The Effect of Sea Surface Temperature on Relative Humidity and Atmospheric Visibility of a Winter Sea Fog Event over the Yellow-Bohai Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
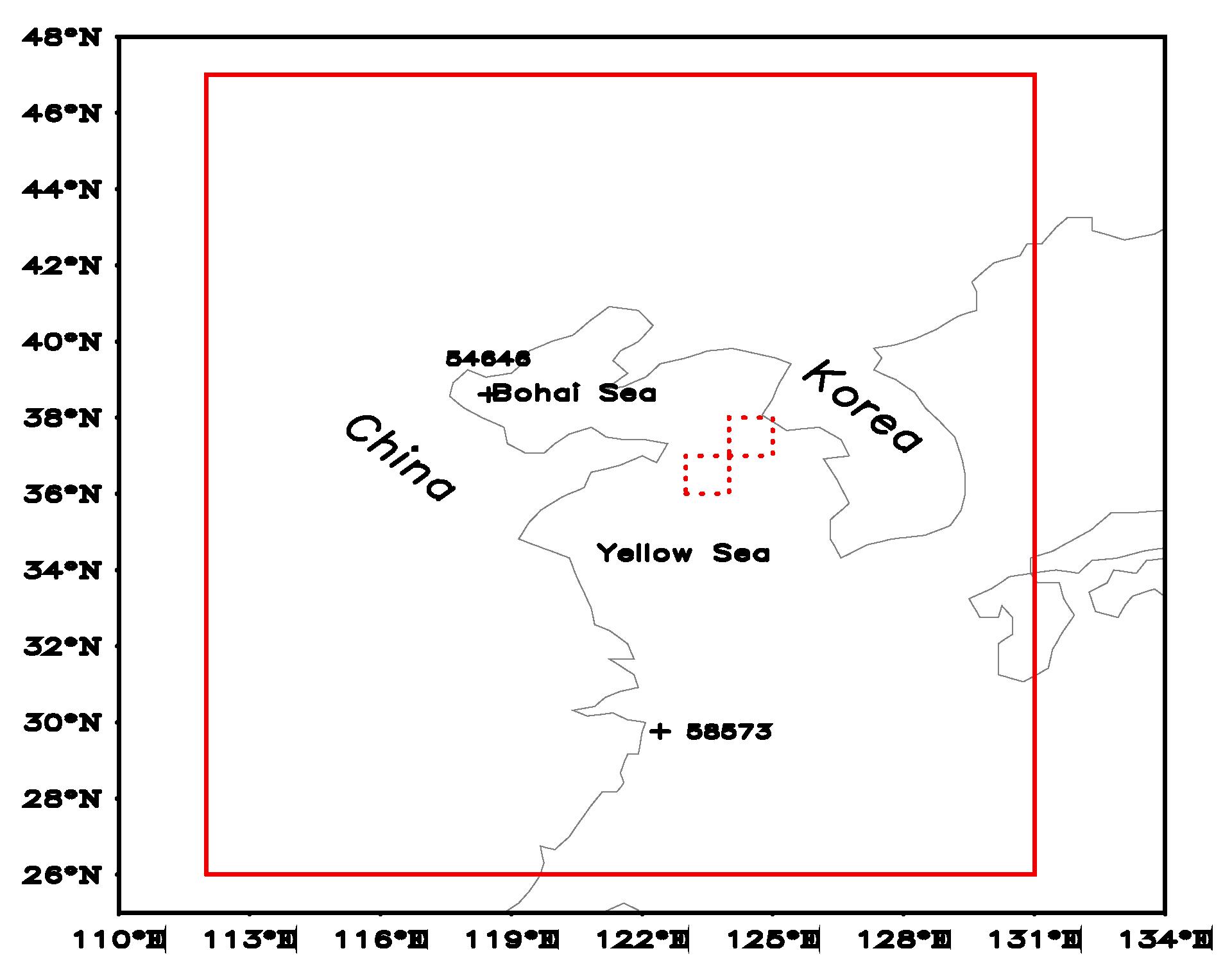
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Methods
2.2.1. Modeling and Experimental Design of Sea Fog Simulation
2.2.2. Time-Varying Equation of Relative Humidity
2.2.3. Atmospheric Visibility Method
3. Results
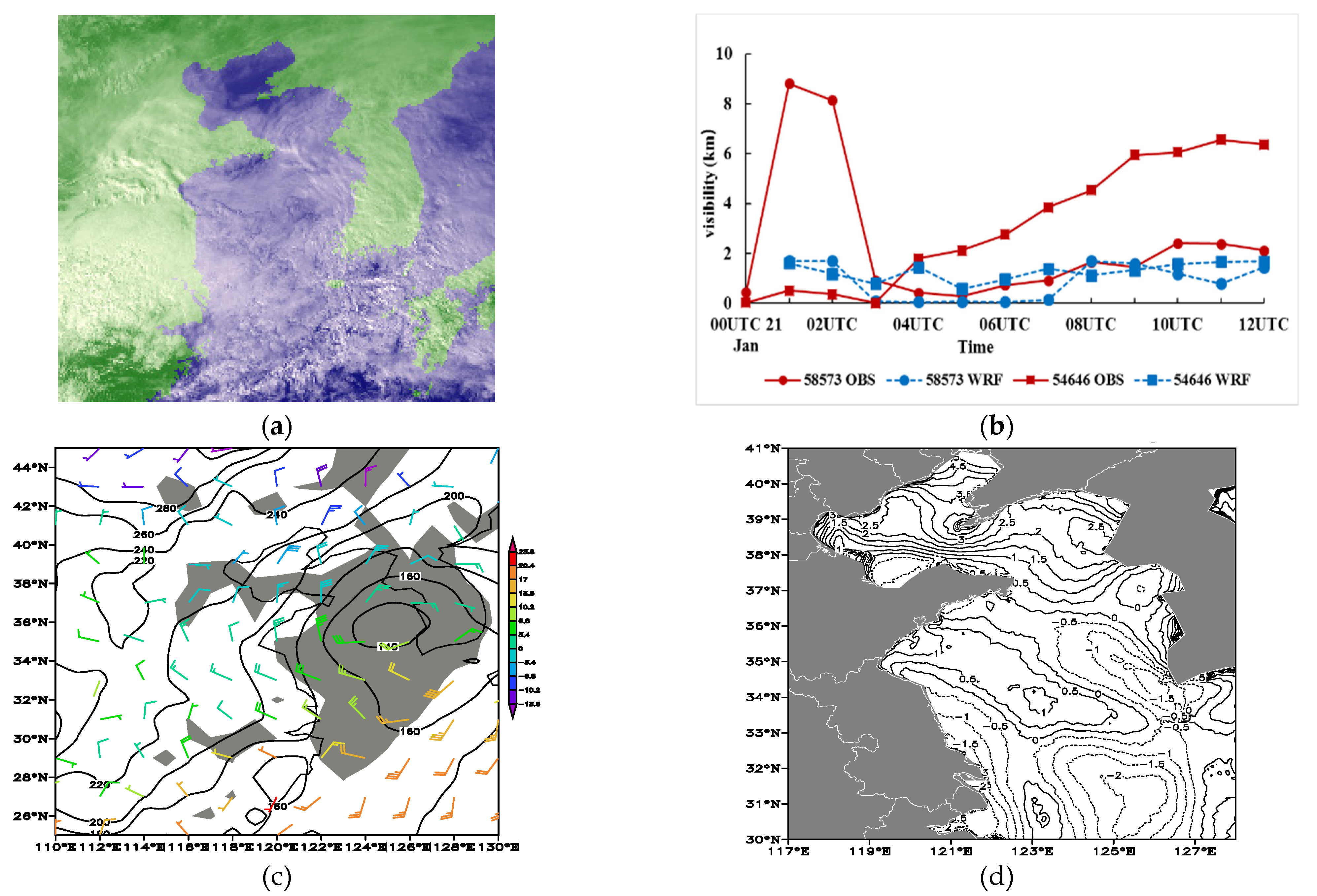
3.1. Observational Analysis and Comparison between Simulation and Observation
3.2. Atmospheric Visibility Simulation Results
4. Discussion
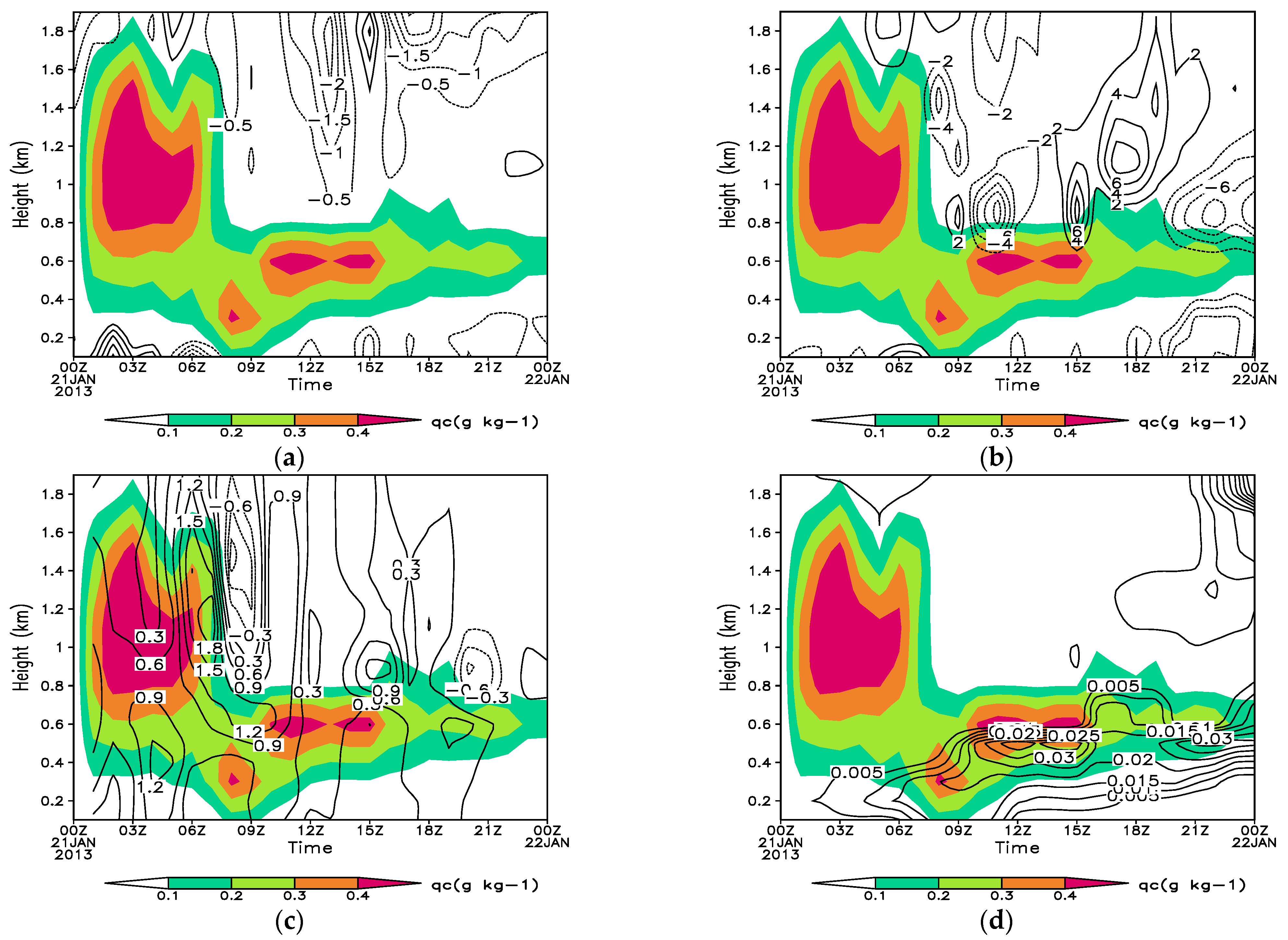
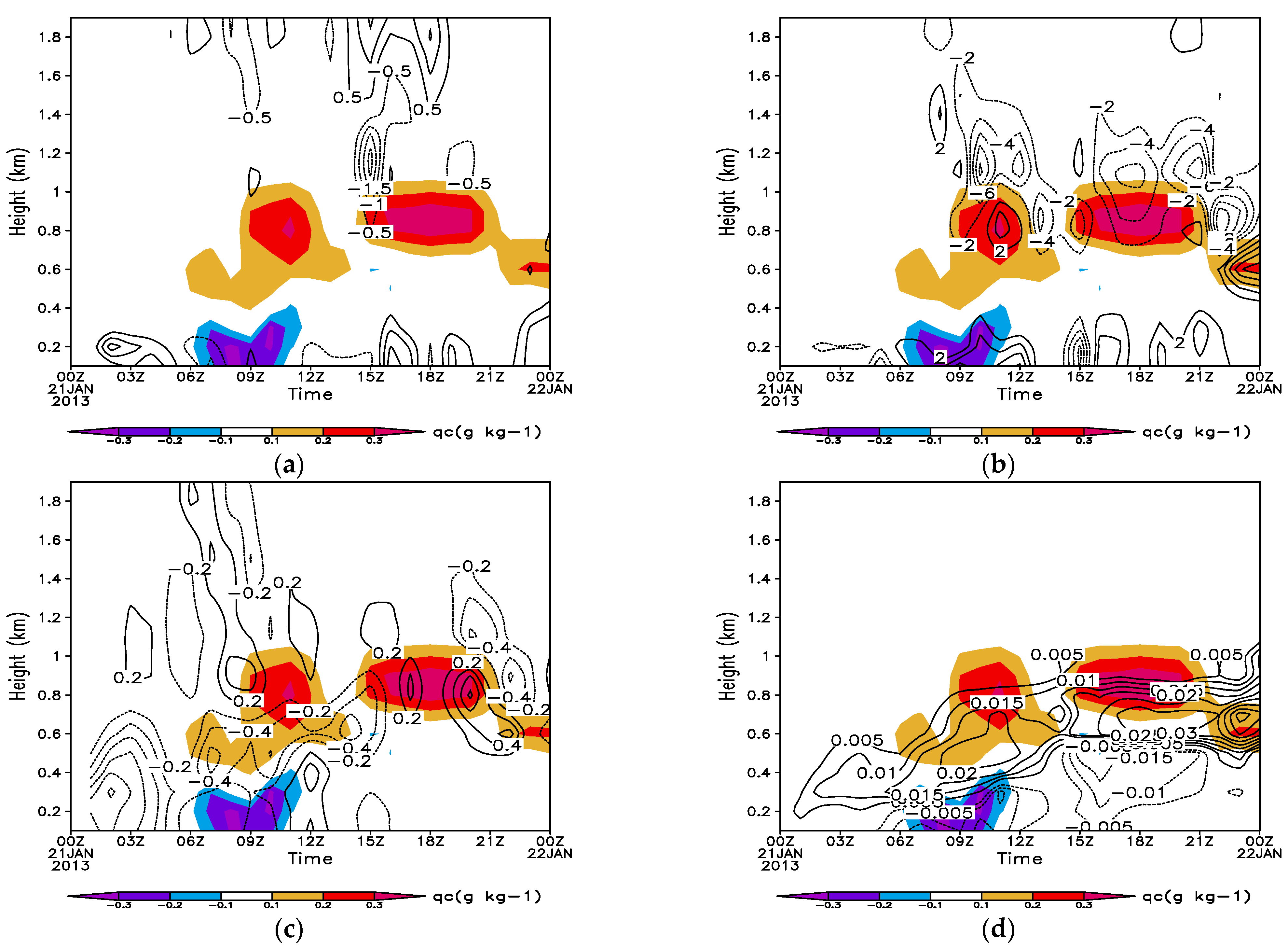
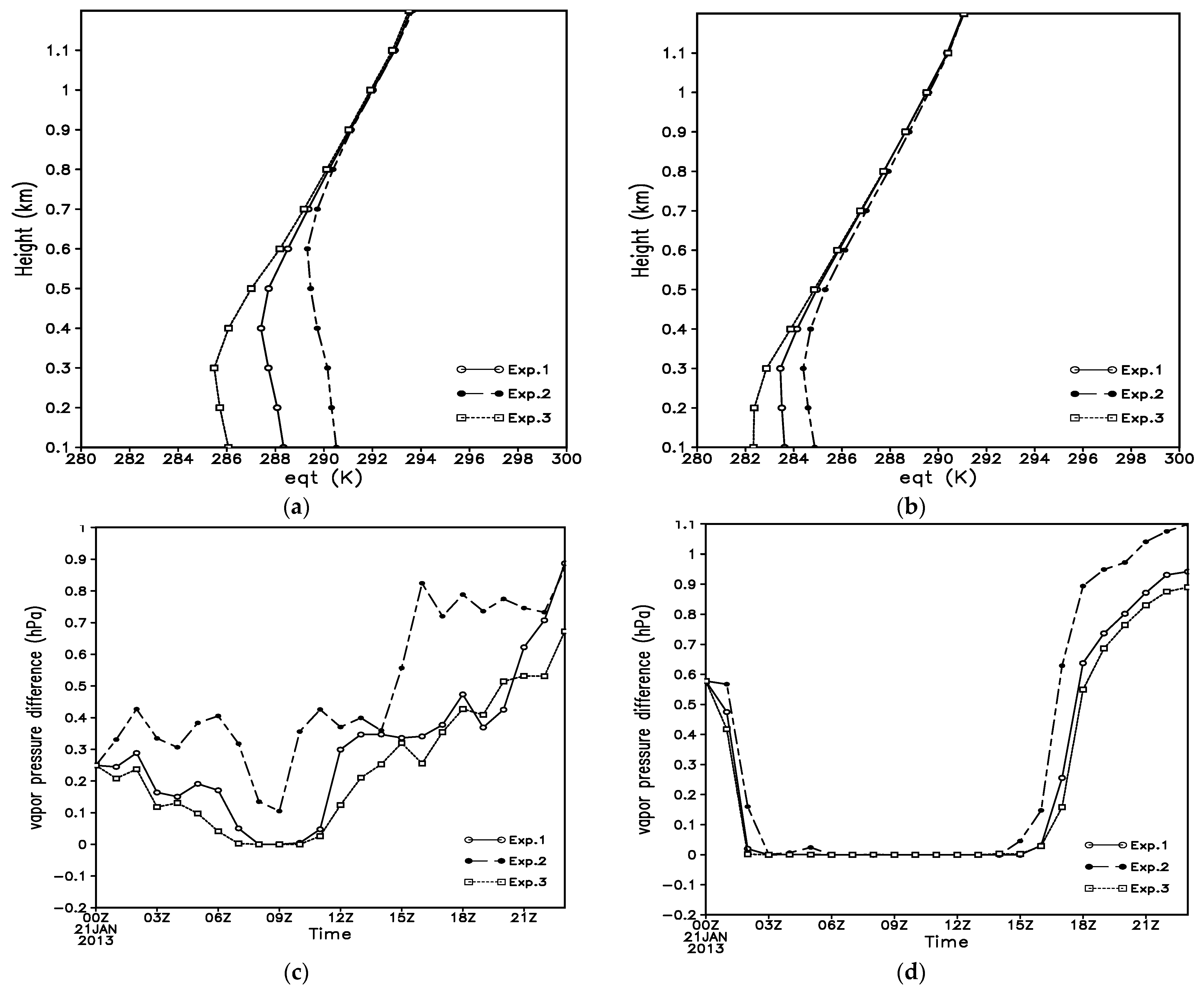
4.1. Analysis of Humidifying Effects of Advection, Radiation, and Turbulence
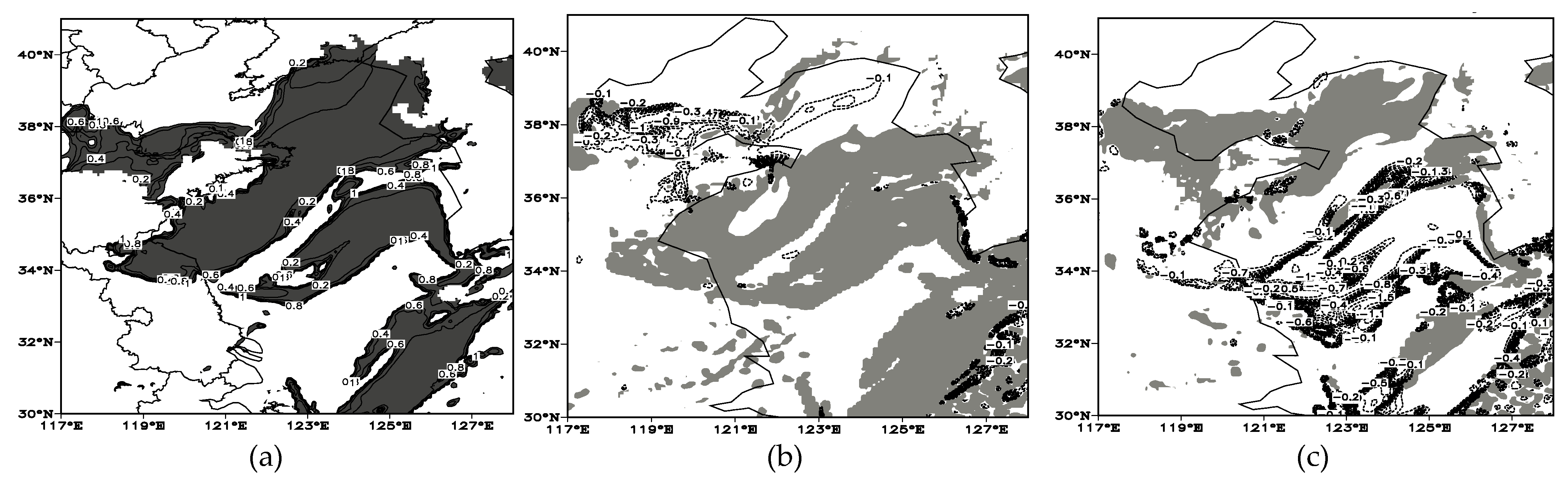
4.2. Analysis of the Effect of SST Changes on Sea Fog
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WMO. International Meteorological Vocabulary, 2nd ed.; Secretariat of the World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1992; p. 782. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.Y.; Chen, S.F.; Chen, W.; Guo, J.P.; Cheng, C.L.; Wang, Y. Distinct evolutions of haze pollution from winter to the following spring over the North China Plain: Role of the North Atlantic sea surface temperature anomalies. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 1669–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Yoo, J.W.; Song, S.K.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, S.H. Numerical study on advective fog formation and its characteristic associated with cold water upwelling. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Moon, J.H.; Kim, T. A coupled numerical modeling study of a sea fog case after the passage of Typhoon Muifa over the Yellow Sea in 2011. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD033875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Li, P.Y.; Zhang, S.P.; Gao, S.H. A brief overview of the sea fog study in China. Adv. Met. S. T. 2016, 6, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.B.; Zhang, S.P.; Xue, D.Q. The mechanism of winter sea fog over Yellow sea in February, 2010. Period. Ocean Univ. China 2012, 2, 24–33. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.W.; Sun, Y.; Yang, L. Interannual variability in summertime sea fog over the Northern Yellow Sea and its association with the local sea surface temperature. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD034439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Q. An observational and numerical study on a sea fog event over the Yellow and Bohai seas in spring of 2005. Master’s Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.P.; Bao, X.W. The main advances in sea fog research in China. Period. Ocean Univ. China 2008, 38, 359–366. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.G.; Zhang, S.P. The effect of cold SST on summer atmosphere boundary layer and sea fog over the Yellow sea. Period. Ocean Univ. China 2012, 42, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koračin, D.; Clive, E.D.; John, M.L.; James, G.H.; Eric, M.W.; Alicia, T. Marine fog: A review. Atmos. Res. 2014, 143, 142–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Qu, P.; Liu, L.L.; Wang, Q.L. Diurnal variation of SST in relation to season and weather phenomena in the Bohai region. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2019, 25, 339–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, P.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z.J.; Gong, X.Q.; Shi, C.X.; Xu, B. Assessment of a fusion sea surface temperature product for numerical weather predictions in China: A case study. Atmospher 2021, 12, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.P.; Ren, Z.P. The influence of the thermal effect of underlaying surface on the spring sea fog over the Yellow sea: Observations and numerical simulations. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2010, 68, 439–449. [Google Scholar]
- Hee, P.S.; Keen, S.S.; Park, H. Temporal and Spatial variations of marine meteorological elements and characteristics of sea fog occurrence in Korean coastal waters during 2013–2017. J. Environ. Sci. Int. 2020, 29, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.J.; Liu, H.N.; Huang, J.; Mao, W.K.; Bi, X.Y. Atmospheric boundary layer structure and turbulence during sea fog on the Southern China coast. Mon. Weather Rev. 2015, 143, 1907–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Xu, J.M.; Shi, D.D.; Liu, L.S. Deformation feature of a continuous sea fog process over the Yellow sea and Bohai sea and its genesis analysis. Meteorol. Mon. 2018, 44, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.B.; Zhang, S.P.; Koracin, D.; Yi, L.; Zhang, X. Atmospheric conditions conductive to marine fog over the northeast Pacific in winters of 1979-2019. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 942846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.H.; Lin, H.; Shen, B.; Fu, G. A heavy sea fog event over the Yellow sea in March 2005: Analysis and numerical modeling. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2007, 24, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, S.H. Sensitivity study of vertical resolution in WRF numerical simulation for sea fog over the Yellow sea. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2016, 74, 974–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, T.H.; Fovell, R.G. Modeling the evolution and life cycle of radiative cold pools and fog. Weather Forecast. 2018, 33, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.K.; Yum, S.S. A numerical study of sea-fog formation over cold sea surface using a one-dimensional turbulence model coupled with the Weather Research and Forecasting model. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2012, 143, 481–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Ha, K.J. Physical processes in sea fog formation and characteristics of turbulent air-sea fluxes at Socheongcho ocean research station in the Yellow sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 825973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, J.W.; Ren, Z.P.; Xie, S.P.; Zhang, S.P.; Gao, S.H. Atmospheric conditions for advection-radiation fog over the western Yellow Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 5455–5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, S.H. The impact of turbulent diffusion driven hy fog-top cooling on sea fog development. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2019JD031562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.X.; Huang, G.; Wang, X.Q.; Cheng, G.H. Investigation of changes in extreme temperature and humidity over China through a dynamical downscaling approach. Earths Future 2017, 5, 1136–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.J.; Dong, K.H.; ZHOU, F.X. Numerical experiments with the advection, turbulence and radiation effects in the sea fog formation process. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2006, 24, 156–165. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.Y.; Lim, J. The WRF single-moment 6-Class microphysics scheme (WSM6). J. Korean Meteor. Soc. 2006, 42, 129–151. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.Y.; Noh, Y.; Dudhia, J. A new vertical diffusion package with an explicit treatment of entrainment processes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 2318–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mlawer, E.J.; Taubman, S.J.; Brown, P.D.; Iacono, M.J.; Clough, S.A. Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmospheres: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the longwave. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 16663–16682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dudhia, J. A nonhydrostatic version of the Penn State-NCAR mesoscale model: Validation tests and simulation of an Atlantic cyclone and cold front. Mon. Weather Rev. 1993, 121, 1493–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.J.; Zhou, F.X. Effects of advection, turbulence and radiation on formation of sea fog Ⅰ. A theoretical analysis. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 1998, 20, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.F.; Guo, J.P.; Song, L.Y.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Cohen, J.B. Inter-annual variation of the spring haze pollution over the North China Plain: Roles of atmospheric circulation and sea surface temperature. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 783–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel, B.A. Parameterization of droplet terminal velocity and extinction coefficient in fog models. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1984, 23, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoelinga, M.T.; Warner, T.T. Nonhydrostatic mesobeta-scale model simulations of cloud ceiling and atmospheric visibility for an east coast winter precipitation event. J. Appl. Meteor. 1999, 38, 385–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousta, I.; Javadizadeh, F.; Dargahian, F.; Olafsson, H.; Shiri-Karimvandi, A.; Vahedinejad, S.H.; Doostkamian, M.; Vargas, E.R.M.; Asadolahi, A. Investigation of vorticity during prevalent winter precipitation in Iran. Adv. Meteorol. 2018, 2018, 6941501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, E.; Kim, J.H.; Heo, K.Y.; Cho, Y.K. Advection fog over the eastern Yellow Sea: WRF simulation and its verification by satellite and in Situ observation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.F.; Liu, D.Y.; Gultep, I.; Lin, H.J.; Cai, N.H.; Cao, S.Y.; Wang, Z.D. Boundary layer features of one winter fog in the Yangze River delta, China. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2022, 179, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousta, I.; Doostkamian, M.; Haghighi, E.; Mirzakhani, B. Statistical-synoptic analysis of the atmosphere thickness pattern of Iran’s pervasive frosts. Climate 2016, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rousta, I.; Doostkamian, M.; Taherian, A.M.; Haghighi, E.; Malamiri, H.R.G.; Ólafsson, H. Investigation of the spatio-temporal variations in atmosphere thickness pattern of Iran and the Middle East with special focus on precipitation in Iran. Climate 2017, 5, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rousta, I.; Nasserzadeh, M.H.; Jalali, M.; Haghighi, E.; Ólafsson, H.; Ashrafi, S.; Doostkamian, M.; Ghasemi, A. Decadal spatial-temporal variations in the spatial pattern of anomalies of extreme precipitation thresholds (Case study: Northwest Iran). Atmosphere 2017, 8, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Experiment Name | Experimental Design |
|---|---|
| Exp.1 | control experiment (RTG_SST+FNL) |
| Exp.2 | sensitivity experiment: increasing SST by 2 degrees |
| Exp.3 | sensitivity experiment: decreasing SST by 2 degrees |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wei, W. The Effect of Sea Surface Temperature on Relative Humidity and Atmospheric Visibility of a Winter Sea Fog Event over the Yellow-Bohai Sea. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13101718
Liu L, Wang X, Li Y, Wei W. The Effect of Sea Surface Temperature on Relative Humidity and Atmospheric Visibility of a Winter Sea Fog Event over the Yellow-Bohai Sea. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(10):1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13101718
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Lili, Xuelian Wang, Yinghua Li, and Wang Wei. 2022. "The Effect of Sea Surface Temperature on Relative Humidity and Atmospheric Visibility of a Winter Sea Fog Event over the Yellow-Bohai Sea" Atmosphere 13, no. 10: 1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13101718
APA StyleLiu, L., Wang, X., Li, Y., & Wei, W. (2022). The Effect of Sea Surface Temperature on Relative Humidity and Atmospheric Visibility of a Winter Sea Fog Event over the Yellow-Bohai Sea. Atmosphere, 13(10), 1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13101718





