Evaluation of the Performance of CMIP6 Climate Models in Simulating Rainfall over the Philippines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
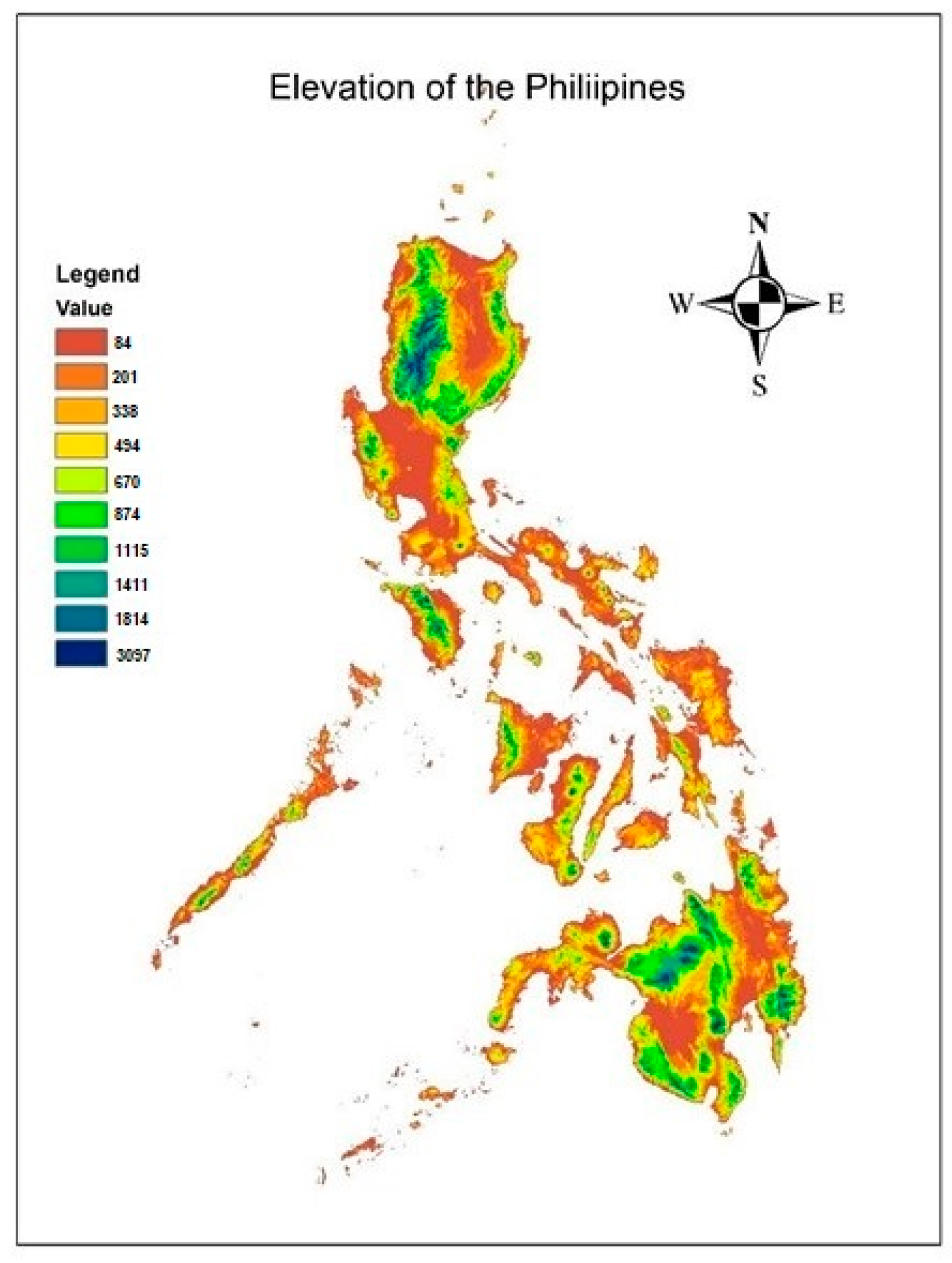
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Evaluation Metrics
3. Results
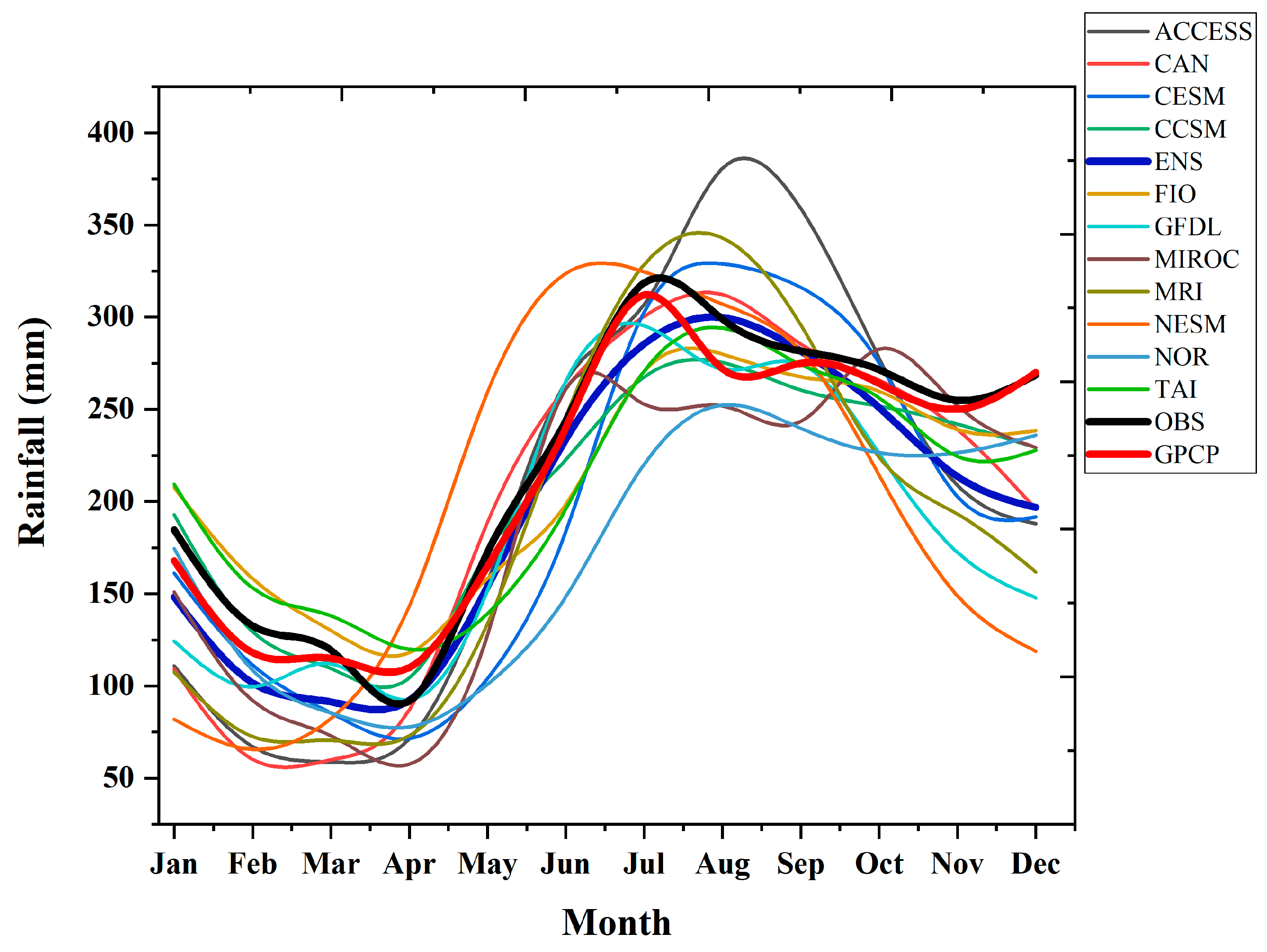
3.1. Annual Rainfall Cycle
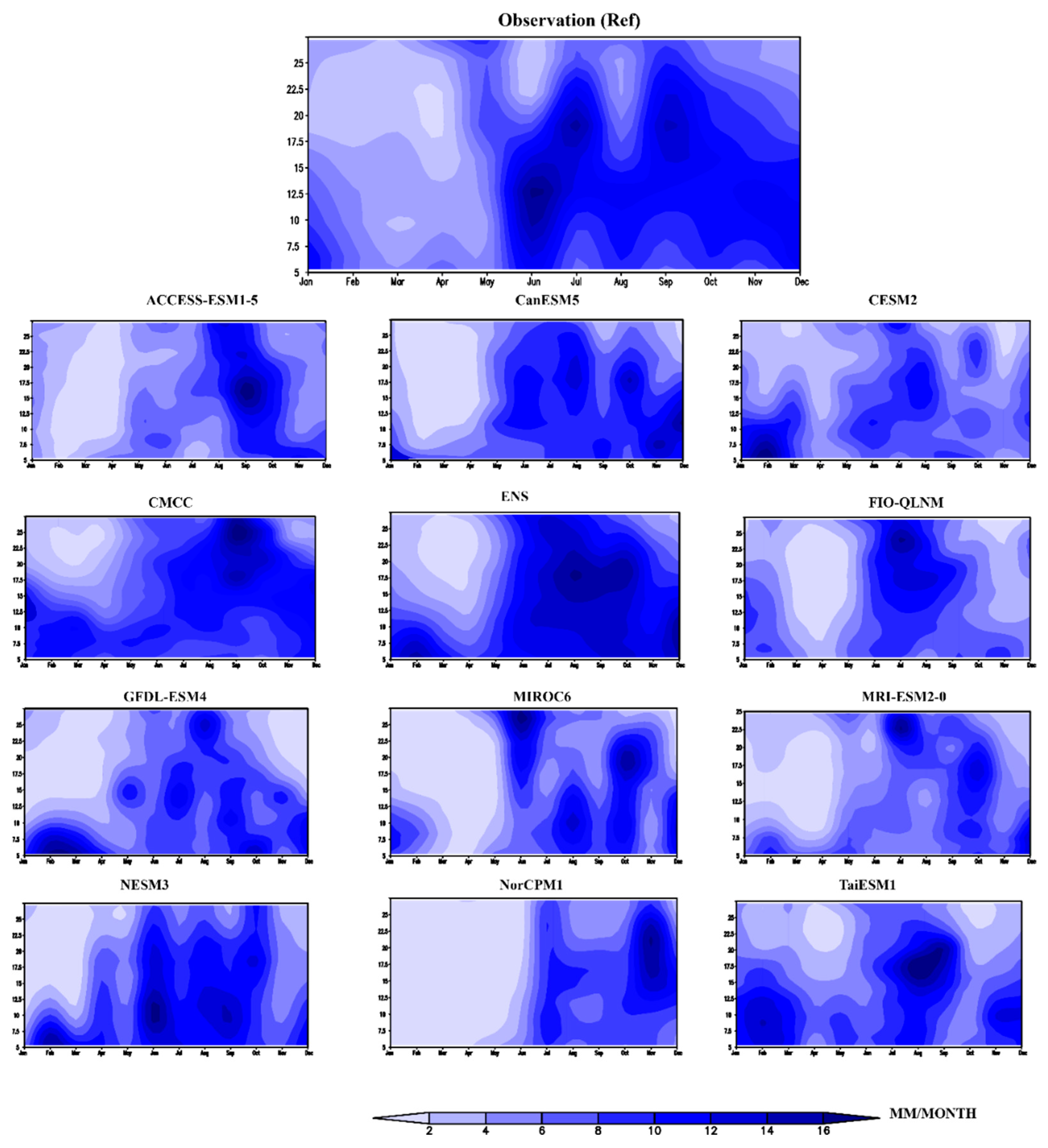
3.2. Latitudinal Spatial Rainfall Distribution (Hovmöller Diagram)
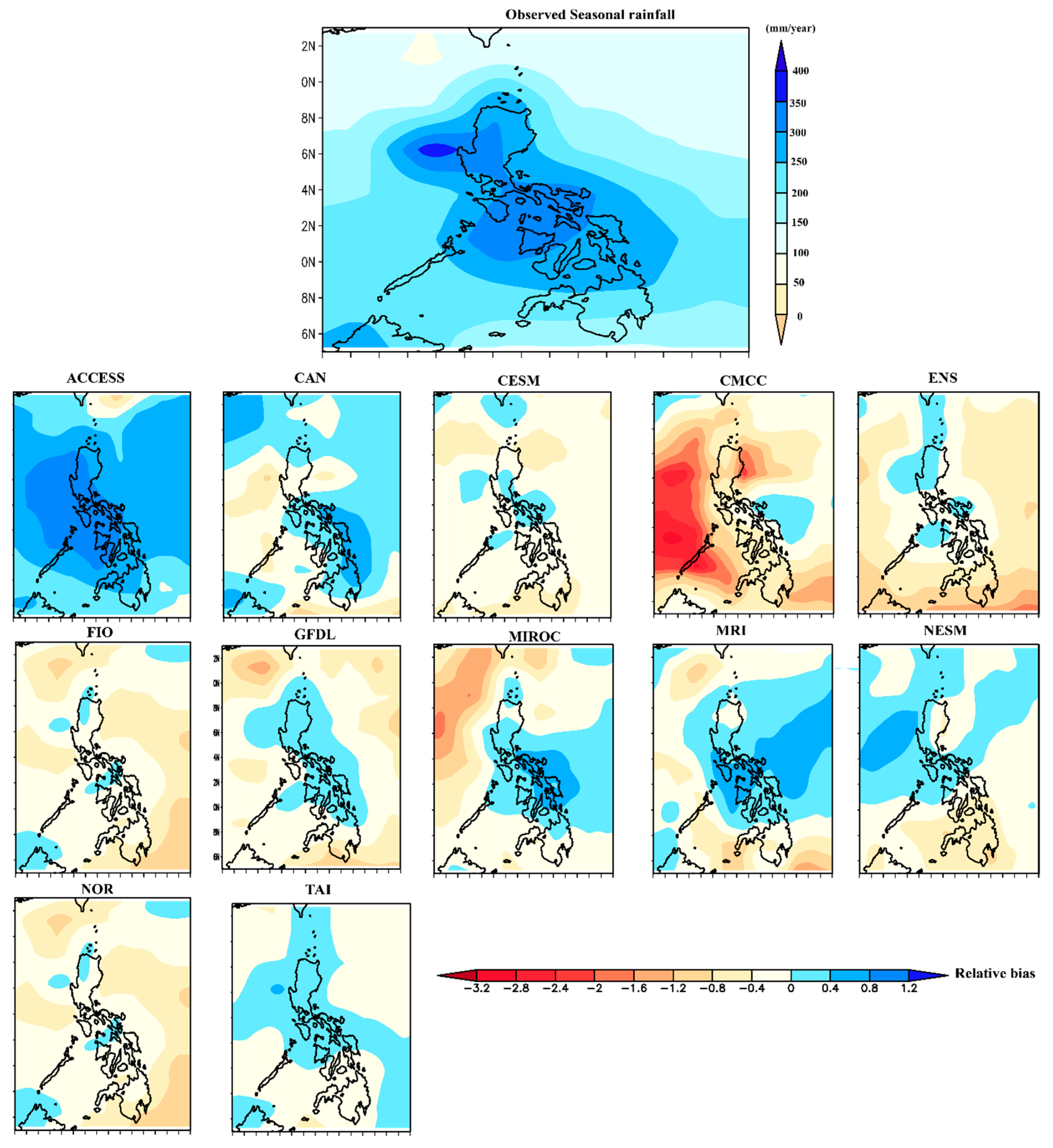
3.3. Spatial Distribution of Rainy-Season Rains and Related Biases in CMIP6
3.4. Descriptive Statistics of the Observed Rainy-Season Rainfall and CMIP6 Models’ Simulations
3.5. Spatial Dissemination of Annual Rainfall and Associated CMIP6 Relative Biases
3.6. Mean Statistical Features of the CMIP6 Climate Models in Comparison with the Observed Annual Rainfall
3.7. Gauging the Multiple Skills of CMIP6 Models in Simulating Observed Monsoonal Summer Rainfall over the Philippines
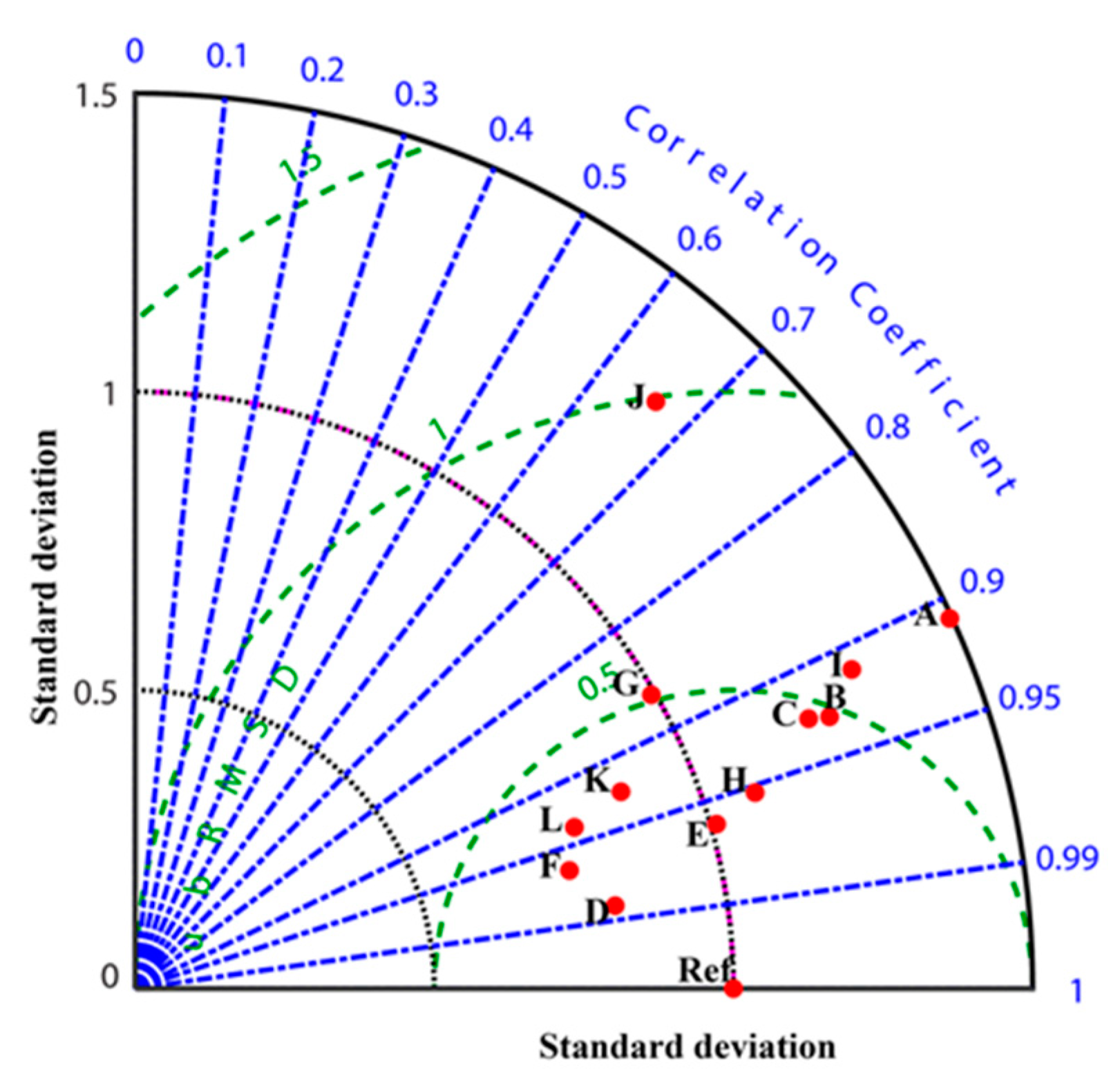
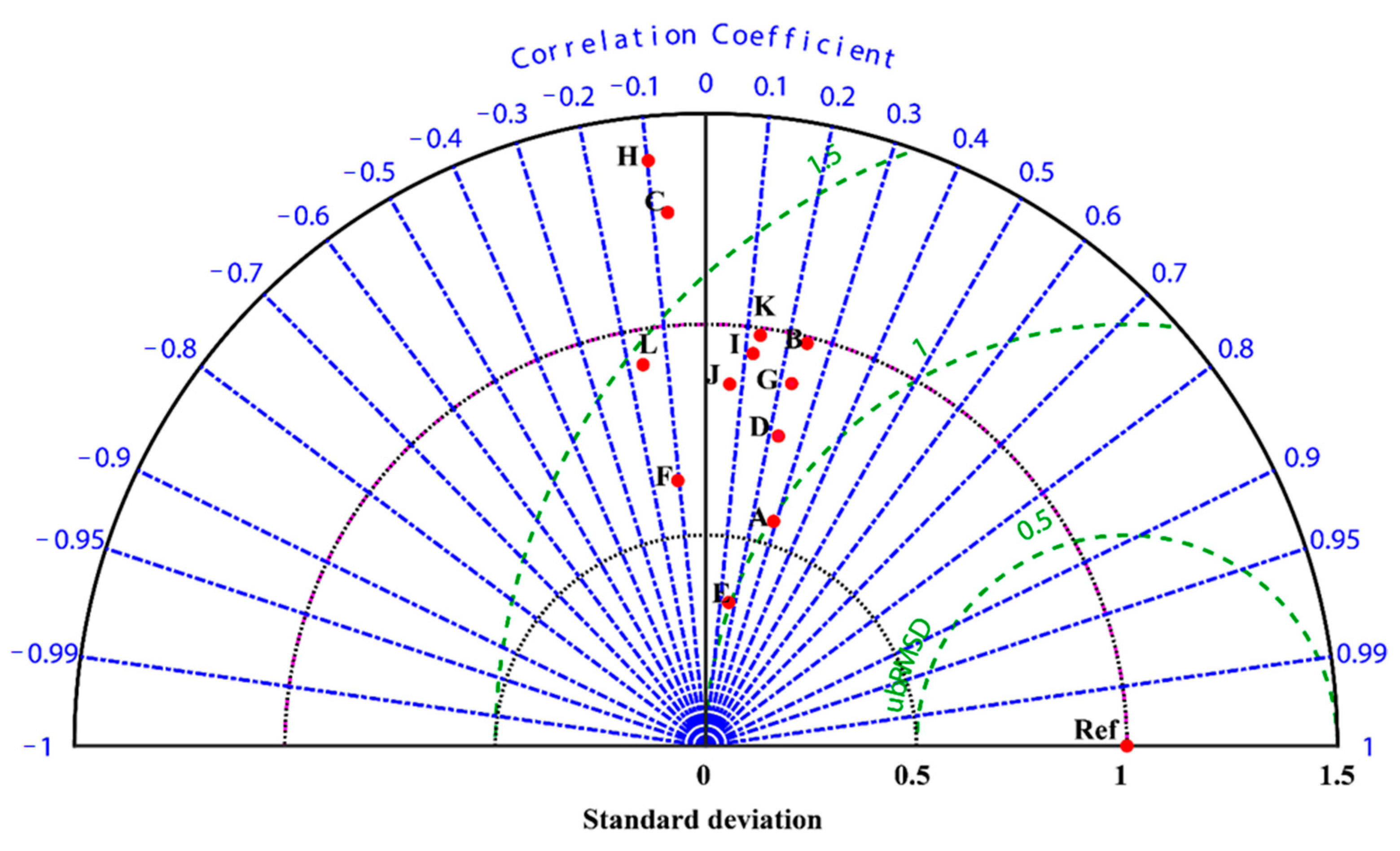
3.8. Taylor Diagram of CMIP6 Models Skills in Simulating Observed Annual Rainfall
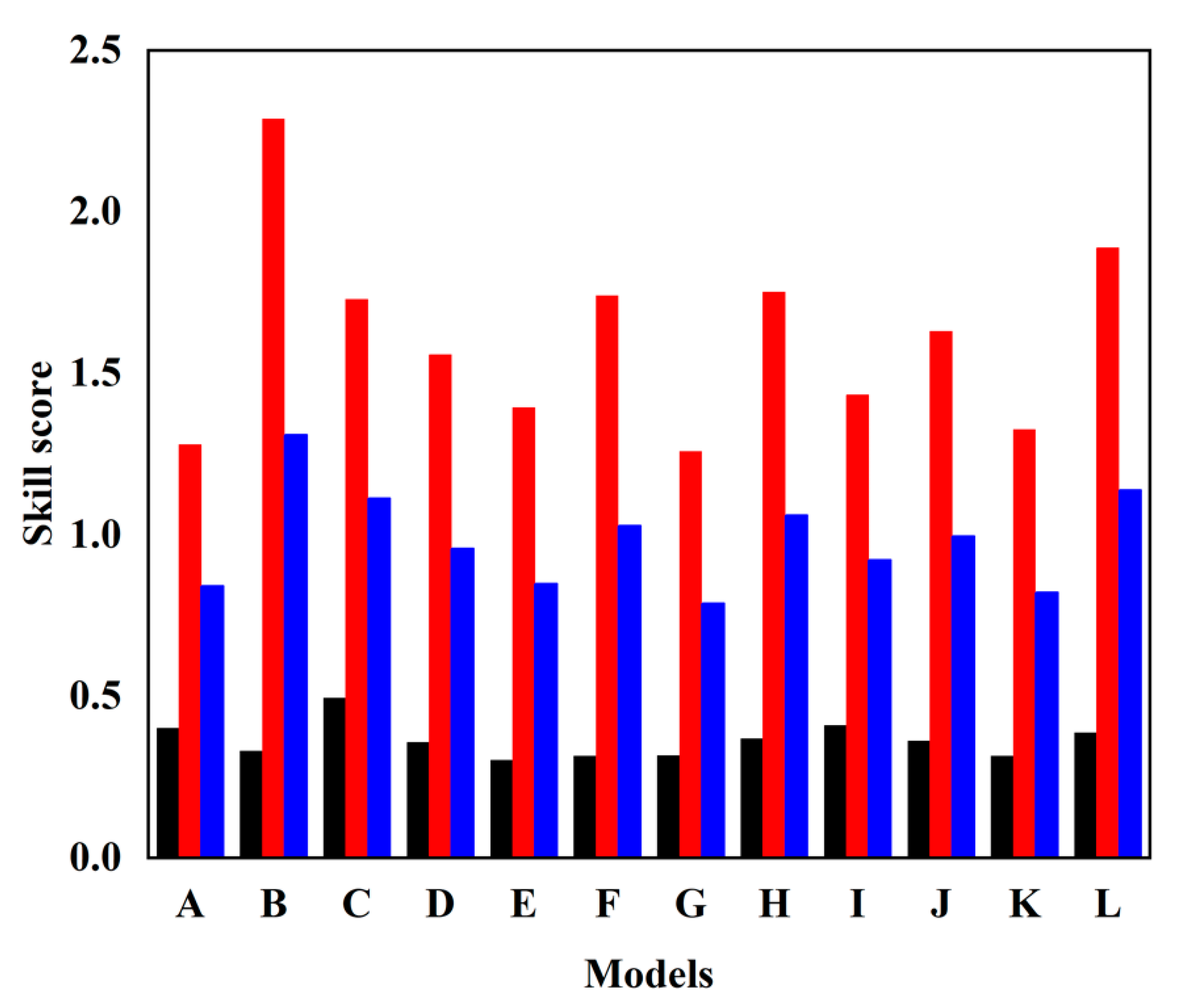
3.9. Skill Score Ranking of CMIP6 over the Philippines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, T.; Luo, J.-J.; Peng, K.; Qi, L.; Tang, S. Over-Projected Pacific Warming and Extreme El Niño Frequency Due to CMIP5 Common Biases. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, nwab056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, K.E.; Stouffer, R.J.; Meehl, G.A. An Overview of CMIP5 and the Experiment Design. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyring, V.; Bony, S.; Meehl, G.A.; Senior, C.A.; Stevens, B.; Stouffer, R.J.; Taylor, K.E. Overview of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) Experimental Design and Organization. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2016, 9, 1937–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidden, M.J.; Riahi, K.; Smith, S.J.; Fujimori, S.; Luderer, G.; Kriegler, E.; van Vuuren, D.P.; van den Berg, M.; Feng, L.; Klein, D.; et al. Global Emissions Pathways under Different Socioeconomic Scenarios for Use in CMIP6: A Dataset of Harmonized Emissions Trajectories through the End of the Century. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2019, 12, 1443–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oduro, C.; Shuoben, B.; Ayugi, B.; Beibei, L.; Babaousmail, H.; Sarfo, I.; Ullah, S.; Ngoma, H. Observed and Coupled Model Intercomparison Project 6 Multimodel Simulated Changes in Near-surface Temperature Properties over Ghana during the 20th Century. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 3681–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Yu, D.; Oh, J.; Byun, Y.; Boo, K.; Chung, I.; Park, J.; Park, D.R.; Min, S.; Sung, H.M. Performance Evaluation of CMIP5 and CMIP6 Models on Heatwaves in Korea and Associated Teleconnection Patterns. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD032583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, D.; Babel, M.S.; Abatan, A.A.; Collins, M. An Evaluation of CMIP5 and CMIP6 Climate Models in Simulating Summer Rainfall in the Southeast Asian Monsoon Domain. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 1181–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Shu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Bao, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhou, X.; Wang, G. Evaluation of the Ability of CMIP6 Global Climate Models to Simulate Precipitation in the Yellow River Basin, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 751974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoma, H.; Wen, W.; Ayugi, B.; Babaousmail, H.; Karim, R.; Ongoma, V. Evaluation of Precipitation Simulations in CMIP6Models over Uganda. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 4743–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiru, M.S.; Chung, E.S. Performance Evaluation of CMIP6 Global Climate Models for Selecting Models for Climate Projection over Nigeria. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2021, 146, 599–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Duan, Q.; Shen, C.; Wu, Y.; Xing, C. Evaluation of Historical CMIP6 Model Simulations and Future Projections of Temperature over the Pan-Third Pole Region. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 26214–26229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, V.; Albert, J.R.G.; Perez, R.T. Climate-Related Disasters in Asia and the Pacific. ADB Econ. Work. Pap. Ser. 2013, 358, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- Pour, S.H.; Wahab, A.K.A.; Shahid, S. Physical-Empirical Models for Prediction of Seasonal Rainfall Extremes of Peninsular Malaysia. Atmos. Res. 2020, 233, 104720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gariano, S.L.; Guzzetti, F. Landslides in a Changing Climate. Earth Sci. Rev. 2016, 162, 227–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabari, H. Climate Change Impact on Flood and Extreme Precipitation Increases with Water Availability. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Z.; Shahid, S.; Ahmed, K.; Ismail, T.; Ziarh, G.F.; Chung, E.-S.; Wang, X. Evaluation of CMIP6 GCM Rainfall in Mainland Southeast Asia. Atmos. Res. 2021, 254, 105525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloria, A.; Perez, G.J.; Tapang, G.; Comiso, J. Improved Rainfall Data in the Philippines through Concurrent Use of GPM IMERG and Ground-Based Measurements. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kripalani, R.H.; Kulkarni, A. Climatic Impact of El Niño/La Niña on the Indian Monsoon: A New Perspective. Weather 1997, 52, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, F.T.; Narisma, G.T.; Villafuerte, M.Q.; Cheng Chua, K.U.; Olaguera, L.M. A Climatological Analysis of the Southwest Monsoon Rainfall in the Philippines. Atmos. Res. 2013, 122, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaousmail, H.; Hou, R.; Ayugi, B.; Ojara, M.; Ngoma, H.; Karim, R.; Rajasekar, A.; Ongoma, V. Evaluation of the Performance of CMIP6 Models in Reproducing Rainfall Patterns over North Africa. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric Tests Against Trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods, 4th ed.; Griffin: London, UK, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the Regression Coefficient Based on Kendall’s Tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Kang, S.; Wu, H.; Yuan, X. Detection of Spatio-Temporal Variability of Air Temperature and Precipitation Based on Long-Term Meteorological Station Observations over Tianshan Mountains, Central Asia. Atmos. Res. 2018, 203, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumo, L.; Yu, J. Gauging the Performance of CMIP5 Historical Simulation in Reproducing Observed Gauge Rainfall over Kenya. Atmos. Res. 2020, 236, 104808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayugi, B.; Tan, G.; Gnitou, G.T.; Ojara, M.; Ongoma, V. Historical Evaluations and Simulations of Precipitation over East Africa from Rossby Centre Regional Climate Model. Atmos. Res. 2020, 232, 104705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Liu, Z.; Charles, S.P.; Xu, Z.; Yao, Z. A Score-Based Method for Assessing the Performance of GCMs: A Case Study of Southeastern Australia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 4154–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.; Sperber, K.R.; Slingo, J.; Meehl, G.; Mechoso, C.R.; Kimoto, M.; Giannini, A. Modelling Monsoons: Understanding and Predicting Current and Future Behaviour. In Global Monsoon System, the Research and Forecast, 2nd ed.; World Scientific Pub Co., Ltd.: Singapore, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee, P.S.; Zaitchik, B.F. Perspectives on CMIP5 Model Performance in the Nile River Headwaters Regions. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 4262–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, S.E. The West African Sahel: A Review of Recent Studies on the Rainfall Regime and Its Interannual Variability. ISRN Meteorol. 2013, 2013, 453521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, S.M.; Kirtman, B.P.; Vimont, D.J. A Framework to Decompose Wind-Driven Biases in Climate Models Applied to CCSM/CESM in the Eastern Pacific. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 8763–8782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalai, H.; Hamilton, K.; Sperber, K.R. The South Asian Summer Monsoon and Its Relationship with ENSO in the IPCC AR4 Simulations. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 1071–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.G.; Annamalai, H. Climate Change and the South Asian Summer Monsoon. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haywood, J.M.; Jones, A.; Dunstone, N.; Milton, S.; Vellinga, M.; Bodas-Salcedo, A.; Hawcroft, M.; Kravitz, B.; Cole, J.; Watanabe, S.; et al. The Impact of Equilibrating Hemispheric Albedos on Tropical Performance in the HadGEM2-ES Coupled Climate Model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, J.E.; Wall, C.; Yettella, V.; Medeiros, B.; Hannay, C.; Caldwell, P.; Bitz, C. Global Climate Impacts of Fixing the Southern Ocean Shortwave Radiation Bias in the Community Earth System Model (CESM). J. Clim. 2016, 29, 4617–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauer, A.; Jones, C.; Eyring, V.; Evaldsson, M.; Hagemann, S.; Mäkelä, J.; Martin, G.; Roehrig, R.; Wang, S. Process-Level Improvements in CMIP5 Models and Their Impact on Tropical Variability, the Southern Ocean, and Monsoons. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2018, 9, 33–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.; García-Herrera, R.; Peña-Angulo, D.; Tomas-Burguera, M.; Domínguez-Castro, F.; Noguera, I.; Calvo, N.; Murphy, C.; Nieto, R.; Gimeno, L.; et al. Do CMIP models capture long-term observed annual precipitation trends? Clim. Dyn. 2022, 58, 2825–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, R.C.; Turner, A.G.; Marathayil, D.; Martin, G.M. The Role of Northern Arabian Sea Surface Temperature Biases in CMIP5 Model Simulations and Future Projections of Indian Summer Monsoon Rainfall. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 41, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandeep, S.; Ajayamohan, R.S. Origin of Cold Bias over the Arabian Sea in Climate Models. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, R.C.; Turner, A.G. Dependence of Indian Monsoon Rainfall on Moisture Fluxes across the Arabian Sea and the Impact of Coupled Model Sea Surface Temperature Biases. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 38, 2167–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favre, A.; Philippon, N.; Pohl, B.; Kalognomou, E.-A.; Lennard, C.; Hewitson, B.; Nikulin, G.; Dosio, A.; Panitz, H.-J.; Cerezo-Mota, R. Spatial Distribution of Precipitation Annual Cycles over South Africa in 10 CORDEX Regional Climate Model Present-Day Simulations. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 46, 1799–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xie, S.-P.; Kosaka, Y. Mechanisms for Tropical Tropospheric Circulation Change in Response to Global Warming. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 2979–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, S.V.; Liu, J.; Nguyen, N.S.; Vu, M.T.; Liong, S.Y. Assessment of CMIP5 Historical Simulations of Rainfall over Southeast Asia. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 132, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haarsma, R.J.; Roberts, M.J.; Vidale, P.L.; Senior, C.A.; Bellucci, A.; Bao, Q.; Chang, P.; Corti, S.; Fučkar, N.S.; Guemas, V.; et al. High-resolution model intercomparison project (HighResMIP v1.0) for CMIP6. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 4185–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenegger, C.; Brockhaus, P.; Schär, C. Towards Climate Simulations at Cloud-Resolving Scales. Meteorol. Z. 2008, 17, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Model Abbreviation | Alphabet Used | Horizontal Resolution | Modeling Centre |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACCESS-ESM1-5 | ACCESS (A) | 250 km | Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization and Bureau of Meteorology, Australia |
| CanESM5 | CAN (B) | 500 km | Canadian Centre for Climate Modeling and Analysis (Canada) |
| CESM2 | CESM (C) | 100 km | National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) Boulder, CO, USA |
| CMCC | CMCC (D) | 100 km | Fondazione Centro Euro-Mediterraneo sui Cambiamenti Climatici, Lecce 73100, Italy |
| FIO-QLNM | FIO (F) | 100 km | First Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration, Qingdao 266061, China), QNLM (Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, Qingdao 266237, China) |
| GFDL-ESM4 | GFDL (G) | 100 km | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory, Princeton, NJ 08540, USA |
| MIROC6 | MIROC(H) | 250 km | JAMSTEC (Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology, Kanagawa, Japan), AORI (Atmosphere and Ocean Research Institute, The University of Tokyo, Chiba, Japan), and NIES (National Institute for Environmental Studies, Ibaraki, Japan |
| MRI-ESM2-0 | MRI (I) | 100 km | Meteorological Research Institute, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0052, Japan |
| NESM3 | NESM (J) | 250 km | The Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, 210044, China |
| NorCPM1 | NOR (K) | 250 km | NorESM Climate modeling Consortium consisting of CICERO (Center for International Climate and Environmental Research, Oslo 0349), MET-Norway (Norwegian Meteorological Institute, Oslo 0313), NERSC (Nansen Environmental and Remote Sensing Center, Bergen 5006), NILU (Norwegian Institute for Air Research, Kjeller 2027), UiB (University of Bergen, Bergen 5007), UiO (University of Oslo, Oslo 0313) and UNI (Uni Research, Bergen 5008), Norway. Mailing address: NCC, c/o MET-Norway, Henrik Mohns plass 1, Oslo 0313, Norway |
| TaiESM1 | TAI (L) | 100 km | Research Center for Environmental Changes, Academia Sinica, Nankang, Taipei 11529, Taiwan |
| Class | Mean | stdev | Bias | RMSE | nRMSE | MMK | TSSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obs | 268.1 | 17.3 | 0.16 | 0.32 | |||
| ACCESS | 302.5 | 26.1 | 13.3% | 89.7 | 0.34 | 0.14 | 0.6 |
| CAN | 278.1 | 18.2 | 4.1% | 64.1 | 0.24 | 0.28 | 0.72 |
| CESM | 267.9 | 26.5 | 0.3% | 60.9 | 0.23 | −0.12 | −0.42 |
| CMCC | 255.0 | 14.5 | −4.5% | 43.2 | 0.16 | −0.02 | −0.02 |
| ENS | 261.3 | 6.2 | −2.2% | 47.3 | 0.18 | 0.15 | 0.13 |
| FIO | 240.1 | 14.9 | −10.1% | 31.7 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.21 |
| GFDL | 250.0 | 21.0 | −6.4% | 41.8 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.48 |
| MIROC | 255.9 | 22.3 | −4.2% | 47.1 | 0.18 | 0.01 | 0.005 |
| MRI | 271.5 | 19.2 | 1.6% | 59.6 | 0.22 | −0.04 | −0.22 |
| NESM | 265.7 | 16.7 | −0.5% | 53.0 | 0.20 | −0.03 | −0.075 |
| NOR | 217.1 | 19.9 | −15.7% | 25.5 | 0.10 | 0.02 | −0.05 |
| TAI | 255.7 | 15.5 | −4.3% | 45.7 | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.3 |
| Class | Mean | stdev | Bias | RMSE | nRMSE | MMK | TSSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obs | 206.1 | 18.4 | 0.20 | 0.53 | |||
| ACCESS | 174.5 | 10.3 | −15.3% | 40.7 | 0.20 | 0.11 | 0.13 |
| CAN | 218.2 | 18.2 | 5.9% | 118.2 | 0.57 | 0.28 | 0.69 |
| CESM | 195.2 | 23.4 | −5.3% | 44.9 | 0.22 | 0.03 | 0.08 |
| CMCC | 206.5 | 14.4 | 0.2% | 49.0 | 0.24 | 0.01 | 0.05 |
| ENS | 196.3 | 6.4 | −4.7% | 38.8 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 0.09 |
| FIO | 189.3 | 11.7 | −8.1% | 35.3 | 0.17 | −0.04 | −0.05 |
| GFDL | 186.2 | 16.3 | −9.6% | 32.2 | 0.16 | 0.06 | 0.20 |
| MIROC | 188.6 | 25.7 | −8.5% | 42.1 | 0.20 | −0.03 | −0.08 |
| MRI | 187.0 | 17.3 | −9.2% | 34.2 | 0.17 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| NESM | 193.7 | 15.9 | −6.0% | 39.2 | 0.19 | −0.06 | −0.07 |
| NOR | 194.7 | 18.1 | −5.5% | 26.9 | 0.13 | −0.01 | −0.05 |
| TAI | 211.5 | 16.9 | 2.7% | 56.2 | 0.27 | 0.13 | 0.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ignacio-Reardon, S.J.I.; Luo, J.-j. Evaluation of the Performance of CMIP6 Climate Models in Simulating Rainfall over the Philippines. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1459. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14091459
Ignacio-Reardon SJI, Luo J-j. Evaluation of the Performance of CMIP6 Climate Models in Simulating Rainfall over the Philippines. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(9):1459. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14091459
Chicago/Turabian StyleIgnacio-Reardon, Shelly Jo Igpuara, and Jing-jia Luo. 2023. "Evaluation of the Performance of CMIP6 Climate Models in Simulating Rainfall over the Philippines" Atmosphere 14, no. 9: 1459. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14091459
APA StyleIgnacio-Reardon, S. J. I., & Luo, J.-j. (2023). Evaluation of the Performance of CMIP6 Climate Models in Simulating Rainfall over the Philippines. Atmosphere, 14(9), 1459. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14091459









