Modeling Investigation of Brown Carbon Aerosol and Its Light Absorption in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model Description
2.1. Emissions
2.2. Treatment of Brown Carbon
3. Results
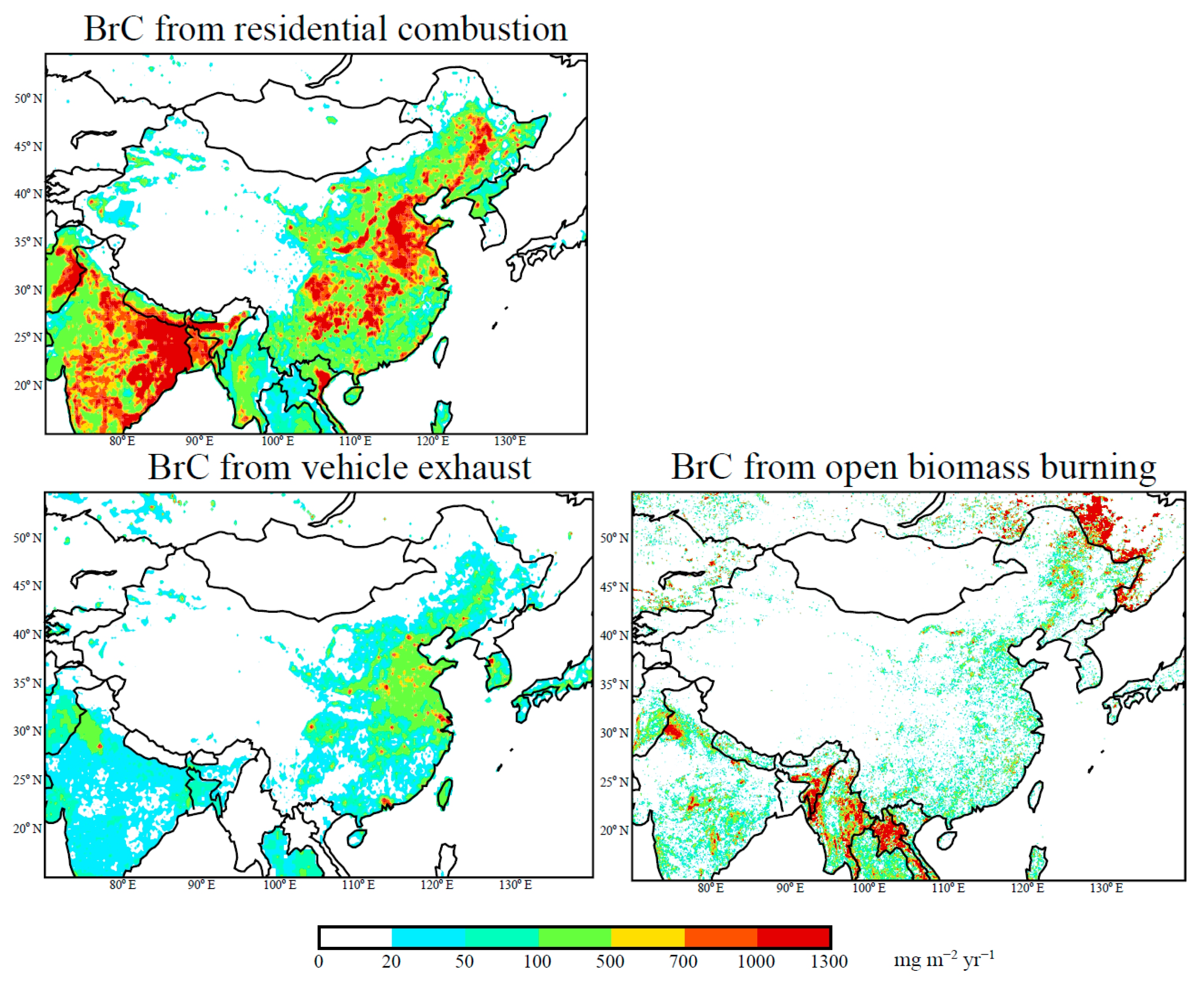
3.1. BrC Emissions in China
3.2. Surface Concentrations in China
3.3. BrC Absorption in China
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andreae, M.O.; Gelencsér, A. Black carbon or brown carbon? The nature of light-absorbing carbonaceous aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 3131–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laskin, A.; Laskin, J.; Nizkorodov, S.A. Chemistry of atmospheric brown carbon. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 4335–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moise, T.; Flores, J.M.; Rudich, Y. Optical properties of secondary organic aerosols and their changes by chemical processes. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 4400–4439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.E.; Ramanathan, V.; Decremer, D. Observationally constrained estimates of carbonaceous aerosol radiative forcing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11624–11629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, Y.; Ramanathan, V.; Kotamarthi, V.R. Brown carbon: A significant atmospheric absorber of solar radiation? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 8607–8621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saleh, R.; Robinson, E.S.; Tkacik, D.S.; Ahern, A.T.; Liu, S.; Aiken, A.C.; Sullivan, R.C.; Presto, A.A.; Dubey, M.K.; Yokelson, R.J.; et al. Brownness of organics in aerosols from biomass burning linked to their black carbon content. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 647–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Penner, J.E.; Flanner, M.G.; Sillman, S.; Xu, L.; Zhou, C. Radiative forcing of organic aerosol in the atmosphere and on snow: Effects of SOA and brown carbon. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 7453–7476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexander, D.T.L.; Crozier, P.A.; Anderson, J.R. Brown Carbon Spheres in East Asian Outflow and Their Optical Properties. Science 2008, 321, 833–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Wang, X.; Gong, P.; Wang, C.; Cong, Z. Review of brown carbon aerosols: Recent progress and perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 1475–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Forrister, H.; Liu, J.; Dibb, J.; Anderson, B.; Schwarz, J.P.; Perring, A.E.; Jimenez, J.L.; Campuzano-Jost, P.; Wang, Y.; et al. Top-of-atmosphere radiative forcing affected by brown carbon in the upper troposphere. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Lin, W.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, B. Climate Impacts of the Biomass Burning in Indochina on Atmospheric Conditions over Southern China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 9, 2707–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voliotis, A.; Prokeš, R.; Lammel, G.; Samara, C. New insights on humic-like substances associated with wintertime urban aerosols from central and southern Europe: Size-resolved chemical characterization and optical properties. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 166, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; He, K.-b.; Du, Z.-y.; Engling, G.; Liu, J.-m.; Ma, Y.-l.; Zheng, M.; Weber, R.J. The characteristics of brown carbon aerosol during winter in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 127, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.J.; Yang, L.; Shen, J.; Yuan, W.; Gong, Y.; Guo, J.; Cao, W.; Duan, J.; Ni, H.; Zhu, C.; et al. Water-Insoluble Organics Dominate Brown Carbon in Wintertime Urban Aerosol of China: Chemical Characteristics and Optical Properties. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7836–7847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Tian, Q.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Li, K.; Li, L. Estimate of aerosol absorbing components of black carbon, brown carbon, and dust from ground-based remote sensing data of sun-sky radiometers. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 6534–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; He, K.B.; Zheng, M.; Duan, F.K.; Ma, Y.L.; Du, Z.Y.; Tan, J.H.; Yang, F.M.; Liu, J.M.; Zhang, X.L.; et al. Mass absorption efficiency of elemental carbon and water-soluble organic carbon in Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2011, 11, 24727–24764. [Google Scholar]
- Hecobian, A.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, M.; Frank, N.; Edgerton, E.S.; Weber, R.J. Water-Soluble Organic Aerosol material and the light-absorption characteristics of aqueous extracts measured over the Southeastern United States. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 5965–5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, Z.; He, K.; Cheng, Y.; Duan, F.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, M.; Weber, R. A yearlong study of water-soluble organic carbon in Beijing II: Light absorption properties. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 89, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Cao, F.; Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y. Contribution of biomass burning on light absorption property of water soluble organic carbon in PM 2.5 in Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2019, 28, 523–530. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Bergin, M.; Guo, H.; King, L.; Kotra, N.; Edgerton, E.; Weber, R.J. Size-resolved measurements of brown carbon in water and methanol extracts and estimates of their contribution to ambient fine-particle light absorption. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 12389–12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.; Yu, G.-H.; Lee, S. Optical absorption characteristics of brown carbon aerosols during the KORUS-AQ campaign at an urban site. Atmos. Res. 2018, 203, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, R.K.; Moosmüller, H.; Chen, L.W.A.; Lewis, K.; Arnott, W.P.; Mazzoleni, C.; Dubey, M.K.; Wold, C.E.; Hao, W.M.; Kreidenweis, S.M. Brown carbon in tar balls from smoldering biomass combustion. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 6363–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, M.; Hays, M.D.; Holder, A.L. Light-absorbing organic carbon from prescribed and laboratory biomass burning and gasoline vehicle emissions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lack, D.A.; Langridge, J.M.; Bahreini, R.; Cappa, C.D.; Middlebrook, A.M.; Schwarz, J.P. Brown carbon and internal mixing in biomass burning particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 14802–14807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Zhi, G.; Hitzenberger, R.; Chen, Y.; Tian, C.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, J.; et al. Emission factors and light absorption properties of brown carbon from household coal combustion in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 4769–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Saturno, J.; Chi, X.; Walter, D.; Lavric, J.V.; Moran-Zuloaga, D.; Ditas, F.; Pöhlker, C.; Brito, J.; Carbone, S.; et al. Modeling investigation of light-absorbing aerosols in the Amazon Basin during the wet season. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 14775–14794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saleh, R.; Marks, M.; Heo, J.; Adams, P.J.; Donahue, N.M.; Robinson, A.L. Contribution of brown carbon and lensing to the direct radiative effect of carbonaceous aerosols from biomass and biofuel burning emissions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 10–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, J.; Zhi, G.; Chen, Y.; Meng, F.; Xue, Z.; Li, J.; Fang, Y. A Preliminary Study on Brown Carbon Emissions from Open Agricultural Biomass Burning and Residential Coal Combustion in China (in Chinese). Res. Environ. Sci. 2014, 27, 455–461. [Google Scholar]
- Lucchesi, R.; File Specification for GEOS-FP. GMAO Office Note No. 4 (Version 1.2) 2018; p. 61. Available online: http://gmao.gsfc.nasa.gov/pubs/office_notes (accessed on 2 May 2021).
- Park, R.J.; Jacob, D.J.; Chin, M.; Martin, R.V. Sources of carbonaceous aerosols over the United States and implications for natural visibility. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, R.; Darmenov, A.; Silva, A. The Quick Fire Emissions Dataset (QFED): Documentation of Versions 2.1, 2.2 and 2.4; Technical Report Series on Global Modeling and Data Assimilation; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; Volume 38. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhi, G.; Hitzenberger, R.; Jin, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Tian, C.; Li, Z.; Chen, R.; et al. Brown carbon’s emission factors and optical characteristics in household biomass burning: Developing a novel algorithm for estimating the contribution of brown carbon. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 2329–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Tao, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Shen, H.; Shen, G.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Huang, Y.; et al. Black carbon emissions in China from 1949 to 2050. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7595–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Li, J.; Su, T.; Han, Y.; Mo, Y.; Jiang, H.; Cui, M.; Jiang, B.; Chen, Y.; Tang, J.; et al. Molecular compositions and optical properties of dissolved brown carbon in biomass burning, coal combustion, and vehicle emission aerosols illuminated by excitation–emission matrix spectroscopy and Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry analysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 2513–2532. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Fan, X.; Zhu, M.; Zou, C.; Song, J.; Wei, S.; Jia, W.; Peng, P. Abundance and Light Absorption Properties of Brown Carbon Emitted from Residential Coal Combustion in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, S.; Wang, T.; Li, D.; Tan, H. Effects of coal types and combustion conditions on carbonaceous aerosols in flue gas and their light absorption properties. Fuel 2020, 277, 118148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pani, S.K.; Lin, N.H.; Griffith, S.M.; Chantara, S.; Lee, C.T.; Thepnuan, D.; Tsai, Y.I. Brown carbon light absorption over an urban environment in northern peninsular Southeast Asia. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 276, 116735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Song, W.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Ponsawansong, P.; Prapamontol, T.; Wang, Y. Contribution of brown carbon to the light absorption and radiative effect of carbonaceous aerosols from biomass burning emissions in Chiang Mai, Thailand. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 118544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Weber, R.J.; Song, Y.; Ke, Z.; Zou, Y. Modeling the global radiative effect of brown carbon: A potentially larger heating source in the tropical free troposphere than black carbon. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 1901–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, M.; Howell, S.G.; Zhuang, J.; Huebert, B.J. Attribution of aerosol light absorption to black carbon, brown carbon, and dust in China—Interpretations of atmospheric measurements during EAST-AIRE. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 2035–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, Y.; Gui, K.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Sheng, Z.; Sun, T.; Zhang, X.; Che, H. Impact of Biomass Burning in South and Southeast Asia on Background Aerosol in Southwest China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 1188–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, L.; Yang, X.; Lai, S.; Ren, H.; Yue, S.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; et al. Impacts of springtime biomass burning in the northern Southeast Asia on marine organic aerosols over the Gulf of Tonkin, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, Y.; Wang, G.; Chen, L. Identification of Long-Range Transport Pathways and Potential Sources of PM10 in Tibetan Plateau Uplift Area: Case Study of Xining, China in 2014. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.; Eck, T.F.; Smirnov, A.; Kaufman, Y.; King, M.; Tanré, D.; Slutsker, I. Variability of Absorption and Optical Properties of Key Aerosol Types Observed in Worldwide Locations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 590–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Tests | Emissions |
|---|---|
| Base | Default |
| Case 1 | Without residential combustion |
| Case 2 | Without vehicle exhaust |
| Case 3 | Without open biomass burning |
| Sources | MAE (m2 gC−1) | EBrC/BC | Emissions (Tg yr−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Residential combustion | 2.1 | 3.9 | 2.42 |
| Vehicle exhaust | 0.74 | 1.7 | 0.49 |
| Open biomass burning | 2.3 | 9.9 | 0.51 |
| Sources | Concentration (%) | AAOD (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Winter | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | Spring | Summer | Autumn | |
| Residential combustion | 82 | 48 | 56 | 64 | 83 | 58 | 79 | 80 |
| Vehicle exhaust | 15 | 17 | 32 | 27 | 12 | 8.9 | 12 | 12 |
| Open biomass burning | 3.0 | 35 | 12 | 8.3 | 4.8 | 33 | 9.3 | 7.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yang, X.; Yang, N.; Wang, X. Modeling Investigation of Brown Carbon Aerosol and Its Light Absorption in China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12070892
Zhu Y, Wang Q, Yang X, Yang N, Wang X. Modeling Investigation of Brown Carbon Aerosol and Its Light Absorption in China. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(7):892. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12070892
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yong, Qiaoqiao Wang, Xiajie Yang, Ning Yang, and Xurong Wang. 2021. "Modeling Investigation of Brown Carbon Aerosol and Its Light Absorption in China" Atmosphere 12, no. 7: 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12070892
APA StyleZhu, Y., Wang, Q., Yang, X., Yang, N., & Wang, X. (2021). Modeling Investigation of Brown Carbon Aerosol and Its Light Absorption in China. Atmosphere, 12(7), 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12070892





