Review: Fractal Geometry in Precipitation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Geometrical Motivation
1.2. Fractal Measure Background
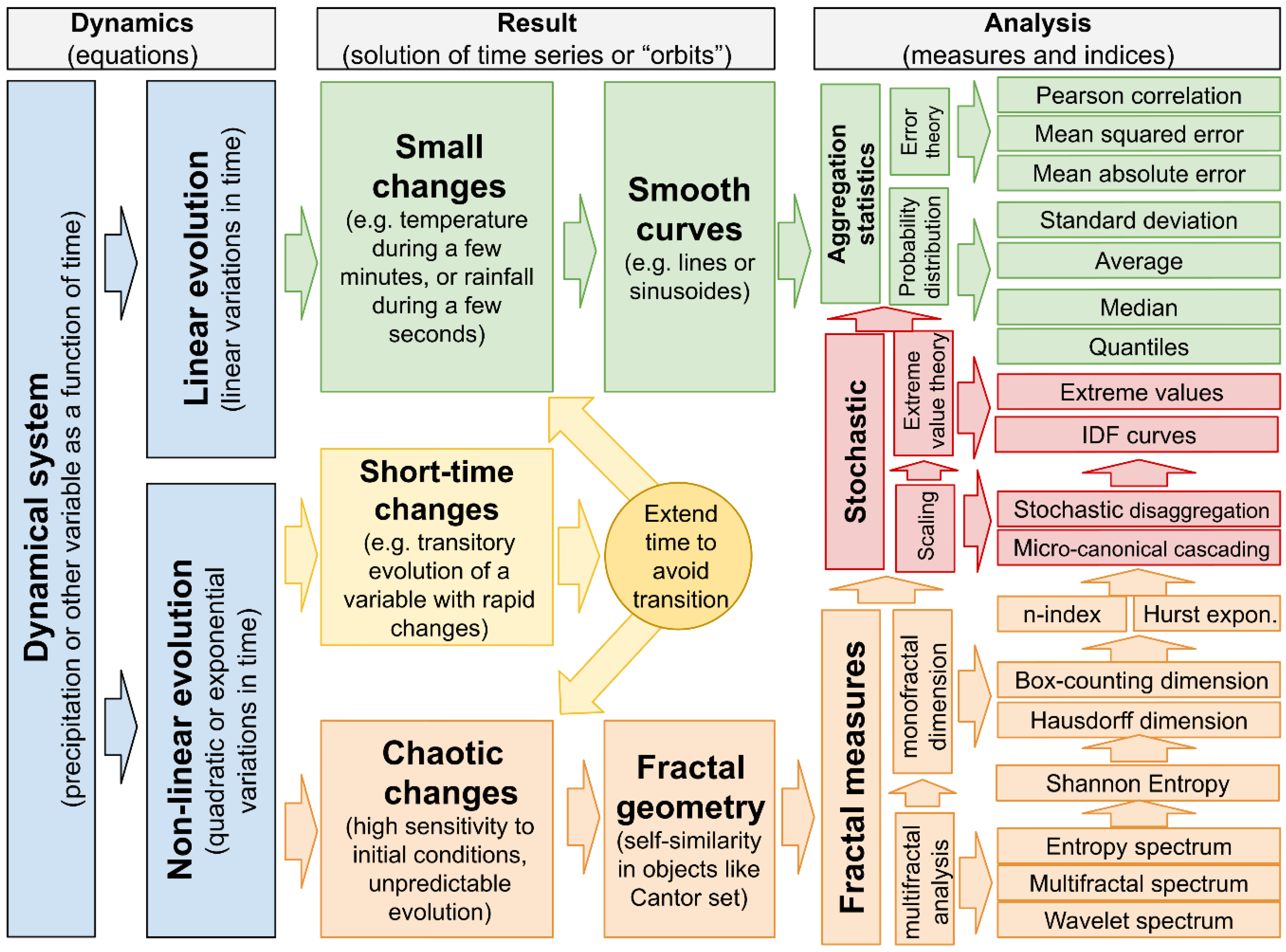
1.3. Geometry in Dynamical Systems
1.4. Structure of the Review
2. Classical Perspectives of Precipitation Fractality
2.1. Monofractal Dimension
2.2. Temporal Concentration
2.2.1. Classical Indices
2.2.2. Multifractal Approach
2.3. Other Measures
2.3.1. Entropy
2.3.2. Hurst Exponent
- calculate the mean;
- create a mean-adjusted series;
- calculate the cumulative deviate series Z;
- compute the range R;
- compute the standard deviation S;
- calculate the rescaled range R(δ)/S(δ) and average over all the partial time series of length δ.
- ✓
- A value of H = 0.5 suggests that a series is random;
- ✓
- If 0 < H < 0.5, it suggests an anti-persistent series where an upward value is more likely followed by a downward value, and vice versa;
- ✓
- If 0.5 < H < 1, it indicates a persistent series where the direction of the next value is more likely to be the same as the current value.
2.3.3. IDF Curves
- (i)
- Storm index or K-method
- (ii)
- Scale invariance
- (iii)
- Bartlett–Lewis rectangular pulse model
3. New Perspectives of Precipitation Fractality
3.1. Temporal and Spatial Relationships
3.2. Classification of Climatic Features
3.3. Future Challenges
4. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Monjo, R.; Locatelli, L.; Milligan, J.; Torres, L.; Velasco, M.; Gaitán, E.; Pórtoles, J.; Redolat, D.; Russo, B.; Ribalaygua, J. Estimation of future extreme rainfall in Barcelona (Spain) under monofractal hypothesis. Int. J. Clim. 2023, 43, 4047–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redolat, D.; Monjo, R.; Paradinas, C.; Pórtoles, J.; Gaitán, E.; Prado-López, C.; Ribalaygua, J. Local decadal prediction according to statistical/dynamical approaches. Int. J. Clim. 2020, 40, 5671–5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, J.; Gulakaram, V.S.; Vissa, N.K.; Bhaskaran, P.K.; Dash, M.K. Recent Warming Trends in the Arabian Sea: Causative Factors and Physical Mechanisms. Climate 2023, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mutairi, M.; Labban, A.; Abdeldym, A.; Abdel Basset, H. Trend Analysis and Fluctuations of Winter Temperature over Saudi Arabia. Climate 2023, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, J.; Guan, T.; Jin, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, G.; Bao, Z. Centennial Precipitation Characteristics Change in Haihe River Basin, China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H.; Katsuta, N.; Muraki, Y.; Heimhofer, U.; Ichinnorov, N.; Asahi, H.; Ando, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Murayama, M.; Ohta, T.; et al. Decadal–centennial-scale solar-linked climate variations and millennial-scale internal oscillations during the Early Cretaceous. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Sun, W.; Liu, J.; Wan, L. Centennial Variation and Mechanism of the Extreme High Temperatures in Summer over China during the Holocene Forced by Total Solar Irradiance. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rull, V.; Blasco, A.; Calero, M.Á.; Blaauw, M.; Vegas-Vilarrúbia, T. A Continuous Centennial Late Glacial-Early Holocene (15–10 cal kyr BP) Palynological Record from the Iberian Pyrenees and Regional Comparisons. Plants 2023, 12, 3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Muraja, D.O.; Klausner, V.; Prestes, A.; Aakala, T.; Macedo, H.G.; Rojahn da Silva, I. Exploring the Centennial-Scale Climate History of Southern Brazil with Ocotea porosa (Nees & Mart.) Barroso Tree-Rings. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morata, A.; Martín, M.; Luna, M.; Valero, F. Self-similarity patterns of precipitation in the Iberian Peninsula. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2006, 85, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidvarnia, A.; Mesbah, M.; Pedersen, M.; Jackson, G. Range Entropy: A Bridge between Signal Complexity and Self-Similarity. Entropy 2018, 20, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redolat, D.; Monjo, R. Statistical predictability of Euro-Mediterranean subseasonal anomalies: The TeWA approach. Weather Forecast, 2024; under review. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Z.; Singh, V.P.; Hao, F. Compound Extremes in Hydroclimatology: A Review. Water 2018, 10, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monjo, R.; Royé, D.; Martin-Vide, J. Meteorological drought lacunarity around the world and its classification. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Bhattarai, R.; Chen, L. Elevated Risk of Compound Extreme Precipitation Preceded by Extreme Heat Events in the Upper Midwestern United States. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiano, L.; Monjo, R.; Royé, D.; Martin-Vide, J. Will the world experience more fractal droughts? Atmos. Res. 2024; under review. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velhinho, J. Topics of Measure Theory on Infinite Dimensional Spaces. Mathematics 2017, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkelsinis, T.; Karagrigoriou, A. Theoretical Aspects on Measures of Directed Information with Simulations. Mathematics 2020, 8, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inguaggiato, S.; Vita, F.; Diliberto, I.S.; Mazot, A.; Calderone, L.; Mastrolia, A.; Corrao, M. The Extensive Parameters as a Tool to Monitoring the Volcanic Activity: The Case Study of Vulcano Island (Italy). Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biró, T.S.; Deppman, A. Non-Additive Entropy Formulas: Motivation and Derivations. Entropy 2023, 25, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbo, S.; Ghiraldini, A.; Dramis, A.; Dal Ferro, N.; Morari, F. Estimation of Hail Damage Using Crop Models and Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbazo, N.M.; Tall, M.; Sylla, M.B. Nonlinear Trend and Multiscale Variability of Dry Spells in Senegal (1951–2010). Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monjo, R. Measure of rainfall time structure using the dimensionless n-index. Clim. Res. 2016, 67, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meseguer-Ruiz, O.; Olcina Cantos, J.; Sarricolea, P.; Martín-Vide, J. The temporal fractality of precipitation in mainland Spain and the Balearic Islands and its relation to other precipitation variability indices. Int. J. Clim. 2017, 37, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meseguer-Ruiz, O.; Osborn, T.J.; Sarricolea, P.; Jones, P.D.; Cantos, J.O.; Serrano-Notivoli, R.; Martin-Vide, J. Definition of a temporal distribution index for high temporal resolution precipitation data over Peninsular Spain and the Balearic Islands: The fractal dimension; and its synoptic implications. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 52, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B. Intermittent turbulence in self-similar cascades–divergence of high moments and dimension of car-rier. J. Fluid Mech. 1974, 62, 331–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B. Les Objects Fractals: Forme, Hasard et Dimension; Flammarion: Paris, France, 1975; Volume 17. [Google Scholar]
- Jahanmiri, F.; Parker, D.C. An Overview of Fractal Geometry Applied to Urban Planning. Land 2022, 11, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhoria, A.; Panwar, A.; Sajid, M. Mandelbrot and Julia Sets of Transcendental Functions Using Picard–Thakur Iteration. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastassiou, G.A.; Kouloumpou, D. Approximation of Brownian Motion on Simple Graphs. Mathematics 2023, 11, 4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B.B. How long is the coast of Britain? Statistical self-similarity and fractional dimension. Science 1967, 156, 636–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Xia, Z. Fractals in physical geography. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 1996, 20, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuček, P.; Marek LPaszto, V.; Janoška, Z.; Dančák, M. Fractal perspectives of GIScience based on the leaf shape analysis. In GeoComputation Conference Proceedings; University College London: London, UK, 2011; pp. 169–176. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Q.; Russel, H.; Sharpe, D.; Kenny, F.; Qin, P. GIS-based statistical and fractal/multifractal analysis of surface stream patterns in the Oak Ridges Moraine. Comput. Geosci. 2001, 27, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Vide, J. Dimensión fractal de las costas gallega y catalana. Notes De Geogr. Física 1992, 20–21, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, J. On Fractal Mechanism of Coastline—A Case Study of China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2002, 12, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, P.M.; Tate, N.J. Spatial Scale Problems and Geostatistical Solutions: A Review. Prof. Geogr. 2004, 52, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S. Study of Saudi Arabian climatic conditions using Hurst exponent and climatic predictability index. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2009, 39, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangarajan, G.; Sant, D.A. A climate predictability index and its applications. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangarajan, G.; Sant, D.A. Fractal dimensional analysis of Indian climatic dynamics. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2004, 19, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodri, L. Fractal Analysis of Climatic Data: Mean Annual Temperature Records in Hungary. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 1994, 49, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hateren, J.H. A fractal climate response function can simulate global average temperature trends of the modern era and the past millennium. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 40, 2651–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, S.A.; Romani, L.A.S.; Avila, A.M.H.; Coltri, P.P.; Traina, C.; Cordeiro, R.L.F.; de Sousa, E.P.M.; Traina, A.J.M. Fractal-based Analysis to Identify Trend Changes in Multiple Climate Time Series. J. Inform. Data Manag. 2011, 2, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, S.A.; Romani, L.A.S.; Avila, A.M.H.; Coltri, P.P.; Traina, C.; Cordeiro, R.L.F.; de Sousa, E.P.M.; Traina, A.J.M. Analysis of Large Scale Climate Data: How Well Climate Change Models and Data from Real Sensor Networks Agree? In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on World Wide Web, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 13–17 May 2013; Schwabe, D., Almeida, V., Glaser, H., Baeza-Yates, R., Moon, S., Eds.; pp. 517–526. [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier, J.D. Analysis and modelling of the natural variability of climate. J. Clim. 1997, 10, 1331–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez-Cepeda, R.D.; Hernandez-Ramirez, D.; Mendoza, B.; Valdes-Galicia, J.; Maravilla, D. Fractality of monthly extreme minimum temperature. Fractals 2003, 11, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.R. Fractal analysis of eight glacial cycles from an Antarctic ice core. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2005, 25, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raidl, A. Estimating the fractal dimension, K-2-entropy, and the predictability of the atmosphere. Czechoslov. J. Phys. 1996, 46, 296–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahay, J.D.; Sreenivasan, K.R. The search for a low-dimensional characterization of a local climate system. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. 1996, 354, 1715–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusev, A.A.; Ponomoreva, V.V.; Braitseva, O.A.; Melekestsev, I.V.; Sulerzhitsky, L.D. Great explosive eruptions on Kamchatka during the last 10,000 years: Self-similar irregularity of the output of volcanic products. J. Geophys. Res.-Solid Earth 2003, 108, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzarella, A.; Rapetti, F. Scale-invariance laws in the recurrence interval of extreme floods: An application to the upper Po river valley (northern Italy). J. Hydrol. 2004, 288, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almatroud, A.O.; Khennaoui, A.-A.; Ouannas, A.; Grassi, G.; Al-sawalha, M.M.; Gasri, A. Dynamical Analysis of a New Chaotic Fractional Discrete-Time System and Its Control. Entropy 2020, 22, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.-W.; Pielke, R.A., Sr.; Zeng, X. One Saddle Point and Two Types of Sensitivities within the Lorenz 1963 and 1969 Models. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Lu, T.; Pi, J.; Anwar, W. The Retentivity of Four Kinds of Shadowing Properties in Non-Autonomous Discrete Dynamical Systems. Entropy 2022, 24, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moysis, L.; Tutueva, A.; Volos, C.; Butusov, D.; Munoz-Pacheco, J.M.; Nistazakis, H. A Two-Parameter Modified Logistic Map and Its Application to Random Bit Generation. Symmetry 2020, 12, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakinyan, R.; Zakinyan, A.; Ryzhkov, R. Phases of the Isobaric Surface Shapes in the Geostrophic State of the Atmosphere and Connection to the Polar Vortices. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimont, F.; Dupuy, J.-L.; Linn, R.R.; Sauer, J.A.; Muñoz-Esparza, D. Pressure-Gradient Forcing Methods for Large-Eddy Simulations of Flows in the Lower Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Carreño, F.; Rosales-Romero, L.; Salazar, J.; Acosta-Vargas, P.; Mendoza-Cedeño, H.-F.; Verde-Luján, H.E.; Flor-Unda, O. Simulation of Wave Propagation Using Finite Differences in Oil Exploration. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusset, A.M.; Fuziki, M.E.K.; Balthazar, J.M.; Andrade, D.I.; Lenzi, G.G. Dynamic Analysis and Control of a Financial System with Chaotic Behavior Including Fractional Order. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prykarpatski, A.K.; Pukach, P.Y.; Vovk, M.I. Symplectic Geometry Aspects of the Parametrically-Dependent Kardar–Parisi–Zhang Equation of Spin Glasses Theory, Its Integrability and Related Thermodynamic Stability. Entropy 2023, 25, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Anwar, W.; Li, R.; Lu, T.; Mo, Z. Distributional Chaos and Sensitivity for a Class of Cyclic Permutation Maps. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takens, F. Detecting Strange Attractors in Turbulence. In Dynamical Systems and Turbulence, Warwick 1980; Rand, D., Young, L.-S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981; pp. 366–381. [Google Scholar]
- Frunzete, M. Quality Evaluation for Reconstructing Chaotic Attractors. Mathematics 2022, 10, 4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.H. Bootstrap Prediction Intervals of Temporal Disaggregation. Stats 2022, 5, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guariglia, E.; Guido, R.C.; Dalalana, G.J.P. From Wavelet Analysis to Fractional Calculus: A Review. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutan-pour, K.; Dutilleul, P.; Smith, D.L. Advances in the implementation of the box-counting method of fractal dimension estimation. Appl. Math. Comput. 1999, 105, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovejoy, S.; Schertzer, D.; Tsonis, A.A. Functional box-counting and multiple elliptical dimensions in rain. Science 1987, 235, 1036–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandelbrot, B.B. Fractals and Chaos: The Mandelbrot Set and Beyond Softcover; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Wu, Y.; Ma, D.; Xu, Y.P. A new fractal-theory-based criterion for hydrological model calibration. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 3675–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breslin, M.C.; Belward, J.A. Fractal dimensions for rainfall time series. Math. Comput. Simul. 1999, 48, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Vide, J. Spatial distribution of a daily precipitation concentration index in Peninsular Spain. Int. J. Clim. 2004, 24, 959–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monjo, R.; Martin-Vide, J. Daily precipitation concentration around the world according to several indices. Int. J. Clim. 2016, 36, 3828–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncho, R.; Belda, F.; Caselles, V. Climatic study of the exponent “n” in IDF curves: Application for the Iberian Peninsula. Tethys 2009, 6, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncho, R.; Belda, F.; Caselles, V. Distribución probabilística de los extremos globales de precipitación. Nimbus 2011, 27–28, 119–135. [Google Scholar]
- Huff, F.A. Time distribution of rainfall in heavy storms. Water Resour. Res. 1967, 3, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordery, I.; Pilgrim, D.M. Time patterns of rainfall for estimating design floods on a frequency basis. Water Sci. Technol. 1984, 16, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.K.; Singh, V.P.; Singh, P.K. Revisiting the soil conservation service curve number method. In Hydrologic Modeling: Select Proceedings of ICWEES-2016; Singh, V., Yadav, S., Yadava, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; Volume 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C. Gaussian-distribution-based hyetographs and their relationships with debris flow initiation. J. Hydrol. 2011, 411, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, W.; Yoo, C. Evaluation of rainfall temporal distribution models with annual maximum rainfall events in Seoul Korea. Water 2018, 10, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Meshgi, A.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Tay, S.H.X.; Pijcke, G.; Manocha, N.; Ong, M.; Nguyen, M.T.; Babovic, V. Three resampling approaches based on method of frag-ments for daily-to-subdaily precipitation disaggregation. Int. J. Clim. 2018, 38, 1119–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafatnejad, A.; Tavakolifar, H.; Nazif, S. Evaluation of the climate change impact on the extreme rainfall amounts using modified method of fragments for sub-daily rainfall disaggregation. Int. J. Clim. 2022, 42, 908–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, D.; Achberger, C.; Chen, D. A multi-state weather generator for daily precipitation for the Torne River basin, northern Sweden/western Finland. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2016, 7, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, N.; Fatichi, S.; Paschalis, A.; Molnar, P.; Burlando, P. An advanced stochastic weather generator for simulating 2-D high resolution climate variables. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2017, 9, 1595–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onofrio, D.; Palazzi, E.; von Hardenberg, J.; Provenzale, A.; Calmanti, S. Stochastic rainfall downscaling of climate models. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 830–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, C.; Aly, C.; Vischel, T.; Panthou, G.; Blanchet, J.; Quantin, G.; Lebel, T. Stochastorm: A stochastic rainfall simulator for convective storms. J. Hydrometeor. 2021, 22, 387–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Thomy, H. Temporal rainfall disaggregation using a micro-canonical cascade model: Possibilities to improve the autocorrelation. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Barros, A.P. An evaluation of the statistics of rainfall extremes in rain gauge observations, and satellite-based and reanalysis products using universal multifractals. J. Hydrometeor. 2010, 11, 388–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaume, E.; Mouhous, N.; Andrieu, H. Rainfall stochastic disaggregation models: Calibration and validation of a multiplicative cascade model. Adv. Water Resour. 2007, 30, 1301–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Xu, Y.-P.; Zhu, Q.; Bai, Z.; Liu, L. Stochastic generation of daily rainfall events: A single-site rainfall model with Copula-based joint simulation of rainfall characteristics and classification and simulation of rainfall patterns. J. Hydrol. 2018, 564, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Marin, A.P.; Ayuso-Munoz, J.L.; Jimenez-Hornero, F.J.; Estevez, J. Selecting the best IDF model by using the multifractal approach. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Liu, D.; Fu, Q.; Li, M.; Faiz, M.A.; Ali, S.; Khan, M.I.; Li, T. Application of an improved multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis approach for estimation of the complexity of daily precipitation. Int. J. Clim. 2021, 41, 4653–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masugi, M.; Takuma, T. Multi-fractal analysis of IP-network traffic for assessing time variations in scaling properties. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 2007, 225, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäcker, A.; Haque, M.; Khaymovich, I.M. Multifractal dimensions for random matrices, chaotic quantum maps, and many-body systems. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 100, 032117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, F.G.; Huang, Y. Stochastic Analysis of Scaling Time Series: From Turbulence Theory to Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 623–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeGrauwe, P.; Dewachter, H.; Embrechts, M. Exchange Rate Theory Chaotic Models of Foreign Exchange Markets; Blackwell Publishers: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Peitgen, H.O.; Saupe, D. The Science of Fractal Images; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Hurst, H. Long term storage capacity of reservoirs. Trans. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1951, 6, 770–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B.B.; Wallis, J.R. Robustness of the rescaled range R/S in the measurement of noncyclic long-run statistical dependence. Water Resour. Res. 1969, 5, 967–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvi, T.; Selvaraj, S. Fractal dimension analysis of Northeast monsoon of Tamil Nadu. Univers. J. Environ. Res. Technol. 2011, 1, 219–221. [Google Scholar]
- Barbulescu, A.; Serban, C.; Maftei, C. Evaluation of Hurst exponent for precipitation time series. In Proceedings of the 14th WSEAS International Conference on Computers: Part of the 14th WSEAS CSCC Multiconference—Volume II Latest Trends on Computers, Venice, Italy, 21–23 November 2007; Volume 2, pp. 590–595. [Google Scholar]
- Saad Al-Wagdany, A. Intensity-duration-frequency curve derivation from different rain gauge records. J. King Saud Univ.—Sci. 2020, 32, 3421–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangüesa, C.; Rivera, D.; Pizarro, R.; García-Chevesich, P.; Ibáñez, A.; Pino, J. Spatial and temporal behavior of annual maximum sub-hourly rainfall intensities from 15-minute to 24-hour durations in central Chile. Aqua-LAC 2021, 13, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro, R.; Valdés, R.; Abarza, A.; García-Chevesich, P. A simplified storm index method to extrapolate intensity–duration–frequency (IDF) curves for ungauged stations in central Chile. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kossieris, P.; Makropoulos, C.; Onof, C.; Koutsoyiannis, D. A rainfall disaggregation scheme for sub-hourly time scales: Coupling a Bartlett-Lewis based model with adjusting procedures. J. Hydrol. 2018, 556, 980–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, H.L.; Nguyen, H.L. A spatio-temporal statistical downscaling approach to deriving extreme rainfall IDF relations at ungauged sites in the context of climate change. EPiC Ser. Eng. 2018, 3, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar]
- Diez-Sierra, J.; del Jesus, M. Subdaily rainfall estimationthrough daily rainfall downscaling using Random Forests in Spain. Water 2019, 11, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangüesa, C.; Pizarro, R.; Ingram, B.; Ibáñez, A.; Rivera, D.; García-Chevesich, P.; Pino, J.; Pérez, F.; Balocchi, F.; Peña, F. Comparing Methods for the Regionalization of Intensity–Duration–Frequency (IDF) Curve Parameters in Sparsely-Gauged and Ungauged Areas of Central Chile. Hydrology 2023, 10, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanmi, H.; Bargaoui, Z.; Mallet, C. Estimation of intensity-duration-frequency relationships according to the property of scale invariance and regionalization analysis in a Mediterranean coastal area. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira-Gandra, C.F.A.; Damé, R.C.F. Bartlett-Lewis of rectangular pulse modified model: Estimate of parameters for simulation of precipitation in sub-hourly duration. Eng. Agrícola 2014, 34, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershfield, D.M. Estimating the Probable Maximum Precipitation. J. Hydraul. Div. 1961, 87, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, M.; Basistha, A.; Bakimchandra, O.; Singh, C.K. Comparison of Spatial Interpolation Methods for Mapping Rainfall in Indian Himalayas of Uttarakhand Region. In Geostatistical and Geospatial Approaches for the Characterization of Natural Resources in the Environment; Raju, N., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, B. Is a chaotic multi-fractal approach for rainfall possible? Hydrol. Process. 2001, 15, 943–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovejoy, S.; Mandelbrot, B.B. Fractal properties of rain, and a fractal model. Tellus 1985, 37, 209–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, S.; Yamada, T.; Ikuta, S.; Müller, S.C. Fractal geometry of precipitation patterns. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1989, 58, 3445–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchiguirinskaia, I.; Schertzer, D.; Hoang, C.T.; Lovejoy, S. Multifractal study of three storms with different dynamics over the Paris region. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Urban Drainage, Porto Alegre, Brazil, 11–16 September 2011; pp. 421–426. [Google Scholar]
- Paulson, K.S. Fractal interpolation of rain rate time series. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovejoy, S.; Schertzer, D. Multifractals, cloud radiances and rain. J. Hydrol. 2006, 322, 59–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licznar, P.; Deidda, R. A space-time multifractal analysis on radar rainfall sequences from central Poland. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, Vienna, Austria, 27 April–2 May 2014; Volume 16, p. 10485. [Google Scholar]
- Licznar, P.; De Michele, C.; Dzugaj, D.; Niesobska, M. Variability of multifractal parameters in an urban precipitation monitoring network. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2014, Geophysical Research Abstracts, Vienna, Austria, 27 April–2 May 2014; Volume 16, p. 4343. [Google Scholar]
- Deidda, R. Rainfall downscalling in a space-time multifractal framework. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 1779–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B.B. Multifractal Measures, especially for the Geophysicist. Pure Appl. Geophys. 1989, 131, 5–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, Y. Short-Term Rainfall Prediction Using a Multifractal Model. Master’s Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003; 53p. [Google Scholar]
- Pathirana, A. Fractal Modelling of Rainfall: Downscaling in Time and Space for Hydrological Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, Civil Engineering Department, Tokyo University, Tokyo, Japan, 2001; 145p. [Google Scholar]
- Pathirana, A.; Herath, S.; Yamada, T. Estimating rainfall distributions at high temporal resolutions using a multifractal model. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2003, 7, 668–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X. Fractal and Multifractal Analysis of Runoff Time Series and Stream Networks in Agricultural Watersheds. Ph.D. Thesis, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2004; 135p. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.S.; Siddiqui, T.A. Estimation of fractal dimension of a noisy time series. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2012, 45, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hsui, A.T.; Rust, K.A.; Klein, G.D. A fractal analysis of Quaternary, Cenozoic-Mesozoic, and Late Pennsylvanian sea level changes. J. Geophys. Res. 1993, 98, 21963–21967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oñate Rubalcaba, J.J. Fractal Analysis of Climatic Data: Annual Precipitation Records in Spain. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 1997, 56, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, S.P.; Sierra, E.M.; Massobrio, M.J.; Momo, F.R. Análisis fractal de la precipitación anual en el este de la Provincia de la Pampa, Argentina. Rev. De Climatol. 2009, 9, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Amaro, I.R.; Demey, J.R.; Macchiavelli, R. Aplicación del análisis R/S de Hurst para estudiar las propiedades fractales de la precipitación en Venezuela. Interciencia 2004, 29–11, 617–620. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakumar, B. Fractal analysis of rainfall observed in two different climatic regions. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2000, 45, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, B. A preliminary investigation on the scaling behavior of rainfall observed in two different climates. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2000, 45, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.; Siddiqi, A.H. Wavelet based Hurst exponent and fractal dimensional analysis of Saudi climatic dynamics. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2009, 40, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Hou, X. Trends and Multifractals Analyses of Precipitation Data from Shandong Peninsula, China. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 8, 271–279. [Google Scholar]
- Dunkerley, D. Rain event properties in nature and in rainfall simulation experiments: A comparative review with recommendations for increasingly systematic study and reporting. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 4415–4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Marín, A.P.; Jiménez-Hornero, F.J.; Ayuso-Muñoz, J.L. Universal multifractal description of an hourly rainfall time series from a location in southern Spain. Atmósfera 2008, 21, 347–355. [Google Scholar]
- Langousis, A.; Veneziano, D.; Furcolo, P.; Lepore, C. Multifractal rainfall extremes: Theoretical analysis and practical estimation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2009, 39, 1182–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veneziano, D.; Furcolo, P. Multifractality of rainfall and scaling of intensity-duration-frequency curves. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veneziano, D.; Langousis, A.; Furcolo, P. Multifractality and rainfall extremes: A review. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W06D15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Marín, A.P. Análisis Multifractal de Series de Datos Pluviométricos en Andalucía. Ph.D. Thesis, Departamento de Ingeniería Rural, Escuela Técnica Superior de Ingenieros Agrónomos y Montes, Universidad de Córdoba, Córdoba, Spain, 2007; 162p. [Google Scholar]
- López-Lambraño, A.A. Análisis Multifractal y Modelación de la Precipitación. Ph.D. Thesis, Facultad de Ingeniería, Universidad Autónoma de Querétaro, Santiago de Querétaro, Mexico, 2012; 189p. [Google Scholar]
- Dunkerley, D.L. How do the rain rates of sub-events intervals such as the maximum 5- and 15-min rates (I5 or I30) relate to the properties of the enclosing rainfall event? Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 2425–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutiel, H.; Trigo, R.M. The rainfall regime in Lisbon in the last 150 years. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2014, 118, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiser, H.; Kutiel, H. Rainfall uncertainty in the Mediterranean: Intraseasonal rainfall distribution. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2010, 100, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, M.I.P.; Grasman, J. Multifractal analysis of 15-min and daily rainfall from a semi-arid región in Portugal. J. Hydrol. 1999, 220, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkerley, D. Indentifying individual rain events from pluviograph records: A review with analysis of data from an Australian dryland site. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 5024–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiely, G.; Ivanova, K. Multifractal Analysis of Hourly Precipitation. Phys. Chem. Earth 1999, 24, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, J.; Niemczynowicz, J. Multifractal analysis of daily spatial rainfall distributions. J. Hydrol. 1996, 187, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesca, L.; Lapenna, V.; Scalcione, E.; Summa, D. Searching for time-scaling features in rainfall sequences. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2007, 32, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, R.; Casas, M.C.; Redaño, A. Multifractal analysis of the rainfall time distribution on the metropolitan area of Barcelona (Spain). Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2013, 121, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanmi, H.; Bargaoui, Z.; Mallet, C. Investigation of the fractal dimension of rainfall occurrence in a semi-arid Mediterranean climate. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalauzi, A.; Cukic, M.; Millá, H.; Bonafoni, S.; Biondi, R. Comparison of fractal dimension oscillations and trends of rainfall data from Pastaza Province, Ecuador and Veneto, Italy. Atmos. Res. 2009, 93, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardiola-Albert, C.; Rivero-Honegger, C.; Monjo, R.; Díez-Herrero, A.; Yagüe, C.; Bodoque, J.M.; Tapiador, F.J. Automated convective and stratiform precipitation estimation in a small mountainous catchment using X-band radar data in Central Spain. J. Hydroinform. 2017, 19, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monjo, R.; Gaitán, E.; Pórtoles, J.; Ribalaygua, J.; Torres, L. Changes in extreme precipitation over Spain using statistical downscaling of CMIP5 projections. Int. J. Clim. 2016, 36, 757–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaitán, E.; Monjo, R.; Pórtoles, J.; Pino-Otín, M.R. Impact of climate change on drought in Aragon (NE Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutahir, H.; Juan Bellot, J.; Monjo, R.; Bellot, P.; Garcia, M.; Touhami, I. Likely effects of climate change on groundwater availability in a Mediterranean region of Southeastern Spain. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

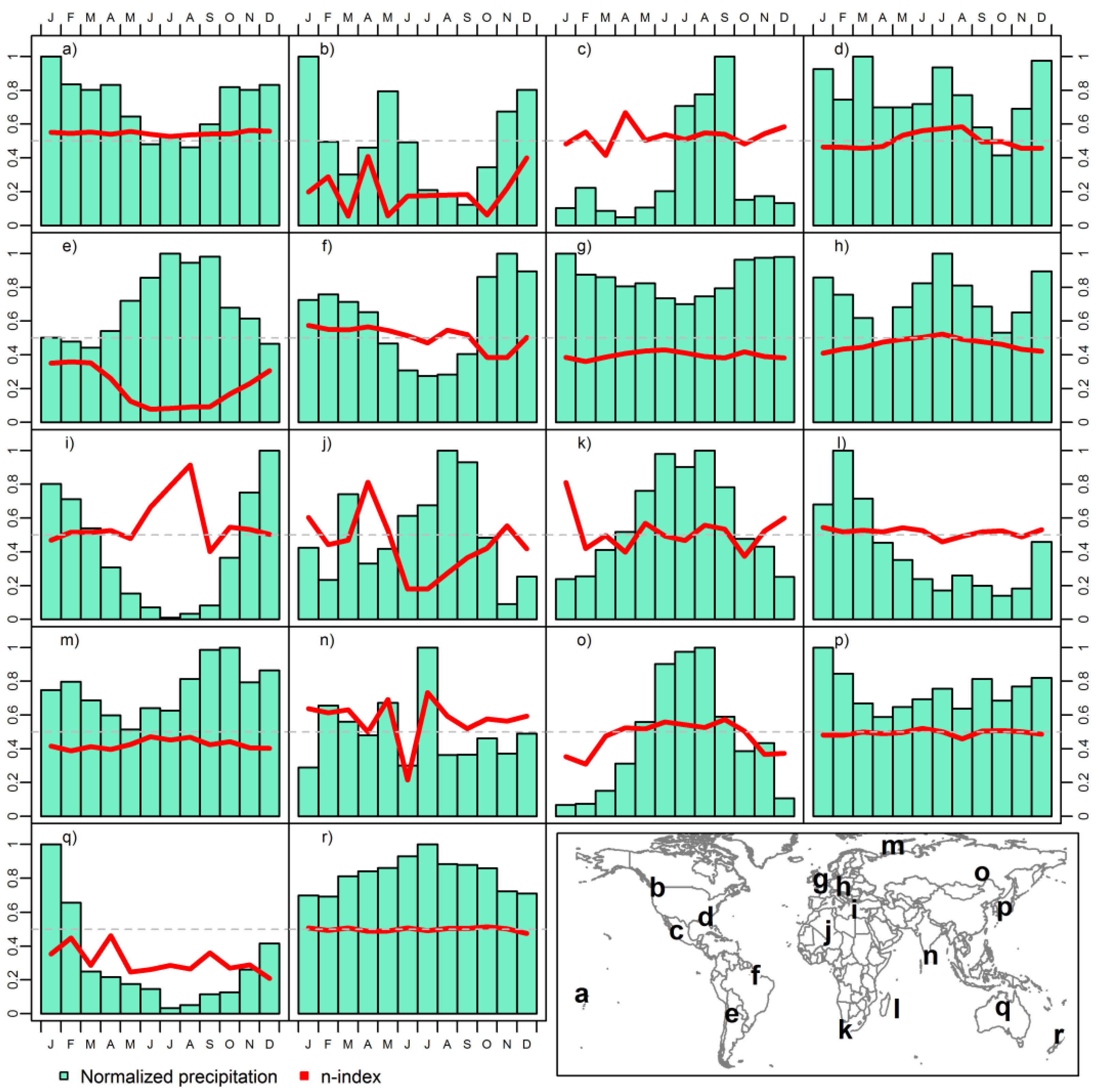
| Name | Description | DSS n-Index | WSL (Days) | Examples of Areas That Experience This Climate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hs | Long droughts with short wet spells | >0.4 | <3 | Arid and semi-arid regions |
| Hℓ | Long droughts with long wet spells | ≥3 | Tropical and monsoon regions | |
| Ms | Medium droughts with short wet spells | [0.3, 0.4] | <3 | Transition areas |
| Mℓ | Medium droughts with long wet spells | ≥3 | Oceanic areas | |
| Ls | Short droughts with short wet spells | <0.3 | <3 | Frequent extratropical–cyclonic areas |
| Lℓ | Short droughts with long wet spells | ≥3 | Equatorial climate and regular polar jet streams (e.g., southern annular mode) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Monjo, R.; Meseguer-Ruiz, O. Review: Fractal Geometry in Precipitation. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15010135
Monjo R, Meseguer-Ruiz O. Review: Fractal Geometry in Precipitation. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(1):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15010135
Chicago/Turabian StyleMonjo, Robert, and Oliver Meseguer-Ruiz. 2024. "Review: Fractal Geometry in Precipitation" Atmosphere 15, no. 1: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15010135
APA StyleMonjo, R., & Meseguer-Ruiz, O. (2024). Review: Fractal Geometry in Precipitation. Atmosphere, 15(1), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15010135







