UAV Inspection of Compliance of Fuel Sulfur Content of Sailing Ships in the Pearl River Delta, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
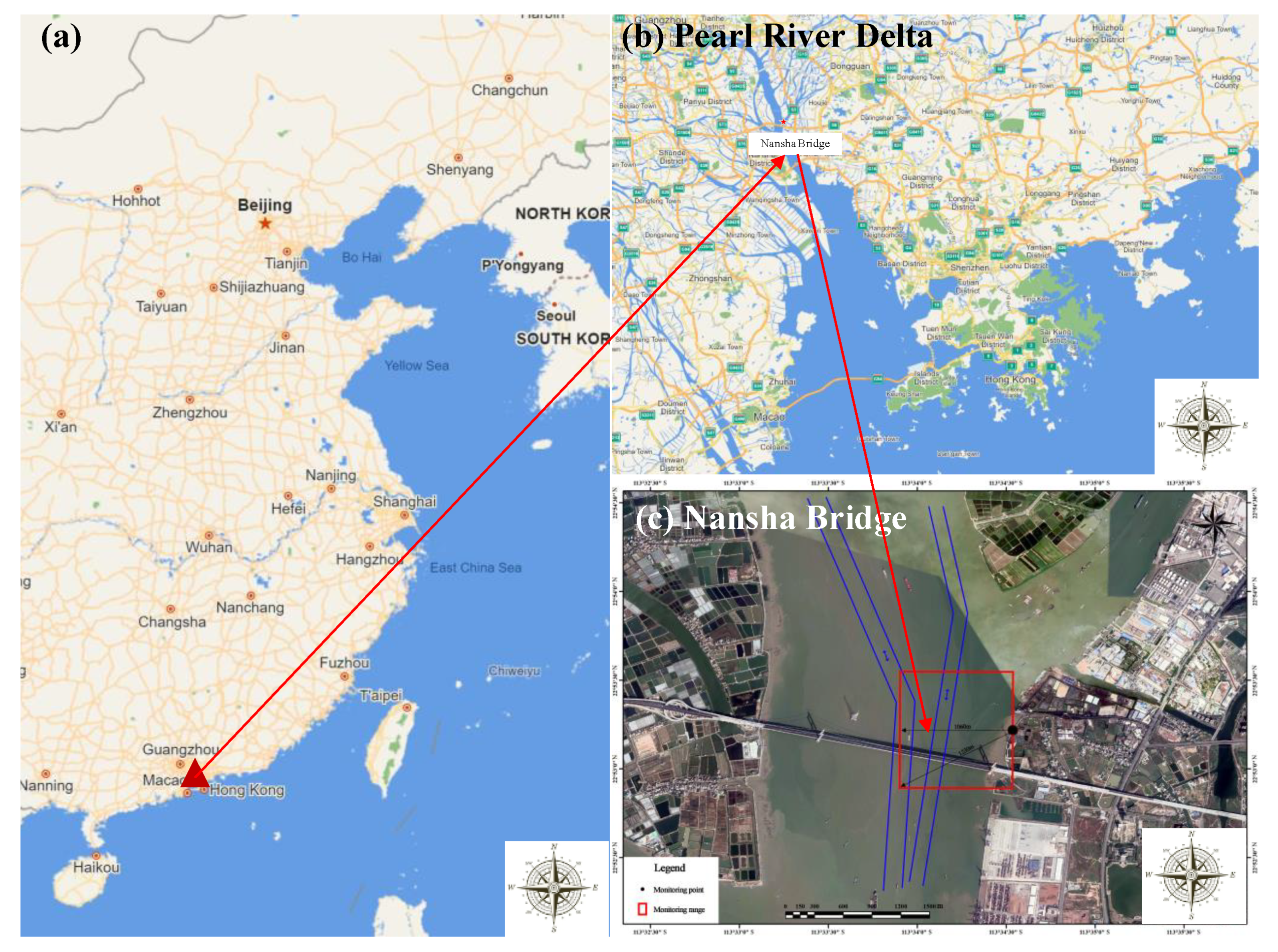
2.1. Measurement Site
2.2. Measurement Method
2.3. Instrumentation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Monitoring Results in Pearl River Delta
3.2. Analysis of Monitoring Results of Different Ship Lengths
3.3. Analysis of Monitoring Results of Different Ship Types
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eyring, V.; Isaksen, I.; Berntsen, T.; Collins, W.; Corbett, J.; Endresen, O.; Grainger, R.; Moldanova, J.; Schlager, H.; Stevenson, D. Transport impacts on atmosphere and climate: Shipping. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 4735–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthias, V.; Bewersdorff, I.; Aulinger, A.; Quante, M. The contribution of ship emissions to air pollution in the North Sea regions. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2241–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berglen, T.F.; Bernsten, T.K.; Isaksen, I.S.A.; Sundet, J.K. A global model of the coupled sulfur/oxidant chemistry in the troposphere: The sulfur cycle. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Ambient Air Pollution: Health Impacts. Health Risks; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Jasper Shinichi, H.; Zhang, S.; Paula, P.; Bryan, C.; Elena, H.; Wendela, S.V.D.L.; Tristan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hiroyuko, K.; Masaki, A.; et al. Fourth IMO GHG Study 2020: Full Report; International Maritime Organization: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sofiev, M.; Winebrake, J.J.; Johansson, L.; Carr, E.W.; Prank, M.; Soares, J.; Vira, J.; Kouznetsov, R.; Jalkanen, J.P.; Corbett, J.J. Cleaner fuels for ships provide public health benefits with climate tradeoffs. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, H.K.; Tsang, H.; Chau, J.; Lee, C.H.; McGhee, S.M.; Hedley, A.J.; Wong, C.M. Health impact assessment of marine emissions in Pearl River Delta region. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 66, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fu, M.; Jin, X.; Shang, Y.; Shindell, D.; Faluvegi, G.; Shindell, C.; He, K. Health and climate impacts of ocean-going vessels in East Asia. Nat. Clim. Change. 2016, 6, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Kwan, S.; Lu, T.; Fu, Q.; Cheng, J.; Streets, D.G.; Wu, Y.; Li, J. An emission inventory of marine vessels in shanghai in 2003. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 5183–5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Liu, H.; Ying, Q.; Fu, M.; Meng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wei, W.; Gong, H.; He, K. Impacts of shipping emissions on PM2.5 pollution in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 15811–15824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IMO: Revised MARPOL Annex IV. 2008. Available online: https://www.bahamasmaritime.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/MN059-MARPOL-Annex-IV-Sewage-Pollution-Prevention-v1.0.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- International Maritime Organization (IMO): Sulphur Oxides (SOx) and Particulate Matter (PM)–Regulation 14. 2016. Available online: https://www.imo.org/en/OurWork/Environment/Pages/Sulphur-oxides-(SOx)-%E2%80%93-Regulation-14.aspx (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- MOT. Implementation of the Ship Emission Control Area in Pearl River Delta, the Yangtze River Delta and the Bohai Rim (Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Area), Ministry of Transport, C., Beijing, China, 2015. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2015-12/04/content_5019932.htm (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- MOT. Implementation Scheme of the Domestic Emission Control Areas for Atmospheric Pollution from Vessels, Ministry of Transport, C., Beijing, China, 2018. Available online: https://www.msa.gov.cn/public/documents/document/mte1/odi2/~edisp/20190124115826051.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Kattner, L.; Mathieu-üffing, B.; Burrows, J.P.; Richter, A.; Schmolke, S.; Seyler, A.; Wittrock, F. Monitoring compliance with sulfur content regulations of shipping fuel by in situ measurements of ship emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 10087–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alföldy, B.; Lööv, J.B.; Lagler, F.; Mellqvist, J.; Berg, N.; Beecken, J.; Weststrate, H.; Duyzer, J.; Bencs, L.; Horemans, B.; et al. Measurements of air pollution emission factors for marine transportation in SECA. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1777–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzani Lööv, J.M.; Alfoldy, B.; Gast, L.F.L.; Hjorth, J.; Lagler, F.; Mellqvist, J.; Beecken, J.; Berg, N.; Duyzer, J.; Westrate, H.; et al. Field test of available methods to measure remotely SOx and NOx emissions from ships. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 2597–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mellqvist, J.; Ekholm, J.; Beecken, J.; Salo, K. Identification of gross polluting ships to promote a level playing field within the shipping sector. In Final Report to Vinnova (2008-03884), Technical Report, Earth and Space Sciences; Chalmers University of Technology: Göteborg, Sweden, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Anand, A.; Wei, P.; Gali, N.K.; Sun, L.; Yang, F.; Westerdahl, D.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; et al. Protocol development for real-time ship fuel sulfur content determination using drone-based plume sniffing microsensor system. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, N.; Mellqvist, J.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Balzani, J. Ship emissions of SO2 and NO2: DOAS measurements from airborne platforms. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 1085–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seyler, A.; Wittrock, F.; Kattner, L.; Mathieu-Üffing, B.; Peters, E.; Richter, A.; Schmolke, S.; Burrows, J.P. Monitoring shipping emissions in the German Bight using MAX-DOAS measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 10997–11023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seyler, A.; Meier, A.C.; Wittrock, F.; Kattner, L.; Mathieu-Üffing, B.; Peters, E.; Richter, A.; Ruhtz, T.; Schönhardt, A.; Schmolke, S.; et al. Studies of the horizontal inhomogeneities in NO2 concentrations above a shipping lane using ground-based multi-axis differential optical absorption spectroscopy (MAX-DOAS) measurements and validation with airborne imaging DOAS measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 5959–5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, D.A. HCB, PCB, PCDD and PCDF emissions from ships. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 4901–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggleston, H.S.; Buendia, L.; Miwa, K.; Ngara, T.; Tanabe, K. 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Institute for Global Environmental Strategies (IGES): Hayama, Japan, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jana, M.; Erik, F.; Olga, P.; Benjamin, D.; Victoria, T.; Alessandro, F.; Cristian, F. Characterisation of particulate matter and gaseous emissions from a large ship diesel engine. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2632–2641. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.; Wang, S.; Huang, M.; Yao, K. SO2 and SO2−4 Dry Deposition Velocities Computed Using Resistance Model and MM5. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. China 2003, 33, 692–700. [Google Scholar]
- Beecken, J.; Mellqvist, J.; Mellqvist, J. Remote Measurements of Gas and Particulate Matter Emissions from Individual Ships. Ph.D. Thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Beecken, J.; Mellqvist, J.; Salo, K.; Ekholm, J.; Jalkanen, J.P. Airborne emission measurements of SO2, NOx and particles from individual ships using a sniffer technique. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 1957–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhu, J.; Peng, S.; Zhao, H.; Hong, N. Sniffing method: A technique to estimate sulfur content in marine fuel through in situ measurements of ship emissions. J. Waterw. Harbor 2018, 39, 619–625. [Google Scholar]
- Wvr, A.; Rs, A.; Bvr, A.; Ks, A.; Avn, A.; Fm, B. Airborne monitoring of compliance to sulfur emission regulations by ocean-going vessels in the Belgian North Sea area. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101445. [Google Scholar]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Deng, M.; Peng, S.; Qi, Z. UAV Inspection of Compliance of Fuel Sulfur Content of Sailing Ships in the Pearl River Delta, China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1894. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111894
Hu J, Deng M, Peng S, Qi Z. UAV Inspection of Compliance of Fuel Sulfur Content of Sailing Ships in the Pearl River Delta, China. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(11):1894. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111894
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Jianbo, Mengtao Deng, Shitao Peng, and Zhaoyu Qi. 2022. "UAV Inspection of Compliance of Fuel Sulfur Content of Sailing Ships in the Pearl River Delta, China" Atmosphere 13, no. 11: 1894. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111894
APA StyleHu, J., Deng, M., Peng, S., & Qi, Z. (2022). UAV Inspection of Compliance of Fuel Sulfur Content of Sailing Ships in the Pearl River Delta, China. Atmosphere, 13(11), 1894. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111894








