOD | Co-Occurrence of El Niño and IOD |
|---|---|---|
| 1965/66 | 1961 | 1963/64 |
| 1969/70 | 1994 | 1972/73 |
| 1991/92 | 2006 | 1982/83 |
| 2004/05 | 2011 | 1987/88 |
| 2009/10 | 2012 | 1997/98 |
| 2002/03 2015/16 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amirudin, A.A.; Salimun, E.; Tangang, F.; Juneng, L.; Zuhairi, M. Differential Influences of Teleconnections from the Indian and Pacific Oceans on Rainfall Variability in Southeast Asia. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 886. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11090886
Amirudin AA, Salimun E, Tangang F, Juneng L, Zuhairi M. Differential Influences of Teleconnections from the Indian and Pacific Oceans on Rainfall Variability in Southeast Asia. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(9):886. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11090886
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmirudin, Abdul Azim, Ester Salimun, Fredolin Tangang, Liew Juneng, and Muhamad Zuhairi. 2020. "Differential Influences of Teleconnections from the Indian and Pacific Oceans on Rainfall Variability in Southeast Asia" Atmosphere 11, no. 9: 886. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11090886
APA StyleAmirudin, A. A., Salimun, E., Tangang, F., Juneng, L., & Zuhairi, M. (2020). Differential Influences of Teleconnections from the Indian and Pacific Oceans on Rainfall Variability in Southeast Asia. Atmosphere, 11(9), 886. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11090886






