“Military Parade Blue Skies” in Beijing: Decisive Influence of Meteorological Factors on Transport Channel and Atmospheric Pollutant Concentration Level
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Experiments
2.2. Model Simulation
3. Results and Discussion
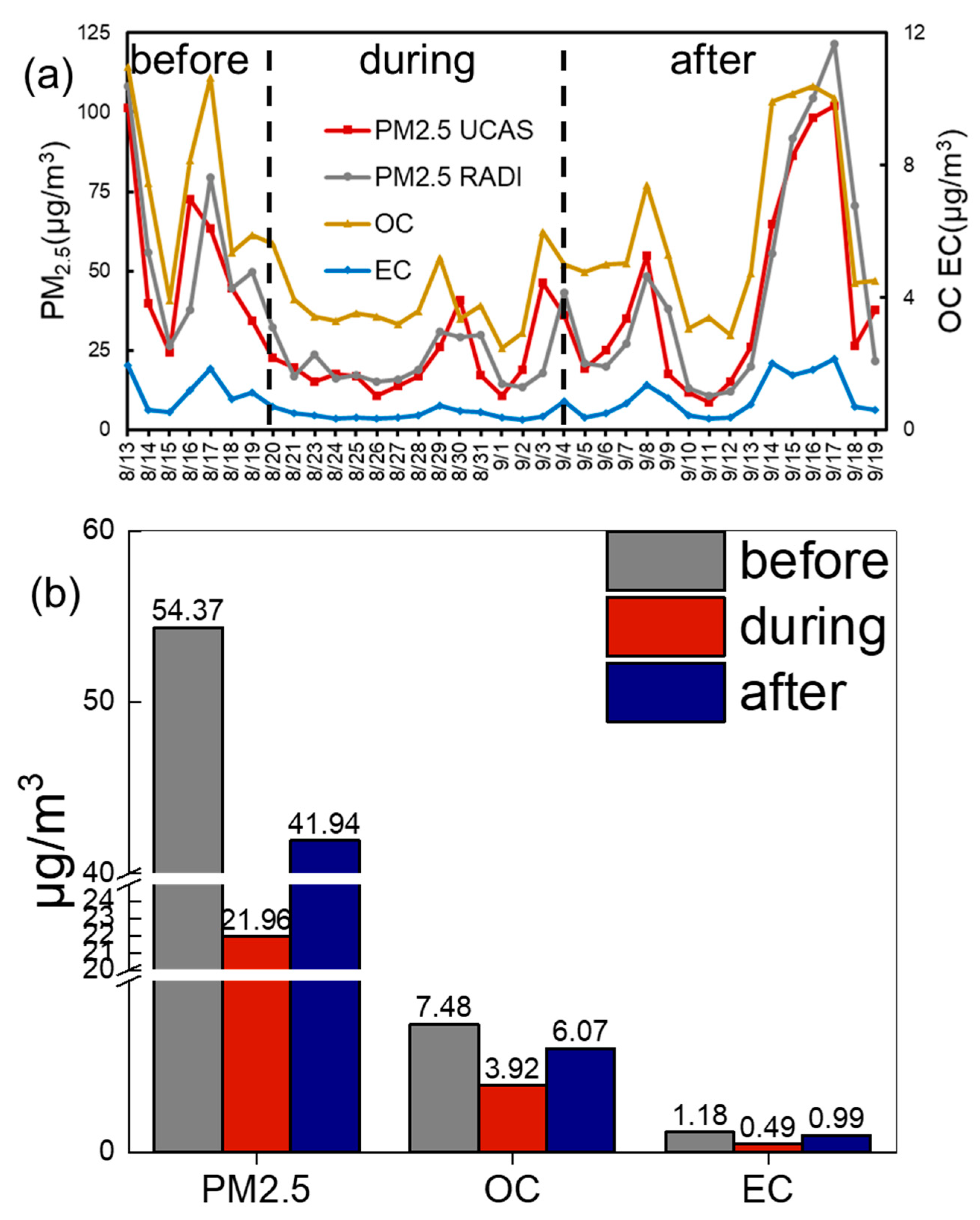
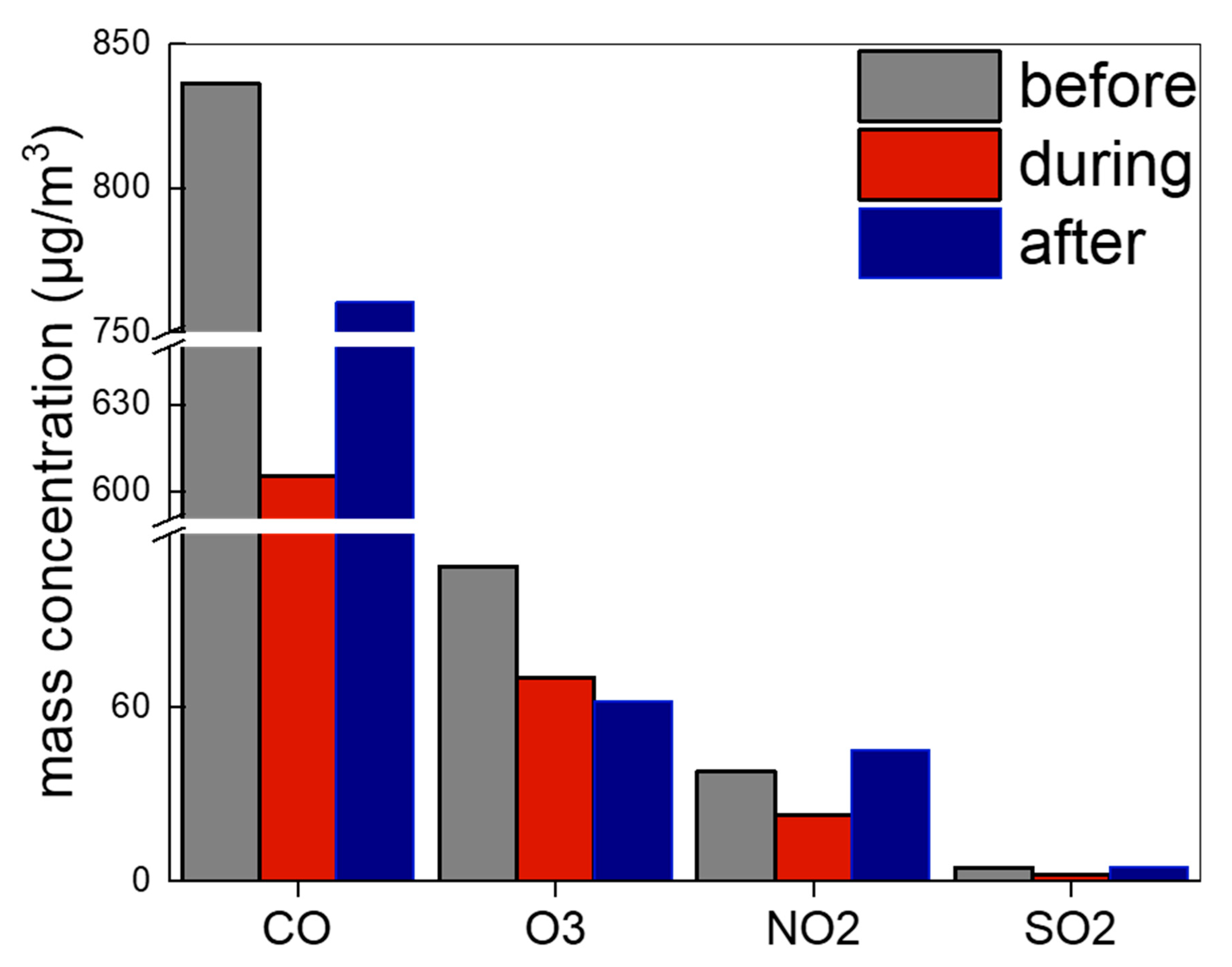
3.1. PM2.5, OC, EC and Gaseous Compounds
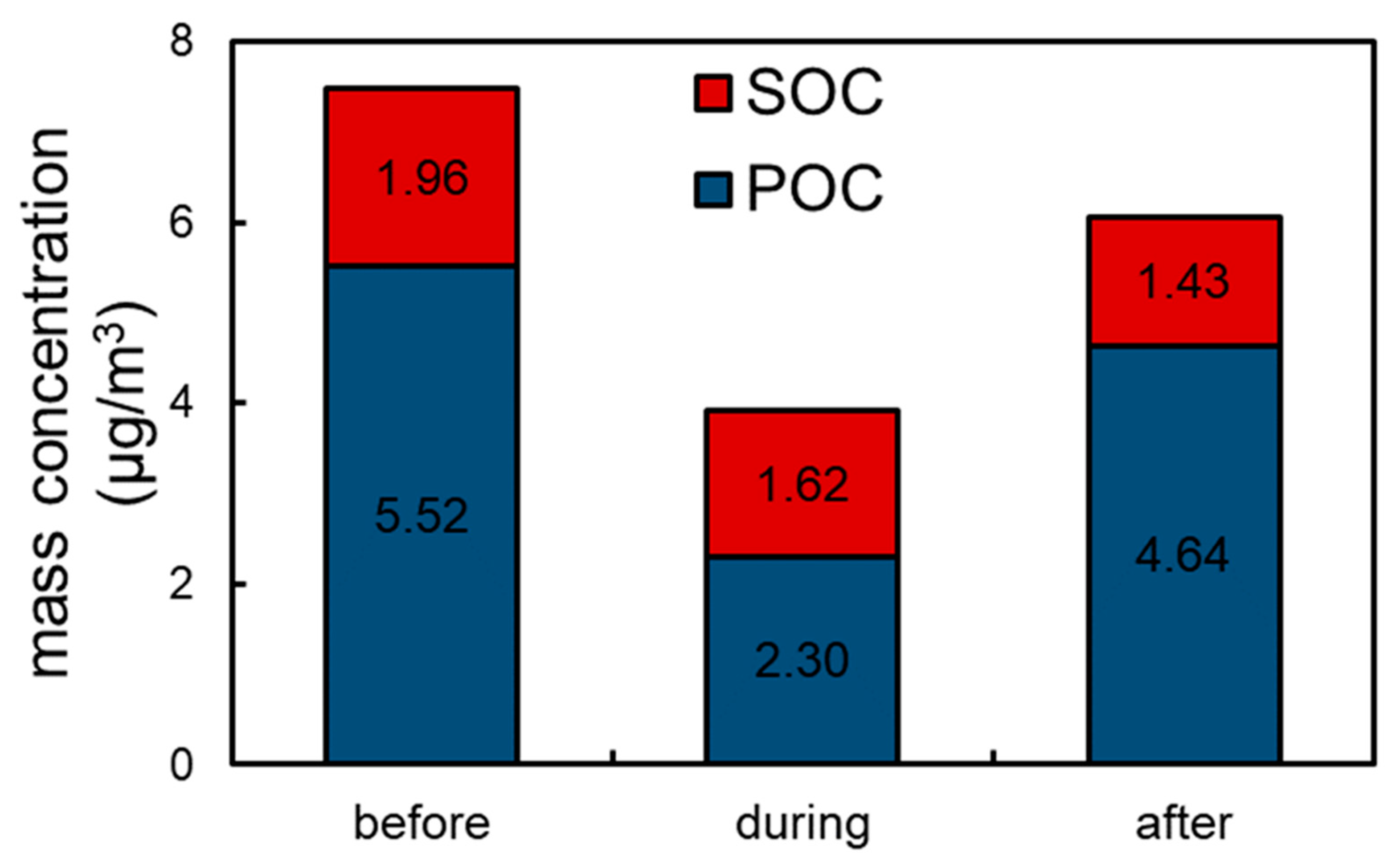
3.2. Primary and Secondary OC
3.3. Organic Matter Species
3.4. Model Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Anyah, R.O.; Tian, J. Exploring the trend, prediction and driving forces of aerosols using satellite and ground data, and implications for climate change mitigation. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 223, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, M.-T.; Chel Gee Ooi, M.; Lin, N.-H.; Fu, J.S.; Lee, C.-T.; Wang, S.-H.; Yen, M.-C.; Kong, S.S.-K.; Huang, W.-S. Study on the impact of three Asian industrial regions on PM2.5 in Taiwan and the process analysis during transport. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xiao, Z.; Tang, M.; Xu, H.; Li, L.; Chen, K.; Deng, X. Particulate Pollution Characteristics of Typical Sand Dust Wearthe in Tianjin. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2020, 36, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Liu, K. Evaluating the Use of DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Imagery in Predicting PM2.5 Concentrations in the Northeastern United States. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, N.L.; Zhang, D.W.; Li, Y.T.; Chen, T.; Sun, F.; Li, L.J.; Cheng, B.F. Characteristics of NOx concentrations during IAAF World Championships in Athletics and 9.3 military parade periods in 2015 in Beijing. J. Univ. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2016, 33, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zheng, Y.F.; Xu, J.X.; Wang, Z.S.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, J.Q.; Chu, Z.F. Evaluation of the improvement of the air quality during the parade in Beijing. China Environ. Sci. 2016, 36, 2881–2889. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, J.; Guo, X.R.; Cheng, S.Y. Numerical study on the characteristics of PM2.5 in Beijing and the assessment of pollution control measures during APEC. China Environ. Sci. 2016, 36, 2337–2346. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.F.; Guan, Y.C.; Dong, H.Y. Variations of Water Soluble Ions in PM2.5 during the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation Summit in Tianjin and Surrounding Cities. Environ. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 6, 213–217. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.B.; Li, Z.G.; Lu, N.; Xu, M.; Yang, P.; Gao, K.N.; Wang, J.G.; Jin, W. Online Sources about Atmospheric Fine Particles During the 70th Anniversary of Victory Parade in Shijiazhuang. Environ. Sci. 2016, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Song, X.H. Environmental and Meteorological Conditions and Effect of Emergency Emission Reduction in South Hebei. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2016, 32, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Cheng, S.Y.; Yang, X.W. Characterization and sources of Carbon components in PM2.5 from Tang Shan city before and after the Military Parade. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the Chinese Society for Environmental Sciences, Haikou, Hainan, China, 6–8 September 2016; pp. 2621–2627. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, J.; Gao, J.; Zhang, L.M.; Wang, H.; Qiu, X.H.; Zhang, Z.S.; Wu, Y.F.; Chai, F.H.; Wang, S.L. Chemical and optical characteristics of atmospheric aerosols in Beijing during the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation China 2014. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 144, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, S.X.; Wang, J.D.; Jiang, J.K.; Zhang, T.S.; Song, Y.; Kang, L.; Zhou, W.; Cai, R.L.; Wu, D.; et al. Investigating the impact of regional transport on PM2.5 formation using vertical observation during APEC 2014 Summit in Beijing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 15451–15460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.L.; He, J.; Guo, J.P.; Miao, Y.C.; Yin, J.F.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, H.; Yan, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. The blue skies in Beijing during APEC 2014: A quantitative assessment of emission control efficiency and meteorological influence. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 167, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Song, W.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.H.; Liu, D.Y.; Tang, A.H.; Yang, D.W.; Wang, D.D.; et al. Air quality improvement in a megacity: Implications from 2015 Beijing Parade Blue pollution control actions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cass, G.R. Organic molecular tracers for particulate air pollution sources. Trends Anal. Chem. 1998, 17, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, J.J.; Kleeman, M.J.; Cass, G.R.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Measurement of emissions from air pollution sources. 3. C1-C29 organic compounds from fireplace combustion of wood. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1716–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Shao, M.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zeng, L.M.; He, L.Y.; Zhu, B.; Wei, Y.J.; Zhu, X.L. Source profiles of particulate organic matters emitted from cereal straw burnings. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Schauer, J.J.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zeng, L.M.; Wei, Y.J.; Liu, Y.; Shao, M. Characteristics of particulate carbon emissions from real-world Chinese coal combustion. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5068–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, E.A.; Snyder, D.C.; Sheesley, R.J.; Sullivan, A.P.; Weber, R.J.; Schauer, J.J. Source apportionment of fine organic aerosol in Mexico City during the MILAGRO experiment 2006. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheesley, R.J.; Schauer, J.J.; Chowdhury, Z.; Cass, G.R.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Characterization of organic aerosols emitted from the combustion of biomass indigenous to South Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herner, J.D.; Green, P.G.; Kleeman, M.J. Measuring the Trace Elemental Composition of Size-Resolved Airborne Particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1925–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schauer, J.J.; Mader, B.T.; Deminter, J.T.; Heidemann, G.; Bae, M.S.; Seinfeld, J.H.; Flagan, R.C.; Cary, R.A.; Smith, D.; Huebert, B.J.; et al. ACE-Asia Intercomparison of aThermal-Optical Method for the Determination of Particle-Phase Organic and Elemental Carbon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huan, N.; Zhou, N.; Zeng, L.M.; Dong, H.B.; Shao, M.; Yu, Z.Y.; Cui, L.; Luo, Z.M.; Mao, J.T. Measurement and Discussion of Carbonaceous PM2.5 during Winter in Beijing. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2006, 42, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, M.S.; Hong, C.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Han, J.S.; Moon, K.J.; Kondo, Y.; Komazaki, Y.; Miyazaki, Y. Intercomparison of two different thermal-optical elemental carbons and optical black carbon during ABC-EAREX2005. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 2791–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X. Study on Speciation of Particulate Organic Matter from Combustion Sources; Beking University: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, L.M.; Pio, C.A.; Harrison, R.M.; Smith, D.J.T. Carbonaceous aerosol in urban and rural European atmospheres: Estimation of secondary organic carbon concentrations. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 2771–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brioude, J.; Arnold, D.; Stohl, A.; Cassiani, M.; Morton, D.; Seibert, P.; Angevine, W.; Evan, S.; Dingwell, A.; Fast, J.D.; et al. The Lagrangian particle dispersion model FLEXPART-WRF version 3.1. Geosci. Model Dev. 2013, 6, 1889–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Bruyère, C.; Duda, M.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.; Kavulich, M.; Keene, K.; Lin, H.-C.; Michalakes, J.; Rizvi, S.; et al. ARW Version 3 Modeling System User’s Guide; NCAR: Boulder, CO, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- De Foy, B.; Krotkov, N.A.; Bei, N.; Herndon, S.C.; Huey, L.G.; Mart´ınez, A.-P.; Ruiz-Su´arez, L.G.; Wood, E.C.; Zavala, M.; Molina, L.T. Hit from both sides: Tracking industrial and volcanic plumes in Mexico City with surface measurements and OMI SO2 retrievals during the MILAGRO field campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 9599–9617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heo, J.b.; de Foy, B.; Olson, M.R.; Pakbin, P.; Sioutas, C.; Schauer, J.J. Impact of regional transport on the anthropogenic and biogenic secondary organic aerosols in the Los Angeles Basin. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 103, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Foy, B.; Caetano, E.; Magana, V.; Zitácuaro, A.; Cárdenas, B.; Retama, A.; Ramos, R.; Molina, L.T.; Molina, M.J. Mexico City basin wind circulation during the MCMA-2003 field campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 2267–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashbaugh, L.L.; Malm, W.C.; Sadeh, W.Z. A residence time probability analysis of sulfer concentrations at grand canyon national park. Atmos. Environ. 1985, 19, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Foy, B.; Lei, W.; Zavala, M.; Volkamer, R.; Samuelsson, J.; Mellqvist, J.; Galle, B.; Mart´ınez, A.-P.; Grutter, M.; Retama, A.; et al. Modelling constraints on the emission inventory and on vertical dispersion for CO and SO2 in the Mexico City Metropolitan Area using Solar FTIR and zenith sky UV spectroscopy. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 781–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stohl, A.; Hittenberger, M.; Wotawa, G. Validation of the lagrangian partical dispersion model flexpart again large-scarle tracer experiment data. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 4245–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Draxler, R.R. TrajStat: GIS-based software that uses various trajectory statistical analysis methods to identify potential sources from long-term air pollution measurement data. Environ. Model. Softw. 2009, 24, 938–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wu, J.J.; Jia, R.J.; Liang, N.; Zhang, F.Y.; Ni, Y.; Liu, M. Investigation of Temporal-Spatial Characteristics and Underlying Risk Factors of PM2.5 Pollution in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Area. Res. Environ. Sci. 2016, 29, 483–493. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Chen, C.H.; Yu, J.X. Designing photochemical smog pollution regional total control schemes by using EKMA diagram. Plateau Meteorol. 1998, 2, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Guideline For Use of City-specific EKMA in Preparing Ozone SIPs; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1981.
- Fang, D.Q.; Wei, Y.J.; Huang, W.; Cai, T.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.Y.; Zhang, Y.X. Characterization and Source Apportionment of Organic Carbon during a Heavy Haze Episode in Beijing in October 2014. Res. Environ. Sci. 2016, 29, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.Y.; Hu, M.; Huang, X.F.; Zhang, Y.H. Determination of organic molecular tracers in PM2.5 in the atmosphere of Beijing. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2005, 25, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Q.; Zhang, Z.S.; Liu, S.X.; Zhu, L.H. Characterization and Sources of Water-soluble Organic Carbon in PM2.5 at Urban Guangzhou. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xie, S.D.; Zeng, L.M.; Li, L.Y.; Li, Y.Q.; Wu, R.R. Characterization of ambient volatile organic compounds and their sources in Beijing, before, during, and after Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation China 2014. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 7945–7959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urban System Planning of Hebei Province (2016–2030); Hebei Provincial Department of Housing and Urban-Rural Development Hebei: Shijiazhuang, China, 2017.
- Yao, S.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Wang, X.-Q.; Yang, S.-S. Air Pollution Characteristics and Quantitative Evaluation of Multi-scale Transport in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region in January 2016. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xing, Y.; Cheng, S.; Wang, X.; Guan, P. Characterization of multiple atmospheric pollutants during haze and non-haze episodes in Beijing, China: Concentration, chemical components and transport flux variations. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 246, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Shen, N.-C.; Li, L.-J.; Wu, G.-F.; Tao, J.; Zhao, W.-J. Analysis of Changes and Factors Influencing Air Pollutants in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Chen, Y.; Han, Y.; Cui, M.; Wei, P.; Zheng, M.; Hu, J. High-time-resolutionPM2.5 source apportionment based onmulti-model with organic tracers in Beijing during haze episodes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Bei, N.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, L.; Wang, R.; Yu, J.; Le, T.; Zuo, M.; et al. Insights into particulate matter pollution in the North China Plain during wintertime: Local contribution or regional transport? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 2229–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, T.; Kong, S.; Lei, Y.; Wang, Q.; Tao, J.; Zhang, R.; Wei, P.; Wei, C.; et al. Spatial distribution and sources ofwinter black carbon and brown carbon in six Chinese megacities. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Tian, H.; Luo, L.; Liu, H.; Wu, B.; Liu, S.; Bai, X.; Liu, W.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; et al. Temporal variation characteristics and source apportionment of metal elements in PM2.5 in urban Beijing during 2018–2019. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, G.; Wang, M.; Liu, B.; Hu, B.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y. Impact of residual layer transport on air pollution in Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, P.; Wang, X.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, H. Temporal and spatial characteristics of PM 2.5 transport fluxes of typical inland and coastal cities in China. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 103, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, T.U.; Wild, O.; Ryan, E.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Z. Temporally resolved sectoral and regional contributions to air pollution in Beijing: Informing short-term emission controls. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

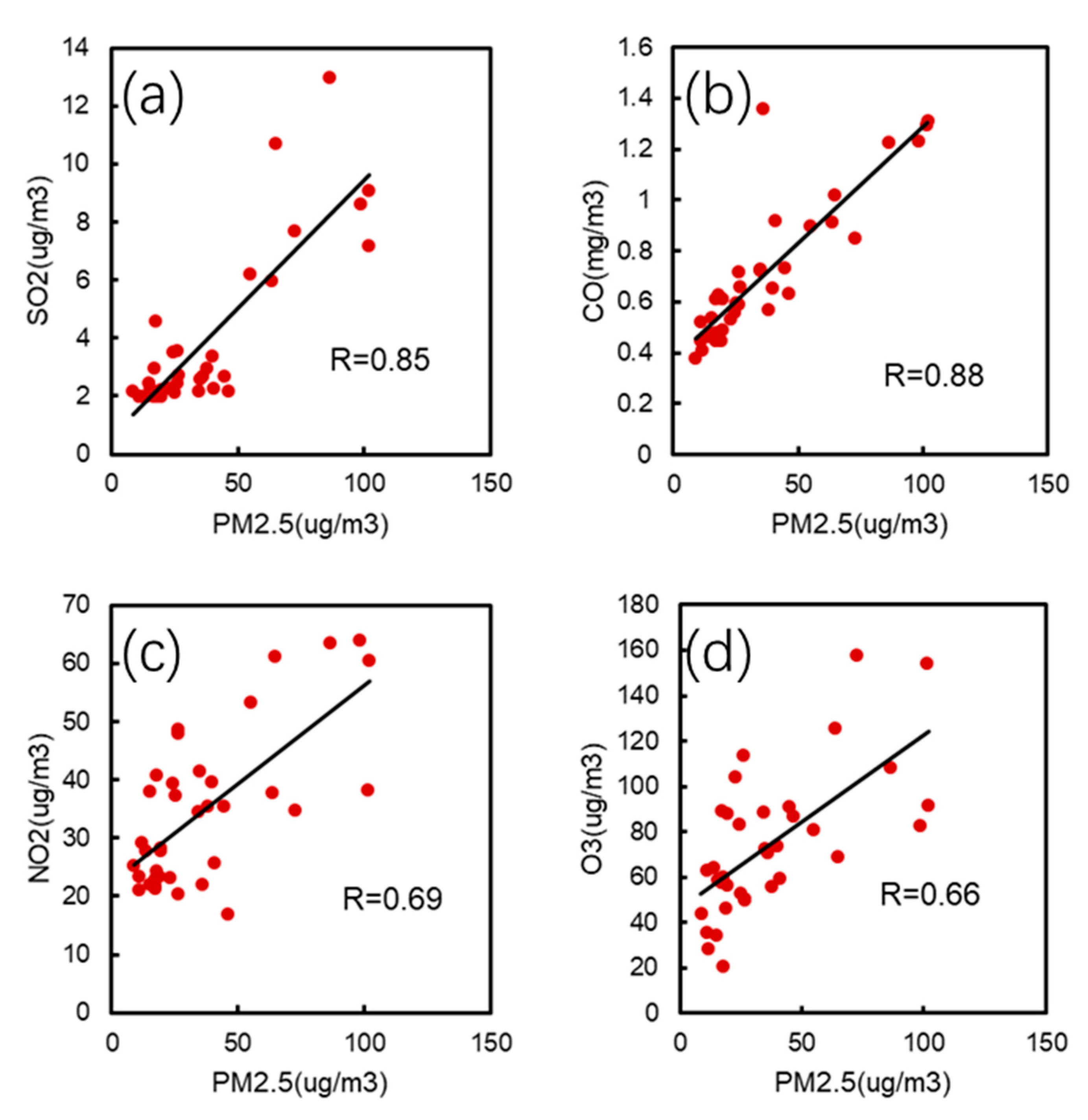


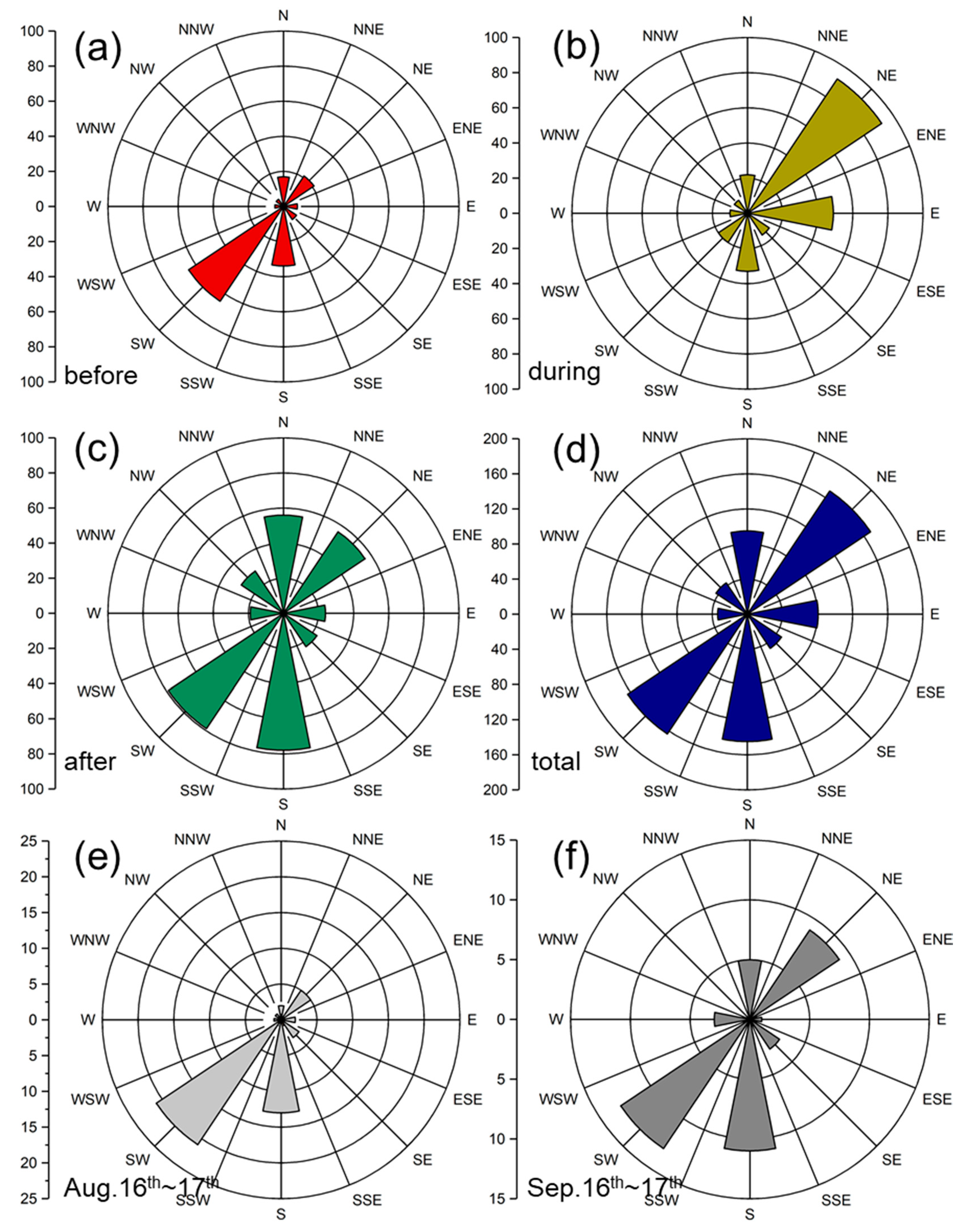

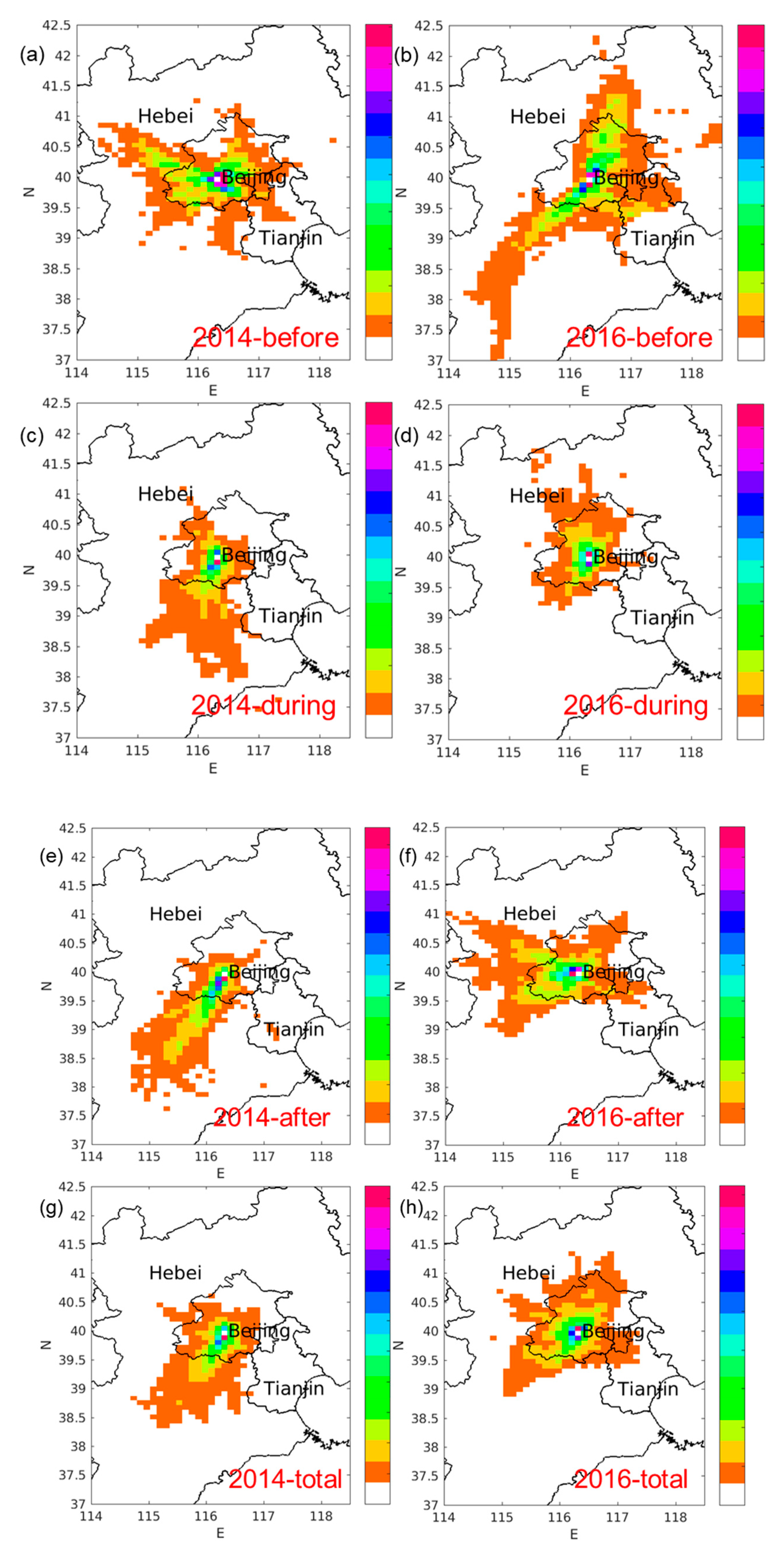

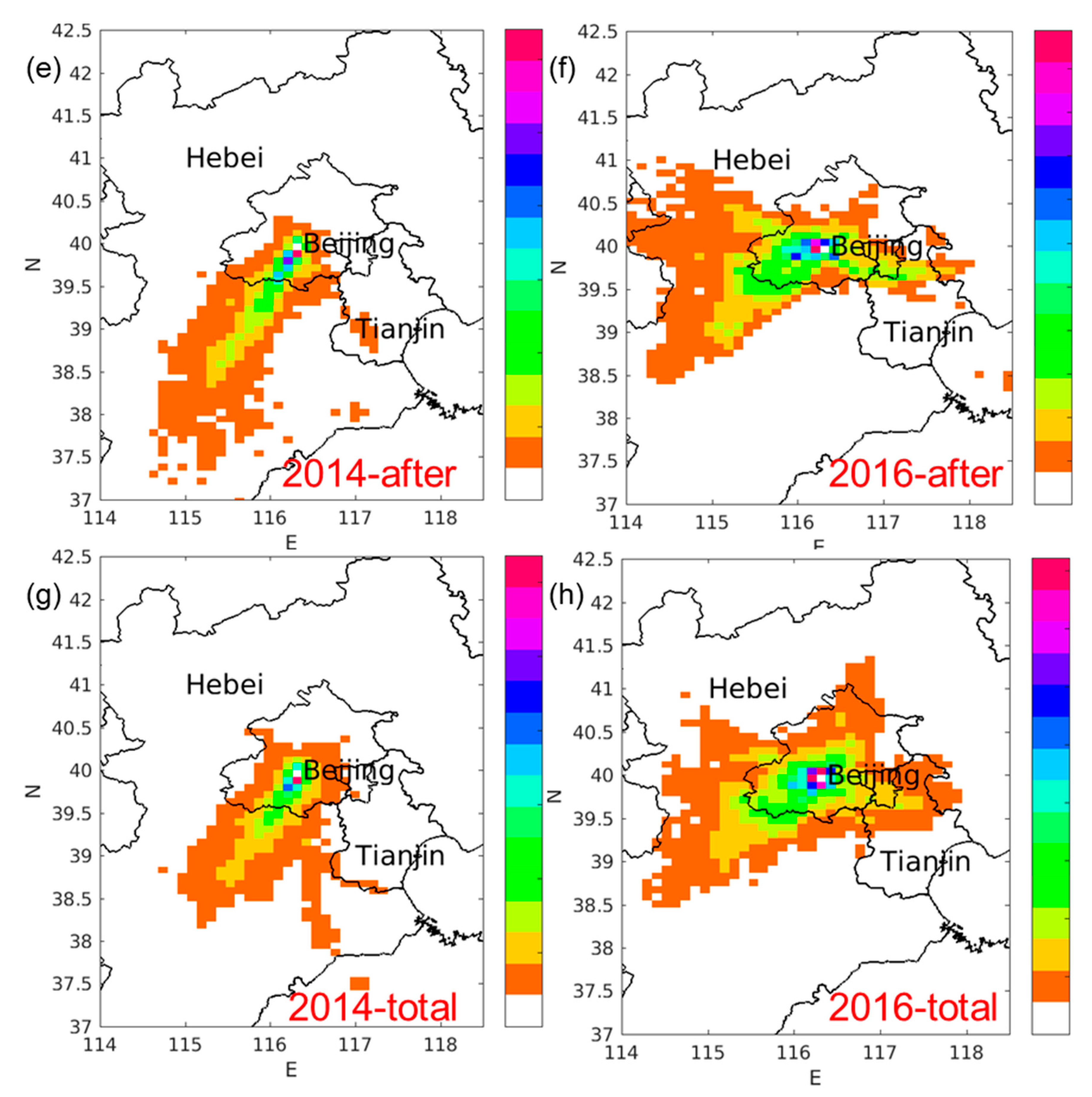
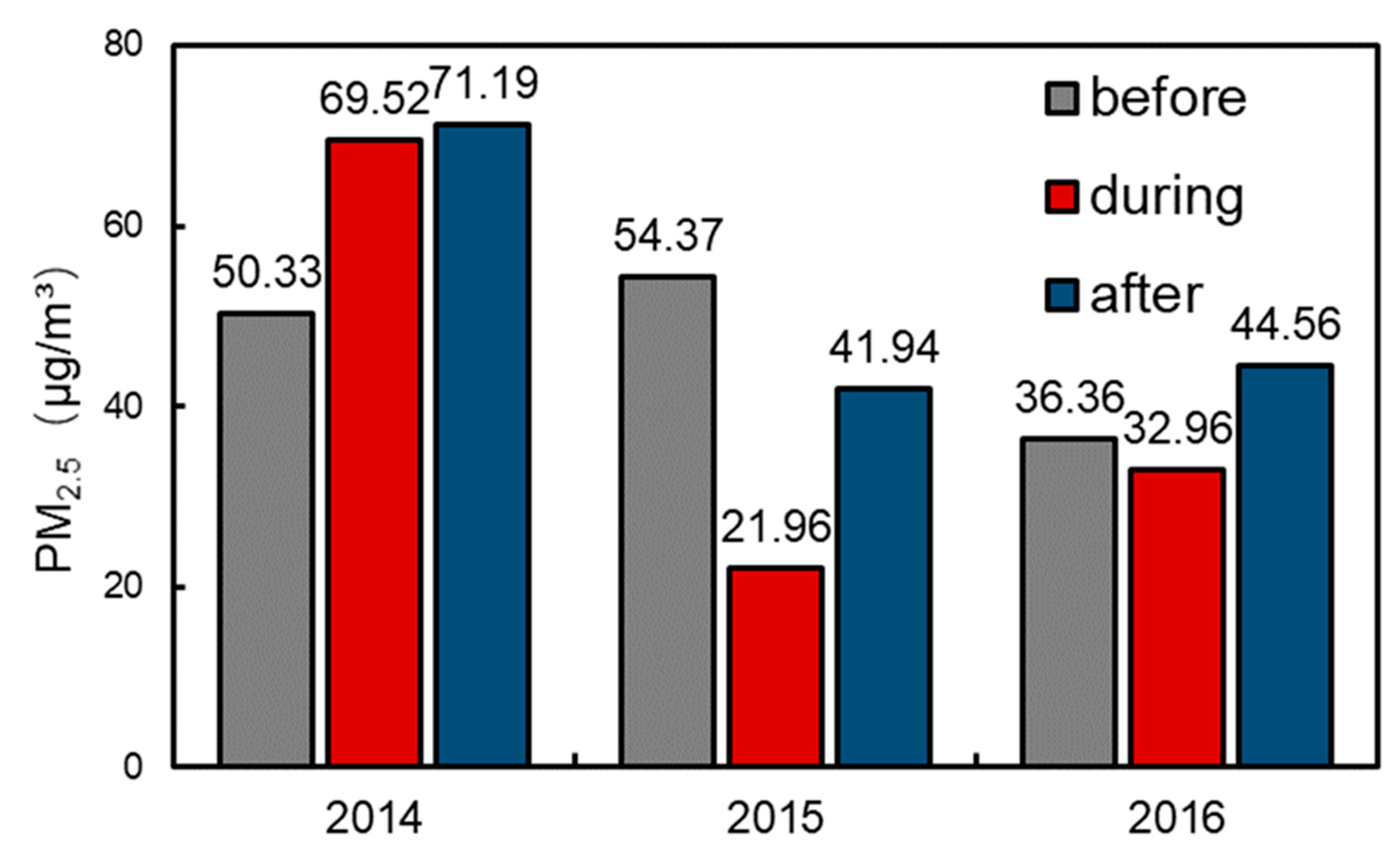
| PM2.5 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SO2 | 0.85 | SO2 | ||||
| CO | 0.88 | 0.74 | CO | |||
| NO2 | 0.69 | 0.80 | 0.59 | NO2 | ||
| O3 | 0.66 | 0.48 | 0.52 | 0.15 | O3 | |
| OC | 0.92 | 0.86 | 0.80 | 0.70 | 0.67 | OC |
| EC | 0.90 | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.74 | 0.57 | 0.94 |
| Aldehydes | Alkanols | Sterols | |
|---|---|---|---|
| before | 472.84 | 150.57 | 13.13 |
| during | 227.91 | 115.59 | 10.55 |
| after | 381.19 | 158.19 | 12.47 |
| Temperature | Wind Speed | Dew Point Temperature | |
|---|---|---|---|
| OM | 23.82 | 2.31 | 16.62 |
| SM | 28.85 | 3.67 | 8.33 |
| R | 0.88 | 0.47 | 0.46 |
| RMSE | 5.36 | 2.12 | 9.01 |
| MAE | 5.04 | 1.58 | 8.64 |
| Total | Before | During | After | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | SW | 52.7 | 52.57 | - | 68.56 |
| NE | - | - | 60.54 | - | |
| others | 34.79 | 35.69 | 18.42 | 21.79 | |
| local | 12.51 | 11.74 | 21.04 | 9.65 | |
| OC | SW | 42.39 | 43.87 | - | 59.19 |
| NE | - | - | 62.66 | - | |
| others | 43.47 | 40.53 | 12.56 | 29.39 | |
| local | 14.14 | 15.60 | 24.78 | 11.42 | |
| EC | SW | 44.11 | 43.01 | - | 59.58 |
| NE | - | - | 54.68 | - | |
| others | 40.64 | 41.11 | 20.58 | 27.35 | |
| local | 15.25 | 15.88 | 24.74 | 11.07 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Shang, J.; Li, Z.; de Foy, B.; Schauer, J.J.; Zhang, Y. “Military Parade Blue Skies” in Beijing: Decisive Influence of Meteorological Factors on Transport Channel and Atmospheric Pollutant Concentration Level. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050636
Yang S, Zhang Y, Shang J, Li Z, de Foy B, Schauer JJ, Zhang Y. “Military Parade Blue Skies” in Beijing: Decisive Influence of Meteorological Factors on Transport Channel and Atmospheric Pollutant Concentration Level. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(5):636. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050636
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Shujian, Yang Zhang, Jing Shang, Zhengqiang Li, Benjamin de Foy, James Jay Schauer, and Yuanxun Zhang. 2021. "“Military Parade Blue Skies” in Beijing: Decisive Influence of Meteorological Factors on Transport Channel and Atmospheric Pollutant Concentration Level" Atmosphere 12, no. 5: 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050636
APA StyleYang, S., Zhang, Y., Shang, J., Li, Z., de Foy, B., Schauer, J. J., & Zhang, Y. (2021). “Military Parade Blue Skies” in Beijing: Decisive Influence of Meteorological Factors on Transport Channel and Atmospheric Pollutant Concentration Level. Atmosphere, 12(5), 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050636







