Analysis on the Characteristics of Air Pollution in China during the COVID-19 Outbreak
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Data
2.1.1. Air Quality Data
2.1.2. Meteorological Data
2.1.3. Government Control Measures
2.2. Methods
Euclidean Distance
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Pollutants in China during Study Period 2015–2020
3.2. Changes in AQI and Air Pollutants during COVID-19 after the eliMination of Meteorological Field
3.2.1. Meteorological Similarity
3.2.2. Changes in Pollutants during the Pandemiccovid-19 Compared with the Background Field
3.3. Anthropogenic Control of Contributions to Atmospheric Pollutants
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chan, C.K.; Yao, X. Air Pollution in Mega Cities in China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hao, J. Air Quality Management in China: Issues, Challenges, and Options. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, K.; Che, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, T.; Zhang, X. Satellite-Derived Pm2.5 Concentration Trends over Eastern China from 1998 to 2016: Relationships to Emissions and Meteorological Parameters. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Guo, H.; Tang, Y.; Wang, P.; Deng, W.; Zhao, X.; Hu, J.; Ying, Q.; Zhang, H. Local and Regional Contributions to Fine Particulate Matter in the 18 Cities of Sichuan Basin, Southwestern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 5791–5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brunekreef, B.; Holgate, S.T. Air Pollution and Health. Lancet 2002, 360, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.; Slater, D.; Larson, T.V.; Pierson, W.E.; Koenig, J.Q. Particulate Air Pollution and Hospital Emergency Room Visits for Asthma in Seattle. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1993, 147, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesaroni, G.; Badaloni, C.; Gariazzo, C.; Stafoggia, M.; Sozzi, R.; Davoli, M.; Forastiere, F. Long-Term Exposure to Urban Air Pollution and Mortality in a Cohort of More Than a Million Adults in Rome. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goudarzi, G.; Daryanoosh, S.M.; Godini, H.; Hopke, P.K.; Sicard, P.; de Marco, A.; Rad, H.D.; Harbizadeh, A.; Jahedi, F.; Mohammadi, M.J.; et al. Health Risk Assessment of Exposure to the Middle-Eastern Dust Storms in the Iranian Megacity of Kermanshah. Public Health 2017, 148, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, A.; Amoatey, P.; Khaniabadi, Y.O.; Sicard, P.; Hopke, P.K. Mortality and Morbidity for Cardiopulmonary Diseases Attributed to Pm2.5 Exposure in the Metropolis of Rome, Italy. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 57, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berktas, B.M.; Bircan, A. Effects of Atmospheric Sulphur Dioxide and Particulate Matter Concentrations on Emergency Room Admissions Due to Asthma in Ankara. Tuberk. Toraks 2003, 51, 231–238. [Google Scholar]
- Weinmayr, G.; Romeo, E.; de Sario, M.; Weiland, S.K.; Forastiere, F. Short-Term Effects of Pm10 and No2 on Respiratory Health among Children with Asthma or Asthma-Like Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nuvolone, D.; Petri, D.; Voller, F. The Effects of Ozone on Human Health. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 25, 8074–8088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akyuz, M.; Cabuk, H. Meteorological Variations of Pm2.5/Pm10 Concentrations and Particle-Associated Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Atmospheric Environment of Zonguldak, Turkey. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.Z.; Shi, G.L.; Huang-Fu, Y.Q.; Song, D.L.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhou, L.D.; Feng, Y.C. Seasonal and Regional Variations of Source Contributions for Pm10 and Pm2.5 in Urban Environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 557–558, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Wu, D.; Fan, Q.; Wang, B.M.; Li, H.W.; Fan, S.J. Observational Studies of the Meteorological Characteristics Associated with Poor Air Quality over the Pearl River Delta in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 10755–10766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, Q.; Cai, A.; Wang, F.; Yang, L.; Xu, C.; Liu, Z. Spatio-Temporal Variability of Particulate Matter in the Key Part of Gansu Province, Western China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, Z.; Cui, L.; Fu, H.; Zhang, L.; Kong, L.; Chen, W.; Chen, J. Air Pollution Characteristics in China During 2015-2016: Spatiotemporal Variations and Key Meteorological Factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 902–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Sun, Y.; Tao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, S. Pollution Characteristics in a Dusty Season Based on Highly Time-Resolved Online Measurements in Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2545–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhong, K.; Chen, Y.; Kang, Y. Simulations of the Impacts of Building Height Layout on Air Quality in Natural-Ventilated Rooms around Street Canyons. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 23620–23635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Simonich, S.; Tao, S. New Discoveries to Old Problems: A Virtual Issue on Air Pollution in Rapidly Industrializing Countries. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11497–11501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.L.; Yang, C.H.; Chien, L.C. Spatial Vulnerability under Extreme Events: A Case of Asian Dust Storm’s Effects on Children’s Respiratory Health. Environ. Int. 2013, 54, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, C.; Wang, S.; Hu, J. Identifying the Socioeconomic Determinants of Population Exposure to Particulate Matter (Pm2.5) in China Using Geographically Weighted Regression Modeling. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krotkov, N.A.; McLinden, C.A.; Li, C.; Lamsal, L.N.; Celarier, E.A.; Marchenko, S.V.; Swartz, W.H.; Bucsela, E.J.; Joiner, J.; Duncan, B.N.; et al. Streets. Aura Omi Observations of Regional So2 and No2 Pollution Changes from 2005 to 2015. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 4605–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ou, J.; Meng, J.; Zheng, J.; Mi, Z.; Bian, Y.; Yu, X.; Liu, J.; Guan, D. Demand-Driven Air Pollutant Emissions for a Fast-Developing Region in China. Appl. Energy 2017, 204, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, H.; Guan, Q.; Lin, J.; Wang, Q.; Yang, L.; Tan, Z.; Wang, N. Air Pollution Characteristics and Human Health Risks in Key Cities of Northwest China. J. Environ. Manage. 2020, 269, 110791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-S.; Wu, T.; Shi, G.-L.; Fu, X.; Tian, Y.-Z.; Feng, Y.-C.; Wu, X.-F.; Wu, G.; Bai, Z.-P.; Zhang, W.-J. Potential Source Analysis for Pm10 and Pm2.5 in Autumn in a Northern City in China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Wu, L.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Q.; He, K.; Chang, Q.; Li, X.; Yang, F.; Ying, Q.; Zhang, H. Source Contributions and Regional Transport of Primary Particulate Matter in China. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 207, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Liu, G.; Zhang, H.; Hu, R.; Wang, X. Similarities and Differences in Pm10 and Pm2.5 Concentrations, Chemical Compositions and Sources in Hefei City, China. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, P.; Lesne, O.; Alexandre, N.; Mangin, A.; Collomp, R. Air Quality Trends and Potential Health Effects—Development of an Aggregate Risk Index. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Zhang, X.; Gong, S.; An, X.; Wang, Y. Emission Inventories of Primary Particles and Pollutant Gases for China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, J.; Shen, Z.; Chow, J.C.; Qi, G.; Watson, J.G. Seasonal Variations and Sources of Mass and Chemical Composition for Pm10 Aerosol in Hangzhou, China. Particuology 2009, 7, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.J.; Zhuang, X.L.; Jiang, G.B.; Shi, J.B.; Lu, Y.H. Environmental Problems and Challenge in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 7597–7602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, Q.; Zheng, J.; Ye, S.; Shen, X.; Yuan, Z.; Yin, S. Emission Trends and Source Characteristics of So2, Nox, Pm10 and Vocs in the Pearl River Delta Region from 2000 to 2009. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 76, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, L.E.; Newmark, G.L.; Higgins, M.J.; Wang, Z. Nitrogen Oxides and Ozone in Urban Air: A Review of 50 Plus Years of Progress. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2020, 39, e13484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmasrene, T.; Lee, J.W. Assessing the Dynamic Impact of Tourism, Industrialization, Urbanization, and Globalization on Growth and Environment in Southeast Asia. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2016, 24, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.C.; Miao, Y.M.; Gao, C.; Long, R.Y.; Chen, H.; Zhao, B.; Wang, S.X. Regional Differences in Impacts of Economic Growth and Urbanization on Air Pollutants in China Based on Provincial Panel Estimation. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Oh, D.-W. Economic Growth and the Environment in China: Empirical Evidence Using Prefecture Level Data. China Econ. Rev. 2015, 36, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Zhao, C.; Yang, Y. A Comprehensive Analysis of the Spatio-Temporal Variation of Urban Air Pollution in China During 2014–2018. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 220, 117066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Zhao, C.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, K.; Gao, J.; Qiao, Q.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chai, F. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of No2 and So2 in Inner Mongolia Urban Agglomeration Obtained from Satellite Remote Sensing and Ground Observations. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 188, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.; Zhao, M.; Xue, P.; Liang, X.; Fan, G.; Ding, B.; Liu, J.; Liu, J. New Indicators for Air Quality and Distribution Characteristics of Pollutants in China. Build. Environ. 2020, 172, 106723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Wang, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.J.; Ma, C. National Air Pollution Distribution in China and Related Geographic, Gaseous Pollutant, and Socio-Economic Factors. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Du, P.; Samat, A.; Xia, J.; Che, M.; Xue, Z. Spatiotemporal Pattern of Pm2.5 Concentrations in Mainland China and Analysis of Its Influencing Factors Using Geographically Weighted Regression. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fang, X.; Ji, H.; Li, X.; Zhao, Z. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Recent Pm2.5 Concentrations over Typical Urban Agglomerations in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yang, S.; Zhang, J.; Qian, Y. Coal-Based Synthetic Natural Gas (Sng) for Municipal Heating in China: Analysis of Haze Pollutants and Greenhouse Gases (Ghgs) Emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 1350–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Deng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Duan, L.; Hao, J.; Jiang, J. Air Pollutant Emissions from Coal-Fired Power Plants in China over the Past Two Decades. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Teng, F. Air Quality Benefit of China’s Mitigation Target to Peak Its Emission by 2030. Clim. Policy 2018, 18, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Y.; McGoogan, J.M. Characteristics of and Important Lessons from the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (Covid-19) Outbreak in China Summary of a Report of 72,314 Cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 323, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yu, R.; Shen, H.; Wang, S.; Hu, Q.; Cui, J.; Yan, Y.; Huang, H.; Hu, G. Chemical Characteristics, Sources, and Formation Mechanisms of Pm2.5 before and During the Spring Festival in a Coastal City in Southeast China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 251, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Sun, P.; Hu, X.; Zhao, W.; Wu, M.; Fu, J. The Chemical Composition and Sources of Pm2.5 During the 2009 Chinese New Year’s Holiday in Shanghai. Atmos. Res. 2012, 118, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Pant, P.; Pope, F.D. Air Quality During and after Festivals: Aerosol Concentrations, Composition and Health Effects. Atmos. Res. 2019, 227, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wan, X.; Bai, S.; Guo, D.; Ren, C.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, X. The Characteristics of Air Pollutants During Two Distinct Episodes of Fireworks Burning in a Valley City of North China. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhuang, G.; Xu, C.; An, Z. The Air Pollution Caused by the Burning of Fireworks During the Lantern Festival in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Wang, D.; Fu, Q.; Qiao, L.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Sun, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; et al. The Effects of Firework Regulation on Air Quality and Public Health During the Chinese Spring Festival from 2013 to 2017 in a Chinese Megacity. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yan, C.; Fu, Q.; Xiao, K.; Yu, Y.; Han, D.; Wang, W.; Cheng, J. Possible Environmental Effects on the Spread of Covid-19 in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, Q.; Huang, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, A.; Xu, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Shi, L.; Li, R.; et al. Air Quality Changes During the Covid-19 Lockdown over the Yangtze River Delta Region: An Insight into the Impact of Human Activity Pattern Changes on Air Pollution Variation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafa, M.K.; Gamal, G.; Wafiq, A. The Impact of Covid 19 on Air Pollution Levels and Other Environmental Indicators—A Case Study of Egypt. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, M.J.; Oh, J.; Choi, Y.-H. Changes in Air Pollution Levels after Covid-19 Outbreak in Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovrić, M.; Pavlović, K.; Vuković, M.; Grange, S.K.; Haberl, M.; Kern, R. Understanding the True Effects of the Covid-19 Lockdown on Air Pollution by Means of Machine Learning. Environ. Pollut. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, J.; Austin, E.; Gould, T.; Larson, T.; Shirai, J.; Liu, Y.; Marshall, J.; Seto, E. Impacts of the Covid-19 Responses on Traffic-Related Air Pollution in a Northwestern US City. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, J.N.; Yung, Y.L.; Li, G.H.; Seinfeld, J.H. Unexpected Air Pollution with Marked Emission Reductions During the Covid-19 Outbreak in China. Science 2020, 369, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Brown, P.E. Population-Weighted Exposure to Air Pollution and Covid-19 Incidence in Germany. Spat. Stat. 2021, 41, 100480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travaglio, M.; Yu, Y.; Popovic, R.; Selley, L.; Leal, N.S.; Martins, L.M. Links between Air Pollution and Covid-19 in England. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monasterolo, I.; Billio, M.; Battiston, S. The Importance of Compound Risk in the Nexus of Covid-19, Climate Change and Finance; Working Papers No. 2020; Ca’ Foscari University of Venice: Venice, Italy, 2020; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- Mofijur, M.; Fattah, I.M.R.; Alam, M.A.; Islam, A.B.M.S.; Ong, H.C.; Rahman, S.M.A.; Najafi, G.; Ahmed, S.F.; Uddin, M.A.; Mahlia, T.M.I. Impact of Covid-19 on the Social, Economic, Environmental and Energy Domains: Lessons Learnt from a Global Pandemic. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 26, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, Y.K.; Webbink, J.F. Reflecting on Reflections on Covid-19. Cent. Eur. Rev. Econ. Manag. 2020, 4, 7–19. [Google Scholar]
- Leal Filho, W.; Brandli, L.L.; Salvia, A.L.; Rayman-Bacchus, L.; Platje, J. Covid-19 and the Un Sustainable Development Goals: Threat to Solidarity or an Opportunity? Sustainability 2020, 12, 5343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asare Vitenu-Sackey, P.; Barfi, R. The Impact of Covid-19 Pandemic on the Global Economy: Emphasis on Poverty Alleviation and Economic Growth. Econ. Financ. Lett. 2021, 8, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, J.; Kajino, M. Rethinking Air Quality and Climate Change after Covid-19. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, P.; de Marco, A.; Agathokleous, E.; Feng, Z.; Xu, X.; Paoletti, E.; Rodriguez, J.J.D.; Calatayud, V. Amplified Ozone Pollution in Cities During the Covid-19 Lockdown. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, G.T.; Kahlbaum, D.F.; Heuss, J.M. The Vanishing Ozone Weekday/Weekend Effect. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2013, 63, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Ding, A.; Gao, J.; Zheng, B.; Zhou, D.; Qi, X.; Tang, R.; Wang, J.; Ren, C.; Nie, W.; et al. Enhanced Secondary Pollution Offset Reduction of Primary Emissions During Covid-19 Lockdown in China. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xie, B.; Zhao, S.-Y.; Chen, Q. Pm2.5 and Tropospheric O3 in China and an Analysis of the Impact of Pollutant Emission Control. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2014, 5, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ren, L.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, P.; Chen, L.; Yue, X.; Liao, H. Fast Climate Responses to Aerosol Emission Reductions During the Covid-19 Pandemic. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL089788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colwell, R. Global Climate Change and Infectious Diseases. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1998, 4, 451–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khasnis, A.A.; Nettleman, M.D. Global Warming and Infectious Disease. Arch. Med. Res. 2005, 36, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, K.M.; Auzenbergs, M.; Jafari, Y.; Liu, Y.; Flasche, S.; Lowe, R. Effective Transmission across the Globe: The Role of Climate in Covid-19 Mitigation Strategies. Lancet Planet. Health 2020, 4, e172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

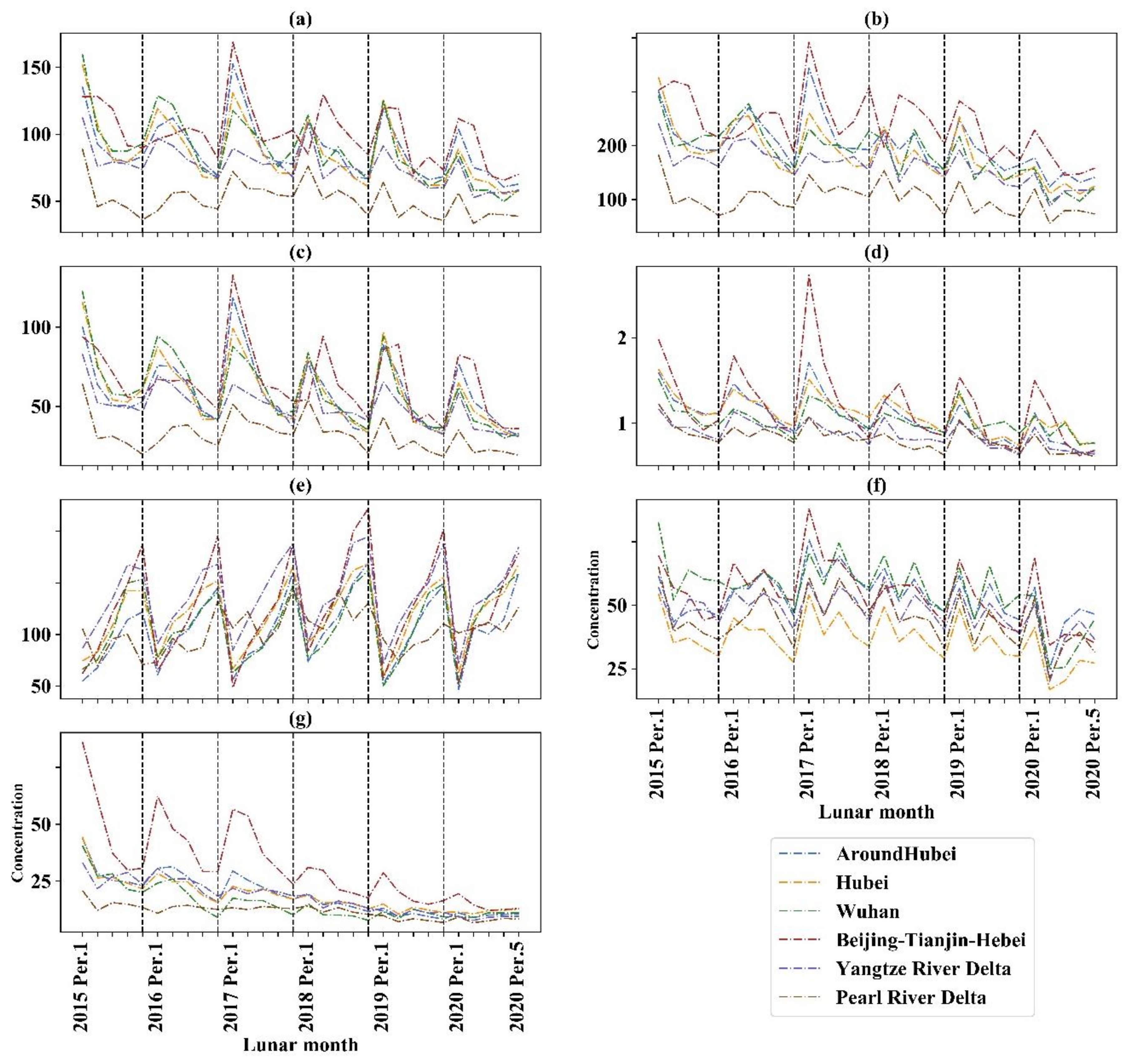


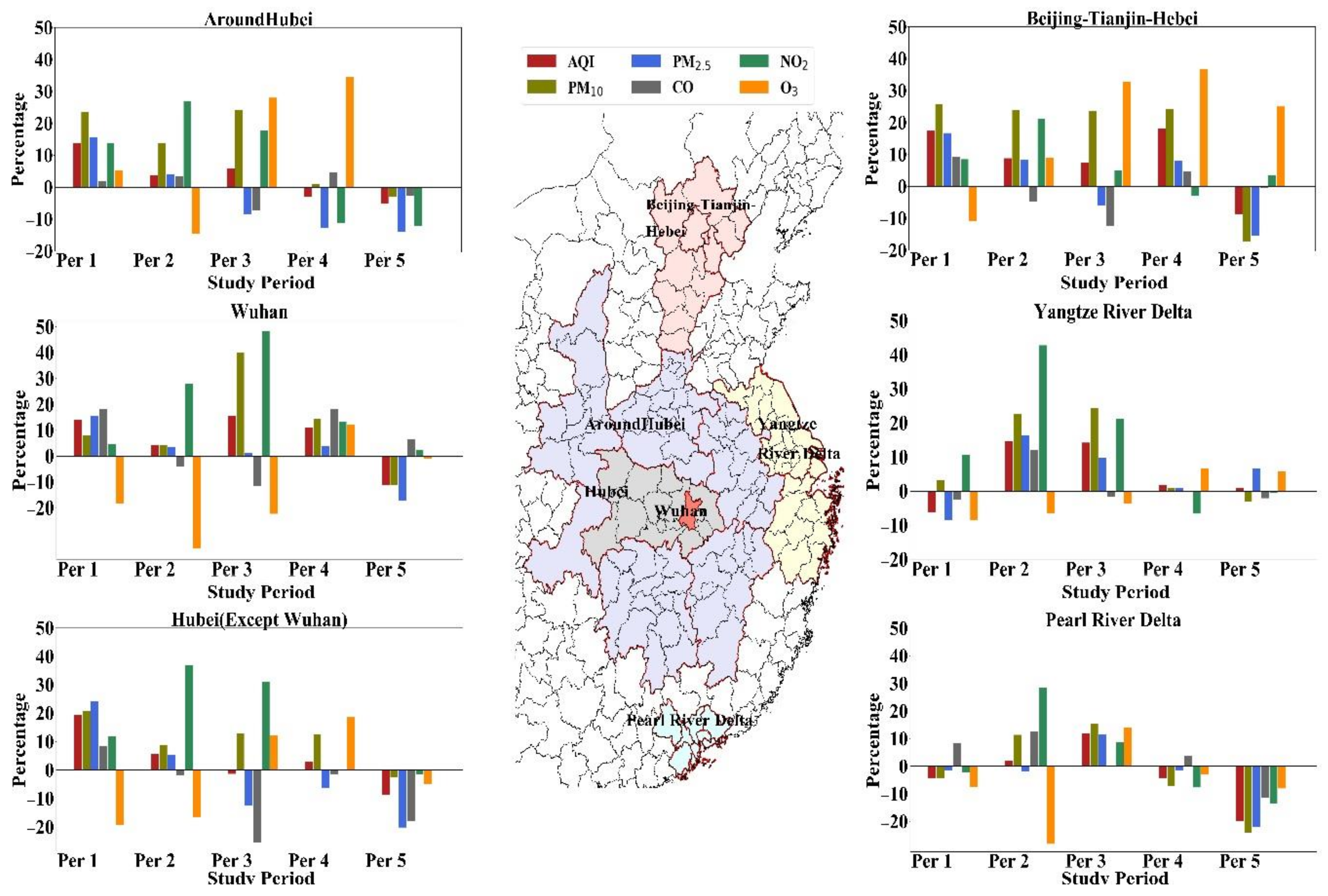
| Study Period | Date |
|---|---|
| Period 1 | 26 December 2019–24 January 2020 |
| Period 2 | 25 January 2020–22 February 2020 |
| Period 3 | 23 February 2020–23 March 2020 |
| Period 4 | 24 March 2020–22 April 2020 |
| Period 5 | 23 April 2020–22 May 2020 |
| Study Period | Period 1 | Period 2 | Period 3 | Period 4 | Period 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location | ||||||
| Around Hubei | None | Traffic suspension; Delay the resumption of work; No school; Village isolation. | Traffic resumption; To promote the resumption of work and production; Part of scenic spots open. | The normal life order was restored in an orderly manner, and work was resumed in an all-round way; Schools open in batches. | Restore full order to life. | |
| Hubei | None | All buses, trains and flights were stopped; Industrial was suspended; The community takes lockdown measures. | Key projects to promote the resumption of work; community, village closed control. | Enterprises have gradually resumed work; Traffic was restored in different regions; School extension; Some communities and villages have been closed off. | The living order was restored in an orderly manner; Schools open in batches. | |
| Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei | None | Traffic control; some communities are closed; Resumption of work was delayed. | Return to work and production; part of the park open; part of the community, village closed management. | Current limit management in scenic spots to increase an operating rate; All kinds of schools are postponed. | Restore the order of life in an all-round way. | |
| Yangtze River Delta | None | Some traffic has been suspended; some communities have closed management; and the resumption of work has been postponed. | Enterprises have gradually resumed work; traffic has been partially restored; some communities have been closed off. | Comprehensively promote the resumption of work in enterprises; promote normal life order. | Life order was fully restored, and schools opened in batches. | |
| Pearl River Delta | None | Traffic control; Some production was suspended; some communities and villages were closed for management. | Promote the resumption of work and production; Enterprises in low-risk areas return to working; Community and villages are strictly controlled in and out. | Full resumption of work; Control overseas import. | Restore life order in an all-round way; Schools open in batches. | |
| Elements | 500 hPa | 750 hPa | Surface | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | ||||
| Per 1.F | 2019 | 2017 | 2016 | |
| Per 1.M | 2019 | 2017 | 2019 | |
| Per 1.L | 2015 | 2017 | 2019 | |
| Per 2.F | 2019 | 2016 | 2019 | |
| Per 2.M | 2019 | 2017 | 2015 | |
| Per 2.L | 2018 | 2017 | 2017 | |
| Per 3.F | 2016 | 2016 | 2017 | |
| Per 3.M | 2019 | 2015 | 2017 | |
| Per 3.L | 2017 | 2018 | 2017 | |
| Per 4.F | 2016 | 2016 | 2017 | |
| Per 4.M | 2017 | 2018 | 2018 | |
| Per 4.L | 2017 | 2015 | 2017 | |
| Per 5.F | 2019 | 2015 | 2017 | |
| Per 5.N | 2019 | 2015 | 2017 | |
| Per 5.L | 2019 | 2016 | 2017 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, L.; Chen, B.; Huang, Y.; Song, Z.; Yang, T. Analysis on the Characteristics of Air Pollution in China during the COVID-19 Outbreak. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020205
Dong L, Chen B, Huang Y, Song Z, Yang T. Analysis on the Characteristics of Air Pollution in China during the COVID-19 Outbreak. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(2):205. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020205
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Li, Bin Chen, Yue Huang, Zhihao Song, and Tingting Yang. 2021. "Analysis on the Characteristics of Air Pollution in China during the COVID-19 Outbreak" Atmosphere 12, no. 2: 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020205
APA StyleDong, L., Chen, B., Huang, Y., Song, Z., & Yang, T. (2021). Analysis on the Characteristics of Air Pollution in China during the COVID-19 Outbreak. Atmosphere, 12(2), 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020205







