Centennial Precipitation Characteristics Change in Haihe River Basin, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
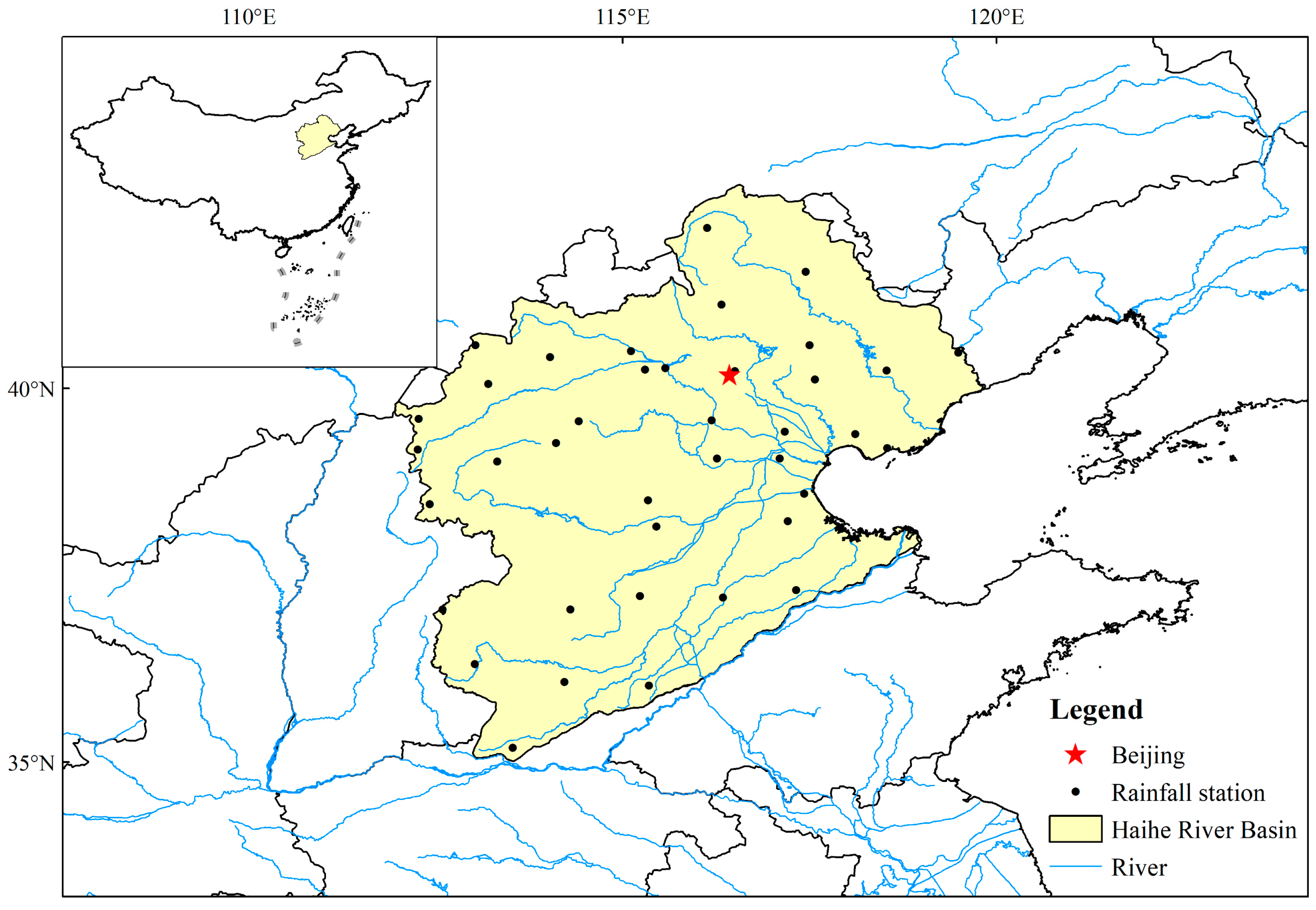
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Applicability Evaluation Index
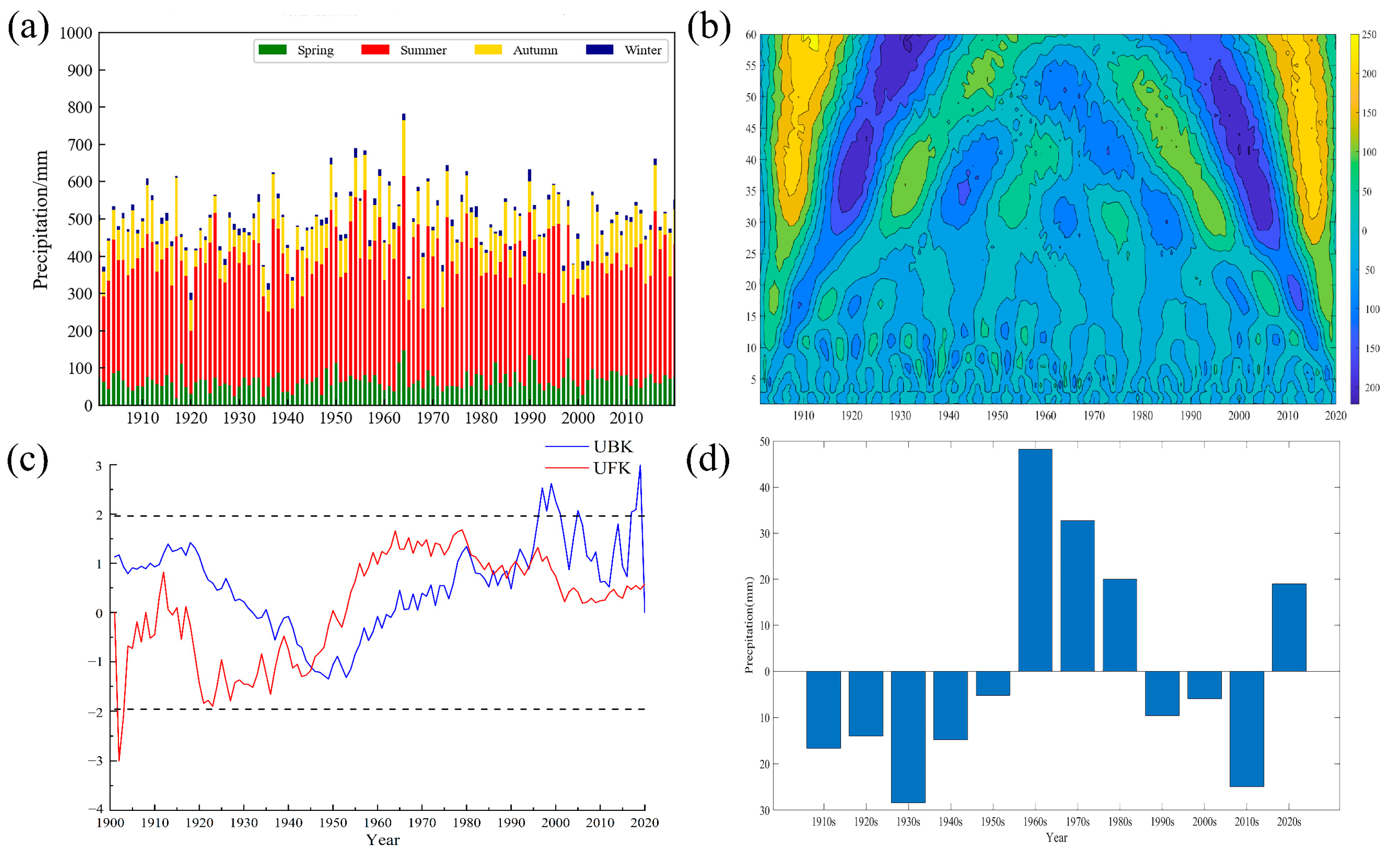
2.3.2. Mutation Point and Periodic Change Identification
2.3.3. Pearson Type III Distribution Probability Density Function
2.3.4. Precipitation Concentration Index
2.3.5. Standardized Precipitation Index
3. Results
3.1. Applicability Analysis
3.2. Precipitation Characteristics of the Haihe River Basin
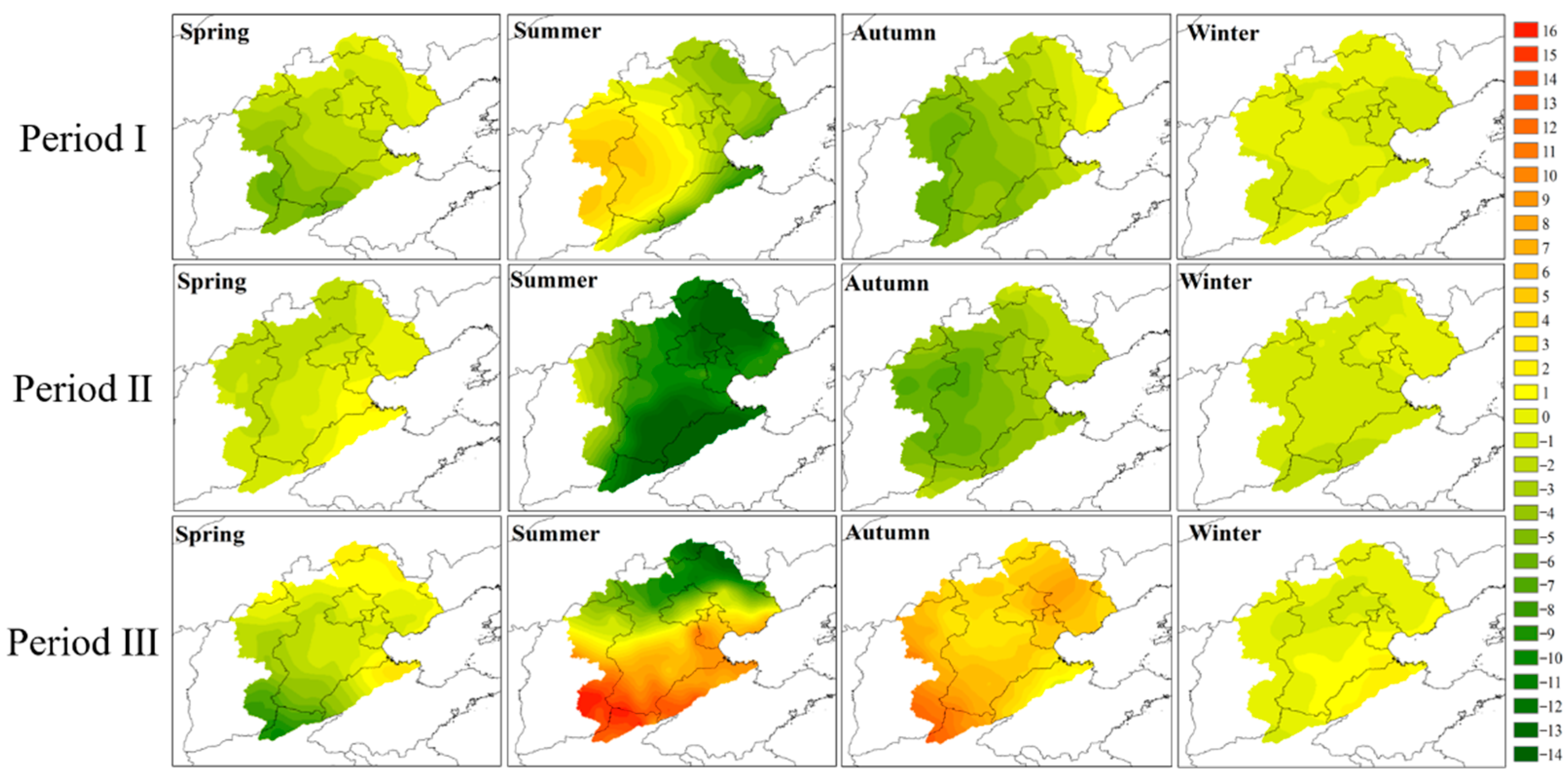
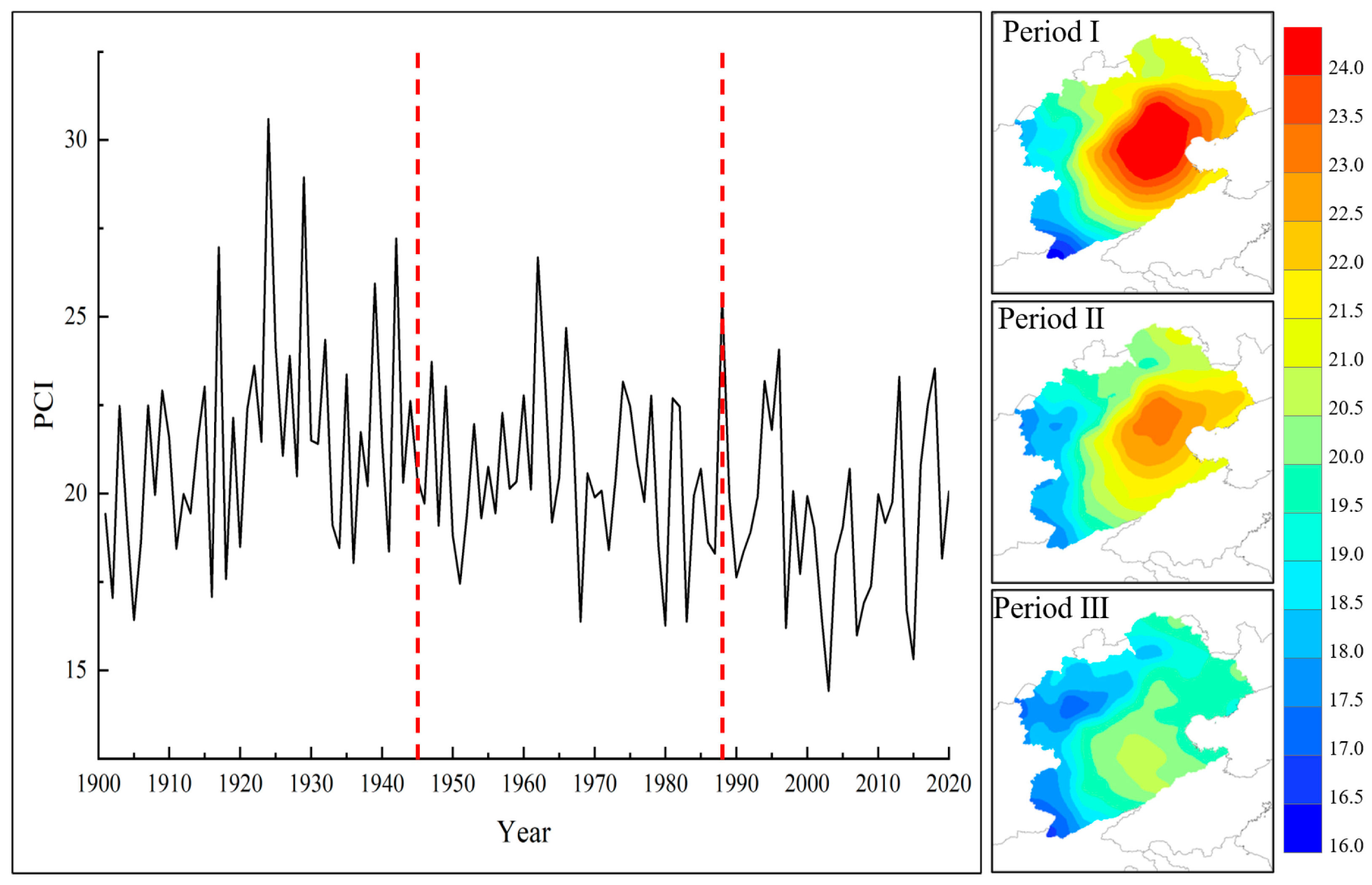
3.3. Spatial and Temporal Variation Patterns of Precipitation in the Haihe River Basin in Different Periods
- Changes in seasonal precipitation tendency rate
- Changes in precipitation concentration index
- Changes in standardized precipitation index
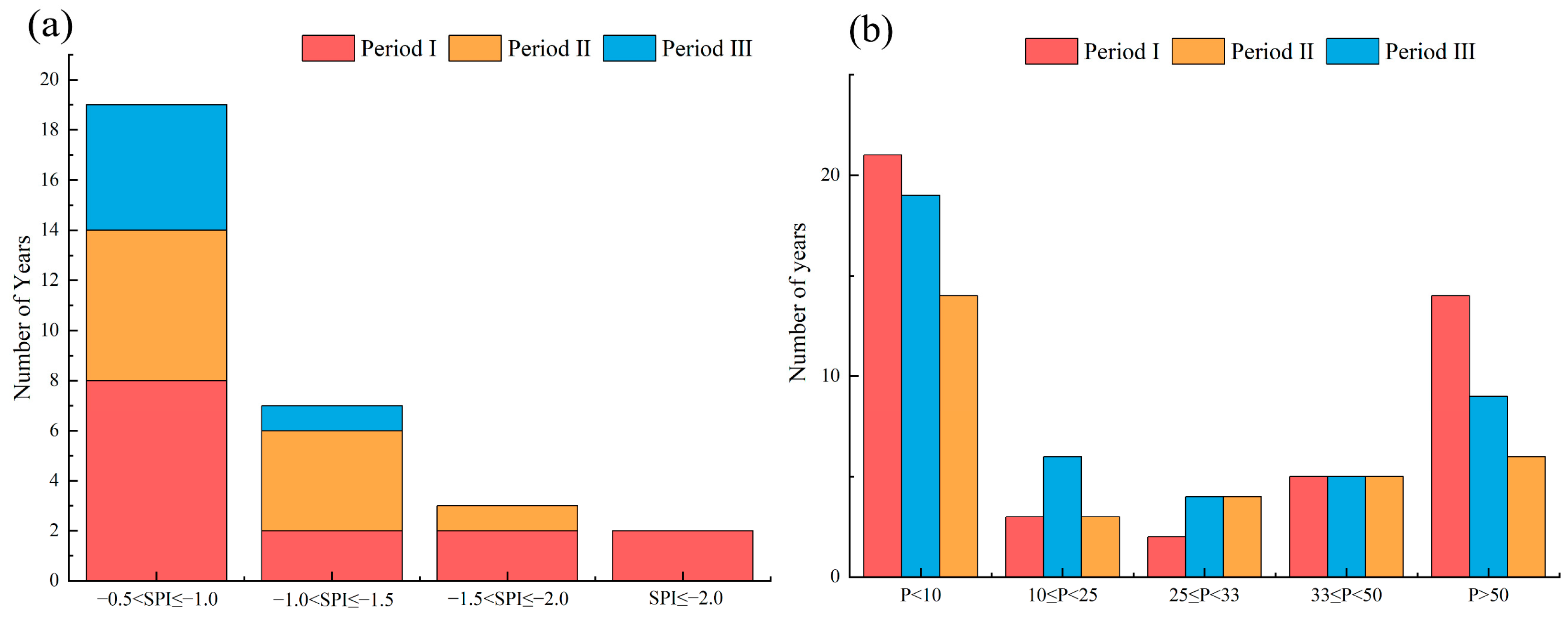
- Changes in extreme precipitation probability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, H.; Su, F. Precipitation correction and reconstruction for streamflow simulation based on 262 rain gauges in the upper brahmaputra of southern Tibetan plateau. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Shahid, S.; Guan, E.H.; He, R.M. Adaptation to climate change impacts on water demand. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2016, 21, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Lott, F.C.; Sun, Y.; Stott, P.A.; Christidis, N. Detectable anthropogenic influence on changes in summer precipitation in China. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 5357–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimri, A.P.; Allen, S.; Huggel, C.; Mal, S.; Pandey, A. Climate change, cryosphere and impacts in the Indian Himalayan region. Curr. Sci. 2021, 120, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uma, L.; Kamol, P.N.S.; Nigel, J. Climate change and dengue risk in central region of Thailand. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2019, 30, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulange, J.; Hanasaki, N.; Dai, Y.; Pokhrel, Y. Role of dams in reducing global flood exposure under climate change. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voropay, N.; Ryazanova, A.; Dyukarev, E. High-resolution bias-corrected precipitation data over South Siberia, Russia. Atmos. Res. 2021, 254, 107440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidu, M.R.; Csaba, H.; Cheveresan, M.; Andric, I.; Stoica, F. Assessing hydrological impact of forested area change: A remote sensing case study. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutti, P.R.; Dubreuil, V.; Bezerra, B.G.; Arvor, D.; de Oliveira, C.P.; Santos e Silva, C.M. Assessment of Gridded CRU TS Data for Long-Term Climatic Water Balance Monitoring over the São Francisco Watershed, Brazil. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalisa, W.; Zhang, J.; Igbawua, T.; Ujoh, F.; Ebohon, O.J.; Namugize, J.N.; Yao, F. Spatio-temporal analysis of drought and return periods over the east african region using standardized precipitation index from 1920 to 2016. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 237, 106195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morice, C.P.; Kennedy, J.J.; Rayner, N.A.; Winn, J.P.; Simpson, I.R. An Updated Assessment of Near-Surface Temperature Change From 1850: The HadCRUT5 Data Set. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 126, e2019JD032361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, G.; Jonathan, H. Contiguous US summer maximum temperature and heat stress trends in CRU and NOAA Climate Division data plus comparisons to reanalyses. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Zhang, W.J.; Xu, H.M. Possible impact of spatial and temporal non-uniformity in land surface temperature data on trend estimation. J. Meteorol. Res. 2018, 32, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Shen, W.; Wu, X.; Wang, P. Applicability of long-term satellite-based precipitation products for drought indices considering global warming. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 255, 109846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Xu, M.H.; Wang, Z.L.; Gao, P.; Lai, C.G. Applicability of two satellite-based precipitation products for assessing rainfall erosivity in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 757, 143975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, B.; Chen, Y.; Guo, H.; Lian, L. Remote sensing applicability evaluation of multisource satellite precipitation data for hydrological research in arid mountainous areas. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Huang, G. Applicability and hydrologic substitutability of tmpa satellite precipitation product in the feilaixia catchment, China. Water 2020, 12, 1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Yang, W.; Luan, Y.; Du, J.; Lin, A.; Zhao, L. Evaluation of the TRMM 3b42 and GPM IMERG products for extreme precipitation analysis over China. Atmos. Res. 2019, 223, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Gao, W.; Hu, J.; Du, L.; Du, L. Capability of imerg v6 early, late, and final precipitation products for monitoring extreme precipitation events. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Yuan, H.; Sun, R.; Yang, C. Streamflow simulations using error correction ensembles of satellite rainfall products over the Huaihe river basin. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.Y.; Yin, S.Q.; Wang, W.T. Spatial interpolation of the extreme hourly precipitation at different return levels in the haihe river basin. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, J. Gbrt-based estimation of terrestrial latent heat flux in the haihe river basin from satellite and reanalysis datasets. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, S.; Liu, B.; Xu, D. Spatial and temporal variation characteristics of snowfall in the haihe river basin from 1960 to 2016. Water 2021, 13, 1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.Y.; Cheng, S.J.; Ma, N.; Guo, J. Intraseasonal evolution of the key areas of precipitation in the Haihe River Basin and quantitative analysis of its associated atmospheric circulation during summer. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Wu, J. Frequency analysis and its spatiotemporal characteristics of precipitation extremes in the Haihe River Basin during 1951–2010. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 43, 381–391. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ren, G.; Wang, T.; Guo, J.; Hao, Z.; Zhan, Y. Characteristics of precipitation variations in Haihe River Basin in modern times. Adv. Sci. Technol. Water Resour. 2015, 35, 102–111. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, R.M.; Zhang, J.Y.; Bao, Z.X.; Yan, X.L.; Wang, G.Q.; Liu, C.S. Response of runoff to climate change in the Haihe River basin. Adv. Water Sci. 2015, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, K.H.; Ramachandra Rao, A. A modified Mann-Kendall trend test for autocorrelated data. J. Hydrol. 1998, 204, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Fang, C.; Qiu, J.; Wang, J. Analysis of Ozone Pollution Characteristics and Influencing Factors in Northeast Economic Cooperation Region, China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.P.; Singh, K. Derivation of the Pearson type (PT) III distribution by using the principle of maximum entropy (POME). J. Hydrol. 1987, 80, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, J.E. Monthly precipitation distribution: A comparative index. Prof. Geogr. 1980, 32, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A.A.Z.; Bellie, S.; Ashish, S. Droughts in a warming climate: A global assessment of Standardized precipitation index (SPI) and Reconnaissance drought index (RDI). J. Hydrol. 2015, 526, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gong, D.; Ye, J.; Chen, Z. Seasonal Precipitation Series of Eastern China Since 1880 and the Variability. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2000, 55, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hua, Y.; Zhou, H.; Ye, L.; Wang, G.; Jin, J.; Bao, Z. Precipitation variation and trend projection in the eastern monsoon region of China since 1470. Adv. Water Sci. 2022, 33, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, B.; Xu, D.; Xu, Z. Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics of Precipitation in the Haihe River Basin under the Influence of Climate Change. Water 2021, 13, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Xia, J.; Zeng, S.; She, D.; Liu, J. Variations and statistical probability characteristic analysis of extreme precipitation events under climate change in Haihe River Basin, China. Hydrol. Processes 2014, 28, 913–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Men, B. Evaluation of Water Resources Carrying Capacity in Haihe River Basin Based on Combinatorial Game Theory. Water Resour. Power 2021, 39, 61–64. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; Fu, G.; He, R.; Yan, X.; Jin, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, A. Attribution for decreasing streamflow of the Haihe River basin, northern China: Climate variability or human activities? J. Hydrol. 2012, 460–461, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| SPI | Level |
|---|---|
| SPI ≤ −2.0 | Extremely Drought |
| −2.0 < SPI ≤ −1.5 | Severely Drought |
| −1.5 < SPI ≤ −1.0 | Moderately Drought |
| −1.0 < SPI ≤ −0.5 | Mild drought |
| −0.5 < SPI | No Drought |
| Reference Object | R | BIAS (%) | RMSE (mm/mon) | MAE (mm/mon) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area rainfall (based on ground station) | 0.99 | 10.93 | 9.79 | 4.87 |
| Dataset of gridded daily precipitation in China | 0.99 | 7.00 | 10.15 | 3.26 |
| Anyang Station | 0.89 | 47.84 | 31.91 | 13.55 |
| Baoding Station | 0.90 | 33.22 | 30.03 | 0.92 |
| Beijing Station | 0.92 | 31.51 | 29.42 | 0.90 |
| Datong Station | 0.94 | 24.19 | 12.68 | 7.54 |
| Duolun Station | 0.92 | 26.18 | 15.38 | 0.92 |
| Tianjin Station | 0.93 | 27.88 | 24.44 | 0.93 |
| Wutaishan Station | 0.93 | 38.91 | 37.66 | 0.38 |
| Weixian Station | 0.91 | 36.38 | 21.31 | 0.36 |
| Yuanping Station | 0.90 | 37.53 | 22.50 | 0.37 |
| Yushe Station | 0.89 | 31.83 | 25.34 | 0.31 |
| Xingtai Station | 0.81 | 39.97 | 41.56 | 0.39 |
| Xinxiang Station | 0.82 | 40.42 | 40.15 | 0.40 |
| Fengning Station | 0.92 | 31.19 | 21.02 | 0.31 |
| Weichang Station | 0.89 | 35.06 | 23.34 | 0.35 |
| Zhangjiakou Station | 0.89 | 37.78 | 22.01 | 0.37 |
| Huailai Station | 0.91 | 39.27 | 20.83 | 0.39 |
| Miyun Station | 0.91 | 39.94 | 43.86 | 0.39 |
| Chengde Station | 0.90 | 30.54 | 24.63 | 0.30 |
| Zunhua Station | 0.91 | 40.27 | 53.61 | 0.40 |
| Qinglong Station | 0.92 | 38.22 | 47.74 | 0.38 |
| Langfang Station | 0.90 | 36.10 | 30.81 | 0.36 |
| Tangshan Station | 0.94 | 32.57 | 32.09 | 0.32 |
| Leting Station | 0.89 | 35.81 | 37.52 | 0.35 |
| Raoyang Station | 0.87 | 40.53 | 34.89 | 0.40 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, J.; Guan, T.; Jin, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, G.; Bao, Z. Centennial Precipitation Characteristics Change in Haihe River Basin, China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071025
Chen X, Liu Y, Sun Z, Zhang J, Guan T, Jin J, Liu C, Wang G, Bao Z. Centennial Precipitation Characteristics Change in Haihe River Basin, China. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(7):1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071025
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xin, Yanli Liu, Zhouliang Sun, Jianyun Zhang, Tiesheng Guan, Junliang Jin, Cuishan Liu, Guoqing Wang, and Zhenxin Bao. 2022. "Centennial Precipitation Characteristics Change in Haihe River Basin, China" Atmosphere 13, no. 7: 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071025
APA StyleChen, X., Liu, Y., Sun, Z., Zhang, J., Guan, T., Jin, J., Liu, C., Wang, G., & Bao, Z. (2022). Centennial Precipitation Characteristics Change in Haihe River Basin, China. Atmosphere, 13(7), 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071025








