Improved Estimates of the Vertical Structures of Rain Using Single Frequency Doppler Radars
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Basic Considerations
2.2. An Example
3. Some Results of Analyses
3.1. Lighter Convective Rain during Later Period of Convection
3.2. Convective Rain Early Period
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
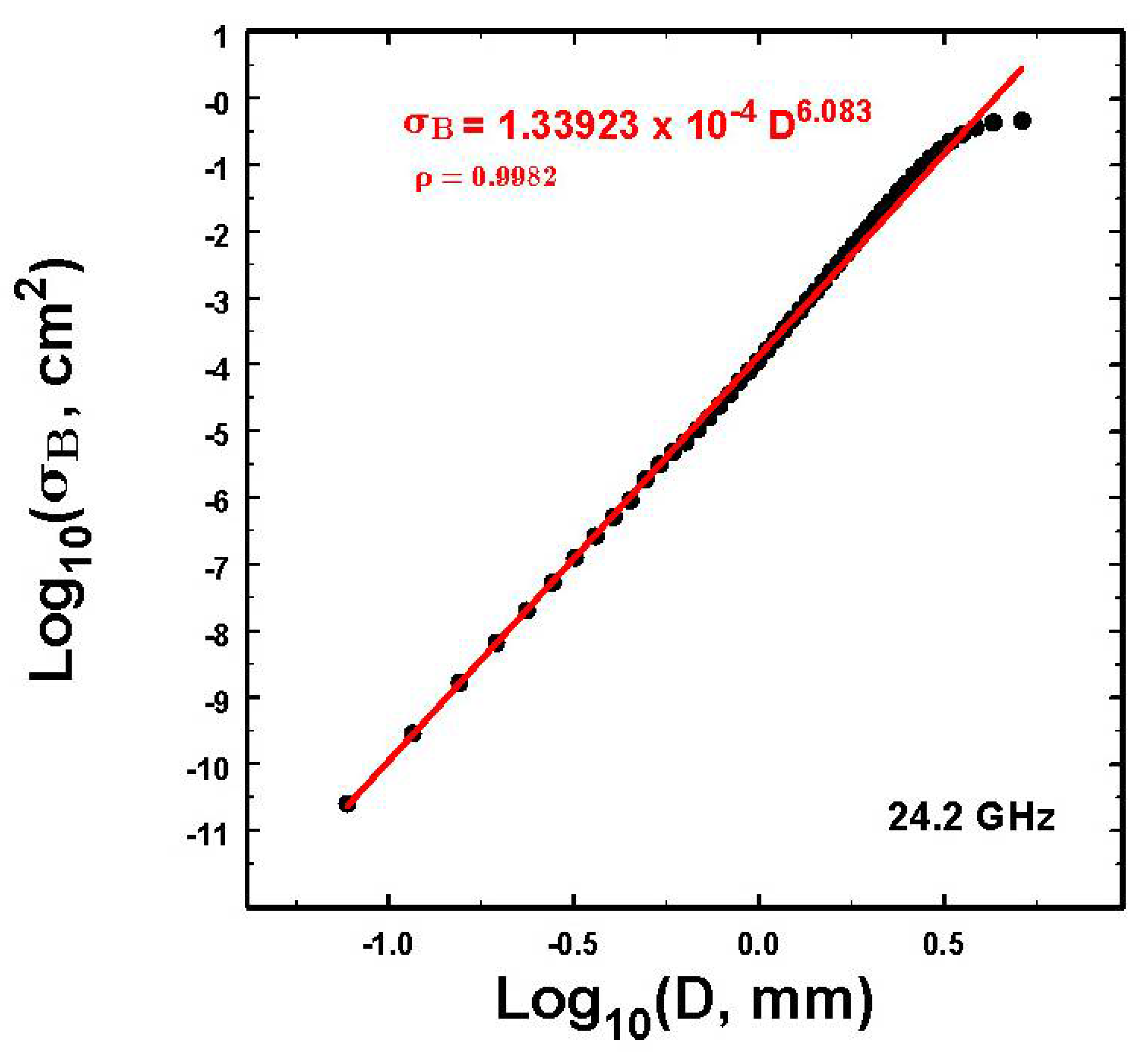
Appendix A.1. Backscatter Cross-Sections Used

Appendix A.2. Corrections to MRR Z



Appendix A.3. Examples of Solution Time–Height Profiles

References
- Probert-Jones, J.R.; Harper, W.G. Vertical Air Motion in Showers Revealed by Doppler Radar. In Proceedings of the Preprints of Papers; American Meteor Society: Kansas City, MO, USA, 1961; pp. 225–232. [Google Scholar]
- Caton, P.G.F. A Study of Raindrop-Size Distribution in the Free Atmosphere. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1966, 92, 577–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toit, P.S.D. Doppler Radar Observation of Drop Sizes in Continuous Rain. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1967, 6, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spilhaus, A.F. Raindrop Size, Shape and Falling Speed. J. Meteorol. 1948, 5, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gunn, R.; Kinzer, G.D. The Terminal Velocity OffallL for Water Droplets in Stagnant Air. J. Meteorol. 1949, 6, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foote, G.B.; Du Toit, P.S. Terminal Velocity of Raindrops Aloft. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1969, 8, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Battan, L.J. Some Observations of Vertical Velocities and Precipitation Sizes in a Thunderstorm. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1964, 3, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogers, R.R. An Extension of the Z-R Relation for Doppler Radar. In Proceedings of the Preprints of Papers; American Meteor Society: Boulder, CO, USA, 1964; pp. 158–161. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, R.R. Doppler Radar Investigation of Hawaiian Rain1. Tellus 1967, 19, 432–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhermitte, R.M. Observation of Rain at Vertical Incidence with a 94 GHz Doppler Radar: An Insight on Mie Scattering. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1988, 15, 1125–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhon, R.S.; Srivastava, R.C. Doppler Radar Observations of Drop-Size Distributions in a Thunderstorm. J. Atmos. Sci. 1971, 28, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Löffler-Mang, M.; Kunz, M.; Schmid, W. On the Performance of a Low-Cost K-Band Doppler Radar for Quantitative Rain Measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1999, 16, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, S.; Rakshit, G.; Maitra, A. Aliasing Effect Due to Convective Rain in Doppler Spectrum Observed by Micro Rain Radar at a Tropical Location. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 62, 2443–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameson, A.R. A Comparison of Microwave Techniques for Measuring Rainfall. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1991, 30, 32–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atlas, D. Advances in Radar Meteorology. In Advances in Geophysics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1964; Volume 10, pp. 317–478. ISBN 978-0-12-018810-9. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, J.S.; Palmer, W.M.K. The Distribution of Raindrops with Size. J. Meteorol. 1948, 5, 165–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameson, A.R.; Larsen, M.L.; Kostinski, A.B. Disdrometer Network Observations of Finescale Spatial–Temporal Clustering in Rain. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 72, 1648–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jameson, A.R.; Larsen, M.L. The Variability of the Rainfall Rate as a Function of Area. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 746–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beard, K.V.; Jameson, A.R. Raindrop Canting. J. Atmos. Sci. 1983, 40, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, C.R. Simultaneous Ambient Air Motion and Raindrop Size Distributions Retrieved from UHF Vertical Incident Profiler Observations: Simultaneous Ambient Air Motion and Raindrop Size Distributions. Radio Sci. 2002, 37, 8-1–8-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schumacher, C.; Stevenson, S.N.; Williams, C.R. Vertical Motions of the Tropical Convective Cloud Spectrum over Darwin, Australia: Vertical Motions of the Tropical Convective Cloud Spectrum. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 141, 2277–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brawn, D.; Upton, G. On the Measurement of Atmospheric Gamma Drop-Size Distributions. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2008, 9, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


















Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jameson, A.R.; Larsen, M.L.; Wolff, D.B. Improved Estimates of the Vertical Structures of Rain Using Single Frequency Doppler Radars. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12060699
Jameson AR, Larsen ML, Wolff DB. Improved Estimates of the Vertical Structures of Rain Using Single Frequency Doppler Radars. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(6):699. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12060699
Chicago/Turabian StyleJameson, Arthur R., Michael L. Larsen, and David B. Wolff. 2021. "Improved Estimates of the Vertical Structures of Rain Using Single Frequency Doppler Radars" Atmosphere 12, no. 6: 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12060699
APA StyleJameson, A. R., Larsen, M. L., & Wolff, D. B. (2021). Improved Estimates of the Vertical Structures of Rain Using Single Frequency Doppler Radars. Atmosphere, 12(6), 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12060699





