Sensitive Grain-Size Components of Last Glacial Loess on Chinese Loess Plateau and Their Response to East Asian Winter Monsoon
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
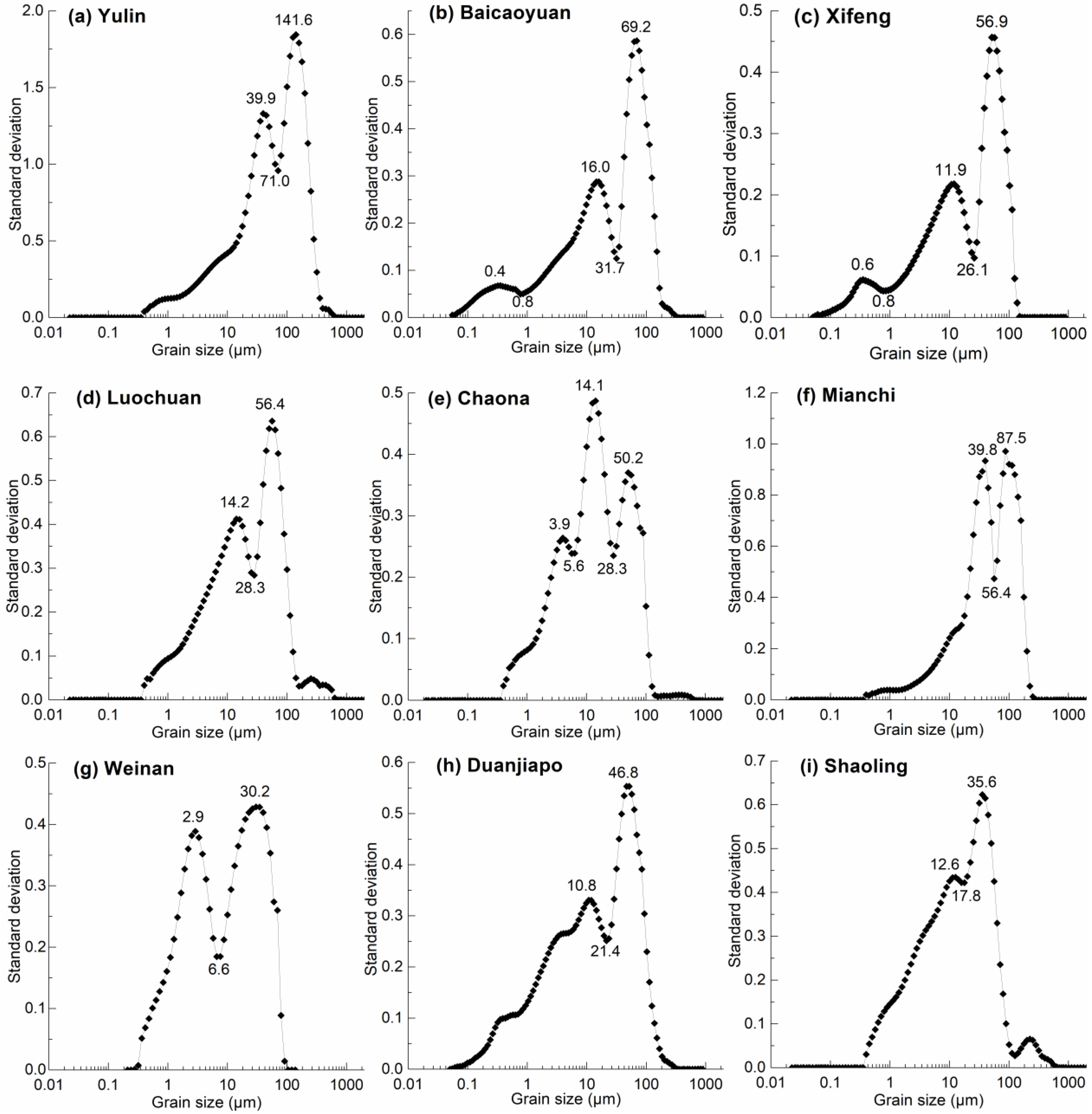
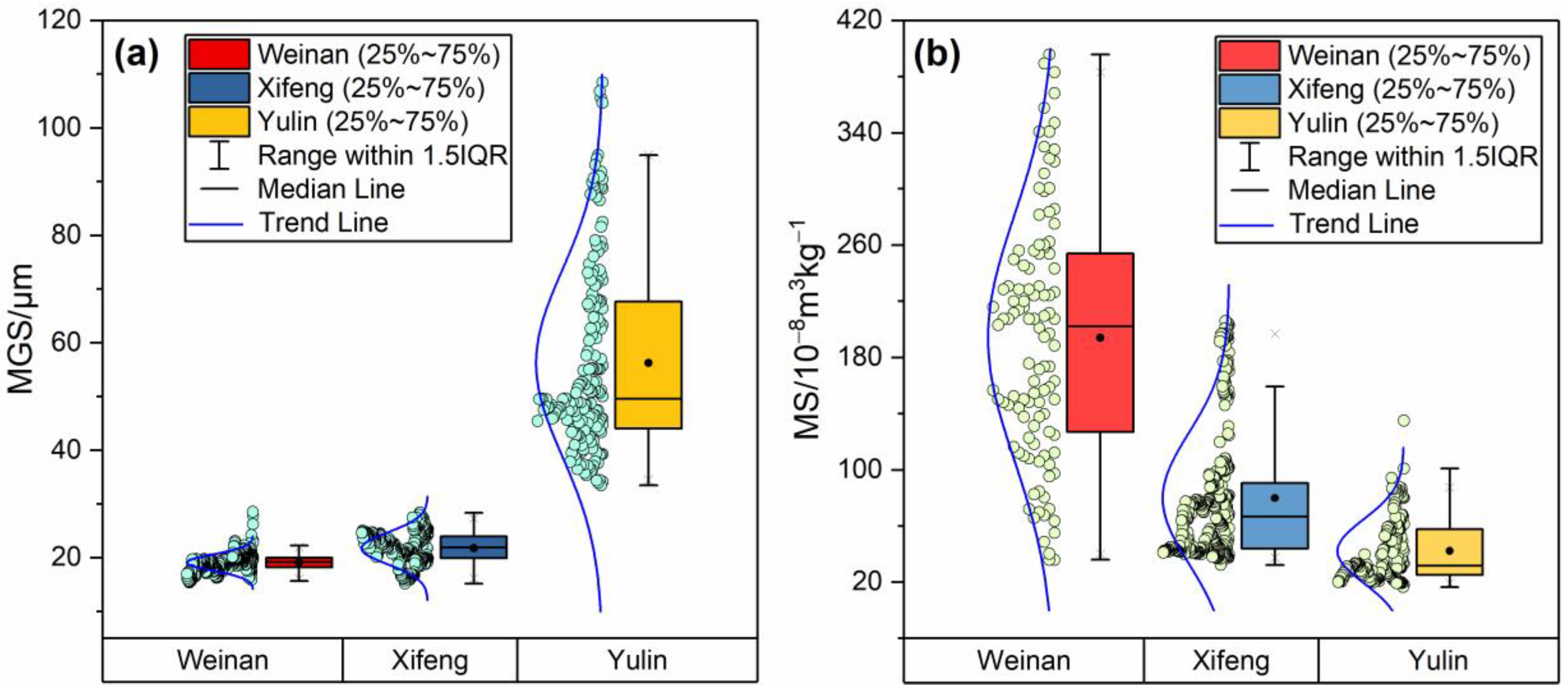
3. Results
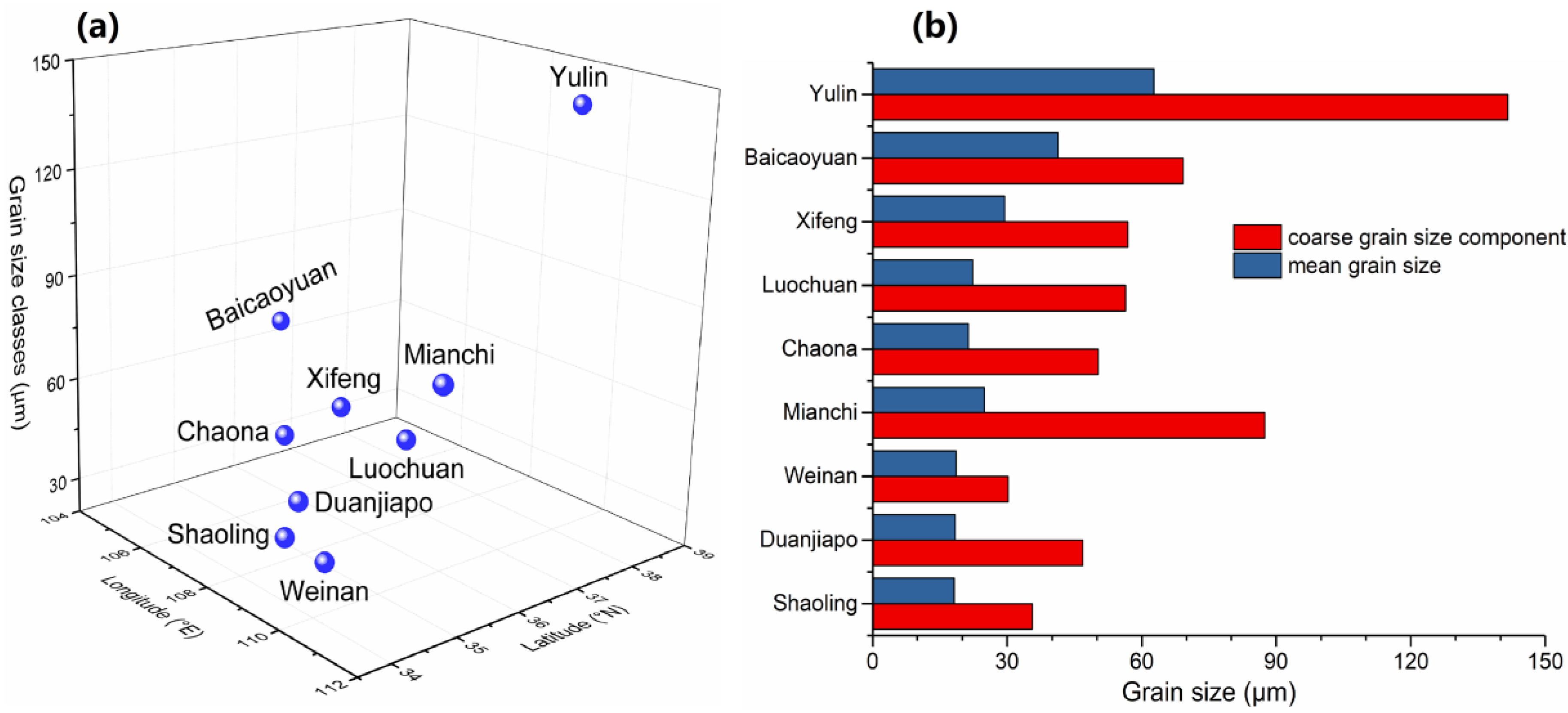
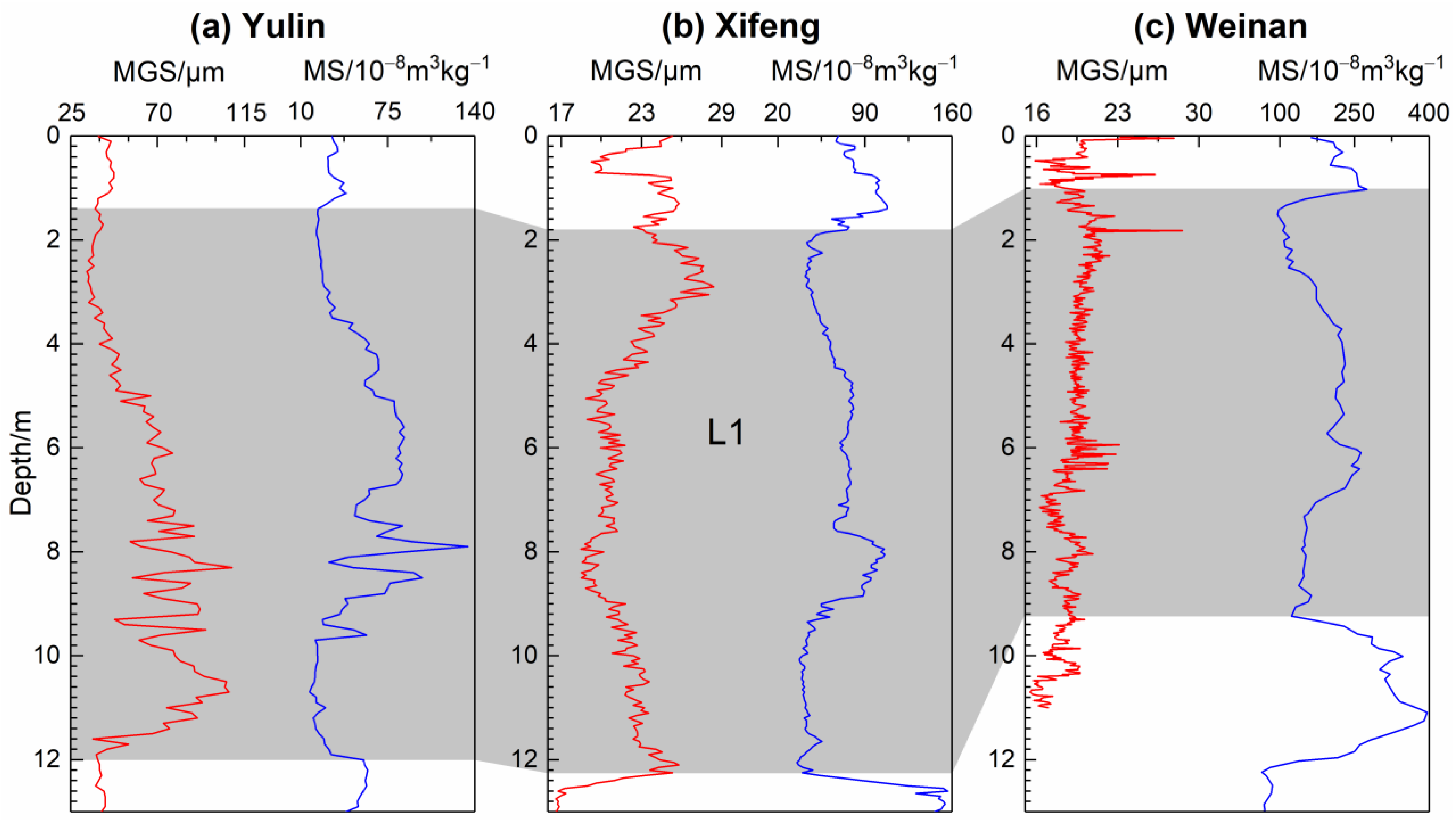
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial Variations in Sensitive Grain-Size Components of Last Glacial Loess on CLP
4.2. The EAWM Implicated by Coarse Sensitive Grain-Size Component
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- An, Z.; Liu, T.; Lu, Y.; Porter, S.C.; Kukla, G.; Wu, X.; Hua, Y. The long-term paleomonsoon variation recorded by the loess-paleosol sequence in central China. Quat. Int. 1990, 7–8, 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- An, Z.; Kukla, G.; Porter, S.C.; Xiao, J. Late Quaternary dust flow on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Catena 1991, 18, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z. Late Cenozoic Climate Change in Asia: Loess, Monsoon and Monsoon-Arid Environment Evolution; Developments in Paleoenvironmental Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.S. Loess and the Environment; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Kukla, G.; An, Z. Loess stratigraphy in Central China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1989, 72, 203–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Sun, D. Pathways of dust input to the Chinese Loess Plateau during the last glacial and interglacial periods. Catena 2000, 40, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, B.A. Palaeoclimatic records of the loess/palaeosol sequences of the Chinese Loess Plateau. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2016, 154, 23–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhs, D.R.; Bettis, A.E. Quaternary loess-Paleosol sequences as examples of climate-driven sedimentary extremes. Geol. Soc. Am. Spec. Pap. 2003, 370, 53–74. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, S.C. Chinese loess record of monsoon climate during the last glacial–interglacial cycle. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2001, 54, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, J.; Clemens, S.C.; Liu, Q.; Ji, J.; Tada, R. East Asian monsoon variability over the last seven glacial cycles recorded by a loess sequence from the northwestern Chinese Loess Plateau. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2006, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Qiang, X.; Hu, S.; Zhao, H.; Fu, C.; Zhao, Q. Records of the Mid-Brunhes Event in Chinese loess-paleosol sequences. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2020, 543, 109596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; An, Z.; Chen, T.; Zhang, G.Y.; Arimoto, R.; Ray, B.J. Late Quaternary records of the atmospheric input of eolian dust to the center of the Chinese Loess Plateau. Quat. Res. 1994, 41, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Qiang, X.; Xu, X.; Sun, Y. Iron oxide characteristics of the Chinese loess-red clay sequences and their implications for the evolution of the East Asian summer monsoon since the Late Oligocene. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2020, 543, 109604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Clemens, S.C.; Guo, F.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Liang, L. High-sedimentation-rate loess records: A new window into understanding orbital- and millennial-scale monsoon variability. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 220, 103731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Ding, Z. Chinese loess and the paleomonsoon. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1998, 26, 111–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Újvári, G.; Kok, J.F.; Varga, G.; Kovács, J. The physics of windblown loess: Implications for grain size proxy interpretations in Quaternary paleoclimate studies. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 154, 247–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zheng, H.; Li, J.; Xie, X.; Mei, X. Dynamic control on grain-size distribution of terrigenous sediments in the western South China Sea: Implication for East Asian monsoon evolution. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Liu, Q.; Torrent, J.; Barrón, V.; Jin, C. Characterizing and quantifying iron oxides in Chinese loess/paleosols: Implications for pedogenesis. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 369–370, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Liu, Q.; Heslop, D.; Roberts, A.P.; Jin, C. Soil moisture balance and magnetic enhancement in loess–paleosol sequences from the Tibetan Plateau and Chinese Loess Plateau. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2015, 409, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Wang, B.; Lu, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Xia, D. New insights into the magnetic characteristics of high mountain loess in Central Asia and its paleoclimatic implications. Quat. Int. 2019, 502, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; King, J.W.; Fang, X. Enhancement mechanisms of magnetic susceptibility in the Chinese red-clay sequence. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Song, Y.; King, J.W.; Egli, R. Consistent grain size distribution of pedogenic maghemite of surface soils and Miocene loessic soils on the Chinese Loess Plateau. J. Quat. Sci. 2010, 25, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Fang, X.; King, J.W.; Li, J.; Naoto, I.; An, Z. Magnetic parameter variations in the Chaona loess/paleosol sequences in the central Chinese Loess Plateau, and their significance for the middle Pleistocene climate transition. Quat. Res. 2014, 81, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Su, R.; Bloemendal, J.; Lu, H. Grain-size and accumulation rate records from Late Cenozoic aeolian sequences in northern China: Implications for variations in the East Asian winter monsoon and westerly atmospheric circulation. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2008, 264, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Clemens, S.C. Impacts of post-depositional processes on rapid monsoon signals recorded by the last glacial loess deposits of northern China. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 289, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, J.; Li, X.; Fang, X.; Zhang, W.; Yan, M.; Mao, Z. Grain-size analysis of Upper Pliocene red clay deposits from Linxia Basin: Implications for Asian monsoon evolution on the NE margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2018, 511, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Lu, H.; Yi, S.; Stevens, T.; Xu, Z.; Zhuo, H.; Yu, K.; Zhang, H. Long-term Pleistocene aridification and possible linkage to high-latitude forcing: New evidence from grain size and magnetic susceptibility proxies from loess-paleosol record in northeastern China. Catena 2017, 154, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doeglas, D.J. Grain-size indices, classification and environment. Sedimentology 1968, 10, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, J. Loess particle size data indicative of stable winter monsoons during the last interglacial in the western part of the Chinese Loess Plateau. Catena 2000, 39, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zan, J.; Yang, R.; Fang, X.; Yang, S. Grain-size-dependent geochemical characteristics of Middle and Upper Pleistocene loess sequences from the Junggar Basin: Implications for the provenance of Chinese eolian deposits. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2020, 538, 109458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Mu, G.; Xu, L.; Zhao, X. The origin of bimodal grain-size distribution for aeolian deposits. Aeolian Res. 2016, 20, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, H. Stepwise coupling between Chinese loess deposition and global temperature since the early Pleistocene tested by a multiple-state model. Quat. Int. 2022, 620, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, W.; Xiang, R.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L. Re-examining the potential of using sensitive grain size of coastal muddy sediments as proxy of winter monsoon strength. Quatern. Int. 2014, 333, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sun, Y.; Vandenberghe, J.; Li, Y.; An, Z. Palaeoenvironmental implication of grain-size compositions of terrace deposits on the western Chinese Loess Plateau. Aeolian Res. 2018, 32, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Vandenberghe, J.; An, Z.; Li, Y.; Jin, Z.; Dong, J.; Sun, Y. Grain size of Lake Qinghai sediments: Implications for riverine input and Holocene monsoon variability. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2016, 449, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; An, Z. Palaeoclimatic significance of grain size of loess–palaeosol sequence of Central China. Sci. China Series D-Earth Sci. 1998, 41, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, G.A.; Heslop, D. New methods for unmixing sediment grain size data. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2015, 16, 4494–4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Bloemendal, J.; Rea, D.K.; Vandenberghe, J.; Jiang, F.; An, Z.; Su, R. Grain-size distribution function of polymodal sediments in hydraulic and aeolian environments, and numerical partitioning of the sedimentary components. Sed. Geol. 2002, 152, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Sun, J.; Gong, Z. Loess deposits in Beijing and their paleoclimatic implications during the last interglacial-glacial cycle. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2017, 177, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberghe, J. Grain size of fine-grained windblown sediment: A powerful proxy for process identification. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2013, 121, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberghe, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Abels, H.A.; Liu, X. Grain-size characterization of reworked fine-grained aeolian deposits. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 177, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Porter, S.C.; An, Z.; Kumai, H.; Yoshikawa, S. Grain Size of Quartz as an Indicator of Winter Monsoon Strength on the Loess Plateau of Central China during the Last 130,000 Yr. Quat. Res. 1995, 43, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Chang, Z.; Fan, H.; Zhou, L.; Xhai, D.; Wen, R.; Qin, X. The link between grain-size components and depositional processes in a modern clastic lake. Sedimentology 2012, 59, 1050–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, T.; Qiang, M.; Matishov, G.G.; Velichko, A.A.; Zeng, B.; Xu, M.; Shi, P. Interpretation of sedimentary subpopulations extracted from grain size distributions in loess deposits at the Sea of Azov, Russia. Aeolian Res. 2020, 45, 100597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Qian, H.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, W.; Ren, W.; Wang, H. Relationship between fractal characteristics of grain-size and physical properties: Insights from a typical loess profile of the loess Plateau. Catena 2021, 207, 105653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprafke, T.; Schulte, P.; Meyer-Heintze, S.; Händel, M.; Einwögerer, T.; Simon, U.; Peticzka, R.; Schäfer, C.; Lehmkuhl, F.; Terhorst, B. Paleoenvironments from robust loess stratigraphy using high-resolution color and grain-size data of the last glacial Krems-Wachtberg record (NE Austria). Quat. Sci. Rev. 2020, 248, 106602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, C.; Wang, N.; Qiu, H.; Wang, H.; Xiao, Q.; Chen, D.; Lin, X.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Late Pleistocene-Holocene aeolian loess-paleosol sections in the Yellow River source area on the northeast Tibetan Plateau: Chronostratigraphy, sediment provenance, and implications for paleoclimate reconstruction. Catena 2022, 208, 105777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Zhang, C.; Li, Q.; Wang, R.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Y. Grain-size composition of the surface sediments in Chinese deserts and the associated dust emission. Catena. 2022, 219, 106615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugteren, G.; Vandenberghe, J. Spatial climatic variability on the Central Loess Plateau (China) as recorded by grain size for the last 250 kyr. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2004, 41, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lu, H.; An, Z. Grain size of loess, palaeosol and Red Clay deposits on the Chinese Loess Plateau: Significance for understanding pedogenic alteration and palaeomonsoon evolution. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2006, 241, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Lu, H.; Qiang, X. Changes in grain-size and sedimentation rate of the Neogene Red Clay deposits along the Chinese Loess Plateau and implications for the palaeowind system. Sci. China Ser. D 2005, 48, 1452–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prins, M.A.; Vriend, M.; Nugteren, G.; Vandenberghe, J.; Lu, H.Y.; Zheng, H.B.; Weltje, G.J. Late Quaternary aeolian dust input variability on the Chinese Loess Plateau: Inferences from unmixing of loess grain-size records. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2007, 435, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, P.; Lehmkuhl, F. The difference of two laser diffraction patterns as an indicator for post-depositional grain size reduction in loess-paleosol sequences. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2018, 509, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Gao, S.; Li, J. Preliminary analysis of grain-size populations with environmentally sensitive terrigenous components in marginal sea setting. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2003, 48, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vriend, M.; Prins, M.A.; Buylaert, J.P.; Vandenberghe, J.; Lu, H. Contrasting dust supply patterns across the north-western Chinese Loess Plateau during the last glacial-interglacial cycle. Quat. Int. 2011, 240, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Yu, Z.; Yang, S.; Sun, J.; Xiong, S.; Liu, T. Coeval changes in grain size and sedimentation rate of eolian loess, the Chinese Loess Plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 2097–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nottebaum, V.; Stauch, G.; Hartmann, K.; Zhang, J.; Lehmkuhl, F. Unmixed loess grain size populations along the northern Qilian Shan (China): Relationships between geomorphologic, sedimentologic and climatic controls. Quat. Int. 2015, 372, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberghe, J.; An, Z.; Nugteren, G.; Lu, H.; Van Huissteden, J. New absolute time scale for the Quaternary climate in the Chinese loess region by grain-size analysis. Geology 1997, 25, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulay, S.; Colin, C.; Trentesaux, A.; Pluquet, F.; Bertaux, J.; Blamart, D.; Buehring, C.; Wang, P. Mineralogy and sedimentology of Pleistocene sediment in the South China Sea (ODP Site 1144). Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program. Sci. Results 2003, 184, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Ding, X.; Yu, L.; Ni, Z. Palaeoclimatic implications of aeolian sediments on the Miaodao Islands, Bohai Sea, East China, based on OSL dating and proxies. Aeolian Res. 2015, 19, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Xiao, J.; Nakamura, T.; Liu, B.; Inouchi, Y. Holocene East Asian monsoonal precipitation pattern revealed by grain-size distribution of core sediments of Daihai Lake in Inner Mongolia of north-central China. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 233, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Pan, B.; Gui, H.; Zhang, C. Discussion of the relationship between dustfall grain size and the desert border, taking the southern border of the Tengger Desert and the southern dust deposit area as an example. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2013, 386, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, A.C.; Wan, S.M. Sensitive grain-size records of Holocene East Asian summer monsoon in sediments of northern South China Sea slope. Quat. Res. 2017, 75, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, R.; Yang, Z.; Yoshiki, S.; Guo, Z.; Fan, D.; Li, Y.; Xiao, S.; Shi, X.; Chen, M. East Asia Winter Monsoon changes inferred from environmentally sensitive grain-size component records during the last 2300 years in mud area southwest off Cheju Island, ECS. Sci. China, Ser. D 2006, 49, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Li, A.; Liu, J.P.; Chen, M.; Xie, Q.; Jiang, F.; Li, T.; Xiang, R.; Chen, Z. Coherence between solar activity and the East Asian winter monsoon variability in the past 8000 years from Yangtze River-derived mud in the East China Sea. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2006, 237, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Qi, H.; Sun, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z. Annual lamination and its sedimentary implications in the Yangtze River delta inferred from High-resolution biogenic silica and sensitive grain-size records. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, I.; Daele, M.V.; Tanghe, N.; Batist, M.D.; Verschuren, D. Reconstructing East African monsoon variability from grain-size distributions: End-member modeling and source attribution of diatom-rich sediments from Lake Chala. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2020, 247, 106574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mahiques, M.M.; YGoya, S.C.; Da Silva, M.C.; De Oliveira, R.A.U.; Mi Kim, B.S.; De Lima Ferreira, P.A.; Lopes Figueira, R.C.; Bícegoa, M.C. Grain-size end-members and environmentally sensitive grain-size components: A comparative study in the mud shelf depocenters off southern Brazil. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2021, 36, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Xu, S.; Han, M.; Chen, H.; Miao, X.; Kong, X.; Jia, G. Application of grain size endmember analysis in the study of dust accumulation processes: A case study of loess in Shandong Province, East China. Sediment. Geol. 2021, 416, 105868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.C.; Zhang, J.F.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhou, L.P. Origin and provenance of Red Clay in north Hunan Province, China: Inferred from grain-size analysis and end-member modelling. Aeolian Res. 2021, 51, 100714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; An, Z. Pretreated methods on loess-palaeosol samples granulometry. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1998, 43, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Kukla, G.J.; Porter, S.C.; Xiao, J. Magnetic susceptibility evidence of monsoon variation on the Loess Plateau of Central China during the last 130,000 years. Quat. Res. 1991, 36, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Porter, S.C. Millennial-scale climatic oscillations during the last interglaciation in central China. Geology 1997, 25, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Ono, Y.; Fukusawa, H.; Pan, B.; Li, J.; Guan, D.; Oi, K.; Tsukamoto, S.; Torii, M.; Mishima, T. Asian summer monsoon instability during the past 60,000 years: Magnetic susceptibility and pedogenic evidence from the western Chinese Loess Plateau. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1999, 168, 219–232. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, X.; Zhou, W.; Back, J.; Xian, F.; Qiang, X.; Ao, H.; Wu, Z.; An, Z. Loess magnetic susceptibility flux: A new proxy of East Asian monsoon precipitation. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2020, 201, 104489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
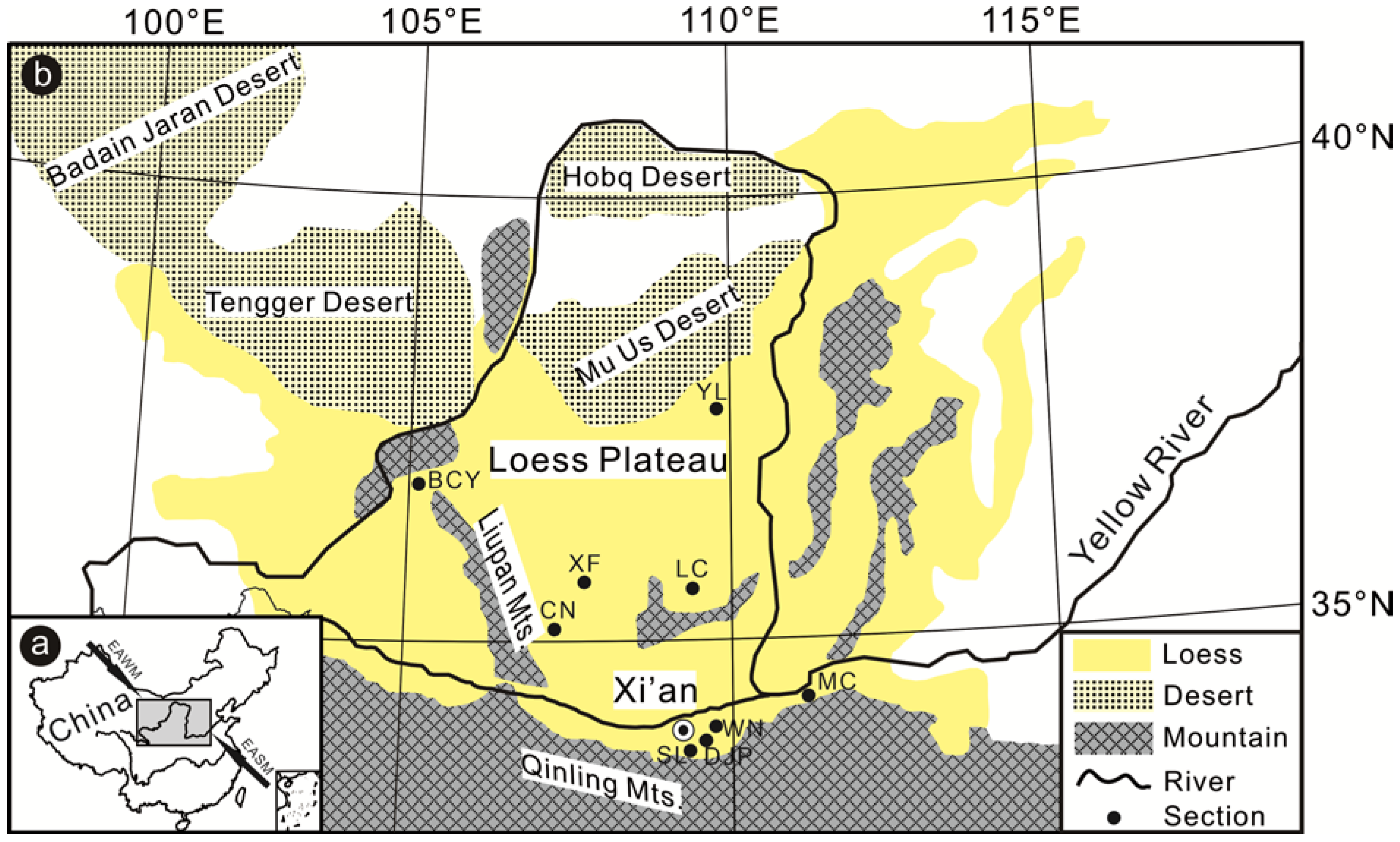
| Sampling | Sections | Samples | Latitude | Longitude | Altitude | L1 Thickness | L1 MGS 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site | Abbreviations | ° N | ° E | m | m | μm | |
| Yulin | YL | 200 | 38.271 | 109.792 | 1197 | 11.60 | 62.75 |
| Baicaoyuan | BCY | 210 | 36.218 | 105.024 | 1830 | 13.35 | 41.33 |
| Xifeng | XF | 205 | 35.783 | 107.623 | 1352 | 11.80 | 29.41 |
| Luochuan | LC | 56 | 35.752 | 109.416 | 1065 | 8.04 | 22.37 |
| Chaona | CN | 208 | 35.147 | 107.224 | 1464 | 6.18 | 21.32 |
| Mianchi | MC | 130 | 34.772 | 111.777 | 535 | 7.12 | 24.87 |
| Weinan | WN | 288 | 34.415 | 109.562 | 787 | 8.20 | 18.62 |
| Duanjiapo | DJP | 209 | 34.188 | 109.233 | 593 | 5.00 | 18.41 |
| Shaoling | SL | 91 | 34.138 | 108.965 | 443 | 6.70 | 18.15 |
| Ranks | Grain Size | Ranks | Grain Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.90 | 10 | 39.80 |
| 2 | 10.80 | 11 | 39.90 |
| 3 | 11.90 | 12 | 46.80 |
| 4 | 12.60 | 13 | 50.20 |
| 5 | 14.10 | 14 | 56.40 |
| 6 | 14.20 | 15 | 56.90 |
| 7 | 16.00 | 16 | 69.20 |
| 8 | 30.20 | 17 | 87.50 |
| 9 | 35.60 | 18 | 141.60 |
| Group 1 | Group 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Grain Size | Ranks | Grain Size | Ranks |
| 39.90 | 11 | 141.80 | 18 |
| 16.00 | 7 | 69.20 | 16 |
| 11.90 | 3 | 56.90 | 15 |
| 14.20 | 6 | 56.40 | 14 |
| 14.10 | 5 | 50.20 | 13 |
| 39.80 | 10 | 87.50 | 17 |
| 2.90 | 1 | 30.20 | 8 |
| 10.80 | 2 | 46.80 | 12 |
| 12.60 | 4 | 35.60 | 9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Song, Y.; Duan, L.; Li, J. Sensitive Grain-Size Components of Last Glacial Loess on Chinese Loess Plateau and Their Response to East Asian Winter Monsoon. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020304
Wang Q, Song Y, Duan L, Li J. Sensitive Grain-Size Components of Last Glacial Loess on Chinese Loess Plateau and Their Response to East Asian Winter Monsoon. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(2):304. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020304
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qiansuo, Yougui Song, Linqiong Duan, and Jinchan Li. 2023. "Sensitive Grain-Size Components of Last Glacial Loess on Chinese Loess Plateau and Their Response to East Asian Winter Monsoon" Atmosphere 14, no. 2: 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020304
APA StyleWang, Q., Song, Y., Duan, L., & Li, J. (2023). Sensitive Grain-Size Components of Last Glacial Loess on Chinese Loess Plateau and Their Response to East Asian Winter Monsoon. Atmosphere, 14(2), 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020304







