Detecting Relationship between the North–South Difference in Extreme Precipitation and Solar Cycle in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data and Temporal Coverage
2.2. Methods
3. Results
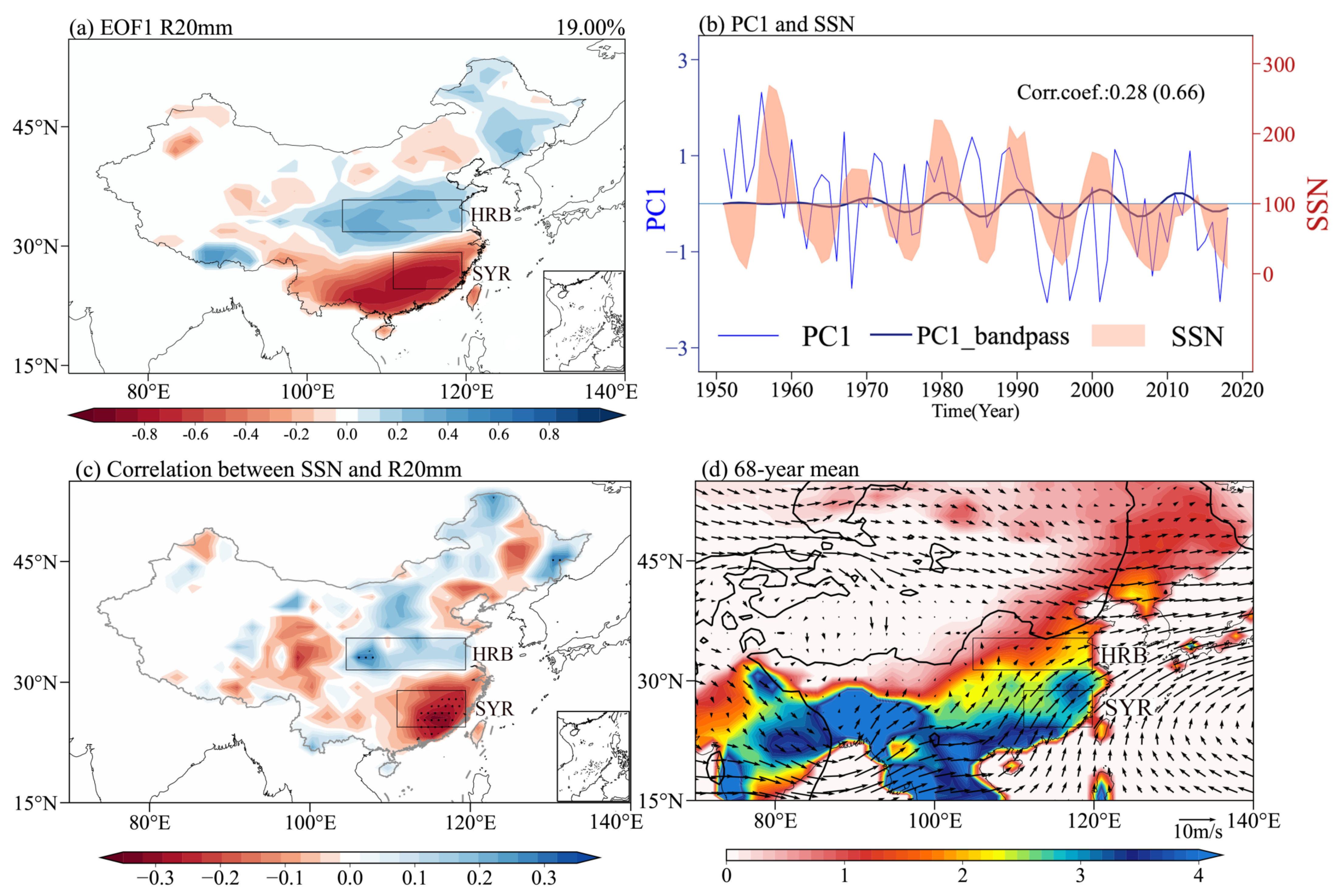
3.1. Relationship between Solar Activity and Extreme Summer Precipitation in China
3.2. Mechanism Analysis
3.3. Solar Signals in CMIP6 Simulations
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lean, J.L. Estimating solar irradiance since 850 CE. Earth Space Sci. 2018, 5, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, P.; Ren, Z.; Zong, W.; Qi, J.; Huang, C.; Xu, Y.; Lu, Y. Energy transmission processes in the effectuation chain of solar forcing to the terrestrial atmosphere—A review. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 1164636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, L.J.; Beer, J.; Geller, M.; Haigh, J.D.; Lockwood, M.; Matthes, K.; Cubasch, U.; Fleitmann, D.; Harrison, G.; Hood, L.; et al. Solar influences on climate. Rev. Geophys. 2010, 48, RG4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppälä, A.; Matthes, K.; Randall, C.; Mironova, I. What is the solar influence on climate?—Overview of activities during CAWSES-II. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2014, 1, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillett, N.P.; Shiogama, H.; Funke, B.; Hegerl, G.; Knutti, R.; Matthes, K.; Santer, B.D.; Stone, D.; Tebaldi, C. The Detection and Attribution Model Intercomparison Project (DAMIP v1.0) contribution to CMIP6. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 3685–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ineson, S.; Scaife, A.; Knight, J.; Manners, J.C.; Dunstone, N.J.; Gray, L.J.; Haigh, J.D. Solar forcing of winter climate variability in the Northern Hemisphere. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthes, K. Solar cycle and climate predictions. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 735–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodera, K.; Kuroda, Y. Dynamical response to the solar cycle. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, M. Solar change and climate: An update in the light of current exceptional solar minimum. Proc. R. Soc. A 2010, 466, 303–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolotova, N.V.; Ponyavin, D.I. Is the new Grand mini-mum in progress? J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2014, 119, 3281–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiodo, G.; Garcíaherrera, R.; Calvo, N.; Vaquero, J.M.; A Añel, J.; Barriopedro, D.; Matthes, K. The impact of a future solar minimum on climate change projections in the Northern Hemisphere. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 034015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodera, K.; Thiéblemont, R.; Yukimoto, S.; Matthes, K. How can we understand the global distribution of the solar cycle signal on the Earth’s surface? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 12925–12944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogurtsov, M. Long-Term Variability of Summer Temperature in the Southern Part of South America—Is There a Connection with Changes in Solar Activity? Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, N.D.; Svensmark, H. Cosmic Rays, Clouds, and Climate. Space Sci. Rev. 2000, 94, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usoskin, I.G.; Schuessler, M.; Solanki, S.K.; Mursula, K. Solar activity, cosmic rays, and Earth’s temperature: A millennium-scale comparison. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, A10102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veretenenko, S.; Ogurtsov, M.G. Stratospheric circumpolar vortex as a link between solar activity and circulation of the lower atmosphere. Geomagn. Aeron. 2012, 52, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfîcă, L.; Beck, C.; Nita, A.I.; Voiculescu, M.; Birsan, M.V.; Philipp, A. Cloud cover changes driven by atmospheric circulation in Europe during the last decades. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41 (Suppl. S1), 2211–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CMA Climate Change Centre. Blue Book on Climate Change in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R.H.; Xu, Y.H.; Zhou, L.T. The interdecadal variation of summer precipitations in China and the drought trend in North China. Plateau Meteor. 1999, 18, 465–476. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Herman, J.R.; Goldberg, R.A. Sun, Weather and Climate; University Press of the Pacific: Forest Grove, OR, USA, 2005; 376p. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H. Solar cycle signature in decadal variability of monsoon precipitation in China. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2012, 90, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Yan, M.; Ning, L. Decadal Variations of the East Asian Summer Monsoon Forced by the 11-Year Insolation Cycle. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 2735–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Chen, H.; Gray, L.; Zhou, L.; Li, X.; Wang, R.; Zhu, S. Changing response of the North Atlantic/European winter climate to the 11 year solar cycle. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 13, 034007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, L. Statistical tests for a correlation between decadal variation in June precipitation in China and sunspot number. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D23117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Xiao, Z. Amplification of solar signal in summer monsoon rainband in China by a synergistic action of different dynamical responses. J. Meteor. Res. 2017, 31, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barde, V.; Upadhyay, A.; Bulusu, J.; Dimri, A.P. Impact of solar variability on Indian summer monsoon through large scale circulations. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2023, 252, 1364–6826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Miller, P.A.; Zhang, Q.; Berntell, E.; Smith, B. Impacts of large-scale Sahara solar farms on global climate and vegetation cover. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL090789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghrabi, A.H.; Alamoudi, H.A.; Alruhaili, A.S. Investigation of a Possible Link between Solar Activity and Climate Change in Saudi Arabia: Rainfall Patterns. Atmos. Clim. Sci. 2023, 13, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haigh, J.D. The impact of solar variability on climate. Science 1996, 272, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haigh, J.D. The role of stratospheric ozone in modulating the solar radiative forcing of climate. Nature 1994, 370, 544–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haigh, J.D.; Blackburn, M.; Day, R. The response of tropospheric circulation to perturbations in lower-stratospheric temperature. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 3672–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindell, D.; Rind, D.; Balachandran, N.; Lean, J.; Lonergan, P. Solar cycle variability, ozone, and climate. Science 1999, 284, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hood, L.L.; Misios, S.; Mitchell, D.M.; Rozanov, E.; Gray, L.J.; Tourpali, K.; Matthes, K.; Schmidt, H.; Chiodo, G.; Thieblemont, R.; et al. Solar signals in CMIP-5 simulations: The ozone response. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 141, 2670–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, I.; Haigh, J.D. Solar cycle signals in sea level pressure and sea surface temperature. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 3147–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misios, S.; Mitchell, D.M.; Gray, L.J.; Tourpali, K.; Matthes, K.; Hood, L.; Schmidt, H.; Chiodo, G.; Thiéblemont, R.; Rozanov, E.; et al. Solar signals in CMIP-5 simulations: Effects of atmosphere-ocean coupling. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 142, 928–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meehl, G.A.; Arblaster, J.M.; Matthes, K.; Sassi, F.; van Loon, H. Amplifying the Pacific Climate System Response to a Small 11-Year Solar Cycle Forcing. Science 2009, 325, 1114–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newell, R.E.; Zhu, Y.; Browell, E.V.; Read, W.G.; Waters, J.W. Walker circulation and tropical upper tropospheric water vapor. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1996, 101, 1961–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.L.; Ishizaki, N.; Kitoh, A. Trend and interannual variability of Walker, monsoon and Hadley circulations defined by velocity potential in the upper troposphere. Tellus A 2004, 56, 250–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.L.; Ishizaki, N.; Nohara, D. Intercomparison of the intensities and trends of Hadley, Walker and monsoon circulations in the global warming projections. SOLA 2005, 1, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misios, S.; Gray, L.J.; Knudsen, M.F.; Karoff, C.; Schmidt, H.; Haigh, J.D. Slowdown of the Walker circulation at solar cycle maximum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 7186–7191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misios, S.; Kasoar, M.; Kasoar, E.; Gray, L.; Haigh, J.; Stathopoulos, S.; Kourtidis, K.; Myhre, G.; Olivié, D.; Shindell, D.; et al. Similar patterns of tropical precipitation and circulation changes under solar and greenhouse gas forcing. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 104045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, W.; Xiao, Z.; Zhao, L. Phase-Locked Impact of the 11-year solar cycle on tropical pacific decadal variability. J. Clim. 2022, 36, 421–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, R.J.H.; Donat, M.G.; Alexander, L.V. Investigating uncertainties in global gridded datasets of climate extremes. Clim. Past 2014, 10, 2171–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, R.J.H.; Alexander, L.V.; Donat, M.G.; Zhang, X.; Bador, M.; Herold, N.; Lippmann, T.; Allan, R.; Aguilar, E.; Barry, A.A.; et al. Development of an updated global land in-situ-based dataset of temperature and precipitation extremes: HadEX3 JGR-A. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2019JD032263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyring, V.; Bony, S.; Meehl, G.A.; Senior, C.A.; Stevens, B.; Stouffer, R.J.; Taylor, K.E. Overview of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) experimental design and organization. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 1937–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, D.M.; Misios, S.; Gray, L.J.; Tourpali, K.; Matthes, K.; Hood, L.; Schmidt, H.; Chiodo, G.; Thiéblemont, R.; Rozanov, E.; et al. Solar signals in CMIP-5 simulations: The stratospheric pathway. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 141, 2390–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukimoto, S.; Koshiro, T.; Kawai, H.; Oshima, N.; Yoshida, K.; Urakawa, S.; Tsujino, H.; Deushi, M.; Tanaka, T.; Hosaka, M.; et al. MRI MRI-ESM2.0 Model Output Prepared for CMIP6 DAMIP Hist-Sol; Earth System Grid Federation: Online, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, M.; Schmidt, G.A.; Nazarenko, L.; Bauer, S.E.; Ruedy, R.; Russell, G.L.; Ackerman, A.S.; Aleinov, I.; Bauer, M.; Bleck, R.; et al. GISS-E2.1: Configurations and climatology. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2020, 12, e2019MS002025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swart, N.C.; Cole, J.N.S.; Kharin, V.V.; Lazare, M.; Scinocca, J.F.; Gillett, N.P.; Anstey, J.; Arora, V.; Christian, J.R.; Jiao, Y.; et al. CCCma CanESM5 Model Output Prepared for CMIP6 DAMIP Hist-Sol; Earth System Grid Federation: Online, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiogama, H. MIROC MIROC6 Model Output Prepared for CMIP6 DAMIP Hist-CO2; Earth System Grid Federation: Online, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies (NASA/GISS). NASA-GISS GISS-E2.1G Model Output Prepared for CMIP6 DAMIP Hist-Sol; Earth System Grid Federation: Online, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies (NASA/GISS). NASA-GISS GISS-E2-2-G Model Output Prepared for CMIP6 DAMIP Hist-Sol; Earth System Grid Federation: Online, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I.T. Principal components in regression analysis. In Principal Component Analysis; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Bjornsson, H.; Venegas, S. A manual for EOF and SVD analyses of climatic data. CCGCR Rep. 1997, 97, 112–134. [Google Scholar]
- Ionita, M.; Lohmann, G.; Rimbu, N.; Scholz, P. Dominant modes of Diurnal Temperature Range variability over Europe and their relationships with large-scale atmospheric circulation and sea surface temperature anomaly patterns. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D15111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Moore, J.C. (Eds.) Chapter 6—Empirical Orthogonal Functions. In Mathematical and Physical Fundamentals of Climate Change; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 161–197. [Google Scholar]
- Grinsted, A.; Moore, J.C.; Jevrejeva, S. Application of the cross wavelet transform and wavelet coherence to geophysical time series. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2004, 11, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metropolis, N.; Rosenbluth, A.W.; Rosenbluth, M.N.; Teller, A.H.; Teller, E. Equation of State Calculations by Fast Computing Machines. J. Chem. Phys. 1953, 21, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, M.P.; Gray, L.J.; Dunkerton, T.J.; Hamilton, K.; Haynes, P.H.; Randel, W.J.; Holton, J.R.; Alexander, M.J.; Hirota, I.; Horinouchi, T.; et al. The quasi-biennial oscillation. Rev. Geophys. 2001, 39, 179–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, M.P.; Stephenson, D.B.; Thompson, D.W.; Dunkerton, T.J.; Charlton, A.J.; O’Neill, A. Stratospheric memory and skill of extended-range weather forecasts. Science 2003, 301, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bednarz, E.M.; Maycock, A.C.; Braesicke, P.; Telford, P.J.; Abraham, N.L.; Pyle, J.A. Separating the role of direct radiative heating and photolysis in modulating the atmospheric response to the amplitude of the 11-year solar cycle forcing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 9833–9846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodera, K. Solar influence on the Indian Ocean Monsoon through dynamical processes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L24209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, L.L.; Soukharev, B.E. The lower-stratospheric response to 11-Yr solar forcing: Coupling to the tropospheretd-Ocean response. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 69, 1841–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Model | Horizontal (°) | Levels | Model Top (hPa) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CanESM5 | 2.8 × 2.8 | 49 | 1 | Swart et al., 2019 [49] |
| MIROC6 | 1.4 × 1.4 | 81 | 0.004 | Shiogama et al., 2019 [50] |
| GISS-E2-1-G | 2.5 × 2.0 | 40 | 0.1 | (NASA/GISS), 2018 [51] |
| GISS-E2-2-G | 2.0 × 2.5 | 102 | 0.002 | (NASA/GISS), 2021 [52] |
| MRI-ESM2-0 | 1.1 × 1.1 | 80 | 0.01 | Yukimoto et al., 2019 [47] |
| SC Number | Cycle Years | HSY | LSY |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18 | 1944–1954 | 1953, 1954 | |
| 19 | 1954–1964 | 1956, 1957, 1958 | 1955, 1963, 1964 |
| 20 | 1964–1976 | 1967, 1968, 1969 | 1965, 1975, 1976 |
| 21 | 1976–1986 | 1978, 1979, 1980 | 1977, 1985, 1986 |
| 22 | 1986–1996 | 1988, 1989, 1990 | 1987, 1995, 1996 |
| 23 | 1996–2008 | 1999, 2000, 2001 | 1997, 2007, 2008 |
| 24 | 2008–2019 | 2013, 2014, 2015 | 2009, 2018 |
| Total years (1951–2018) | 68 | 18 | 19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Z. Detecting Relationship between the North–South Difference in Extreme Precipitation and Solar Cycle in China. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15020175
Liu J, Zhao L, Wang J, Xiao Z. Detecting Relationship between the North–South Difference in Extreme Precipitation and Solar Cycle in China. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(2):175. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15020175
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jinjuan, Liang Zhao, Jingsong Wang, and Ziniu Xiao. 2024. "Detecting Relationship between the North–South Difference in Extreme Precipitation and Solar Cycle in China" Atmosphere 15, no. 2: 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15020175
APA StyleLiu, J., Zhao, L., Wang, J., & Xiao, Z. (2024). Detecting Relationship between the North–South Difference in Extreme Precipitation and Solar Cycle in China. Atmosphere, 15(2), 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15020175







