Abstract
It is necessary to consider all aspects of environmental factors when assessing the health impact of an eco-building environment on its occupants. However, the multi-criteria and imprecise nature of the indoor-environment in the eco-buildings has caused difficulties in quantifying the indoor environmental pollution level. This paper describes the optimal classification and priority weight methods, which are particularly useful for assessing the indoor environmental quality (IEQ) of an eco-building to demonstrate its innovative applications. The analytic hierarchy process (AHP) was used to set up the strategic decision-making evaluation system for computing the indoor environment index (IEI) risk ranking of eco-buildings. Combined with this, a Microsoft Delphi-based IEQ intelligent forecasting software simulations package was developed, and the innovative application of indoor environmental comprehensive assessment was verified by a case study in Shanghai. The evaluation result was analyzed by the priority weight methods and the AHP decision-making system noted above. This health assessment method and system provides an innovative way for the indoor environment risk evaluation of eco-buildings and is helpful to standardize the local building market.
1. Introduction
When considering the health effects of indoor environments, the national health and medical council of Australia (NHMRC) defines an “indoor environment” as “non-industrial indoor space spent more than one hour per day” [1]. The national institute for occupational safety and health (NIOSH) uses the term “indoor environmental quality” (IEQ) to describe environmental problems in different buildings [2,3,4]. Surveys found that these environmental problems were caused by secondary factors such as air quality, thermal comfort, sound, light, ergonomics, and work-related psychological stress [1]. These factors may act independently or together on employees and have adverse effects on the health of residents, such as health and SBS (Sick Building Syndrome) [2]. Therefore, it is necessary to objectively evaluate the indoor environment of eco-buildings and find out the main influencing factors of environmental problems on the health, comfort, and work efficiency of residents. To sum up, the use of IEQ can objectively reflect actual indoor problems. There is also a strong relationship between IEQ and productivity, and efforts to improve indoor environments demonstrate significant payoffs [5]. For example, a filter costs $23 per person, and the energy bill is $1 per person [6]. Good indoor environmental quality also ameliorates the impacts of building-related illness, absenteeism, and productivity loss, thereby improving overall job performance. As people spend 80–90% of their time indoors on average, an unhealthy indoor environment directly threatens people’s health [7,8]. The purpose of establishing the indoor environment evaluation system is to evaluate the indoor environment from the perspective of the environmental needs of personnel, to find out key factors affecting the indoor environment and their causes [1,9], and to take corresponding measures in the aspects of design, construction, and later improvements in order to achieve both efficiency and a healthy and comfortable indoor environment [10].
The indoor environmental impact assessment is also very important. The research content of the indoor environment mainly includes indoor air quality, indoor thermal comfort, indoor sound environment, and indoor light environment [3,4,11,12,13]. The purpose of studying the relationship between buildings and people in the indoor environment is to understand the needs of people and the environment [14]. The purpose of establishing an indoor environment evaluation system is to find a set of reasonable and appropriate index systems, establish the indoor environment evaluation model, and further search for ways to improve the indoor environment [10,15]. Since environmental assessment methodologies are designed to stimulate market demand for sustainable practices, the indoor environmental quality depends on the design and operation of eco-building systems that control thermal comfort, indoor air quality, acoustics, and light [1]. Indoor environmental issues must become an important part of global sustainable development, which is the consensus of “eco-building” activities [16]. The sustainable development of buildings is an important part of urban and even national sustainable development strategies [17].
Determining the design standard of eco-buildings is a critically impending task. The main goal of eco-building design is to provide a comfortable and healthy indoor environment while minimizing dependence on traditional mechanical equipment [18]. Therefore, for health reasons, the eco-building standard [19] is stricter than that of normal buildings, and these buildings: (1) try to use healthier green building materials to create higher air quality; (2) improve household “energy efficiency” and reduce CO2 emissions to below 1000 ppm; (3) control the concentration of particulate matter to below 0.15 mg/m3 [5]; (4) ensure thermal comfort. The implementation of thermal comfort has depended heavily on personal experience and the applicability of common estimation methods. PMV (predicted mean vote) and PPD (predicted percentage dissatisfied) cannot conclusively be predicted in advance [4]. Humidity will lead to mold growth, and rain will eventually enter the building, causing problems. Therefore, the ventilation system is designed to keep the indoor relative humidity between 40% and 70% for the thermal index. The temperature in winter should be controlled between 17 °C and 27 °C, which is different from the temperature range in summer [20]. (5) Noise would be controlled to below 50 dB [1]. (6) Ensure adequate lighting, utilizing sunshine and appropriate insulation to make the house more efficient in cooling and heating [20]. Therefore, it is a global trend to develop a system that comprehensively evaluates eco-buildings at different environmental scales: global, local, and indoor issues [21,22].
Researchers have established several indoor environmental evaluation systems based on local environmental and economic conditions. Researchers have also used different methodologies to describe a similar goal, including the IEQ model [21,23], the IEQ index [9,13], and scoring systems [24,25]. As used in this study, IEQ includes acoustics, indoor air quality, lighting, and thermal comfort. There are many methods to determine the weights of the indoor environment factors in a comprehensive evaluation, such as Yu et al. [10], Cao et al. [26], Nizam et al. [27] and Ncube & Riffat [28], etc., who use the multiple linear regression of occupant response to determine the category weight. Heinzerling et al. [21] and Sarbu & Sebarchievici [22] also summarized many literature reviews on IEQ category weights. To investigate the relationship between IEQ classification and overall job satisfaction, Piasecki & Barbara Kostyrko [29] used a mixed-model logistic regression to provide a detailed analysis of the relative importance of IEQ categories and building characteristics. Xinheng Wang et al. [30] proposed a localization and mapping (SLAM) method for sustainable performance evaluation and building envelope design. Hüls et al. [24] used a test room for controlled experiments, exposing occupants to variable IEQ conditions and a different number of adaptive control opportunities. Generally, residential and office buildings have considered separately. However, the rooms for different purposes are not divided in detail. Yu et al. [10] used the expert scoring method to measure and analyze the weight distributions of magnetic fields existing in all indoor environments. Shad et al. [31] developed an Iranian green building assessment tool using decision-making methods and GIS and used it in the city of Mashhad. Iwaro et al. [32] developed a comprehensive standard weighting framework for environmental evaluation. Alyami et al. [33] also established an indoor environmental assessment system for office buildings in Saudi Arabia, where the climate is hot and dry.
Therefore, it is necessary to establish a set of comprehensive eco-building indoor environment evaluation systems considering all acoustics, indoor air quality, lighting, and thermal comfort indexes suitable for national conditions and regional climate conditions.
2. Methodology
To develop an integrated sustainable performance evaluation framework for the standard weight of building envelope, we evaluated several subjective weighting methods, including the expert evaluation, experience weighting, statistical average, index, index of the phase comparison, flexible preference matrix, sampling weight, proportion of weighting, stepwise regression, the grey correlation, and principal component analysis (PCA) methods [19,24,25,26,27,34,35]. One major shortcoming of these methods is that they are solely based on the judgment of policymakers, and lack of knowledge and experience may have a negative influence on the judgment of the decision-makers [19,20]. To avoid these shortcomings, this study used the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) to determine the decision-making system. The principle of the AHP decision-making system is strictly mathematical, and it is widely used in complex systems analysis and decision-making [36,37,38]. C. Chiang et al. [39,40] used the AHP decision-making system to sample professionals to determine the appropriate weights in Taiwan. Chiang & Lai [25] used the AHP decision-making system to score the indoor environment of a building, which was divided into four categories: indoor air quality (IAQ), thermal comfort, insulation, and lighting. To overcome the above-mentioned technical challenges, this study intends to design a reliable priority weighting system to conduct the IEQ health assessment for eco-buildings. The AHP decision-making system has been widely used in many fields, such as innovation management [26,27,28]. As AHP decision-making methods involve both quantitative and qualitative aspects, its unique analytical structure transforms natural thinking into a quantitative process. Furthermore, AHP technology can improve decision analysis and provide a powerful tool for dealing with complex decisions. Therefore, this study used AHP to develop a suitable decision-making system.
In IEQ risk assessment of eco-building, the indoor environment includes indoor air quality, thermal, acoustics, and lighting. Each factor is controlled by various indicators that have a synergistic effect. The comprehensive IEQ index health risk assessment includes four sub-indicators: the indoor air quality (IAQ), thermal comfort (TC), acoustics (AC), and lighting quality (L) indexes. It is feasible to evaluate environmental quality by combining the above four sub-indicators. This paper uses the analytic hierarchy decision-making method to evaluate and analyze the optimal classification and priority weight of the evaluation indicators.
2.1. Optimal Classification and Priority Weight Methods
Multiply the four sub-indexes (M) by their respective weight Wi (Table 1) to obtain the final IEQ index. The comprehensive index, the indoor environment score (IEQ) was proposed to evaluate the indoor environment of eco-buildings, as shown in Equation (1).

Table 1.
Priority Weight Matrix.
In Equation (1), Si is the correlation between all functions Si = f(x) and the indoor air quality and physical environment parameters. For example, if x selects the IAQ index (IAQi), thermal comfort index (TCi), acoustic index (ACi), and lighting quality index (Li), the IEQ index will be rewritten as Equation (2).
IEQ index =W1 × IAQi + W2 × TCi + W3 × ACi + W4 × Li
Wi is calculated in Equation (3),
where, aij is the index element of eco-building. The evaluation scores of the ith index in category x and Sxi are evaluated on a score grade of 40, 60, 80, and 100, respectively, which correspond to the environmental risk value of the eco-building to human health, comfort, and productivity. When the Sxi score exceeds 60, there is no health risk. If Sxi < 60, that is, the ith index does not meet the requirements of national standards, then Sx is the minimum value of Sxi; otherwise, Sx is the weighted average value of Sxi. To calculate Si, Equation (4) is used, where PPD is the predicted percentage dissatisfied and PD (Si) is the percentage dissatisfied with the IEQ subcomponent (Si) level.
SD (Si) =SD (PD (Si))
2.2. AHP Decision-Making System
To remedy potential defects in the evaluation and weighting methods, especially in determining the classification of weight and index features, the AHP decision-making system was used. Based on the four environmental categories of thermal comfort, indoor air quality, acoustics, and light, the sensitivity curves of the four environmental categories unsatisfactory to the human body were determined as shown in Equation (5). The results were that: thermal index PD(TC) ≤ 10% (−0.5 ≤ PMV ≤ 0.5), acoustic index PD(AC) ≤ 20% (LAeq ≤ 50 dB), photosensitive index PD(L) ≤ 20%(illuminance: 500–1000 lx), indoor air quality index PD(IAQ) ≤ 20% (dp < 3) were considered unsatisfactory. The judgment matrix S was thus obtained:
Based on the above method, the indoor air quality index (IAQi) of office buildings was selected based on the survey results of the indoor air quality of office buildings in Shanghai [31]. Optimal classification was based on national and international standards. Most indicators can be divided into four categories. The value that each index sets in the national standard is equivalent to 3. According to the influence of indoor air pollutants on the human body, the indoor air quality index was priority-weighted [29]. Professor Fanger proposed the thermal comfort equation, PMV, and PPD [41]. Using these methods, researchers have established a series of thermal comfort standards over the past decades, such as Fanger 198063, ASHRAE 55, and ISO 7730 [42,43]. The standard gives a range of thermal environmental parameters that most people (80%) consider acceptable. So, in this study, the thermal comfort index (TCi) was selected according to ISO 7730 and ASHRAE 55, which dictate that thermal comfort can be achieved based on an 80% or greater occupant satisfaction rate. The remaining percentage of people can experience 10% dissatisfaction based on whole-body discomfort (all listed influencing factors of PMV) and 10% dissatisfaction based on local discomfort/partial body discomfort (includes fewer factors than whole-body) [44]. Due to the different requirements of different seasons, the classification of some thermal indicators (indoor temperature and relative humidity) are also considered seasonally. To balance academic research and practicability and to comply with ASHRAE 55, the recommended thermal limit on the 7-point scale of PMV was between −0.5 and 0.5.
There are three kinds of acoustics indexes (ACi) related to eco-buildings. The first is the indoor background index, used to evaluate the noise generated by HVAC systems and electrical equipment. Since it could not evaluate low-frequency noise and because of the inconvenience, it was not adopted in our system. The second is the time-weighted equalization sound pressure (LAeq) and time-distributed statistical sound pressure (Ln) levels, which can be used to evaluate the real noise situation. The third category is related to sound interference, including reverberation time (T60), and sound interference level (SIL), which can be used for meeting rooms, multi-function halls, and open office acoustic environment assessments. Among them, the classification of T60 is related to the use and size of the room. In order to consider impulse noises such as ringing telephones, the time-noise statistical sound pressure level (L5) was selected as the additional point in the office assessment score. When evaluating the lighting quality index (Li), researchers usually choose the index associated with lamps and pay attention to the spatial configuration of the office, such as illuminance, illuminance uniformity ratio, brightness, glare index, color temperature, color rendering index, day lighting ratio, etc. The relationship between the weight of the acoustic and lighting indicators and the intensities of their impact on the human body is not clear, so the relative weight of these indicators in the respective evaluation items were the same in this study. To facilitate the AHP decision making process, this paper uses software development to further evaluate the Shanghai case study, including the optimal classification and priority weighting methods described above.
3. Case studies
3.1. IEQ Priority Weight Calculation
The overall goal of this case study is to demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed priority weighted system, combined with the AHP decision-making system, to measure IEQ. The practical application of this study was carried out in selected offices and residences in one of the largest cities in Shanghai [45]. In this paper, indoor air quality and thermal standard use international standards such as EN 16798-1, ISO 7730; ASHRAE 55 [42,43], and EN 12464 were used as the indoor air pollutant and thermal indexes [29], and the civil building noise insulation standard design ASTM E1374 was used as the architectural acoustics index [46], and the lighting design EN12464-1 standard was adopted [47]. According to Equations (3)–(5), the IEQ weight index was deduced from four factors, including thermal comfort, IAQ, acoustic comfort, and lighting, as shown in Table 2. The AHP was used to calculate the IEQ parameters decision-making system, and the results were compared with those in Table 3.

Table 2.
Various environmental health assessment index classifications and weighting.

Table 3.
The weighting of IEQ parameters compared with the literature.
The average weight of the IEQ parameters was then compared with some references [26,28,38], as shown in Table 3 below. References also indicate that different types of eco-buildings may use different IEQ weights, which will be further examined in the case studies.
Once the weighting of the IEQ parameters was attained. Equation (1) could be rewritten as Equation (6).
3.2. AHP Decision-Making
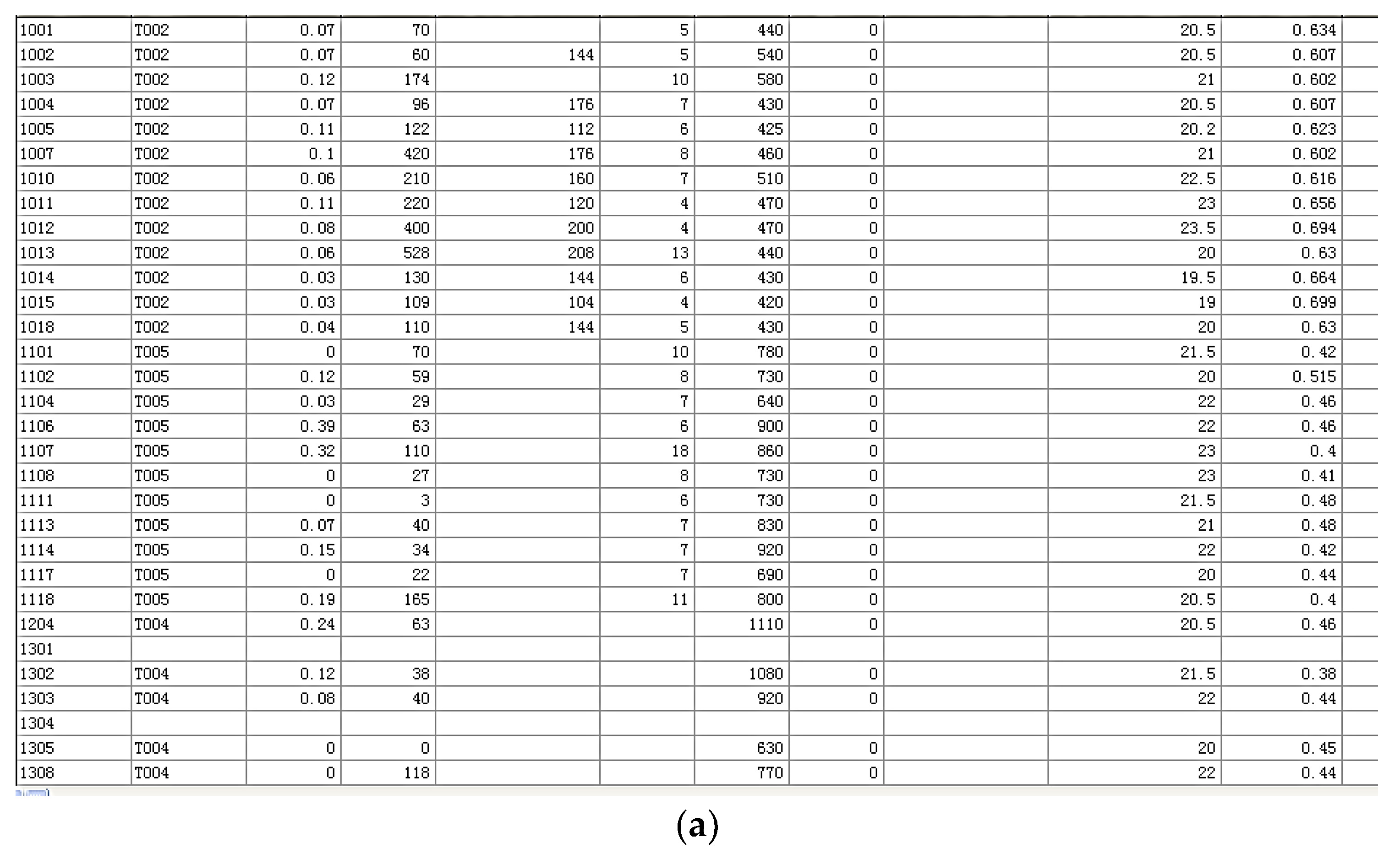
In this study, based on Table 2 of Section 3.1, the case study parameters mainly considered various factors such as thermal, light, heat, and IAQ to select the indexes and their classifications. The selection of indexes was based on comprehensiveness and operability. Input data were chosen according to the indoor environment characteristics of the different function rooms and the different degrees of the influence of the environmental factors on the human body. The weight of each factor in evaluating the indoor environment was determined according to Table 3. The standards of choosing the data and their scoring sequences can be divided into: questionnaires, single index grading and scoring, similar multiple indicators weighting, and multiple environmental factors weighting to finally complete the indoor environment grading and scoring of a single room. According to the standard, 109 tests and 190 questionnaires were carried out on the comprehensive environmental health assessment of residence and offices in Shanghai for one year, covering four different seasons. The indoor thermal environment parameters mainly included indoor air temperature, average radiant temperature, relative wind speed, and relative humidity. However, the average (mean) radiant temperature is relatively difficult to test in practice, as it is not included in the national civil building standards relating to Chinese buildings. Therefore, the selection of objective thermal environment assessment system indicators was only considered by the thermal questionnaires in this case study. The main IAQ indexes reflecting indoor air pollution mainly include formaldehyde, TVOC, benzene, ammonia, and radon. The results of each test area in the indoor environment are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Indoor environmental data summary.
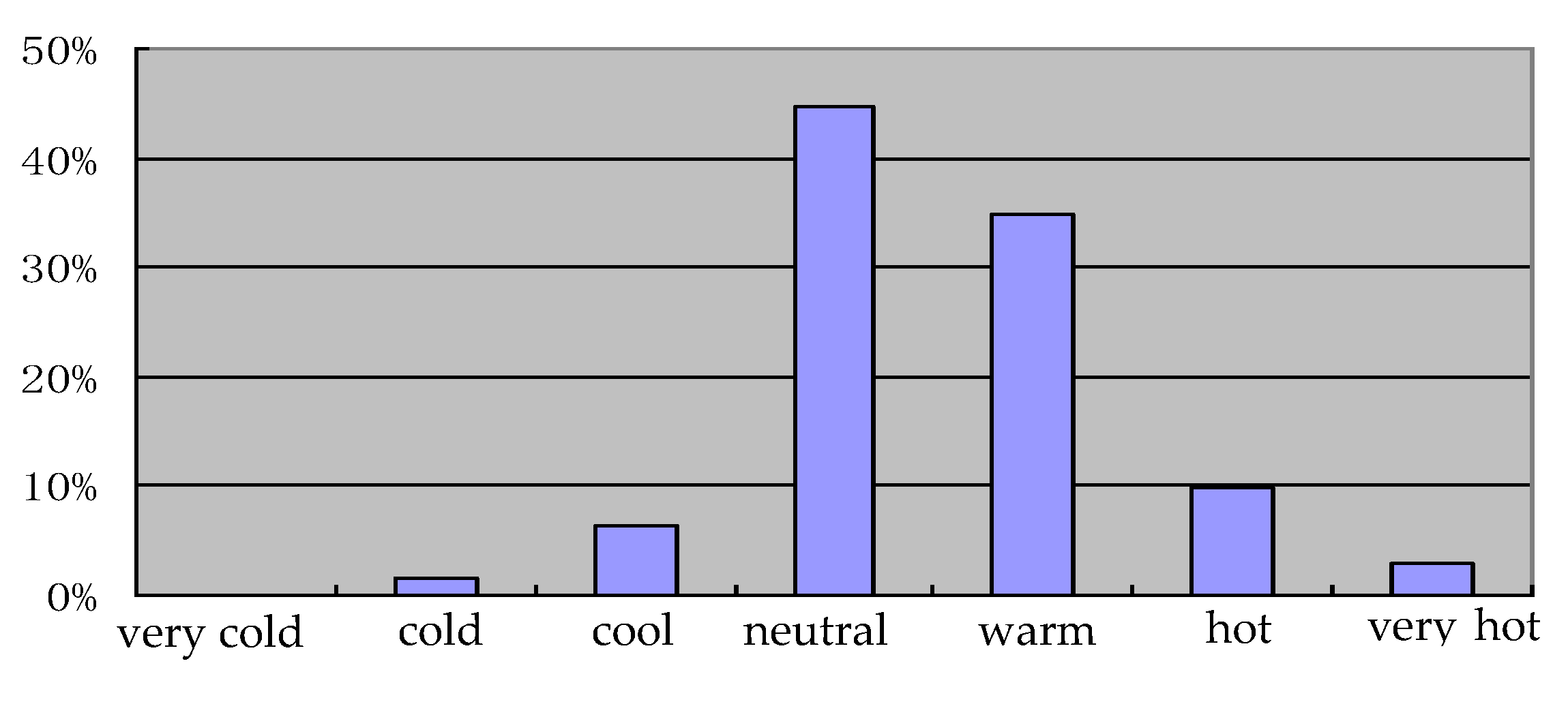
For indoor air quality, the main detection items were the concentrations of formaldehyde, TVOC, benzene, toluene, and xylene, while the other detection items were indoor temperature, background noise; the thermal, acoustic, and light environments; subjective satisfaction etc. The main IAQ instruments used in this experiment were an atmospheric sampler (SQC-1000), an ultraviolet spectrophotometer (Genesys II), a gas chromatography-mass spectrometer (Trace DSQ), and an environmental radon meter (FD216). Acoustic and lighting monitors were used for the noise and lighting indexes, and a data logger, sensors for humidity, air temperature, and airspeed at heights of 0.1 m, 0.6 m and 1.1 m to comply with ASHRAE 55-2017 were used in conjunction with an occupant questionnaire to evaluate the acceptability of the indoor thermal environment [42]. The results of the questionnaire results are listed in Figure 1. According to the test results analysis (see Figure 1), the thermal-neutral temperature in the Shanghai area under natural ventilation should be between 27.8 °C and 28.1 °C. The results are very reasonable since electric fans are primarily used from June to October, while air conditioners are mostly used from July to September in Shanghai. Heating in winter is used mainly from December to January in Shanghai.
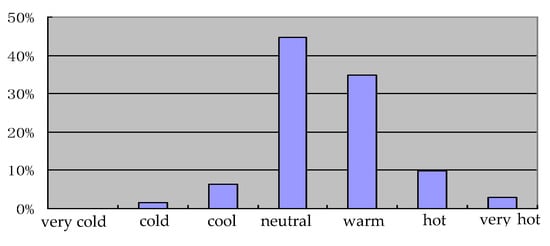
Figure 1.
Indoor objective thermal index evaluated score results.
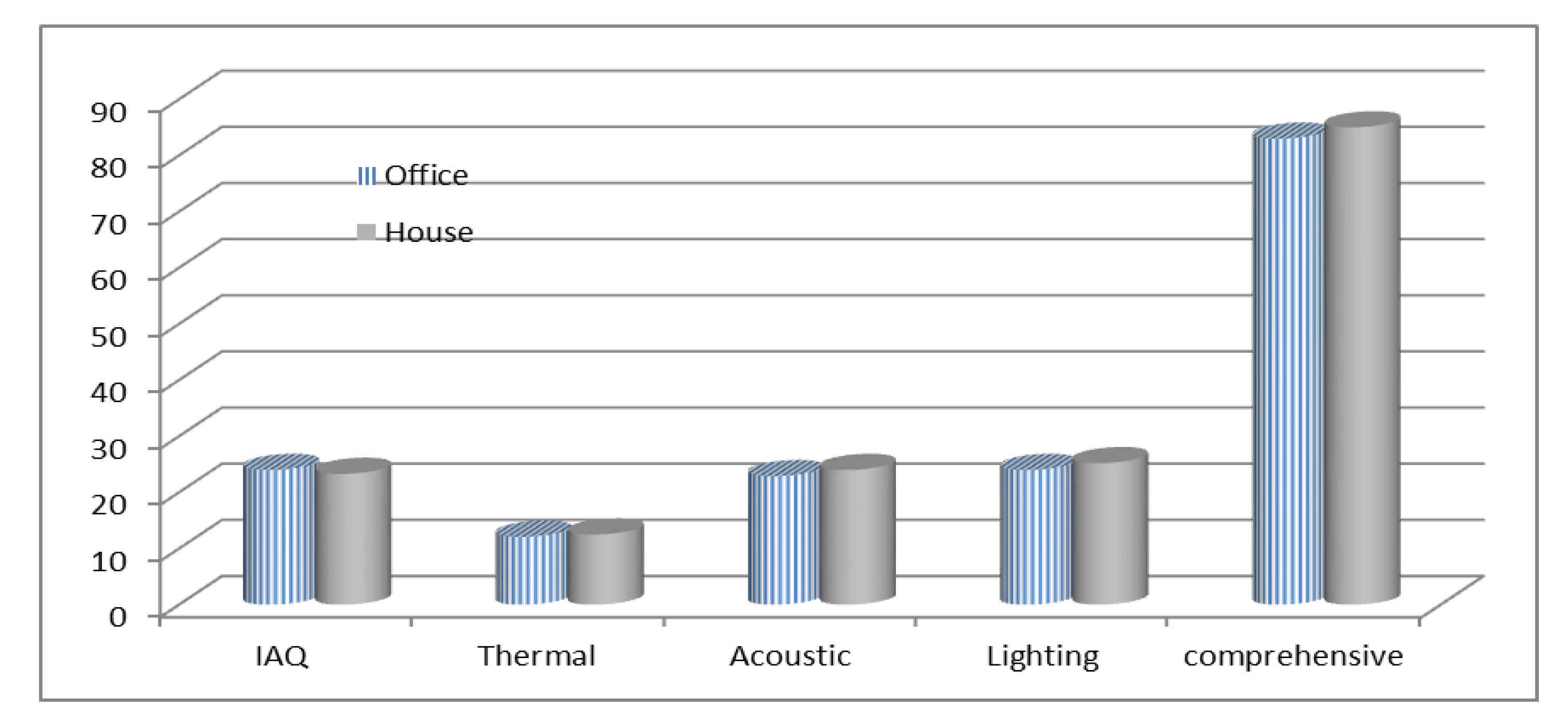
The case study results show how to use the proposed AHP decision-making system for the analysis data collected in Table 4. Using Equation (6), the final results of this case study are demonstrated in Figure 2. The method described above can be carried out to evaluate the indoor environment of different types of eco-buildings. An assessment structure needs to consist of the scores derived from all the rooms in the building for an office building. The weighting means method was used to organize the scores of the rooms. At first, the assessment was of a single room and then it was included in the integrated assessment of the whole building. The building rooms were sorted into meeting rooms, general offices, open-plan offices, and designing and drawing rooms, after evaluation. Rooms with the same purpose were evaluated together. Finally, the score values were the weighted means of all the rooms. The weighting was based on the area of the room. In conclusion, the building was evaluated by the scores of all the purpose rooms. The weighting was also based on the total area of the rooms with the same purpose.
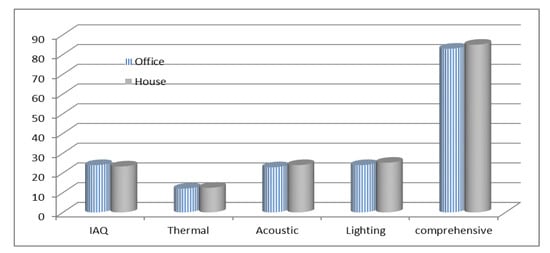
Figure 2.
Indoor environmental index (IAQ, thermal, acoustic, lighting, and comprehensive index) evaluated score results.
3.3. Intelligent Forecasting
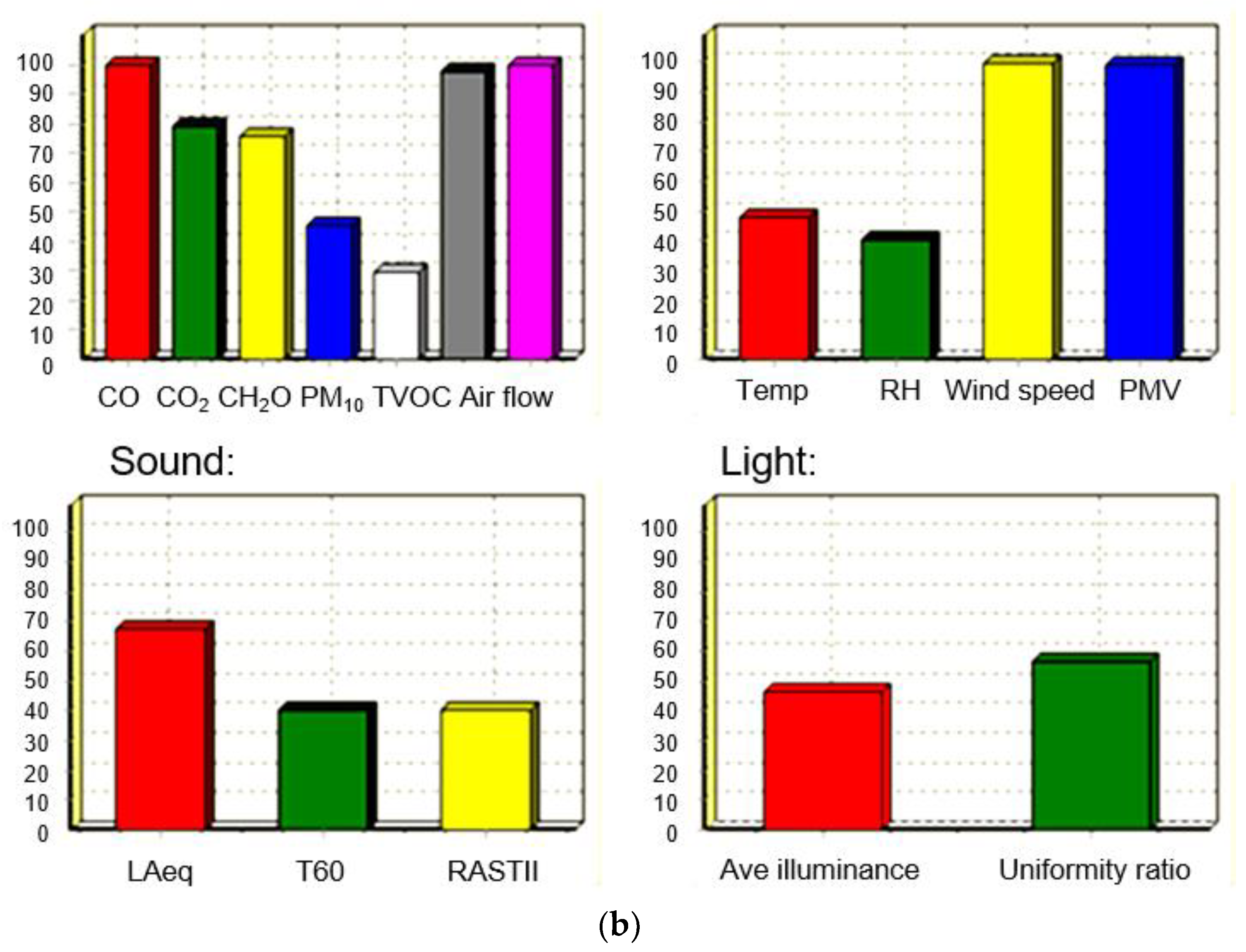
This research makes use of the AHP decision-making system for the comprehensive evaluation of the indoor environment, and a Microsoft Delphi-based IEQ intelligent forecasting software simulations package was developed (Figure 3) [45]. This software played an essential role in the verification of the environmental assessment methods [34]. For example, in Figure 3a, the forecasting software first analyzed the historical meteorological data of Shanghai belonging to this case, including temperature, relative humidity, air pressure, wind speed, etc. Furthermore, a comprehensive assessment of the thermal comfort, IAQ, acoustic, and lighting indexes and their environmental impacts, as well as a database of environmental conditions, building materials and construction properties, were input in the software in Figure 3b [29,34].
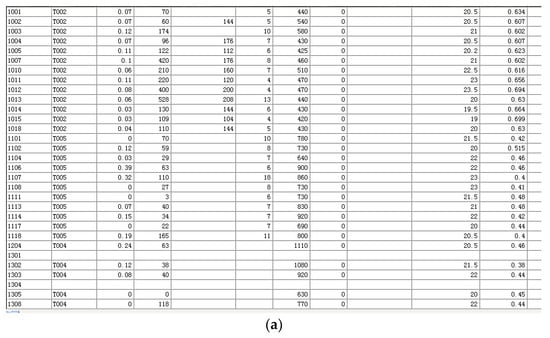
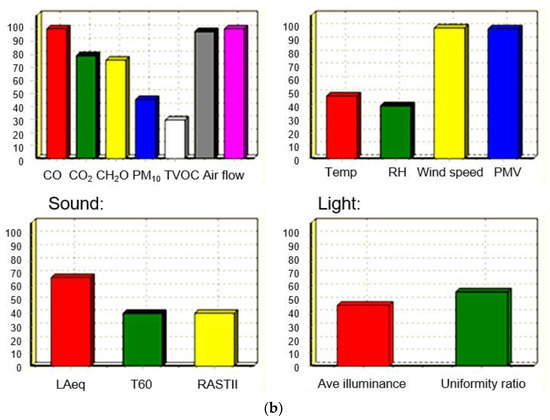
Figure 3.
The Microsoft Delphi-based IEQ simulation tool of IEQ comprehensive health assessment: (a) database; (b) modeling results.
The indoor environmental assessment, the main component of the software, includes three main parts: detection, evaluation, and improvement (Figure 3b). The evaluation part includes testing, which involves elements of standards, instruments, personnel, testing systems, and other aspects of the input elements. The evaluation part includes time, place, and the corresponding assessment model. The improvement part includes the eco-building itself. Finally, the data in Table 4 were calculated in the model, and the evaluation conclusion was obtained (Figure 3b). In Figure 3b, measurements of indoor environmental variables, such as indoor air quality pollutants, air temperature, relative humidity, air velocity, luminance, and a-weighted sound pressure level, are listed.
4. Discussion
The comprehensive evaluation of the indoor environment using the AHP decision-making system can make indoor environmental impact assessments more quantitative. For example, considering all kinds of factors such as sound, light, heat and IAQ, the selection of indexes and their grading, the selection of indexes is comprehensive and operable. According to the indoor environment characteristics of the different functional rooms in the case study and the different degree of the influence on the human body of the environmental factors, the weight of each factor in evaluating the indoor environment was determined. The analytic hierarchy framework effectively adjusts the priority weighting evaluation system and makes the assessment results more reasonable. The analytic hierarchy process (AHP) was used to obtain the corresponding weights of the indoor environment, and then the classes with weights lower than 0.1 were removed. Finally, the classes that needed to be considered in the evaluation of the indoor environment were obtained, which were, in order of weight, IAQ (0.286), thermal comfort (0.142), acoustic environment (0.286), and light environment (0.286).
There are some limitations to this study. For example, in order to keep these results reasonable, some factors that can affect the assessment should be paid attention to. For example, physical measurements of acoustics and light environments will continue to be limited to relatively inexpensive, accurate, and widely available ranges, which provide minimal and necessarily different images of indoor environments and surveys of their actual users. Secondly, a complete evaluation system needs to be based on a standardized data acquisition method, and only on this data basis can there be a comparison between the objects evaluated. Thirdly, AHP decision-making is an evaluation framework to study the process of dynamic change, which requires a large quantity of data. Therefore, in the future, it is necessary to continue to study more data fom field measurements and subjective questionnaires from local office buildings to obtain better AHP decision-making results. As the main tool for analyzing the input data, the comprehensive evaluation software, needs to be updated with the updated measurement data or questionnaire data.
5. Conclusions
To better measure and assess their health effects and take an innovative applications study on new green building techniques, the paper presents an optimal classification and priority weight method to perform the indoor environmental health assessments of eco-buildings.
This paper describes that the optimal classification and priority weight methods are effective methods to evaluate the indoor health quality of eco-buildings. These methods were used to set up the strategic decision-making evaluation system for computing the indoor environment index (IEI) risk ranking of eco-buildings. The following lists the main conclusions: (1) An analytic hierarchy process (AHP) strategic decision-making system was set up to provide a quantitative method to evaluate the health situation of eco-buildings and to promote their strategic risk rankings. (2) The optimal classification and priority weight methods were used to evaluate IEI risk ranking. IEQ parameters accounted for the IAQ (IAQi), thermal comfort (TCi), acoustic (ACi), and lighting quality (Li) indexes. Numerical values of IEQ improvement in the Shanghai case study were 83 for an office and 85 for a house. (3) A Microsoft Delphi-based IEQ intelligent forecasting software simulations package was developed. Moreover, (4) An indoor environmental comprehensive assessment was verified by a case study in Shanghai to demonstrate its innovative applications. The case study in Shanghai, including the above optimal classification and priority weight methods, was developed to facilitate the AHP decision-making process. It could serve as a multi-level IEQ assessment framework.
A better IEQ can guide the further use of some new advanced intelligent integrated control systems in eco-buildings. This new indoor environmental impact assessment framework can repeatedly test the sustainability and health level of eco-buildings until better environmental quality is achieved.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.Z.; Funding acquisition, L.Z.; Investigation, G.A.S.; English checking, M.V.; Project administration, writing, review & editing—original draft, J.Y.; review & editing, L.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding, and the APC was funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- Yang, W.; Moon, H.J. Combined effects of acoustic, thermal, and illumination conditions on the comfort of discrete senses and overall indoor environment. Build. Environ. 2019, 148, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Health Risk Assessment of Air Pollution—General Principles, World Health Organization. 2016. Available online: http://www.euro.who.int/pubrequest%0A (accessed on 20 July 2016).
- D’Ambrosio, F.R.A.; Olesen, B.W.; Palella, B.I.; Riccio, G. Thermal comfort: Design and assessment for energy saving. Energy Build. 2014, 81, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellia, L.; Alfano, F.R.D.; Fragliasso, F.; Palella, B.I.; Riccio, G. On the interaction between lighting and thermal comfort: An integrated approach to IEQ. Energy Build. 2021, 231, 110570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdou, A.A.A.; Abdou, O.A.; El Kholy, G.M. Correlation between indoor environmental quality and productivity in buildings. In Proceedings of the 19th IASP Conference, Alexandria, Egypt, 20–21 May 2006; p. 732. [Google Scholar]
- Tham, K.W.; Parshetti, G.K.; Anand, P.; Cheong, D.K.W.; Sekhar, C. Performance characteristics of a fan filter unit (FFU) in mitigating particulate matter levels in a naturally ventilated classroom during haze conditions. Indoor Air 2021, 31, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Yuan, J.; Fleck, B. Fleck Indoor Environmental Quality Evaluation of Lecture Classrooms in an Institutional Building in a Cold Climate. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yuan, J.; Wang, B. Prediction and analysis of PM2.5 in Fuling District of Chongqing by artificial neural network. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskari, M.; Karatasou, S.; Santamouris, M. A methodology for the determination of indoor environmental quality in residential buildings through the monitoring of fundamental environmental parameters: A proposed Dwelling Environmental Quality Index. Indoor Built Environ. 2017, 26, 813–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Li, B.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q. A development of a rating method and weighting system for green store buildings in China. Renew. Energy 2015, 73, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.L.; Zhang, L.Z. Membrane-based enthalpy exchanger: Material considerations and clarification of moisture resistance. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 189, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofia-Natalia, B.; Irulegi, O.; Santamouris, M. Energy Performance of Buildings; Boemi, N., Irulegi, O., Santamouris, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Litti, G.; Audenaert, A.; Braet, J.; Fabbri, K.; Weeren, A. Synthetic scan and simultaneous index aimed at the Indoor Environmental Quality evaluation and certification for people and artworks in heritage buildings. Energy Procedia 2015, 78, 1365–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Meng, Q.; Li, L.; Mu, J. Interaction between sound and thermal influences on patient comfort in the hospitals of China’s northern heating region. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluyssen, P.M.; Janssen, S.; van den Brink, L.H.; de Kluizenaar, Y. Assessment of wellbeing in an indoor office environment. Build. Environ. 2011, 46, 2632–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda, C.A.; Lipsett, M. A Review of Sustainability Assessment and Sustainability/Environmental Rating Systems and Credit Weighting Tools. J. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 4, 36–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonstra, C.; Pettersen, T.D. Tools for environmental assessment of existing buildings. Ind. Environ. 2003, 26, 80–83. [Google Scholar]
- Assefa, G.; Glaumann, M.; Malmqvist, T.; Kindembe, B.; Hult, M.; Myhr, U.; Eriksson, O. Environmental assessment of building properties—Where natural and social sciences meet: The case of EcoEffect. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 1458–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, P. Criteria for Design of Indoor Environment in Sustainable Buildings; IAQ Standards & Guidelines: ROC, Taiwan, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chinazzo, G.; Wienold, J.; Andersen, M. Influence of indoor temperature and daylight illuminance on visual perception. Lighting Res. Technol. 2020, 52, 350–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinzerling, D.; Schiavon, S.; Webster, T.; Arens, E. Indoor environmental quality assessment models: A literature review and a proposed weighting and classification scheme. Build. Environ. 2013, 70, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbu, I.; Sebarchievici, C. Aspects of indoor environmental quality assessment in buildings. Energy Build. 2013, 60, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, M.P.; Stout, N.K.; Adamkiewicz, G.; Geggel, A.; Ren, C.; Sandel, M.; Levy, J.I. The effects of indoor environmental exposures on pediatric asthma: A discrete event simulation model. Environ. Health 2012, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hüls, A.; Krämer, U.; Carlsten, C.; Schikowski, T.; Ickstadt, K.; Schwender, H. Comparison of weighting approaches for genetic risk scores in gene-environment interaction studies. BMC Genet. 2017, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, C.M.; Lai, C.M. A study on the comprehensive indicator of indoor environment assessment for occupants’ health in Taiwan. Build. Environ. 2002, 37, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Ouyang, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, L.; Hu, H.; Deng, G. Development of a multivariate regression model for overall satisfaction in public buildings based on field studies in Beijing and Shanghai. Build. Environ. 2012, 47, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizam, S.; Choen, E.; Lou, W.; Fung, P.; Wood, R.; Che-ani, A.I. Developing weighting system for refurbishment building assessment scheme in Malaysia through analytic hierarchy process (AHP) approach. Energy Policy 2018, 112, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ncube, M.; Riffat, S. Developing an indoor environment quality tool for assessment of mechanically ventilated office buildings in the UK—A preliminary study. Build. Environ. 2012, 53, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piasecki, M.; Kostyrko, K.B. Indoor environmental quality assessment, part 2: Model reliability analysis. J. Build. Phys. 2018, 42, 288–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, F.; Dong, Y.; Xu, X. Exponentially weighted particle filter for simultaneous localization and mapping based on magnetic field measurements. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2017, 66, 1658–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shad, R.; Khorrami, M.; Ghaemi, M. Developing an Iranian green building assessment tool using decision making methods and geographical information system: Case study in Mashhad city. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 324–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaro, J.; Mwasha, A.; Williams, R.G.; Zico, R. An Integrated Criteria Weighting Framework for the sustainable performance assessment and design of building envelope. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 29, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyami, S.H.; Rezgui, Y.; Kwan, A. The development of sustainable assessment method for Saudi Arabia built environment: Weighting system. Sustain. Sci. 2015, 10, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Moon, H.J.; Jeon, J.Y. Comparison of response scales as measures of indoor environmental perception in combined thermal and acoustic conditions. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S. Quantitative Risk Assessment of Environmental Hazards. Annu. Rev. Public Health 1985, 6, 247–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myhr, U. Assessing the Outdoor Environment Close To Buildings. Building 2005, 2005, 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaian, S.; Jozi, S.A. Health- Safety and Environmental Risk Assessment of Refineries Using of Multi Criteria Decision Making Method. APCBEE Procedia 2012, 3, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, L.G.V.; Thomas, L. Models, Methods, Concepts & Applications of the Analytic Hierarchy Process; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, C.; Chou, P.; Lai, C.; Li, Y.; Tu, Y. A Study of the Comprehensive Indicators for Indoor. Build. Environ. 2002, 37, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.K.; Li, H. Application of the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) in multi-criteria analysis of the selection of intelligent building systems. Build. Environ. 2008, 43, 108–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanger, P.O. Thermal Comfort; Danish Technical Press: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Ashrae Standard Project Committee. Thermal Environmental Conditions For Human Occupancy; American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Airconditioning Engineers, Inc.: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 7730:2005. Ergonomics of the Thermal Environment—Analytical Determination and Interpretation of Thermal Comfort Using Calculation of the PMV and PPD Indices and Local Thermal Comfort Criteria; International Organization for Standardization [ISO]: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- D’Ambrosio, F.R.A.; Olesen, B.W.; Palella, B.I.; Pepe, D.; Riccio, G. Fifty Years of PMV Model: Reliability, Implementation and Design of Software for Its Calculation. Atmosphere 2019, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhong, L.; Wang, B. Indoor air quality management based on fuzzy risk assessment and its case study. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM-E1374. Standard Guide for Office Acoustics and Applicable; ASTM Standards: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- EN 12464-1. Light and Lighting—Lighting of Work Places—Part 1: Indoor Work Places; Comite Europeen de Normalisation: Brussels, Belgium, 2011. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).