How to Reduce the Emission of Microorganisms from a Biofilter Used to Treat Waste Gas from a Food Industry Plant
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
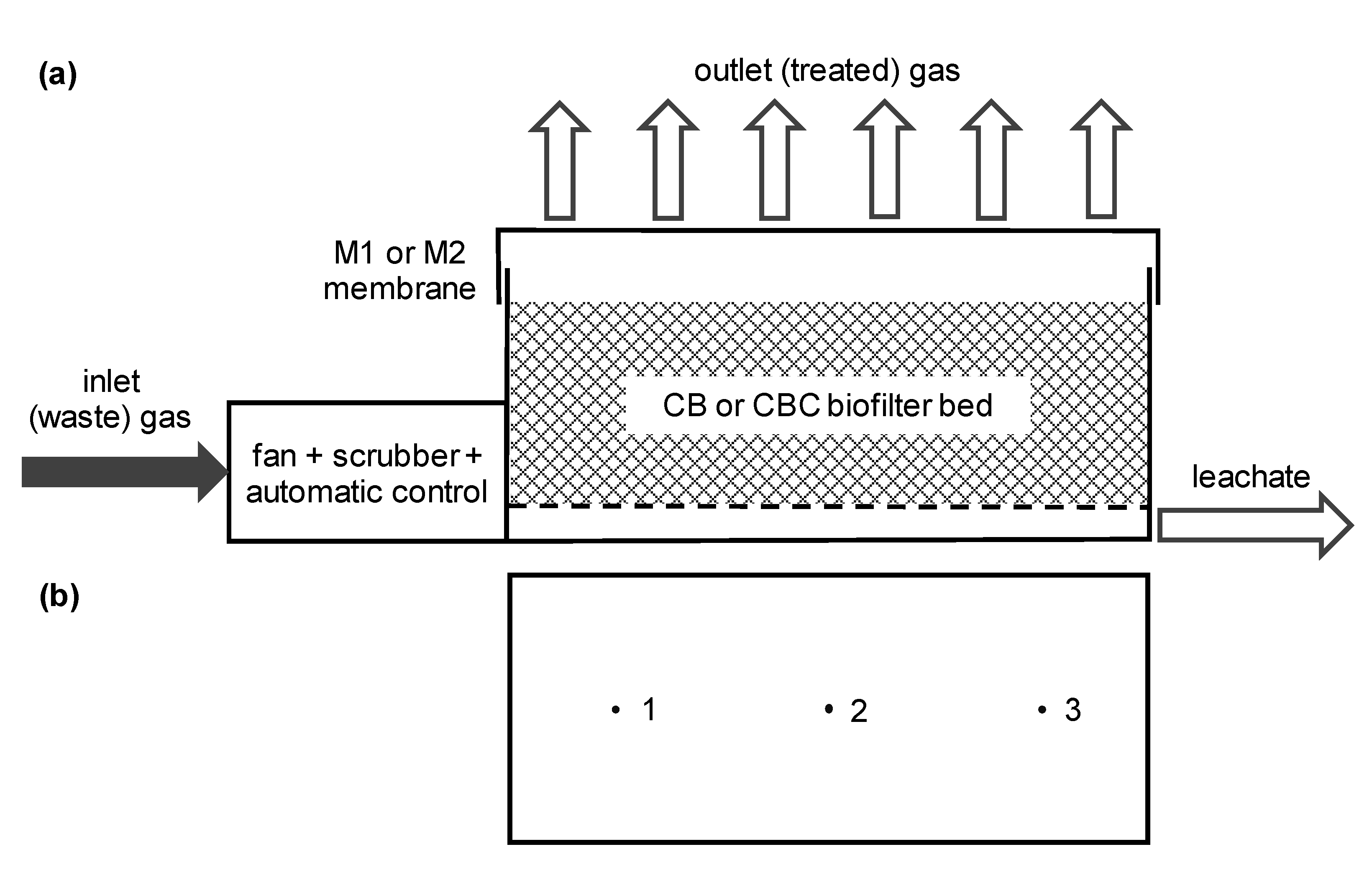
2.1. Biofilter
2.2. Gas Sampling
- Point 1 was located symmetrically (centrally) in relation to the longer walls of the biofilter, but 50 cm from the shorter wall of the biofilter;
- Point 2 was located in the middle of the biofilter (at the same distance from all walls);
- Point 3 was located symmetrically (centrally) in relation to the longer walls of the biofilter, but 250 cm from the shorter wall of the biofilter.
2.3. Microbiological Analyses
2.4. Statistical Measures and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kennes, C.; Rene, E.R.; Veiga, M.C. Bioprocesses for air pollution control. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 1419–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ralebitso-Senior, T.K.; Senior, E.; Di Felice, R.; Jarvis, K. Waste gas biofiltration: Advances and limitations of current approaches in microbiology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 8542–8573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybarczyk, P.; Szulczyński, B.; Gębicki, J.; Hupka, J. Treatment of malodorous air in biotrickling filters: A review. Biochem. Eng. J. 2019, 141, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergas, S.J.; Cárdenas-González, B. Biofiltration: Past, present and future directions. BioCycle 2004, 45, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, E.; Hirai, M.; Shoda, M. Removal of p-xylene with Pseudomonas sp. NBM21 in biofilter . J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2006, 102, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dewulf, J.; Vercruyssen, A.; Van Langenhove, H. Performance of a composite membrane bioreactor treating toluene vapors: Inocula selection, reactor performance and behavior under transient conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 2381–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Chen, H.; Zeng, G.; Zhu, X.; Suidan, M.T. Performance of rotating drum biofilter for volatile organic compound removal at high organic loading rates. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudliar, S.; Giri, B.; Padoley, K.; Satpute, D.; Dixit, R.; Bhatt, P.; Pandey, R.; Juwarkar, A.; Vaidya, A. Bioreactors for treatment of VOCs and odours-a review. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 1039–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, R.; Daugulis, A.J.; Hernandez, M.; Quijano, G. Recent advances in two-phase portioning bio-reactors for the treatment of volatile organic com-pounds. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 1707–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikrant, K.; Kim, K.H.; Szulejko, J.E.; Pandey, S.K.; Singh, R.S.; Giri, B.S.; Brown, R.J.C.; Lee, S.H. Bio-filters for the treatment of VOCs and odors-A review. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 11, 139–152. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, T.P.; Rahul, M.A.; Chandrajit, B. Biofiltration of Volatile Organic Compounds(VOCs)—An Overview. Res. J. Chem. Sci. 2011, 1, 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, M.C.; Álvarez-Hornos, F.J.; Portune, K.; Gabaldón, C. Abatement of styrene waste gas emission by biofilter and biotrickling filter: Comparison of packing materials and inoculation procedures. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 99, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turała, A.; Wieczorek, A. Biofiltration of contaminated air—Current status, development trends. Rocz. Ochrona Środowiska 2019, 21, 1001–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich, U.; Prior, K.; Altendorf, K.; Lipski, A. High bacterial diversity of a waste gas-degrading community in an industrial biofilter as shown by a 16S rDNA clone library. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 4, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, E.; Galera, M.M.; Lorenzana, A.; Chung, W.-J. Ethylbenzene, o-xylene, and BTEX removal by Sphingomonas sp. D3K1 in rock wool-compost biofilters. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2009, 26, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.-S.; Yoo, S.-K.; Ryu, H.W. Thermophilic biofiltration of benzene and toluene. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 17, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.J.; Shoda, M. Removal of a high load of ammonia by a marine bacterium, Vibrio alginolyticus in biofilter. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2002, 7, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkmann, W.; Altendorf, K.; Stackerbrandt, E.; Lipski, A. Characterization of N2O-producing Xanthomonas-like isolates from biofilters as Stenotrophomonas nitritireducens sp. nov., Luteimonas mephitis gen. nov., sp. nov. and Pseudoxanthomonas broegbernensis gen. nov., sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000, 50, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.J.; Nah, S.S.; Min, B.R. A new technique for preparation of PDMS pervaporation membrane for VOC removal. Adv. Environ. Res. 2002, 6, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.F.; Huang, D.L.; Yang, F.L. Toluene recovery from simulated gas effluent using POMS membrane separation technique. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 66, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara-Fernandez, A.; Salgado-Ismodes, V.; Pino, M.; Hernandez, S.; Revah, S. Temperature and moisture effect on spore emission in the fungal biofiltration of hydrophobic VOCs. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2012, 47, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saucedo-Lucero, J.O.; Quijano, G.; Arriaga, S.; Munoz, R. Hexane abatement and spore emission control in a fungal biofilter-photoreactor hybrid unit. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 276, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilli, M.; Gianluca, C.; Nicolella, C. Detachment and emission of airborne bacteria in gas phase biofilm reactors. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 91, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottengraf, S.P.P.; Konings, J.H.G. Emission of microorganisms from biofilters. Bioprocess Eng. 1991, 7, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez-Monedero, M.A.; Stentiford, E.I.; Mondini, C. Biofiltration at composting facilities: Effectiveness for bioaerosol control. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4299–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielowiec-Korzeniowska, A.; Tymczyna, L.; Skórska, C.; Sitkowska, J.; Cholewa, G.; Dutkiewicz, J. Efficacy of a novel biofilter in hatchery sanitation: I. Removal of airborne bacteria, dust and endotoxin. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2007, 14, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vyskocil, J.M.; Létourneau, V.; Girard, M.; Lévesque, A.; Duchaine, C. Reduction of bioaerosols emitted from a swine confinement building by a percolating biofilter during a 10-month period. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, S.; Naidu, G.; Leiknes, T.O.; Vigneswaran, S. Comprehensive Membrane Science and Engineering. In Membrane Biofouling: Biofouling Assessment and Reduction Strategies in Seawater Reverse Osmosis Desalination, 2nd ed.; Drioli, E., Giorno, L., Fontananova, E., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK; Waltham, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 48–71. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, G.M.; Meier, J.; Kottke, V. Fouling in membrane apparatus: The mechanisms of particle deposition. Food Bioprod. Process. 1999, 77, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelicińska-Serafin, K.; Rolewicz-Kalińska, A.; Manczarski, P. VOC removal performance of a joint process coupling biofiltration and membrane-filtration treating food industry waste gas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rolewicz-Kalińska, A.; Lelicińska-Serafin, K.; Manczarski, P. Volatile organic compounds, ammonia and hydrogen sulphide removal using a two-stage membrane biofiltration process. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2021, 165, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirskaya, E.; Agranovski, I.E. Sources and mechanisms of bioaerosol generation in occupational environments. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 44, 739–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutgring, K.R.; Linton, R.H.; Zimmerman, N.J.; Peugh, M.; Heber, A.J. Distribution and quantification of bioaerosols in poultry-slaughtering plant. J. Food Protect. 1997, 60, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millner, P.D. Bioaerosols associated with animal production operations. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5379–5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lues, J.F.R.; Theron, M.M.; Venter, P.; Rasephei, M.H.R. Microbial composition in bioaerosols of a high-throughput chicken-slaughtering facility. Poultry Sci. 2007, 86, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlegelmilch, M.; Herold, T.; Streese, J.; Hensel, A.; Stegmann, R. The potential to reduce emissions of airborne microorganisms by means of biological waste gas treatment systems. Waste Manag. 2005, 25, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, D.D.; Smith, T.C.; Donham, K.J.; Hoff, S.J. The efficiency of biofilters at mitigating airborne MRSA from a swine nursery. J. Agric. Saf. Health 2015, 21, 217–227. [Google Scholar]
- Esquivel-Gonzalez, S.; Aizpuru, A.; Patrón-Soberano, A.; Arriaga, S. Characterization of bioaerosol emissions from two biofilters during treatment of toluene vapours using epifluorescence microscopy. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 123, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederickson, J.; Boardman, C.P.; Gladding, T.L.; Simpson, A.E.; Howell, G.; Sgouridis, F. Evidence: Biofilter Performance and Operation as Related to Commercial Composting; Environment Agency: Bristol, UK, 2013.
- Kummer, V.; Thiel, W.R. Bioaerosols–sources and control measures. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2008, 211, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühner, M. Kompostierung Unter Semipermeablen Membranen; Stuttgarter Berichte zur Abfallwirtschaft 78, Bielefeld, Schmidt, 2001. Available online: https://katalog.ub.tu-braunschweig.de/vufind/Search/Results?lookfor=%223-503-05788-9%22&type=ISN&sort=year (accessed on 23 May 2021).



| Parameter | CB | CBC |
|---|---|---|
| Total organic matter (% d.m.) | 86.0 (85.0–87.5) | 45.0 (40.6–47.8) |
| Total moisture content (%) | 63.4 (60.6–66.3) | 46.8 (42.7–50.5) |
| pH | 6.77 (6.75–6.79) | 7.44 (7.27–7.70) |
| Specific surface (m2/g) | 0.55 (0.37–0.67) | 1.67 (1.53–1.80) |
| Substitute diameter (mm) | 37.1 (34.8–39.6) | 8.7 (6.7–9.9) |
| Biofilter Bed | Membrane | Configuration |
|---|---|---|
| stumpwood chips and pine bark (CB) | none | CB |
| Pro Eko Tex UV (M1) | CB + M1 | |
| Pro Eko Tex UV 6 (M2) | CB + M2 | |
| stumpwood chips, pine bark, and compost from green waste (CBC) | none | CBC |
| Pro Eko Tex UV (M1) | CBC + M1 | |
| Pro Eko Tex UV 6 (M2) | CBC + M2 |
| Configuration | CB | CB + M1 | CB + M2 | Ambient Air (CB) | CBC | CBC + M1 | CBC + M2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CB + M1 | 0.00 (10) | ||||||
| CB + M2 | 0.00 (22) | 0.24 (1.4) | |||||
| Ambient Air (CB) | 0.02 (5.8) | 0.04 (4.1) | 0.18 (1.8) | ||||
| CBC | 0.51 (0.4) | ||||||
| CBC + M1 | 0.17 (1.9) | 0.00 (26) | |||||
| CBC + M2 | 0.44 (0.6) | 0.00 (42) | 0.75 (0.1) | ||||
| Ambient air (CBC) | 0.03 (4.6) | 0.00 (48) | 0.00 (10) | 0.00 (9.4) |
| Configuration | CB | CB + M1 | CB + M2 | Ambient air (CB) | CBC | CBC + M1 | CBC + M2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CB + M1 | 0.00 (32) | ||||||
| CB + M2 | 0.00 (>>4) | 0.06 (3.6) | |||||
| Ambient air (CB) | 0.00 (29) | 0.04 (4.1) | 0.65 (0.2) | ||||
| CBC | 0.00 (27) | ||||||
| CBC + M1 | 0.00 (31) | 0.00 (50) | |||||
| CBC + M2 | 0.00 (>>4) | 0.90 (0.01) | 0.00 (>>4) | ||||
| Ambient air (CBC) | 0.00 (>>4) | 0.00 (12) | 0.03 (4.8) | 0.00 (23) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muszyński, A.; Tabernacka, A.; Załęska-Radziwiłł, M. How to Reduce the Emission of Microorganisms from a Biofilter Used to Treat Waste Gas from a Food Industry Plant. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12060673
Muszyński A, Tabernacka A, Załęska-Radziwiłł M. How to Reduce the Emission of Microorganisms from a Biofilter Used to Treat Waste Gas from a Food Industry Plant. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(6):673. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12060673
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuszyński, Adam, Agnieszka Tabernacka, and Monika Załęska-Radziwiłł. 2021. "How to Reduce the Emission of Microorganisms from a Biofilter Used to Treat Waste Gas from a Food Industry Plant" Atmosphere 12, no. 6: 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12060673
APA StyleMuszyński, A., Tabernacka, A., & Załęska-Radziwiłł, M. (2021). How to Reduce the Emission of Microorganisms from a Biofilter Used to Treat Waste Gas from a Food Industry Plant. Atmosphere, 12(6), 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12060673






