Analysis of the Causes of an O3 Pollution Event in Suqian on 18–21 June 2020 Based on the WRF-CMAQ Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Model Configuration
2.2. Data Source
2.3. The Integrated Process Rate Analysis
2.4. Scenario Setting
3. Results and Discussion
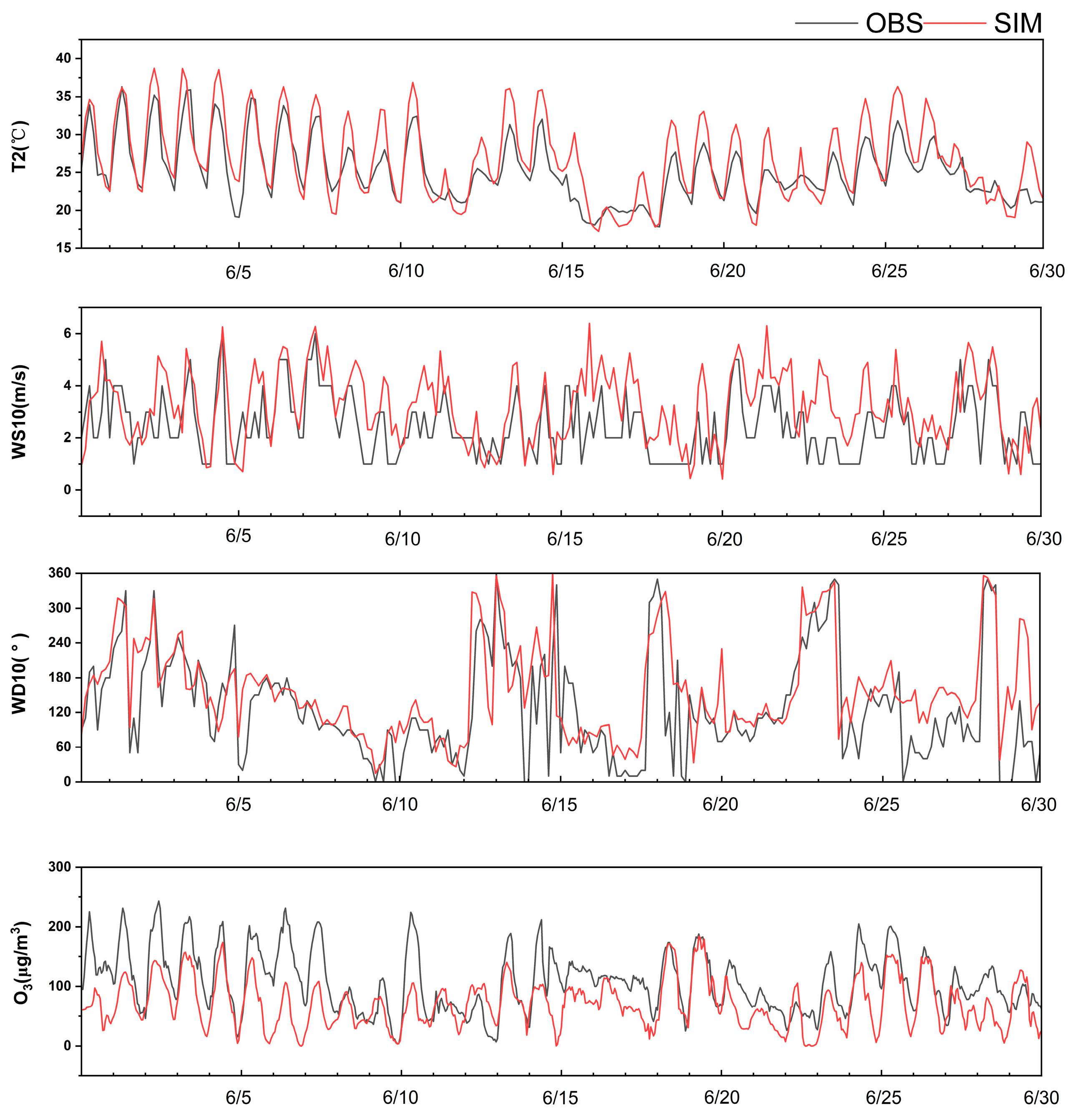
3.1. Evaluation of the Model Performances
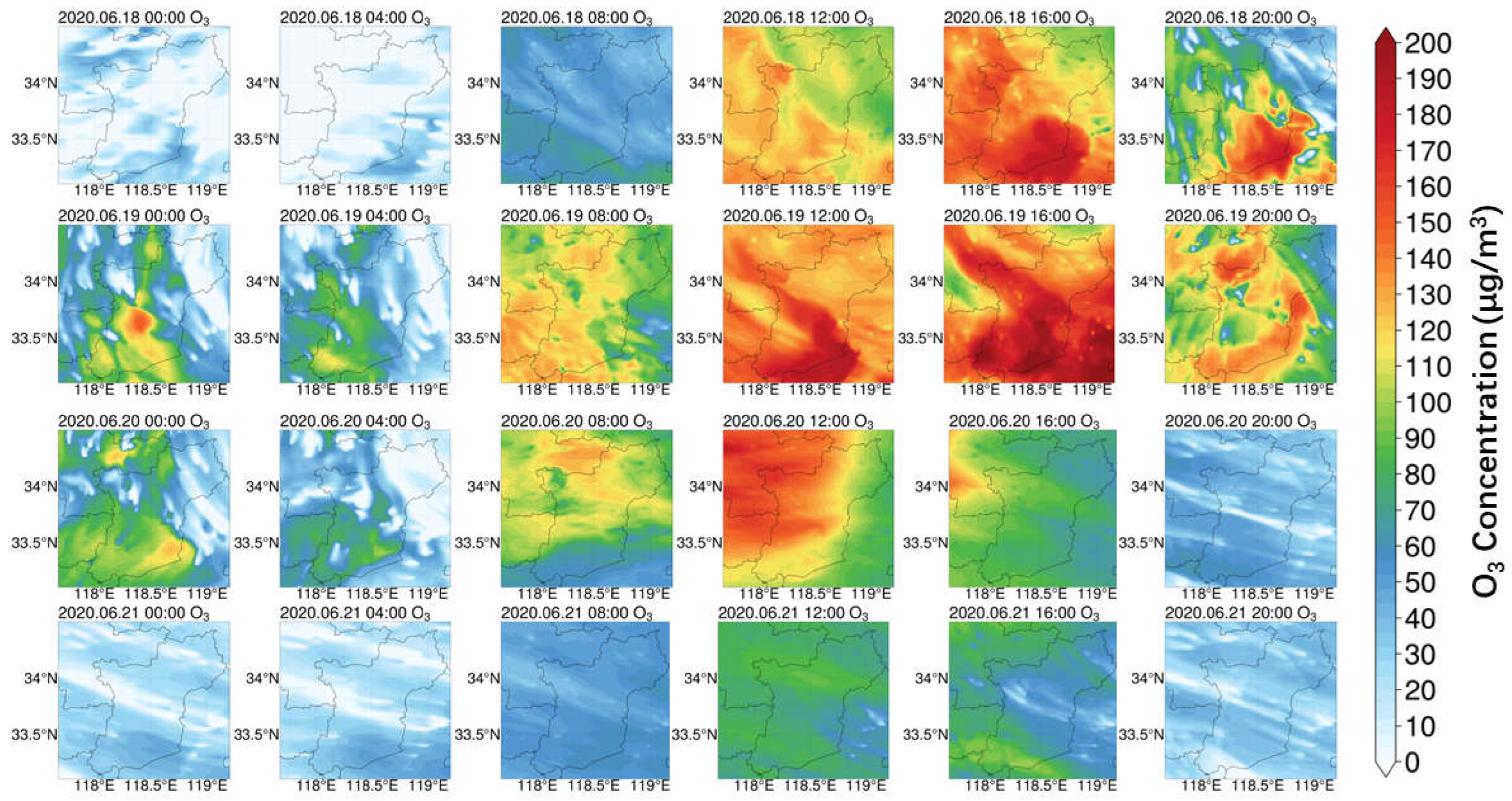
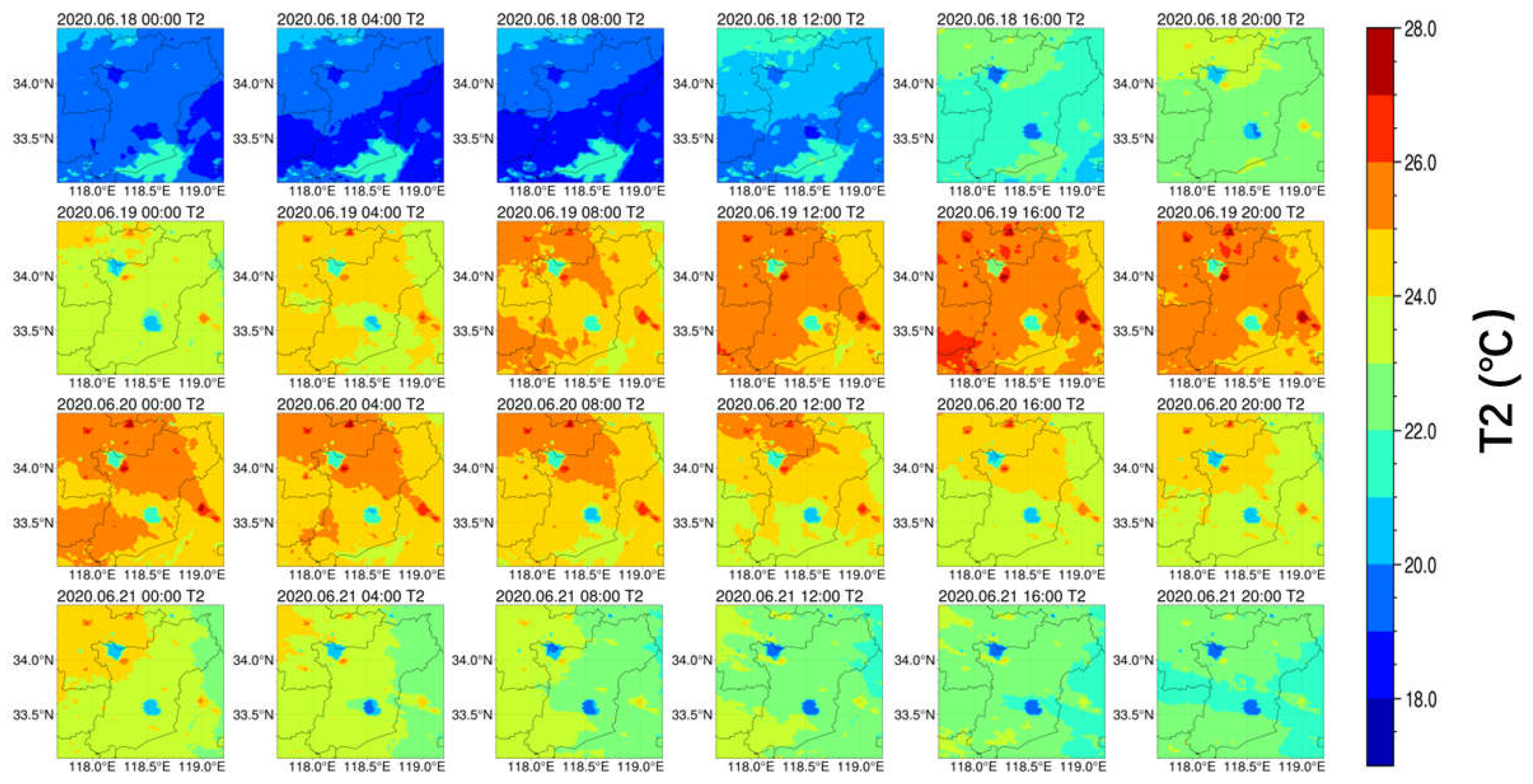
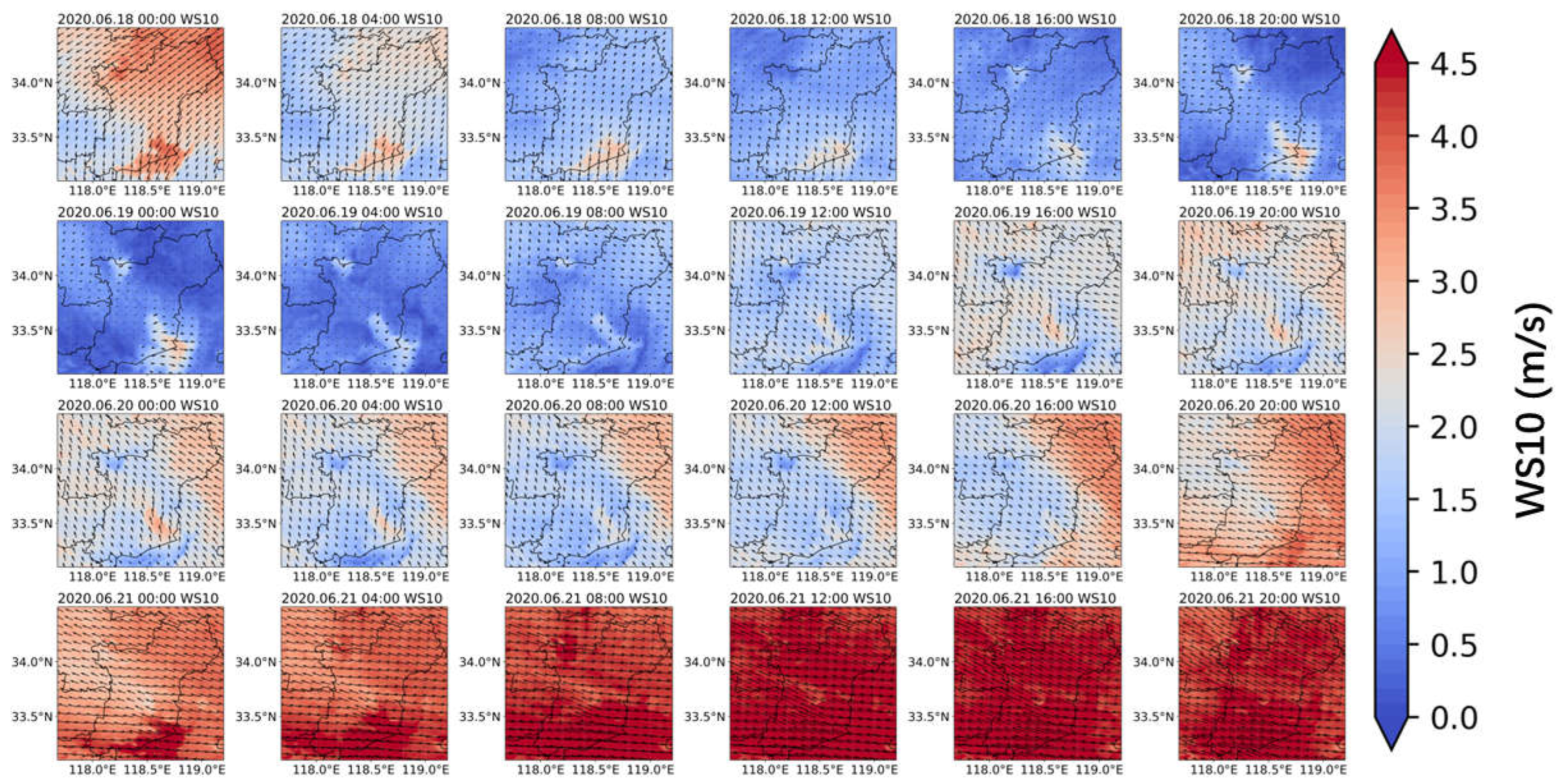
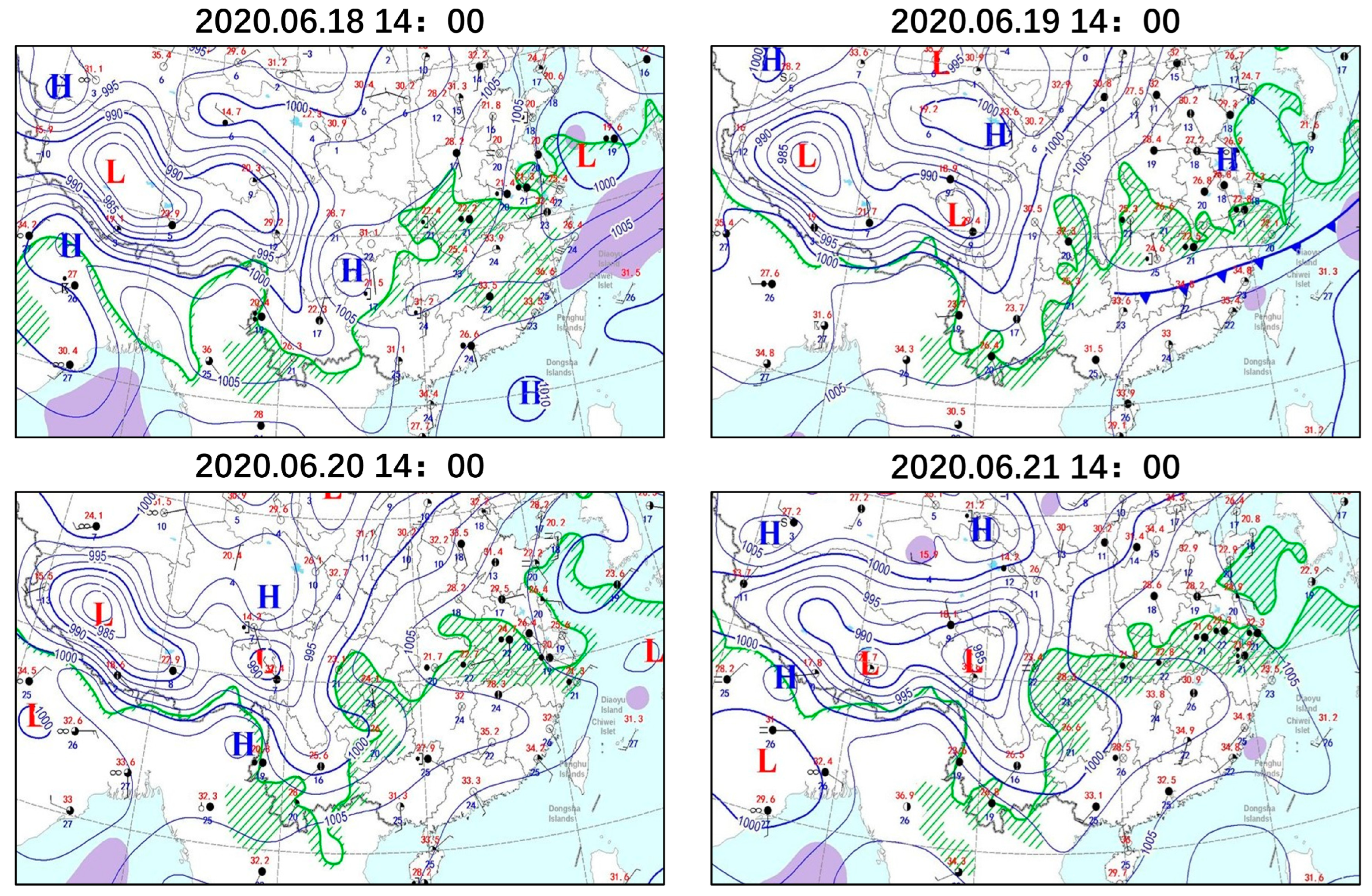
3.2. Spatio-Temporal Characterization of O3 Concentration Change and Meteorological Conditions
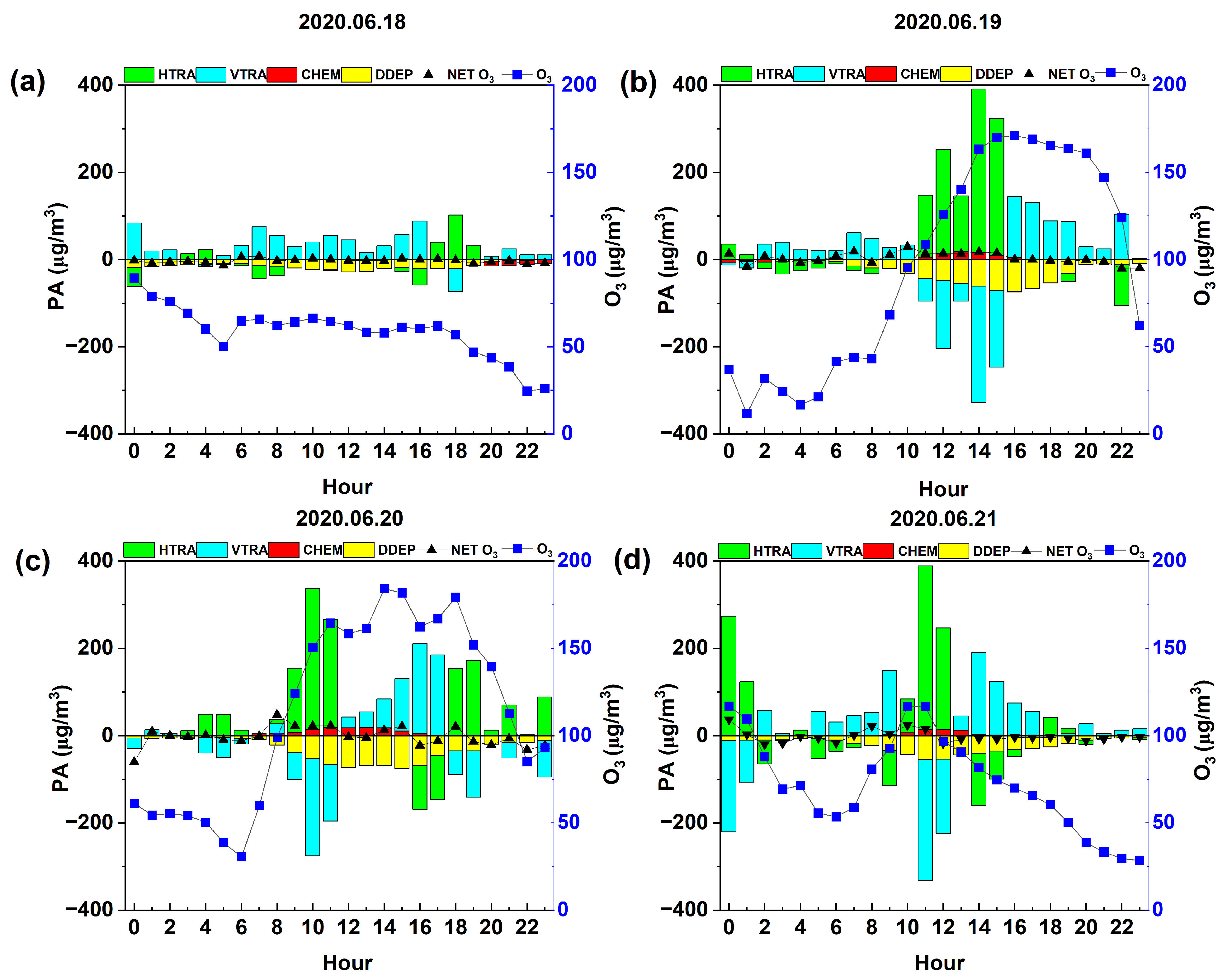
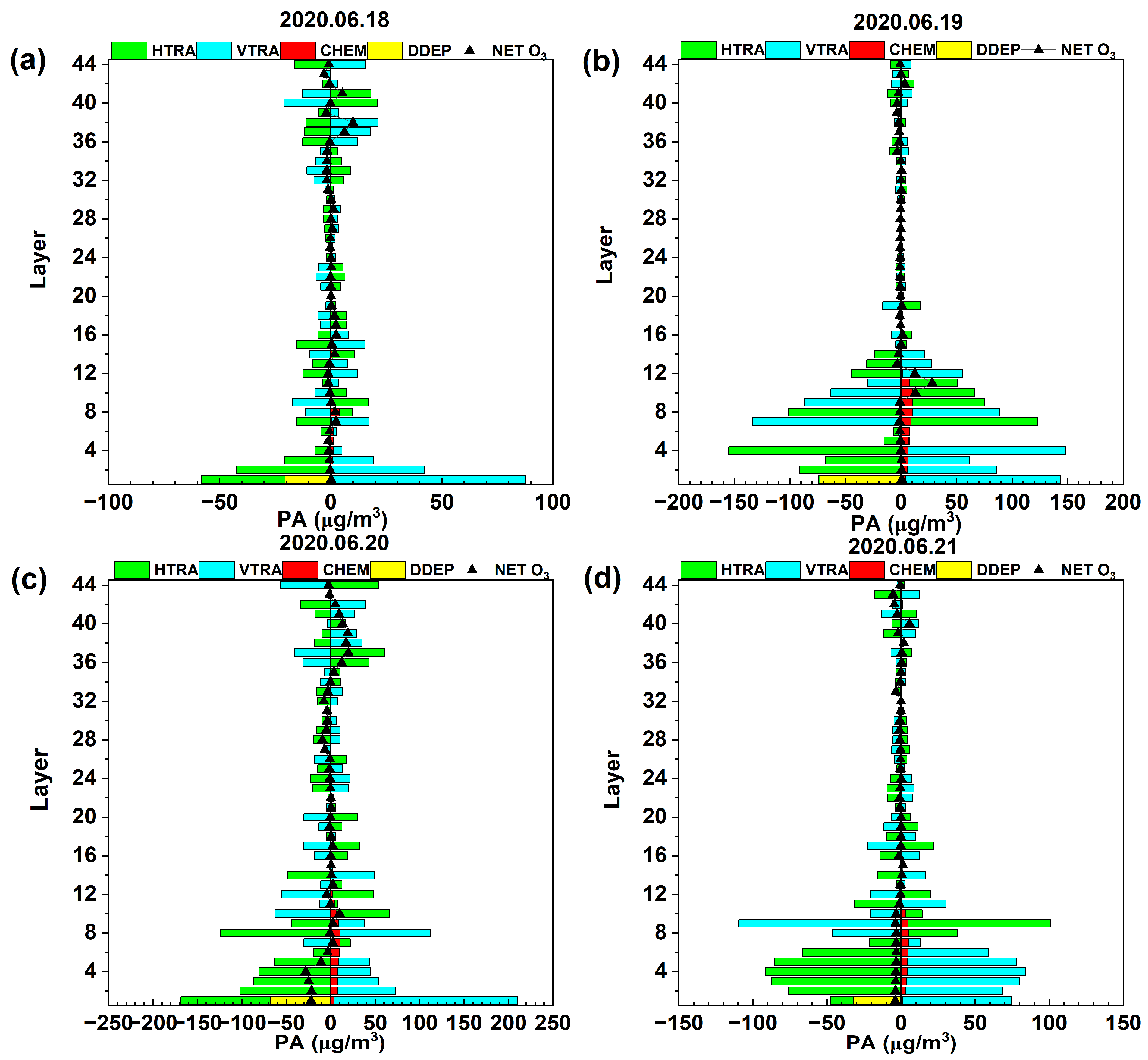
3.3. Process Analysis of O3
3.4. Source Analysis of O3
3.4.1. Regional Source Analysis of O3
3.4.2. Industry Source Analysis of O3
3.5. Emission Reduction Strategies for O3
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Huang, R.; Wu, J.; Xiao, Y.; Hu, M.; Fu, Q.; Duan, Y.; Chen, J. Regional transport of PM2.5 and O3 based on complex network method and chemical transport model in the Yangtze River Delta, China. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2022, 127, e2021JD034807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Xue, W.; Herrmann, H.; Brasseur, G.P.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z. Evolution of ozone pollution in China: What track will it follow? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Parrish, D.D.; Wang, S.; Bao, F.; Ni, R.; Li, X.; Yang, S.; Wang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Su, H. Long-term trend of ozone pollution in China during 2014–2020: Distinct seasonal and spatial characteristics and ozone sensitivity. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 8935–8949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, K.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, T.; Zhang, H. Coordinated control of PM2.5 and O3 is urgently needed in China after implementation of the “Air pollution prevention and control action plan”. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 129441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; He, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Chu, L.; Ni, J. Policy implications for synergistic management of PM2.5 and O3 pollution from a pattern-process-sustainability perspective in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 916, 170210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhao, H.; Kota, S.H.; Zhang, H. Rice yield losses due to O3 pollution in China from 2013 to 2020 based on the WRF-CMAQ model. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 401, 136801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yang, Y.; Xue, D.; Ren, L.; Tang, J.; Leung, L.R.; Liao, H. Aerosols overtake greenhouse gases causing a warmer climate and more weather extremes toward carbon neutrality. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Xue, L.; Brimblecombe, P.; Lam, Y.F.; Li, L.; Zhang, L. Ozone pollution in China: A review of concentrations, meteorological influences, chemical precursors, and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1582–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yuan, B.; Shao, M.; Wang, X.; Lu, S.; Lu, K.; Wang, M.; Chen, L.; Chang, C.-C.; Liu, S.C. Variations of ground-level O3 and its precursors in Beijing in summertime between 2005 and 2011. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 6089–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Lu, S.; Pan, W.; Zhang, Y. Multi-scale analysis of the impacts of meteorology and emissions on PM2.5 and O3 trends at various regions in China from 2013 to 2020 2. Key weather elements and emissions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Lu, K.; Su, R.; Tan, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Fu, Q.; Zhai, C.; Tan, Q.; Yue, D.; et al. Ozone formation and key VOCs in typical Chinese city clusters. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 1130–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jacob, D.J.; Liao, H.; Qiu, Y.; Shen, L.; Zhai, S.; Bates, K.H.; Sulprizio, M.P.; Song, S.; Lu, X.; et al. Ozone pollution in the North China Plain spreading into the late-winter haze season. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2015797118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Lau, A.K.; Fung, J.C.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Tao, M.; Lu, X.; Ma, J.; Lao, X.Q. Removing the effects of meteorological factors on changes in nitrogen dioxide and ozone concentrations in China from 2013 to 2020. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, R.; Liao, H.; Fu, Y. Quantifying the anthropogenic and meteorological influences on summertime surface ozone in China over 2012–2017. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Kang, P.; Jaffe, D.A.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Wu, K.; Zhou, M. Understanding the impact of meteorology on ozone in 334 cities of China. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 248, 118221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zheng, B.; Li, K.; Liu, Y.; Lin, J.; Fu, T.-M.; Zhang, Q. Exploring 2016–2017 surface ozone pollution over China: Source contributions and meteorological influences. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 8339–8361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Ban, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; He, M.; Li, S.; Shi, W.; Li, T. Random forest model based fine scale spatiotemporal O3 trends in the Beijing Tianjin-Hebei region in China, 2010 to 2017. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 276, 116635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Xing, J.; Wang, S.; Chang, X.; Hao, J. Impacts of emissions and meteorological changes on China’s ozone pollution in the warm seasons of 2013 and 2017. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2019, 13, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, K.; Zhao, T.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Bai, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xin, Y. Influence of stratosphere-to-troposphere transport on summertime surface O3 changes in North China Plain in 2019. Atmos. Res. 2022, 276, 106271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouza, F.; Leblanc, T.; Brewer, M.; Wang, P.; Piazzolla, S.; Pfister, G.; Kumar, R.; Drews, C.; Tilmes, S.; Emmons, L.; et al. The impact of Los Angeles Basin pollution and stratospheric intrusions on the surrounding San Gabriel Mountains as seen by surface measurements, lidar, and numerical models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 6129–6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Liu, J.; Zhao, T.; Xu, X.; Han, H.; Wang, H.; Shu, Z. Atmospheric transport drives regional interactions of ozone pollution in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akritidis, D.; Zanis, P.; Pytharoulis, I.; Mavrakis, A.; Karacostas, T. A deep stratospheric intrusion event down to the earth’s surface of the megacity of Athens. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2010, 109, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Hu, C.; Yuan, Z.; Xu, D.; Zhang, S.; Luo, H.; Wang, J.; Jiang, R. A modeling study of the impact of stratospheric intrusion on ozone enhancement in the lower troposphere over the Hong Kong regions, China. Atmos. Res. 2021, 247, 105158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Huang, J.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, X.; Liu, X.; Ma, W.; Wang, Y.; et al. Impact of Stratospheric Intrusions on Ozone Enhancement in the Lower Troposphere and Implication to Air Quality in Hong Kong and Other South China Regions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD033955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Huang, J.; Liu, X.; Ma, W.; Xu, D.; Jiang, R.; Duan, Y.; Fu, Q.; et al. Understanding the underlying mechanisms governing the linkage between atmospheric oxidative capacity and ozone precursor sensitivity in the Yangtze River Delta, China: A multi-tool ensemble analysis. Environ. Int. 2022, 160, 107060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, C.; Liu, J.; Cheng, X.; Fang, K.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z.; Hu, J.; Jiang, D.; Shen, L.; Yang, M. Impact of regional transport on high ozone episodes in southeast coastal regions of China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, T. Worsening urban ozone pollution in China from 2013 to 2017—Part 1: The complex and varying roles of meteorology. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 6305–6321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, D.; Yan, W.; Kang, Z.; Liu, R.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z. Spatio-temporal distribution, transport characteristics and synoptic patterns of ozone pollution near surface in Jiangsu province, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Gao, X. A New Study on Air Quality Standards: Air Quality Measurement and Evaluation for Jiangsu Province Based on Six Major Air Pollutants. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Liu, J.; Yuan, H.; Wang, T.; Zhuang, B.; Zhang, X. Foreign influences on tropospheric ozone over East Asia through global atmospheric transport. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 12495–12514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xie, Y.; Liu, J.; Shen, L.; Cheng, X.; Han, H.; Yang, M.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, T.; Hu, J. Distinct seasonality in vertical variations of tropospheric ozone over coastal regions of southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, B.; Tong, D.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Hong, C.; Geng, G.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Peng, L.; Qi, J.; et al. Trends in China’s anthropogenic emissions since 2010 as the consequence of clean air actions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 14095–14111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, D.; Cheng, J.; Liu, Y.; Yu, S.; Yan, L.; Hong, C.; Qin, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zheng, Y.; Geng, G.; et al. Dynamic projection of anthropogenic emissions in China: Methodology and 2015–2050 emission pathways under a range of socio-economic, climate policy, and pollution control scenarios. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 5729–5757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Gao, C.; Wu, K.; Liu, K.Y.; Wang, H.F.; Dan, M.; Ji, X.H.; Tong, Q.Q. ISAT v2.0: An integrated tool for nested-domain configurations and model-ready emission inventories for WRF-AQM. Geosci. Model Dev. 2023, 16, 1961–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Wu, Y.; Huang, J.; Gronoff, G.; Berkoff, T.A.; Arend, M.; Moshary, F. Identification of the roles of urban plume and local chemical production in ozone episodes observed in Long Island Sound during LISTOS 2018: Implications for ozone control strategies. Environ. Int. 2023, 174, 107887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Z.; Zhao, T.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, F.; Jiang, Y.; He, G.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Y. Terrain effect on atmospheric process in seasonal ozone variation over the Sichuan Basin, Southwest China. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 338, 122622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.; Li, J.; Li, N.; Liao, H. Stratospheric intrusion may aggravate widespread ozone pollution through both vertical and horizontal advections in eastern China during summer. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 10, 1115746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Liang, J.; Li, S.; Chen, G.; Chen, Z.; Tang, B.; Zhu, J.; Li, X. Diurnal emission variation of ozone precursors: Impacts on ozone formation during Sep. 2019. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 929, 172591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Han, X.; Xu, L.; Guan, X.; Gong, A.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M. Nocturnal ozone enhancement in Shandong Province, China, in 2020–2022: Spatiotemporal distribution and formation mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 925, 171542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Fang, T.; Yim, S.H.L. Source emission contributions to particulate matter and ozone, and their health impacts in Southeast Asia. Environ. Int. 2024, 186, 108578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhao, Y. Performance and application of air quality models on ozone simulation in China—A review. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 293, 119446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Lang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, X. The impacts of ship emissions on ozone in eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Chen, J.; Ying, Q.; Zhang, H. One-year simulation of ozone and particulate matter in China using WRF/CMAQ modeling system. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 10333–10350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Liu, J.; Shu, L.; Wang, T.; Yuan, H. Local and synoptic meteorological influences on daily variability in summertime surface ozone in eastern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Lu, X.; Cai, Z.; Brasseur, G.; Gao, M. Amplified Upward Trend of the Joint Occurrences of Heat and Ozone Extremes in China over 2013–20. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2022, 103, E1330–E1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Shen, L. Meteorology and climate influences on tropospheric ozone: A review of natural sources, chemistry, and transport patterns. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2019, 5, 238–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, B.; Hu, B.; Wang, L.; Bao, F. What have we missed when studying the impact of aerosols on surface ozone via changing photolysis rates? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 10831–10844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zhu, B.; Shi, S.; Lu, W.; Gao, J.; Kang, H.; Liu, D. Impact of aerosol optics on vertical distribution of ozone in autumn over Yangtze River Delta. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 5177–5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Diao, Y.; Zhao, T.; Gu, X.; Shi, S.S. Meteorological influence on persistent O3 pollution events in Wuxi in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 917, 170484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Qiu, X.; Liu, Y.; Yan, X.; Gao, J.; Peng, L. Identifying the dominant driver of elevated surface ozone concentration in North China plain during summertime 2012–2017. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 300, 118912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, J.V.; Palomera, M.J.; Martinez, C.R.; Matamoros, A.H.; Hata, H.; Inoue, K.; Tonokura, K. Ozone responses to reduced precursor emissions: A modeling analysis on how attainable goals can improve air quality in the Mexico City Metropolitan Area. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Zhou, X. A review of the CAMx, CMAQ, WRF-Chem and NAQPMS models: Application, evaluation and uncertainty factors. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 343, 123183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Scenario | NOx Reduction | VOCs Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| B1 | 0% | 0% |
| S1 | 10% | 10% |
| S2 | 10% | 20% |
| S3 | 10% | 30% |
| S4 | 10% | 40% |
| S5 | 10% | 50% |
| S6 | 20% | 10% |
| S7 | 20% | 20% |
| S8 | 20% | 30% |
| S9 | 20% | 40% |
| S10 | 20% | 50% |
| S11 | 30% | 10% |
| S12 | 30% | 20% |
| S13 | 30% | 30% |
| S14 | 30% | 40% |
| S15 | 30% | 50% |
| S16 | 40% | 10% |
| S17 | 40% | 20% |
| S18 | 40% | 30% |
| S19 | 40% | 40% |
| S20 | 40% | 50% |
| S21 | 50% | 10% |
| S22 | 50% | 20% |
| S23 | 50% | 30% |
| S24 | 50% | 40% |
| S25 | 50% | 50% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Shi, W.; Li, X.; Fang, C. Analysis of the Causes of an O3 Pollution Event in Suqian on 18–21 June 2020 Based on the WRF-CMAQ Model. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070831
Wang J, Zhang W, Shi W, Li X, Fang C. Analysis of the Causes of an O3 Pollution Event in Suqian on 18–21 June 2020 Based on the WRF-CMAQ Model. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(7):831. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070831
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ju, Wei Zhang, Weihao Shi, Xinlong Li, and Chunsheng Fang. 2024. "Analysis of the Causes of an O3 Pollution Event in Suqian on 18–21 June 2020 Based on the WRF-CMAQ Model" Atmosphere 15, no. 7: 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070831
APA StyleWang, J., Zhang, W., Shi, W., Li, X., & Fang, C. (2024). Analysis of the Causes of an O3 Pollution Event in Suqian on 18–21 June 2020 Based on the WRF-CMAQ Model. Atmosphere, 15(7), 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070831






