Assessment of Fluxes and Ecological and Health Risks of Toxic Trace Elements in Atmospheric Deposition from the Baicheng-Songyuan Area, Jilin Province, Northeast China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
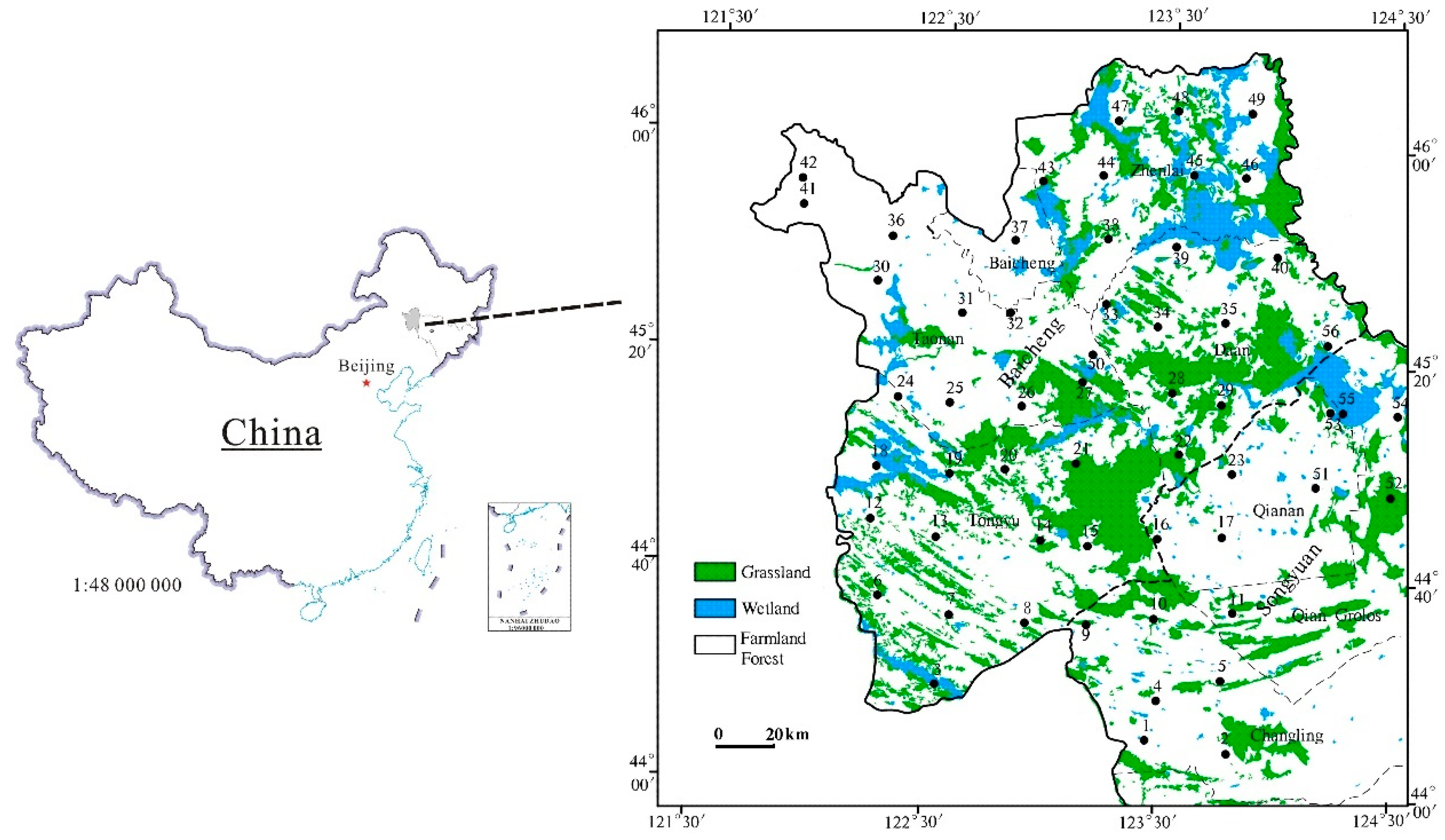
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Pretreatment
2.3. Sample Analysis and Quality Controls
2.4. Pollution and Ecological Risk Evaluation Methods
2.4.1. Geo-Accumulation Index
2.4.2. Enrichment Factor
2.4.3. Potential Ecological Risk Index
2.5. Health Risk Assessment
2.6. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Concentrations of Toxic Trace Elements in Atmospheric Deposition
3.1.1. Dry Atmospheric Deposition
3.1.2. Wet Atmospheric Deposition
3.2. Atmospheric Deposition Fluxes
3.2.1. Bulk Atmospheric Deposition Fluxes
3.2.2. Spatial Variations of Bulk Atmospheric Deposition Fluxes
3.3. Ecological Risk Assessment
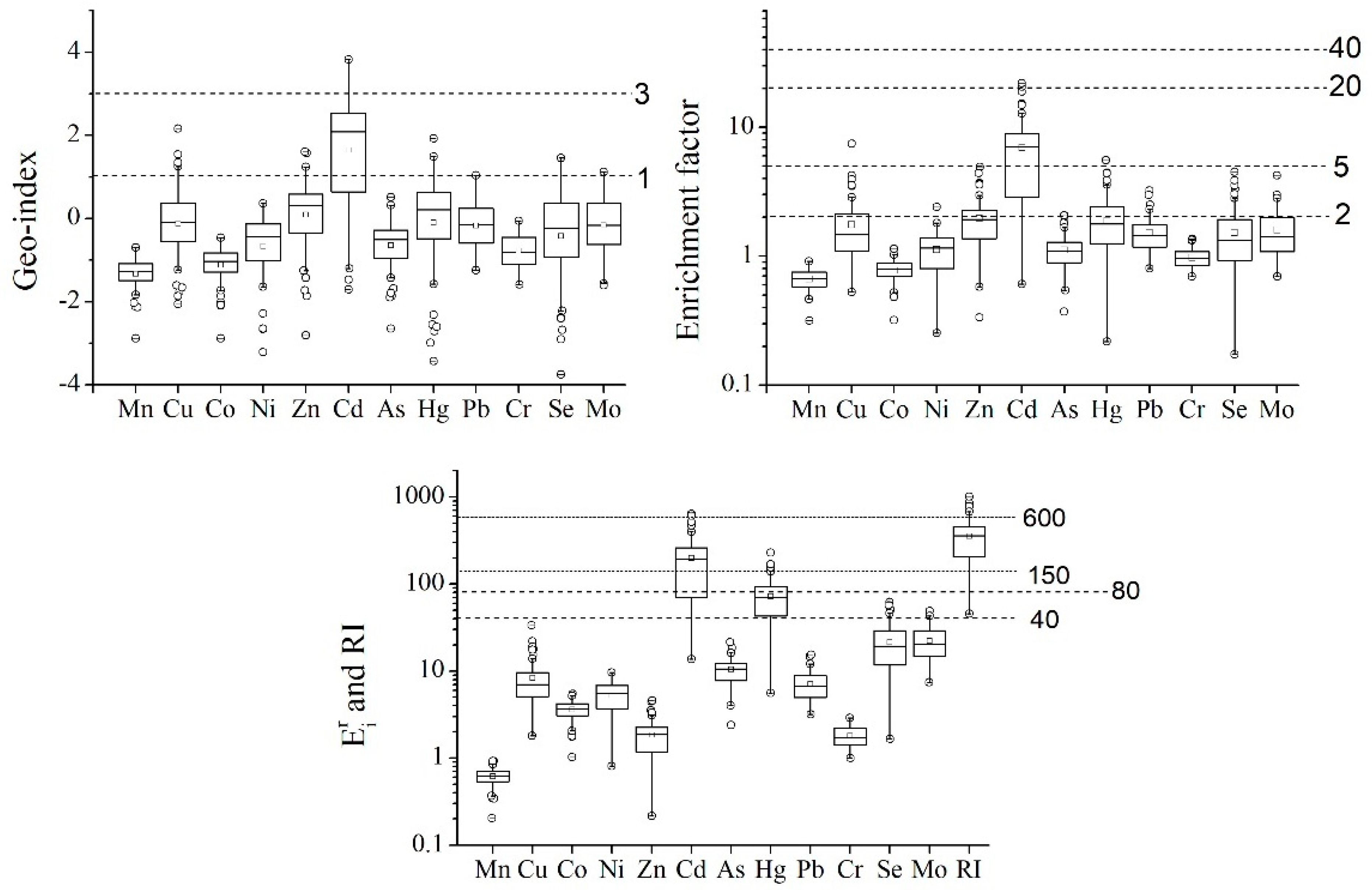
3.3.1. Evaluation with Geo-Accumulation Index
3.3.2. Evaluation with Enrichment Factor
3.3.3. Ecological Risk Evaluation
3.4. Health Risk Assessment
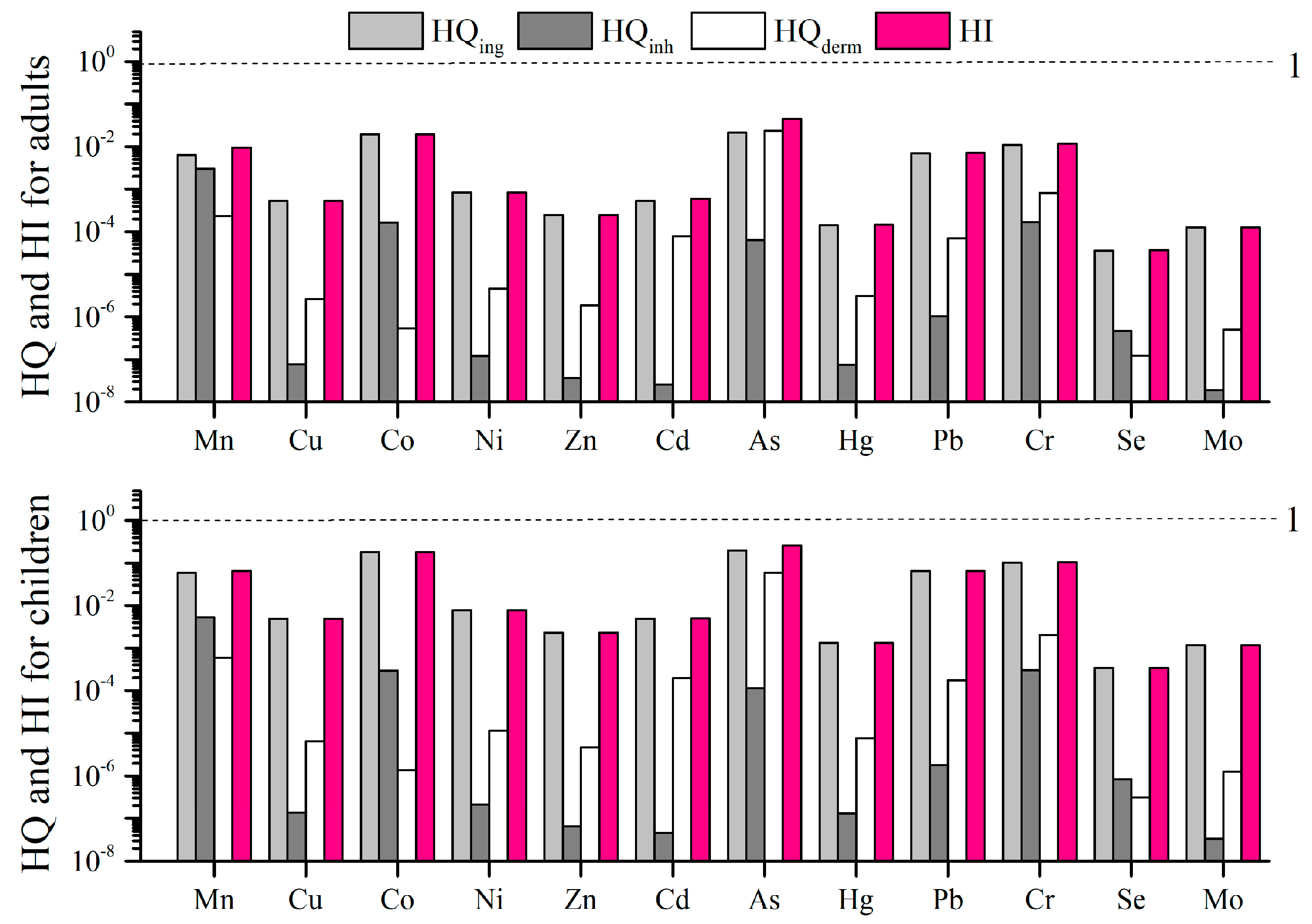
3.4.1. Non-Carcinogenic Risk Evaluation
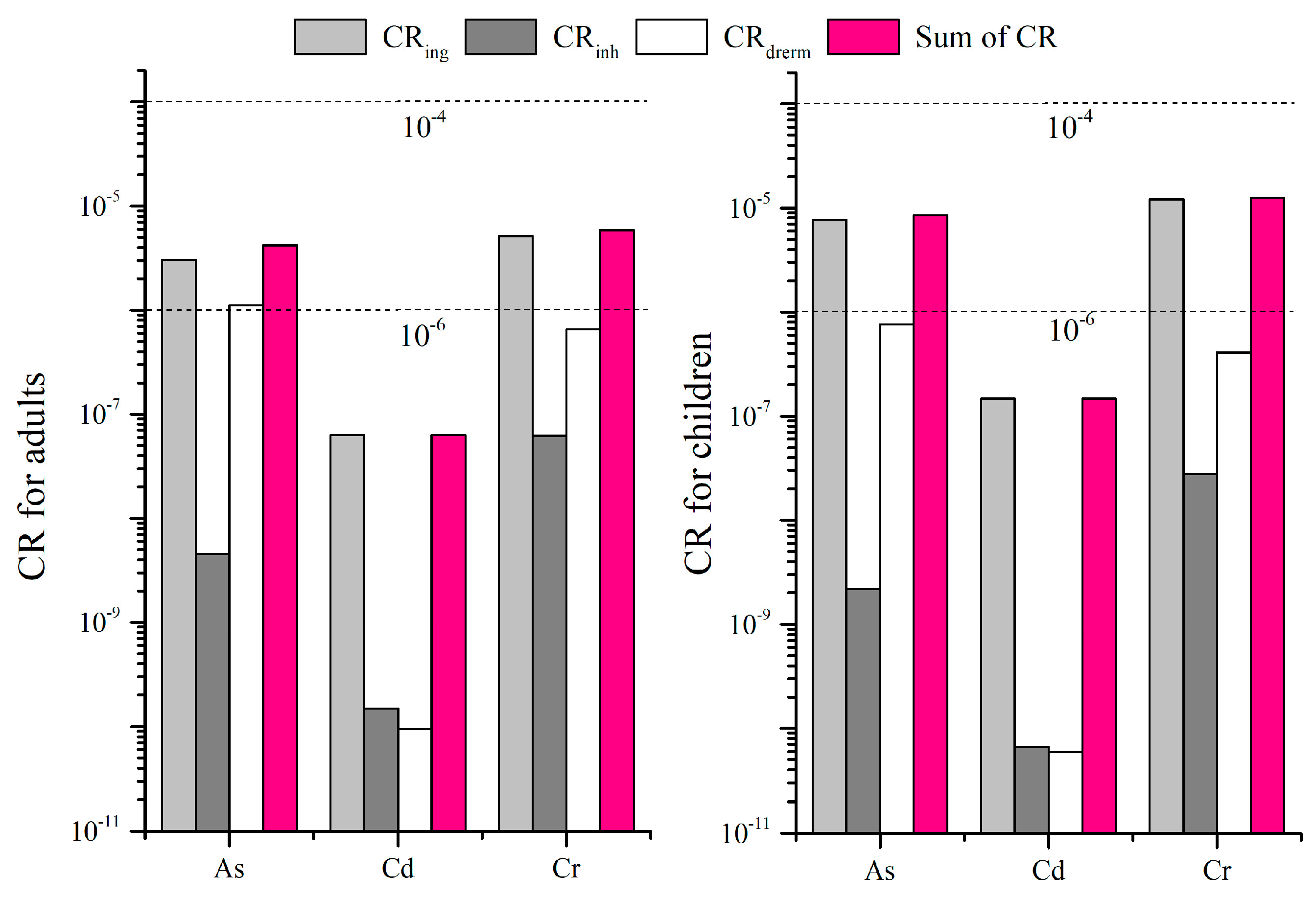
3.4.2. Carcinogenic Risk Evaluation
3.4.3. The Uncertainty of Human Risk Assessment
3.5. Source Identification of Toxic Trace Elements in Dry Fraction of Atmospheric Deposition
3.5.1. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
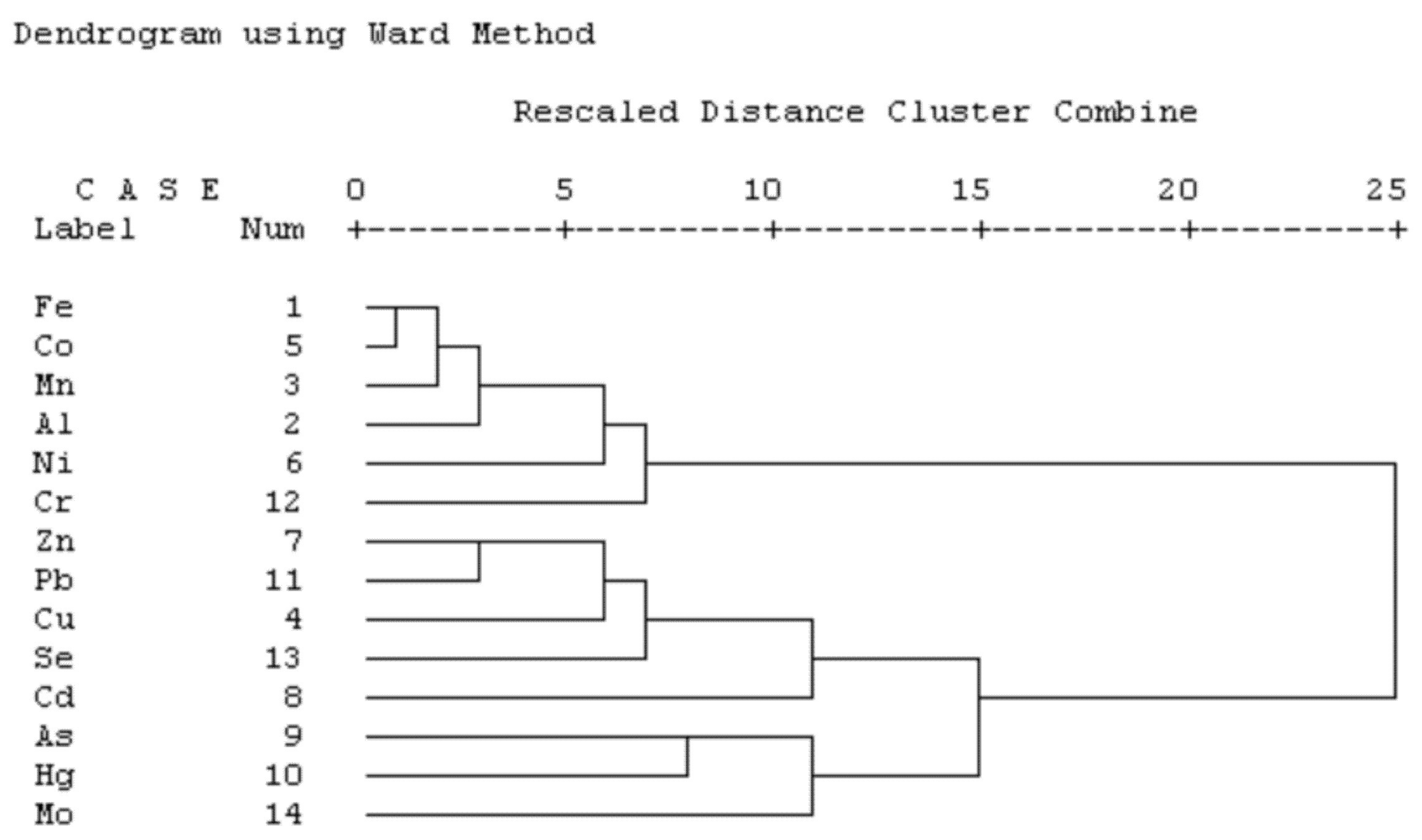
3.5.2. Cluster Analysis (CA)
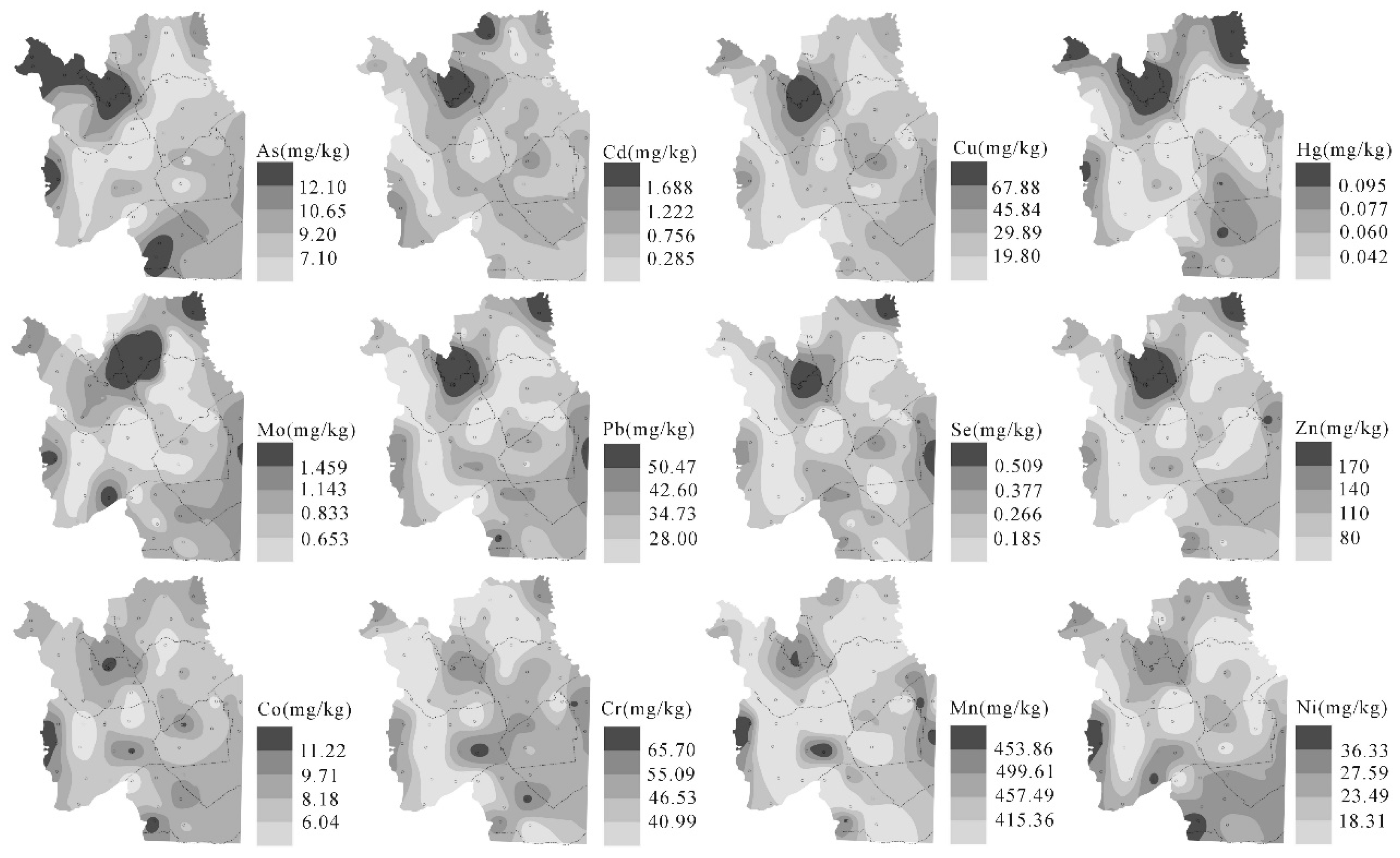
3.5.3. Spatial Distribution of Toxic Trace Elements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nriagu, J.O. A global assessment of natural sources of atmospheric trace metals. Nature 1989, 338, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.S.C.; Li, X.D.; Zhang, G.; Qi, S.H.; Peng, X.Z. Atmospheric deposition of heavy elements in the Pearl River Delta, China. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alastuey, A.; Querol, X.; Plana, F.; Viana, M.; Ruiz, C.R.; Campa, A.S.; Rosa, J.; Mantilla, E.; Santos, S.G. Identification and chemical characterization of industrial particulate matter sources in southwest Spain. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2006, 56, 993–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, F.K.; Liu, X.; Yu, T.; Cachier, H. Identification and estimate of biomass burning contribution to the urban aerosol organic carbon concentrations in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 1275–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, K.; Tainosho, Y. Characterization of heavy element particles embedded in tire dust. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogulei, D.; Hopke, P.K.; Zhou, L.; Pancras, J.P.; Nair, N.; Ondov, J.M. Source apportionment of Baltimore aerosol from combined size distribution and chemical composition data. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, S396–S410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Kitagawa, H.; Jie, D.; Hu, K.; Lim, J. Dust transport from Northeastern China inferred from carbon isotopes of atmospheric dust carbonate. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 4790–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odabasi, M.; Muezzinoglu, A.; Bozlaker, A. Ambient concentrations and dry deposition fluxes of trace elements in Izmir, Turkey. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 5841–5851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandroni, V.; Migon, C. Atmospheric deposition of metallic pollutants over the Ligurian Sea: Labile and residual inputs. Chemosphere 2003, 47, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streets, D.G.; Hao, H.J.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, J.K.; Chan, M.; Tian, H.Z.; Feng, X.B. Anthropogenic mercury emissions in China. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 7789–7806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukuda, S.; Sugiyama, M.; Harita, Y.; Nishimura, K. Atmospheric bulk deposition of soluble phosphorus in Ashiu Experimental Forest, Central Japan: Source apportionment and sample contamination problem. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.F.; Yang, Z.F.; Zhang, B.R.; Feng, H.Y.; Wang, H.G. A study of elements flux and sources from atmospheric bulk deposition in the Chengdu Economic Region. Earth Sci. Front. 2007, 14, 213–222, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cong, Y.; Chen, Y.L.; Yang, Z.F.; Hou, Q.Y.; Wang, H.C. Dry and wet atmospheric deposition fluxes of elements in the Plain area of Beijing Municipality China. Geol. Bull. China. 2008, 27, 257–264, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.S.; Tu, J.; Liu, H.Y.; Hua, M.; Liao, Q.L.; Feng, J.B.; Weng, Z.H.; Huang, G.M. Multivariate analysis of trace element concentrations in atmospheric deposition in the Yangtze River Delta, East China. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5781–5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Han, W.Z.; Li, N.; Li, Z.Y.; Bian, J.M.; Li, H.Y. Multivariate analysis of heavy metal element concentrations in atmospheric deposition in Harbin city, Northeast China. Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 2011, 31, 3087–3091, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Duan, J.C.; Tan, J.H.; Wang, S.L.; Hao, J.M.; Chai, F.H. Size distributions and sources of elements in particulate matter at curbside, urban and rural sites in Beijing. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.P.; Lu, W.X.; Long, Y.Q. Atmospheric dry and wet deposition of heavy metals in Changchun city, China. Res. Environ. Sci. 2009, 22, 28–34, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Duan, J.C.; Tan, J.H. Atmospheric heavy metals and arsenic in China: Situation, sources and control policies. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 74, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Yang, Z.F.; Jiang, W.; Yu, T.; Hou, Q.Y.; Li, D.S.; Wang, J.W. Annual input fluxes and source identification of trace elements in atmospheric deposition in Shanxi Basin, the largest coal base in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 12305–12315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Q.Q.; Huang, B.C.; Zhang, C.X.; Piper, J.D.A.; Pan, Y.P.; Sun, Y. Assessment of heavy metal contamination of dust fall in northern China from integrated chemical and magnetic investigation. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 74, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.W.; Zhang, X.L.; Li, L.Y.; Chen, H. Assessment of metals pollution and health risk in dust from nursery schools in Xi’an, China. Environ. Res. 2014, 128, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuduwailil, J.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, F. Evaluation of the pollution and human health risks posed by heavy metals in the atmospheric dust in Ebinur Basin in Northwest China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 14018–14031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Lu, X.; Qinggeletu; Wu, Y. Health risks and contamination levels of heavy metals in dusts from parks and squares of an industrial city in semi-arid area of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobhanardakani, A. Human health risk assessment of potentially toxic heavy metals in the atmospheric dust of city of Hamedan, west of Iran. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 28086–28093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerasundara, A.; Magana-Arachchi, D.N.; Ziyath, A.M.; Goonetilleke, A.; Vithanage, M. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in atmospheric deposition in a congested city environment in a developing country: Kandy City, Sri Lanka. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 220, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahloul, M. Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in dry atmospheric deposits from Sfax solar saltern area in southeast of Tunisia. J. Environ. Health Sci. 2019, 17, 1085–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, K.; Li, C.; Na, S.Y. Spatial distribution, pollution source, and health risk assessment of heavy metals in atmospheric depositions: A case study from the sustainable city of Shijiazhuang, China. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, A.; Taghavi, M.; Moslem, A.; Neshat, A.A.; LariNajafi, M.; Alahabadi, A.; Ahmadi, E.; Ebrahimi, A.H.; Asour, A.A.; Rezaei, H.; et al. Ecological and health risk assessment of exposure to atmospheric heavy metals. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2019, 184, 109622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobhanardakani, S. Ecological and human health risk assessment of heavy metal content of atmospheric dry deposition, a case study: Kermanshah, Iran. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 187, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.H.; Zhang, D.G.; Wang, Y.T. Characteristics of heavy metals in size-fractionated atmospheric particulate matters and associated health risk assessment based on the respiratory deposition. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjovvi, A.; Soleimani, M.; Mirghaffari, N.; Karimzadeh, H.; Yuan, Y.Z.; Fang, L.P. Monitoring, source identification and environmental risk of potentially toxic elements of dust in Isfahan Province, Central Iran. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 108, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhao, C.S.; Chen, Q.F.; Li, L.Z.; Si, G.R.; Li, L.; Guo, B.B. Characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in atmospheric particulate matter in different regions of the Yellow River Delta in China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 2013–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Human health evaluation manual. In Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund; EPA/540/1e89/002; Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; Volume l. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund: Volume III-Part A, Process for Conducting Probabilistic Risk Assessment; EPA540-R-02-002; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Child Specific Exposure Factors Handbook; EPA-600-P-00-002B; National Center for Environmental Assessment: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Kitagawa, H.; Hu, K.; Jie, D.M.; Yang, J.P.; Lim, J. Element and mineral characterization of dust emission from the saline land at Songnen Plain, Northeastern China. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.J.; Fu, C.B.; Han, Z.W.; Zhu, C.S. Characteristics of elemental composition of PM 2. 5 in the spring period at Tongyu in the semi-arid region of Northeast China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 25, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Shen, Z.X.; Cao, J.J.; Ho, K.F.; Zhang, R.J.; Bie, Z.J.; Chang, H.R.; Liu, S.X. Chemical profiles of urban fugitive dust over Xi’an in the south margin of the Loess Plateau, China. Atmos. Pollu. Res. 2014, 5, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Hong, M.; Zhao, Y.S.; Lin, X.Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Dong, J. Distribution and risk assessment of fluoride in drinking water in the west plain region of Jilin province, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2003, 25, 421–431. [Google Scholar]
- China Geological Survey. Specification of Regional Eco-Geochemical Assessment (DD2005-02); China Geological Survey: Beijing, China, 2005. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.W.; Chai, S.L.; Cai, J.; Gao, L.N. Baseline concentrations of trace metals in grassland topsoils from West Jilin province, Northeast China. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 347–353, 2140–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, A. Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environ. Geol. 2002, 39, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza-Figueroa, D.; DelaO-Villanueva, M.; DelaParra, M.L. Toxic trace element distribution in dust from elementary schools in Hermosillo, Sonora, México. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control-a sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.Q.; Ni, S.J.; Tuo, X.G. Calculation of heavy metals toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 31, 112–115. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.X.; Cao, H.Y.; Deng, Y.Y.; Zhang, Q. Distribution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in atmospheric particulate matter and dust. Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 3575–3584. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, N.; Liu, J.S.; Wang, Q.C.; Liang, Z.Z. Health risk assessment of heavy metal exposure to street dust in the zinc smelting district, Northeast of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.M.; Lu, X.W.; Chen, H.; Gao, P.P.; Fu, Y. Multi-element characterization and source identification of trace metal in road dust from an industrial city in semi-humid area of Northwest China. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2015, 303, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, S.Q.; Chen, X.M.; Lin, C.Y. Estimates of the exposed dermal surface area of Chinese in view of human health risk assessment. J. Saf. Environ. 2008, 8, 152–156. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Exposure Factors Handbook; EPA/600/R-09/052F; National Center for Environmental Assessment: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kamunda, C.; Mathuthu, M.; Madhuku, M. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils from Witwatersrand gold mining basin, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.Q.; Yang, Z.F.; Cui, Y.J.; Li, Y.S.; Hou, Q.Y.; Yu, T. Soil heavy metal concentrations and their typical input and output fluxes on the southern Songnen Plain Heilongjiang Province China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 139, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Seip, H.M.; Wibetoe, G.; Nori, S.; Mcleod, C.W. Heavy coal combustion as the dominant source of particulate pollution in Taiyuan, China, corroborated by high concentrations of arsenic and selenium in PM10. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 370, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.Z.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Z.G.; Cheng, K.; Qu, P.Y.; Chai, F.H.; Hao, J.M. Trend and characteristics of atmospheric emissions of Hg, As, and Se from coal combustion in China, 1980–2007. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 11905–11919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.F.; Masunaga, S.; Masunaga, S. Assessment of the sources of suspended particulate matter aerosol using US EPA PMF 3.0. Environ. Monitor. Assess. 2012, 184, 1063–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Cheng, H.G.; Zhou, T.; Lin, C.Y.; Guo, S. The estimated atmospheric lead emissions in China, 1990–2009. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Cheng, H.G.; Li, Q.; Lin, C.Y. Anthropogenic atmospheric emissions of cadmium in China. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjortenkrans, D.S.T.; Bergback, B.G.; Haggerud, A.V. Metal emissions from brake linings and tires: Case studies of Stockholm, Sweden 1995/1998 and 2005. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 41, 5224–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.L.; Gao, Y. Characterization of trace elements in PM2. 5 aerosols in the vicinity of highways in northeast New Jersey in the U.S. east coast. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2011, 2, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Guo, J.; Chai, S.L.; Cai, J.; Xue, L.; Zhang, Q.W. Source identification of eight heavy metals in grassland soils by multivariate analysis from the Baicheng-Songyuan area, Jilin Province, Northeast China. Chemosphere 2015, 134, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Exposure Parameter | Description | Value | Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adults | Children | |||
| C | Concentration of metals in dry atmospheric deposition | mg/Kg | ||
| IngR | Ingestion rate | 100 | 200 | mg/day |
| EF | Exposure frequency | 180 | 180 | days/year |
| ED | Exposure duration | 24 | 6 | year |
| BW | Body weight | 70 | 15 | Kg |
| AT | Average time for non-carcinogenic effect | ED × 350 | ED × 350 | days |
| Average time for carcinogenic effect | 70 × 350 | 70 × 350 | days | |
| InhR | Inhalation rate | 20 | 7.63 | m3/day |
| PEF | Particular emission factor | 1.36 × 109 | 1.36 × 109 | m3/Kg |
| SA | Exposed skin surface area | 2140 | 1150 | cm2 |
| SL | Skin adherence factor | 0.07 | 0.07 | mg/cm2/day |
| ABF | Dermal absorption factor | 0.001 | 0.001 | unitless |
| CF | conversion factor | 1.00 × 10−6 | 1.00 × 10−6 | Kg/mg |
| Toxic Trace Elements | RfDing (mg/kg·d) | RfDinh (mg/kg·d) | RfDderm (mg/kg·d) | CFing (mg/kg·d)−1 | CFinh (mg/kg·d)−1 | CFderm (mg/kg·d)−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | 3.00 × 10−4 | 1.50 × 10−5 | 3.00 × 10−3 | 1.5 | 15.1 | 1.5 |
| Cd | 1.00 × 10−3 | 1.00 × 10−3 | 1.00 × 10−5 | 0.38 | 6.1 | 0.38 |
| Co | 3.00 × 10−4 | 5.11 × 10−5 | 1.66 × 10−2 | |||
| Cr | 3.00 × 10−3 | 2.86 × 10−5 | 6.00 × 10−5 | 0.5 | 41 | 42 |
| Cu | 4.00 × 10−2 | 4.02 × 10−2 | 1.20 × 10−2 | |||
| Hg | 3.00 × 10−4 | 8.57 × 10−5 | 2.10 × 10−5 | |||
| Mn | 4.60 × 10−2 | 1.43 × 10−5 | 1.84 × 10−3 | |||
| Mo | 5.00 × 10−3 | 4.95 × 10−3 | 1.90 ×10−3 | |||
| Ni | 2.00 × 10−2 | 2.04 × 10−2 | 5.40 × 10−3 | |||
| Pb | 3.50 × 10−3 | 3.52 × 10−3 | 5.25 ×10−4 | |||
| Se | 5.00 × 10−3 | 5.70 × 10−5 | 2.20 × 10−3 | |||
| Zn | 3.00 × 10−1 | 3.00 × 10−1 | 6.00 × 10−2 |
| Heavy Metals | Dry Deposition | Heavy Metals | Wet Deposition | Soil (mg/kg) [46] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Standard Derivation | Variation Coefficient | Mean | Standard Derivation | Variation Coefficient | |||
| As (mg/kg) | 9.17 | 3.36 | 0.37 | As (μg/L) | 39.94 | 15.84 | 0.40 | 8.82 |
| Cd (mg/kg) | 0.75 | 0.55 | 0.73 | Cd (μg/L) | 1.10 | 4.83 | 4.40 | 0.113 |
| Co (mg/kg) | 8.18 | 2.26 | 0.28 | Co (μg/L) | 3.51 | 2.81 | 0.80 | 11.3 |
| Cr (mg/kg) | 46.53 | 11.73 | 0.25 | Cr (μg/L) | 16.48 | 10.75 | 0.65 | 51.39 |
| Cu (mg/kg) | 29.89 | 20.26 | 0.68 | Cu (μg/L) | 14.01 | 6.53 | 0.47 | 17.97 |
| Hg (mg/kg) | 0.061 | 0.038 | 0.62 | Hg (μg/L) | 0.041 | 0.012 | 0.28 | 0.034 |
| Mn (mg/kg) | 415.36 | 102.58 | 0.25 | Mn (μg/L) | 495.02 | 333.08 | 0.67 | 674 |
| Mo (mg/kg) | 0.91 | 0.40 | 0.44 | Mo (μg/L) | 2.49 | 1.42 | 0.57 | 0.61 |
| Ni (mg/kg) | 23.49 | 9.36 | 0.40 | Ni (μg/L) | 15.86 | 10.73 | 0.68 | 22.3 |
| Pb (mg/kg) | 34.73 | 13.10 | 0.38 | Pb (μg/L) | 34.32 | 71.95 | 2.10 | 24.42 |
| Se (mg/kg) | 0.26 | 0.16 | 0.64 | Se (μg/L) | 1.15 | 0.63 | 0.55 | 0.18 |
| Zn (mg/kg) | 105.69 | 52.36 | 0.50 | Zn (μg/L) | 318.75 | 309.85 | 0.97 | 57.22 |
| Al (%) | 6.23 | 0.75 | 0.12 | Al (mg/L) | 14500 | 20465 | 1.41 | 6.79 |
| Fe (%) | 2.22 | 0.73 | 0.33 | Fe (mg/L) | 0.33 | 0.47 | 1.43 | 2.71 |
| Toxic Trace Elements | This Study | Changchun [17] | Southern Songnen [53] | Beijing [13] | Shanxi Basin [19] | Chengdou [12] | Pear River Delta [14] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wet Flux | Dry Flux | Bulk Flux | |||||||
| As | 1.63 | 4.28 | 5.92 | 4.79 | 4.61 | 2.9 | 3.78 | 2.77 | NA |
| Cd | 0.044 | 0.237 | 0.281 | 0.25 | 0.36 | 0.24 | 0.38 | 1.77 | 0.07 |
| Co | 0.15 | 3.99 | 4.14 | NA | NA | NA | 2.31 | NA | 0.19 |
| Cr | 0.67 | 25.29 | 25.96 | 10.67 | 20.33 | 11.86 | 13.4 | NA | 6.43 |
| Cu | 0.58 | 10.85 | 11.43 | 8.22 | 16.93 | 14.19 | 12.2 | NA | 18.6 |
| Hg | 0.002 | 0.018 | 0.020 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.1 | NA |
| Mn | 20.08 | 217.33 | 237.41 | NA | NA | 111.16 | 115 | 64.96 | 8.98 |
| Mo | 0.67 | 9.31 | 9.98 | NA | NA | 0.66 | 0.47 | 0.92 | NA |
| Ni | 1.38 | 16.72 | 18.10 | NA | NA | 6.6 | NA | NA | 8.35 |
| Pb | 0.047 | 0.108 | 0.155 | 12.31 | 19.18 | 21.99 | 25.3 | 45.95 | 12.7 |
| Se | 13.14 | 41.71 | 54.85 | NA | NA | NA | 0.85 | NA | NA |
| Zn | 1.63 | 4.28 | 5.92 | 48.15 | 96.52 | 54.49 | 72.4 | 147.83 | 104 |
| Toxic Trace Elements | Non-Carcinogenic Risk | Carcinogenic Risk | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HQing | HQinh | HQderm | HI | CRing | CRinh | CRderm | TCR | |
| Adults | ||||||||
| As | 2.15 × 10−2 | 6.33 × 10−5 | 2.36 × 10−2 | 4.52 × 10−2 | 3.06 × 10−6 | 4.53 × 10−9 | 1.12 × 10−6 | 4.18 × 10−6 |
| Cd | 5.26 × 10−4 | 2.58 × 10−8 | 7.88 × 10−5 | 6.05 × 10−4 | 6.31 × 10−8 | 1.49 × 10−10 | 9.46 × 10−11 | 6.34 × 10−8 |
| Co | 1.92 × 10−2 | 1.66 × 10−4 | 5.40 × 10−7 | 1.94 × 10−2 | ||||
| Cr | 1.09 × 10−2 | 1.69 × 10−4 | 8.18 × 10−4 | 1.19 × 10−2 | 5.17 × 10−6 | 6.24 × 10−8 | 6.51 × 10−7 | 5.89 × 10−5 |
| Cu | 5.26 × 10−4 | 7.70 × 10−8 | 2.63 × 10−6 | 5.29 × 10−4 | ||||
| Hg | 1.43 × 10−4 | 7.37 × 10−8 | 3.07 × 10−6 | 1.46 × 10−4 | ||||
| Mn | 6.36 × 10−3 | 3.01 × 10−3 | 2.38 × 10−4 | 9.61 × 10−3 | ||||
| Mo | 1.28 × 10−4 | 1.90 × 10−8 | 5.03 × 10−7 | 1.28 × 10−4 | ||||
| Ni | 8.27 × 10−4 | 1.19 × 10−7 | 4.59 × 10−6 | 8.32 × 10−4 | ||||
| Pb | 6.99 × 10−3 | 1.02 × 10−6 | 6.98 × 10−5 | 7.06 × 10−3 | ||||
| Se | 3.63 × 10−5 | 4.68 × 10−7 | 1.23 × 10−7 | 3.68 × 10−5 | ||||
| Zn | 2.48 × 10−4 | 3.65 × 10−8 | 1.86 × 10−6 | 2.50 × 10−4 | ||||
| Children | ||||||||
| As | 2.01 × 10−1 | 1.13 × 10−4 | 5.92 × 10−2 | 2.60 × 10−1 | 7.75 × 10−6 | 2.19 × 10−9 | 7.61 × 10−7 | 8.51 × 10−6 |
| Cd | 4.91 × 10−3 | 4.59 × 10−8 | 1.98 × 10−4 | 5.11 × 10−3 | 1.47 × 10−7 | 6.63 × 10−11 | 5.93 × 10−11 | 1.47 × 10−7 |
| Co | 1.79 × 10−1 | 2.95 × 10−4 | 1.35 × 10−6 | 1.80 × 10−1 | ||||
| Cr | 1.02 × 10−1 | 3.00 × 10−4 | 2.05 × 10−3 | 1.04 × 10−1 | 1.21 × 10−5 | 2.78 × 10−8 | 4.08 × 10−7 | 1.21 × 10−5 |
| Cu | 4.91 × 10−3 | 1.37 × 10−7 | 6.59 × 10−6 | 4.92 × 10−3 | ||||
| Hg | 1.34 × 10−3 | 1.31 × 10−7 | 7.69 × 10−6 | 1.34 × 10−3 | ||||
| Mn | 5.94 × 10−2 | 5.36 × 10−3 | 5.97 × 10−4 | 6.53 × 10−2 | ||||
| Mo | 1.19 × 10−3 | 3.37 × 10−8 | 1.26 × 10−6 | 1.19 × 10−3 | ||||
| Ni | 7.72 × 10−3 | 2.12 × 10−7 | 1.15 × 10−5 | 7.73 × 10−3 | ||||
| Pb | 6.52 × 10−2 | 1.82 × 10−6 | 1.75 × 10−4 | 6.54 × 10−2 | ||||
| Se | 3.38 × 10−4 | 8.33 × 10−7 | 3.10 × 10−7 | 3.40 × 10−4 | ||||
| Zn | 2.32 × 10−3 | 6.50 × 10−8 | 4.66 × 10−6 | 2.32 × 10−3 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Gao, W.; Chai, S. Assessment of Fluxes and Ecological and Health Risks of Toxic Trace Elements in Atmospheric Deposition from the Baicheng-Songyuan Area, Jilin Province, Northeast China. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070744
Liu Y, Gao W, Chai S. Assessment of Fluxes and Ecological and Health Risks of Toxic Trace Elements in Atmospheric Deposition from the Baicheng-Songyuan Area, Jilin Province, Northeast China. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(7):744. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070744
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yinghong, Wen Gao, and Sheli Chai. 2024. "Assessment of Fluxes and Ecological and Health Risks of Toxic Trace Elements in Atmospheric Deposition from the Baicheng-Songyuan Area, Jilin Province, Northeast China" Atmosphere 15, no. 7: 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070744
APA StyleLiu, Y., Gao, W., & Chai, S. (2024). Assessment of Fluxes and Ecological and Health Risks of Toxic Trace Elements in Atmospheric Deposition from the Baicheng-Songyuan Area, Jilin Province, Northeast China. Atmosphere, 15(7), 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070744







