Variations in Key Factors at Different Explosive Development Stages of an Extreme Explosive Cyclone over the Japan Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. EC Identification
2.2.2. Z-O Equation
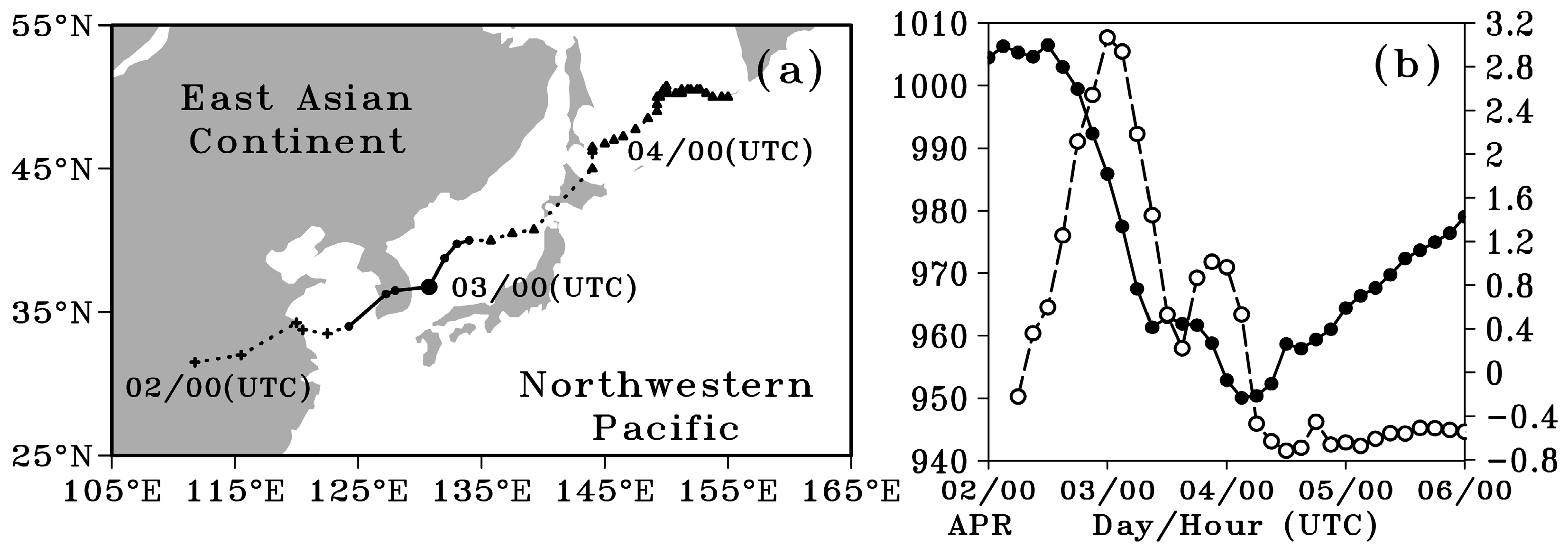
3. Synoptic Overview
3.1. Evolutionary Processes
3.2. Synoptic-Scale Atmospheric Environmental Conditions
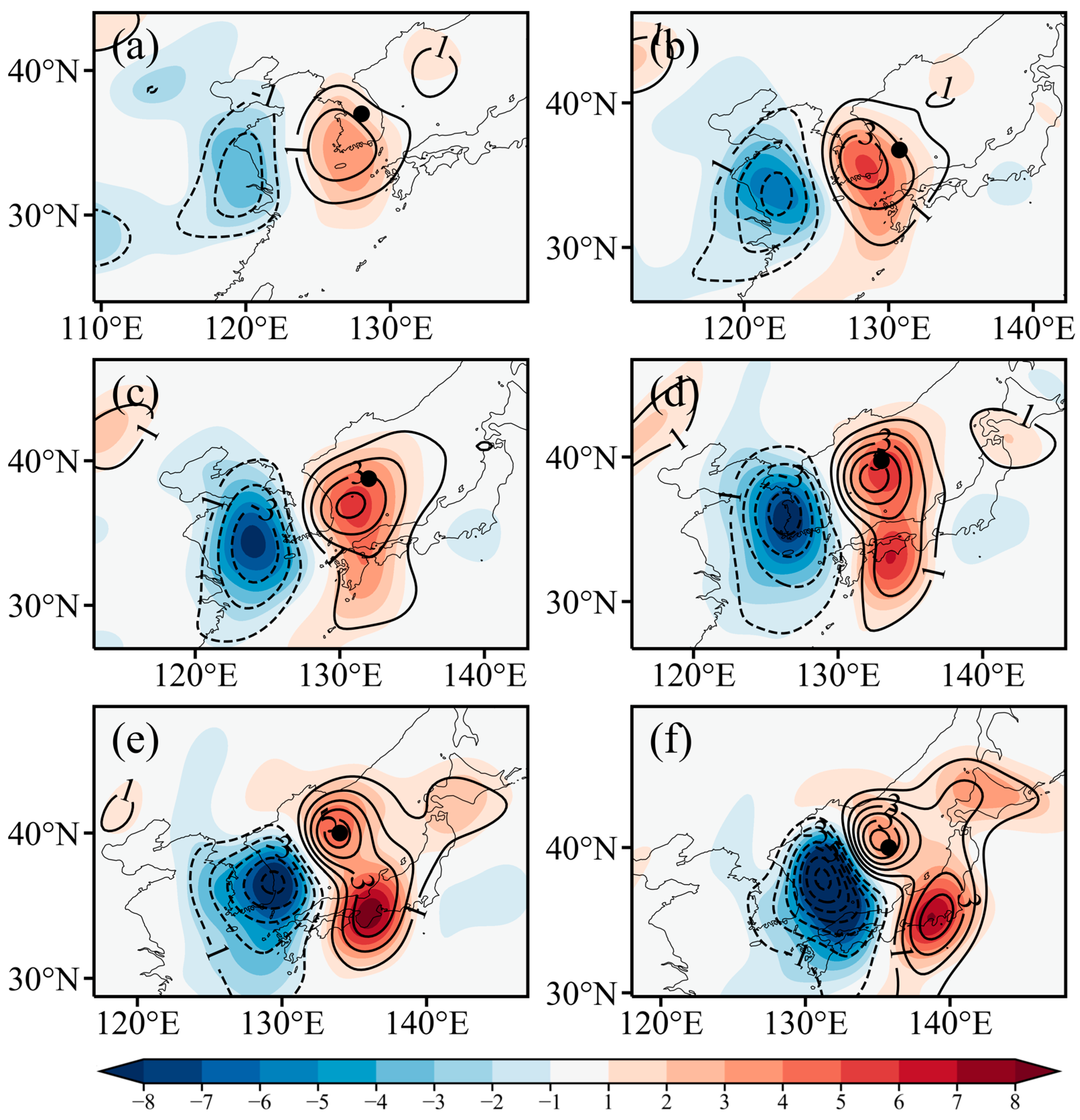
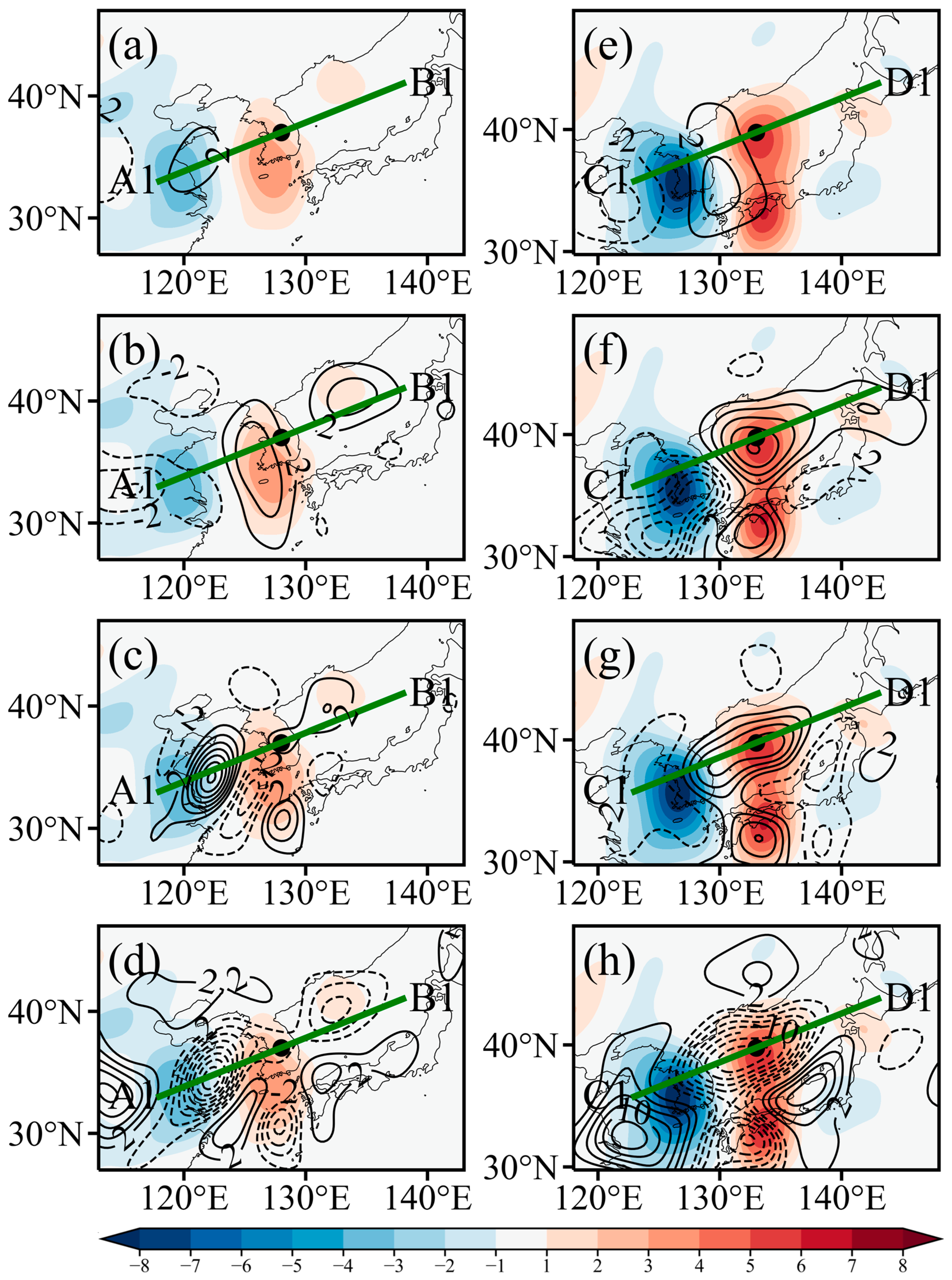
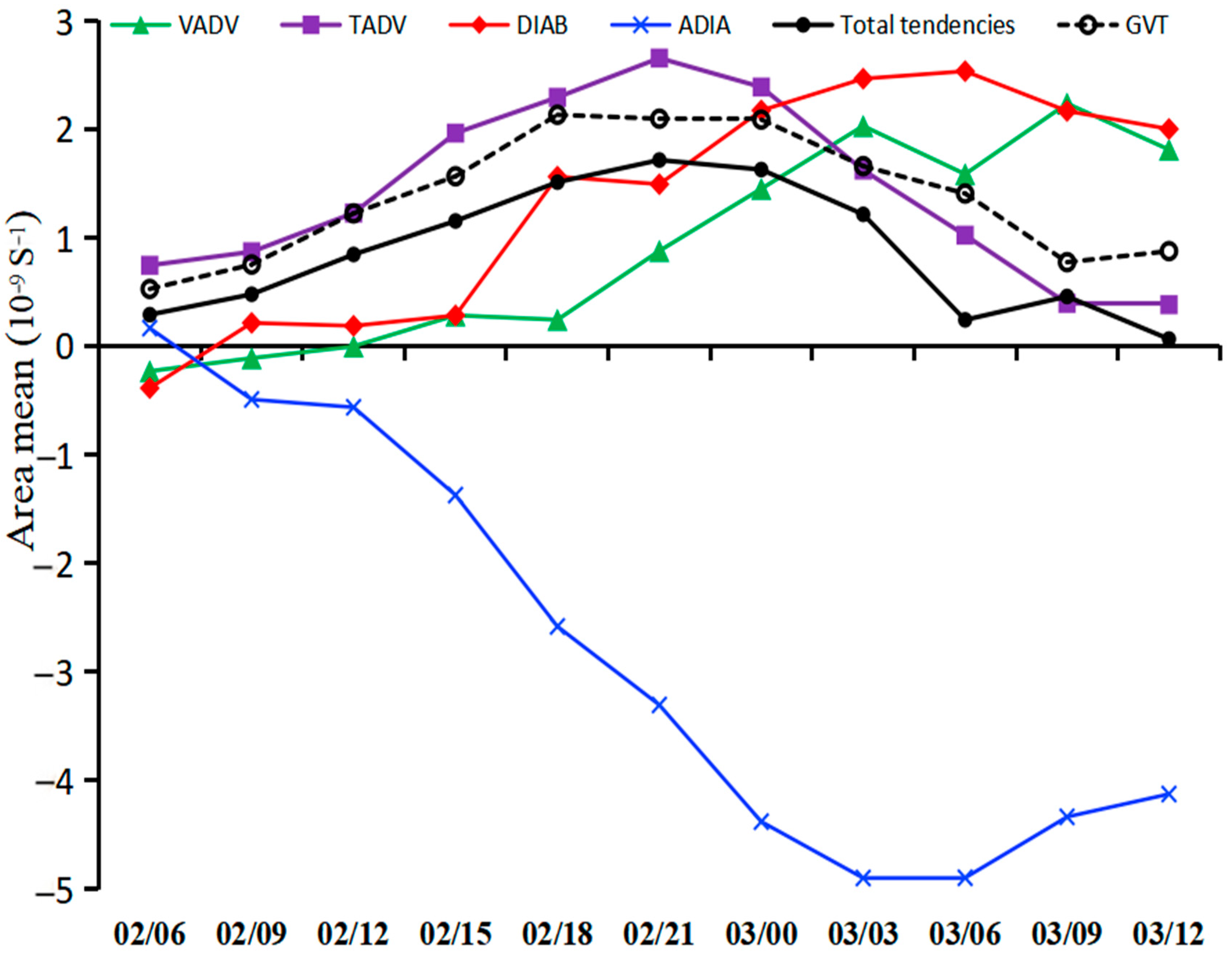
4. Diagnostic Analyses
4.1. Vertically Integrated Characteristics
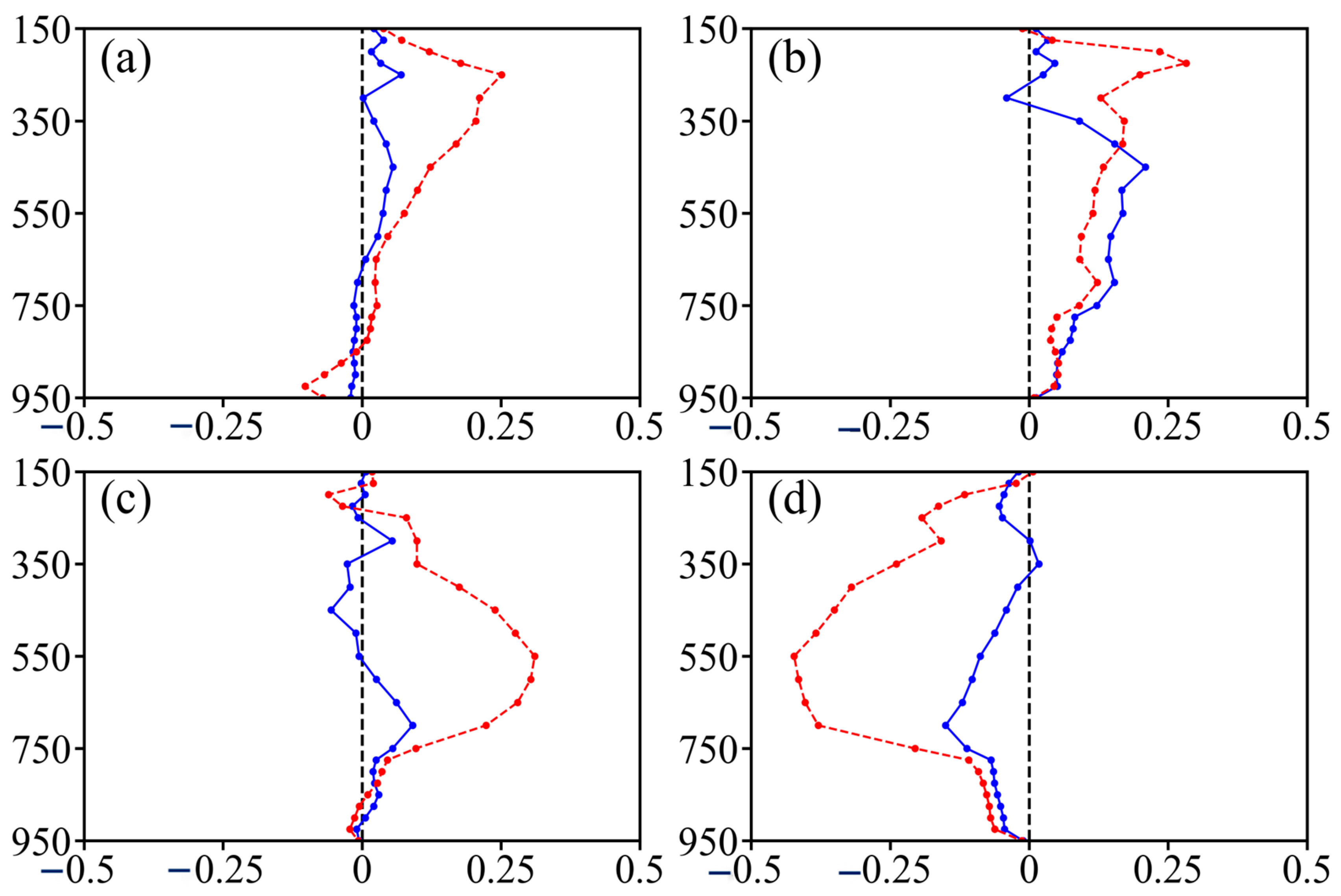
4.2. Vertical Structure
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanders, F.; Gyakum, J.R. Synoptic-dynamic climatology of the “bomb”. Mon. Weather Rev. 1980, 108, 1589–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsafados, P.; Mavromatidis, E.; Papadopoulos, A.; Pytharoulis, I. Numerical simulation of a deep Mediterranean storm and its sensitivity on sea surface temperature. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, A.; Pohle, S.; Pinto, J.G.; Knippertz, P. Diagnosing the influence of diabatic process on the explosive deepening of extratropical cyclones. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2012, 39, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Liberato, M.L.R. The 19 January 2013 windstorm over the North Atlantic: Large scale dynamics and impacts on Iberia. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2014, 5, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roebber, P.J. Statistical analysis and updated climatology of explosive cyclones. Mon. Weather Rev. 1984, 112, 1577–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyakum, J.R.; Anderson, R.; Grumm, H.; Gruner, E.L. North Pacific cold-season surface cyclone activity: 1975–1983. Mon. Weather Rev. 1989, 117, 1141–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, A.; Asuma, Y. Structures and environment of explosively developing extratropical cyclones in the Northwestern Pacific region. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 1121–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Fu, G.; Lu, C.; Liu, J. Characteristics of explosive cyclones over the Northern Pacific. J. Appl. Meteor. Clim. 2017, 56, 3187–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwao, K.; Inatsu, M.; Kimoto, M. Recent changes in explosively developing extratropical cyclones over the winter Northwestern Pacific. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 7282–7296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiler, C.; Zwiers, F.W. How well do CMIP5 climate models reproduce explosive cyclones in the extratropics of the Northern Hemisphere? Clim. Dyn. 2016, 46, 1241–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiler, C.; Zwiers, F.W. How will climate change affect explosive cyclones in the extratropics of the Northern Hemisphere? Clim. Dyn. 2016, 46, 3633–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Sun, Y.W.; Sun, J.L.; Li, P.Y. A 38-year climatology of explosive cyclones over the Northern Hemisphere. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 37, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Dell’osso, L. A numerical case study of East Asian coastal cyclogenesis. Mon. Weather Rev. 1987, 115, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Kuo, Y.H.; Zhang, P.Z.; Bai, Q.F. Climatology of explosive cyclones off the East Asian coast. Mon. Weather Rev. 1992, 120, 3029–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, F.; Davis, C.A. Patterns of thickness anomaly for explosive cyclogenesis over the West-Central North Atlantic Ocean. Mon. Weather Rev. 1988, 116, 2725–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Rogers, J.C. A composite study of explosive cyclogenesis in different sectors of the North Atlantic. Part I: Cyclone structure and evolution. Mon. Weather Rev. 2001, 129, 1481–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, H.; Kawamura, R. Influential role of moisture supply from the Kuroshio/Kuroshio Extension in the rapid development of an extratropical cyclone. Mon. Weather Rev. 2015, 143, 4126–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Xu, J.; Zhang, S.; Tang, R.; Huang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Guan, Z.; Mao, H.; Xue, Y. Physical process contributions to the development of a super explosive cyclone over the Gulf Stream. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 722555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, F. Explosive cyclogenesis in the West-Central North Atlantic Ocean, 1981–1984. Part I: Composite structure and mean behavior. Mon. Weather Rev. 1986, 114, 1781–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, R.; Sorteberg, A. The vorticity budgets of North Atlantic winter extratropical cyclone life cycles in MERRA reanalysis. Part I: Development phase. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 71, 3109–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uccellini, L.W.; Kocin, P.J. The interaction of jet streak circulations during heavy snow events along the east coast of United States. Weather Forecast. 1987, 2, 289–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wash, C.H.; Peak, J.E.; Calland, W.E.; Cook, W.A. Diagnostic study of explosive cyclogenesis during FGGE. Mon. Weather Rev. 1988, 116, 431–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fu, G.; Pang, H. Structure analyses of the explosive extratropical cyclone: A case study over the Northwestern Pacific in March 2007. J. Ocean Univ. China 2017, 16, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwano-Yoshida, A.; Enomoto, T. Predictability of explosive cyclogenesis over the Northwestern Pacific region using ensemble reanalysis. Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 3769–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Fu, G. Structures and evolution of explosive cyclones over the Northwestern and Northeastern Pacific. J. Ocean Univ. China 2018, 17, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.M.; Lee, J.; Son, S.W.; Kim, J.; Chen, D. The rapid intensification of East Asian cyclones around the Korean Peninsula and their surface impacts. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2019JD031632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwano-Yoshida, A.; Asuma, Y. Numerical study of explosively developing extratropical cyclones in the Northwestern Pacific region. Mon. Weather Rev. 2008, 136, 712–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, K.Y.; Seo, Y.W.; Ha, K.J.; Park, K.S.; Kim, J.; Choi, J.W.; Jun, K.; Jeong, J.K. Development mechanisms of an explosive cyclone over East Sea on 3–4 April 2012. Dyn. Atmos. Ocean. 2015, 70, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, H.; Kawamura, R.; Kato, M.; Shinoda, T. Response of rapidly developing extratropical cyclones to sea surface temperature variations over the western Kuroshio-Oyashio confluence region. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 3843–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, H.; Kawamura, R.; Kato, M.; Shinoda, T. A positive feedback process related to the rapid development of an extratropical cyclone over the Kuroshio/Kuroshio Extension. Mon. Weather Rev. 2018, 146, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, Y.; Yamamoto, M. Influences of surface heat flux on twin cyclone structure during their explosive development over the East Asian marginal seas on 23 January. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2019, 23, 100198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, R.E. A cyclone phase space derived from thermal wind and thermal asymmetry. Mon. Weather Rev. 2003, 131, 585–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwack, P.; Okossi, B. A new method for solving the quasi-geostrophic omega equation by incorporating surface pressure tendency data. Mon. Weather Rev. 1986, 114, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupo, A.R.; Smith, P.J.; Zwack, P. A diagnosis of the explosive development of two extratropical cyclones. Mon. Weather Rev. 1992, 120, 1490–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strahl, J.L.S.; Smith, P.J. A diagnostic study of an explosively developing extratropical cyclone and an associated 500-hPa trough merger. Mon. Weather Rev. 2001, 129, 2310–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, W.E.; Smith, P.J. Cyclolysis: A diagnosis of two extratropical cyclones. Mon. Weather Rev. 2001, 129, 2714–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, R.L.M.; Smith, P.J. A diagnosis of a model simulated explosively developing extratropical cyclone. Mon. Weather Rev. 1996, 124, 875–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holton, J.R. An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology, 4th ed.; International Geophysics Series; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004; Volume 88, p. 535. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, R. Smoothing, filtering, and boundary effects. Rev. Geophys. 1970, 8, 359–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, F. Analytic solutions of the nonlinear omega and vorticity equations for a structurally simple model of disturbances in the baroclinic westerlies. Mon. Weather Rev. 1971, 99, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrenfeltz, L.L.; Elsberry, R.L. Superposition effects in rapid cyclogenesis-Linear model studies. J. Atmos. Sci. 1989, 46, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, T. Variations in Key Factors at Different Explosive Development Stages of an Extreme Explosive Cyclone over the Japan Sea. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14091327
Zhang S, Tang Y, Zhang L, Liao Q, Zhang T. Variations in Key Factors at Different Explosive Development Stages of an Extreme Explosive Cyclone over the Japan Sea. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(9):1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14091327
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shuqin, Yuan Tang, Liwen Zhang, Qinghua Liao, and Tianyu Zhang. 2023. "Variations in Key Factors at Different Explosive Development Stages of an Extreme Explosive Cyclone over the Japan Sea" Atmosphere 14, no. 9: 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14091327
APA StyleZhang, S., Tang, Y., Zhang, L., Liao, Q., & Zhang, T. (2023). Variations in Key Factors at Different Explosive Development Stages of an Extreme Explosive Cyclone over the Japan Sea. Atmosphere, 14(9), 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14091327





