Assessing Spatio-Temporal Hydrological Impacts of Climate Change in the Siliana Watershed, Northwestern Tunisia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Modeling Approach
2.2.1. Hydrological Modeling
Data and Sources
2.2.2. Climate Modeling
2.2.3. SWAT Model Setup Simulation and Validation
Model Setup and Simulation
2.2.4. Hydrologic Indicators
3. Results
3.1. Climate Models Evaluation
3.2. Projected Changes in Water Balance Indicators
3.3. Flow Extremes Magnitude and Frequency
3.4. Magnitude of Flow Extremes Duration
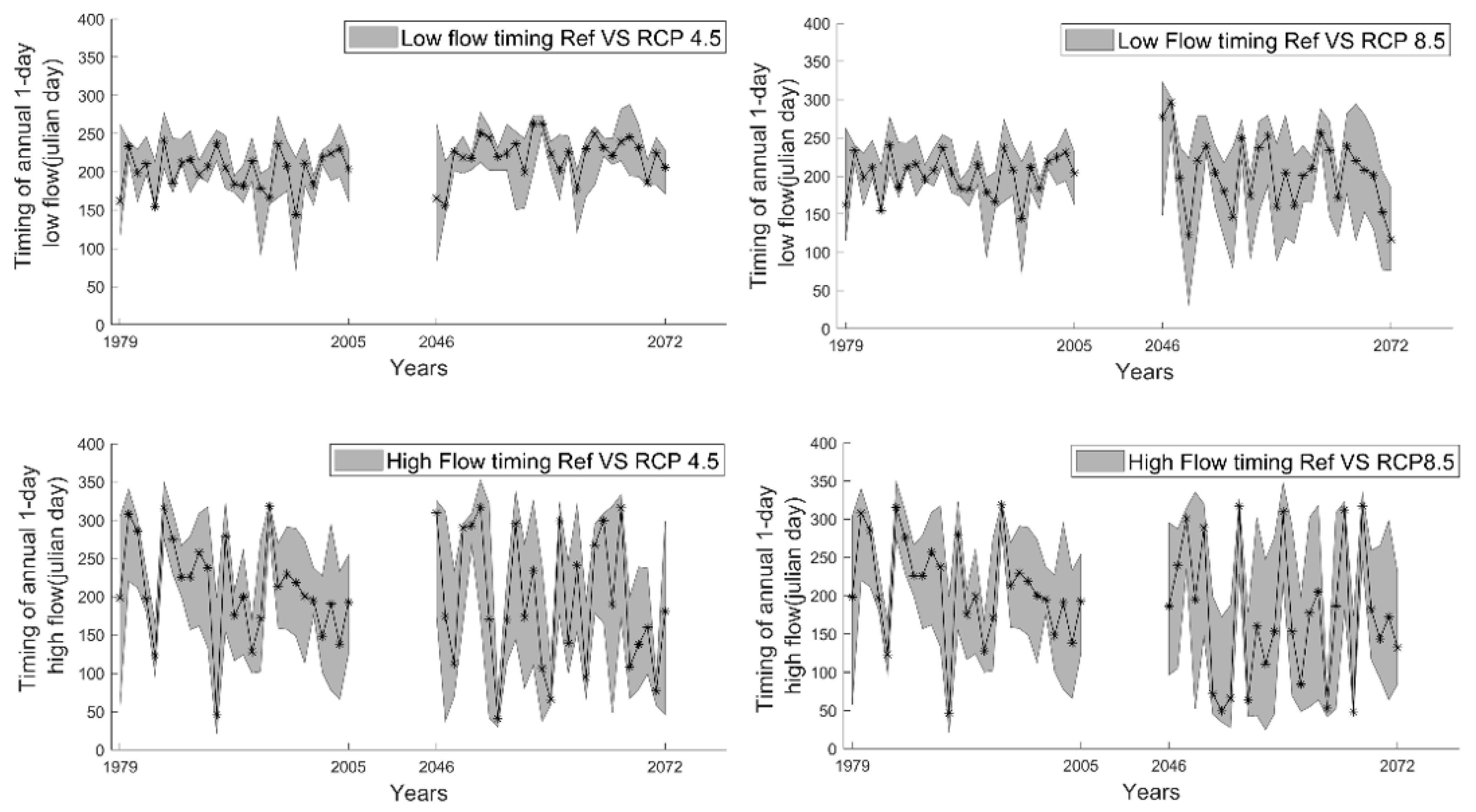
3.5. Timing of Flow Extremes
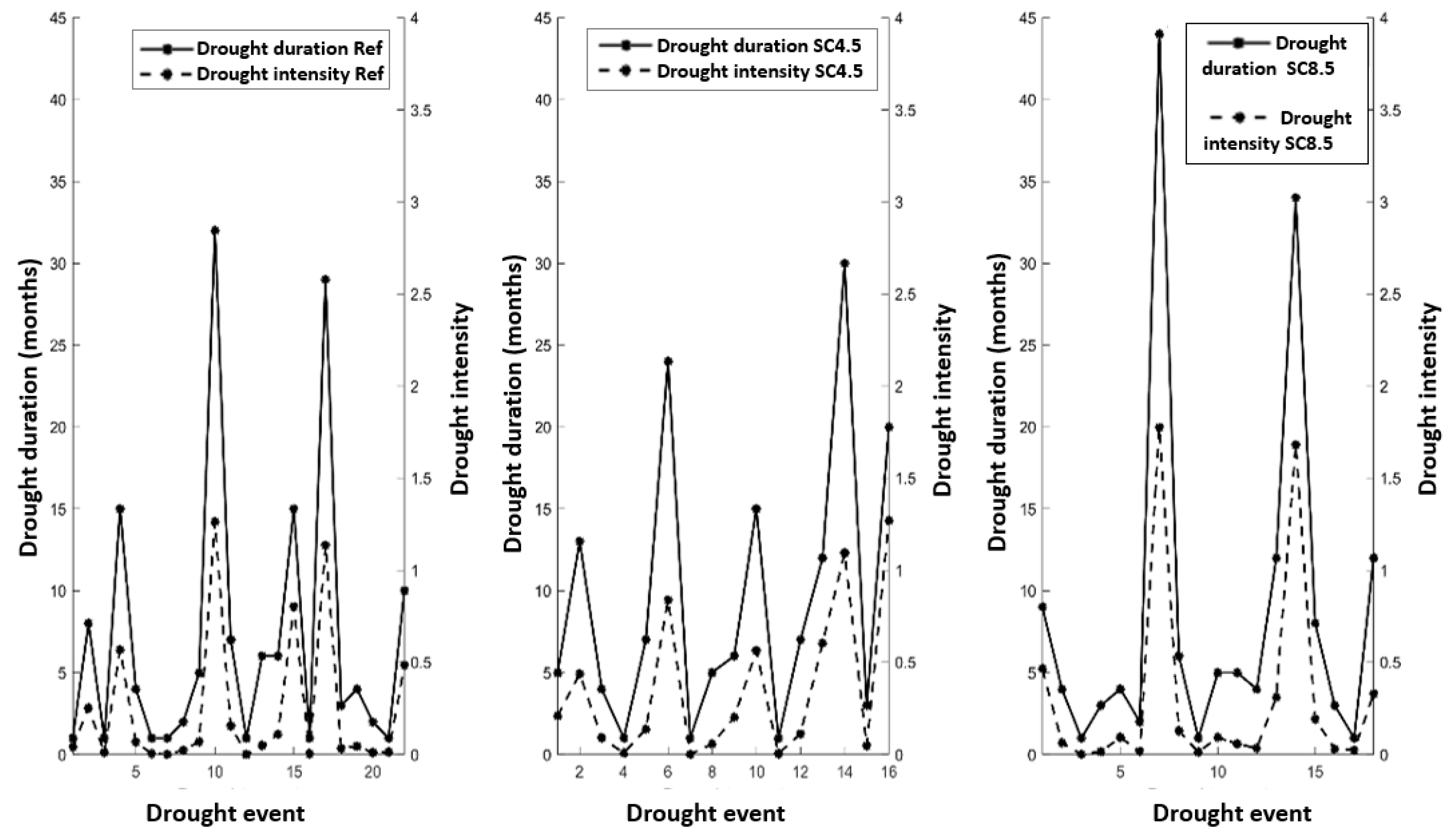
3.6. Drought Duration, Severity and Intensity
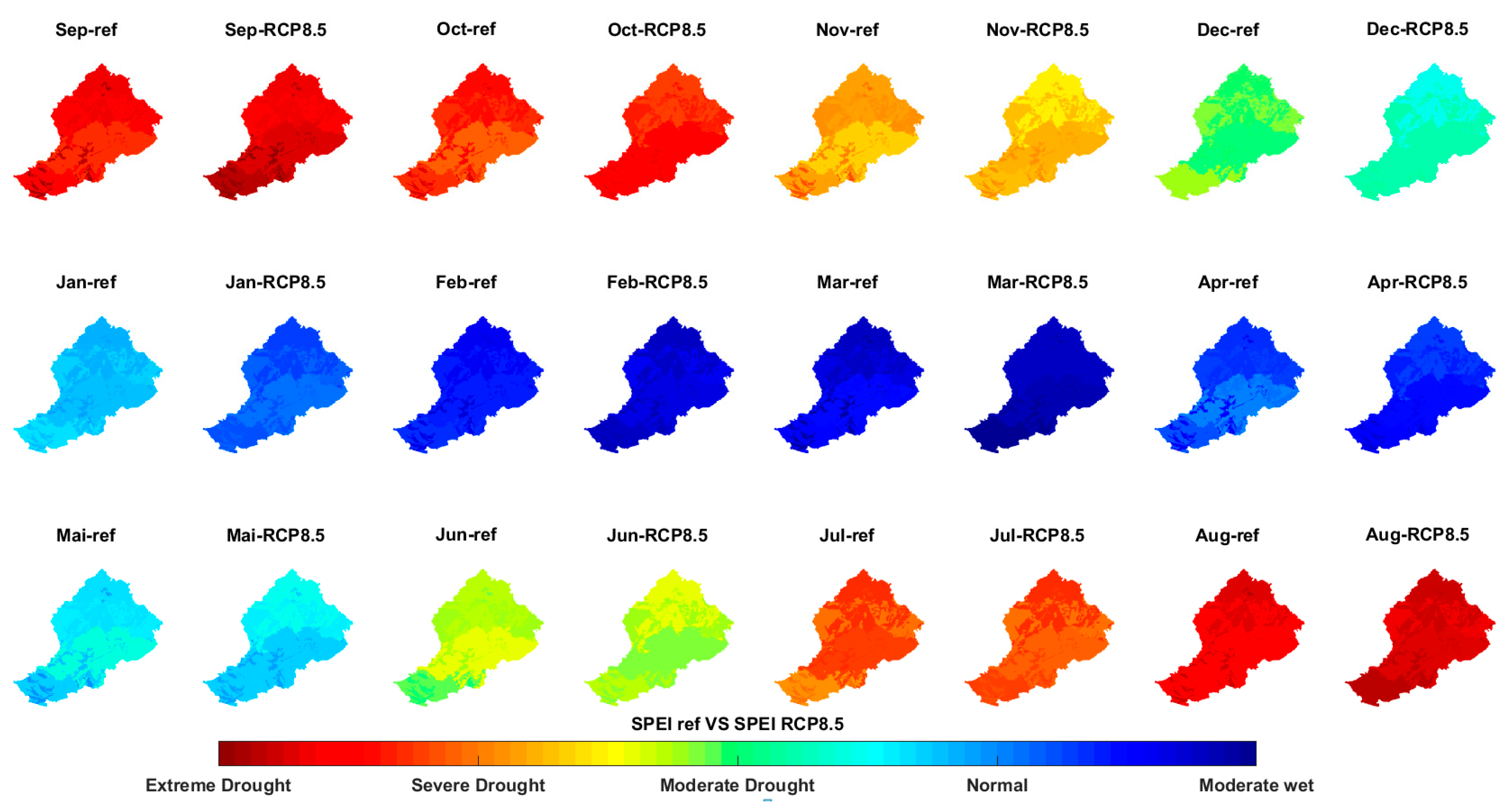
3.7. Spatial Variation of SPEI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Summary for Policymakers. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Technical Report. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. 2021. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/ (accessed on 16 October 2021).
- Sellami, H.; Benabdallah, S.; La Jeunesse, I.; Vanclooster, M. Quantifying hydrological responses of small Mediterranean catchments under climate change projections. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 543 Pt B, 924–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounir, K.; Sellami, H.; La Jeunesse, I.; Elkhanchoufi, A. Assessment of future climate and hydrological changes in semi-arid catchment using the SWAT model and bias-corrected EURO-CORDEX ensemble: A case of the Ouergha catchment, North of Morocco. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2023, 10, 349–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mami, A.; Yebdri, D.; Sauvage, S.; Raimonet, M.; Miguel, J. Spatio-temporal trends of hydrological components: The case of the Tafna basin (northwestern Algeria). J. Water Clim. Chang. 2021, 12, 2948–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido-Velazquez, D.; Collados-Lara, A.J.; Pérez-Sánchez, J.; Segura-Méndez, F.J.; Senent-Aparicio, J. Climate change impacts on the streamflow in Spanish basins monitored under near-natural conditions. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2021, 38, 100937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Salvador, A.; Millares, A.; Eekhout, J.; Conesa-García, C. Assessment of streamflow from euro-cordex regional climate simulations in semi-arid catchments using the swat model. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saade, J.; Atieh, M.; Ghanimeh, S.; Golmohammadi, G. Modeling Impact of Climate Change on Surface Water Availability Using SWAT Model in a Semi-Arid Basin: Case of El Kalb River, Lebanon. Hydrology 2021, 8, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, C.D.; Guglielmo, F.; Joussaume, S.; Bessembinder, J.; Christel, I.; Doblas-Reyes, F.J.; Djurdjevic, V.; Garrett, N.; Kjellström, E.; Krzic, A.; et al. Recommendations for future research priorities for climate modeling and climate services. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2021, 102, E578–E588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, M.; Karamitilios, G.; Halsnæs, K.; She, J.; Madsen, K. Advancing future climate services: Multi-sectorial mapping of the current usage and demand in denmark. Clim. Risk Manag. 2021, 33, 100335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quansah, J.; Naliaka, A.; Fall, S.; Ankumah, R.; El Afandi, G. Assessing future impacts of climate change on streamflow within the alabama river basin. Climate 2021, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teutschbein, C.; Seibert, J. Bias correction of regional climate model simulations for hydrological climate-change impact studies: Review and evaluation of different methods. J. Hydrol. 2012, 456–457, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Liu, T.; Meng, F.; Duan, Y.; Frankl, A.; Bao, A.; De Maeyer, P. Comparing bias correction methods used in downscaling precipitation and temperature from regional climate models: A case study from the Kaidu River Basin in Western China. Water 2018, 10, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awotwi, A.; Annor, T.; Anornu, G.; Quaye-Ballard, J.; Agyekum, J.; Ampadu, B.; Nti, I.; Gyampo, M.; Boakye, E. Climate change impact on streamflow in a tropical basin of Ghana, West Africa. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2021, 34, 100805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Im, E.; Bae, D. Impact of the spatial variability of daily precipitation on hydrological projections: A comparison of GCM– and RCM–driven cases in the Han River basin, Korea. Hydrol. Process. 2019, 14, 2240–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellami, H.; Benabdallah, S.; La Jeunesse, I.; Vanclooster, M. Climate models and hydrological parameter uncertainties in climate change impacts on monthly runoff and daily flow duration curve of a Mediterranean catchment. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 1415–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilori, O.W.; Balogun, I.A. Evaluating the performance of new CORDEX-Africa regional climate models in simulating West African rainfall. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 665–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruti, P.M.; Somot, S.; Giorgi, F.; Dubois, C.; Flaounas, E.; Obermann, A.; Dell’Aquil, A.; Giovanna, P.; Harzallah, A.; Lombardi, E.; et al. MED-CORDEX initiative for Medi- terranean climate studies. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 158, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Balhane, S.; Driouech, F.; Chafki, O.; Manzanas, R.; Chehbouni, A.; Mou-Okia, W. Changes in mean and extreme temperature and precipitation events from different weighted multi-model ensembles over the nrthern half of Morocco. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 58, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marras, P.A.; Lima, D.C.A.; Soares, P.M.M.; Cardoso, R.M.; Medas, D.; Dore, E.; De Giudici, G. Future precipitation in a Mediterranean island and streamfow changes for a small basin using EURO-CORDEX regional climate simulations and the SWAT model. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. LARGE AREA hydrologic modeling and assessment part i: Model development. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Singh, V.P. A review of drought concepts. J. Hydrol. 2010, 391, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaousmail, H.; Hou, R.; Ayugi, B.; Sian, K.T.C.L.K.; Ojara, M.; Mumo, R.; Chehbouni, A.; Ongoma, V. Future changes in mean and extreme precipitation over the mediterranean and sahara regions using bias-corrected cmip6 models. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 7280–7297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdeau-Goulet, S.; Hassanzadeh, E. Comparisons Between CMIP5 and CMIP6 Models: Simulations of Climate Indices Influencing Food Security, Infrastructure Resilience, and Human Health in Canada. Earth’s Future 2021, 9, 0036850420950130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refsgaard, J.C.; Madsen, H.; Andréassian, V.; Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K.; Davidson, T.A.; Drews, M.; Hamilton, D.P.; Jeppesen, E.; Kjellström, E.; Olesen, J.E.; et al. A framework for testing the ability of models to project climate change and its impacts. Clim. Chang. 2014, 122, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Krysanova, V.; Hattermann, F. Projections of climate change impacts on floods and droughts in Germany using an ensemble of climate change scenarios. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2015, 15, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoof, J.T.; Robeson, S.M. Projecting changes in regional temperature and precipitation extremes in the United States. Weather and climate extremes, observed and projected (longer-term). Chang. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2016, 11, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.A.; Xuan, Y. Development of a new quantile-based method for the assessment of regional water resources in a highly-regulated River Basin. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 3187–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelda, R.K.; Mukundan, R.; Owens, E.M.; Abatzoglou, J.T. A practical approach to developing climate change scenarios for water quality models. J. Hydrometeorol. 2019, 20, 1197–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Brissette, F.P.; Chaumont, D.; Braun, M. Finding appropriate bias correction methods in downscaling precipitation for hydrologic impact studies over North America. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 4187–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Potter, N.J.; Chiew FH, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, B.; Vaze, J.; Evans, J.P. How does bias correction of regional climate model precipitation affect modelled runoff? Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Andréasson, J.; Phil Graham, L.; Olsson, J.; Rosberg, J.; Wetterhall, F. Distribution-based scaling to improve usability of regional climate model projections for hydrological climate change impacts studies. Hydrol. Res. 2010, 41, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Kanae, S.; Seto, S.; Yeh, P.J.F.; Hirabayashi, Y.; Oki, T. Intercomparison of bias-correction methods for monthly temperature and precipitation simulated by multiple climate models. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D23114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enayati, M.; Bozorg-Haddad, O.; Bazrafshan, J.; Hejabi, S.; Chu, X. Bias correction capabilities of quantile mapping methods for rainfall and temperature variables. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2020, 12, 401–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bong, T.; Son, Y.-H.; Yoo, S.-H.; Hwang, S.-W. Nonparametric quantile mapping using the response surface method–Bias correction of daily precipitation. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2017, 9, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson, L.; Bremnes, J.B.; Haugen, J.E.; Engen-Skaugen, T. Technical note: Downscaling RCM precipitation to the station scale using statistical transformations–A comparison of methods. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 3383–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, K.C.; Rouholahnejad, E.; Vaghefi, S.; Srinivasan, R.; Yang, H.; Kløve, B. A continental-scale hydrology and water quality model for Europe: Calibration and uncertainty of a high-resolution large-scale SWAT model. J. Hydrol. 2015, 524, 733–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beven, K.; Binley, A. The Future of Distributed Models: Model Calibration and Uncertainty Prediction. Hydrol. Process. 1992, 6, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegegne, G.; Kim, Y.-O.; Seo, S.B.; Kim, Y. Hydrological modelling uncertainty analysis for different flow quantiles: A case study in two hydro-geographically different watersheds. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2019, 64, 473–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teweldebrhan, A.T.; Burkhart, J.F.; Schuler, T.V. Parameter uncertainty analysis for an operational hydrological model using residual-based and limits of acceptability approaches. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 5021–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellami, H.; La Jeunesse, I.; Benabdallah, S.; Vanclooster, M. Parameter and rating curve uncertainty propagation analysis of the SWAT model for two small Mediterranean catchments. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 1635–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ghoul, I.; Sellami, H.; Khlifi, S.; Vanclooster, M. Impact of land use land cover changes on flow uncertainty in Siliana watershed of northwestern Tunisia. Catena 2023, 220, 106733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.D.; Baumgartner, J.V.; Powell, J.; Braun, D.P. A spatial assessment of hydrologic alteration within a river network. Regul. Rivers Res. Manag. 1998, 14, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Yang, D.; Zhao, T.; Yang, H. Changes in the eco-flow metrics of the Upper Yangtze River from 1961 to 2008. J. Hydrol. 2012, 448–449, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellami, H.; La Jeunesse, I.; Benabdallah, S.; Baghdadi, N.; Vanclooster, M. Uncertainty analysis in model parameters regionalization: A case study involving the SWAT model in Mediterranean catchments (Southern France). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 2393–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Beguería, S.; López-Moreno, J.I. A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: The standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.P.; Guo, H.; Yu, F.X. Parameter estimation for 3-parameter log-logistic distribution (LLD3) by Pome. Stoch. Hydrol. Hydraul. 1993, 7, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilinca, C.; Anghel, C.G. Flood-Frequency Analysis for Dams in Romania. Water 2022, 14, 2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosking, J.R.M. L-moments: Analysis and Estimation of Distributions using Linear, Combinations of Order Statistics. J. R. Statist. Soc. 1990, 52, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, V.T.; Maidment, D.R.; Mays, L.W. Applied Hydrology; McGraw-Hill, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Abramowitz, M.; Stegun, I.E. (Eds.) Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs and Mathematical Tables; National Bureau of Standards: Washington, DC, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Yevjevich, V.M. An Objective Approach to Defnitions and Investigations of Continental Hydrologic Droughts; Hydrology Papers; Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1967; No. 23. [Google Scholar]
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–22 January 1993; No. 22. Volume 17, pp. 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi, F.; Lionello, P. Climate change projections for the Mediterranean region. Glob. Planet. Change 2008, 63, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate change 2007: The physical science basis. In Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment. Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Solomon, S., Qin, D., Manning, M., Chen, Z., Marquis, M., Averyt, K.B., Tignor, M., Miller, H.L., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007; p. 996. [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig, R.; Roson, R.; Zografos, C.; Kallis, G. Towards an inter-disciplinary research agenda on climate change, water and security in Southern Europe and neighboring countries. Environ. Sci. Pol. 2011, 14, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.; Laizé; CLR; Acreman, M.C.; Flörke, M. How will climate change modify river flow regimes in Europe? Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakhlaoui, H.; Seibert, J.; Hakala, K. Sensitivity of discharge projections to potential evapotranspiration estimation in northern Tunisia. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2020, 20, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoccimarro, E.; Gualdi, S.; Bellucci, A.; Zampieri, M.; Navarra, A. Heavy precipitation events over the Euro-Mediterranean region in a warmer climate: Results from CMIP5 models. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2016, 16, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piras, M.; Mascaro, G.; Deidda, R.; Vivoni, E.R. Quantification of hydrologic impacts of climate change in a Mediterranean basin in Sardinia, Italy, through high resolution simulations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 5201–5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouabdillah, A.; Ouslati, O.; De Girolamo, A.M.; Lo Porto, A. Modeling the impact of climate change in a Mediterranean catchment (Merguellil, Tunisia). Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2010, 19, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Gain, A.K.; Immerzeel, W.W.; Sperna Weiland, F.C.; Bierkens MF, P. Impact of climate change on the stream flow of the lower Brahmaputra: Trends in high and low flows based on discharge-weighted ensemble modelling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1537–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part A: Global and Sectoral Aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 485–533. [Google Scholar]
- Hattermann, F.F.; Wortmann, M.; Liersch, S.; Toumi, R.; Sparks, N.; Genillard, C.; Schröter, K.; Steinhausen, M.; Gyalai-Korpos, M.; Máté, K.; et al. Simulation of flood hazard and risk in the Danube basin with the Future Danube Model. Clim. Serv. 2018, 12, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinoni, J.; Naumann, G.; Vogt, J.V. Pan-European seasonal trends and recent changes of drought frequency and severity. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2017, 148, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagge, J.H.; Kingston, D.G.; Tallaksen, L.M.; Hannah, D.M. Observed drought indices show increasing divergence across Europe. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, S.; Sellami, H.; Mlayh, A. Climate change impact projections at the catchment scale in Tunisia using the multi-model ensemble mean approach. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Girolamo, A.M.; Barca, E.; Leone, M.; Lo Porto, A. Impact of long-term climate change on fow regime in a Mediterranean basin. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 41, 101061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovats, R.S.; Valentini, R.; Bouwer, L.M.; Georgopoulou, E.; Jacob, D.; Martin, E.; Soussana, J.F. Europe. In Climate Change 2014-Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability, Part B: Regional Aspects-Working Group II Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 2, pp. 1267–1326. [Google Scholar]
- Niang, I.; Ruppel, O.C.; Abdrabo, M.A.; Essel, A.; Lennard, C.; Padgham, J.; Urquhart, P. Africa. In Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part B: Regional Aspects; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Grillakis, M.G. Increase in severe and extreme soil moisture droughts for Europe under climate change. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, B.P.; Breshears, D.D.; Allen, C.D. Ecohydrology of a resource-conserving semiarid woodland: Effects of scale and disturbance. Ecol. Monogr. 2003, 73, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöschl, G.; Hall, J.; Viglione, A.; Perdigão, R.A.P.; Parajka, J.; Merz, B.; Lun, D.; Arheimer, B.; Aronica, G.T.; Bilibashi, A.; et al. Changing climate both increases and decreases European river floods. Nature 2019, 573, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nerantzaki, S.D.; Giannakis, G.V.; Efstathiou, D.; Nikolaidis, N.P.; Sibetheros, I.A.; Karatzas, G.P.; Zacharias, I. Modeling suspended sediment transport and assessing the impacts of climate change in a karstic Mediterranean watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, A.R.; Santos, J.A. Predicting hydrologic flows under climate change: The Tâmega Basin as an analog for the Mediterranean region. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
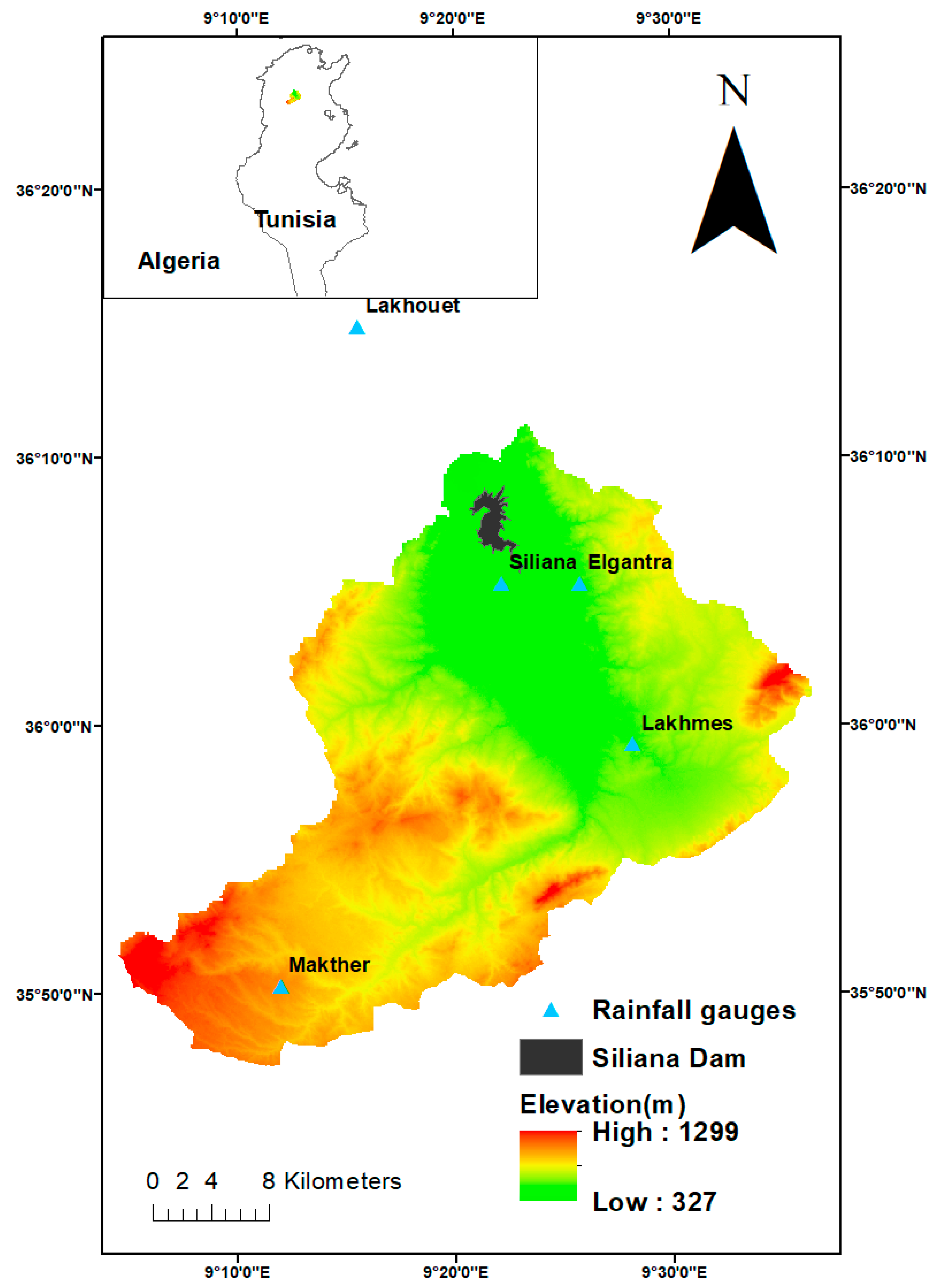

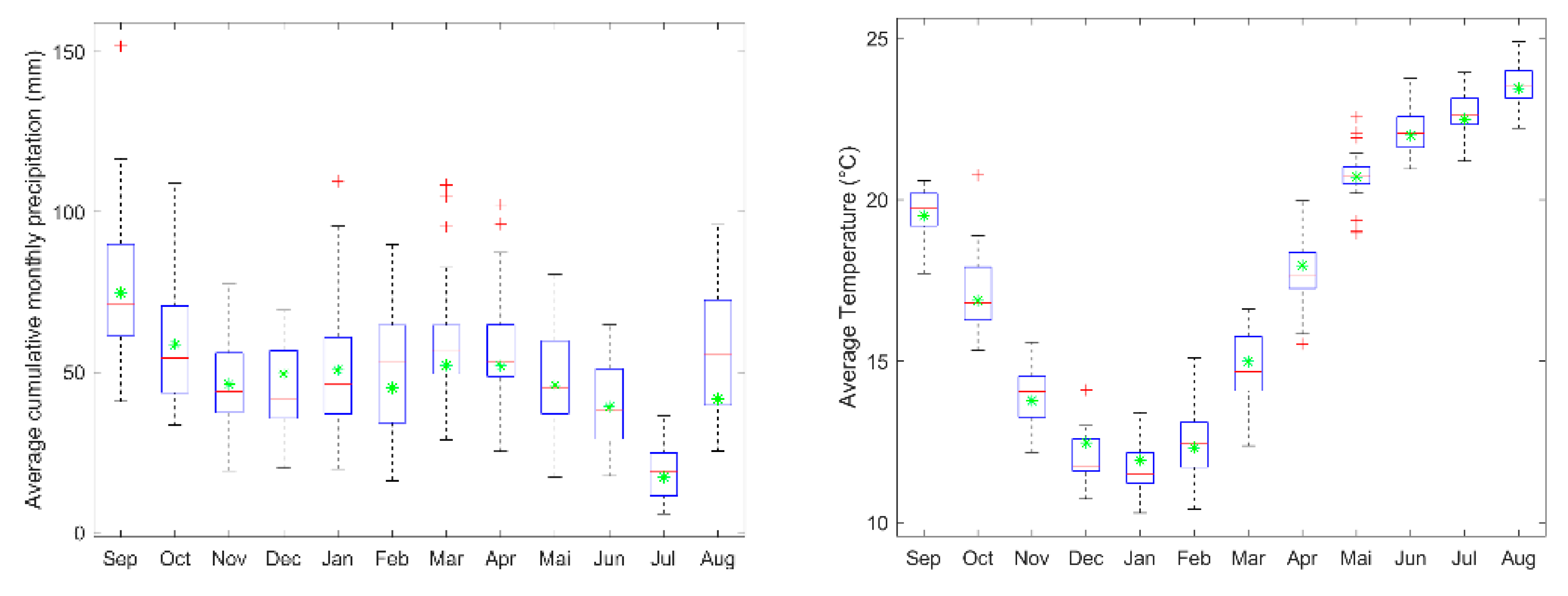
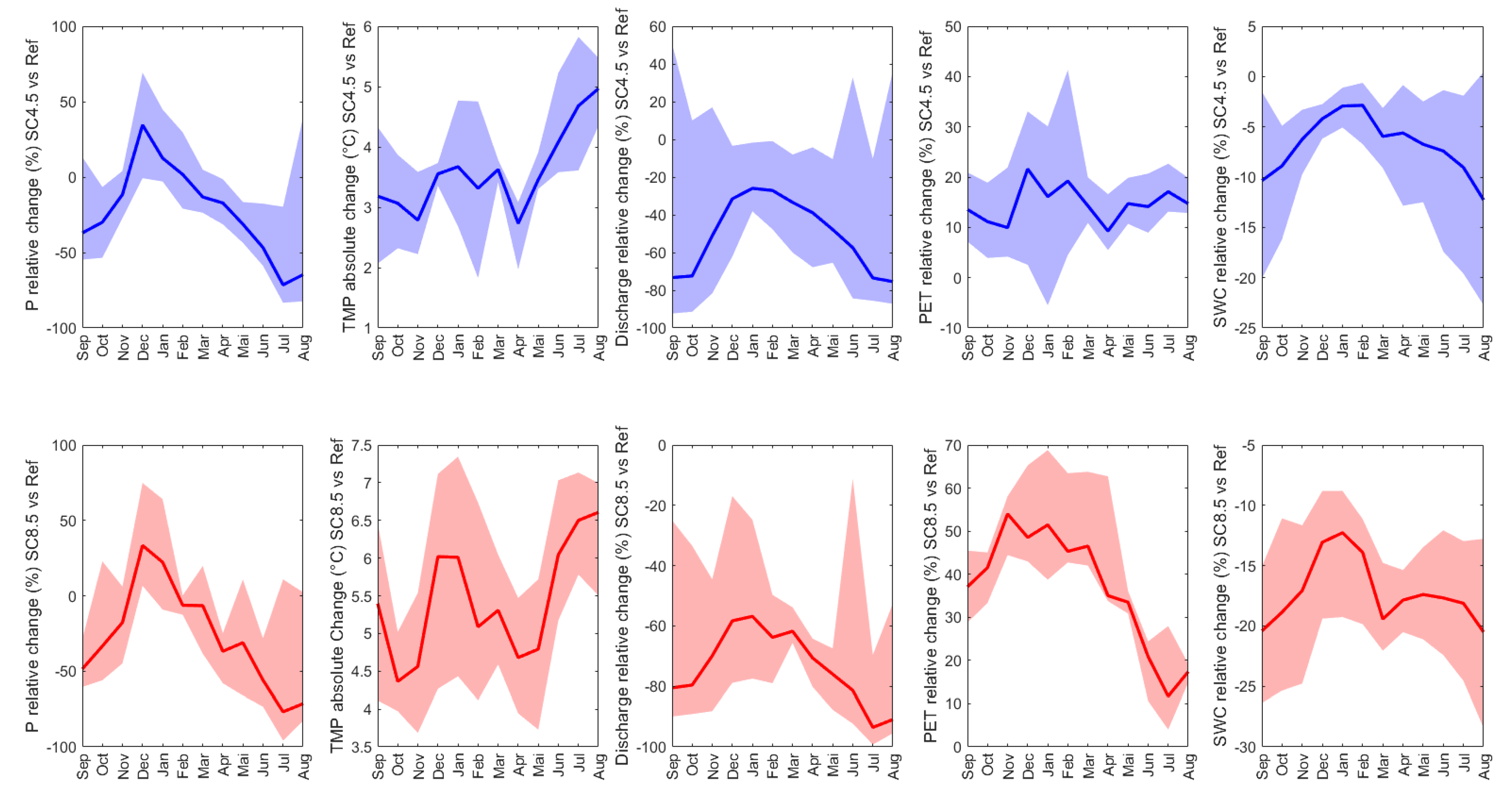

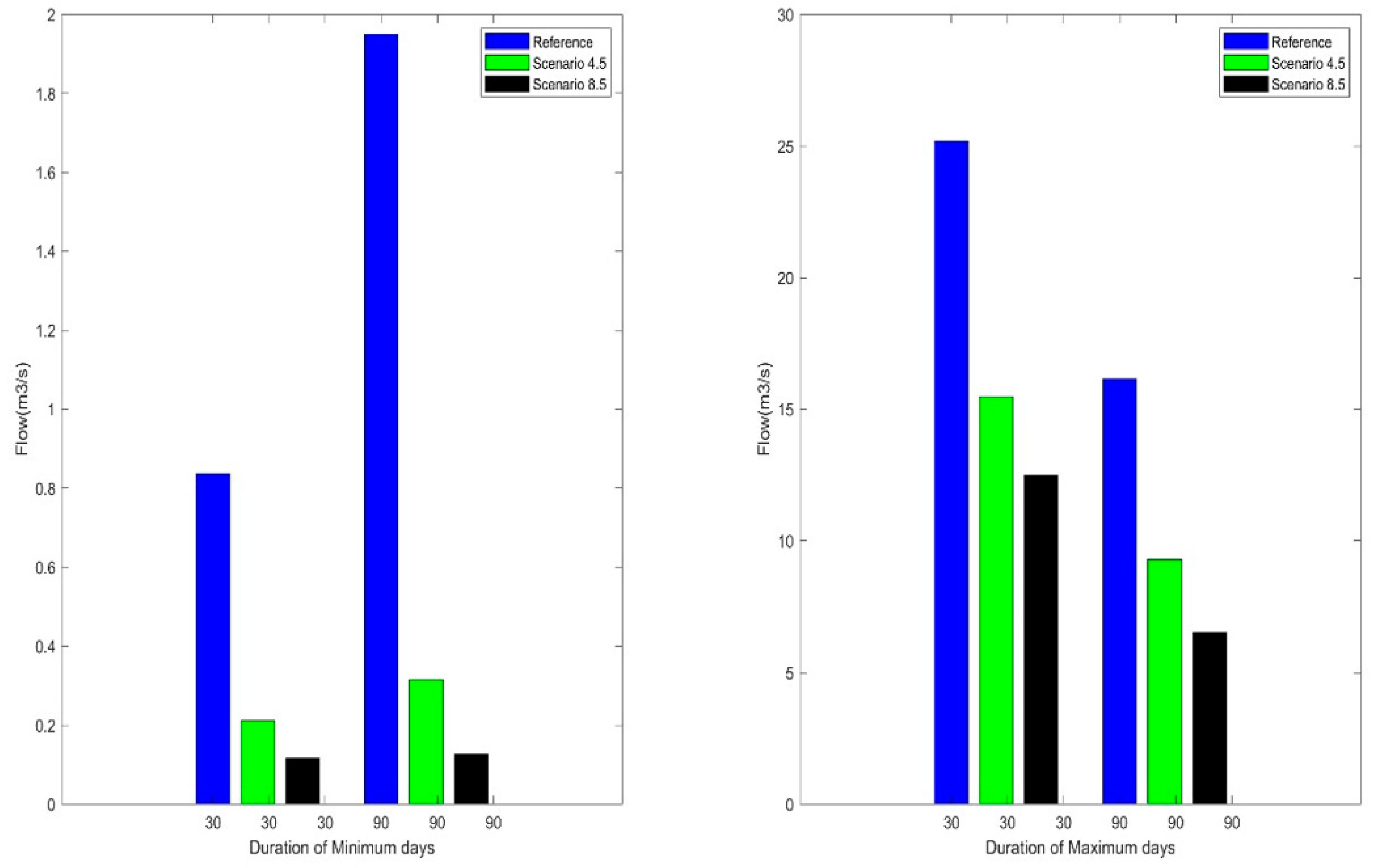
| Available Data | Resolution/Scale | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Precipitation | Daily (1979–2005) | Five stations (Lakhouet, Siliana, Makther, Elgantra, and Lakhmes). Source: General Directorate of Water Resources (Tunisia) |
| Temperature | Daily (1979–2005) | Siliana station. Source: National Meteorological Institute (Tunisia) |
| Solar radiation, wind humidity | Daily (1979–2005) | Nine climatic stations (SWAT). Source: http://swat.tamu.edu/ (accessed on 1 December 2019) |
| Digital elevation model | 30 m | Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) of USGS (http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org/) (accessed on 1 December 2019) |
| Soil map | 1.50,000 | Agricultural map |
| Land-use map | 1.5000 | Agricultural map; Land-use database (SWAT model crop database) |
| Discharge | Monthly (1987–2005) | General Directorate of Dams and Major Hydraulic Structures |
| Institute | Global Climate Model | Regional Climate Model |
|---|---|---|
| CLMcom | CNRM-CERFACS-CNRM-CM5 | CCLM4-8-17 |
| GERICS | NCC-NorESM1-M | REMO2015 |
| KNMI | ICHEC-EC-EARTH | RACMO22E |
| MPI-CSC | MPI-M-MPI-ESM-LR | REMO2009 |
| SPEI Values | |
|---|---|
| +2 | Extremely wet |
| 1.5 to 1.99 | Very wet |
| 1.0 to 1.49 | Moderately wet |
| −0.99 to 0.99 | Near normal |
| −1.0 to −1.49 | Moderately dry |
| −1.5 to −1.99 | Severely dry |
| −2 and less | Extremely dry |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Ghoul, I.; Sellami, H.; Khlifi, S.; Vanclooster, M. Assessing Spatio-Temporal Hydrological Impacts of Climate Change in the Siliana Watershed, Northwestern Tunisia. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15101209
El Ghoul I, Sellami H, Khlifi S, Vanclooster M. Assessing Spatio-Temporal Hydrological Impacts of Climate Change in the Siliana Watershed, Northwestern Tunisia. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(10):1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15101209
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Ghoul, Imen, Haykel Sellami, Slaheddine Khlifi, and Marnik Vanclooster. 2024. "Assessing Spatio-Temporal Hydrological Impacts of Climate Change in the Siliana Watershed, Northwestern Tunisia" Atmosphere 15, no. 10: 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15101209
APA StyleEl Ghoul, I., Sellami, H., Khlifi, S., & Vanclooster, M. (2024). Assessing Spatio-Temporal Hydrological Impacts of Climate Change in the Siliana Watershed, Northwestern Tunisia. Atmosphere, 15(10), 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15101209









