Variability of the Southwestern Patagonia (51°S) Winds in the Recent (1980–2020) Period: Implications for Past Wind Reconstructions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Present Day SWW over Southern Patagonia
2.2. Available Data
2.2.1. Direct Observations
2.2.2. Reanalysis Data
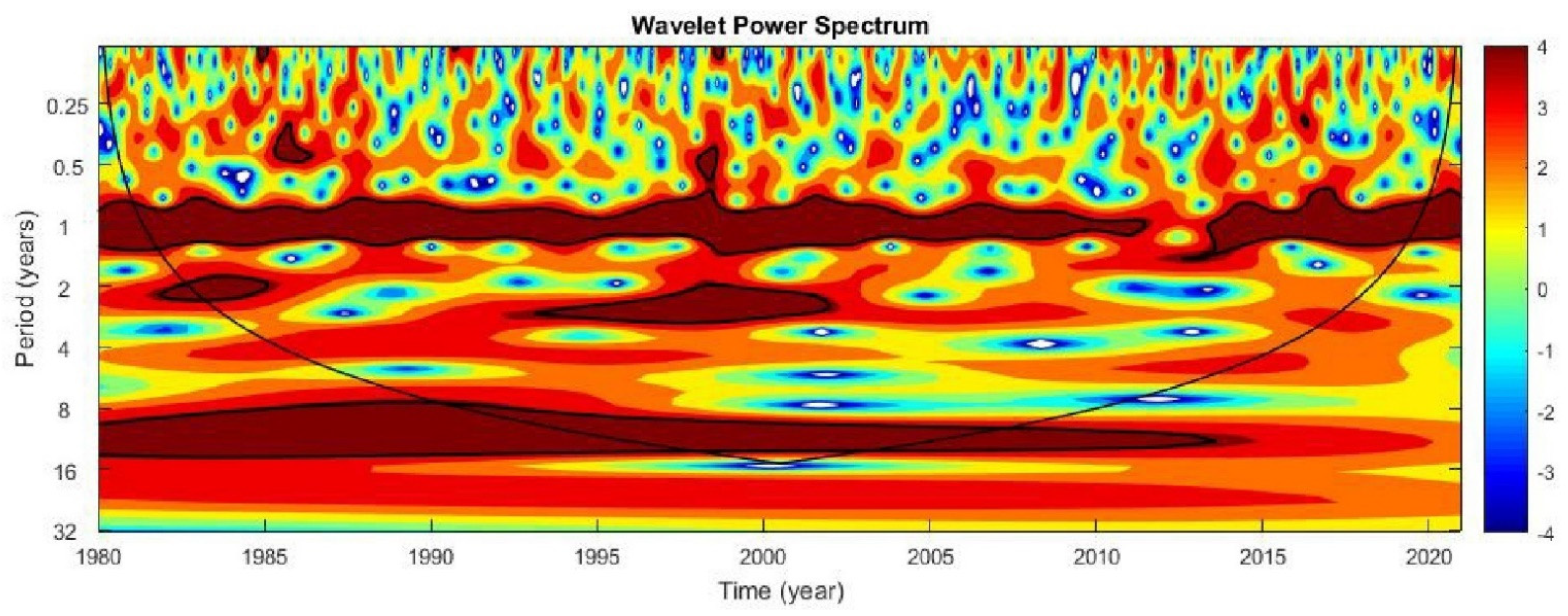
2.3. Analysis of Wind Time Series
3. Results
3.1. Local Wind Variability
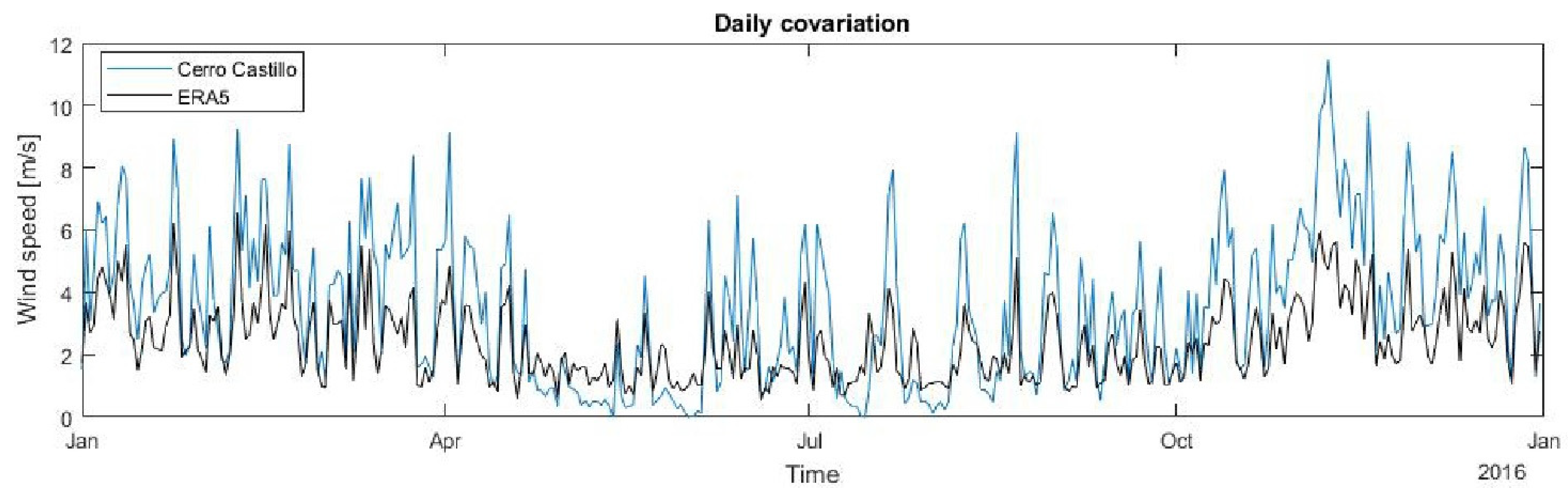
3.2. Reanalysis Validation
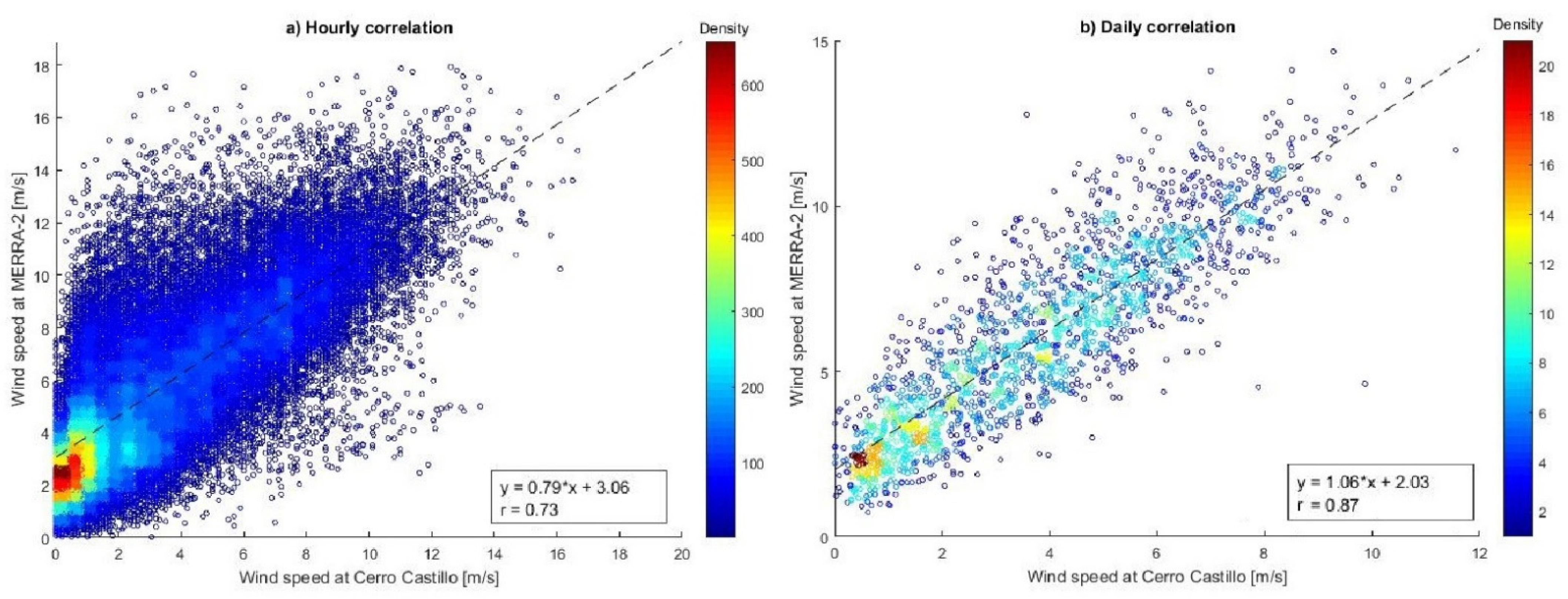
3.2.1. MERRA-2 vs. Cerro Castillo
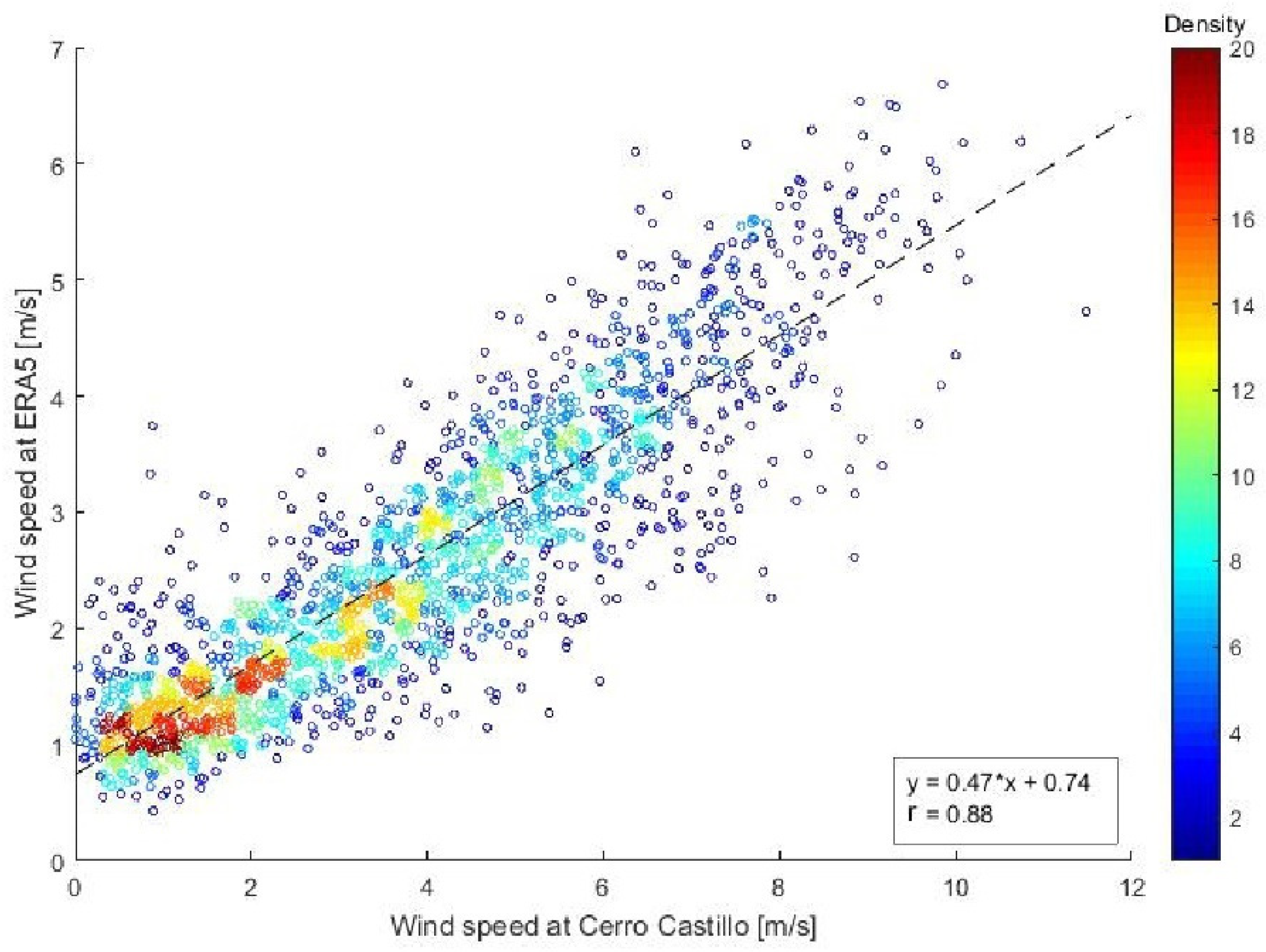
3.2.2. ERA5 vs. Cerro Castillo
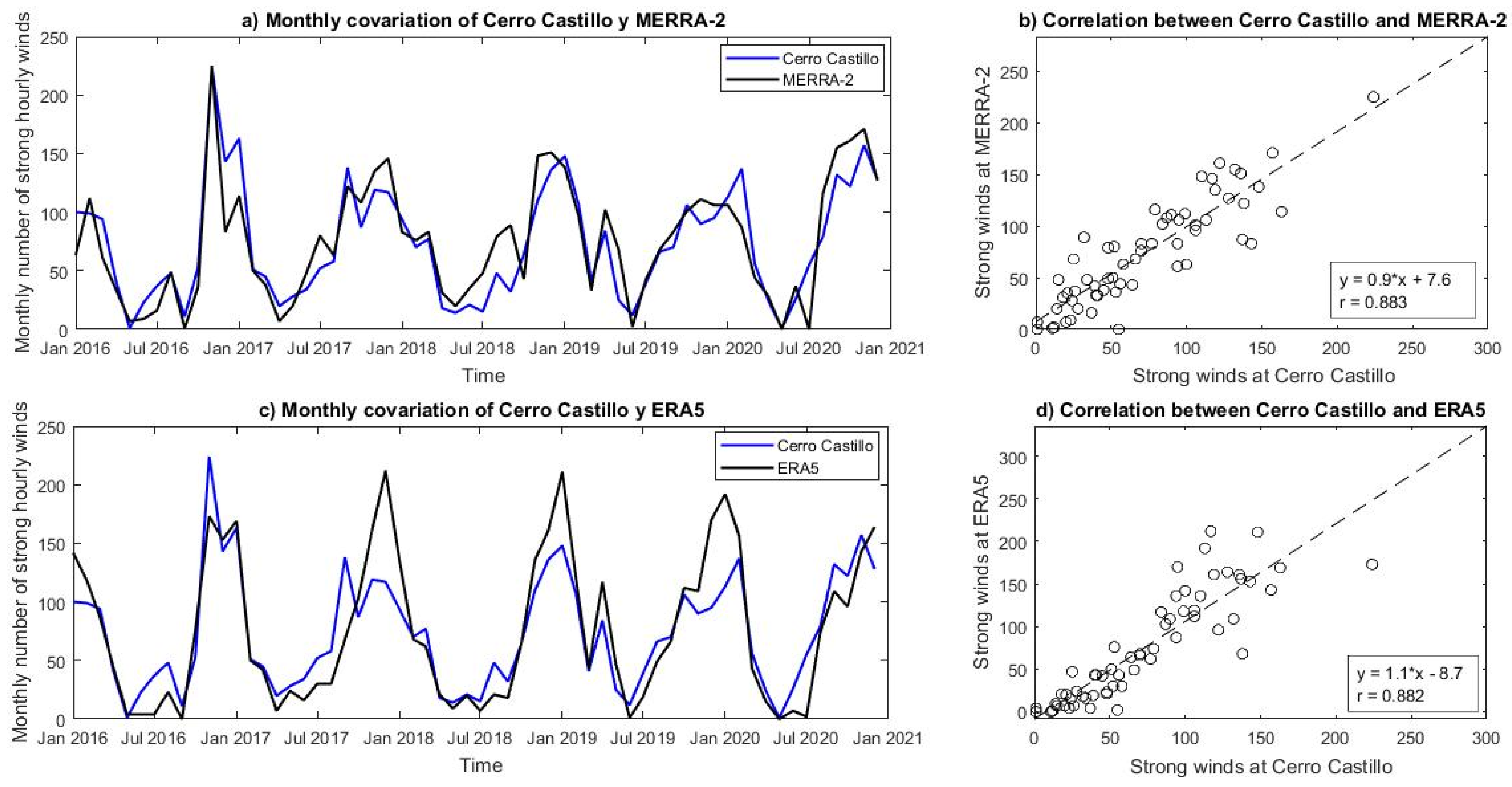
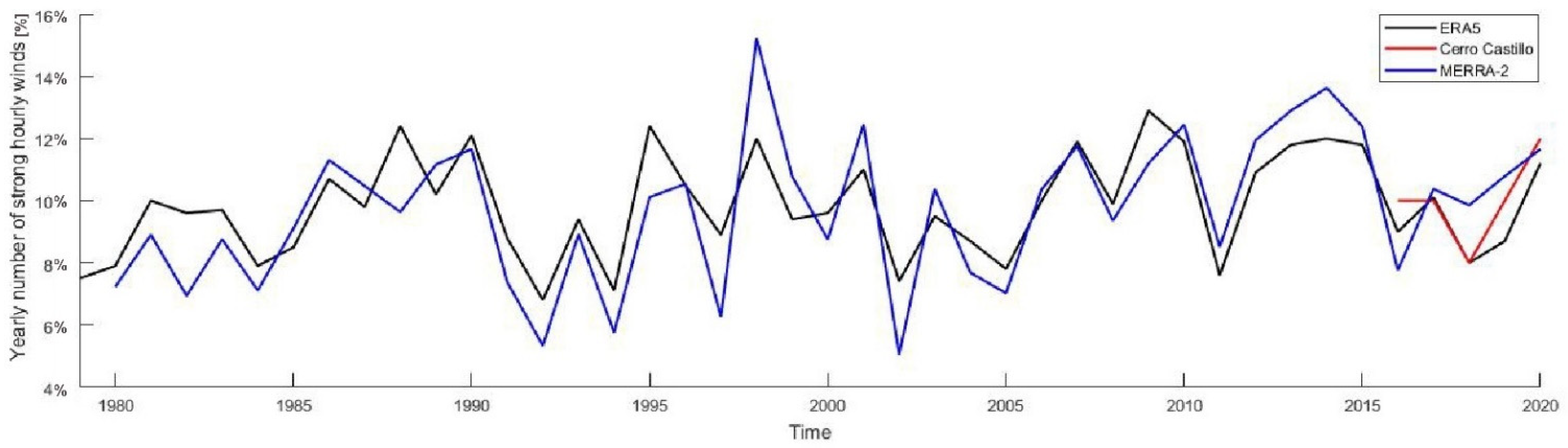
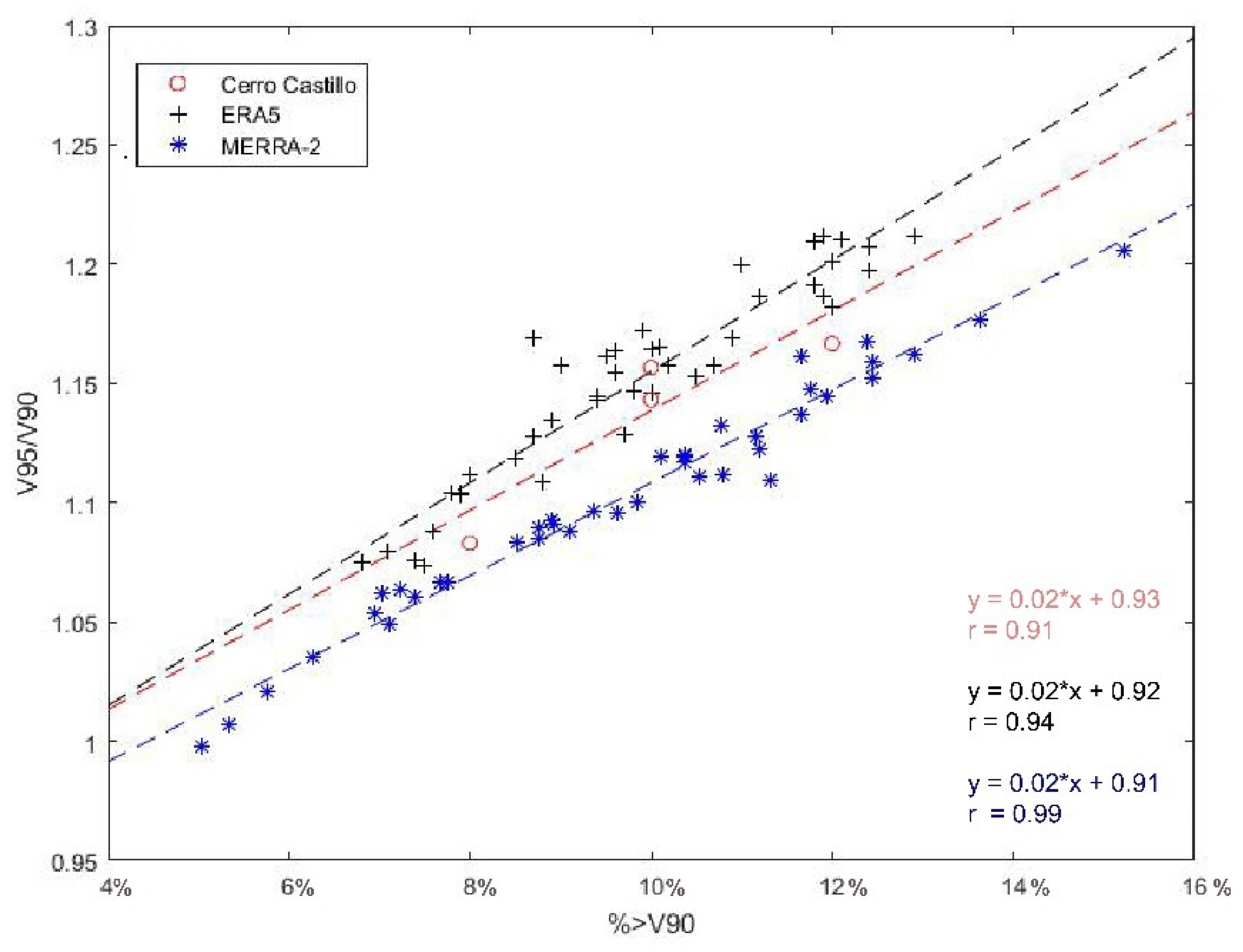
3.3. Ability of the Reanalyses to Simulate the Frequency of Strong Hourly Winds
3.4. Comparison of ‘Calm’ and ‘Strong Winds’ Years
4. Concluding Remarks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garreaud, R.; Vuille, M.; Compagnucci, R.; Marengo, J. Present-day South American climate. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2009, 281, 180–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushner, P.; Held, I.; Delworth, T.L. Southern Hemisphere Atmospheric Circulation Response to Global Warming. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 2238–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toggweiler, J.R. Shifting westerlies. Science 2009, 323, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garreaud, R.; Lopez, P.; Minvielle, M.; Rojas, M. Large-scale control on the Patagonian climate. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, D.A.; Sime, L.C. Southern westerlies and CO2. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 666–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, P.; Videla, J.; Valero-Garcés, B.; Alloway, B.; Heusser, L. A continuous record of vegetation, fire-regime and climatic changes in northwestern Patagonia spanning the last 25,000 years. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2018, 198, 15–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuut, J.-B.W.; Prins, M.A.; Schneider, R.R.; Weltje, G.J.; Jansen, J.H.F.; Postma, G. A 300-kyr record of aridity and wind strength in southwestern Africa: Inferences from grain-size distributions of sediments on Walvis Ridge, SE Atlantic. Mar. Geol. 2002, 180, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Aqueveque, V.; Alfaro, S.C.; Caquineau, S.; Foret, G.; Vargas, G.; Rutllant, J.A. Inter-annual variability of southerly winds in a coastal area of the Atacama Desert: Implications for the export of aeolian sediments to the adjacent marine environment. Sedimentology 2012, 59, 990–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Aqueveque, V.; Alfaro, S.; Vargas, G.; Rutllant, J.A.; Caquineau, S. Aeolian particles in marine cores as a tool for quantitative high-resolution reconstruction of upwelling favorable winds along coastal Atacama Desert, Northern Chile. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, 134, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnold, R.A. The Physics of Blown Sand and Desert Dunes; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 2008; 265p. [Google Scholar]
- Gelaro, R.; McCarty, W.; Suárez, M.; Todling, R.; Molod, A.; Tackacs, L.; Randles, C.; Darmenov, A.; Bosilovich, M.; Reichle, R.; et al. The Modern-Era Retrospective Analysis for Research and Applications, Version 2 (MERRA-2). J. Clim. 2017, 30, 5419–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olauson, J. ERA5: The new champion of wind power modelling? Renew. Energy 2018, 126, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, I.M.; Moy, C.M.; Riesselman, C.R.; Neil, H.L.; Curtin, L.G.; Gorman, A.R.; Wilson, G.S. Late Holocene intensification of the westerly winds at the subantarctic Auckland Islands (51° S), New Zealand. Clim. Past 2017, 13, 1301–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valjarević, A.; Morar, C.; Živković, J.; Niemets, L.; Kićović, D.; Golijanin, J.; Gocić, M.; Bursać, N.M.; Stričević, L.; Žiberna, I.; et al. Long Term Monitoring and Connection between Topography and Cloud Cover Distribution in Serbia. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viale, M.; Bianchi, E.; Cara, L.; Ruiz, L.E.; Villalba, R.; Pitte, P.; Masiokas, M.; Rivera, J.; Zalazar, L. Contrasting Climates at Both Sides of the Andes in Argentina and Chile. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sime, L.C.; Kohfeld, K.E.; Le Quéré, C.; Wolff, E.W.; de Boer, A.M.; Graham, R.M.; Bopp, L. Southern Hemisphere westerly wind changes during the Last Glacial Maximum: Model-data comparison. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2013, 64, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamy, F.; Kilian, R.; Arz, H.W.; Francois, J.P.; Kaiser, J.; Prange, M.; Steinke, T. Holocene changes in the position and intensity of the southern westerly wind belt. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shindell, D.T.; Schmidt, G.A. Southern Hemisphere Climate Response to Ozone Changes and Greenhouse Gas Increases. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L18209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen Gupta, A.; Santoso, A.; Taschetto, A.S.; Ummenhofer, C.C.; Travena, J.; England, M.H. Projected Changes to the Southern Hemisphere Ocean and Sea Ice in the IPCC AR4 Climate Models. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 3047–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, D.W.; Solomon, S.; Kushner, P.J.; England, M.H.; Grise, K.M.; Karoly, D.J. Signatures of the Antarctic ozone hole in Southern Hemisphere surface climate change. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.W.J.; Wallace, J.M.; Hegerl, G.C. Annular modes in the extratropical circulation, Part II: Trends. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 1018–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.W.J.; Solomon, S. Interpretation of recent Southern Hemisphere climate change. Science 2002, 296, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marshall, G.J.; Stott, P.A.; Turner, J.; Connolley, W.M.; King, J.C.; Lachlan-Cope, T.A. Causes of exceptional atmospheric circulation changes in the Southern Hemisphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L14205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillett, N.; Thompson, D. Simulation of Recent Southern Hemisphere Climate Change. Science 2003, 302, 273–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ihara, C.; Kushnir, Y. Change of mean midlatitude westerlies in 21st century climate simulations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L13701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fyfe, J.C.; Saenko, O.A. Simulated changes in the extratropical Southern Hemisphere winds and currents. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 06701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavaillaz, Y.; Codron, F.; Kageyama, M. Southern westerlies in LGM and future (RCP4.5) climates. Clim. Past 2013, 9, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodell, M.; Houser, P.R.; Jambor, U.; Gottschalck, J.; Mitchell, K.; Meng, C.-J.; Arsenault, K.; Cosgrove, B.; Radakovich, J.; Bosilovich, M.; et al. The Global Land Data Assimilation System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF). ERA5 Back Extension 1950–1978 (Preliminary Version). Research Data Archive at the National Center for Atmospheric Research, Computational and Information Systems Laboratory. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5065/YBW7-YG52 (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Fécan, F.; Marticorena, B.; Bergametti, G. Parametrization of the increase of the Aeolian erosion threshold wind friction velocity due to soil moisture for arid and semi-arid areas. Ann. Geophys. 1999, 17, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishizuka, M.; Mikami, M.; Yamada, Y.; Zeng, F.; Gao, W. An observational study of soil moisture effects on wind erosion at a gobi site in the Taklimakan Desert. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alfaro, S.C.; Gomes, L. Improving the large-scale modeling of the saltation flux of soil particles in presence of nonerodible elements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1995, 100, 16357–16366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marticorena, B.; Bergametti, G. Modeling the atmospheric dust cycle: 1. Design of a soil-derived dust emission scheme. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1995, 100, 16415–16430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flores-Aqueveque, V.; Rojas, M.; Aguirre, C.; Arias, P.; González, C. South Pacific Subtropical High from the late Holocene to the end of the 21st century: Insights from climate proxies and general circulation models. Clim. Past 2020, 16, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santana, A.; Olave, C.; Butorovic, N. Climate study high temporal resolution records in camp Posesion (ENAP). Magallanes, Chile. An. Inst. Patagon. 2010, 38, 5–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramon, J.; Lledó, L.; Torralba, V.; Soret, A.; Doblas-Reyes, F.J. What global reanalysis best represents near-surface winds? Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 145, 3236–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tetzner, D.; Thomas, E.R.; Allen, C.S. A Validation of ERA5 Reanalysis Data in the Southern Antarctic Peninsula—Ellsworth Land Region, and Its Implications for Ice Core Studies. Geosciences 2019, 9, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Santos, I.; Seguel, R.; Schneider, W.; Linford, P.; Donoso, D.; Navarro, E.; Amaya-Cárcamo, C.; Pinilla, E.; Daneri, G. Synoptic-scale variability of surface winds and ocean response to atmospheric forcing in the eastern austral Pacific Ocean. Ocean Sci. 2019, 15, 1247–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guozden, T.M.; Bianchi, E.; Solarte, A.; Mulleady, C. Wind resource assessment in the Rio Negro province (Patagonia Argentina) using MERRA Reanalysis. Meteorologica 2017, 43, 47–61. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, G.J. Trends in the Southern Annular Mode from Observations and Reanalyses. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 4134–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cane, M.A. Climate change—A role for the tropical Pacific. Science 1998, 282, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettinger, M.D.; Battisti, D.S.; Garreaud, R.D.; McCabe, G.J.; Bitz, C.M. Interhemispheric Effects of Interannual and Decadal ENSO-Like Climate Variations on the Americas. In Interhemispheric Climate Linkages: Present and Past Climates in the Americas their Societal Effects; Markgraf, V., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Cane, M.A. The evolution of El Niño, past and future. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 230, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.W.J.; Wallace, J.M. Annular modes in the extratropical circulation, Part I: Month-to-month variability. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 1000–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swart, N.C.; Fyfe, J.C. Observed and simulated changes in the Southern Hemisphere surface westerly wind-stress. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, 16711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantua, N.J.; Hare, S.R.; Zhang, Y.; Wallace, J.M.; Francis, R.C. A Pacific interdecadal climate oscillation with impacts on salmon production. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantua, N.J.; Hare, S.R. The Pacific Decadal Oscillation. J. Oceanogr. 2002, 58, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garreaud, R.D.; Battisti, D.S. Interannual (ENSO) and interdecadal (ENSO-like) variability in the Southern Hemisphere tropospheric circulation*. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 2113–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertrand, S.; Hughen, K.; Sepúlveda, J.; Pantoja, S. Late Holocene covariability of the southern westerlies and sea surface temperature in northern Chilean Patagonia. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2014, 105, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamy, F.; Hebbeln, D.; Röhl, U.; Wefer, G. Holocene rainfall variability in southern Chile: A marine record of latitudinal shifts of the Southern Westerlies. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 2001, 185, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moy, C.M.; Dunbar, R.B.; Moreno, P.I.; François, J.P.; Villa- Martínez, R.; Mucciarone, D.M.; Guilderson, T.O.; Garreaud, R. Isotopic evidence for hydrologic change related to the westerlies in SW Patagonia, Chile, during the last millennium. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2008, 27, 1335–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, V.; Prange, M.; Merkel, U.; Kleinen, T.; Lohmann, G.; Pfeiffer, M.; Renssen, H.; Wagner, A.; Wagner, S.; Schulz, M. Holocene evolution of the Southern Hemisphere westerly winds in transient simulations with global climate models. Clim. Past 2012, 8, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henriquez, W.I.; Villa-Martinez, R.; Vilanova, I.; De Pol-Holz, R.; Moreno, P.I. The last glacial termination on the eastern flank of the central Patagonian Andes (47° S). Clim. Past 2017, 13, 879–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
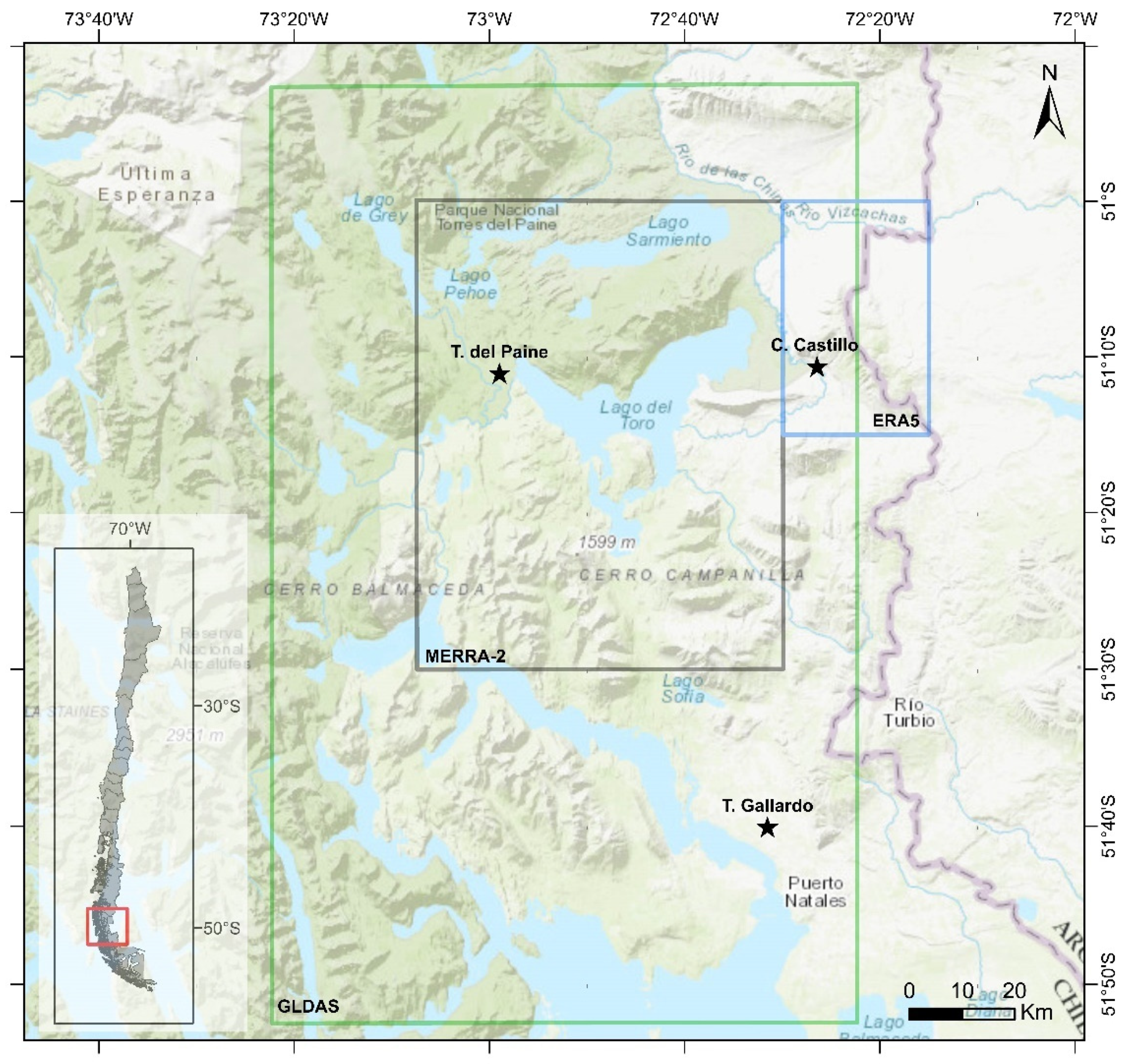
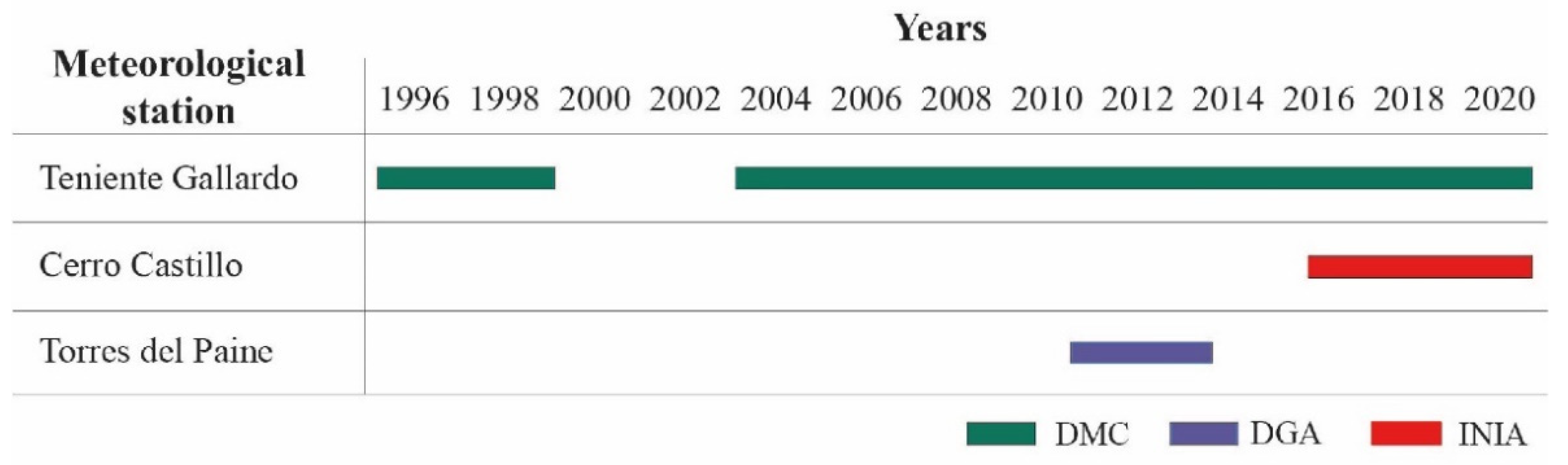

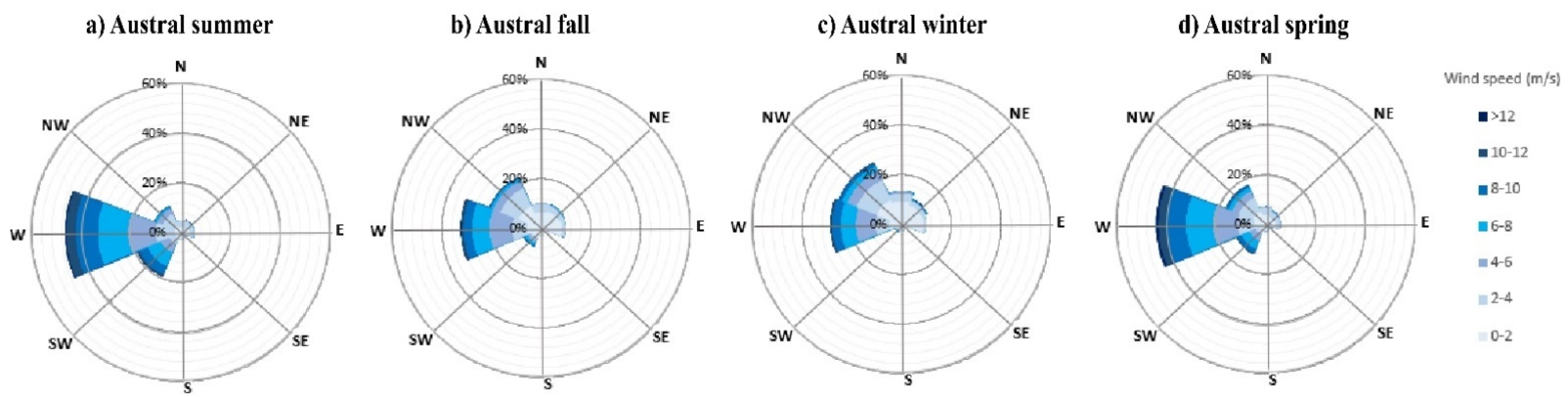
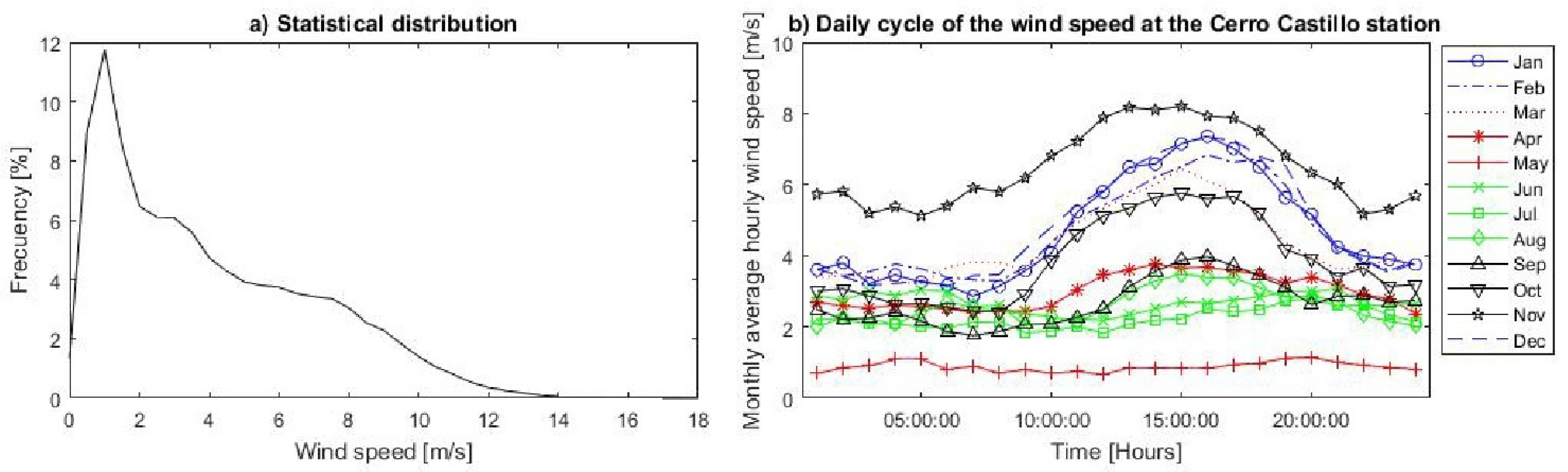

| Meteorological Station | Lat. (°) | Long. (°) | Altitude (m.a.s.l) | Temporal Resolution | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Teniente Gallardo | −51.66 | −72.52 | 69 | Hourly (12:00–20:00 before 2016) | DMC |
| Cerro Castillo | −51.17 | −72.43 | 115 | Hourly | INIA |
| Torres del Paine | −51.18 | −72.98 | 25 | Hourly | DGA |
| Reanalysis | Period Covered | Temporal Resolution | Spatial Resolution | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERA5 | 1979–2020 | Hourly | 0.25° × 0.25° | Hersbach et al. (2020) |
| MERRA-2 | 1980–2020 | Hourly | 0.5° × 0.625° | Gelaro et al. (2017) |
| GLDAS | 1948–2014 | Daily | 1.0° × 1.0° | Rodell et al. (2004) |
| Annual | DJF | MAM | JJA | SON | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | RMSE | Bias | R | RMSE | Bias | R | RMSE | Bias | R | RMSE | Bias | R | RMSE | Bias | |
| MERRA-2 | 0.87 | 2.67 | 2.26 | 0.79 | 2.76 | 2.36 | 0.86 | 2.59 | 2.24 | 0.83 | 2.68 | 2.24 | 0.88 | 2.67 | 2.21 |
| ERA 5 | 0.88 | 1.87 | −1.28 | 0.88 | 1.98 | −1.66 | 0.88 | 1.51 | −0.88 | 0.81 | 1.73 | −0.89 | 0.89 | 2.20 | −1.70 |
| Annual | DJF | MAM | JJA | SON | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | RMSE | Bias | R | RMSE | Bias | R | RMSE | Bias | R | RMSE | Bias | R | RMSE | Bias | |
| MERRA-2 | 0.47 | 2.62 | −0.43 | 0.41 | 2.39 | −0.03 | 0.46 | 2.57 | −0.64 | 0.48 | 2.71 | −0.93 | 0.44 | 2.77 | −0.10 |
| ERA5 | 0.36 | 4.41 | −3.96 | 0.31 | 4.25 | −3.81 | 0.3 | 4.40 | −3.93 | 0.34 | 4.54 | −4.11 | 0.35 | 4.47 | −4.01 |
| Mean | 0.42 | 3.52 | −2.20 | 0.36 | 3.32 | −1.92 | 0.38 | 3.49 | −2.29 | 0.41 | 3.63 | −2.52 | 0.40 | 3.62 | −2.06 |
| Meteorological Station/Reanalysis | Period Analyzed | Temporal Resolution | V90 (ms−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cerro Castillo | 2016–2020 | Hourly | 8.31 |
| ERA5 | 2016–2020 | Hourly | 4.93 |
| MERRA-2 | 2016–2020 | Hourly | 10.66 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gómez-Fontealba, C.; Flores-Aqueveque, V.; Alfaro, S.C. Variability of the Southwestern Patagonia (51°S) Winds in the Recent (1980–2020) Period: Implications for Past Wind Reconstructions. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020206
Gómez-Fontealba C, Flores-Aqueveque V, Alfaro SC. Variability of the Southwestern Patagonia (51°S) Winds in the Recent (1980–2020) Period: Implications for Past Wind Reconstructions. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(2):206. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020206
Chicago/Turabian StyleGómez-Fontealba, Carolina, Valentina Flores-Aqueveque, and Stéphane Christophe Alfaro. 2022. "Variability of the Southwestern Patagonia (51°S) Winds in the Recent (1980–2020) Period: Implications for Past Wind Reconstructions" Atmosphere 13, no. 2: 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020206
APA StyleGómez-Fontealba, C., Flores-Aqueveque, V., & Alfaro, S. C. (2022). Variability of the Southwestern Patagonia (51°S) Winds in the Recent (1980–2020) Period: Implications for Past Wind Reconstructions. Atmosphere, 13(2), 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020206






