An Improved Strategy for Real-Time Troposphere Estimation and Its Application in the Severe Weather Event Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Data and Experiments
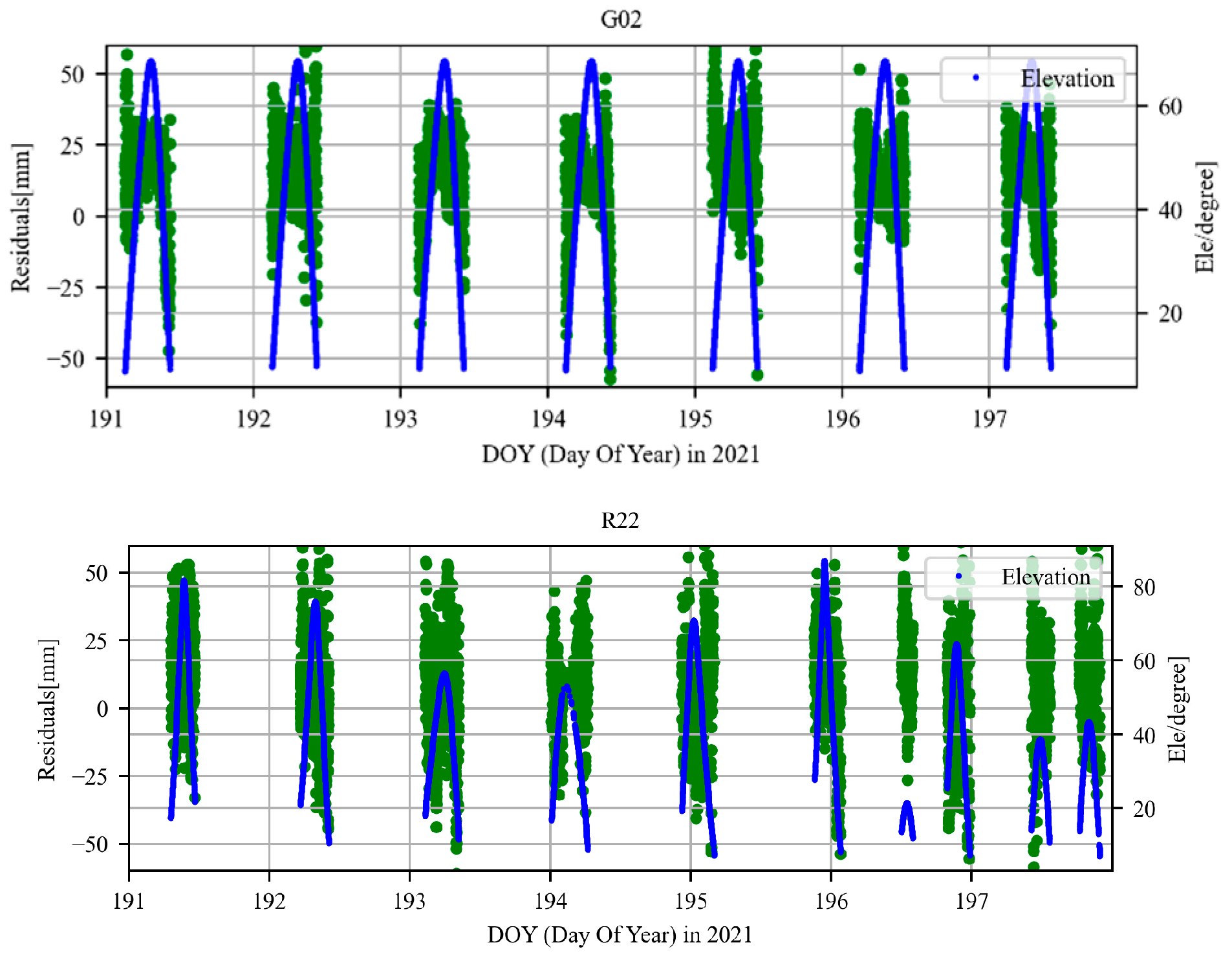
3.1. Validation of Advanced Strategy for Tropospheric Estimation
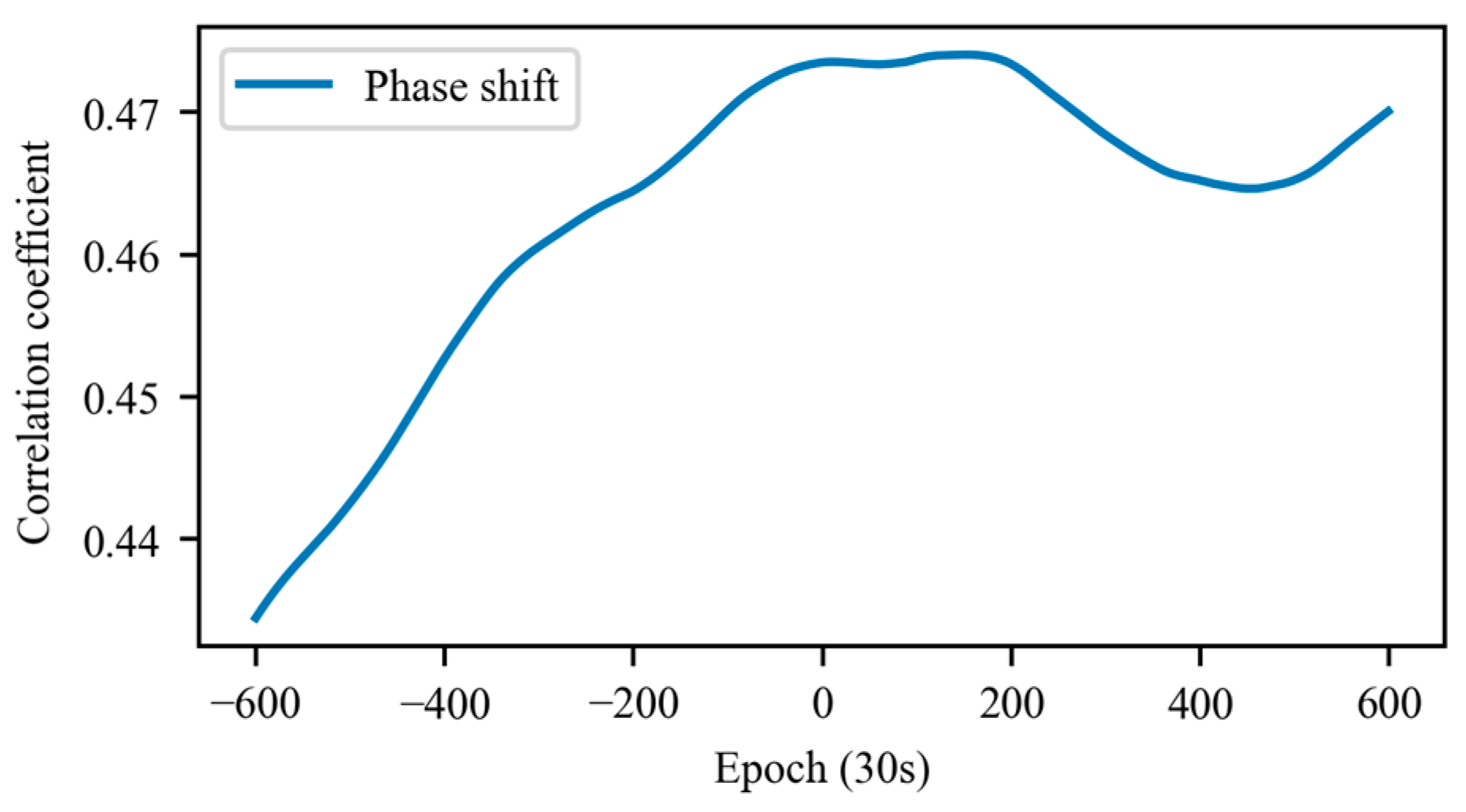
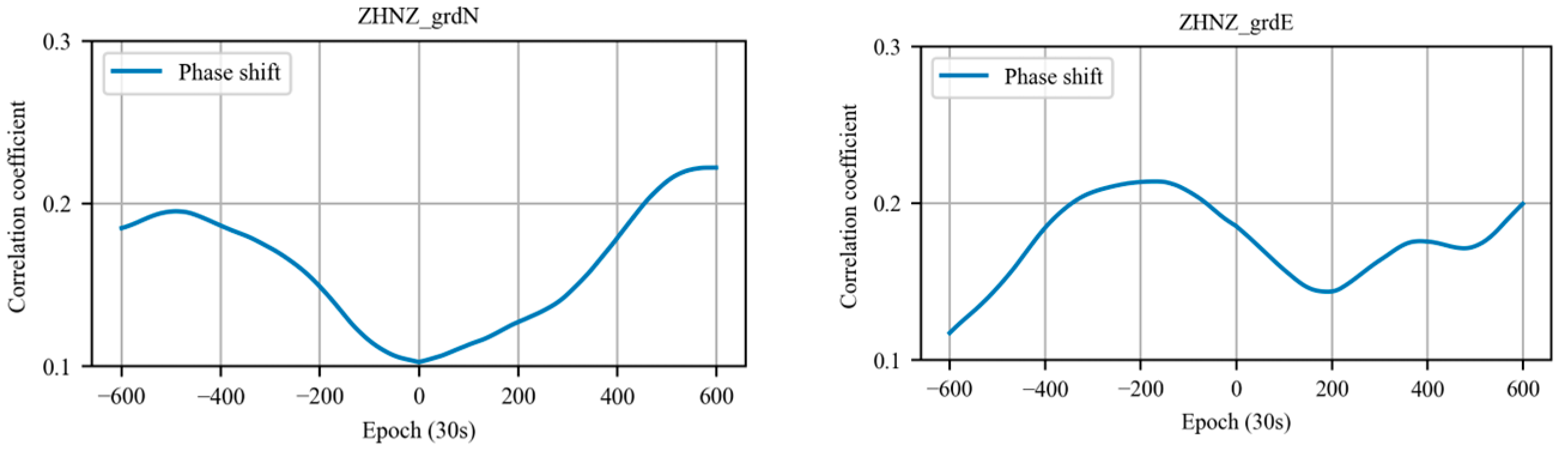
3.2. Correlation Analysis between the GNSS Derived Tropospheric Parameters and Rainfall Event
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baker, H.C.; Dodson, A.H.; Penna, N.T.; Higgins, M.; Offiler, D. Ground-based GPS water vapour estimation: Potential for meteorological forecasting. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2001, 63, 1305–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Václavovic, P.; Douša, J. Performance evaluation of troposphere estimated from galileo-only multi-frequency observations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.L.; Herring, T.A.; Shapiro, I.I.; Rogers, A.; Elgered, G. Geodesy by radio interferometry: Effects of atmospheric modeling errors on estimates of baseline length. Radio Sci. 1985, 20, 1593–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saastamoinen, J. Contributions to the theory of atmospheric refraction. Bull. Géodésique 1972, 105, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhu, G.; Peng, H.; Liu, L.; Ren, C.; Jiang, W. An improved global grid model for calibrating zenith tropospheric delay for GNSS applications. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevis, M.; Businger, S.; Chiswell, S.; Herring, T.A.; Anthes, R.A.; Rocken, C.; Ware, R.H. GPS meteorology: Mapping zenith wet delays onto precipitable water. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1994, 33, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, D.P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liang, H.; Lou, Y.; Cai, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, W. On the suitability of ERA5 in hourly GPS precipitable water vapor retrieval over China. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 1897–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lou, Y.; Haase, J.S.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, G.; Huang, J.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. The use of ground-based GPS precipitable water measurements over China to assess radiosonde and ERA-Interim moisture trends and errors from 1999 to 2015. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 7643–7667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Kuang, C.; Liu, W.; Bai, J. Improved performance of ERA5 in global tropospheric delay retrieval. J. Geod. 2020, 94, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, X.; Xiong, S.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Mo, Z.; Fu, B.; He, H. High-precision GNSS PWV retrieval using dense GNSS sites and in-situ meteorological observations for the evaluation of MERRA-2 and ERA5 reanalysis products over China. Atmos. Res. 2022, 276, 106247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Huang, G.; Xu, Y.; Ta, L.; Jing, C.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Z. Accuracy Evaluation and Analysis of GNSS Tropospheric Delay Inversion from Meteorological Reanalysis Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Jiang, W.; Liu, L.; Chen, H.; Ye, S. A new global grid model for the determination of atmospheric weighted mean temperature in GPS precipitable water vapor. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateus, P.; Catalão, J.; Mendes, V.B.; Nico, G. An ERA5-based hourly global pressure and temperature (HGPT) model. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Xu, C.; Guo, J.; Gao, Y. Real-Time GPS precise point positioning-based precipitable water vapor estimation for rainfall monitoring and forecasting. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 3452–3459. [Google Scholar]
- Barindelli, S.; Realini, E.; Venuti, G.; Fermi, A.; Gatti, A. Detection of water vapor time variations associated with heavy rain in northern Italy by geodetic and low-cost GNSS receivers. Earth Planets Space 2018, 70, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Mo, Z.; Xie, S.; Liu, L.; Chen, J.; Kang, C.; Wang, S. Spatiotemporal characteristics of GNSS-derived precipitable water vapor during heavy rainfall events in Guilin, China. Satell. Navig. 2021, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manandhar, S.; Lee, Y.H.; Meng, Y.S. GPS-PWV based improved long-term rainfall prediction algorithm for tropical regions. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, K.; Wu, S.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Hu, A.; Li, W.; Fu, E.; Zhang, M.; Shen, Z. An Improved Method for Rainfall Forecast Based on GNSS-PWV. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.N.; Lee, Y.H.; Manandhar, S. Rainfall forecasting using GPS derived atmospheric gradient and residual for tropical region. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graffigna, V.; Hernández-Pajares, M.; Azpilicueta, F.; Gende, M. Comprehensive Study on the Tropospheric Wet Delay and Horizontal Gradients during a Severe Weather Event. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heh, D.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Biswas, A.N.; Koh, L.M. GPS-Derived Slant Water Vapor for Cloud Monitoring in Singapore. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaclavovic, P.; Dousa, J.; Gyori, G. G-Nut software library-state of development and first results. Acta Geodyn. Geomater. 2013, 10, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douša, J.; Václavovic, P.; Bezdĕka, P.; Guerova, G. European GNSS troposphere monitoring for meteorological applications. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Prague, Czech Republic, 6–10 September 2021; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 906, p. 012058. [Google Scholar]
- Hadas, T.; Hobiger, T.; Hordyniec, P. Considering different recent advancements in GNSS on real-time zenith troposphere estimates. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmierski, K.; Hadas, T.; Sośnica, K. Weighting of multi-GNSS observations in real-time precise point positioning. Remote Sens 2018, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, S.H.; Bar-Sever, Y.E. A new type of troposphere zenith path delay product of the international GNSS service. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Zheng, X.; Jin, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, R.; Yang, Y. Study on the Remote Sensing Spectral Method for Disaster Loss Inversion in Urban Flood Areas. Water 2022, 14, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douša, J.; Dick, G.; Kačmařík, M.; Brožková, R.; Zus, F.; Brenot, H.; Stoycheva, A.; Möller, G.; Kaplon, J. Benchmark campaign and case study episode in central Europe for development and assessment of advanced GNSS tropospheric models and products. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 2989–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Feng, P.; Barriot, J.; Hopuare, M.; Sichoix, L. Correlation between integrated precipitable water vapor and precipitated water during the heavy rainfall event of February 2018 in the Tahiti Island (South Pacific). In Proceedings of the International Conference on Earth Observations and Societal Impacts (ICEO&SI), Taiwan, China, 1–3 July 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]

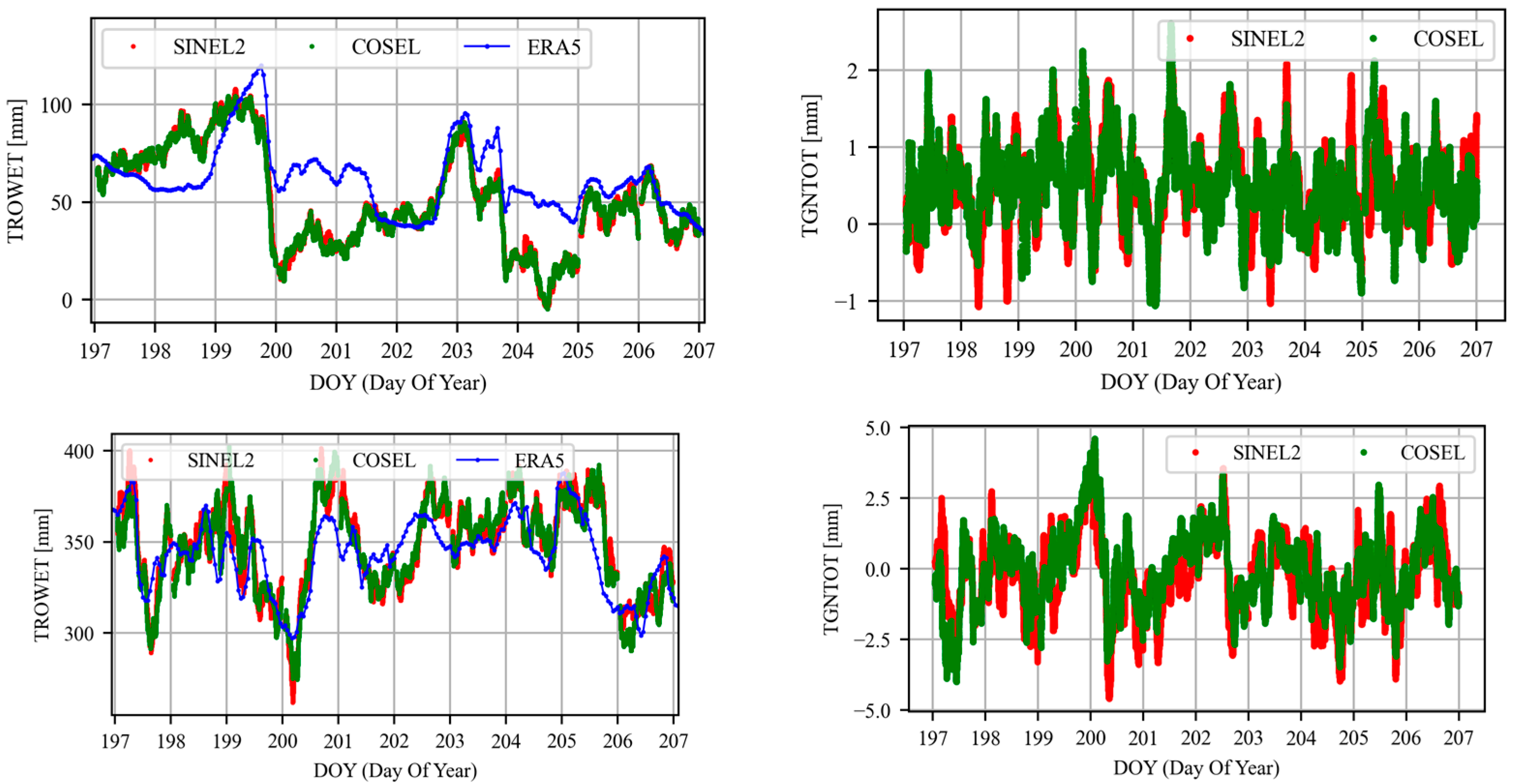


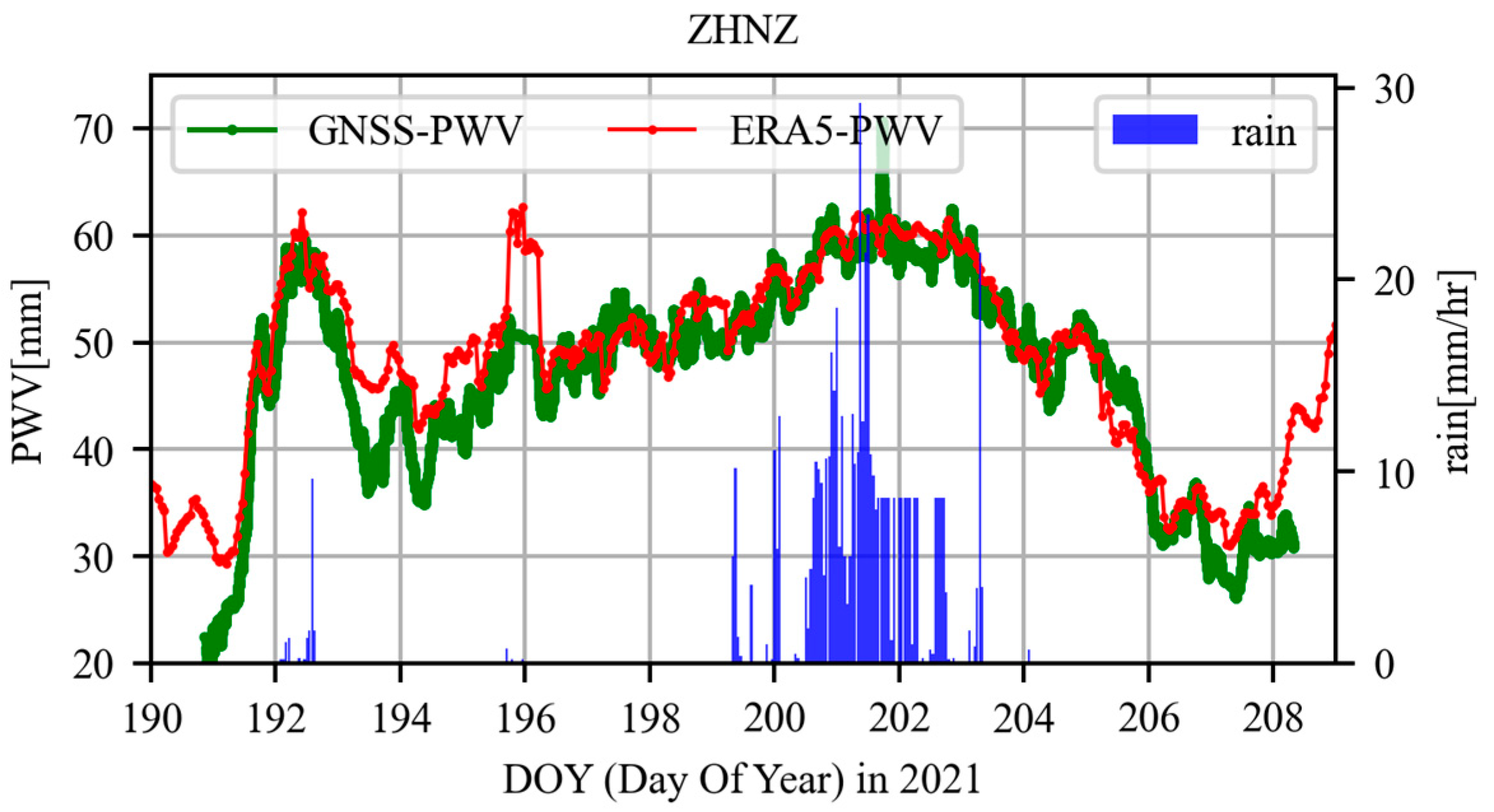
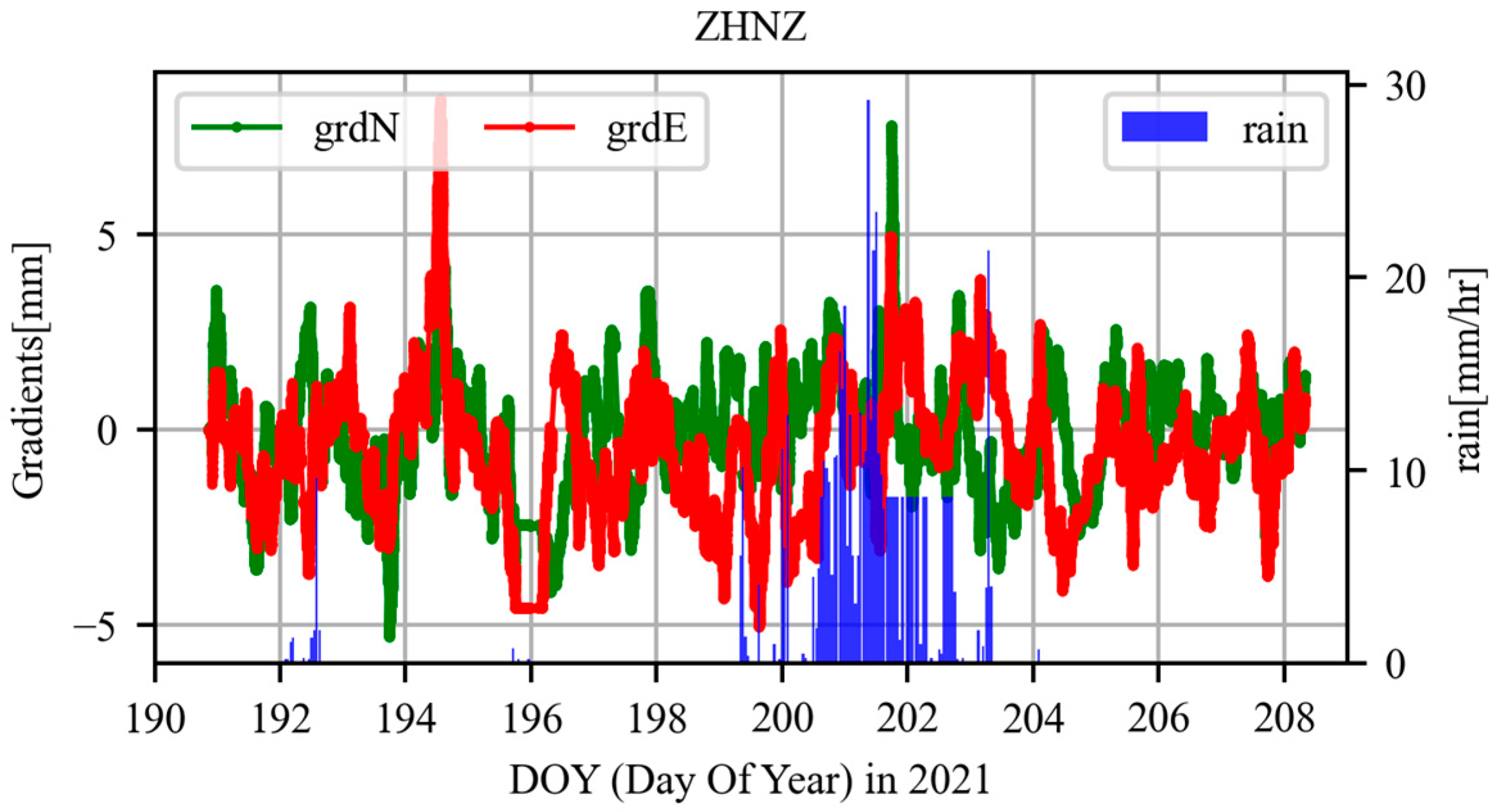
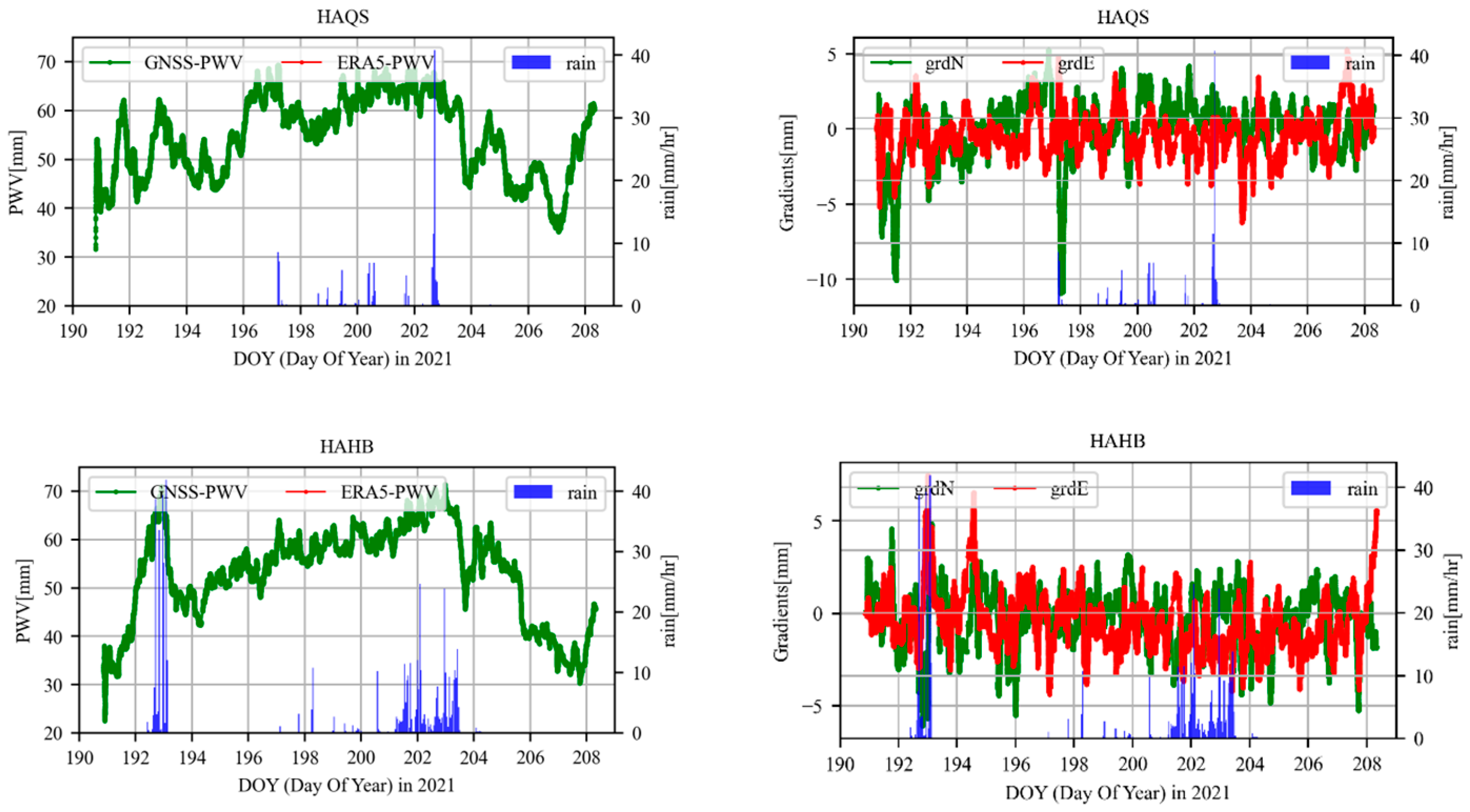

| Item | Strategies |
|---|---|
| Estimator | Forward Kalman |
| Satellite orbit | Fixed with CNES real-time orbits |
| Satellite clock | Fixed with CNES real-time clocks |
| Observations | Carrier phase with a noise of 0.003 m for GPSP seudorange with a noise of 0.3 m for GPS |
| Elevation mask angle | 7 degree |
| Station displacement | Solid Earth tides, ocean tide loading, pole tides, IERS Convention 2010 |
| Earth rotation parameter | Fixed |
| Antenna phase center | Corrected with “igs14_ wwww.atx” file |
| Zenith Tropospheric delay | ZHD: Saastamoinen model ZWD: estimated with random-walk Mapping function: GMF |
| Tropospheric gradients | Estimated, epoch-wise random-walk |
| Receiver clock | Estimated as white noise |
| ISB and IFB | Estimated as constant, GPS as reference |
| Station coordinate | Static: estimated and modeled as constants |
| Phase ambiguities | Estimated as constants, float solution |
| Weighting Function | SISRE Weighting | ZTD [mm] | ZTD + GRD [mm] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | 8.75 | 5.12 | 8.44 | 8.72 | 4.80 | 8.05 | |
| Yes | 8.57 | 3.64 | 6.95 | 8.40 | 3.43 | 6.42 | |
| Yes | 9.26 | 3.75 | 8.11 | 8.77 | 3.78 | 7.23 | |
| GNSS Stations | Meteorological Stations | Latitude (°) | Longitude (°) | Height Difference (m) | Distance (Km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZHNZ | 57082 | 34.52075 | 113.1049 | 71.75 | 10.44 |
| HAHB | 53992 | 35.65847 | 114.5191 | 15.87 | 3.68 |
| HAJY | 53978 | 35.16256 | 112.4475 | 132.44 | 18.97 |
| HAQS | 57294 | 32.84514 | 114.0265 | 13.21 | 5.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, L.; Cui, M.; Song, J. An Improved Strategy for Real-Time Troposphere Estimation and Its Application in the Severe Weather Event Monitoring. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14010046
Zhao L, Cui M, Song J. An Improved Strategy for Real-Time Troposphere Estimation and Its Application in the Severe Weather Event Monitoring. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(1):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14010046
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Lewen, Mingxuan Cui, and Jia Song. 2023. "An Improved Strategy for Real-Time Troposphere Estimation and Its Application in the Severe Weather Event Monitoring" Atmosphere 14, no. 1: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14010046
APA StyleZhao, L., Cui, M., & Song, J. (2023). An Improved Strategy for Real-Time Troposphere Estimation and Its Application in the Severe Weather Event Monitoring. Atmosphere, 14(1), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14010046







