Assessing the Impact of Climate Change on the Biodeterioration Risk in Historical Buildings of the Mediterranean Area: The State Archives of Palermo
Abstract
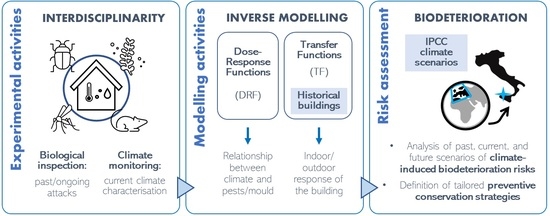
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
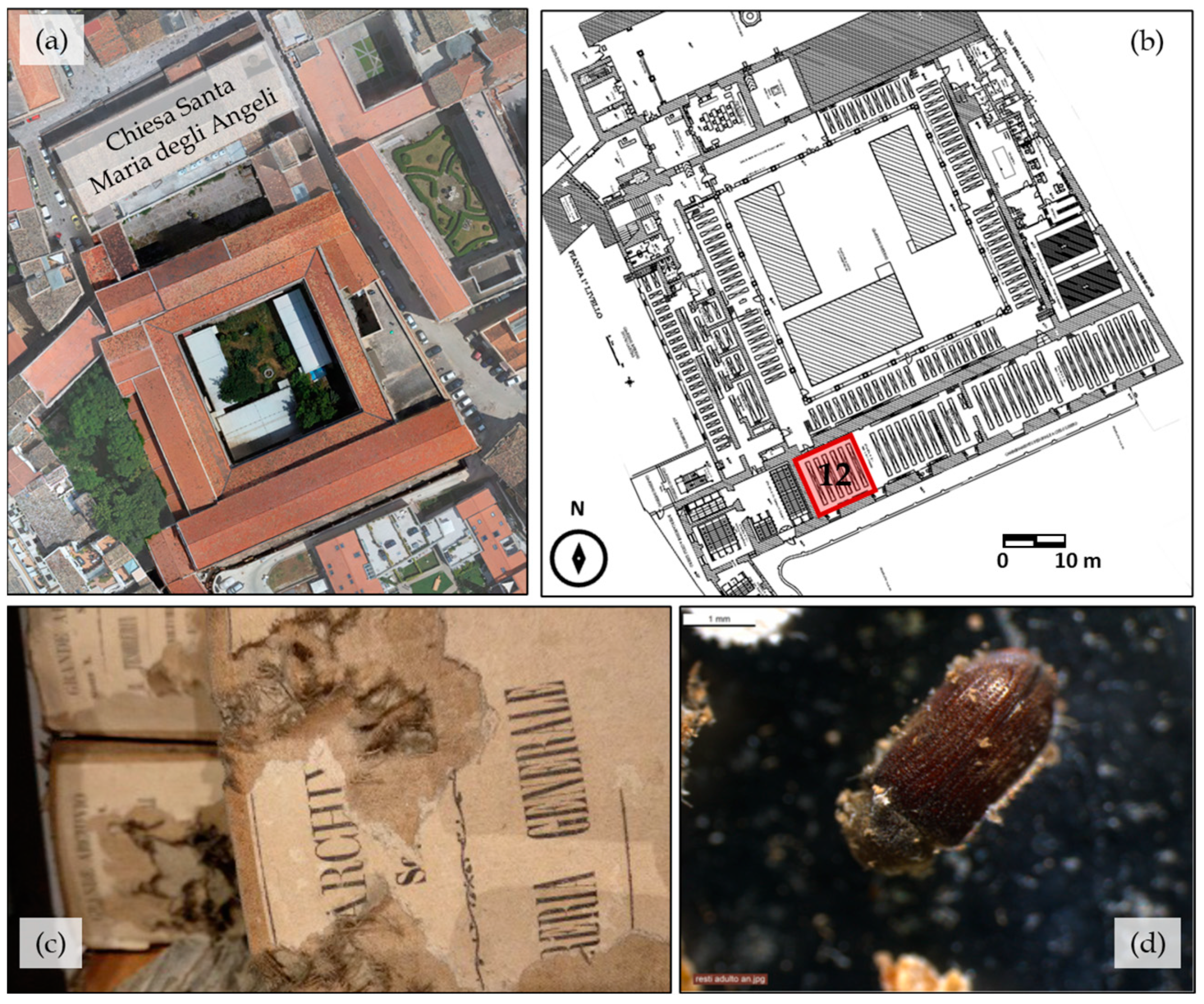
2.1. Case Study, Biological Technical Survey, and Climate Monitoring
2.2. Climate-Induced Risk Assessment
2.2.1. Climate Scenarios at the Mediterranean Site
- SSP1-2.6 represents a sustainable SSP where consumption and population growth are low, and the resulting GHG emissions correspond to a radiative forcing peak of 2.6 W∙m−2 by 2100;
- SSP2-4.5 is an intermediate SSP representing a fossil-fuel-intensive world with a development pattern similar to the current one, in which the radiative forcing is stabilized at approximately 4.5 W∙m−2 after 2100;
- SSP5-8.5 is a SSP representing a fossil-fuel-intensive world with the highest GHG emissions for which the radiative forcing reaches 8.5 W∙m−2 by 2100.
2.2.2. Indoor Climate Scenarios
2.2.3. Biologically Related Dose–Response Functions
3. Results
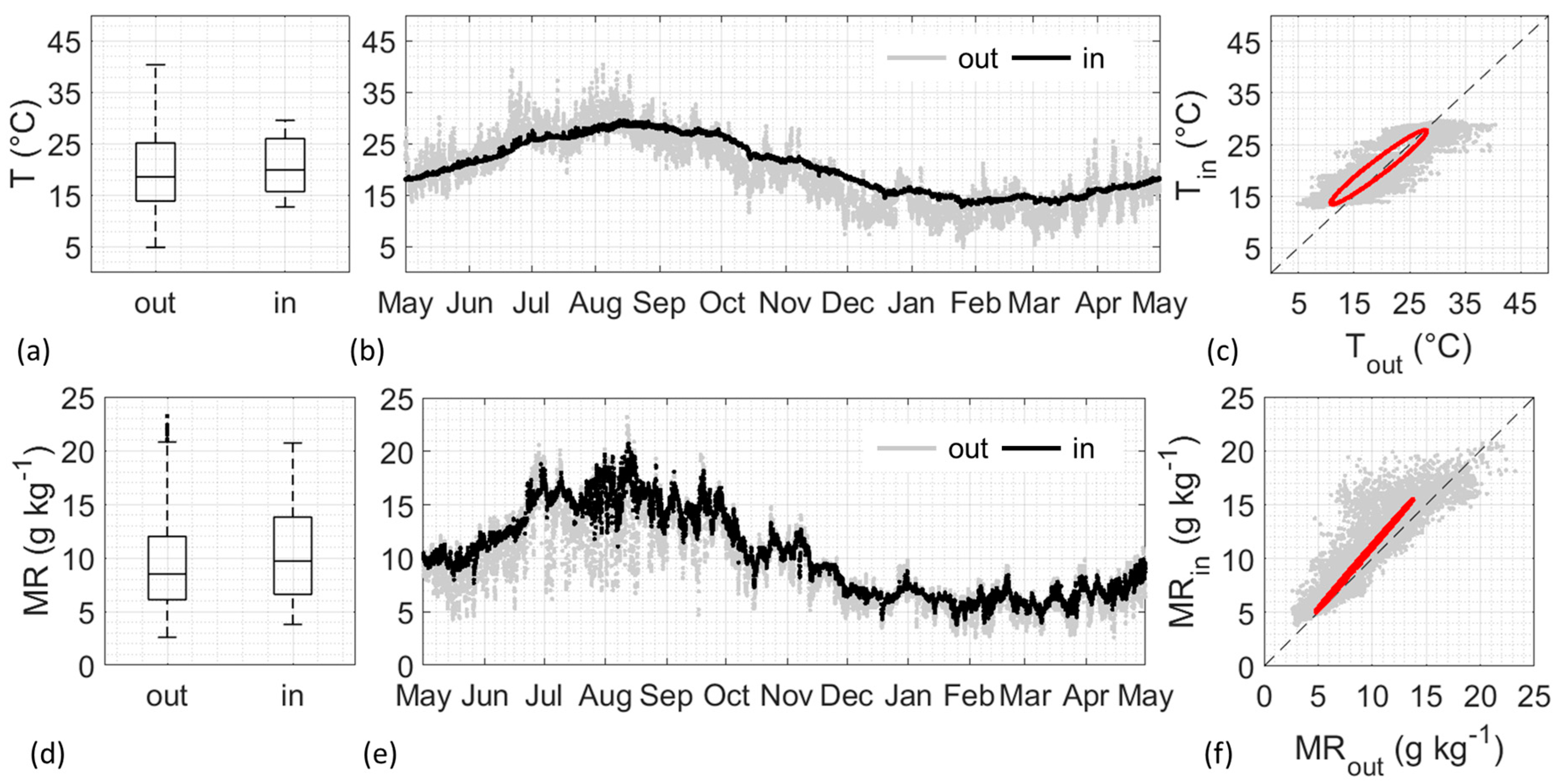
3.1. Characterisation of Current Climate Conditions
3.2. Reconstruction of Indoor Climate Scenarios
3.3. Risk of Biodeteriogens’ Proliferation
4. Discussion
4.1. Characterisation of Current Climate Conditions
4.2. Reconstruction of Indoor Climate Scenarios
4.3. Risk of Biodeteriogens’ Proliferation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ICOM-CC. Terminology to Characterize the Conservation of Tangible Cultural Heritage; ICOM-CC: Paris, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersoli, J.L.J.; Antomarchi, C.; Michalski, S. A Guide to Risk Management of Cultural Heritage; ICCROM, CCI, Eds.; International Centre for the Study of the Preservation and Restoration of Cultural Property: Rome, Italy, 2016; ISBN 9789290772491. [Google Scholar]
- Strlič, M.; Thickett, D.; Taylor, J.; Cassar, M. Damage Functions in Heritage Science. Stud. Conserv. 2013, 58, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonazza, A.; Sardella, A. Climate Change and Cultural Heritage: Methods and Approaches for Damage and Risk Assessment Addressed to a Practical Application. Heritage 2023, 6, 3578–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesana, E.; Gagnon, A.S.; Ciantelli, C.; Cassar, J.A.; Hughes, J.J. Climate Change Impacts on Cultural Heritage: A Literature Review. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2021, 12, e710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verticchio, E.; Frasca, F.; Bertolin, C.; Siani, A.M. Climate-Induced Risk for the Preservation of Paper Collections: Comparative Study among Three Historic Libraries in Italy. Build. Environ. 2021, 206, 108394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leissner, J.; Kilian, R.; Kotova, L.; Jacob, D.; Mikolajewicz, U.; Broström, T.; Ashley-Smith, J.; Schellen, H.L.; Martens, M.; Van Schijndel, J.; et al. Climate for Culture: Assessing the Impact of Climate Change on the Future Indoor Climate in Historic Buildings Using Simulations. Herit. Sci. 2015, 3, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frasca, F.; Verticchio, E.; Cornaro, C.; Siani, A.M. Performance Assessment of Hygrothermal Modelling for Diagnostics and Conservation in an Italian Historical Church. Build. Environ. 2021, 193, 107672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolin, C.; Camuffo, D.; Bighignoli, I. Past Reconstruction and Future Forecast of Domains of Indoor Relative Humidity Fluctuations Calculated According to EN 15757. Energy Build 2015, 102, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bučková, M.; Puškárová, A.; Sclocchi, M.C.; Bicchieri, M.; Colaizzi, P.; Pinzari, F.; Pangallo, D. Co-Occurrence of Bacteria and Fungi and Spatial Partitioning during Photographic Materials Biodeterioration. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 108, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimblecombe, P.; Lankester, P. Long-Term Changes in Climate and Insect Damage in Historic Houses. Stud. Conserv. 2013, 58, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 16790; Conservation of Cultural Heritage—Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for Protection of Cultural Heritage. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2016.
- Querner, P.; Sterflinger, K.; Piombino-Mascali, D.; Morrow, J.J.; Pospischil, R.; Piñar, G. Insect Pests and Integrated Pest Management in the Capuchin Catacombs of Palermo, Italy. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 131, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimblecombe, P.; Querner, P. Webbing Clothes Moth Catch and the Management of Heritage Environments. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 96, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapter 24, Museums, Galleries, Archives, and Libraries. In ASHRAE Handbook—HVAC Applications; American Society of Heating Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019.
- Kotova, L.; Leissner, J.; Winkler, M.; Kilian, R.; Bichlmair, S.; Antretter, F.; Moßgraber, J.; Reuter, J.; Hellmund, T.; Matheja, K.; et al. Making Use of Climate Information for Sustainable Preservation of Cultural Heritage: Applications to the KERES Project. Herit. Sci. 2023, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimblecombe, P.; Sterflinger, K.; Derksen, K.; Haltrich, M.; Querner, P. Thermohygrometric Climate, Insects and Fungi in the Klosterneuburg Monastic Library. Heritage 2022, 5, 4228–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankester, P.; Brimblecombe, P. Future Thermohygrometric Climate within Historic Houses. J. Cult. Herit. 2012, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICOMOS. ICOMOS Statement to the United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP27) 2022. Available online: https://www.icomos.org/images/DOCUMENTS/Secretariat/2022/COP27/Statement_ICOMOS_COP27_20221106_EN.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Climate Heritage Network. Empowering People to Imagine and Realise Climate Resilient Futures Through Culture—From Arts to Heritage; Climate Heritage Network: Wadi Musa, Jordan, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Assessment Report 6 Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/ (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- IPCC. Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report. A Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bertolin, C. Preservation of Cultural Heritage and Resources Threatened by Climate Change. Geosciences 2019, 9, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lankester, P.; Brimblecombe, P. The Impact of Future Climate on Historic Interiors. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 417–418, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Querner, P.; Sterflinger, K.; Derksen, K.; Leissner, J.; Landsberger, B.; Hammer, A.; Brimblecombe, P. Climate Change and Its Effects on Indoor Pests (Insect and Fungi) in Museums. Climate 2022, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, F. The Role of Architecture in Preventive Conservation; International Centre for the Study of the Preservation and Restoration of Cultural Property: Rome, Italy, 2006; Volume 74. [Google Scholar]
- EN 16883; Conservation of Cultural Heritage-Guidelines for Improving the Energy Performance of Historic Buildings. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2017.
- Frasca, F.; Cornaro, C.; Siani, A.M. A Method Based on Environmental Monitoring and Building Dynamic Simulation to Assess Indoor Climate Control Strategies in the Preventive Conservation within Historical Buildings. Sci. Technol. Built. Environ. 2019, 25, 1253–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuffo, D.; Bertolin, C.; Bonazzi, A.; Campana, F.; Merlo, C. Past, Present and Future Effects of Climate Change on a Wooden Inlay Bookcase Cabinet: A New Methodology Inspired by the Novel European Standard EN 15757. J. Cult. Herit. 2014, 15, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbioni, C.; Cassar, M.; Brimblecombe, P.; Tidblad, J.; Kozlowski, R.; Drdácký, M.; Ariño, X. Global Climate Change Impact on Built Heritage and Cultural Landscapes. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Heritage, Weathering and Conservation, HWC, Madrid, Spain, 21–24 June 2006; Gomez-Heras, Vazquez-Calvo, Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2006; pp. 395–401. [Google Scholar]
- Dias Pereira, L.; Saraiva, N.B.; Soares, N. Hygrothermal Behavior of Cultural Heritage Buildings and Climate Change: Status and Main Challenges. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Zimmermann, N.E.; McVicar, T.R.; Vergopolan, N.; Berg, A.; Wood, E.F. Present and Future Köppen-Geiger Climate Classification Maps at 1-Km Resolution. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gallo, A. La Lotta Antitermitica in Italia—Commissione Interministeriale per La Lotta Antitermitica Roma; Novagrafia: Roma, Italy, 1952. [Google Scholar]
- EN 15758; Conservation of Cultural Property—Procedures and Instruments for Measuring Temperatures of the Air and the Surfaces of Objects. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2010.
- EN 16242; Conservation of Cultural Heritage—Procedures and Instruments for Measuring Humidity in the Air and Moisture Exchanges between Air and Cultural Property. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2012.
- Frasca, F.; Siani, A.M.; Casale, G.R.; Pedone, M.; Bratasz, L.; Strojecki, M.; Mleczkowska, A. Assessment of Indoor Climate of Mogiła Abbey in Kraków (Poland) and the Application of the Analogues Method to Predict Microclimate Indoor Conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 13895–13907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pörtner, H.O.; Roberts, D.C.; Adams, H.; Adelekan, I.; Adler, C.; Adrian, R. Technical Summary. In Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Pörtner, H.O., Roberts, D.C., Poloczanska, E.S., Mintenbeck, K., Tignor, M., Alegría, A., Craig, M., Langsdorf, S., Löschke, S., Möller, V., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 37–118. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, B.C.; Tebaldi, C.; van Vuuren, D.P.; Eyring, V.; Friedlingstein, P.; Hurtt, G.; Knutti, R.; Kriegler, E.; Lamarque, J.-F.; Lowe, J.; et al. The Scenario Model Intercomparison Project (ScenarioMIP) for CMIP. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 3461–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lovato, T.; Peano, D.; Butenschön, M.; Materia, S.; Iovino, D.; Scoccimarro, E.; Fogli, P.G.; Cherchi, A.; Bellucci, A.; Gualdi, S.; et al. CMIP6 Simulations with the CMCC Earth System Model (CMCC-ESM2). J. Adv. Model Earth Syst. 2022, 14, e2021MS002814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verticchio, E.; Frasca, F.; Garcìa-Diego, F.J.; Siani, A.M. Investigation on the Use of Passive Microclimate Frames in View of the Climate Change Scenario. Climate 2019, 7, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vereecken, E.; Roels, S. Review of Mould Prediction Models and Their Influence on Mould Risk Evaluation. Build. Environ. 2012, 51, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Bolea, A.; Llop, E.; Ariño, X.; Saiz-Jimenez, C.; Bonazza, A.; Messina, P.; Sabbioni, C. Mapping the Impact of Climate Change on Biomass Accumulation on Stone. J. Cult. Herit. 2012, 13, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuffo, D.; Bertolin, C. Unfavorable Microclimate Conditions in Exhibition Rooms: Early Detection, Risk Identification, and Preventive Conservation Measures. J. Paleontol. Tech. 2016, 15, 144–161. [Google Scholar]
- Kuka, E.; Cirule, D.; Andersone, I.; Andersons, B.; Fridrihsone, V. Conditions Influencing Mould Growth for Effective Prevention of Wood Deterioration Indoors. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 16893; Conservation of Cultural Heritage—Specifications for Location, Construction and Modification of Buildings or Rooms Intended for the Storage or Use of Heritage Collections. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2018.
- Boeri, A.; Longo, D.; Fabbri, K.; Pretelli, M.; Bonora, A.; Boulanger, S. Library Indoor Microclimate Monitoring with and without Heating System. A Bologna University Library Case Study. J. Cult. Herit. 2022, 53, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andretta, M.; Coppola, F.; Seccia, L. Investigation on the Interaction between the Outdoor Environment and the Indoor Microclimate of a Historical Library. J. Cult. Herit. 2016, 17, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruga, L.; Bonofiglio, T.; Orlandi, F.; Romano, B.; Fornaciari, M. Analysis of the Potential Fungal Biodeteriogen Effects in the “Doctorate Library” of the University of Perugia, Italy. Grana 2008, 47, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fabbri, K.; Pretelli, M. Heritage Buildings and Historic Microclimate without HVAC Technology: Malatestiana Library in Cesena, Italy, UNESCO Memory of the World. Energy Build. 2014, 76, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquarella, C.; Balocco, C.; Saccani, E.; Capobianco, E.; Viani, I.; Veronesi, L.; Pavani, F.; Pasquariello, G.; Rotolo, V.; Palla, F.; et al. Biological and Microclimatic Monitoring for Conservation of Cultural Heritage: A Case Study at the De Rossi Room of the Palatina Library in Parma. Aerobiologia 2020, 36, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verticchio, E.; Frasca, F.; Cavalieri, P.; Teodonio, L.; Fugaro, D.; Siani, A.M. Conservation Risks for Paper Collections Induced by the Microclimate in the Repository of the Alessandrina Library in Rome (Italy). Herit. Sci. 2022, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliano, A.; Nocera, F.; Patania, F.; Moschella, A.; Detommaso, M.; Evola, G. Synergic Effects of Thermal Mass and Natural Ventilation on the Thermal Behaviour of Traditional Massive Buildings. Int. J. Sustain. Energy 2016, 35, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkurt, G.G.; Aste, N.; Borderon, J.; Buda, A.; Calzolari, M.; Chung, D.; Costanzo, V.; Del Pero, C.; Evola, G.; Huerto-Cardenas, H.E.; et al. Dynamic Thermal and Hygrometric Simulation of Historical Buildings: Critical Factors and Possible Solutions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 118, 109509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajčić, V.; Skender, A.; Damjanović, D. An Innovative Methodology of Assessing the Climate Change Impact on Cultural Heritage. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2018, 12, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerto-Cardenas, H.E.; Leonforte, F.; Aste, N.; Del Pero, C.; Evola, G.; Costanzo, V.; Lucchi, E. Validation of Dynamic Hygrothermal Simulation Models for Historical Buildings: State of the Art, Research Challenges and Recommendations. Build. Environ. 2020, 180, 107081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menicucci, F.; Palagano, E.; Michelozzi, M.; Cencetti, G.; Raio, A.; Bacchi, A.; Mazzeo, P.P.; Cuzman, O.A.; Sidoti, A.; Guarino, S.; et al. Effects of Trapped-into-Solids Volatile Organic Compounds on Paper Biodeteriogens. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2022, 174, 105469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo, A.; Cappitelli, F.; Villa, F.; Pinzari, F. Biological Invasion in the Indoor Environment: The Spread of Eurotium Halophilicum on Library Materials. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 118, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Materials | Biodeteriogens | Climate Variables | DRF | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Building stone | in | Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus flavus, Stachybotrys chartarum | T, RH | Sedlbauer isopleths | [41] |
| out | Biofilm | T, pr | Biomass accumulation | [42] | |
| Cellulose-based | Stegobium paniceum (Linnaeus) (drugstore beetle) | T, RH | Development time (tD) | [11] | |
| T | Growing degree days (GDDs) | ||||
| T | Number of growth cycles for a year (NGC) (*) | ||||
| Tineola bisselliella (Hummel) (webbing clothes moths) | T | Eggs laid (E) | |||
| Wood | Anobium punctatum (De Geer) (woodworm or furniture beetle) (**) | T | Flying degree days (FDDs) | [11,43] | |
| T | Growing degree days (GDDs) | [11] | |||
| Alternaria alternata, Aspergillus species, Aureobasidium pullulans, Cladosporium cladosporioides, Chaetomium globosum, Paecilomyces variotii, Penicillium spp., Trichoderma viride | T, RH | VTT model | [41,44] | ||
| Climate Variable | Statistical Parameter | RP | NF | FF | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSP1-2.6 | SSP2-4.5 | SSP5-8.5 | SSP1-2.6 | SSP2-4.5 | SSP5-8.5 | |||
| T (°C) | Q2 | 19.9 | 20.8 | 20.8 | 20.9 | 22.5 | 23.2 | 24.6 |
| IQR | 8.2 | 8.5 | 8.4 | 8.5 | 8.4 | 8.6 | 9.1 | |
| Δy | 11.6 | 12.1 | 11.9 | 12.0 | 11.9 | 12.2 | 12.9 | |
| MR (g∙kg−1) | Q2 | 10.9 | 11.4 | 11.4 | 11.6 | 12.5 | 13.1 | 14.0 |
| IQR | 5.8 | 6.3 | 6.2 | 6.4 | 6.9 | 7.5 | 8.5 | |
| Δy | 8.2 | 9.0 | 8.8 | 9.0 | 9.9 | 10.6 | 12.0 | |
| RH (%) | Q2 | 71.5 | 70.5 | 70.5 | 70.6 | 69.5 | 69.4 | 68.3 |
| IQR | 10.7 | 10.0 | 10.4 | 9.9 | 10.9 | 10.5 | 10.4 | |
| Δy | 18.4 | 18.8 | 18.5 | 18.0 | 19.4 | 19.3 | 20.1 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Verticchio, E.; Frasca, F.; Matè, D.; Giammusso, F.M.; Sani, M.; Sebastiani, M.L.; Sclocchi, M.C.; Siani, A.M. Assessing the Impact of Climate Change on the Biodeterioration Risk in Historical Buildings of the Mediterranean Area: The State Archives of Palermo. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071169
Verticchio E, Frasca F, Matè D, Giammusso FM, Sani M, Sebastiani ML, Sclocchi MC, Siani AM. Assessing the Impact of Climate Change on the Biodeterioration Risk in Historical Buildings of the Mediterranean Area: The State Archives of Palermo. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(7):1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071169
Chicago/Turabian StyleVerticchio, Elena, Francesca Frasca, Donatella Matè, Federico Maria Giammusso, Matilde Sani, Maria Letizia Sebastiani, Maria Carla Sclocchi, and Anna Maria Siani. 2023. "Assessing the Impact of Climate Change on the Biodeterioration Risk in Historical Buildings of the Mediterranean Area: The State Archives of Palermo" Atmosphere 14, no. 7: 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071169
APA StyleVerticchio, E., Frasca, F., Matè, D., Giammusso, F. M., Sani, M., Sebastiani, M. L., Sclocchi, M. C., & Siani, A. M. (2023). Assessing the Impact of Climate Change on the Biodeterioration Risk in Historical Buildings of the Mediterranean Area: The State Archives of Palermo. Atmosphere, 14(7), 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071169